Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7340results about "Drilling machines and methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
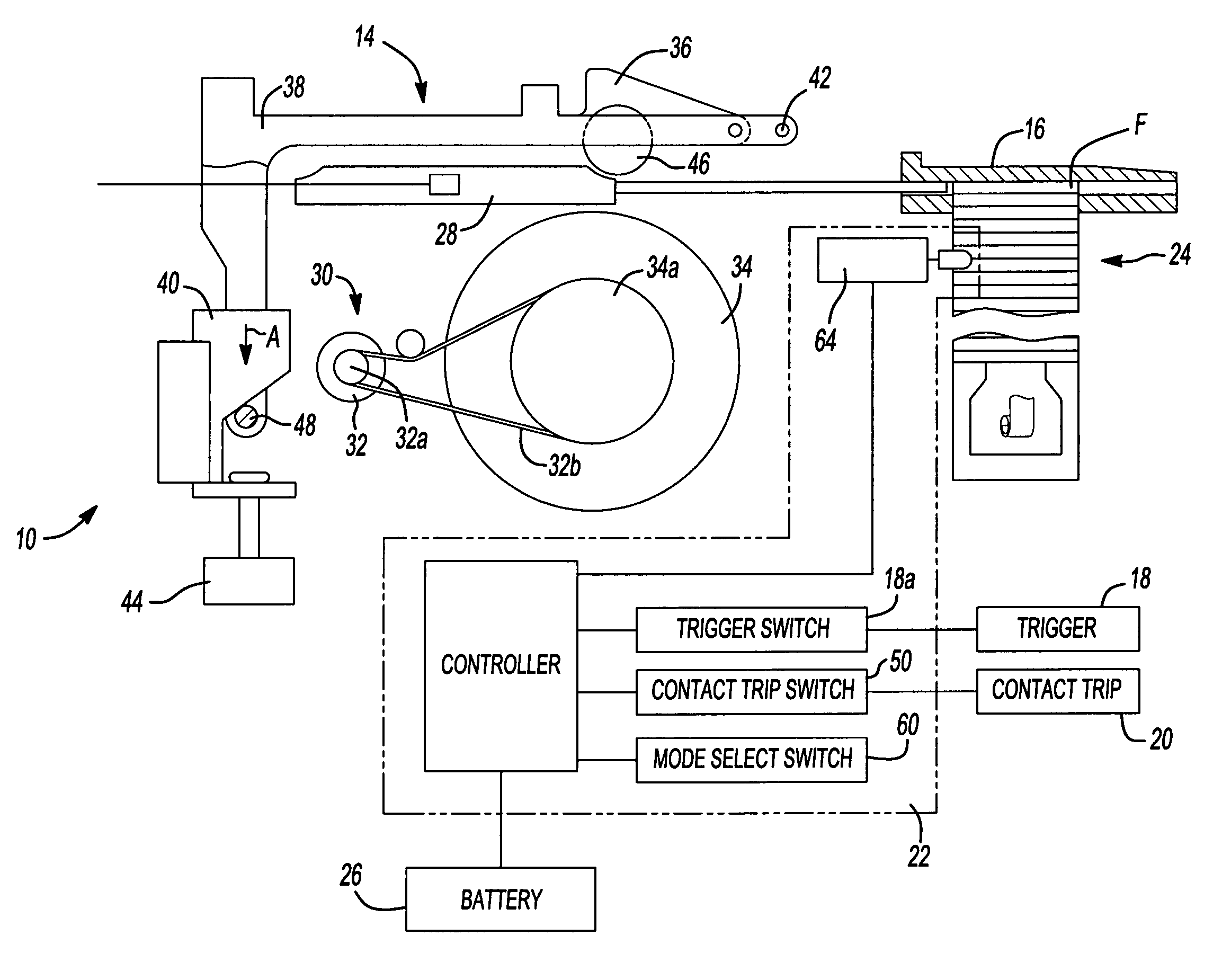
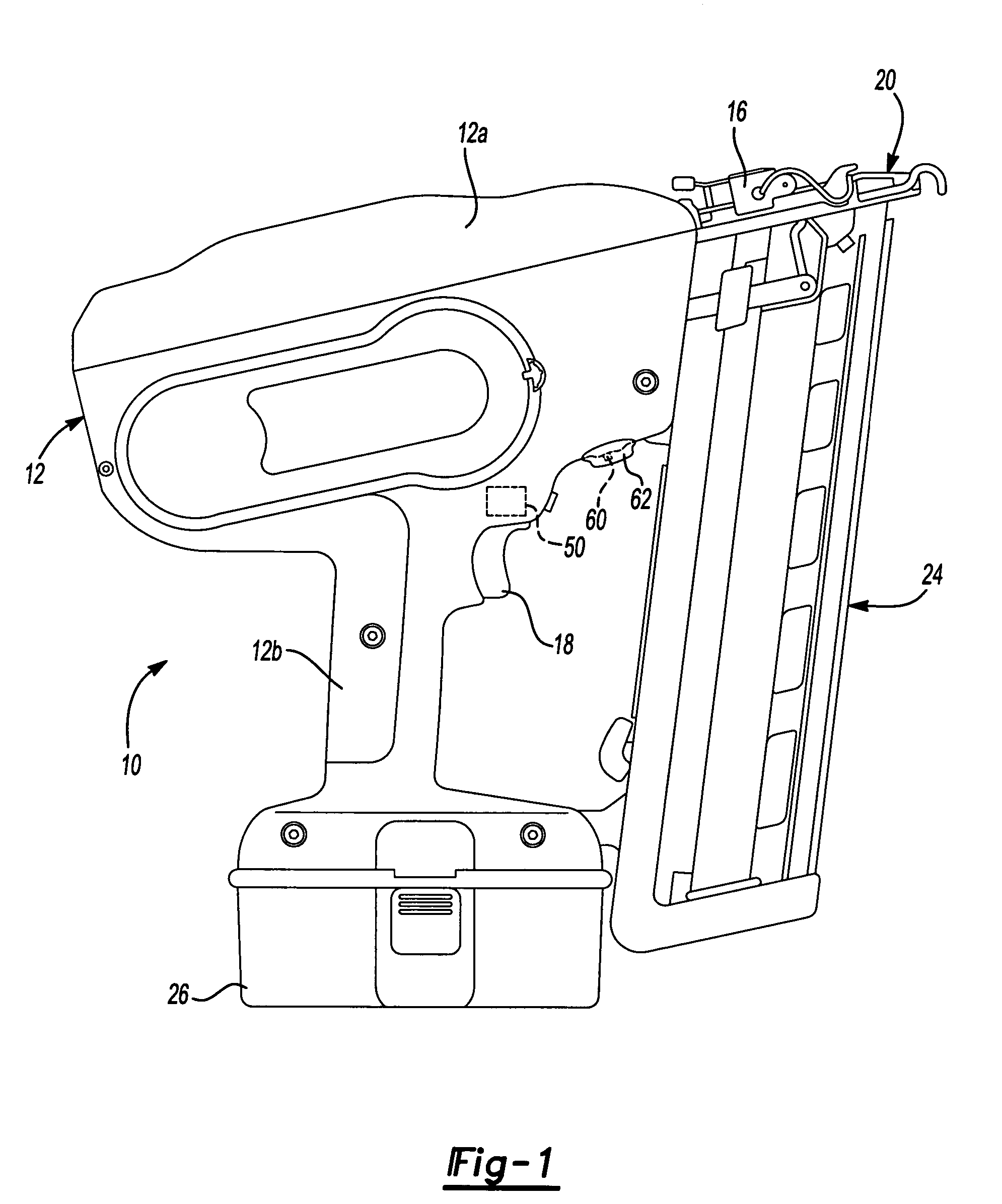
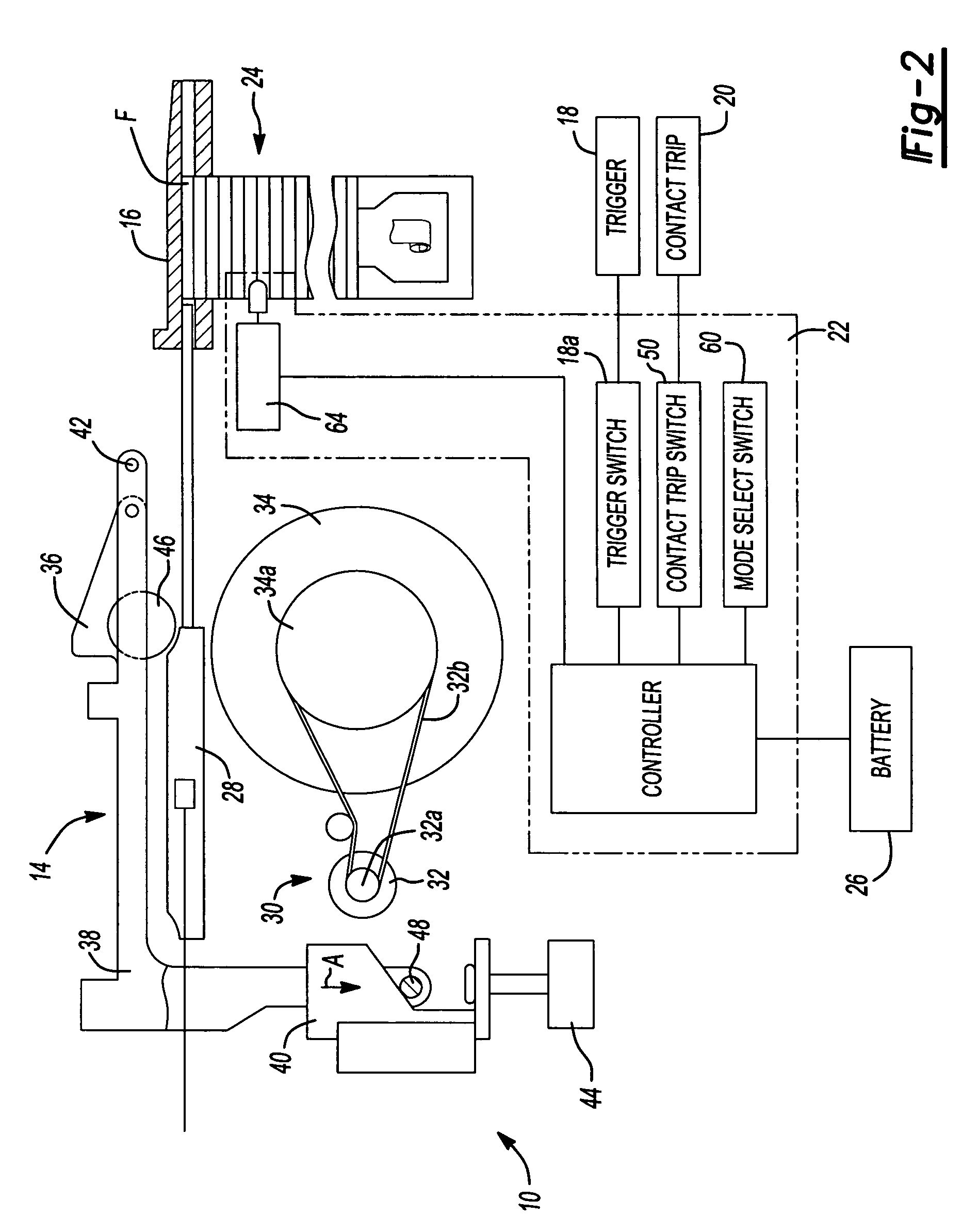
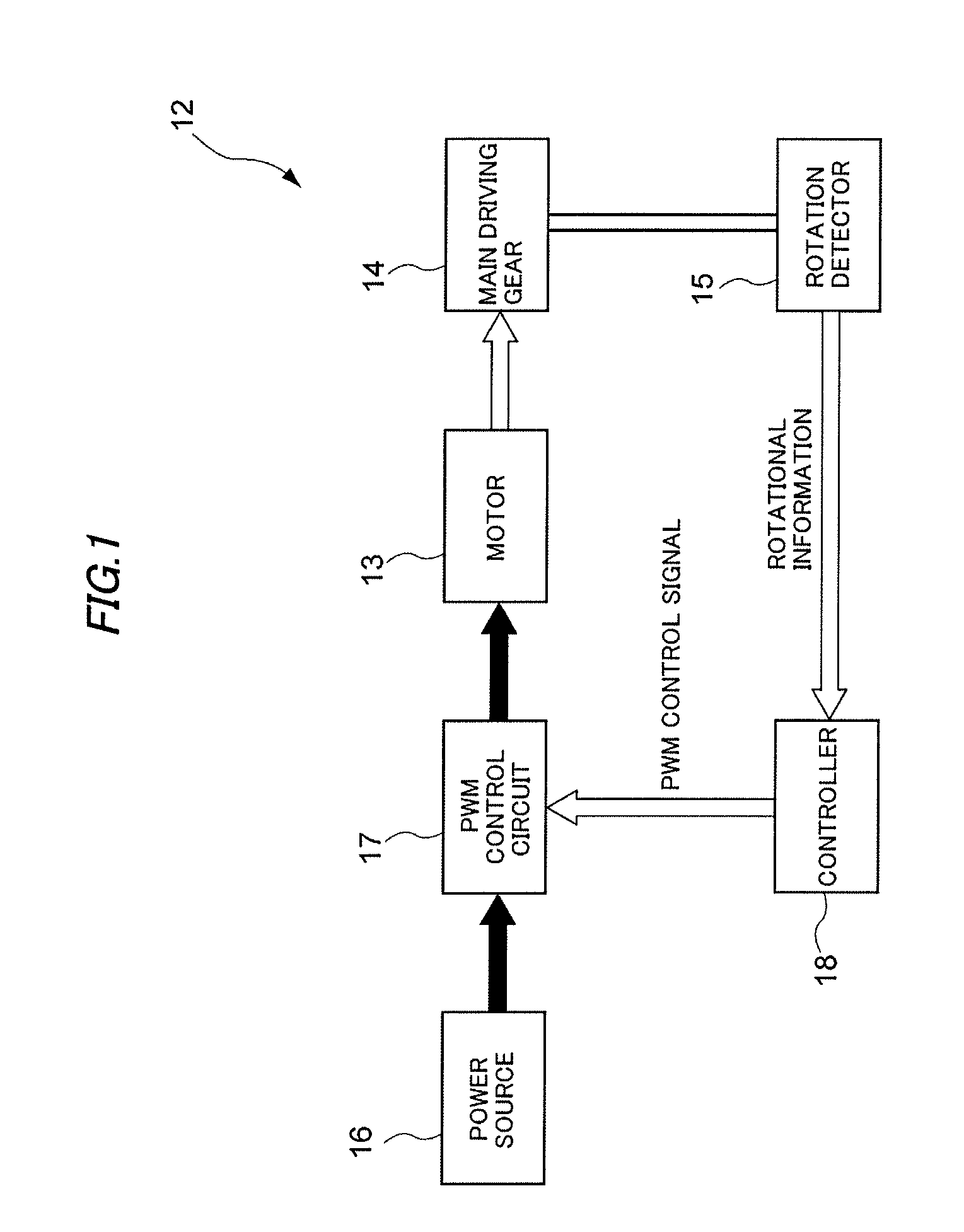
Method for controlling a power driver
A driving tool having a driver, a power source, a sensor and a controller. The power source selectively provides an input to the driver to cause the driver to translate along an axis. The sensor senses a condition in the power