Method for preparing 1T-phase molybdenum disulfide induced by carbon dot doping and application thereof to energy storage material
A technology of molybdenum disulfide and carbon dots, which is applied in the direction of molybdenum sulfide, nano-carbon, hybrid capacitor electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of difficult synthesis of molybdenum disulfide, poor electrochemical performance, and low yield, and achieve excellent electrochemical performance and catalytic performance. Absorbing performance, high specific capacitance, high output effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] In this embodiment, molybdenum source and sulfur source are not added, the content of carbon source monohydrate citric acid is 2.48g, and the obtained product is marked as CASO. Dissolve 2.48 g of citric acid monohydrate in 50 mL of deionized water and mix and stir until a uniform solution is obtained to obtain a precursor solution; pour the precursor solution into a polytetrafluoroethylene autoclave, and move the reactor to an oven. React at 220°C for 10 hours; after the reaction, remove the reactor from the oven, filter the brownish-yellow liquid in the reactor three times under reduced pressure, using a water-based filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 μm. The filtrate was dialyzed using a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut off of 500, and the water was changed every 10 hours on average, and the dialysis process lasted for 72 hours. Remove the liquid in the dialysis bag, and use a rotary evaporator to remove excess water to obtain a yellow concentrated solut...
Embodiment 2
[0030] This example prepares carbon dots doped 1T molybdenum disulfide according to the following steps:
[0031] 1. Preparation of precursor
