Application of carbon quantum dots in targeted cell nucleolus wash-free imaging
A technology of carbon quantum dots and cell nucleoli, which is applied in the application field of carbon quantum dots in the no-clean imaging of targeted cell nucleoli, can solve the problems of complex preparation methods, complex operations, and cell damage, and achieve simple preparation and simple operation process , time-saving effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: Preparation of N-CDs
[0031] Step 1: Accurately weigh 0.05 g of m-phenylenediamine and 0.05 g of p-aminobenzoic acid, completely dissolve them in 10 mL of absolute ethanol, add the resulting solution into a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, and heat at 180°C for 12 h. After the reaction kettle was naturally cooled to room temperature, the brown solution was taken out from the inner tank.
[0032] In step 2, the ethanol solvent in the brown solution was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a brown viscous substance, which was dissolved by adding secondary water, and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 min to obtain a brownish-yellow supernatant.
[0033] Step 3, the brown supernatant was treated with a 500-1000 Da dialysis bag for 2 days, during which the water was changed every 6 h, and the dialyzed solution was freeze-dried to obtain a brown N-CDs solid powder.
[0034] Step 4: Weigh 0.01 g of N-CDs solid powder into a beaker, add 10 mL of secondary water t...
Embodiment 2
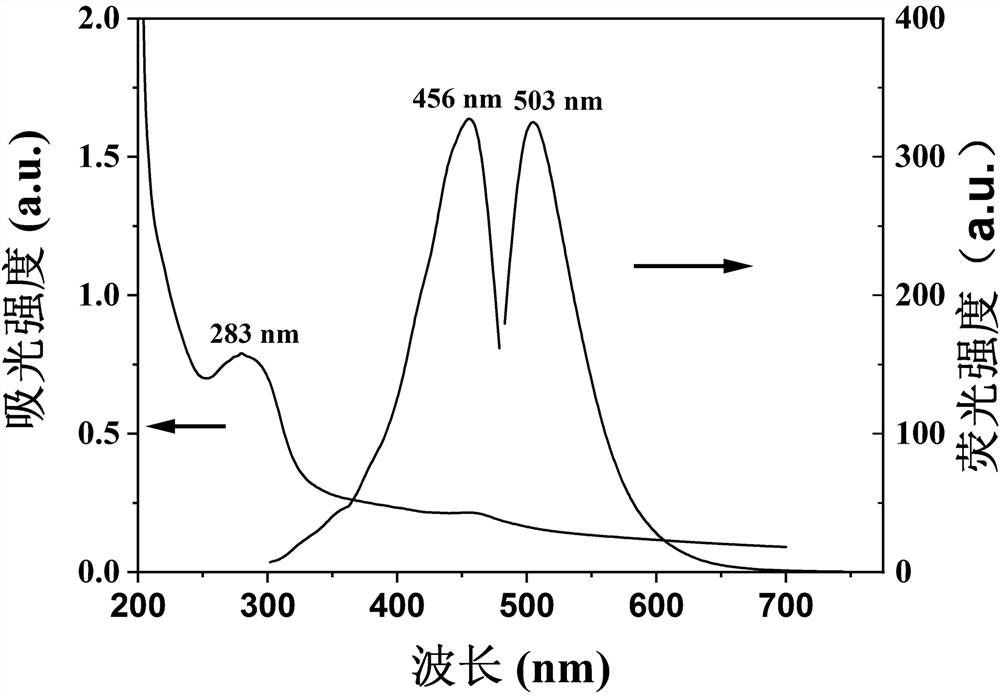
[0035] Example 2: Characterization of N-CDs: See Figure 1-6 . figure 1 In the ultraviolet absorption spectrum of N-CDs, there is a strong absorption peak at 283 nm, which is formed by n→π of C=O * caused by the transition; figure 1 The optimal excitation and emission peaks of the N-CDs are located at 456 nm and 503 nm, respectively.
