Transmucosal dosage forms for brain-targeted steroid chemical delivery systems
ransmucosal technology, applied in the field of cyclodextrin complex of a chemical delivery system for steroids, can solve the problems of inability to formulate aqueous solutions of these derivatives for injection, dihydropyridine derivatives suffer from stability problems, and the tendency to precipitate out, etc., to improve oral and/or transmucosal bioavailability, improve the effect of oral and/or transmucosal bioavail
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
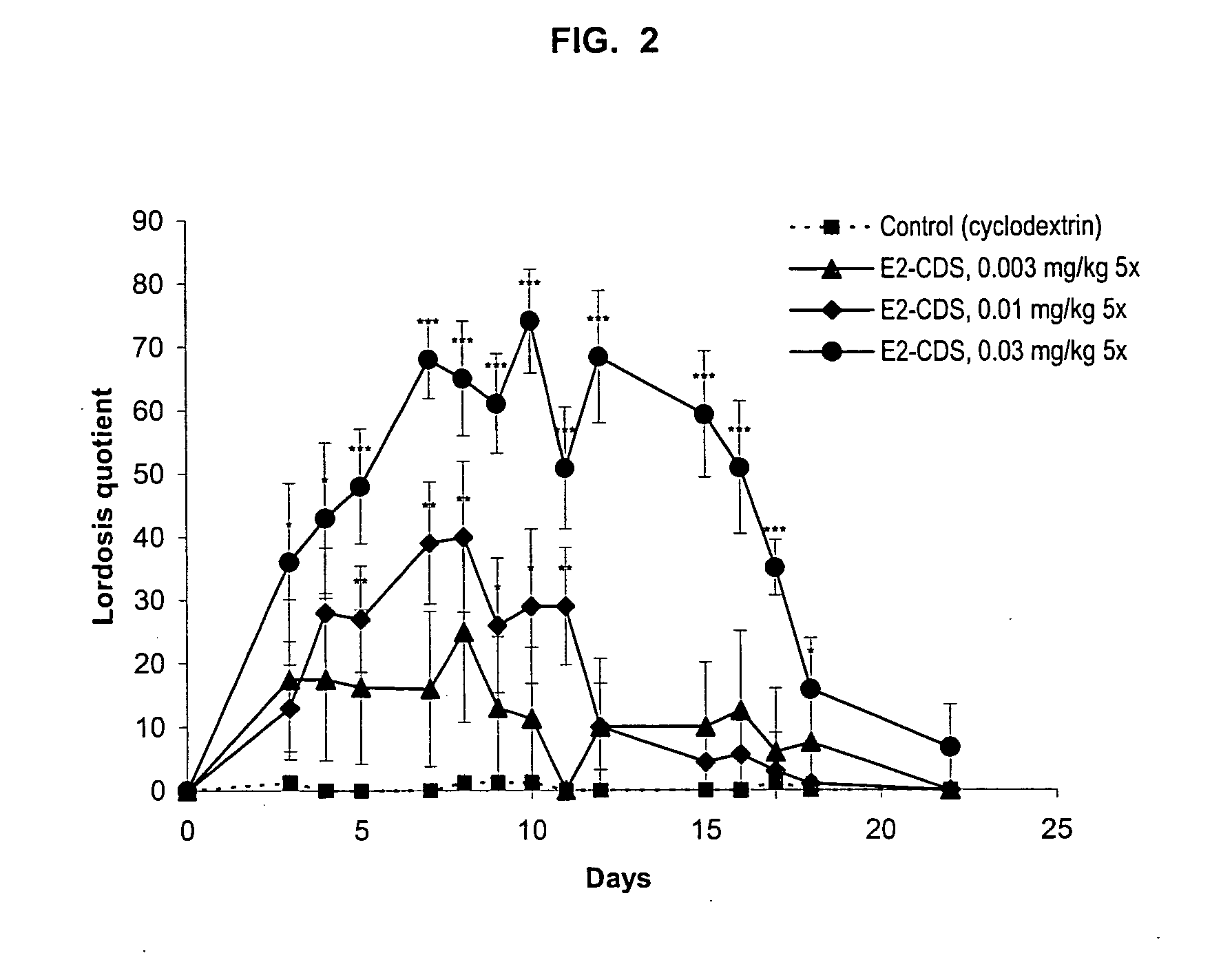
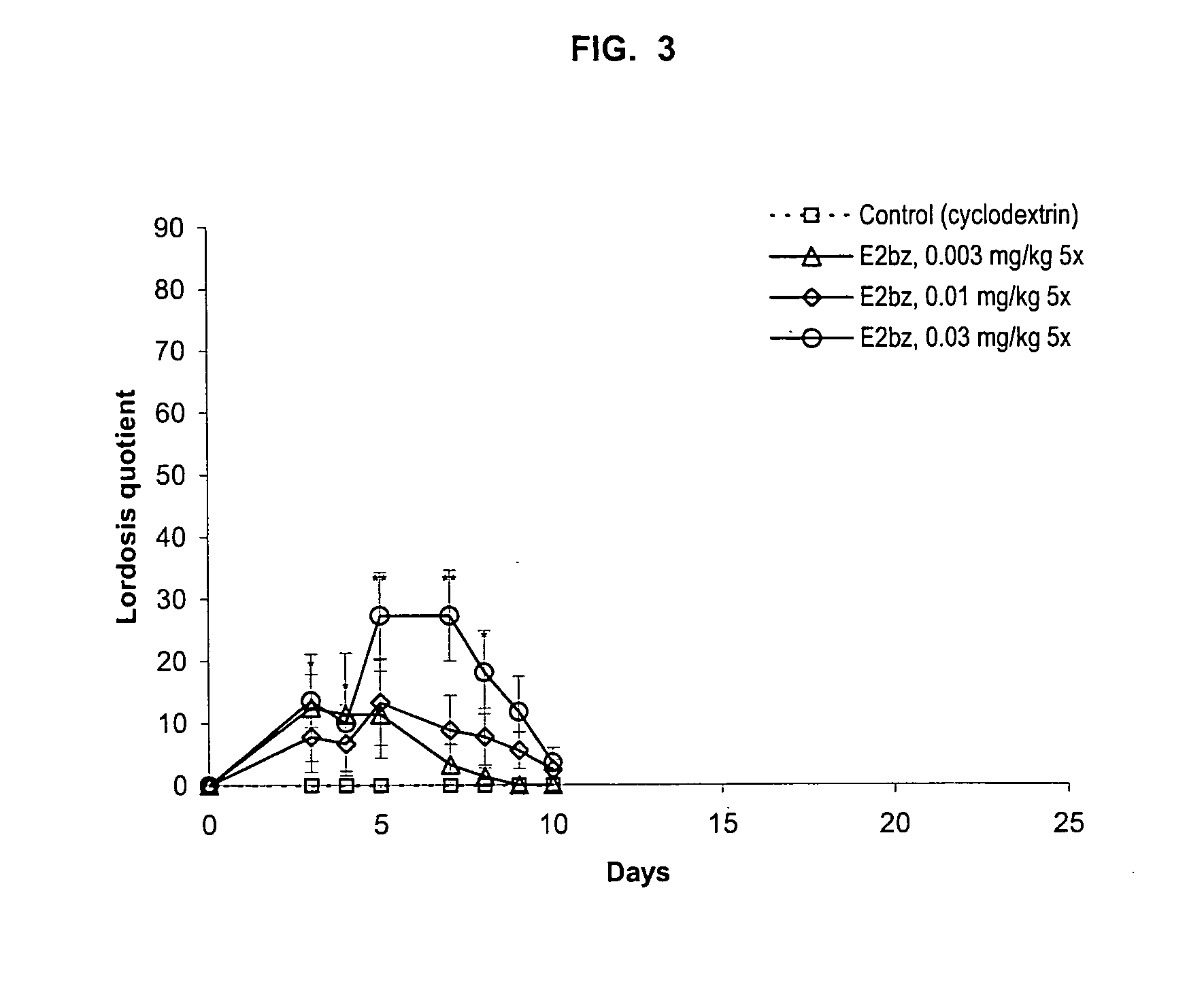
Examples
example 1
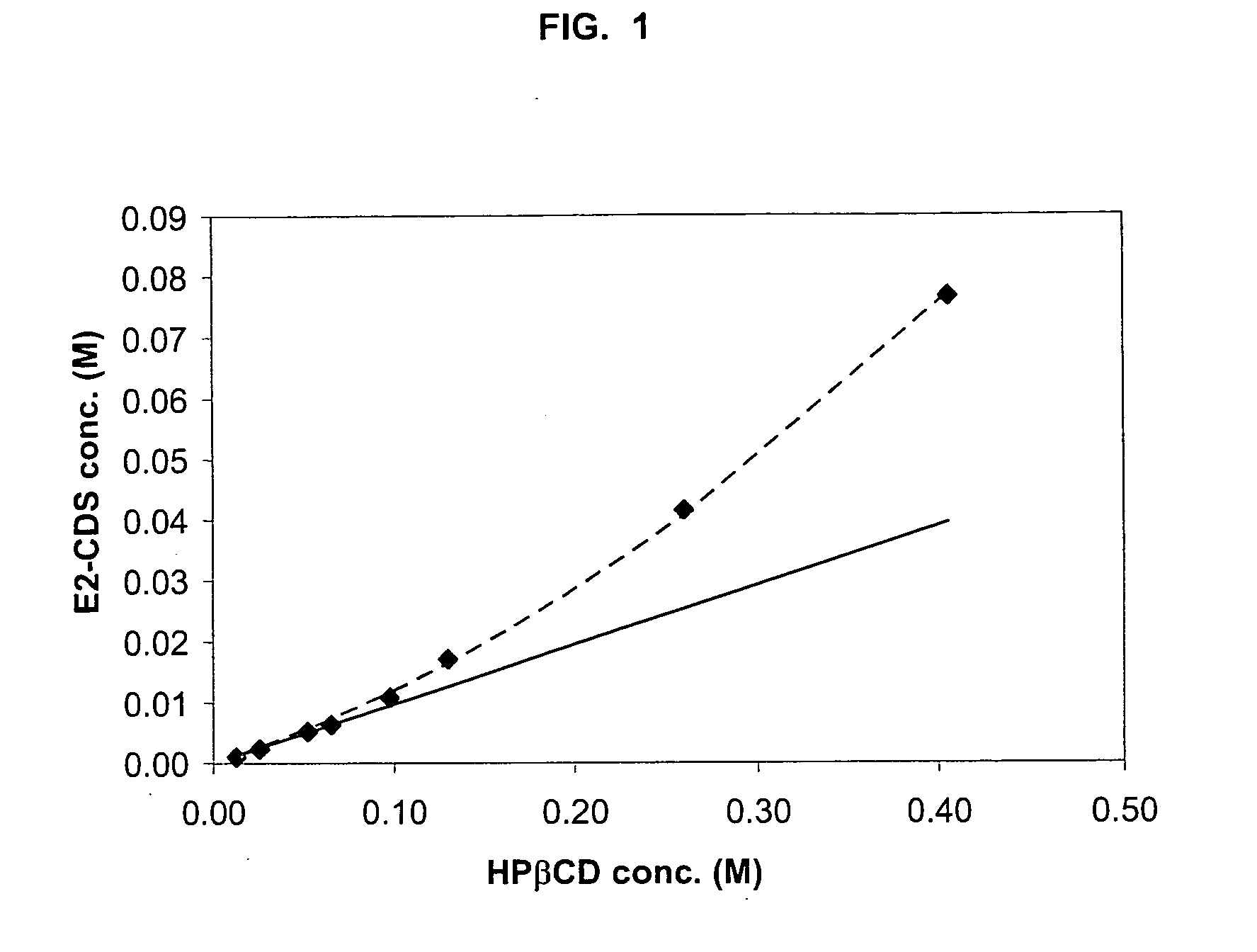
Phase Solubility Study
A phase solubility study is carried out as follows. Excess S-CDS (E2-CDS, DEX-CDS or T-CDS1) in a small amount of ethanol is added to cyclodextrin solutions of various concentrations of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD), hydroxypropyl-γ-cyclodextrin (HPγCD) or carboxymethylethyl-β-cyclodextrin and allowed to complex as described in Example 2, 3 or 4 below. Excess, undissolved S-CDS, if any, is removed by filtration. The amount of S-CDS in the complex is measured to obtain a data point. This process is repeated with different known concentrations