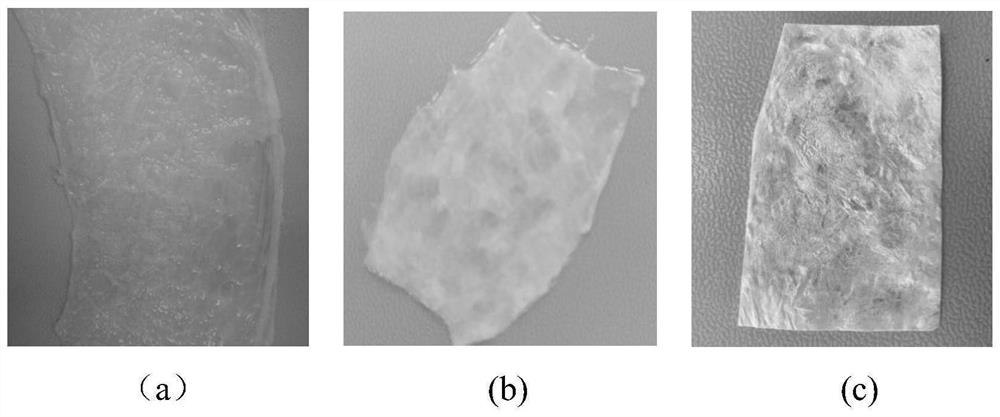
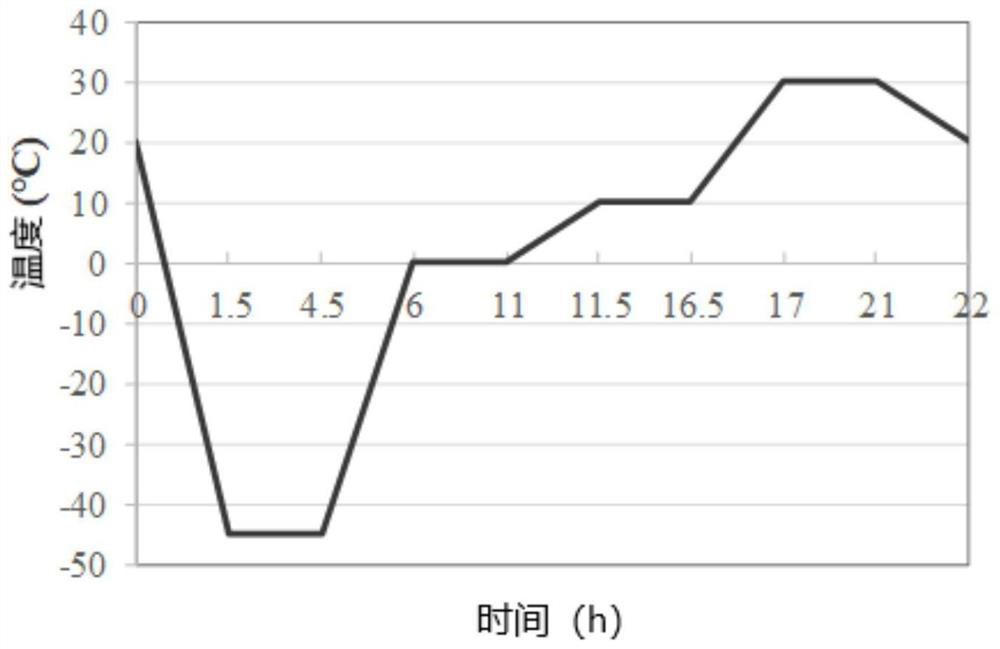
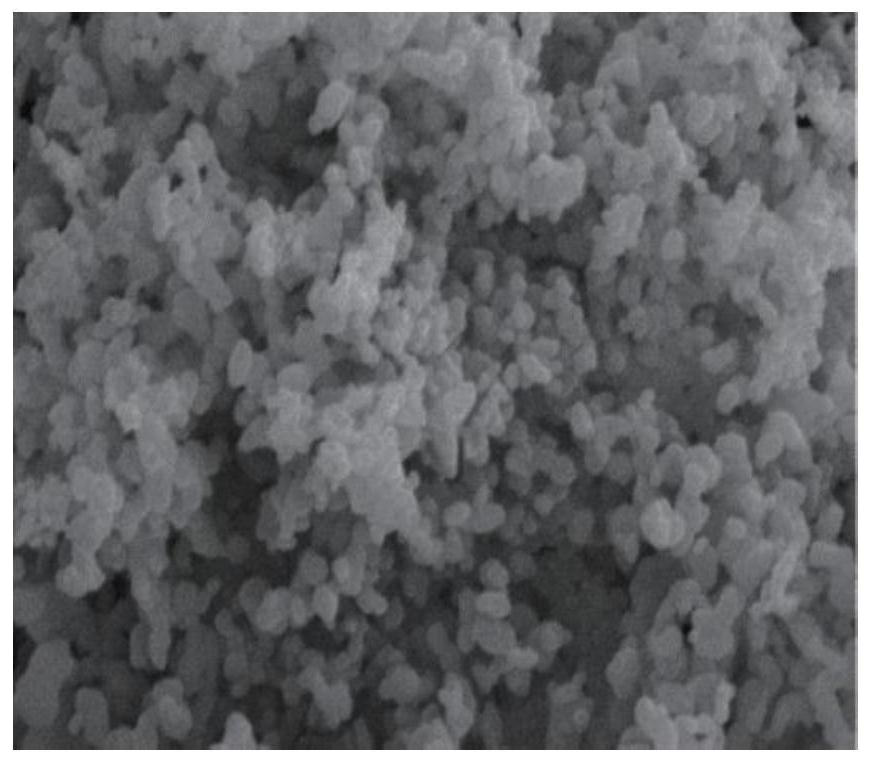
Slow-release antibacterial acellular matrix biological material and preparation method thereof
An acellular matrix and biomaterial technology, which is applied in the field of slow-release antibacterial acellular matrix biomaterials and their preparation, can solve problems such as unfavorable early vascularization, and achieves improved biocompatibility, increased loading, and stable release rate. control effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0052] The slow-release antibacterial acellular matrix biomaterial and its preparation method according to the embodiment of the present invention comprise the following steps:
[0053] Step S1, providing a biological tissue, and performing decellularization and virus inactivation on the biological tissue.
[0054] That is to say, after the biological tissue is obtained, the biological tissue should first be decellularized and virus inactivated.
[0055] Among them, the biological tissue is not particularly limited, and may be, for example, mammalian-derived hollow organ submucosa, tissue basement membrane, dermis, pericardium, peritoneum, pleura, or amnion.
[0056] After the biological tissue is obtained, the biological tissue needs to be decellularized and virus inactivated.
[0057] Wherein, decellularization can be performed by any one of physical methods, chemical methods, and biological methods.
[0058] Wherein, the physical method of decellularization mainly involve...
Embodiment approach
