Medical martensitic stainless steel material and preparation method thereof
A technology of martensitic stainless steel and medical equipment, applied in the field of medical equipment materials, can solve the problems of low oxidation resistance, low corrosion resistance, easy to rust, and high cost, and achieve improved corrosion resistance, simple chemical composition, and low price Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0016] Its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0017] (1) According to the chemical composition and its weight percentage range, according to the batch production situation, electric arc furnace should be used for smelting and casting steel ingots for mass production; non-vacuum induction furnace should be used for smelting and casting steel ingots for small production to reduce costs; in special cases, Vacuum induction furnace is used to melt and cast steel ingots to further improve the quality of steel;
[0018] (2) Heating the steel ingot to 1050-1100°C, forging blanks or forging into forgings with simple shapes; the final forging time temperature is 800°C, and slowly cool to room temperature after hot working;
[0019] (3) Reheat the steel ingot to 1050-1100°C, roll and process it into bars and plates, then put it into a furnace at 800°C-850°C, cool it to 500°C with the furnace, and perform air-cooling annealing treatment to transform it into Pearlite, har...
Embodiment 1
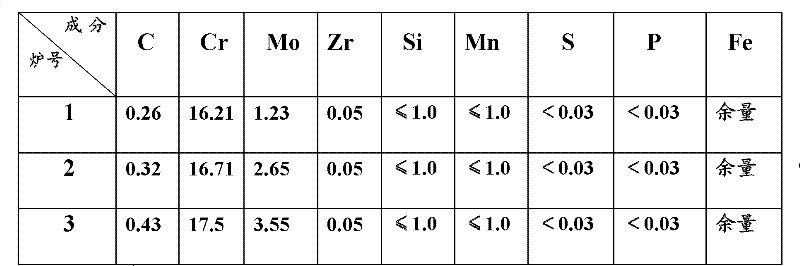
[0025] According to the chemical composition scope and proportioning ratio of stainless steel according to the present invention, carry out batching, melt 3 furnaces with vacuum induction furnace, cast 3 20 kilograms steel ingots respectively, its chemical composition is listed in Table 1.
[0026] The chemical composition of the medical martensitic stainless steel material that table 1 embodiment 1 provides
[0027]
[0028] Wherein Zr is a batching component.
[0029] The above three steel ingots are heated at 1075±25°C, and then forged into Φ10, Φ20, Φ30mm round bars and 20×20×500mm square bars; the final forging temperature is 850°C, and then air-cooled to room temperature.
[0030] The above billets are heated again to 1075±25°C, and rolled into parts of medical devices, such as hammers, bone chisels, bone drills, wire pliers, etc. After hot rolling, they are placed in a furnace at 850°C and cooled to 500°C, then taken out and air-cooled .
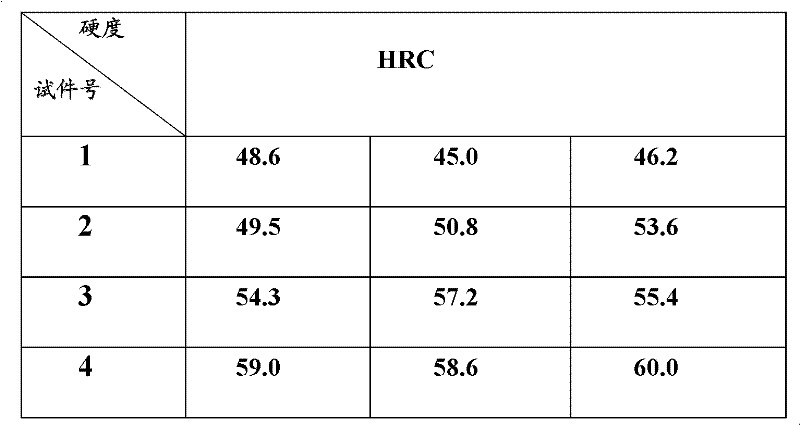
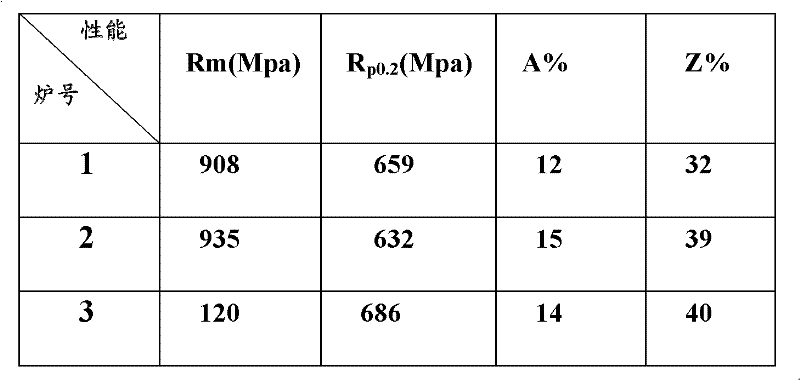
[0031] Finally, the above...
Embodiment 2
[0037] According to the stainless steel chemical composition range and proportioning ratio described in the present invention, carry out batching, melt 2 furnaces with 150kg non-vacuum induction furnace, and cast 2 140kg steel ingots respectively, its chemical composition is listed in Table 4.
[0038] The chemical composition of the medical martensitic stainless steel material that table 4 embodiment 2 provides
[0039]
[0040] Wherein Zr is a batching component.
[0041] The above two steel ingots are heated to 1075±25°C, and then forged to open billets. The steel ingots of non-01-1 furnace number are forged into Φ50mm round bars, and the non-01-2 furnace number steel ingots are forged into 200×45mm thick slabs; the final forging temperature is 850 °C, then air cooled to room temperature.
[0042] The above-mentioned billets are heated again to 1075±25°C, rolled into bars of Φ14, 16, 18, and 20mm, and plates of thickness 18, 20, and 25mm×200mm in width, and put into a f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com