Bio-energy active material and application thereof
An active material and biological technology, applied in the field of biomedical tissue engineering, can solve problems such as the inability to continuously improve cell stability and related biomass activity, hinder the application and development of bioenergy active materials, achieve unique bioenergy activity, and promote adhesion , the effect of long degradation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
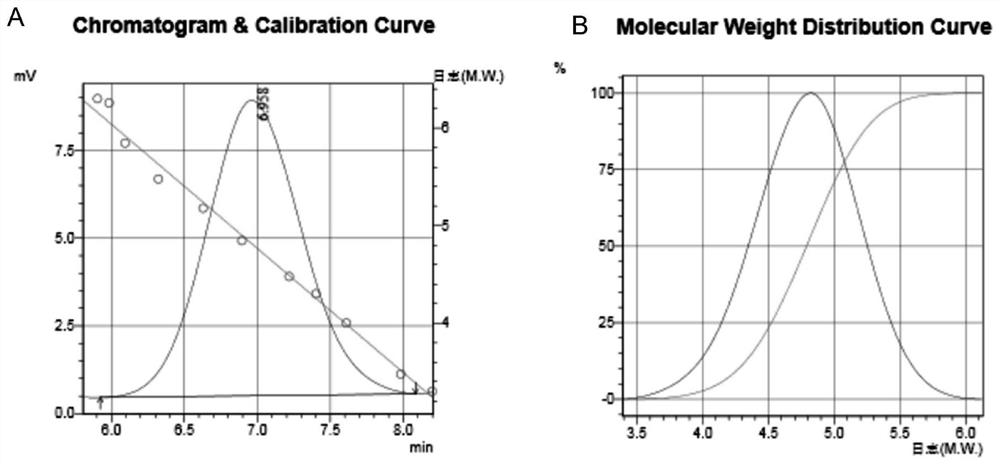
[0037] (1) The microorganism Halomonas that can synthesize 3-hydroxybutyric acid-4-hydroxybutyric acid copolyester was fermented and cultured for 72 hours in 60MMG medium at 37°C and 400-800rpm, and collected after 72 hours The cells are placed at 70° C. to ventilate and dry the cells to obtain dry cell powder containing 3-hydroxybutyric acid-4-hydroxybutyric acid copolyester.
[0038] The composition of 60MMG medium is: glucose 30g / L, yeast extract 1g / L, ammonium sulfate 0.25g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.2g / L, disodium hydrogen phosphate 9.65g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.5g / L, Trace element I 10ml / L, trace element II 1ml / L.
[0039] (2) extract the 3-hydroxybutyric acid-4-hydroxybutyric acid copolyester in the dried thallus powder with chloroform (1g dry thallus powder adds 20ml chloroform), pack in the autoclave after stirring evenly, in React at 100°C for 4 hours.
[0040] (3) After the autoclave is cooled, the cell fragments are removed by filtration or suction filtra...
Embodiment 2
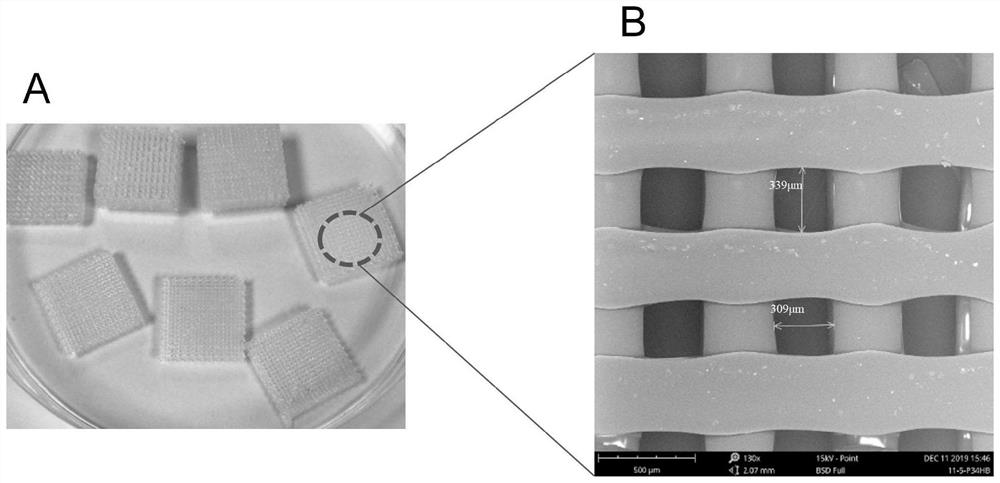
[0047] The 3-hydroxybutyric acid-4-hydroxybutyric acid copolyester material synthesized in Example 1 was loaded into a melt 3D printer (180° C.) to prepare a porous scaffold for bone tissue repair.
