Preparation of terbium-based rare earth crystalline material and its application in fluorescence detection of antibiotics in water
A fluorescence detection, rare earth technology, applied in luminescent materials, analytical materials, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome, time-consuming operation and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
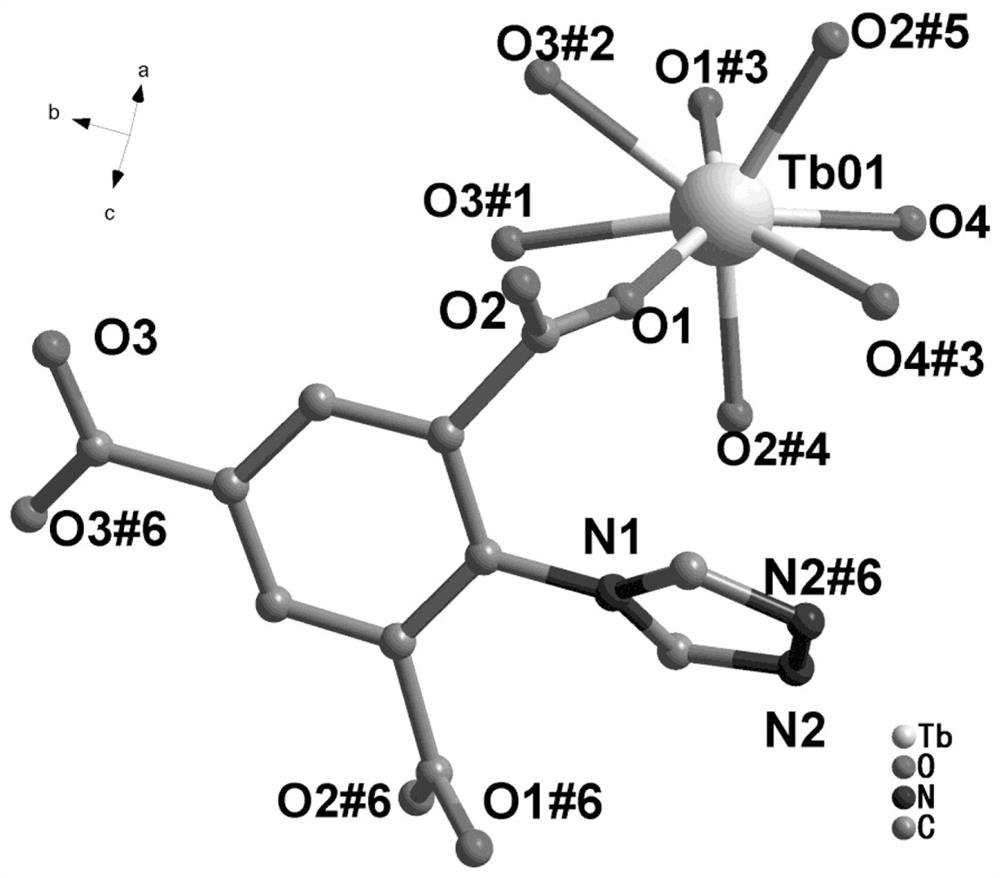
[0035] Weigh 0.0167g of organic ligand, 0.0271g of terbium nitrate hexahydrate, 1mL of N,N-dimethylformamide, 1mL of polyethylene glycol-400 and 3mL of deionized water, adjust the pH of the solution to 2.0 with 6M nitric acid, add In a Teflon-lined stainless steel reactor, react at a constant temperature of 100°C for 24 hours, and cool down to room temperature to obtain a colorless and transparent terbium rare earth crystal material.