source that is indicative of a level of kinetic energy of an element in the power source and generates a sensor signal in response thereto. The controller is coupled to the power source and the sensor and is responsive to the sensor signal for deactivating the power source to inhibit the power source from providing the input to the driver when the level of kinetic energy of the element in the power source is below a predetermined threshold. A method for operating a driving tool is also provided.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
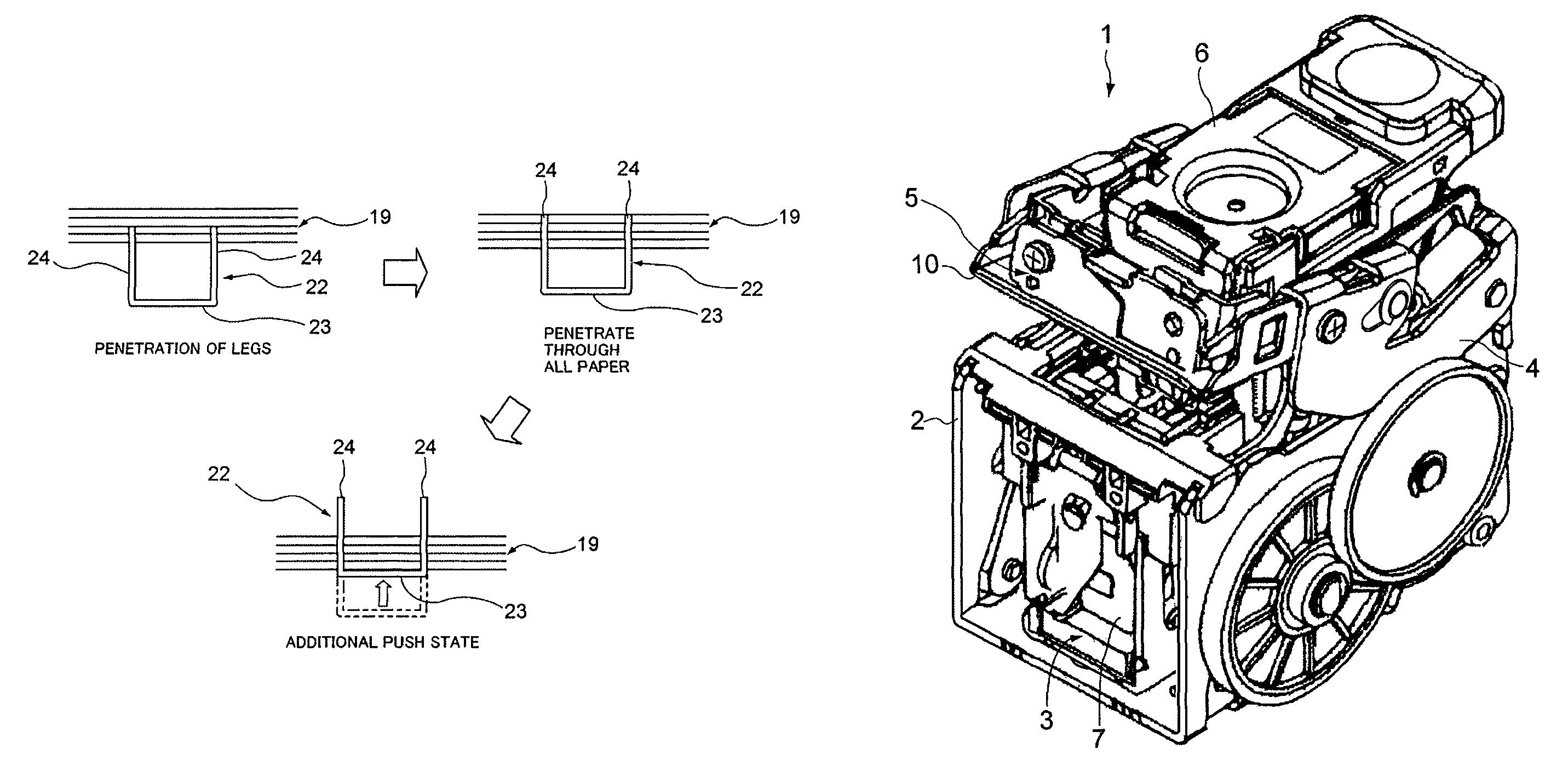