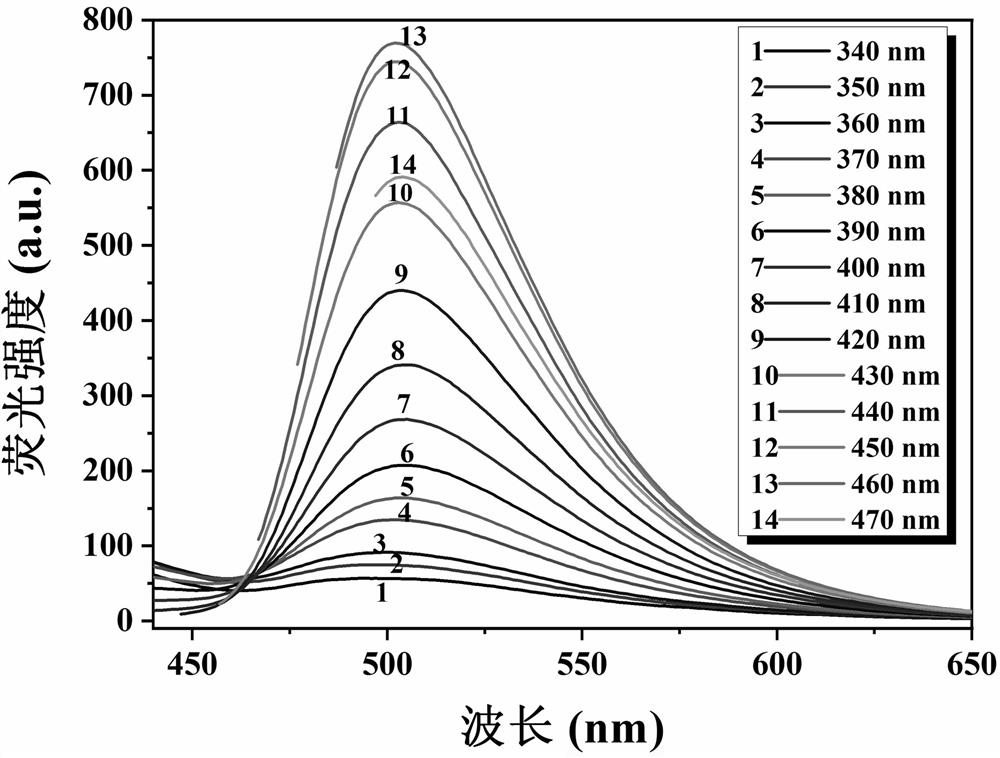
[0036] figure 2 It is the emission spectrum of N-CDs at different excitation wavelengths. When the excitation wavelength changes from 340 nm to 470 nm, the emission wavelength does not shift, indicating that N-CDs have excitation wavelength independence.
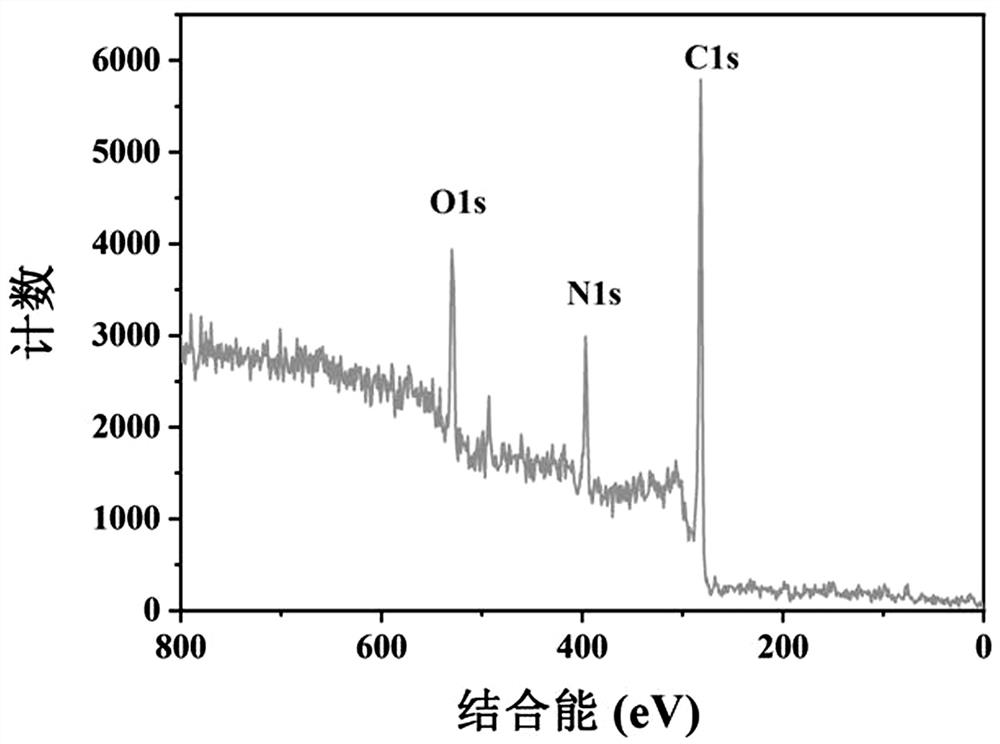
[0037] image 3 It is the X-ray photoelectron spectrum of N-CDs, which shows that N-CDs are mainly composed of three elements: C, N, and O.
[0038] Figure 4 It is the infrared spectrum of N-CDs, which shows that N-CDs are rich in functional groups such as O-H / N-H, C-H, C=N, C-N, C-O, etc., ensuring that N-CDs have good water solubility, and N-CDs have positive potential (25.2 mV ), s...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: Toxicity test of N-CDs on HeLa cells
[0042] HeLa cells were grown in DMEM medium enriched with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U / mL penicillin, and 100 μg / mL streptomycin at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultivated in the environment. Cells in the logarithmic growth phase were divided into 8×10 4 / mL was inoculated into 96-well culture plates (100 μL culture solution per well), and incubated at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Incubate in the environment for 24 h. After the cells were completely adhered to the wall, the cells were divided into a blank control group and an experimental group. There were 6 replicate wells in each group. The final concentrations of N-CDs added to the experimental group were 0.05, 0.5, 5, 25, and 50 µg / mL, respectively. . After the cells were further incubated for 24 h, the liquid in the wells was aspirated, and 100 μL of DMEM medium containing MTT (0.5 mg / mL) was added to each well. After the cells were further incubated for 4 h, the supernatant was aspirated,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com