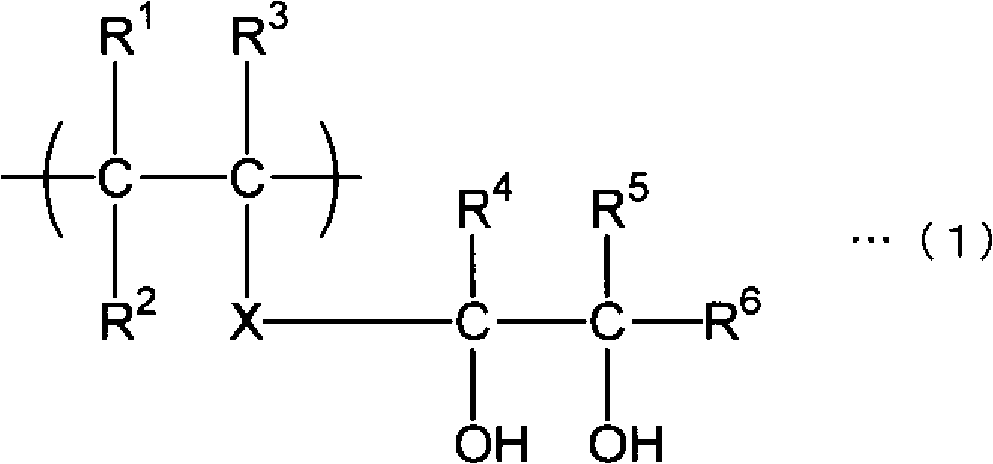
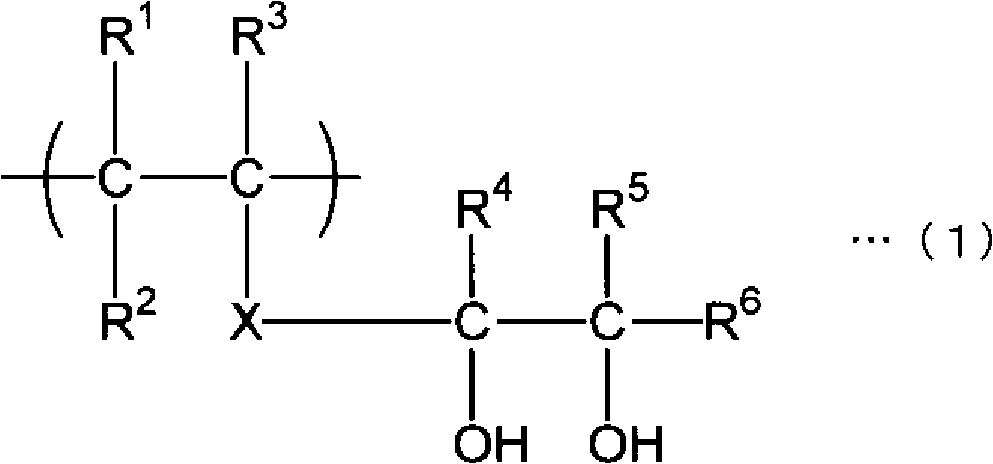
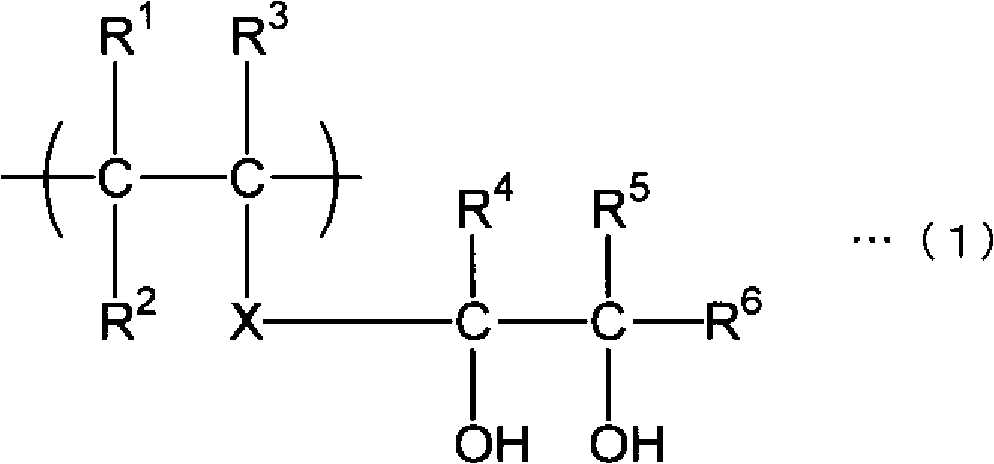
Multi-layer structure
A multi-layer structure and layer structure technology, applied in the direction of layered products, synthetic resin layered products, household components, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient, poor appearance of molded objects, high melting point, etc. Excellent peel resistance and improved interlayer adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0257]
[0258] As the layer (A) forming material shown below, the above-mentioned PET-based resin (IS654) was used, and as the layer (B) forming material, the above-mentioned PVA-based resin (B1-x) was used, and a T-die with two types and three layers was used. A melt extrusion molding machine was used to produce a layer (A) / layer (B) / layer (A) with a layer (A) thickness of 40 μm, a layer (B) thickness of 20 μm, and a layer (A) thickness of 40 μm. Laminated body (film form) with a 3-layer structure (total thickness: 100 μm).
[0259] In addition, extrusion is carried out at a mold temperature of 260°C at a resin temperature of 260 to 280°C for PET-based resins and 240°C for PVA-based resins. A multilayer structure is obtained.
[0260]
[0261] Using the obtained three-layer structure (film), the peel strength between the layer (A) and the layer (B) was measured under the following conditions. The results are shown in Table 1 below.
[0262] Sample: 15mm wide, 200mm lo...
Embodiment 2
[0267] As a layer (A) forming material, PET-based resin, the above-mentioned IG395Z (AV value 28) having a copolymerization ratio of isophthalic acid of 15.0 mol % was used. Except for this, a three-layer structure was produced in the same manner as in Example 1, and evaluated in the same manner. The results are shown in Table 1 below.
Embodiment 3
[0279] A three-layer structure was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the PVA-based resin (B2-x) was used as the layer (B)-forming material in Example 1, and evaluated in the same manner. The results are shown in Table 2 below.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com