[0032] A molybdenum source, a sulfur source, a certain mass of carbon source and water are fully mixed and stirred to a uniform solution in a certain molar ratio to obtain a precursor. Wherein, the molybdenum source adopts ammonium molybdate heptahydrate, the sulfur source adopts thiourea, the molar ratio of the sulfur source and the molybdenum source is 2:1, and the quality is 2.28 and 1.24g respectively; the carbon source adopts citric acid monohydrate, citric acid monohydrate The mass is 0g, and the water uses 50mL of deionized water.
[0033] 2. Preparation of carbon dot doped 1T molybdenum disulfide
[0034] Pour the precursor into a high-pressure reactor and react at 220°C for 10 hours. After the reaction is over, use ethanol and deionized water to filter and wash the dark liquid in the reactor for several times, and finally dr...
Embodiment 3
[0036] In this example, the molar ratio of sulfur source and molybdenum source is 2:1, the masses are 2.28 and 1.24 g respectively, and the carbon source citric acid monohydrate is 2.48 g. Others are the same as in Example 2, and the obtained product is marked as CAS2.
[0037] Concrete preparation parameters in embodiment 1-3 are as follows:
[0038]
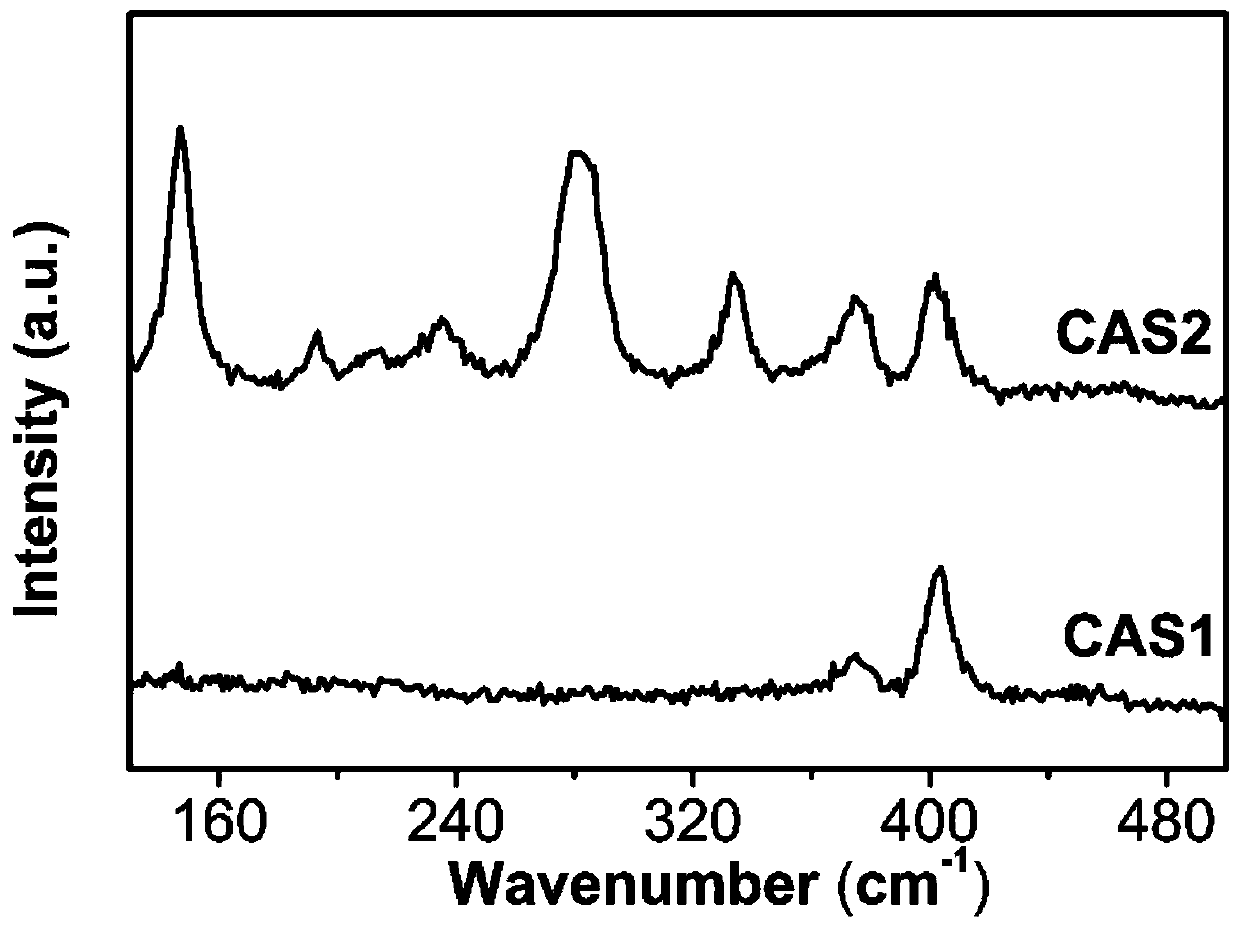
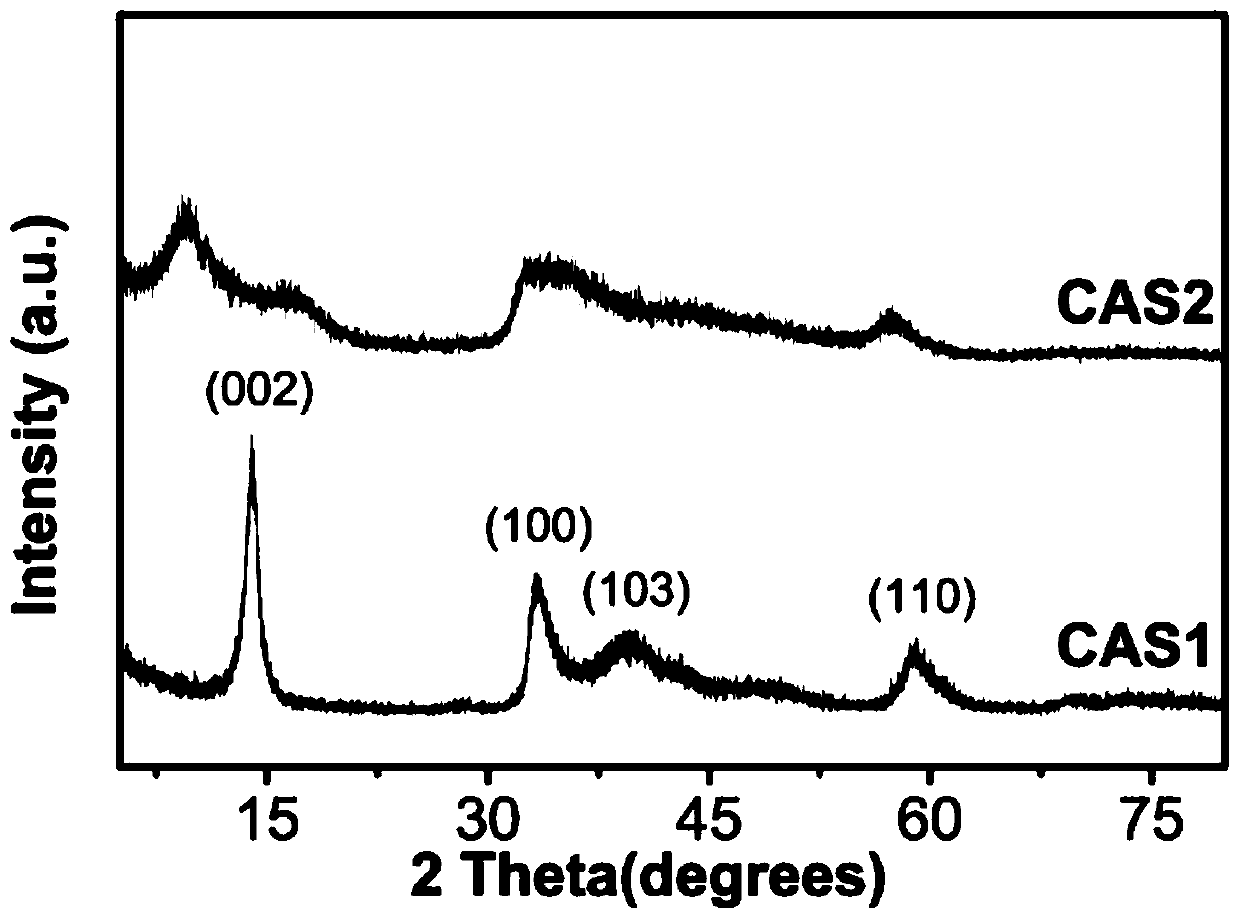
[0039] figure 1 Raman diagram of molybdenum disulfide and carbon dots doped 1T molybdenum disulfide hybrid material, sample CAS2 at 147(J 1 ), 196, 219 (J 2 ),280(E 1g ) and 327 (J 3 )cm -1Shows a distinct Raman peak of the 1T crystal form, unlike CAS1 which only shows E 1 2g and A 1g These two typical Raman peaks are typical of 2H MoS2. This indicates that the carbon dots produced by citric acid induce the generation of the 1T phase crystal structure of MoS2. This is because citric acid enters the lamellar structure of molybdenum disulfide, expanding the interlayer spacing of molybdenum disulfide, and the carbon qu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com