Preparation method of porous metal oxide
A porous metal and oxide technology, applied in ceramic products, applications, household appliances, etc., can solve the problems of difficult removal of templates, low production efficiency, high production cost, and achieve good market prospects, low cost, and high adhesion performance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
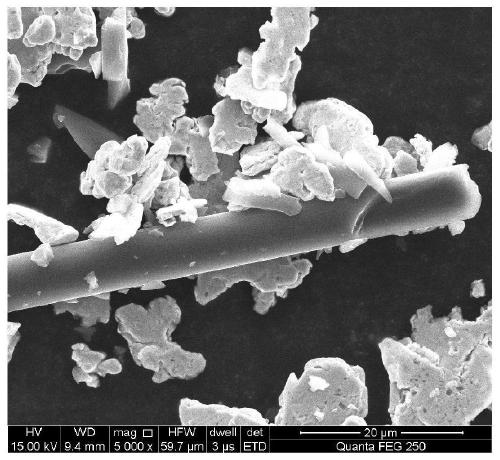
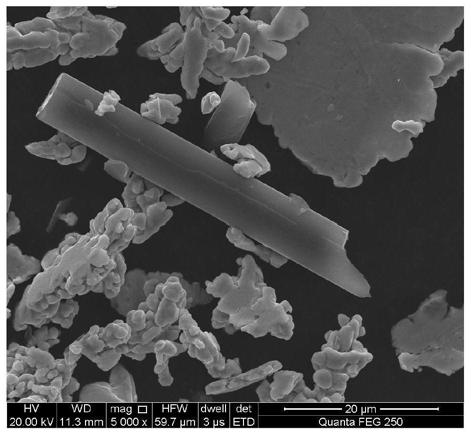
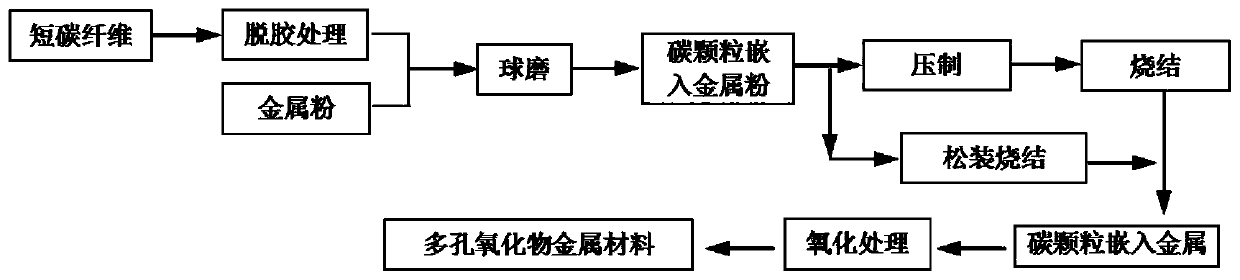
[0062] This example 1 uses commercially available short carbon fibers that have been degummed at 700°C for 60 minutes and electrolytic copper powder with a particle size of 120 μm as the ball mill raw materials. The volume percentage of short carbon fibers is 10%, and the volume percentage of electrolytic copper powder is 90%. The diameter is 6μm and the length is 2mm. The two are added to the ball milling equipment for high-energy ball milling. The speed is 250r / min, the milling time is 6h, and the ball-to-battery ratio is 6:1. The obtained mixed powder was cold pressed at room temperature, the pressing pressure was 50MPa, and the pressure holding time was 20s. The prepared carbon particles embedded in the copper compact were sintered under the protection of hydrogen atmosphere, and sintered at 900℃ for 1h. The heating rate and cooling rate of the furnace The sintered billet is annealed in the air to remove carbon and oxidation. The annealing temperature is 300°C and the holdin...
Embodiment 2
[0064] This example 2 uses commercially available short carbon fibers that have been degummed at 750°C for 60 minutes and electrolytic nickel powder with a particle size of 120 μm as raw materials for ball milling. The volume percentage of short carbon fibers is 25%, and the volume percentage of electrolytic nickel powder is 75%. The diameter is 6μm and the length is 2mm. The two are added to the ball milling equipment for high-energy ball milling, the speed is 280r / min, the milling time is 7h, and the ball-to-battery ratio is 6:1. The obtained mixed powder was sintered directly under the protection of hydrogen atmosphere, and sintered at 850℃ for 1h. The heating rate and cooling rate of the furnace were both 15℃ / min. Then the sintered compact was annealed in the air to remove carbon and oxidation, and the annealing temperature was 500℃. , The holding time is 30 minutes, the porosity of the porous nickel oxide is 22-30%, and the nickel oxide content is 90% of the total mass.
Embodiment 3
[0066] In this example 3, commercially available short carbon fibers and reduced iron powder with a particle size of 150 μm that were degummed at 800°C for 60 minutes were used as the ball mill raw materials. The volume percentage of short carbon fibers was 40%, and the volume percentage of reduced iron powder was 60%. The diameter is 6μm and the length is 2mm. The two are added to the ball milling equipment for high-energy ball milling. The speed is 300r / min, the milling time is 8h, and the ball-to-battery ratio is 6:1. The resulting mixed powder was sintered directly under vacuum and sintered at 980°C for 1 hour. The heating rate and cooling rate of the furnace were both 15°C / min. After that, the sintered compact was annealed in the air to remove carbon and oxidation. The annealing temperature was 500°C, and the temperature was kept warm. The time is 60 minutes, the porosity of the porous iron oxide is 40-48%, and the iron oxide content is 85% of the total mass.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com