Method used for recycling microalgae residue and producing spirulina rich in polysaccharides
A technology of spirulina and microalgae, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitable scale expansion, high corrosion resistance requirements, etc., achieve good sustainability, improve utilization efficiency, The effect of reducing sewage discharge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Spirulina with high protein and low carbohydrate content (protein content 42%, carbohydrate content 16%) is used as algae species, and hydrothermal carbonation liquid is used as nitrogen source and part of carbon source to cultivate spirulina under nitrogen-limited conditions, and the production of spirulina rich in polysaccharide biomass.
[0028] 1) In a 2L stainless steel autoclave, add 1.8L deionized water, and slowly add 180 g of high-sugar spirulina (carbohydrate content 44%) algae residue 180 g into the reactor after extracting 4 hours in hot water at 80 ° C to obtain a solid Uniform algae pulp with a liquid mass ratio of 1:10. The reactor was sealed and purged with nitrogen for 2 min to maintain an inert atmosphere. Heat the reactor to 200°C at a rate of 1.5°C / min, and keep the temperature constant for 3h. Cool the reactor to room temperature at a rate of 3 °C / min with cooling circulating water. Open the purge valve to release residual gas, filter the reactio...
Embodiment 2
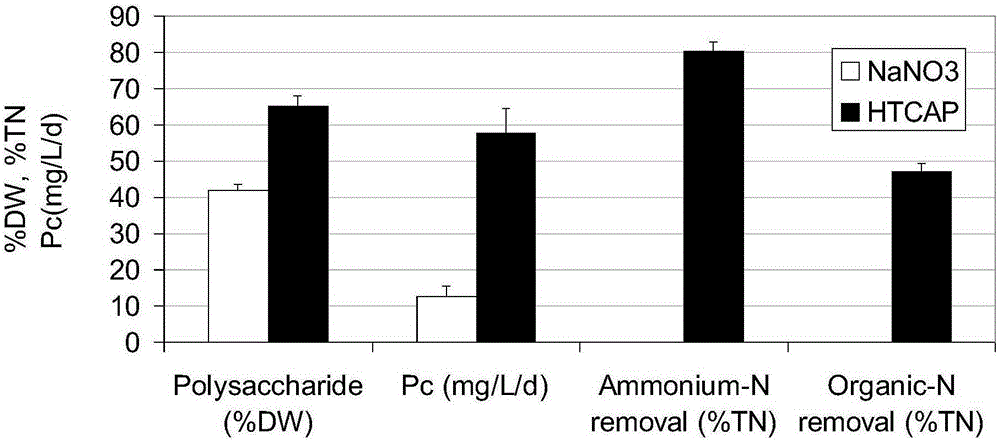
[0033] Spirulina with low protein and high carbohydrate content (protein content 22%, carbohydrate content 53%) is used as algae species, and hydrothermal carbonation liquid is used as nitrogen source and part of carbon source to cultivate spirulina under nitrogen-limited conditions, and the production of spirulina rich in Polysaccharide biomass, while removing most of the ammonia nitrogen and part of the organic nitrogen in the medium.
[0034] 1) The process of hydrothermal carbonization recovery of nutrients in the algae residue is the same as in Example 1.
[0035] 2) Spirulina algae Spirulina algae cells are cultured in nutrient-stressed inorganic salt medium (MSM) to control the initial NaNO 3 The concentration is 85mg / L, the initial inoculation density OD 560 0.3, culture temperature 26~30℃, artificial light-to-dark ratio 14h:10h, light intensity on the light-receiving surface of the culture medium 40μmol / (m 2 s), after 6 days of culture, the algal cells were in a sta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com