High-iron-content samarium-cobalt permanent magnet material and preparation method
A technology of permanent magnet material and content, applied in the direction of magnetic material, inorganic material magnetism, magnetic object, etc., can solve the problem of poor squareness of samarium cobalt permanent magnet, and achieve the effect of improving magnetic field, reducing cost and high magnetic energy product
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
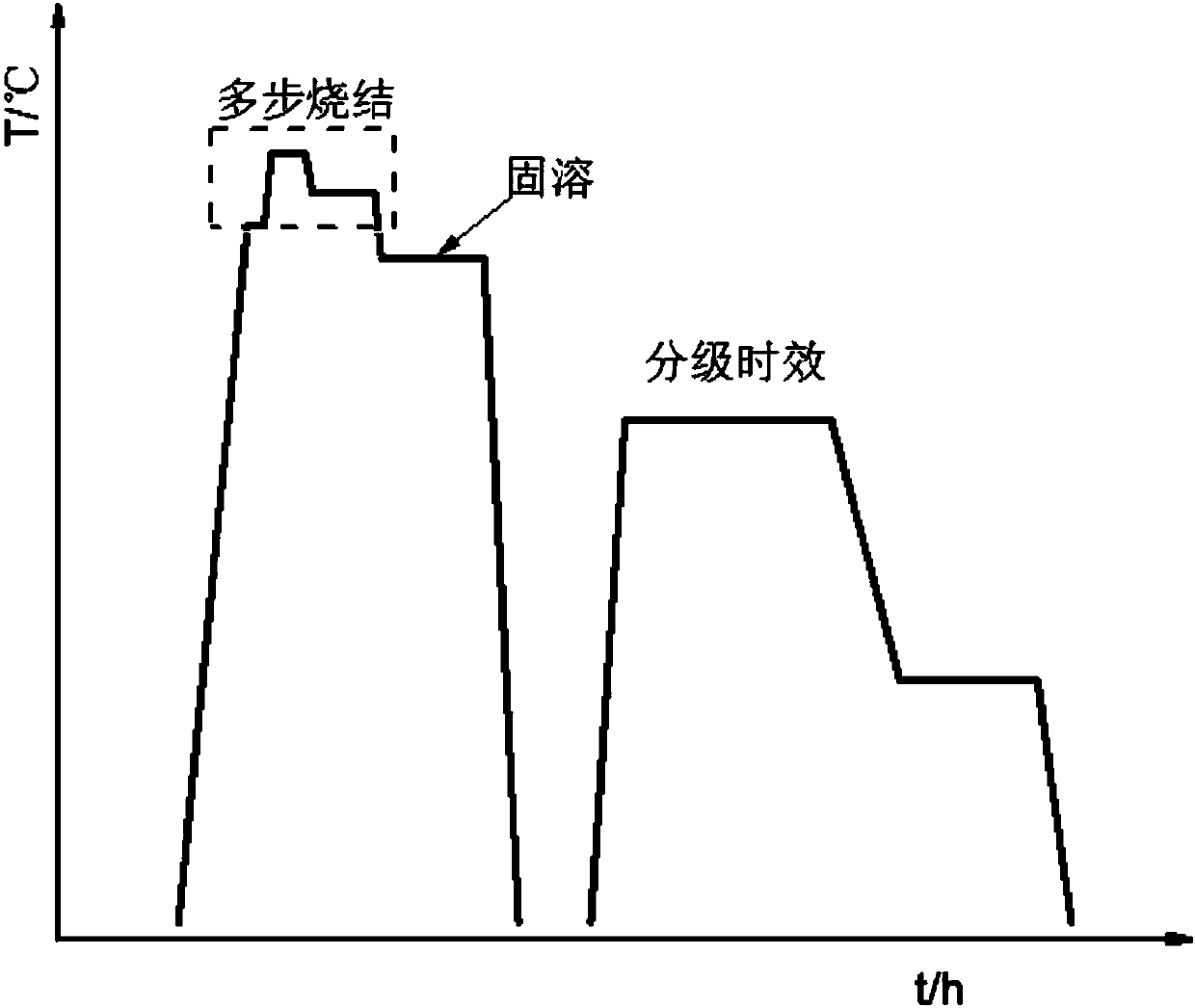
[0031] like figure 1 As shown, a method for preparing a high iron content samarium cobalt permanent magnet material of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0032] The first step is to smelt the ingot
[0033] Configure the target composition alloy, put the target composition master alloy in the vacuum arc melting furnace and smelt until the alloy melt is in a uniform state, and the arc is broken to form an alloy ingot; turn the alloy ingot, and repeatedly smelt 3 to 5 times to prepare an alloy ingot with uniform composition.
[0034] Step 2: Milling
[0035] Sm to be prepared 1-p M p (Co 1-x-y-w Fe x Cu y Zr w ) z The alloy ingot is crushed by a pulverizer to a coarse powder that can pass through an 80-mesh sieve, and then a ball mill or jet mill is used to obtain Sm with a particle size of 3-5μm 1-p M p (Co 1-x-y-w Fe x Cu y Zr w ) z powder;
[0036] The third step, magnetic field forming and cold isostatic pressing
[0037] The dried powder ...
