Method for determining chlorine ions in vanadium electrolyte
An electrolyte and chloride ion technology, applied in measuring devices, material analysis through optical means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of easy to cause errors, harsh experimental conditions, and low accuracy of measurement results, so as to reduce errors and absorb small Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] ① Oxidize the electrolyte sample into an electrolyte containing pentavalent vanadium, and dilute it 25 times at the same time
[0028] Pipette 4ml of vanadium battery electrolyte in a 100ml beaker, add 8ml of sulfur-phosphorus mixed acid (sulfuric acid: phosphoric acid: water volume ratio 1:1:2), then add 5mol / L potassium permanganate dropwise to oxidize until the solution is reddish, static Set aside for 5 minutes, add 5ml of urea (20wt%), dropwise add 4 to 6 drops of sodium nitrite (1wt%) to make the solution yellow, transfer it to a 100ml volumetric flask, shake well, add water to make up to 100ml.
[0029] ②Drawing of working curve
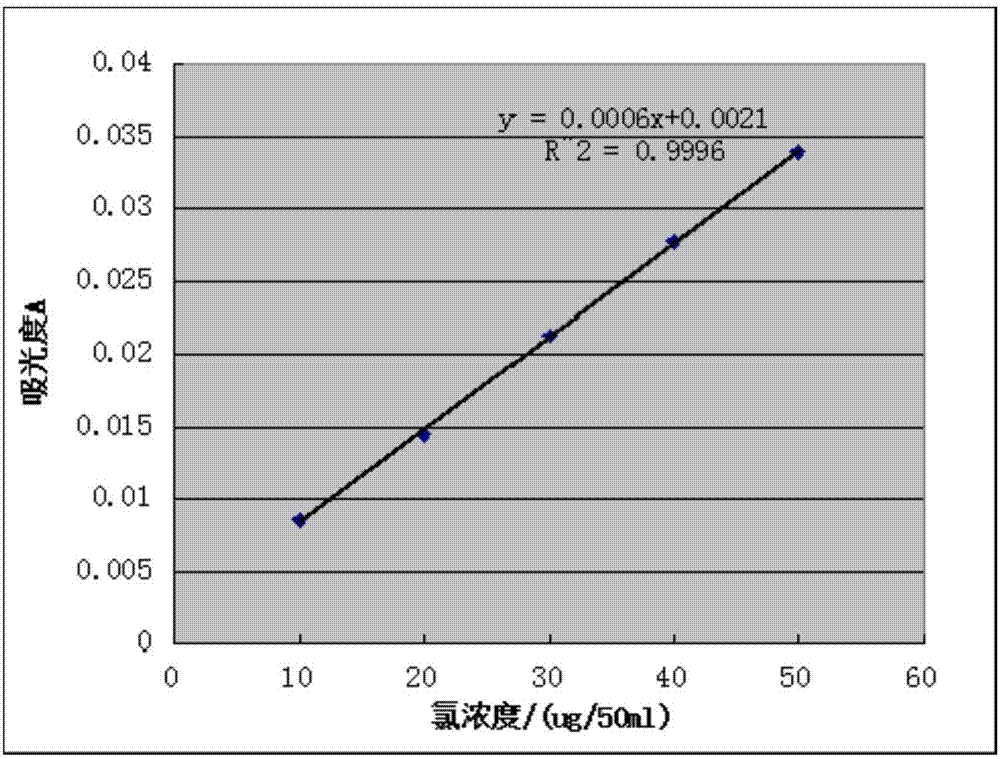
[0030] Take 25ml of pure pentavalent vanadium solution in six 50ml volumetric flasks, respectively add 0mL, 1mL, 2mL, 3mL, 4mL, 5mL chlorine standard solution, then add 2ml of nitric acid (1:1 nitric acid aqueous solution), 2ml of silver nitrate ( 0.1mol / L), add water to dilute to the scale 50ml, after standing for 20min, take the samp...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Except for the following differences, all the others were measured by the same method as that of Example 1 to measure the electrolyte sample of Example 2.