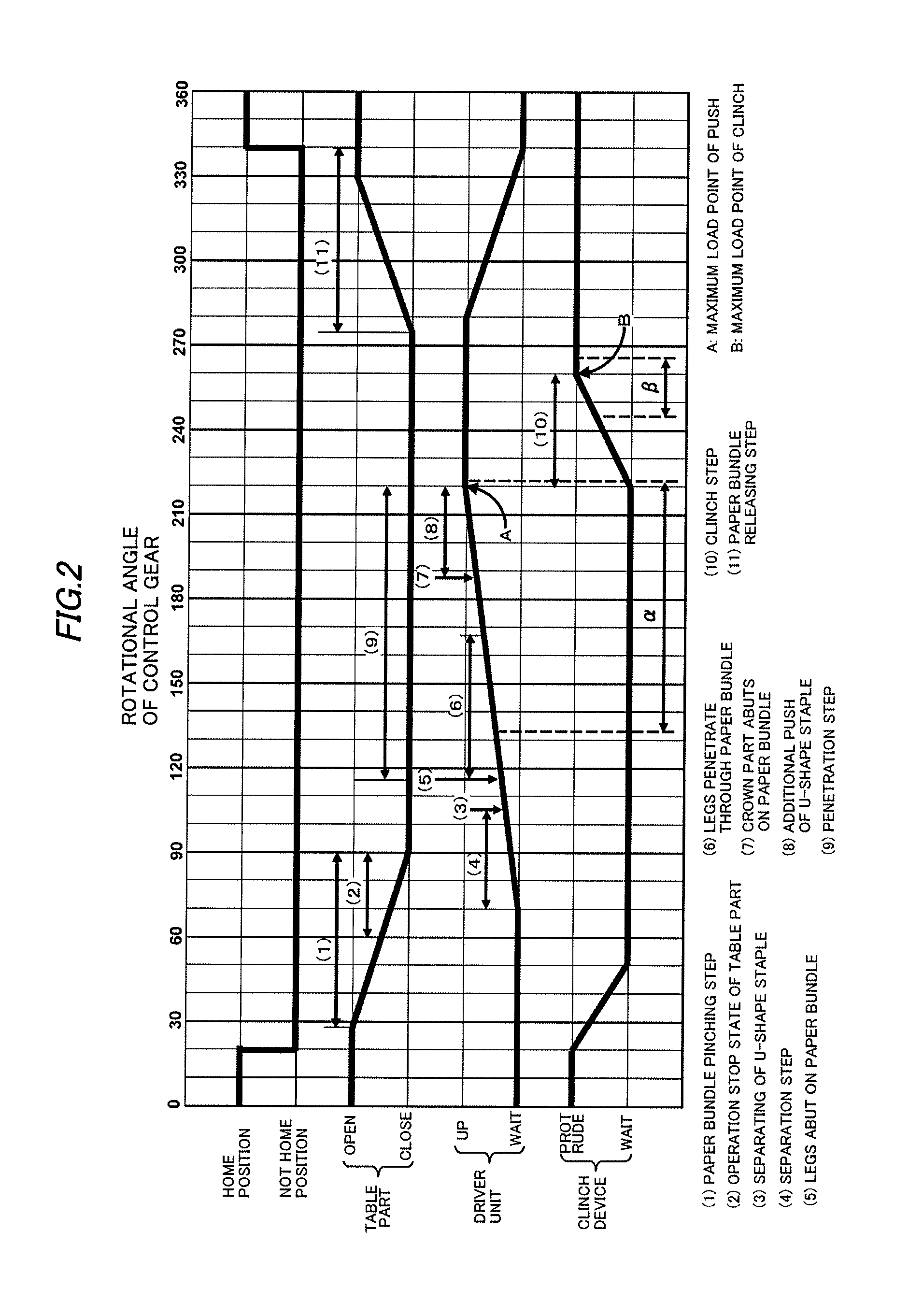
Electric stapler and operation method of electric stapler
ActiveUS8371393B2Reduce running noiseIncrease the number ofStapling toolsDispensing apparatusEngineeringElectric motor
Owner:MAX CO LTD
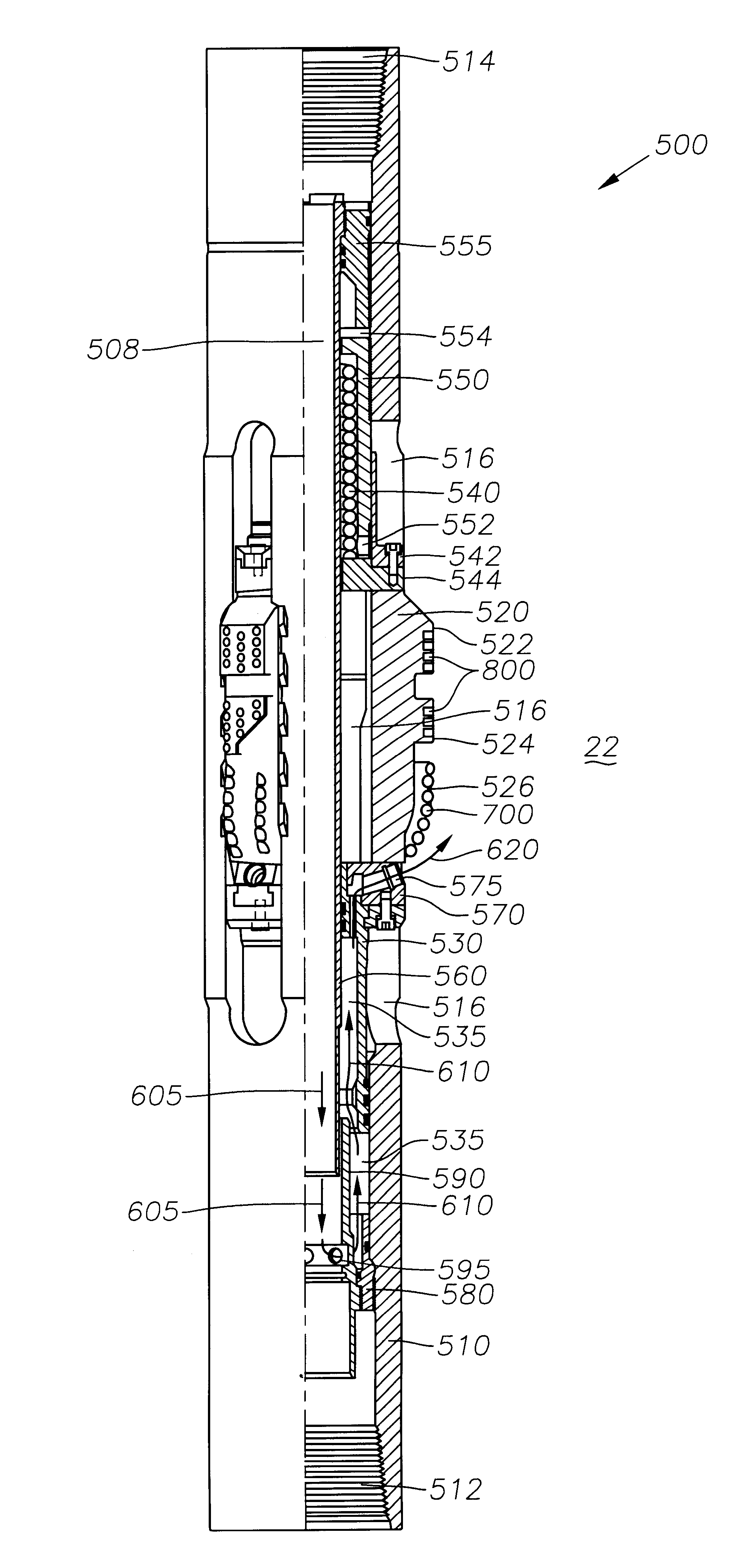
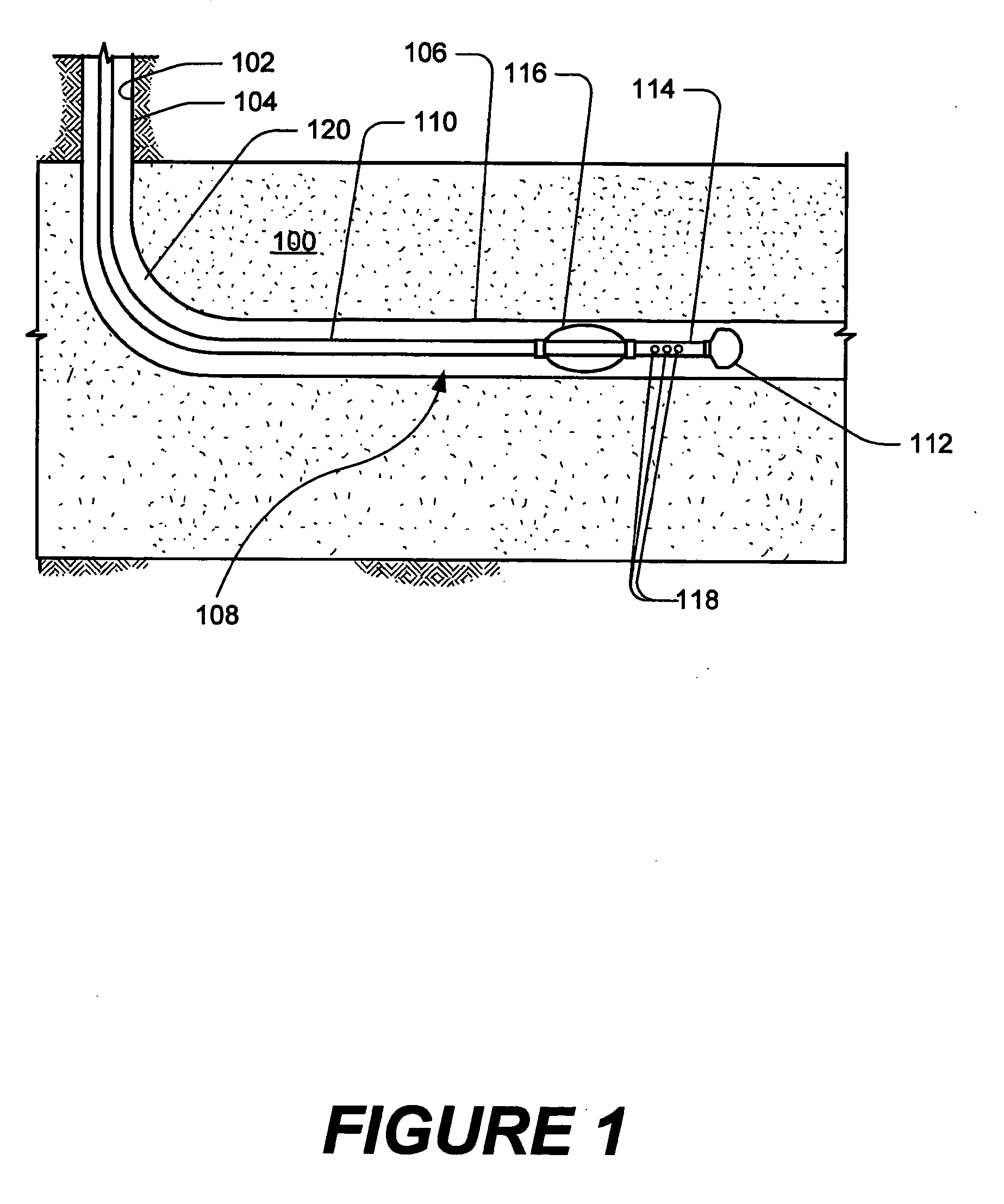
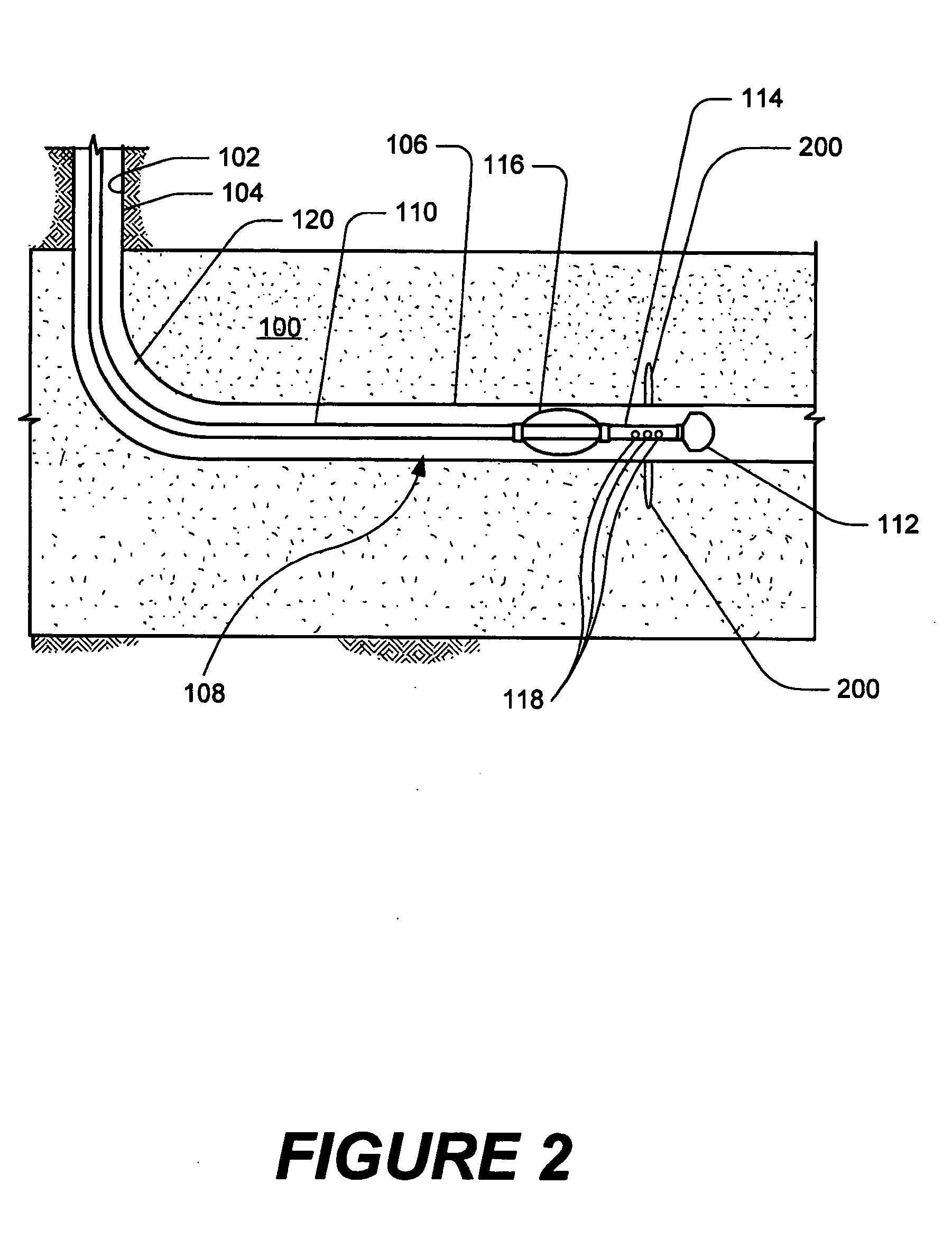
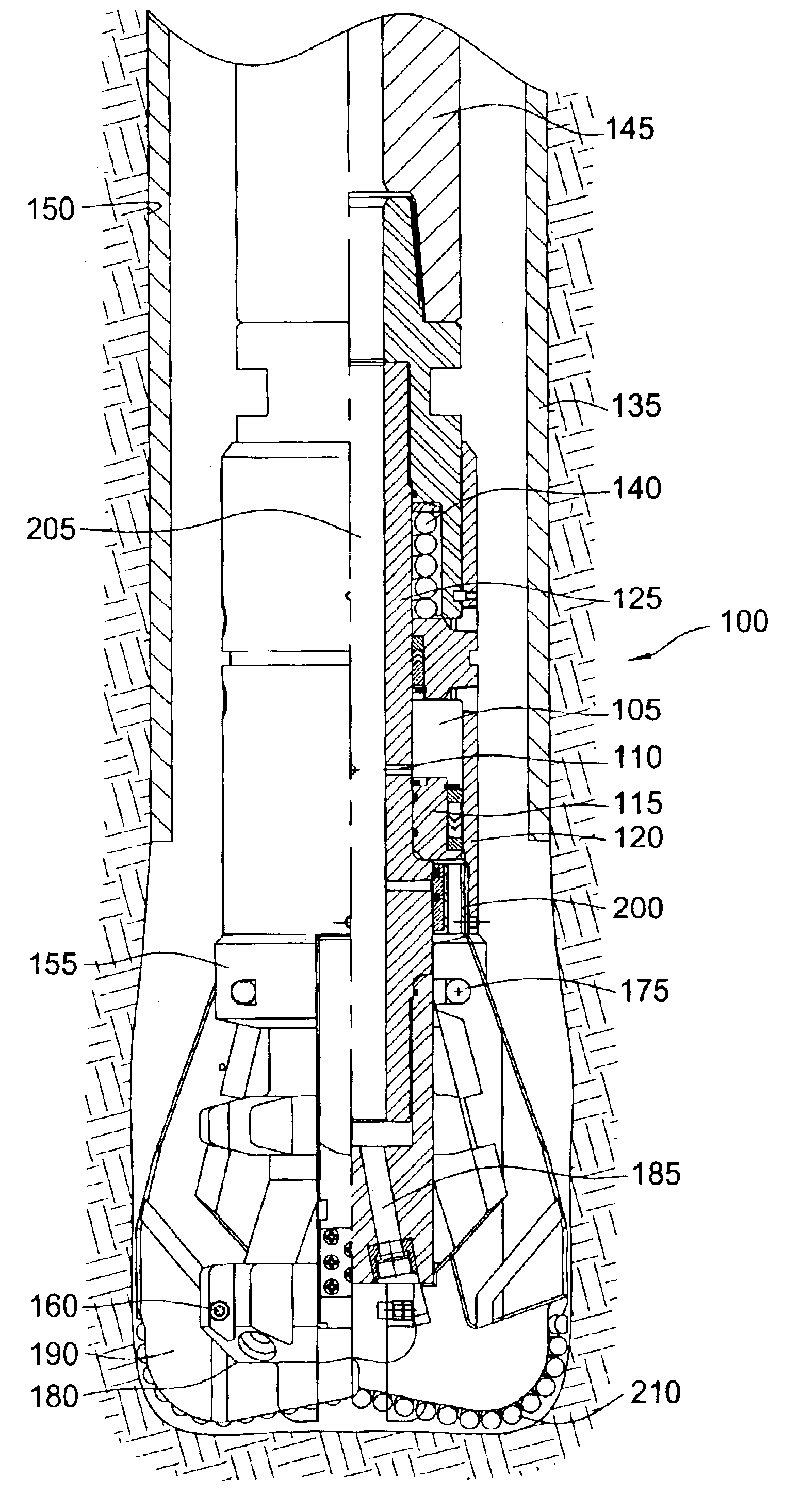
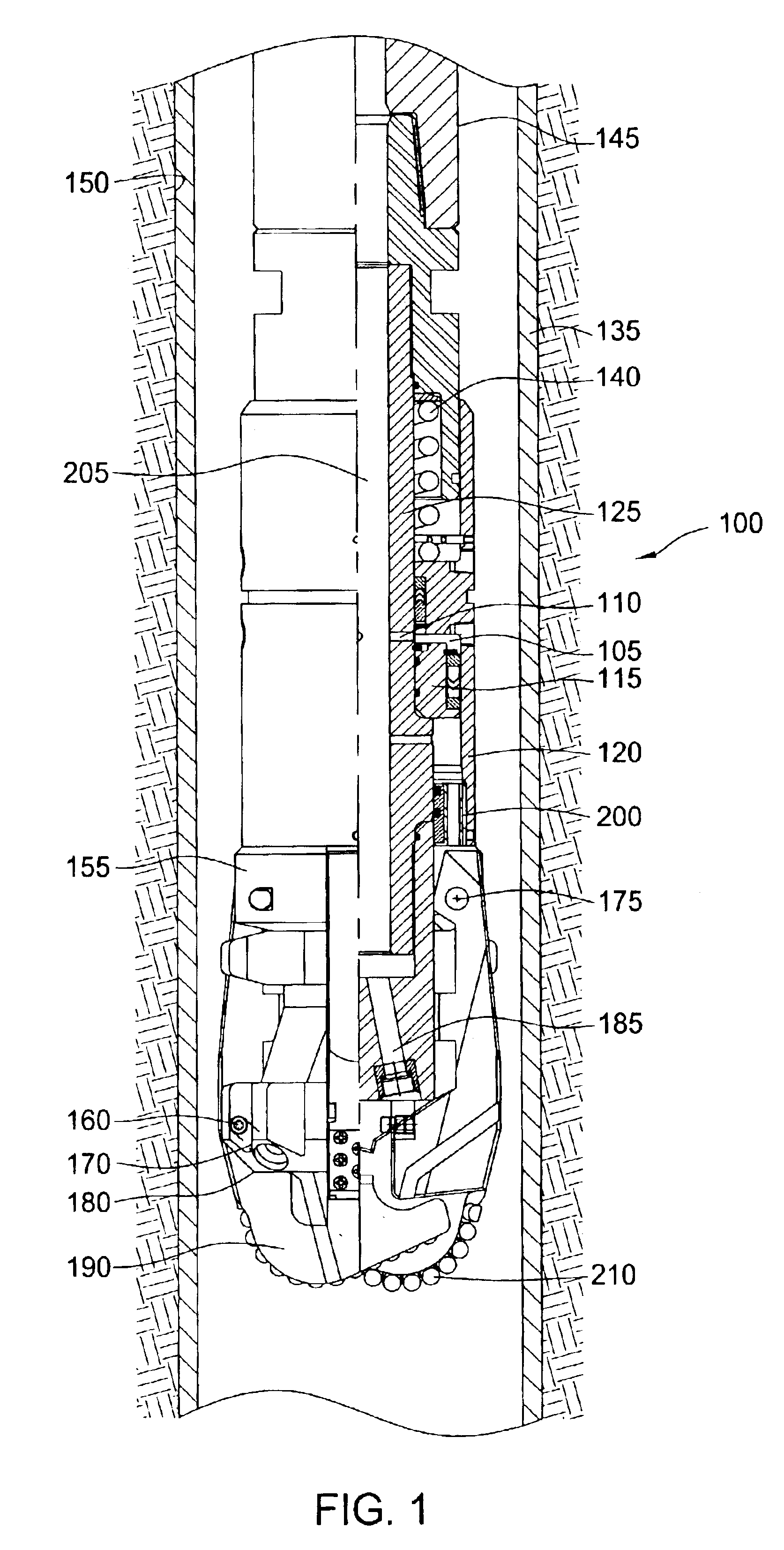
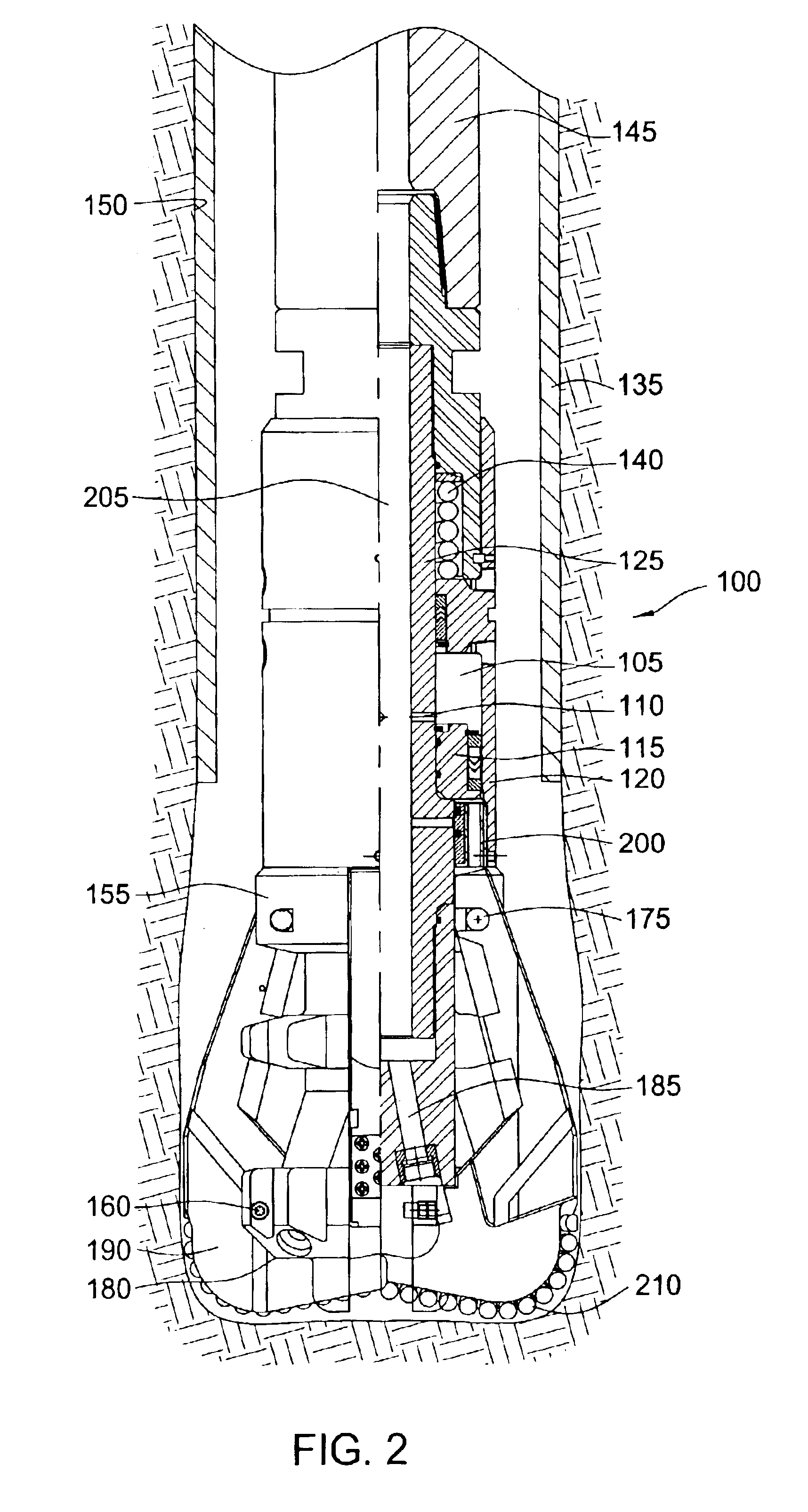
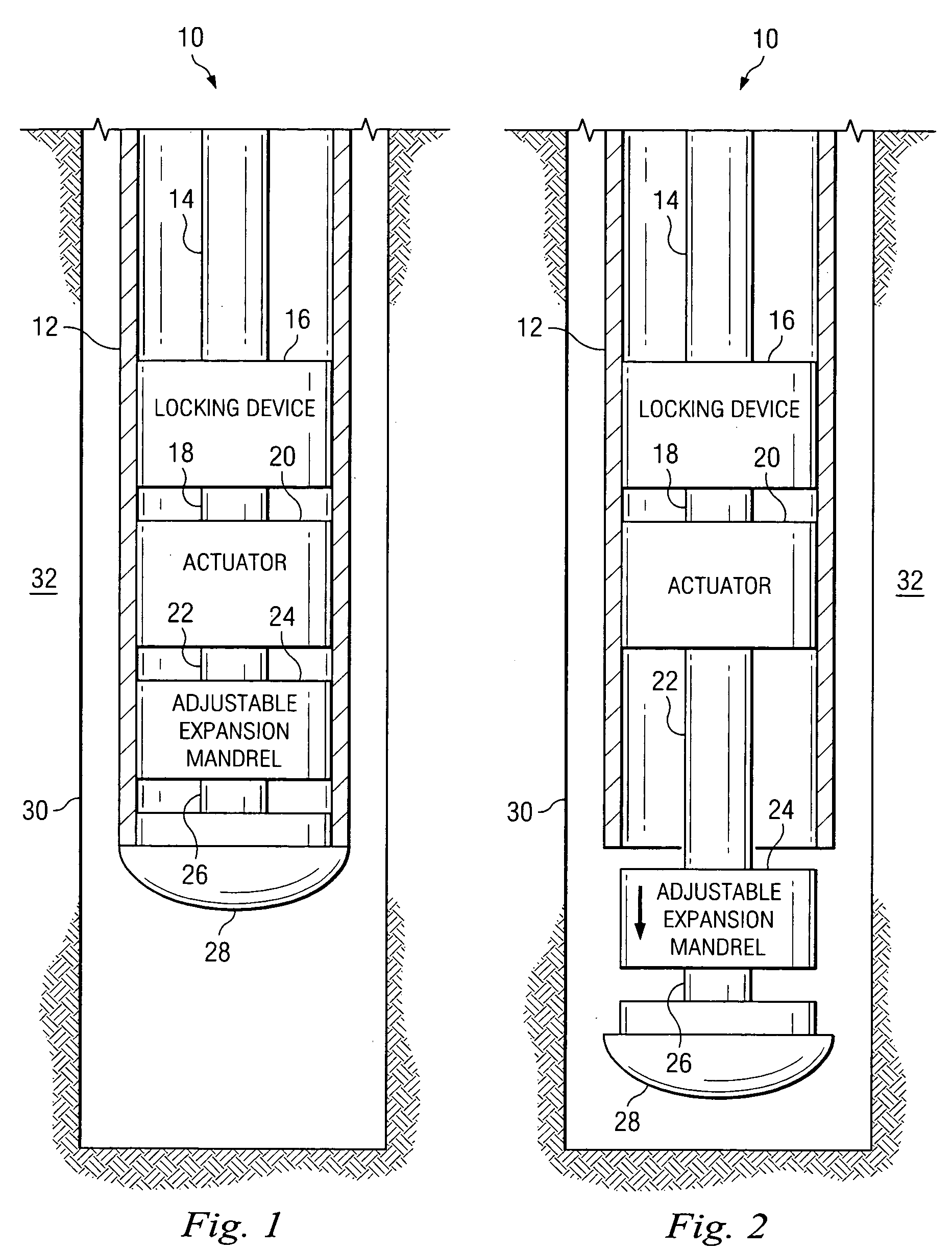
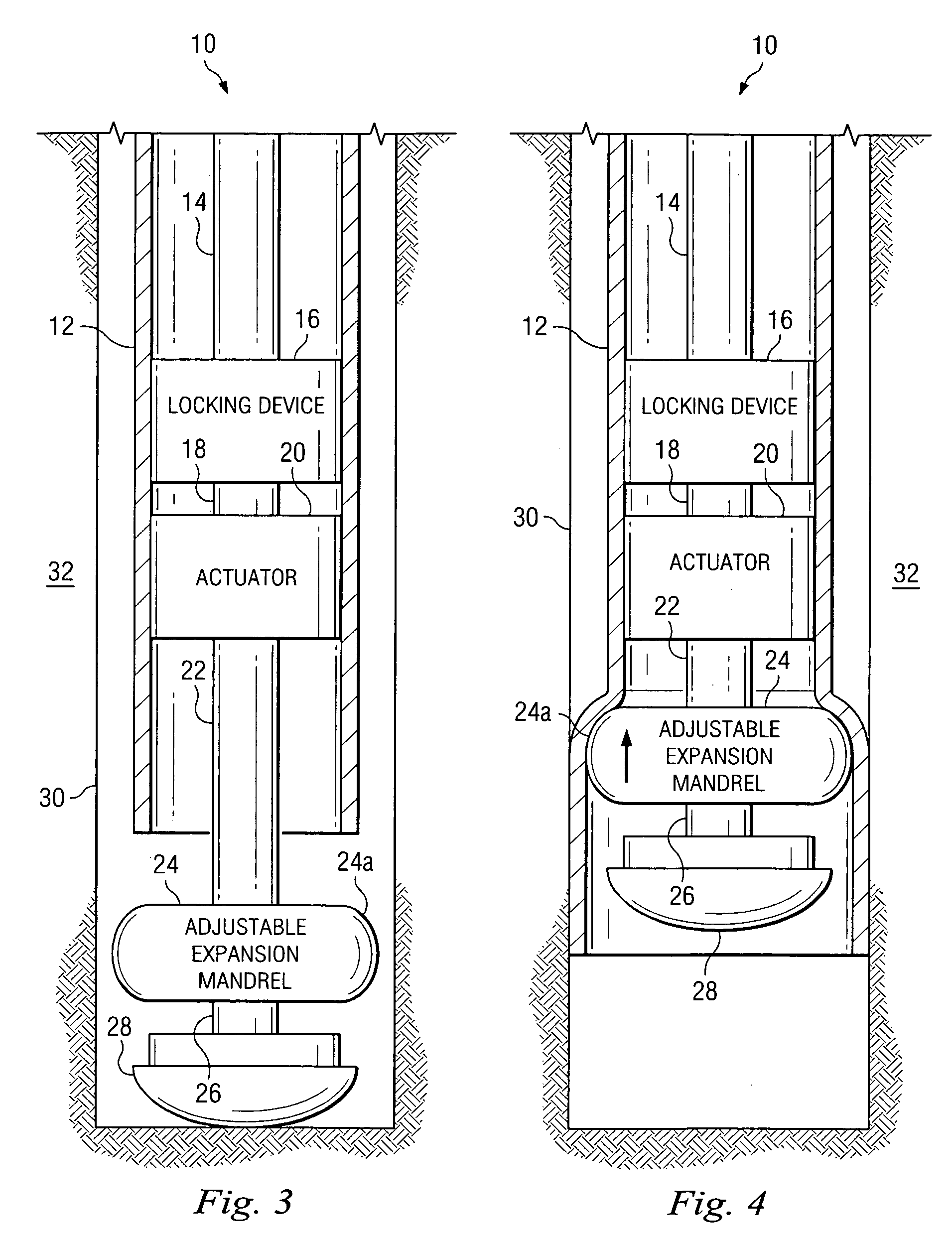