of cyclodextrin until several data points are obtained. These data points are then plotted graphically, each data point representing the maximum amount of the selected S-CDS that can be complexed with a specific concentration of the selected cyclodextrin, i.e. each point represents a saturated S-CDS / cyclodextrin complex. Points on the line generated by the data points represents HTA ratios. Any point on the line r...
example 2
Preparation of Approximately 3% Complex of E2-CDS with HPβCD
Dissolve 232 g of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) (Cerestar, degree of substitution 4.5) in deionized 465 mL water (ASTM Type I) to form an approximately 33% w / v solution. Adjust the pH to 8.4-9.6 with sodium carbonate 1% solution. Degas the solution by passing argon through it. Add slowly, drop-wise, under stirring and bubbling argon, at 20-25° C., a solution of E2-CDS (7.5 g) in ethanol (188 mL). Allow time after each addition for the solution to become clear. The addition takes about 4 hours and it is slower at the end. A clear solution will result. Evaporate the solution to dryness in a rotary evaporator (bath temperature 35° C.). Reconstitute the residue in water, calculated to obtain the initial concentration of the cyclodextrin solution. Filter the solution through a 47 mm, 0.45 μm nylon 66 membrane filter, while covering with argon. Freeze-dry the filtrate, grind the resulting solid in a blender and pass i...
example 3
Preparation of Approximately 2.5% Complex of E2-CDS with HPγCD
Dissolve 45 g of 2-hydroxypropyl-γ-cyclodextrin (HPγCD) (Wacker, Cavasol W8 HP) in deionized 135 mL water (DIUF) to form an approximately 25% w / v solution. Adjust the pH to 8.4-9.6 with sodium carbonate 1% solution. Degas the solution by passing argon through it. Add slowly, drop-wise, under stirring and bubbling argon, at 20-25° C., a solution of E2-CDS (1.5 g) in ethanol (3 mL). Allow time after each addition for the solution to become clear. The addition takes about 4 hours and it is slower at the end. A clear solution will result. Evaporate the solution to dryness in a rotary evaporator (bath temperature 35° C.). Reconstitute the residue in water, calculated to obtain the initial concentration of the cyclodextrin solution. Filter the solution through 47 mm, 0.45 μm nylon 66 membrane filter, while covering with argon. Freeze-dry the filtrate, grind the resulting solid in a blender and pass it through a 60 mesh sieve...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase solubility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com