Coarsening and etching method of large-area controllable surface of SiC substrate light emitting diode (LED) based on laser
A surface roughening and laser technology, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of long roughening etching time, high cost of etching equipment purchase and use, and reduced electrical performance of LEDs, etc., to achieve roughening The effects of flexible and diverse rough etching patterns, low cost of equipment and use, and improved current injection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
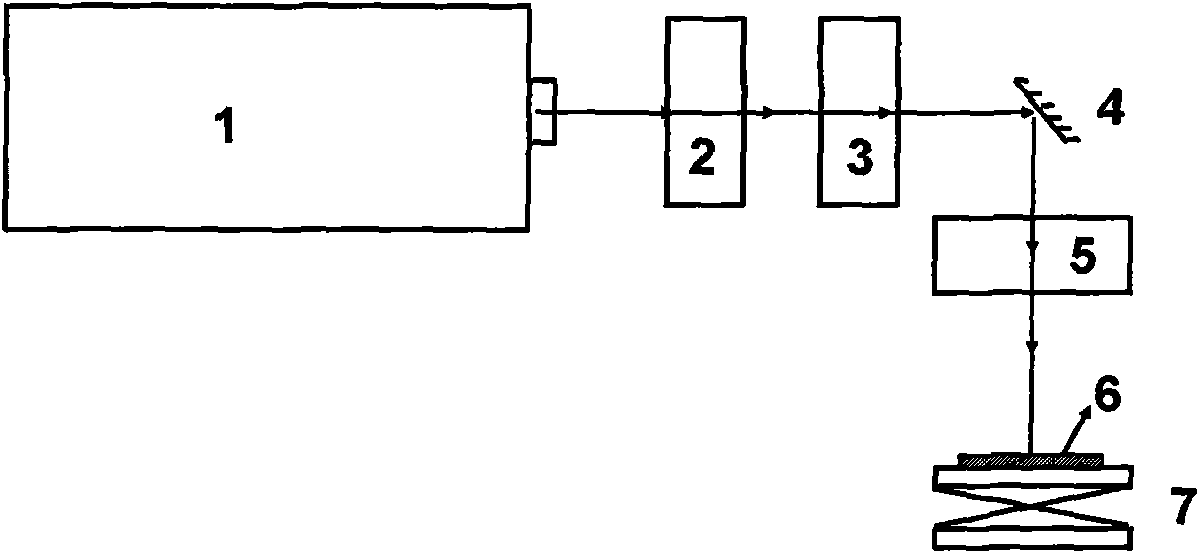
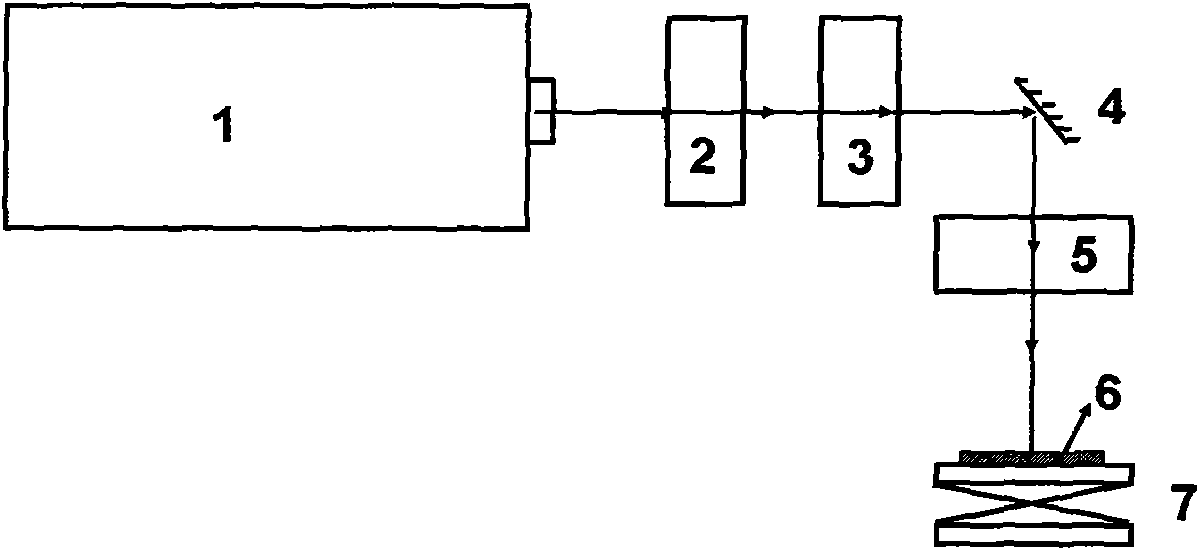
[0036] Taking a GaN-based front-mount LED epitaxial wafer on a 2-inch SiC substrate as an example to illustrate the implementation method of the present invention, the steps are as follows:
[0037] (1) The structure of GaN-based positive LED epitaxial wafers from bottom to top is SiC substrate, buffer layer GaN, intrinsic GaN layer, n-GaN confinement layer, multi-quantum well active light-emitting region, p-GaN confinement layer.
[0038] (2) Rough etching is performed on the p-GaN confinement layer, and the thickness of the p-GaN confinement layer is about 200 nm.
[0039] (3) Turn on the ultraviolet 355nm laser so that its laser output is in a standby state.
[0040] (4) Adjust the laser beam shaping module to obtain the beam energy distribution required for rough etching.
[0041] (5) Fix the GaN-based front-loading LED epitaxial wafer at the center of the lifting sample stage, adjust the lifting sample stage so that the ultraviolet 355nm laser beam is located in the cent...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Take the 2-inch SiC substrate GaN-based vertical process LED epitaxial wafer as an example to illustrate the realization method of the present invention, the steps (4), (5), (9), and (10) are the same as those in Embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0049] (1) The structure of the GaN-based vertical process LED epitaxial wafer from bottom to top is SiC substrate, p-GaN confinement layer, multi-quantum well active light-emitting region, n-GaN confinement layer, and intrinsic GaN layer.
[0050] (2) Rough etching is performed on the intrinsic GaN layer, and the thickness of the intrinsic GaN layer is about 1.5 microns.
[0051] (3) Turn on the ultraviolet 355nm laser so that its laser output is in a standby state.
[0052] (6) Import the required roughening etching pattern into the high-precision electric displacement stage control software, for example, the vertical and horizontal stripe structure with a period of 15 microns, the roughening etching duty cycle is 50%, and t...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The implementation method of the present invention is illustrated by taking a 2-inch SiC substrate GaN-based LED epitaxial wafer as an example, and the steps (4), (5), (9), and (10) are the same as in Embodiment 1, the difference is that:
[0057] (1) The structure of the LED epitaxial wafer from the bottom to the top is the SiC substrate, the n-GaN confinement layer, the multi-quantum well active light-emitting region, and the p-GaN confinement layer.
[0058] (2) Perform roughening and roughening etching on the SiC substrate layer.
[0059] (3) Turn on the 355nm laser so that its laser output is in a standby state.
[0060] (6) Import the required roughening etching pattern into the high-speed galvanometer control software, for example, a concentric ring structure with an inner and outer layer interval of 20 microns, a roughening etching duty cycle of 50%, and a roughening etching area To cover the entire 2-inch SiC substrate.
[0061] (7) Control the output power o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com