[0048] The result is as figure 2 As shown, among them, figure 2 -A porous scaffold prepared for 3D printing, figure 2 -B is a scanning electron microscope image of the cross-section of the scaffold, and the pore diameter of the porous scaffold is about 350-400 μm.
experiment example
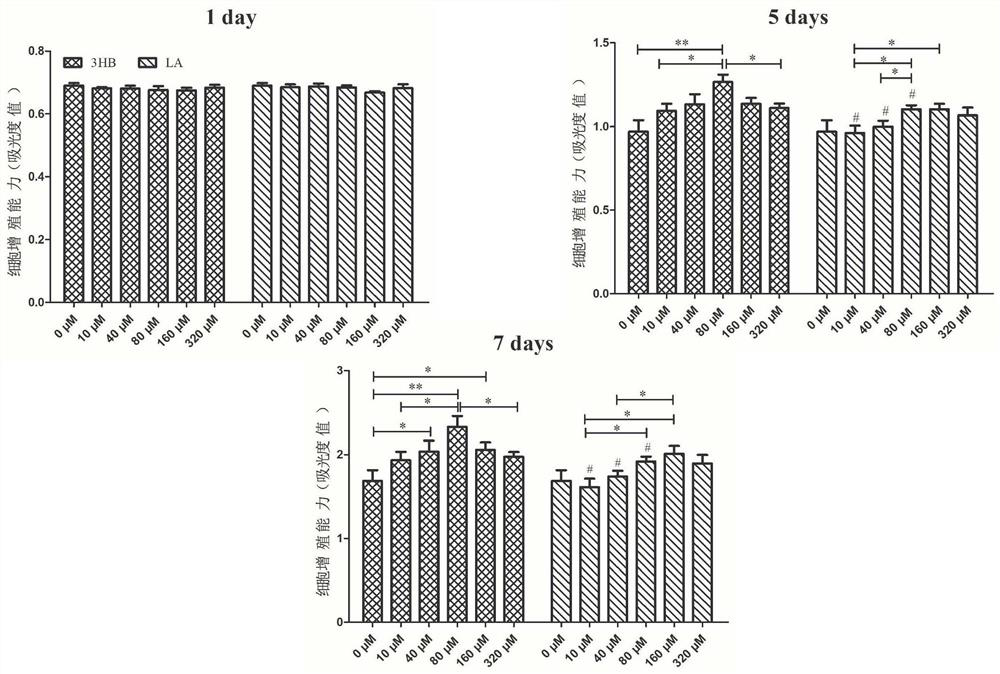
[0050] The 3D porous scaffold in Example 2 was soaked in phosphate buffer for 8 weeks, and the degradation products were collected. In phosphate buffer, the degradation product of 3-hydroxybutyric acid-4-hydroxybutyric acid copolyester is mainly 3-hydroxybutyric acid (3HB). The concentration of the collected degradation products was determined, and then the in vitro experiment was carried out.
[0051] The composition of the phosphate buffer is: sodium chloride 7.9g / L, potassium chloride 0.2g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.24g / L.
[0052] (1) Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs) in good growth state were taken, according to 2×10 4 The cell density was seeded in a 48-well plate. After 4 hours, different concentrations of 3-hydroxybutyric acid (0 μM, 10 μM, 40 μM, 80 μM, 160 μM, 320 μM) were added to the above cells. Cell proliferation was measured respectively. At the same time, lactic acid (LA) was used as the control group.
[0053] The result is as im...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com