Preparation method of iron-doped barium titanate nanoparticles
A nano-particle and barium titanate technology, applied in the directions of titanate, nanotechnology, alkaline earth metal titanate, etc., can solve the problems of high calcination temperature, uneven doping, grain growth, etc., and achieve a large specific surface area. , good crystallinity, promote the effect of lifting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
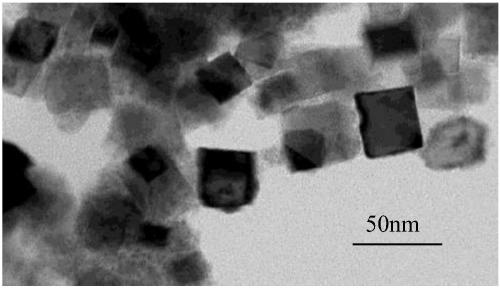
[0019] Weigh 0.7887g of Ba(OH)·8H 2 O and 0.0253g of Fe(NO 3 )·9H 2 O was dissolved in 50 ml of deionized water, 1.185 ml of di(2-hydroxypropionic acid) diammonium titanium hydroxide (50 wt % aqueous solution) was added thereto, and the mixture was fully stirred evenly. Add 11.25ml of 5M NaOH solution to the mixed precursor solution to adjust the pH value of the solution, then add 6.35ml oleic acid (OLA) under magnetic stirring, and transfer the above solution to a 100ml autoclave lining after stirring for 10min. At this time, 2.10 ml of tert-butylamine was added to the lining, and the sealed autoclave was placed at 220° C. for 24 hours, and then cooled to room temperature naturally. The precipitate was firstly washed with dilute hydrochloric acid, then washed several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol, filtered, and dried at 60°C in air to obtain iron-doped barium titanate nanoparticles.
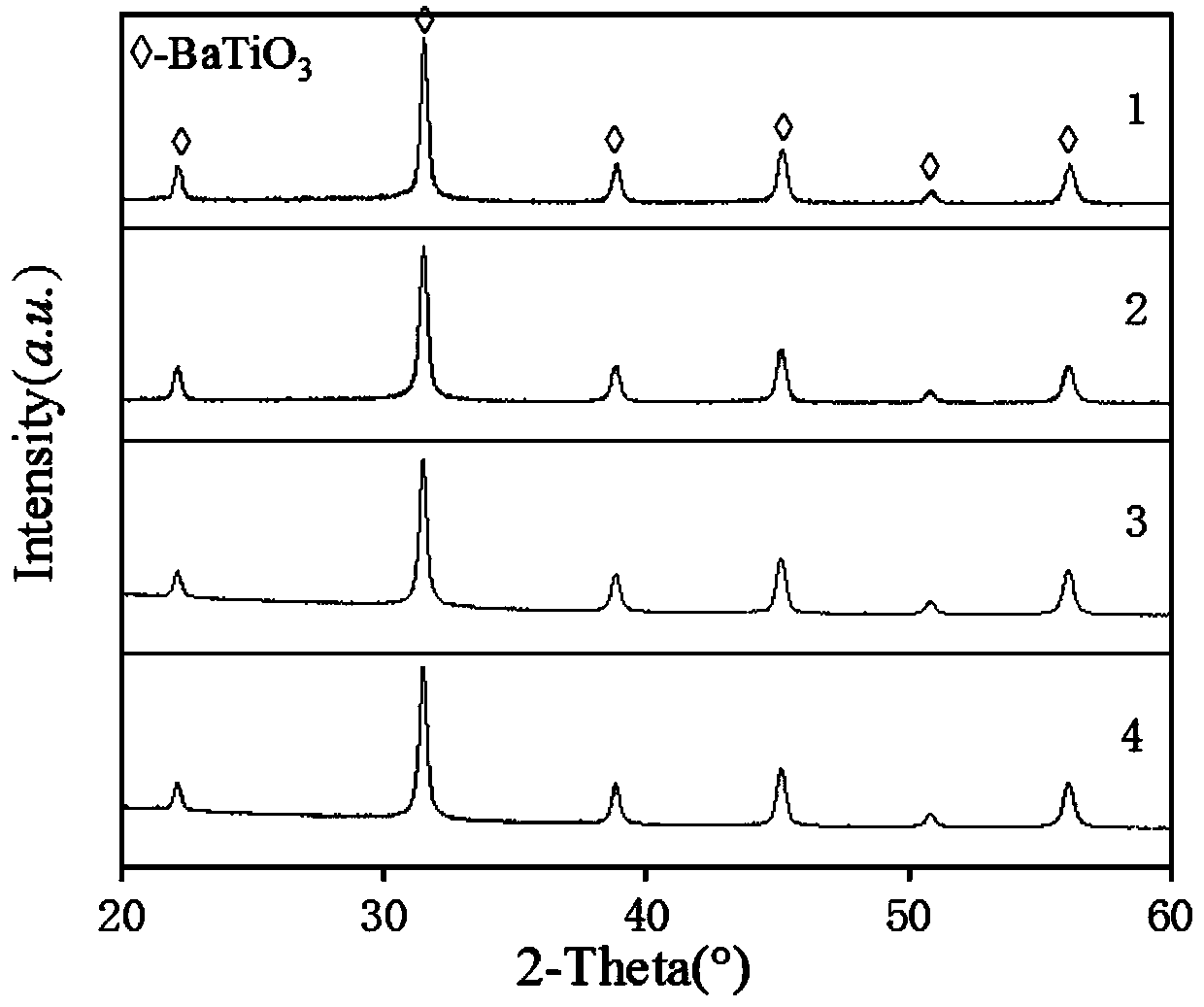
[0020] The XRD pattern of the product is as figure 1 As shown in , all...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Weigh 0.7887g of Ba(OH)·8H 2 O and 0.0505g of Fe(NO 3 )·9H 2 O was dissolved in 50 ml of deionized water, 1.155 ml of titanium di(2-hydroxypropionic acid) diammonium dihydroxide (50 wt % aqueous solution) was added thereto, and the mixture was fully stirred evenly. Add 11.25ml of 5M NaOH solution to the mixed precursor solution to adjust the pH value of the solution, then add 6.35ml oleic acid (OLA) under magnetic stirring, and transfer the above solution to a 100ml autoclave lining after stirring for 10min. At this time, 2.10 ml of tert-butylamine was added to the lining, and the sealed autoclave was placed at 220° C. for 24 hours, and then cooled to room temperature naturally. The precipitate was first washed with dilute hydrochloric acid, then washed several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol, filtered, and dried in air at 60°C to obtain iron-doped barium titanate nanoparticles.
[0023] The XRD pattern of the product is as figure 1 As shown in , all...
Embodiment 3
[0025] Weigh 0.7887g of Ba(OH)·8H 2 O and 0.0169g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O was dissolved in 50 ml of deionized water, 1.185 ml of di(2-hydroxypropionic acid) diammonium titanium hydroxide (50 wt % aqueous solution) was added thereto, and the mixture was fully stirred evenly. Add 11.25ml of 5M NaOH solution to the mixed precursor solution to adjust the pH value of the solution, then add 4.76ml oleic acid (OLA) under magnetic stirring, and transfer the above solution to a 100ml autoclave lining after stirring for 10min. After adding 2.10ml of tert-butylamine into the lining, place the sealed autoclave at 220°C for 24 hours of reaction, and then cool it down to room temperature naturally. The precipitate was firstly washed with dilute hydrochloric acid, then washed several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol, filtered, and dried in air at 60° C. to obtain iron-doped barium titanate nanoparticles.
[0026] The XRD pattern of the product is as figure 1 As shown in , all the d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com