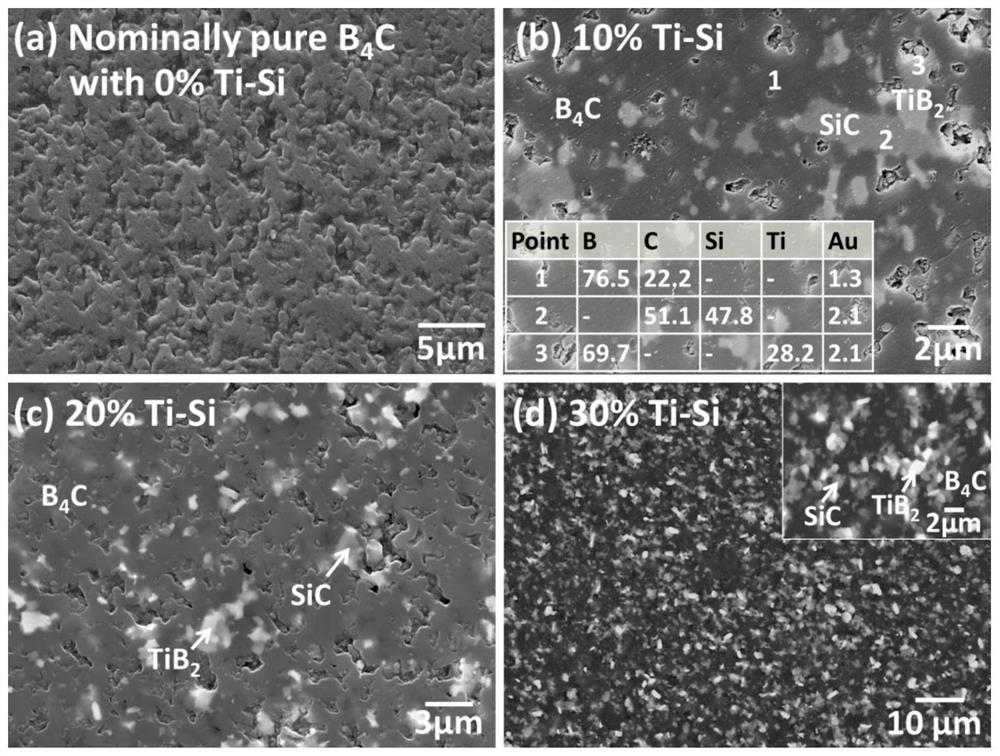
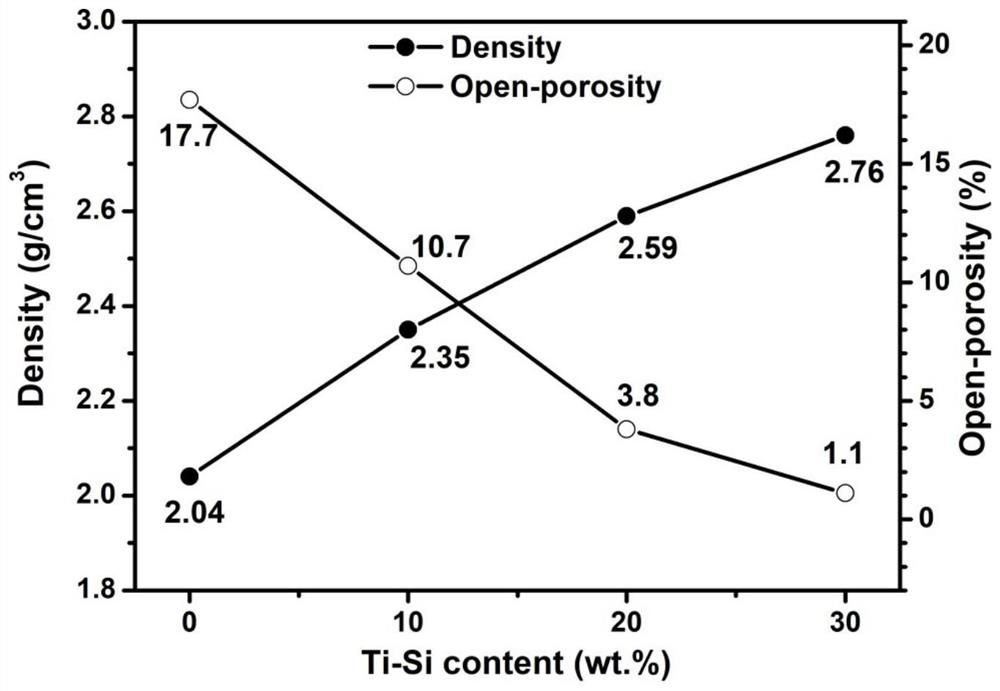
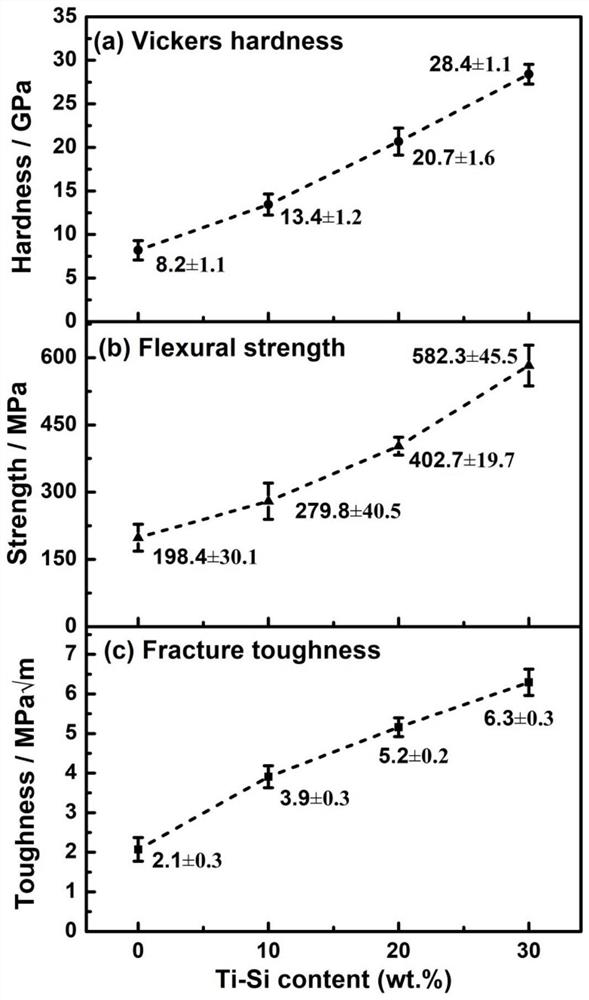
A boron carbide-based composite ceramic sintering aid and sintering process
A technology of composite ceramics and boron carbide, which is applied in the field of sintering aids and sintering technology of boron carbide-based composite ceramics, and can solve problems such as improving the fracture toughness of boron carbide ceramics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: the preparation of sintering aid
[0036] In this example, the preparation method of the sintering aid for in-situ reaction hot-pressing sintering of boron carbide-based composite ceramics is as follows:
[0037] 1. Melt the proportioned amount of titanium and silicon using non-consumable arc smelting equipment. During the smelting process, in order to make the alloy composition uniform, smelting is repeated five times; titanium and silicon are composed of: titanium 24wt%, silicon 76 wt%.
[0038] 2. The alloy block obtained in step 1 is mechanically crushed, and then the powder is ball-milled into alloy powder with an average particle size of 10 μm by a ball mill.
[0039] 3. Mix the alloy powder obtained in step 2 with boron carbide powder (0.5 μm in particle size) and absolute ethanol by means of mechanical stirring and ultrasonic dispersion to obtain a reaction sintering mixed powder. The mass ratio of boron carbide to sintering aid is 7:3.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: the preparation of sintering aid
[0041] In this example, the preparation method of the sintering aid for in-situ reaction hot-pressing sintering of boron carbide-based composite ceramics is as follows:
