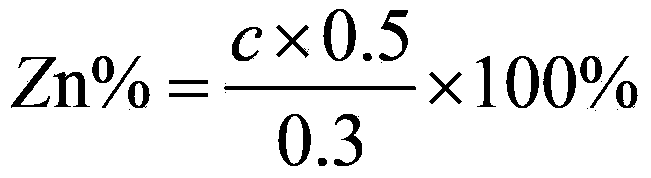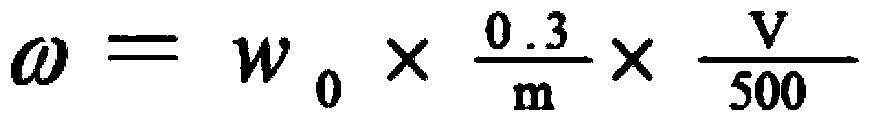Method for determining content of zinc in zinc concentrate through energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry
A fluorescence spectrometry, energy dispersion technology, applied in measurement devices, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient operation proficiency, cumbersome operation steps, long detection period, etc., and achieve high absolute sensitivity. , The effect of low labor intensity and short detection cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
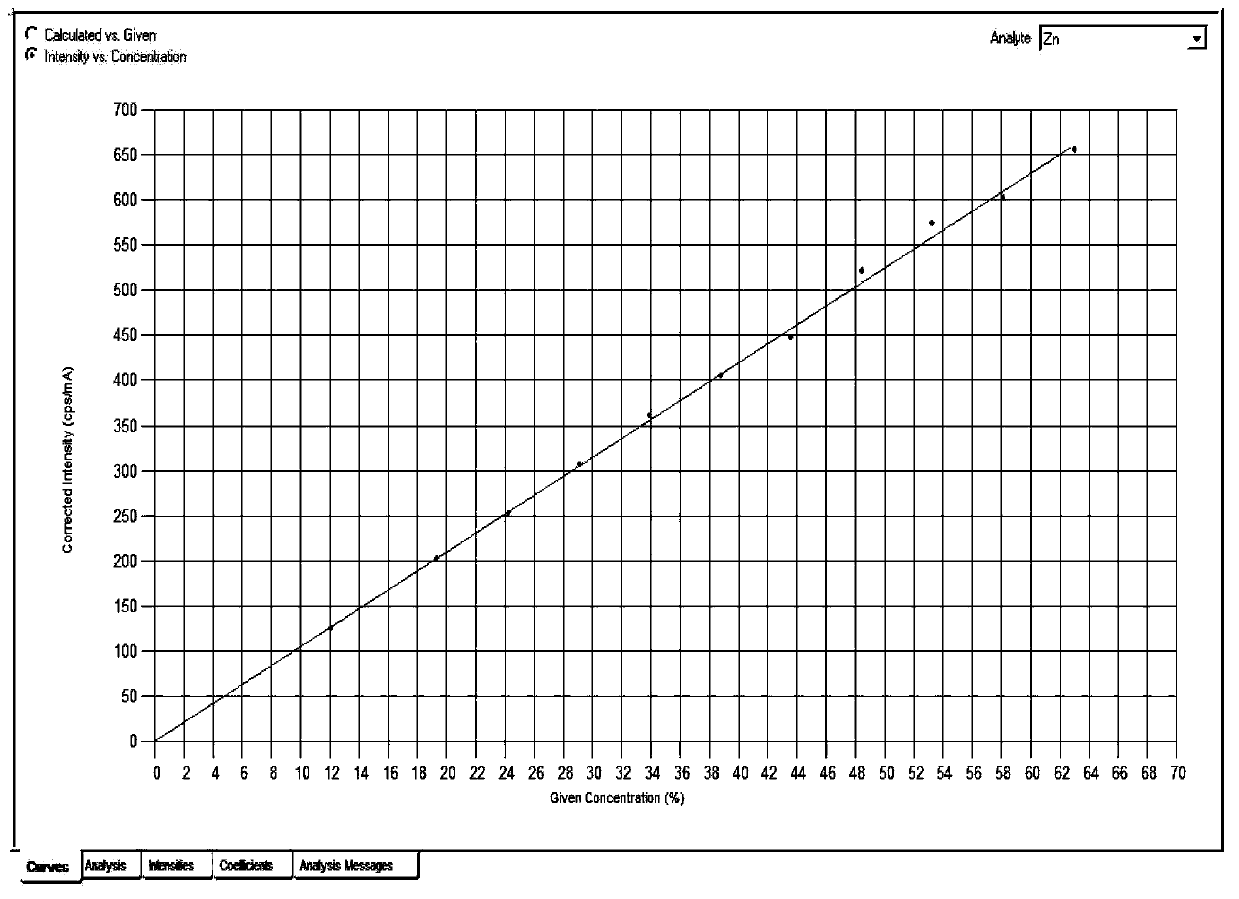
[0036] Embodiment 1: making working curve
[0037] 1) Prepare several parts of zinc-iron working solution (the mass concentration of Zn in the obtained zinc-iron working solution is required to be 0.05-0.40g / L, and the mass concentration of Fe is 0.01-0.09g / L):
[0038] The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0039] Accurately weigh 0.90g of zinc oxide reference material (accurate to 0.1mg) and 0.20g of iron (purity above 99.9%, accurate to 0.1mg when weighing) and place them in a 300mL beaker, add 100mL of water to the beaker and then add 50mL of concentrated nitric acid, heated for 15min until the reaction is complete, cooled to room temperature, transferred to a 500mL volumetric flask, and made to volume.
[0040] Prepare 11 parts of zinc-iron working solution: Pipette 5mL, 8mL, 10mL, 12mL, 14mL, 16mL, 18mL, 20mL, 22mL, 24mL and 26mL of the above-mentioned fixed-volume zinc-iron working solution into a group of 100mL volumetric flasks, add water Dilute to the sca...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2: adopt method of the present invention to measure the control test of national standard substance or standard solution
[0052] Test with the standard substance listed in the purchased table 3 and the zinc standard solution prepared by the method described in the relevant national standard with the zinc oxide standard substance, wherein the zinc nominal content of the standard substance and zinc standard solution is as shown in table 3; When adopting the method described in the present invention to measure, the standard substance is prepared the sample solution by the following method and then carries out zinc content determination.
[0053] 1) Preparation of sample solution:
[0054] Prepare the sample solution with the standard substance No. 1 as the sample, weigh 3 parts of 0.29 ~ 0.31g sample, and the accuracy of weighing is 0.1mg. The amount of dilute nitric acid (HNO 3 content of 44% by mass), and hydrofluoric acid (HF content of 40% by mass) was ad...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Embodiment 3: adopt method of the present invention to the precision test of the detection result of national standard substance
[0070] In this embodiment, the standard substances numbered 1, 2 and 3 in Table 3 were used as samples for testing.
[0071] 1) Preparation of sample solution:
[0072] Prepare the sample solution with the standard substance of No. 1 as the sample, weigh 4 parts of 0.29 ~ 0.31g sample, and the weighing is accurate to 0.1mg, put the first sample in the reaction tank, and test at 100mL / g. Dilute nitric acid (HNO3 content 43% by mass) was added to the sample amount, and hydrofluoric acid (HF content 40% by mass) was added in an amount of 18mL / g sample, and microwave digestion was carried out by using a microwave digestion instrument, and the heating method adopted a staged degree of heating , the specific parameters are shown in Table 4. After the sample is completely dissolved, transfer it, add water to make it up to 500mL, and filter it with...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com