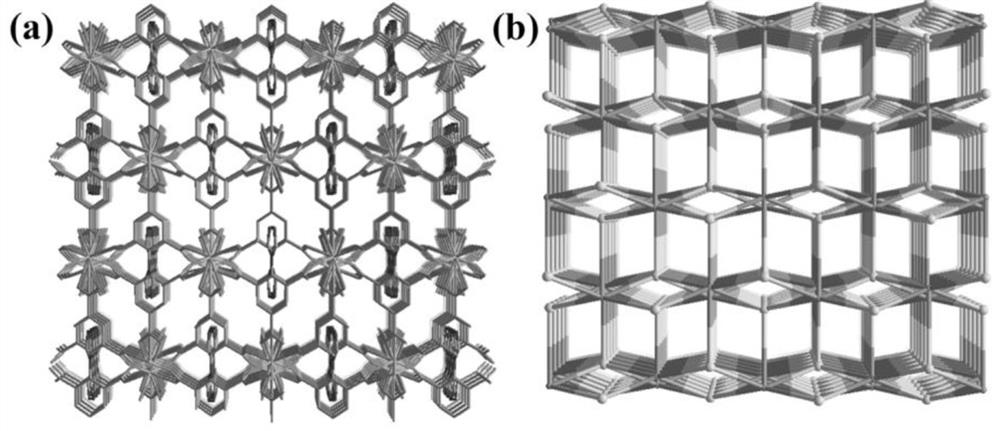
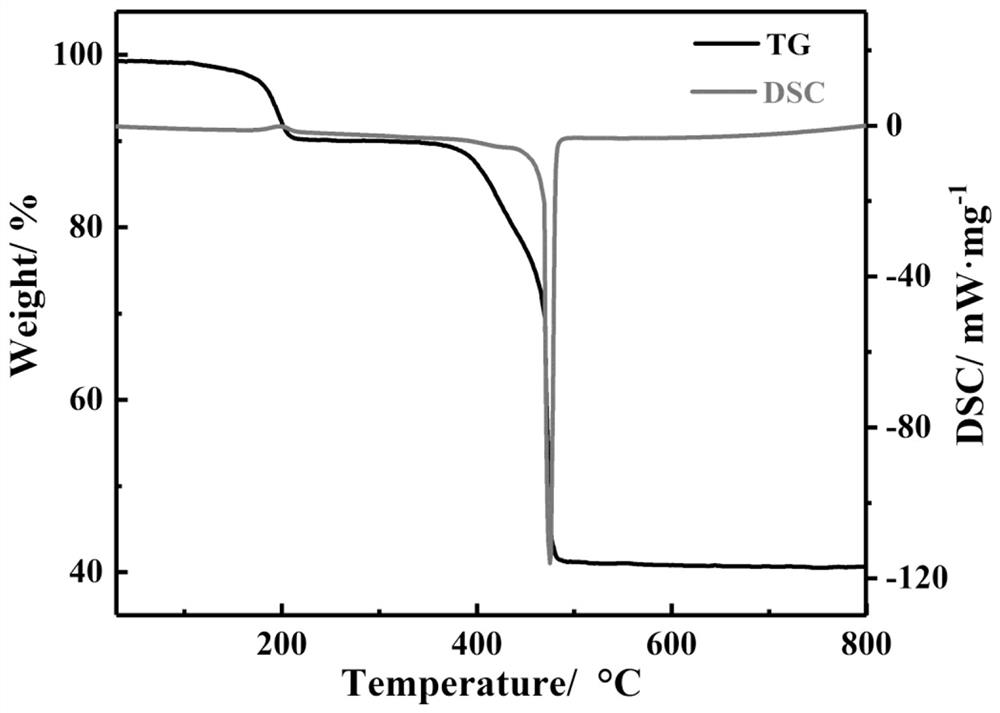
[0036] The single crystal of the terbium rare earth crystalline material synthesized by the present invention uses the small molecule type X-ray single crystal diffractometer of Japan Rigaku Company to carry out structure determination on the crystal, and utilizes the Mo Kα ray monochromated by the graphite monochromator, under 173K The data such as diffraction intensity and unit cell parameters were measured, and the collected data were corrected by empirical absorption using scanning technology. The results obtained were analyzed by the direct me...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Configure 11 antibiotics into 2×10 -4 M solution, 11 antibiotics including penicillin (PCL), florfenicol (FFC), chloramphenicol (CAP), sulfamethazine (SMZ), sulfadiazine (SDZ), ornidazole (ODZ), Dimetridazole (DTZ), metronidazole (MDZ), ronidazole (RDZ), nitrofurantoin (NFT), nitrofurazone (NZF). 5mg of the terbium rare earth crystalline material obtained in Example 1 were added to 10mL 2×10 -4 M antibiotic solution, ultrasonically dispersed at room temperature for 20 minutes, got 3mL suspension and moved it into a cuvette and tested the fluorescence spectrum of the suspension, and focused on comparing the 548nm before and after adding different antibiotics ( 5 D. 4 → 7 f 5 ) changes in fluorescence intensity at the emission peak. The above-mentioned fluorescence tests are all carried out at room temperature and under the conditions of an optimal excitation wavelength of 230nm.
[0043] Figure 5 It is the solid fluorescence emission diagram of the terbium-based ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 5 mg of the terbium rare earth crystalline material in Example 1 were added to 10 mL of SMZ aqueous solutions containing different concentrations, ultrasonically dispersed at room temperature for 20 minutes, and 3 mL of the suspension was transferred into a cuvette and tested at the optimal excitation wavelength of 230 nm. Fluorescence spectra, such as Figure 8 The fluorescence quenching of the material to different concentrations of SMZ antibiotics and the 5 D. 4 → 7 f 5 Fluorescent emission conditions. Figure 8 (a) is the fluorescence intensity variation diagram (in the figure, from top to bottom is H 2 O, 2×10 -6 M, 4×10 -6 M, 5×10 -6 M, 1×10 -5 M, 3×10 -5 M, 5×10 -5 M, 8×10 -5 M, 1×10 -4 M, 1.5×10 -4 M, 2×10 -4 M); (b) is when different concentrations of antibiotic sulfamethazine (SMZ) are added to the aqueous solution of terbium-based rare earth crystalline materials 5 D. 4 → 7 f 5 Fluorescence emission intensity change graph. With the increase...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com