Method for detecting residual principal stress of polymer material products
A technology of polymer materials and principal stress, which is applied in the fields of analyzing materials, using wave/particle radiation for material analysis, measuring devices, etc. wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
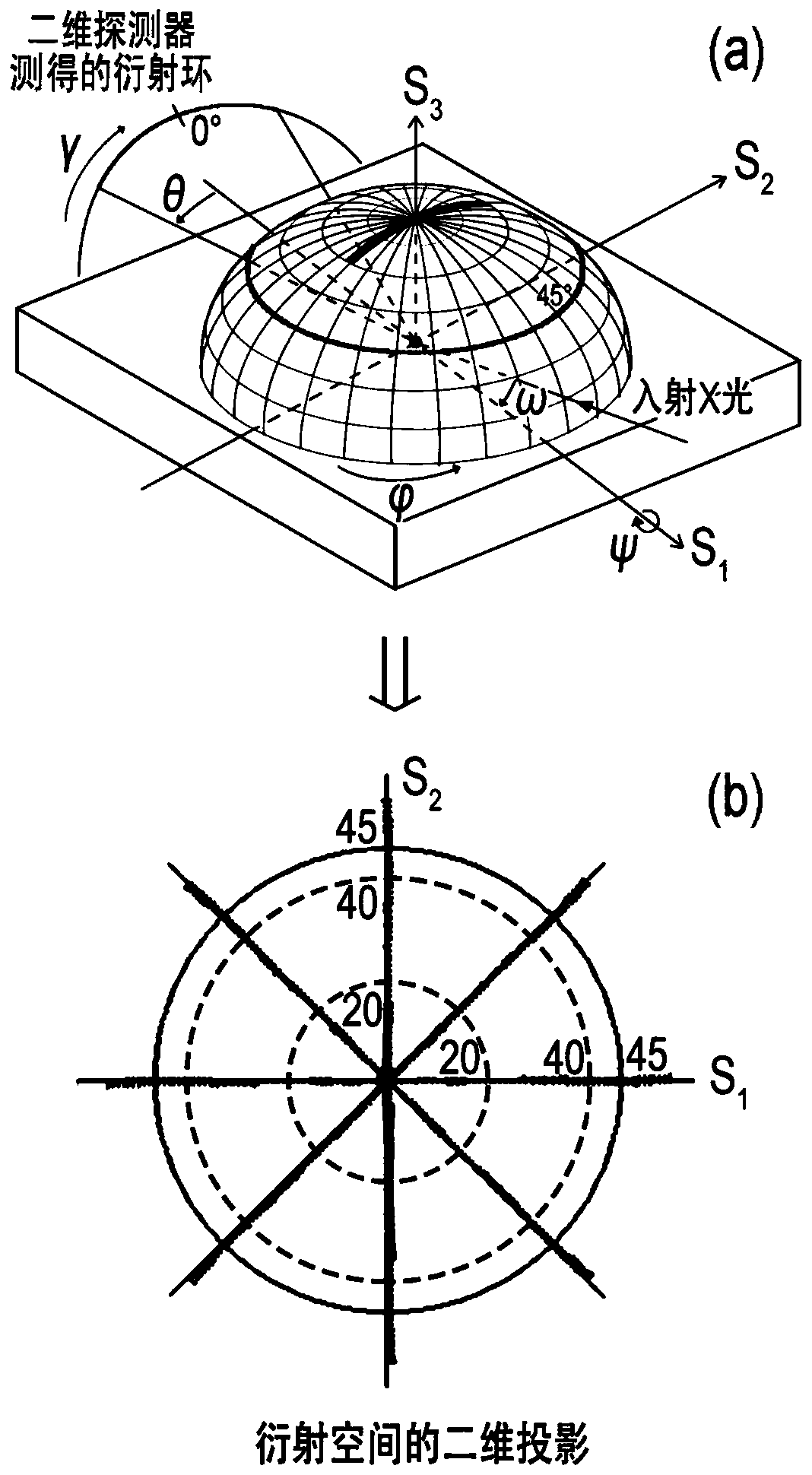
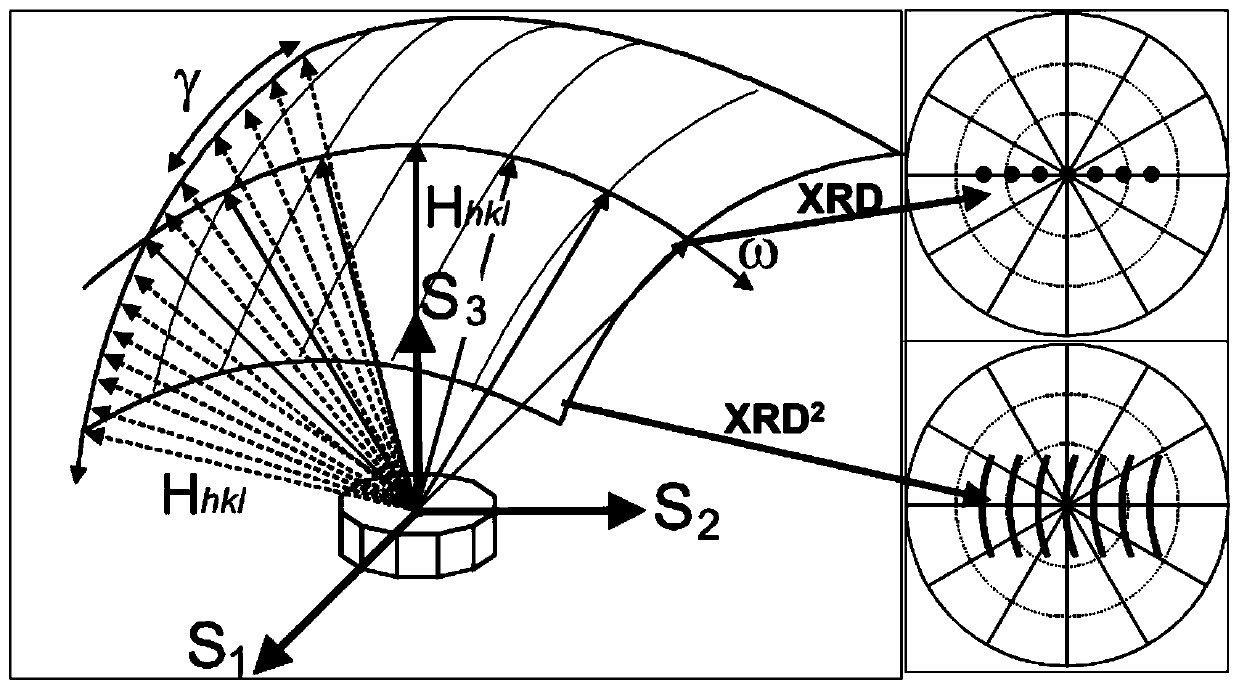
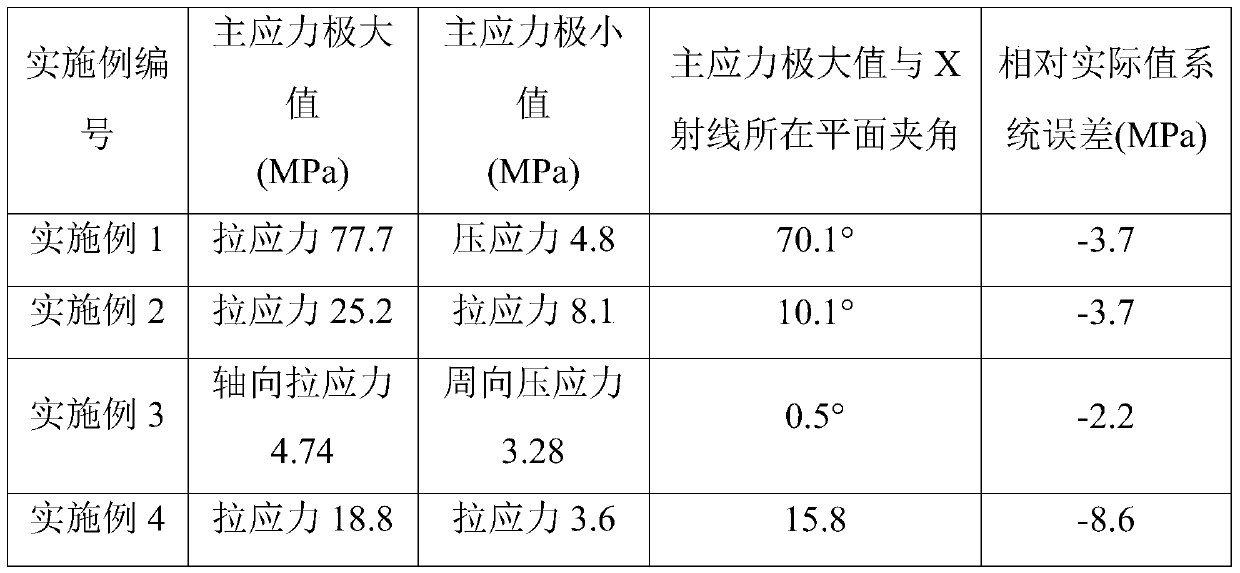
[0052] After the polypropylene material is extruded into a sheet at 230°C, it is cut into a polypropylene material of 7cm×7cm×0.2cm (length×width×height), and the polypropylene material is stretched using a biaxial stretching machine, and the polypropylene material is stretched at 155°C The bottom is stretched to five times along the machine direction (MD) at a rate of 300% deformation per second, and the size of the central position of the stretched polypropylene material is 5cm * 5cm * 0.03cm (length * width * height ) sample, adsorbed on the sample stage with deionized water, adjust the X-ray incident angle and the detector receiving angle to be 13 degrees, collect the X-ray diffraction ring spectrum of the sample, and select