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Preparation of Sm 0.90 Pr 0.10 (Co 0.62 Fe 0.30 Cu 0.06 Zr 0.02 ) 7.7 Permanent magnet material, no third step sintering is added in the sintering process
[0043] The first step is to smelt the ingot
[0044] Configure the target component as Sm 0.90 Pr 0.10 (Co 0.62 Fe 0.30 Cu 0.06 Zr 0.02 ) 7.7 Alloy, put the target composition master alloy in a vacuum arc melting furnace until the alloy melt is in a uniform state, and the arc is broken to form an alloy ingot; turn the alloy ingot, and repeatedly smelt 3 to 5 times to prepare an alloy ingot with uniform composition.
[0045] The second step, milling
[0046] Sm to be prepared 0.90 Pr 0.10 (Co 0.62 Fe 0.30 Cu 0.06 Zr 0.02 ) 7.7 The alloy ingot is crushed by a pulverizer to a coarse powder that can pass through an 80-mesh sieve, and then a ball mill or jet mill is used to obtain Sm with a particle size of 3-5μm 0.90 Pr 0.10 (Co 0.62 Fe 0.30 Cu 0.06 Zr 0.02 ) 7.7 powder;
[0047] ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Preparation of Sm 0.90 Pr 0.10 (Co 0.62 Fe 0.30 Cu 0.06 Zr 0.02 ) 7.7 For permanent magnet materials, 1h is added to the third step of sintering in the sintering process.
[0058] The only difference between this example and Example 1 is that in the fourth step, the temperature is lowered to 1190°C for 1 hour after sintering in an argon atmosphere at 1210°C for 1 hour, and then solution aging treatment is performed under the same conditions. Get the target sample.
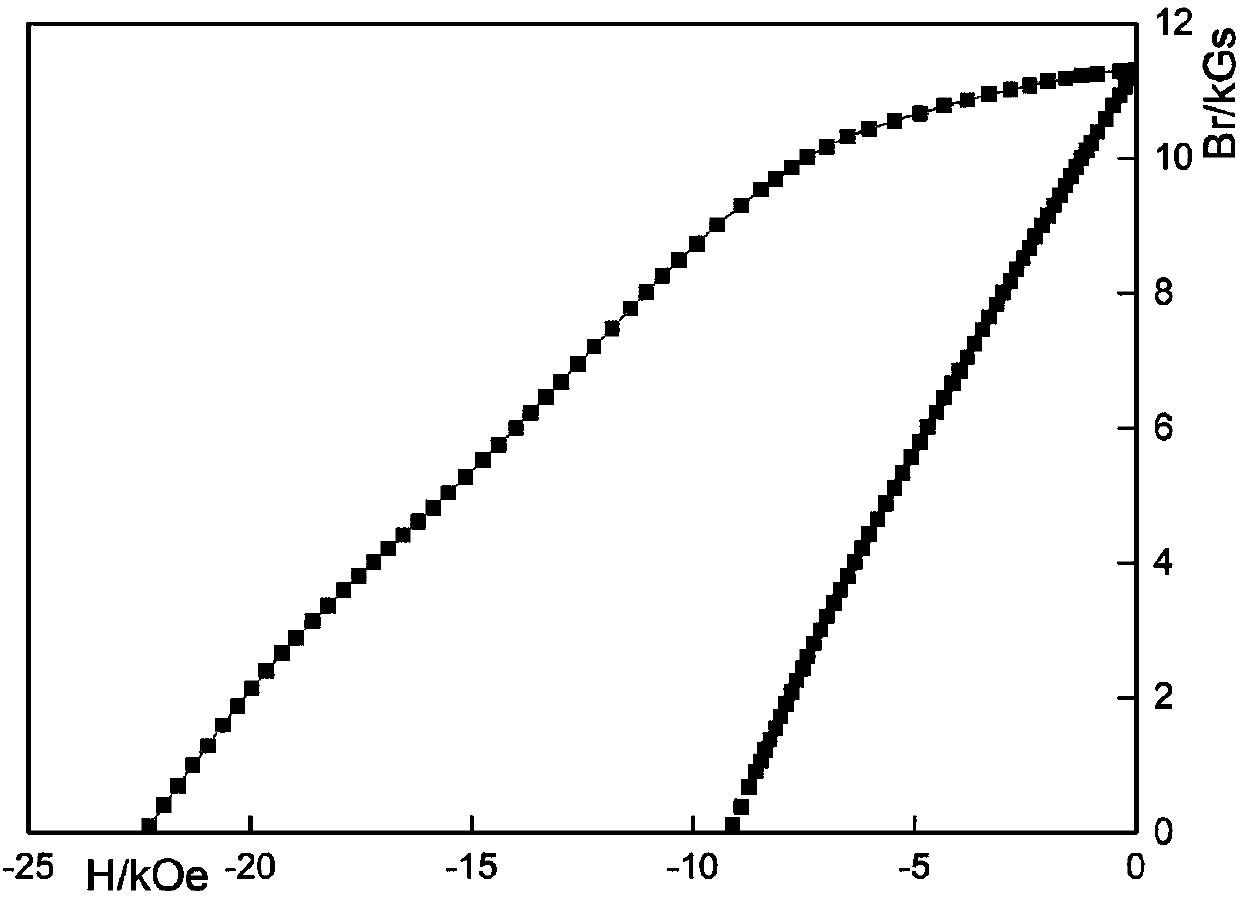
[0059] The magnetic properties of the samples were measured with a permanent magnet material measurement system NIM-500C. Its magnetic performance parameters are shown in Table 2.
[0060] Table 2. Example 2 Sample Sm 0.90 Pr 0.10 (Co 0.62 Fe 0.30 Cu 0.06 Zr 0.02 ) 7.7 Magnetic properties
[0061]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com