Method for removing zero-valent mercury and arsenic hydride through cooperation of magnetic field and photocatalytic oxidation
A technology of photocatalytic oxidation and zero-valent mercury, which is applied in the field of flue gas purification, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of catalyst sunlight, low efficiency of photocatalytic zero-valent mercury, and low catalytic removal efficiency, so as to reduce competitive adsorption and reduce adsorption The effect of competition, simplicity of structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: Catalytic oxidation of arsine and zero-valent mercury by modified titanium dioxide assisted by an external magnetic field, the steps are as follows:
[0027] 1. Catalyst preparation
[0028] Weigh 21mL of absolute ethanol and place it in a beaker, place the beaker in a magnetic stirrer and continue stirring, add 7mL of butyl phthalate, continue stirring for 30min, then add 1.5mL acetylacetone and continue stirring for 30min to obtain a uniformly stirred mixed solution A , Dissolve 0.2525g of ferric nitrate and 0.3234g of nickel nitrate in 5mL of distilled water, add 10mL of absolute ethanol and 1mL of nitric acid to prepare solution B, put solution B in a separatory funnel drop by drop into solution A, use nitric acid or Adjust the pH to 6 with ammonia water, raise the temperature to 70°C and continue to stir until it reaches a gel state. After drying the gel in an oven at 80°C for 12 hours, put the material in a muffle furnace and bake it at 400°C to obtain ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: The method for removing zero-valent mercury and arsine by this magnetic field cooperative photocatalytic oxidation is as follows:
[0033] 1. Commercially purchased bismuth oxide (Bi2O3), lanthanum nitrate, iron nitrate nonahydrate, prepared Fe by impregnation method 2 o 3 -NiO / Bi 2 o 3 Composite catalyst; the specific preparation method is: prepare 3g of catalyst, active components NiO and Fe 2 o 3 The theoretical loading amount of each is 3wt% (mass fraction), and the precursor nickel nitrate hexahydrate Ni(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O and ferric nitrate nonahydrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O), put it in a beaker, add 5mL of deionized water to the beaker, stir it with a glass rod to dissolve it completely, weigh 2.82g of commercially available bismuth oxide and add it to the above solution, continue to stir for 20min, put the solution on the ultrasonic Ultrasonic for 60min, then placed in a water bath and heated at 60°C for 2h to obtain a solid mixture; put the m...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: The method for removing zero-valent mercury and arsine by this magnetic field cooperative photocatalytic oxidation is as follows:
[0037] 1. Prepare titanium dioxide gel by sol-gel method: use tetrabutyl titanate as raw material, add water, glacial acetic acid, and absolute ethanol to tetrabutyl titanate and mix well to obtain a gel, in which water and titanic acid The molar ratio of butyl ester is 3:1; the molar ratio of glacial acetic acid to butyl titanate is 0.5:1; the molar ratio of absolute ethanol to butyl titanate is 20:1, and the prepared gel is dried, Grinding into powder, using the impregnation method to load 0.2525g ferric nitrate and 0.2522g cerium nitrate on the surface of dried 1.8g titanium dioxide to obtain a titanium dioxide catalyst loaded with Fe and Ce, and press it through a 40-60 mesh sieve;
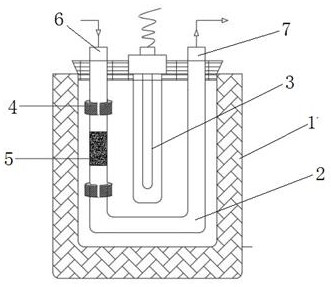
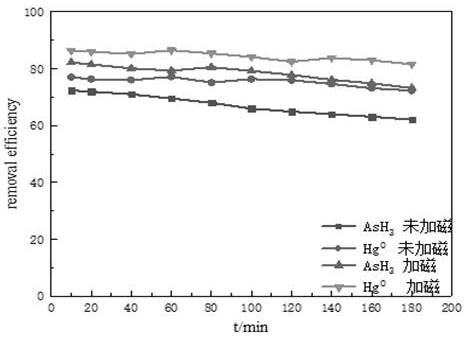
[0038] 2. If figure 2 As shown, the gas-solid photocatalytic device is the same as in Example 1, except that the magnetic field generator i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com