[0041] ① Drawing of working curve
[0042] Pipette 4ml of the prepared trivalent and tetravalent vanadium electrolytes into a 100ml beaker, add a certain amount of sulfur-phosphorus mixed acid, then add potassium permanganate dropwise to oxidize until the solution is reddish, let it stand for 5min, add 5ml of urea, drop 4 ~6 drops of sodium nitrite make the solution yellow, transfer it to a 100ml volumetric flask, shake well, add water to make the solution 100ml.
[0043] Take 25ml of oxidized pentavalent vanadium solution in six 50ml volumetric flasks, add 0mL, 1mL, 2mL, 3mL, 4mL, 5mL of chlorine standard solution, add 2ml of nitric acid, 2ml of silver nitrate, dilute with water to 50ml , after standing still for 20min, take the sample without chlorine standard solution as blank, measure the absorbance of the othe...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Except for the following differences, the same method as that of Example 1 was used to measure the electrolyte sample of Example 3.
[0046] ① Drawing of working curve
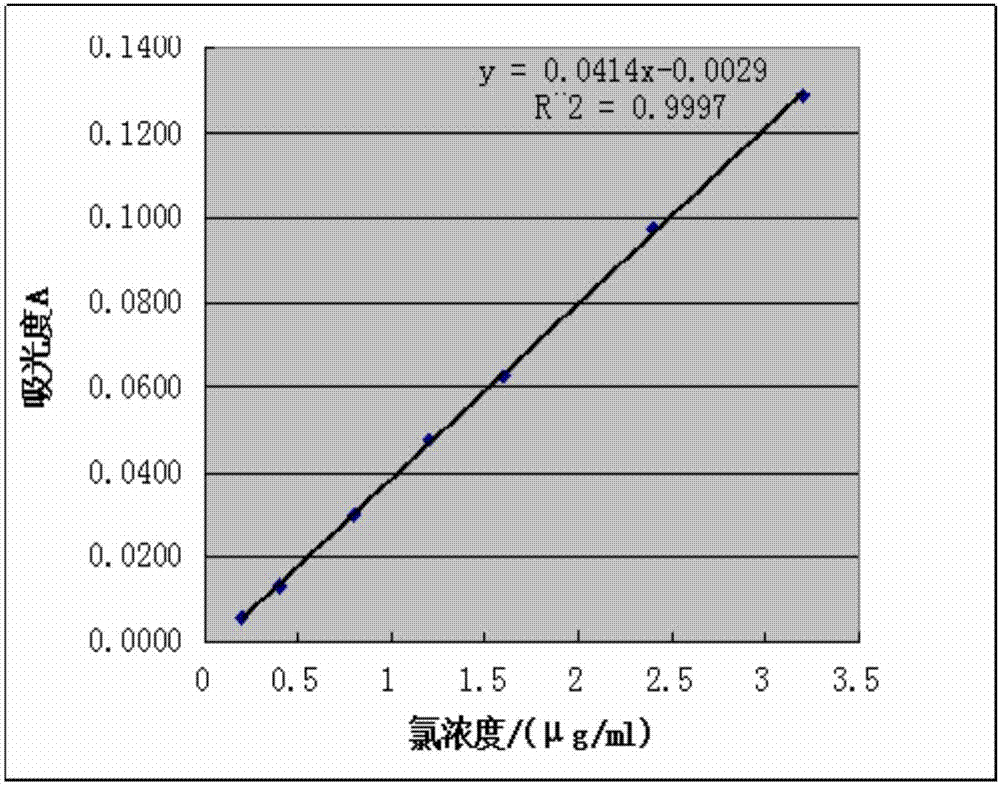
[0047] Take 5ml of pure pentavalent vanadium solution in eight 25ml volumetric flasks, add 0mL, 0.5mL, 1mL, 2mL, 3mL, 4mL, 6mL, 8mL chlorine standard solution, add 2ml of nitric acid, 2ml of silver nitrate, dilute with water to the scale, after standing still for 20 minutes, take the sample without chlorine standard solution as blank, measure the absorbance of other 7 samples at the wavelength of 460nm, take the chloride ion concentration as the abscissa, and the corresponding absorbance as the ordinate, draw the work curve, working curve such as figure 2 shown.
[0048] ②Use a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance of the sample
[0049] Use a pipette to accurately pipette 5mL of pentavalent vanadium electrolyte solution into a 25mL volumetric flask, add 2mL of nitric acid in turn and shake we...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com