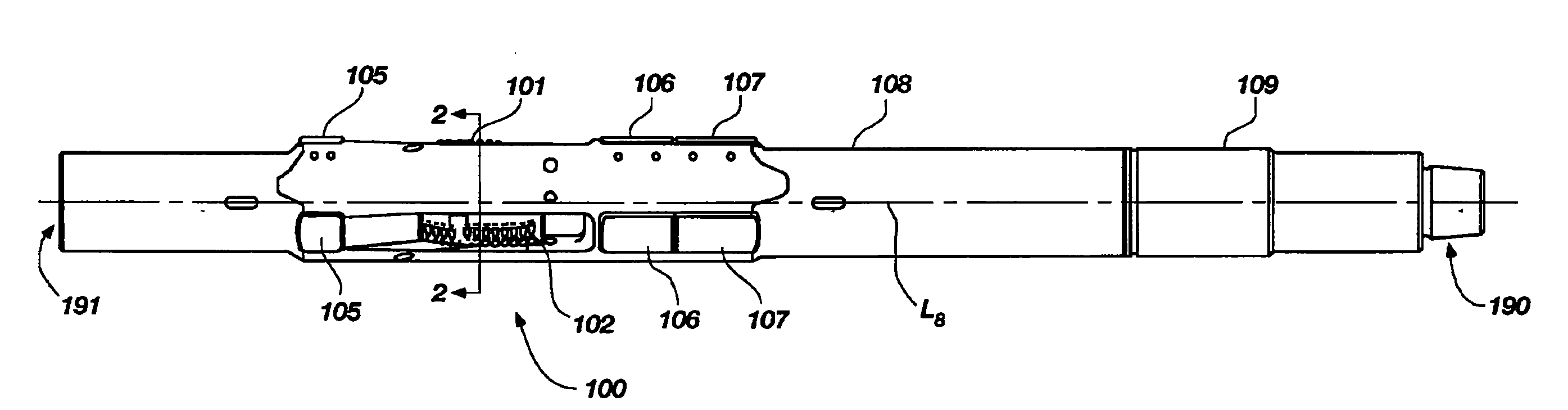
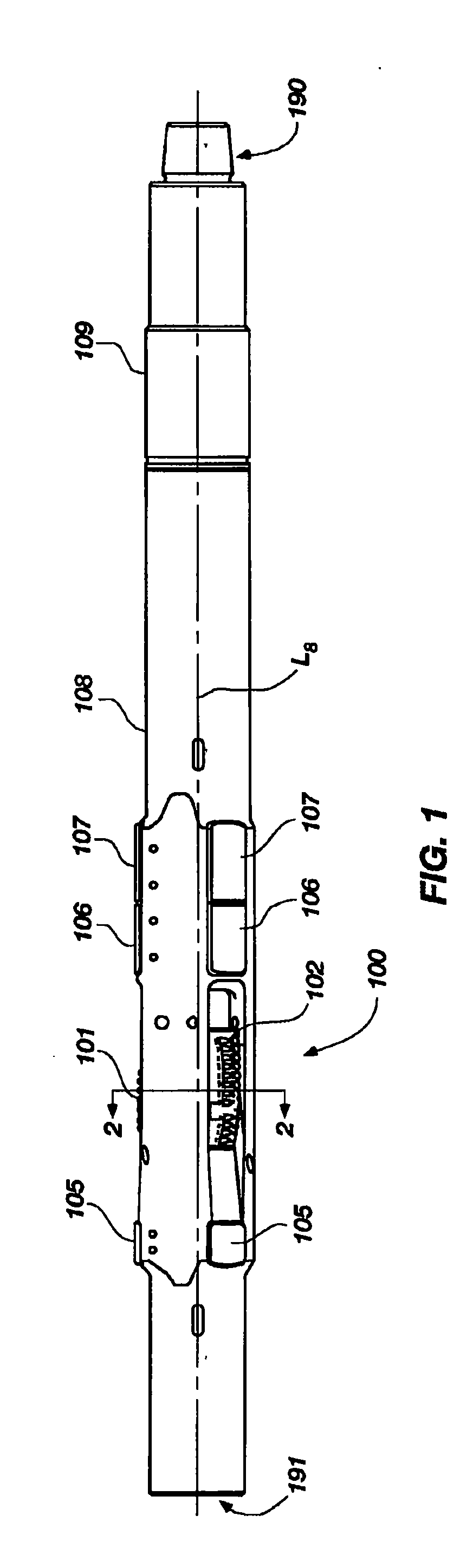
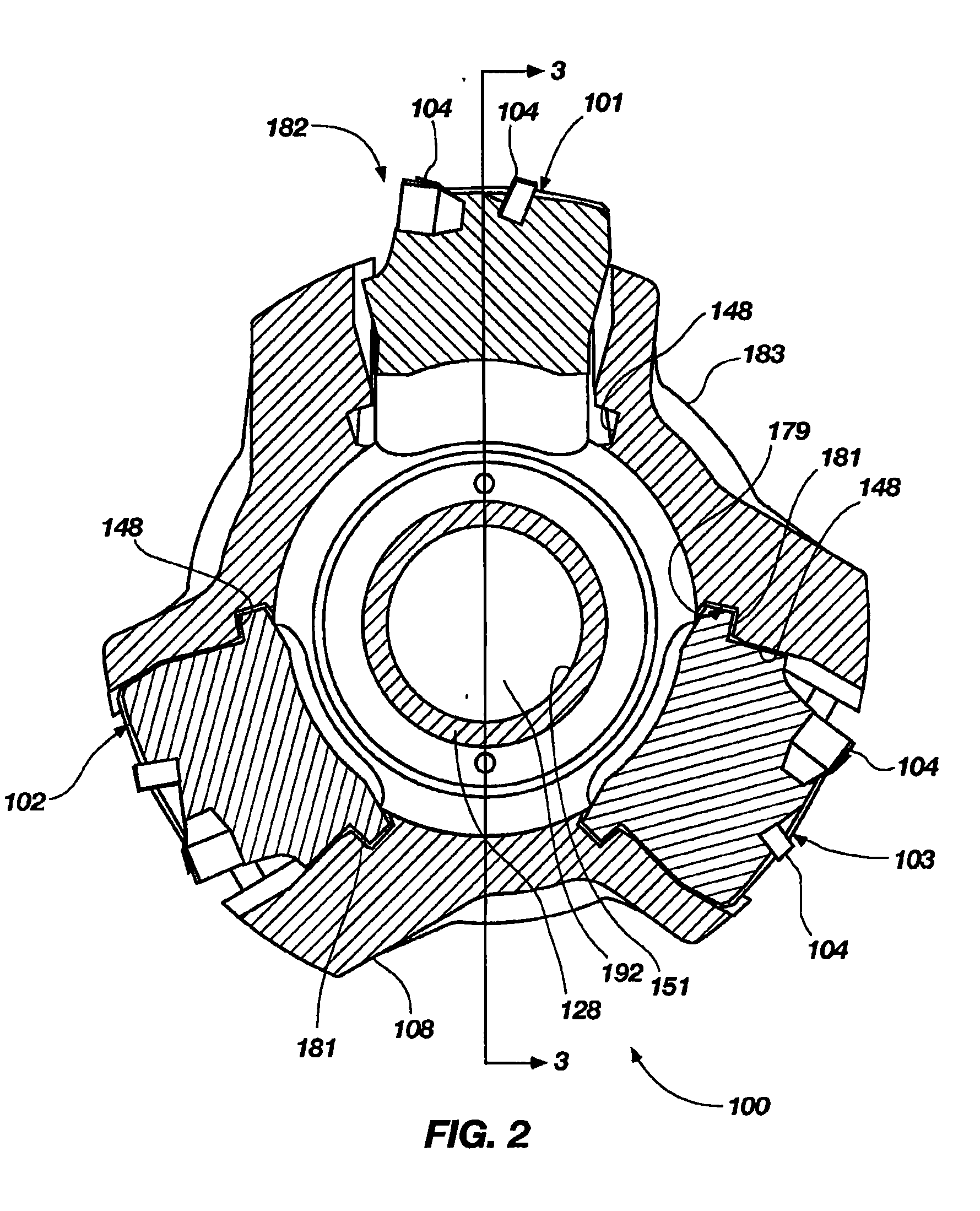
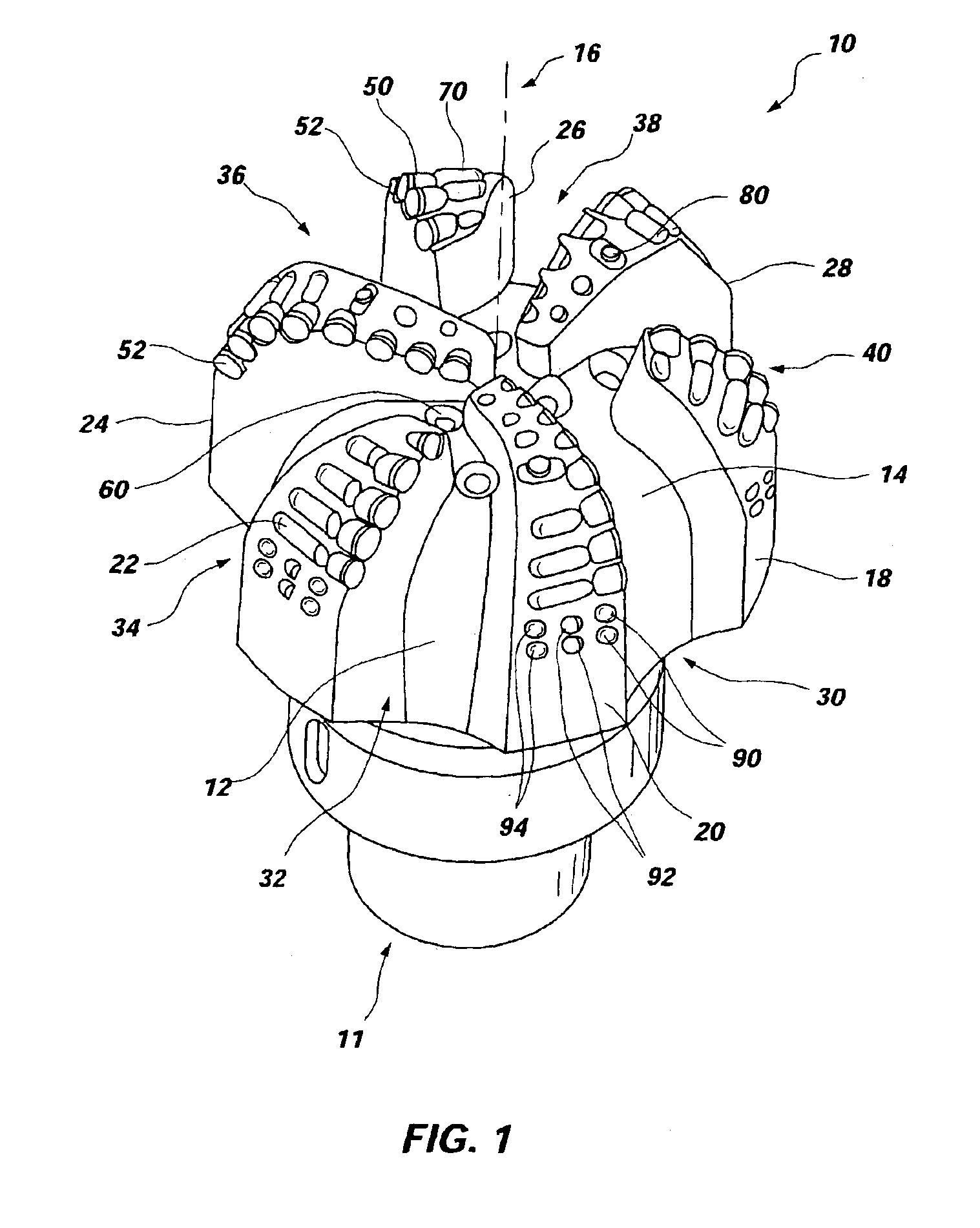
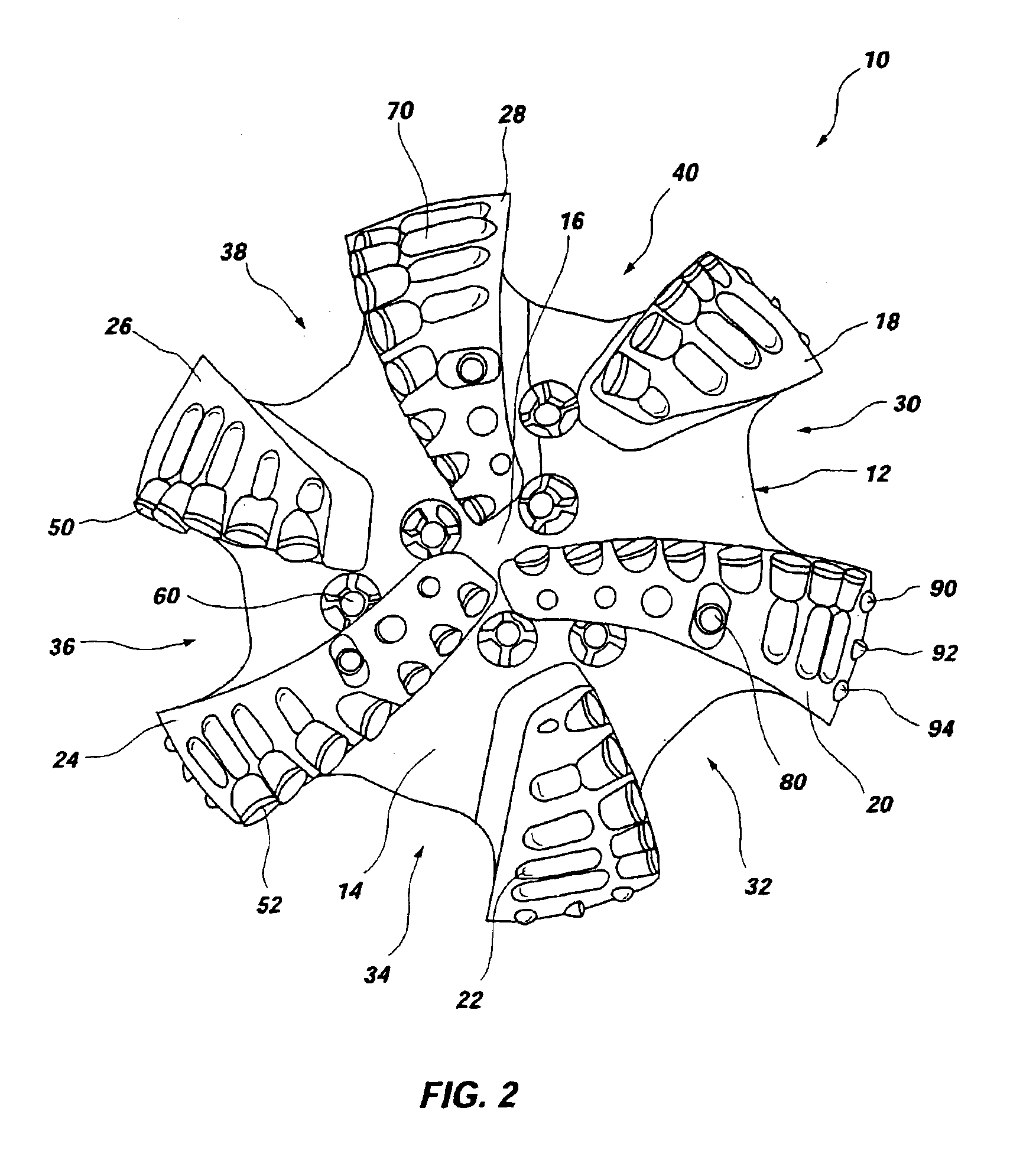
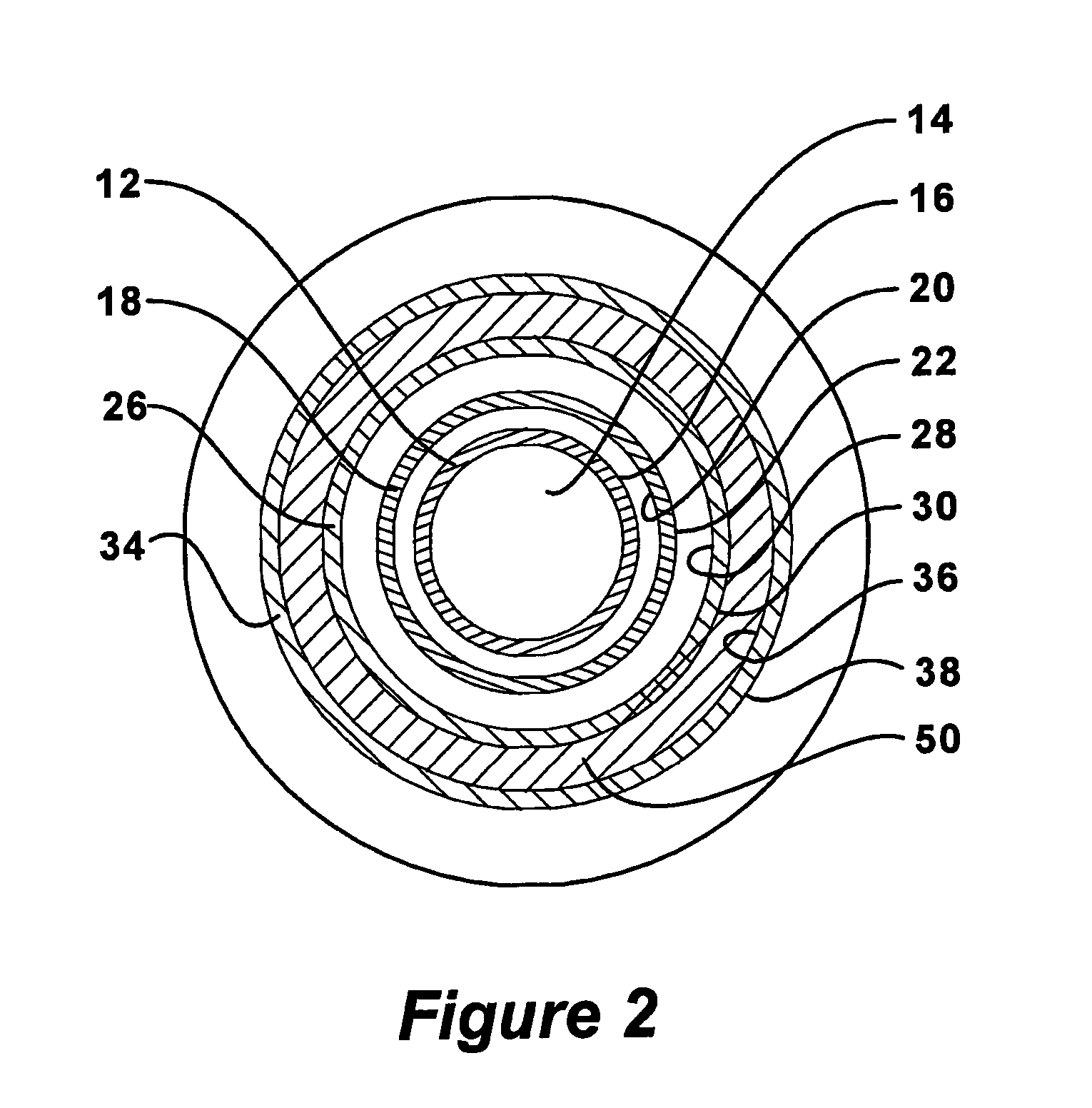
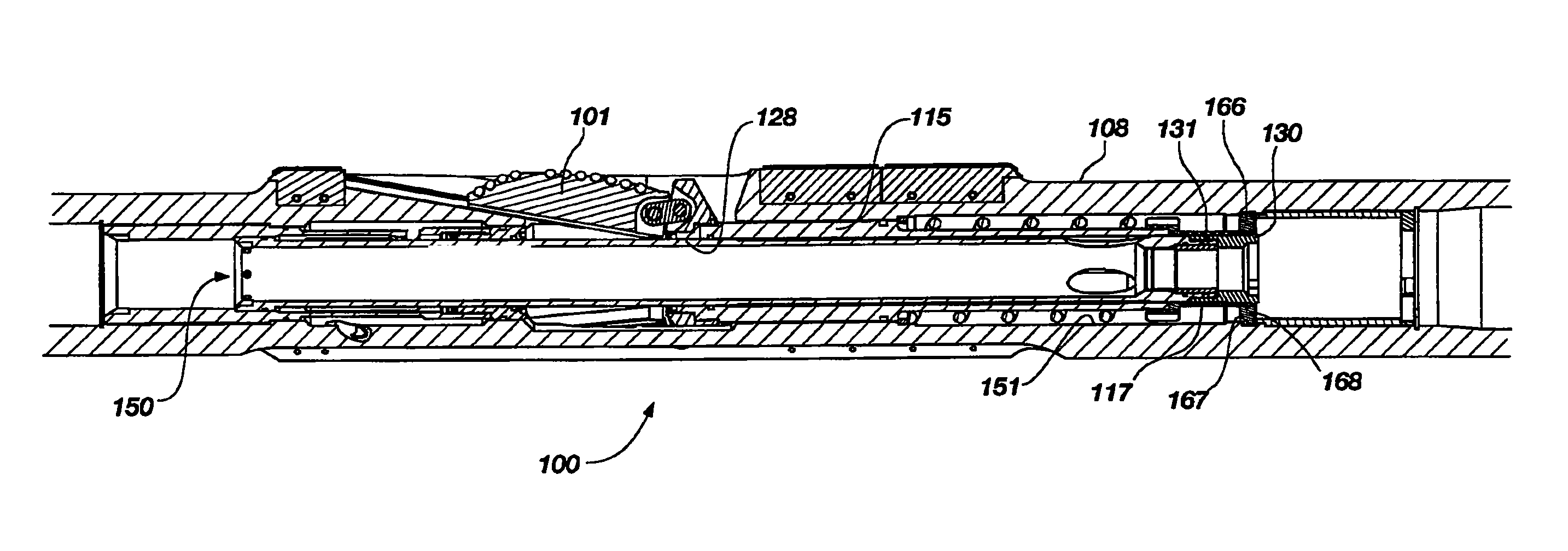
Expandable underreamer/stabilizer
A downhole tool that functions as an underreamer, or alternatively, as a stabilizer in an underreamed borehole. The tool includes one or more moveable arms disposed within a body having a flowbore therethrough in fluid communication with the wellbore annulus. The tool alternates