Cryptography attribute-based access control method and system based on dynamic rule
An access control and cryptography technology, applied in the information field, can solve the problems of not being able to maintain dynamic attributes, not having scalability, etc., to achieve the effect of ensuring consistency and integrity, and efficient authorization access process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
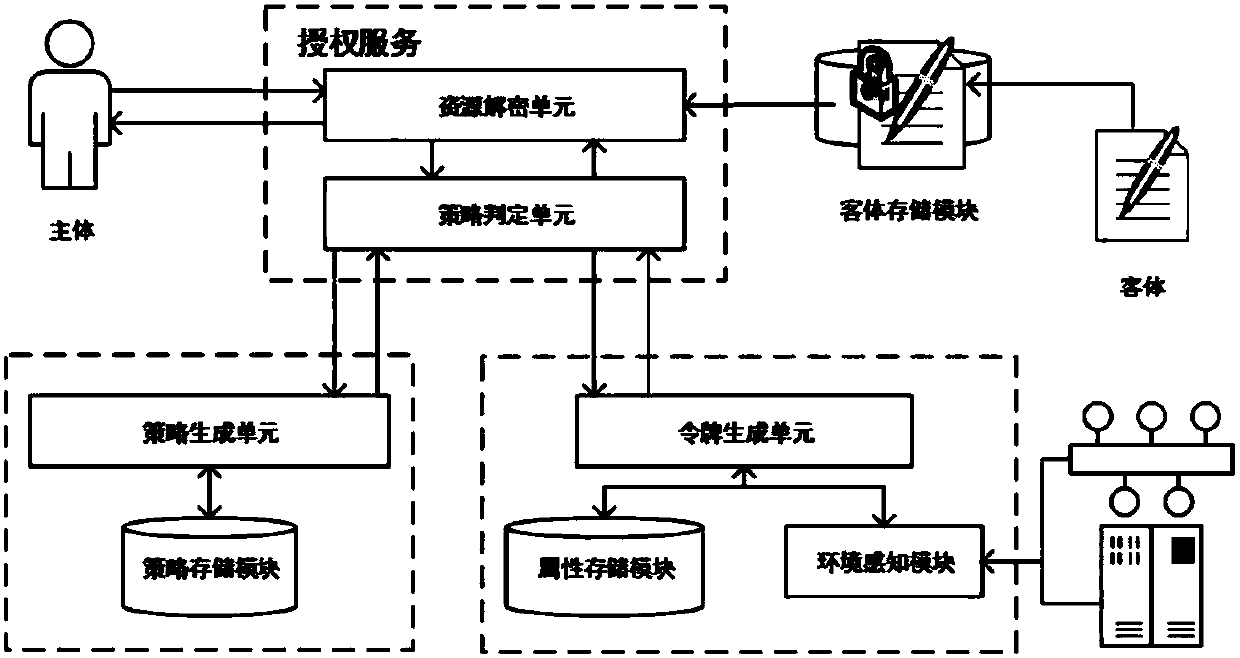
[0090] A cryptographic attribute-based access control method based on dynamic rules. In this embodiment, the method includes four entity attribute sets, corresponding access policies and authorization procedures. The specific embodiments are as follows, which will also be used in subsequent embodiments :
[0091] Subject attribute set S, including: name and occupation, denoted as S 1 ,S 2 . The name is represented by a string, if it contains two members {"ZhangSan","LiSi"}, formally name it as S 1 :={s 11 ,s 12}. Occupation includes two attribute values {Doctor, Nurse}, formally named as S 2 :={s 21 ,s 22}.
[0092] Object attribute set O, including: file name and file type, expressed as O 1 ,O 2 . The filename is a string, formalized as O 1 :={0,1} n . The file type includes two attribute values {WardRecord,PatientArchive} of "Ward Record" and "Patient Archive", which are formally named as O 2 ={o 21 ,o 22}.
[0093] Action attribute set A, including: b...
