Modified lithium iron phosphate, preparation method thereof and lithium ion battery
A lithium iron phosphate, modified technology, applied in the direction of secondary batteries, battery electrodes, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low conductivity, difficulty in meeting the actual needs of high rate performance of electric vehicle power batteries, and amorphous
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
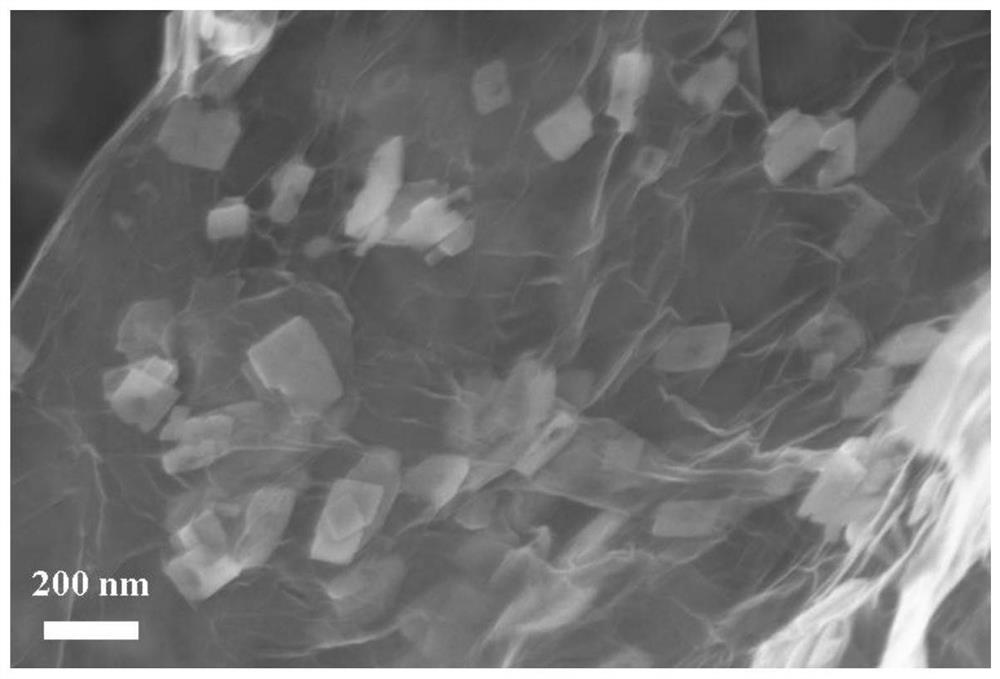
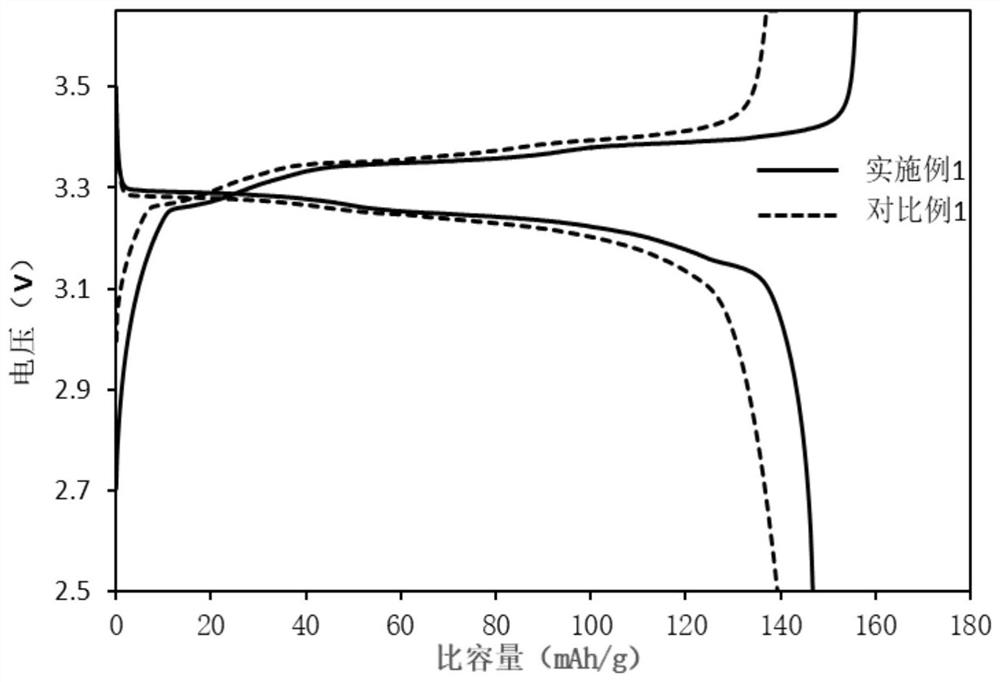
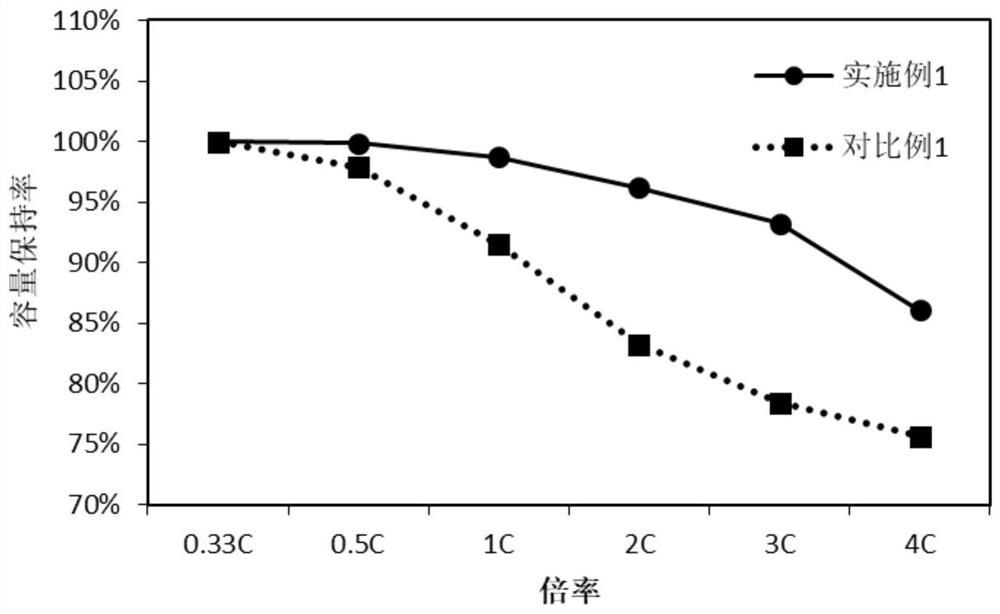
[0025] As described in the background technology, the carbon coating layer in the existing carbon-coated lithium iron phosphate materials is usually in an amorphous state, resulting in low electrical conductivity, which is difficult to meet the actual demand for high rate performance of electric vehicle power batteries The problem. In order to solve the above technical problems, the application provides a method for preparing modified lithium iron phosphate. The method for preparing modified lithium iron phosphate includes: performing a controlled oxidation reaction between chemically expanded graphite and concentrated sulfuric acid containing an oxidant to obtain a controlled oxidation Chemically expanded graphite; in the presence of a solvent, the chemically expanded graphite, lithium source compound, phosphorus source compound and iron source compound are mixed and then subjected to a hydrothermal synthesis reaction to obtain a modified lithium iron phosphate precursor; unde...
Embodiment 1
[0042] The preparation method of modified lithium iron phosphate comprises:
[0043] Step 1, soak 2g of graphite (Sigma, 50 mesh) raw materials in concentrated sulfuric acid (180mL) containing hydrogen peroxide (20mL), let it stand for reaction at normal temperature and pressure for 24h, after washing and filtering, add the above-mentioned chemically expanded graphite to the solution containing 2g In the concentrated sulfuric acid of potassium permanganate oxidant, stir at 35°C for 2 hours to complete the controlled oxidation reaction, and obtain chemically expanded graphite with controlled oxidation;
[0044] Step 2, disperse the controlled oxidation chemical expansion graphite obtained in step 1 in the mixed solution of water and ethylene glycol, and then mix lithium hydroxide, phosphoric acid, ferrous sulfate, tetraisopropyl titanate, and controlled oxidation expansion graphite according to the weight ratio The ratio of 1:1.36:2.11:0.028:0.11 is added to the dispersion of t...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The difference from Example 1 is: based on the total weight of chemically expanded graphite, lithium source compound, phosphorus source compound and iron source compound for controlling oxidation, the percentage of titanium element is 0.20%, and other conditions are the same as in Example 1 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| retention rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com