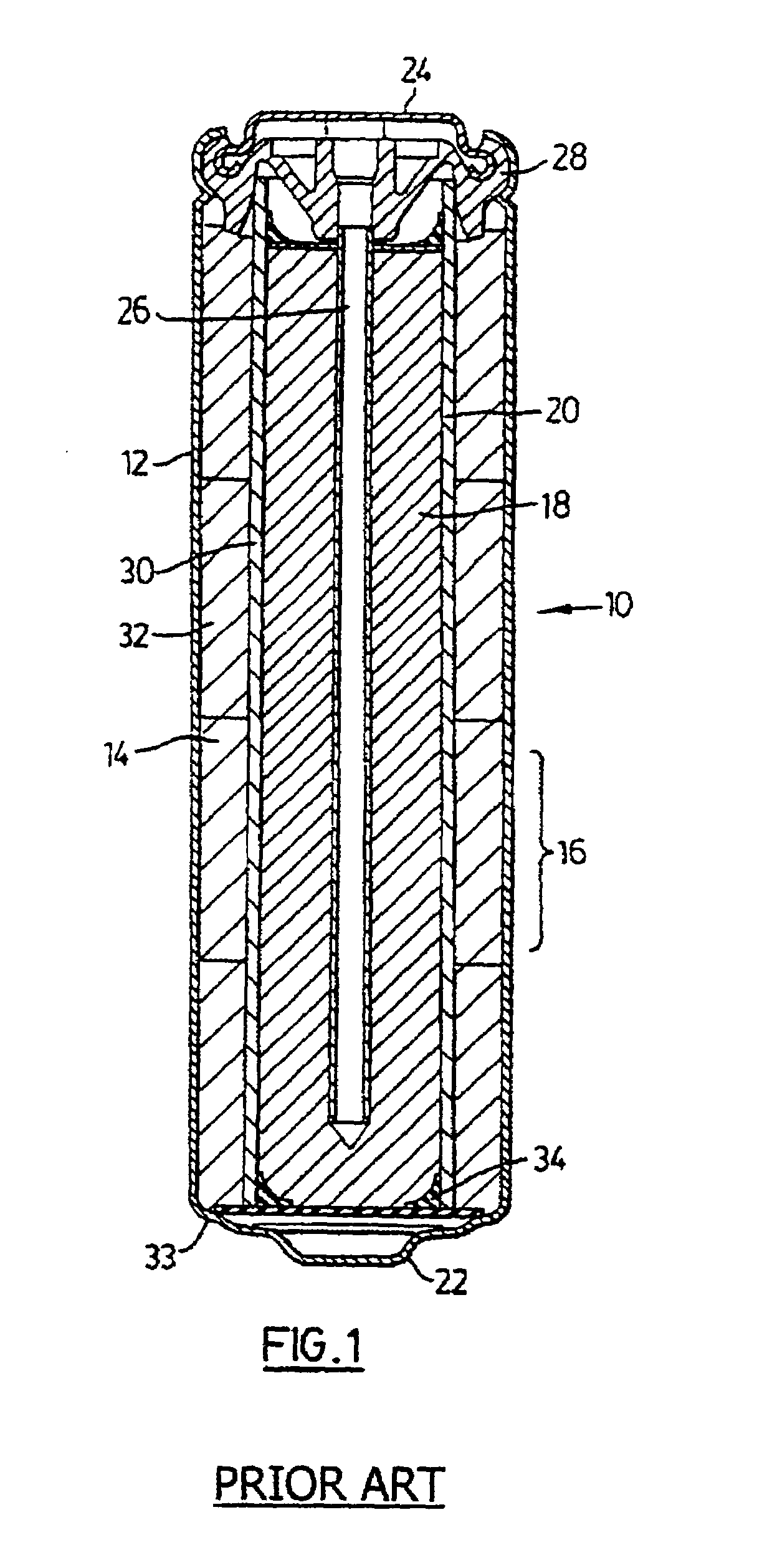
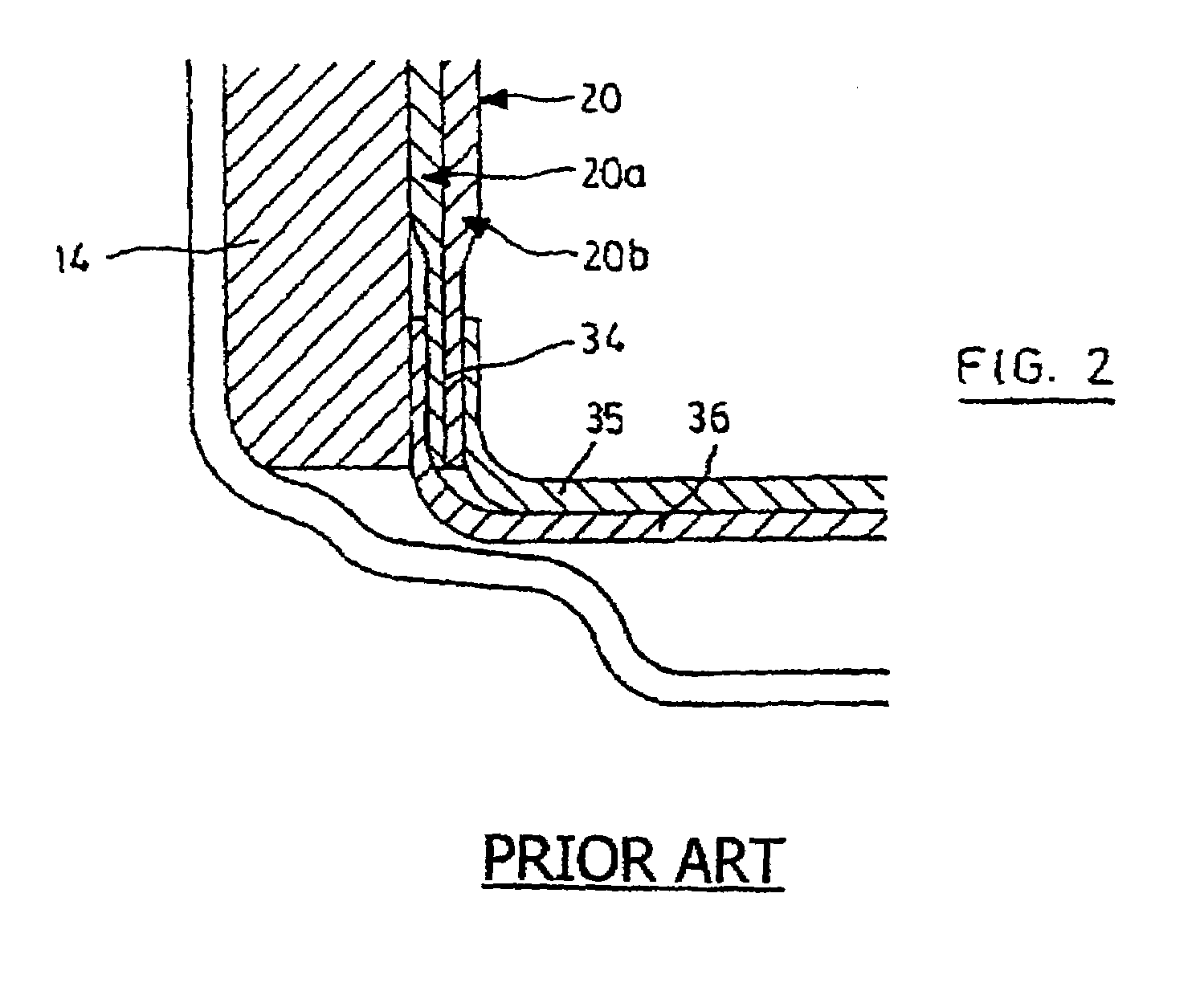
Method of manufacturing anode compositions for use in rechargeable electrochemical cells
a rechargeable cell and composition technology, applied in the direction of negative electrodes, non-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodes, gel electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of low gassing rate, observed shape change, and troublesome recharge process of zinc electrodes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0053]The zinc used in anode designs A through H is a powder of lead-free zinc containing 133 ppm bismuth, with particle size distribution 19% +60 mesh, 30% −60+100 mesh, 21% −100+140 mesh, 20% −140−200 mesh, 9% −200+325 mesh and 0.4% −325 mesh. Test results appear in table 1.
[0054]In design A the anode is prepared according to the prior art method described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,626,988. The zinc in the amount of 65% by weight of the anode is mixed with an aqueous solution of polyethylene glycol surfactant of molecular weight 600 in the amount of 0.05% by weight of surfactant to the weight of the gelled anode. The zinc is then mixed with an aqueous solution of indium sulfate in the amount of 0.1% indium by weight to the weight of zinc in the anode. A portion of the electrolyte is then added and mixed. Carbopol gelling agent is then added in the amount 0.054% by weight to the weight of the anode and mixed. The remaining electrolyte is then added in an amount to provide a total weight o...
example 2
[0063]The zinc powder used in anode designs J through P is lead-free zinc containing 133 ppm bismuth as in example 1, but of a much finer particle size. The particle size distribution is 10%—+60 mesh, 19% −60+100 mesh, 18% −100+140 mesh, 18% −140+200 mesh, 16% −200 +325 mesh and 19% −325 mesh. Test results appear in table 2.