[0042] 1. Carry out vacuum induction melting (vacuum degree at 10 -2 Below Pa, the melting temperature is 1700°C, and the holding time is 10 minutes), cooled with the furnace, and solidified into an alloy block; titanium and silicon are composed of 35wt% titanium and 65wt% silicon.
[0043] 2. The alloy block obtained in step 1 is mechanically crushed, and then the crushed alloy is ground into a powder with an average particle size of less than 1mm by a grinding ballast, and then ball milled into an alloy powder with an average particle size of 20 μm.
[0044] 3. Mix the alloy powder obtained in step 2 with B 4 C powder (particle size 5 μm) was mixed by ball milling to obtain reaction sintering mixed powder. The mass ratio of boron carbide to sinterin...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3: the preparation of sintering aid
[0046] In this example, the preparation method of the sintering aid for in-situ reaction hot-pressing sintering of boron carbide-based composite ceramics is as follows:
[0047] 1. Melt the proportioned amount of titanium and silicon using non-consumable arc smelting equipment. During the smelting process, in order to make the alloy composition uniform, smelting is repeated five times; titanium and silicon are composed of: titanium 30wt%, silicon 70wt%.
[0048] 2. The alloy block obtained in step 1 is mechanically smashed, and then the smashed alloy is ground into a powder with an average particle size of less than 1mm by a grinding ballast, and then ball milled into an alloy powder with an average particle size of 10 μm.
[0049] 3. Mix the alloy powder obtained in step 2 with boron carbide powder (particle size 1 μm) and absolute ethanol by means of mechanical stirring and ultrasonic dispersion to obtain a reaction sint...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com