the second highest angle diffraction peak corresponding to the The (060) crystal plane was used as the diffraction crystal plane for testing. The sample stage is then rotated around S 3 Axis, according to the rotation azimuth angle in the plane of the...
Embodiment 2
[0054] After the polypropylene material is extruded into a sheet at 230°C, it is cut into a polypropylene material of 7cm×7cm×0.0025cm (length×width×height), and the polypropylene material is stretched using a biaxial stretching machine, and the polypropylene material is stretched at 155°C It is stretched to five times along the machine direction (MD) at a rate of 300% deformation per second, and then heated to 173°C, and then stretched to seven times at the same stretching speed perpendicular to the machine direction (TD). Biaxially stretched film, the size of the central position of the stretched polypropylene material is taken as a sample of 5cm × 5cm × 0.0025cm (length × width × height), adsorbed on the sample stage with deionized water, and adjust the X-ray Both the incident angle and the detector receiving angle are 13 degrees. For the sample diffraction ring collected, the (060) crystal plane corresponding to the second highest angle diffraction peak in the field of view...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Cut a PE100 polyethylene pipe with an outer diameter of 4 cm into 12 cm long pieces and fix it on the sample stage so that the highest point of the pipe wall is at the incident point of X-rays. Adjust the X-ray incident angle and the detector receiving angle to be 18 degrees, collect the sample diffraction ring, and select the (040) crystal plane corresponding to the highest angle diffraction peak in the field of view as the diffraction crystal plane for testing. Then tilt the sample stage 22.5° clockwise around the S1 axis, rotate the sample stage around the S3 axis in the plane of the sample stage according to the rotation azimuth angle 0°, 45°, 90°, 135°, 180°, 225°, 270° and 315° are rotated sequentially and the diffraction ring data is collected to obtain 8 diffraction ring data maps, and import the obtained 8 diffraction ring data maps into Bruker DIFFRAC.LEPTOS stress calculation software, set the calculation range of data selection: the start angle of integral ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com