[0064]Anode design J is prepared in the same manner as design A of example 1 and serves as the prior art control design to which the other designs of this example are compared. It gives higher first discharge performance than design A, but similar or lower cumulative performance over 25 cycles. Gassing is a little higher than design A, but at a low level.
[0065]In design K, the surfactant and indium sulfate are mixed in after a portion of the electrolyte as in design B after which a second portion of the electrolyte together with the gelling agent is added and mixed. The alkaline plating process created by adding electrolyte before the surfactant and indium sulfat...
example 3
[0071]The zinc powder used in anode designs Q through V is zinc containing 400–550 ppm lead. The particle size distribution is 22% +60 mesh, 34% −60+100 mesh, 22% −100+140 mesh, 16% −140+200 mesh, 6% −200+325 mesh. Test results appear in table 3.
[0072]Anode design Q is prepared in the same manner as design A of example 1 and serves as the prior art control design to which the other designs of this example are compared. It gives higher first discharge performance than design A, but lower cumulative performance over 25 cycles. Gassing is at a low level.
[0073]In design R, the surfactant and indium sulfate are added and mixed after a first portion of the electrolyte as in design B. This is then followed by the addition and mixing of a second portion of the electrolyte and a gelling agent. The alkaline plating process created by the mixing in of the first portion of the electrolyte before the surfactant and indium sulfate solution provide 10% and 3% benefits in cumulative performance. Ga...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| end voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com