[0059] As an embodiment, the decellularization process of the biological tissue is as follows: the biological tissue is treated by repeated freezing and thawing, and then treated with 1M hypertonic saline for 2 hours and 0.2% Triton X-100 for 2 hours in a constant temperature water bath shaker , 0.4% NaOH treatment for 2h. Wherein, the oscillation rate of the constant temperature water bath oscillator can be, for example, 120 rpm, and the temperature of the water bath is 37°C.
[0060] In addition, the virus inactivation treatment can be performed by a virus inactivation reagent, and the virus inactivation reagent is one or more of peracetic acid, 75% alcohol, and sodium hydroxide.
[0061] As an embodiment, the virus inactivation process of the biological tissue is: the biological tissue after the decellularization treatment is treated with 0.1% peracetic acid (PAA) for 2 hours in a constant temperature water bath shaker, and / or with 75% peracetic acid Fully soak in alcohol ...
Embodiment 1
[0106] 1. Preparation of slow-release antibacterial acellular matrix biomaterials
[0107] (A) Biological tissue and its processing
[0108] Step 1: Dissection of porcine bladder matrix
[0109] 1) After washing the purchased fresh pig bladders, they are quickly frozen at a temperature of -20 to -40°C, and the freezing time is not less than 24 hours.
[0110] Take out the frozen porcine bladder, soak it in tap water at normal temperature to thaw, and soak it for 1 to 2 hours.
[0111] Then rinse it inside and out with tap water.
[0112] 2) Separate the fat and fascia around the bladder.
[0113] 3) Insert one end of the rubber catheter along the urethral opening of the bladder and fix it with a cable tie. The other end of the catheter is connected to the faucet, and water is slowly injected into the bladder through the catheter. The volume of water is about 700-1200 mL until the bladder is fully inflated and the blood vessels are clear.
[0114] 4) Separate the porcine bl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com