Method for quantitatively detecting endophytic bacteria of plant tissue by non-culture method
A technology of plant tissue and endophytic bacteria, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of unknown abundance of non-culturable bacteria, quantitative error of plant endophytic bacteria, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1, plant callus total DNA extraction experimental scheme
[0031] 1) Take about 50 mg of callus (callus obtained by inducing dedifferentiation using rice seeds as material) and place it in a 2ml centrifuge tube, add liquid nitrogen and grind thoroughly.
[0032] 2) Add 567 μl of TE buffer solution (recipe: solvent is water, solute is 10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA; pH 8.0), vortex, and mix thoroughly.
[0033] 3) Add 30 μl of 10% (10 g / 100 ml) SDS and 20 μl of proteinase K (100 μg / ml, AMRESCO, Solon, USA) (equivalent to 0.76 U of proteinase K), vortex, and mix well.
[0034] 4) Add 2 μl of RNase (100 mg / ml, Tiangen Biochemical Technology Co., Beijing), mix by inversion and incubate at 37° C. for 1 hour.
[0035] 5) Add 100μl 5M NaCl, mix by inversion, then add 80μl CTAB / NaCl solution (recipe: solvent is water, solute is 0.7M NaCl, 10% (10g / 100ml) CTAB), incubate at 65℃ after inversion 10min.
[0036] 6) Add an equal volume of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2, making the standard curve of plant tissue absolute bacterial content determination
[0043] The callus is cultured from the surface-sterilized plant tissue in a sterile environment, therefore, the default callus is sterile. The present invention is based on the DNA of callus (the callus obtained by inducing dedifferentiation using rice seeds as materials), adding different copy number gradients of E. coli genomic DNA as a template, and then using the 322F-1 / 796R primer pair for fluorescence Quantitative PCR (qPCR), and draw a standard curve of plant tissue bacterial content and qPCR reaction Ct value according to the results.
[0044] 322F-1: 5'-ACGGHCCARACTCCTACGGAA-3' (SEQ ID No. 1);
[0045] 796R: 5'-CTACCMGGGTATCTAATCCKG-3' (SEQ ID No. 2).
[0046] Wherein, H represents A or C or T; R represents G or A; M represents A or C; K represents G or T.
[0047] Specific steps are as follows:
[0048] 1. Streak culture of E.coli DH5α strain on LB plate, 37°...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3, rice tissue endophytic bacteria absolute content determination
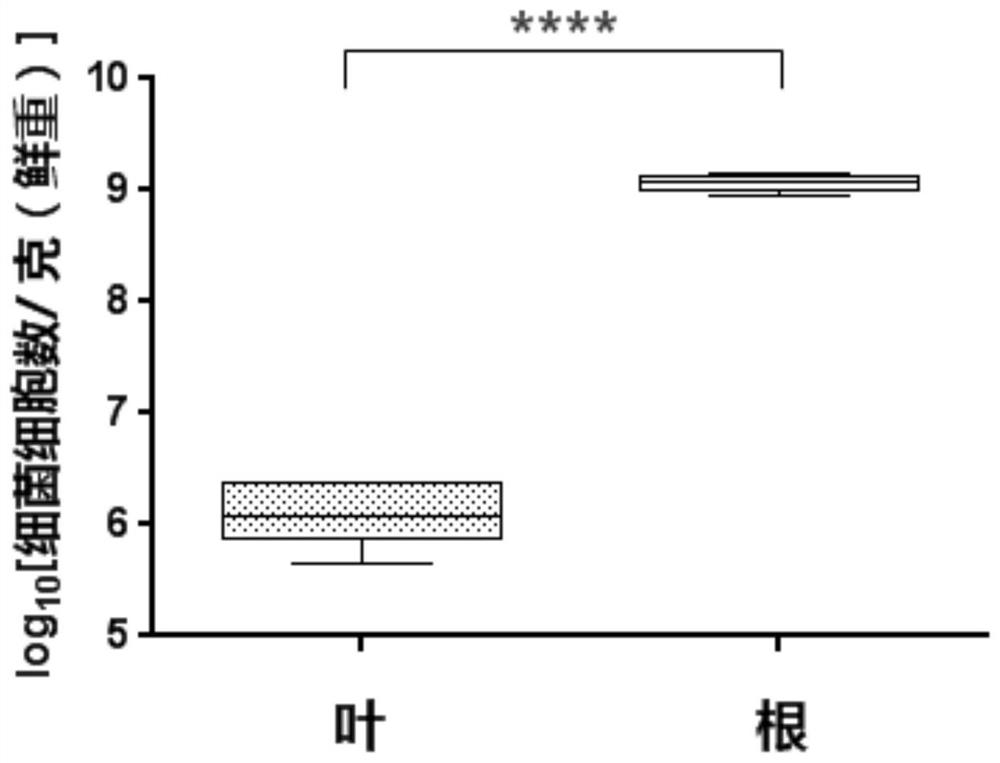
[0062] The standard curve that embodiment 2 draws can calculate the bacterial content of unit weight plant tissue by weighing the plant tissue that is used for DNA extraction, the present invention is example with model plant rice, to rice root, leaf two kinds of tissues The absolute content of endophytic bacteria was determined.
[0063] 1) Disinfection on the surface of rice tissue: first wash with 75% (volume percentage) ethanol for 5 minutes, then transfer the rice leaves to sterile water (ddH 2 O and Tween20 were added at a volume ratio of 1000:1, vortexed for 2-5min), and finally sterilized with ddH 2 O wash 4 times.
[0064] 2) The rice tissue DNA extraction method is the same as in Example 1.
[0065] 3) The qPCR reaction (BIO RAD) system is: 2×iQTM SYBR Green Mix 12.5 μl; template 1 μl (rice root or leaf tissue DNA); primers 322F-1 and 796R (see above for specific sequences) 0.5 μ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com