Embodiment 2
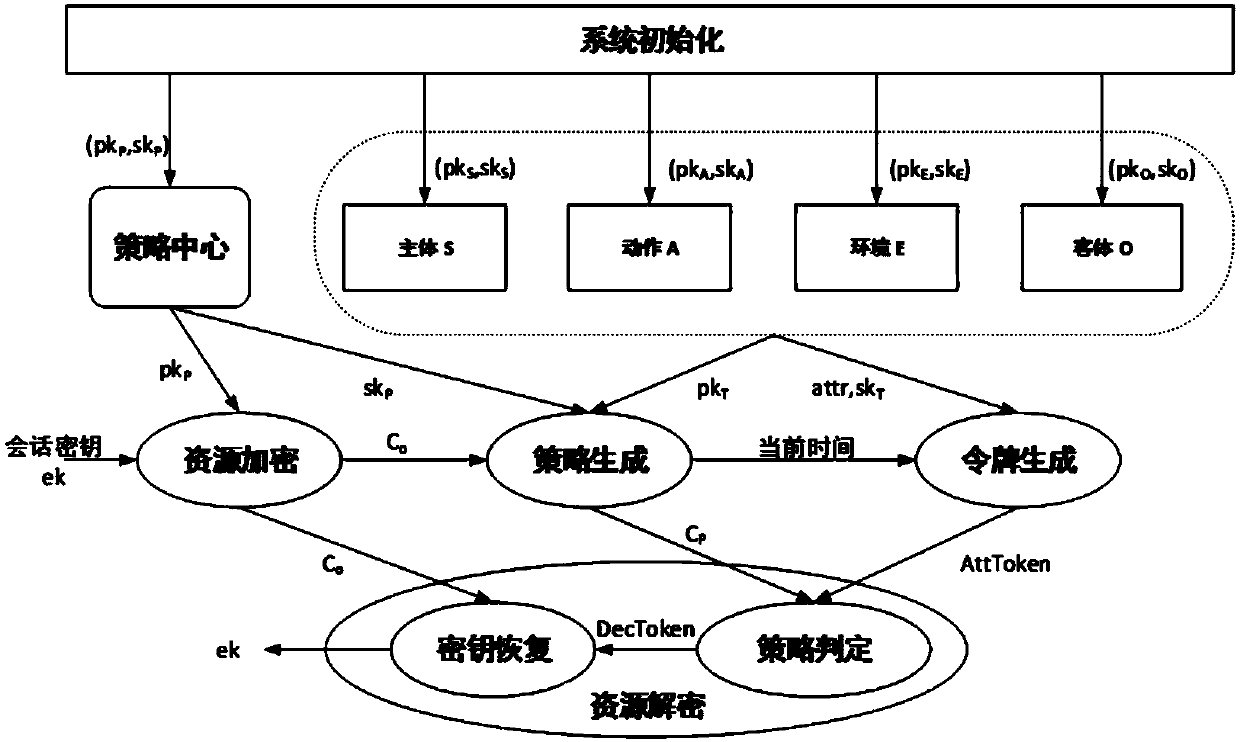
[0106] An encryption scheme is included in the access control system based on said cryptographic attribute, an embodiment of the scheme is as follows:
[0107] 1. System initialization algorithm (Setup): the input is a bilinear mapping system
[0108] The output is the public-private key pair of the policy center and each entity.
[0109] 1) in G 1 ,G 2 The generators g and h are randomly selected on the group;
[0110] 2) at The domain randomly selects the secret exponent α, and calculates g α ;
[0111] 3) The public / private key pair of the output policy center P is pk P =(g,h,g α ) and sk P =(α);
[0112] 4) For each entity T∈Ω in the entity set Ω={S,O,A,E}, in The domain randomly selects the secret exponent β T ,calculate
[0113] 5) The public / private key pair of the output entity T is and sk T =(β T )right
[0114]
[0115] 2. Object Encryption Algorithm (ObjectEnc): The input is the public key pk of the policy center P p , the output is the se...
Embodiment 3
[0155] This example takes the access policy Π in Example 1 as an example, and gives the conversion process of generating the cryptographic representation of the policy Π. This embodiment is also a detailed description of steps 2) and 4) in the policy generation algorithm (PolicyGen) and step 2) in the resource decryption algorithm (ObjectDec).
[0156] An access policy Π is composed of one or more predicates. As mentioned above, in a medical diagnosis record system, the doctor "Zhang San" wants to read the ward records on Monday. At this time, the access policy is set as "doctors can read the ward records at any time or nurses can read the ward records on weekdays." ”, the strategy can be formalized as:
[0157]
[0158] Formally describe this access strategy as the following access matrix:
[0159]
[0160] where P 1 P 5 denote the predicate S 2 =s 21 , S 2 =s 22 ,E 1 =e 11 , O 2 =o 21 and A 1 =a 11 . In this way, the access policy can be formalized as
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com