between collapsed and expanded positions in response to differential fluid pressure between the flowbore and the wellbore annulus. In one embodiment, the tool moves automatically in response to differential pressure. In a second embodiment, the tool must be selectively actuated before it is moveable. When the tool expands, the arms are preferably translated axially upwardly, while simultaneously being extended radially outwardly from the body. The expanded tool diameter is adjustable at the surface without changing components. The arms may include borehole engaging pads that comprise cutting structures or wear structures or both, depending upon the function of the tool.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Underbalanced drill string deployment valve method and apparatus
Apparatus and methods for a deployment valve used with an underbalanced drilling system to enhance the advantages of underbalanced drilling. The underbalanced drilling system may typically comprise elements such as a rotating blow out preventer and drilling recovery system. The deployment valve is positioned in a tubular string, such as casing, at a well bore depth at or preferably substantially below the string light point of the drilling string. When the drilling string is above the string light point then the upwardly acting forces on the drilling string become greater than downwardly acting forces such that the drilling string begins to accelerate upwardly. The deployment valve has a bore sufficiently large to allow passage of the drill bit therethrough in the open position. The deployment valve may be closed when the drill string is pulled within the casing as may be necessary to service the drill string after drilling into a reservoir having a reservoir pressure. To allow the drill string to be removed from the casing, the pressure produced by the formation can be bled off and the drill string removed for servicing. The drill string can then be reinserted, the pressure in the casing above the deployment valve applied to preferably equalize pressure above and below the valve and the drill string run into the hole for further drilling.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
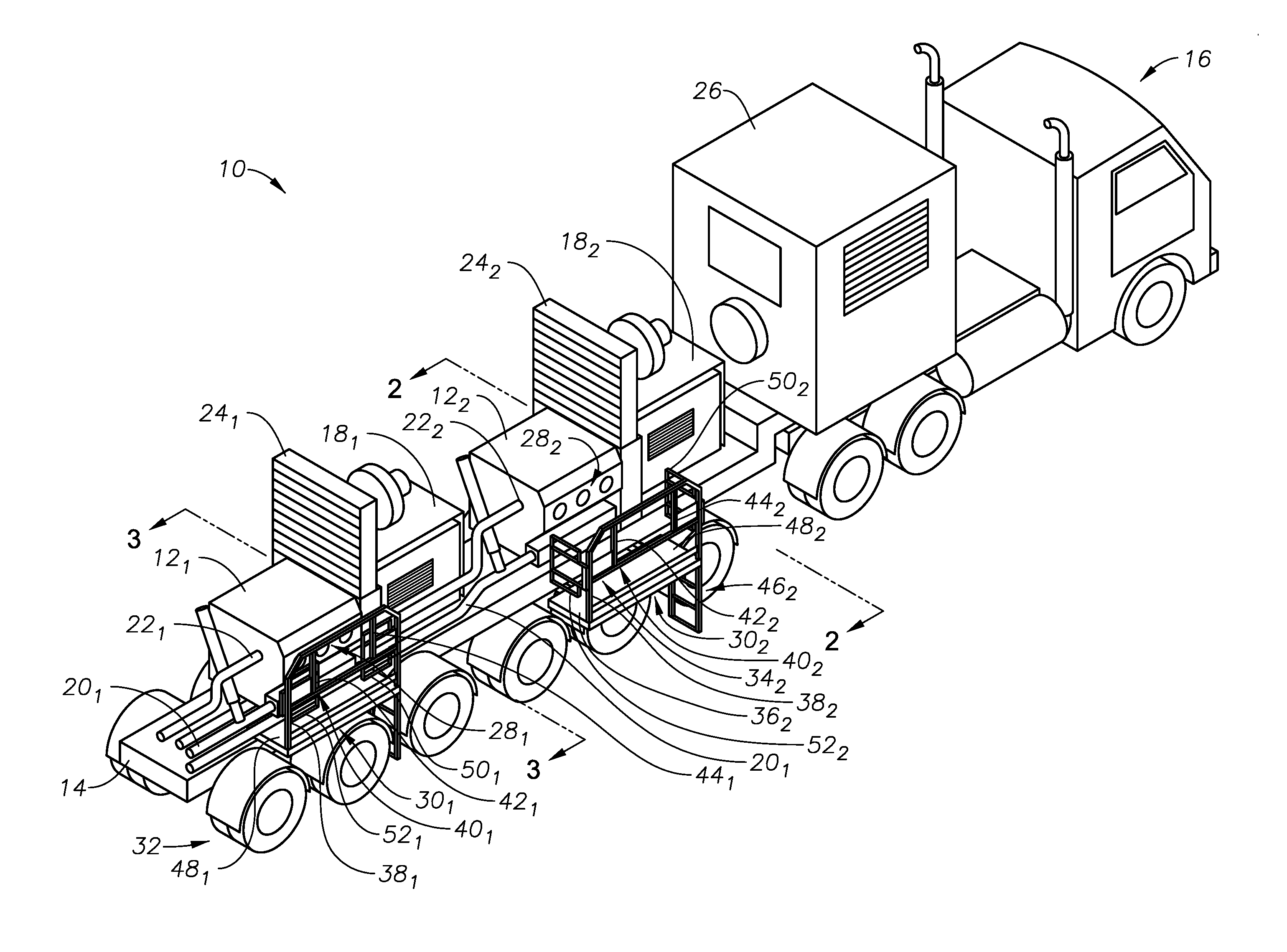
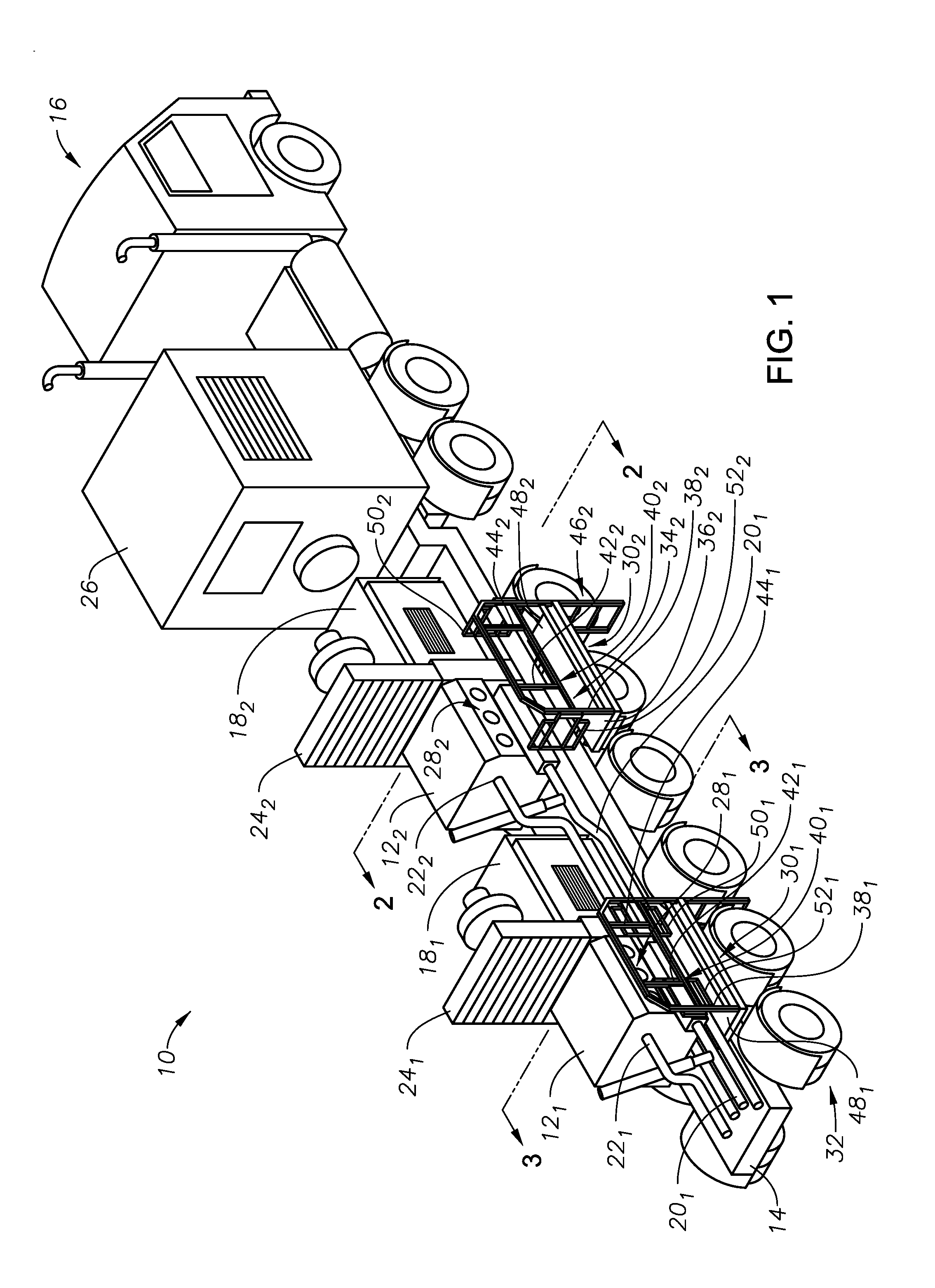
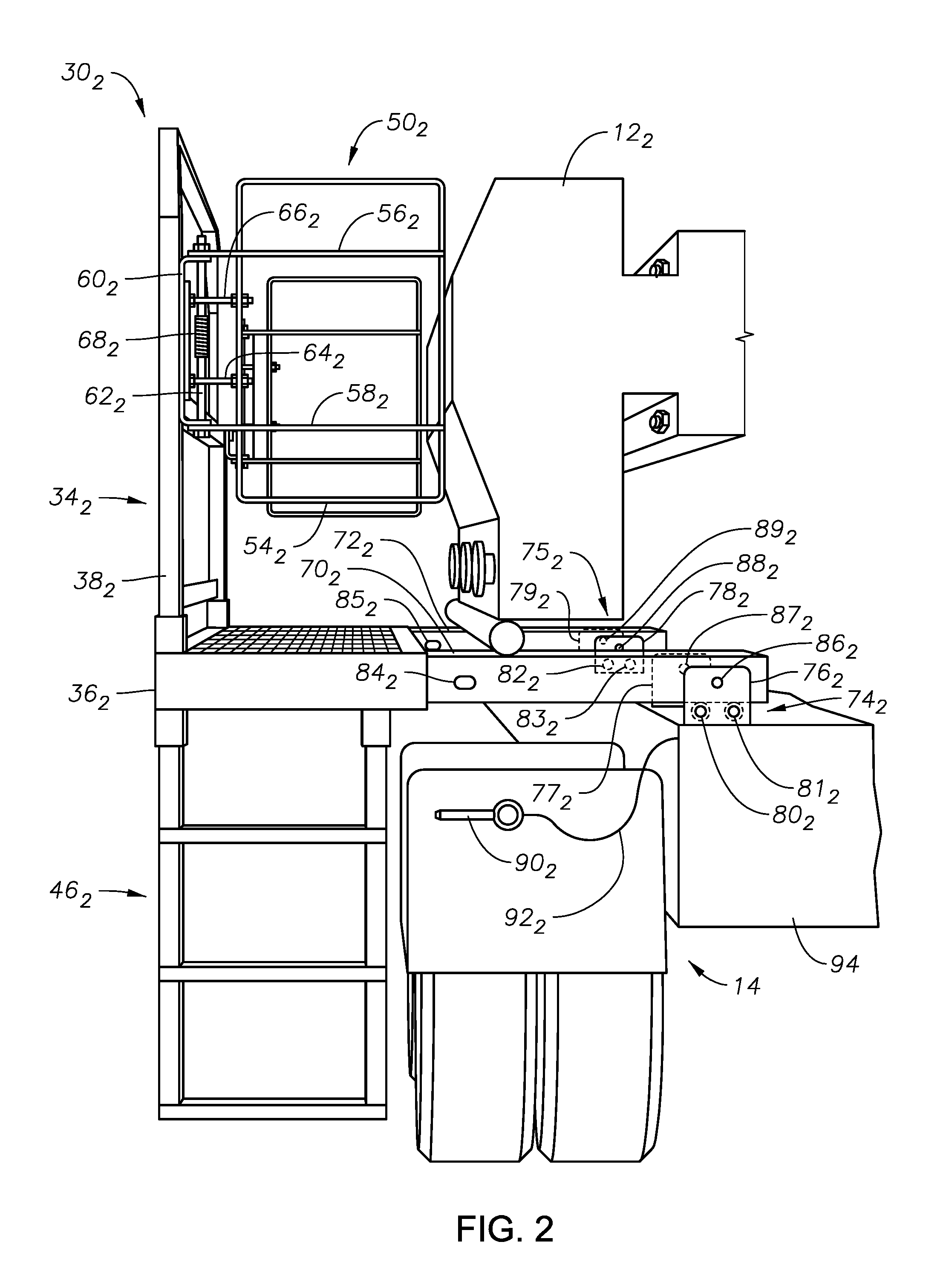
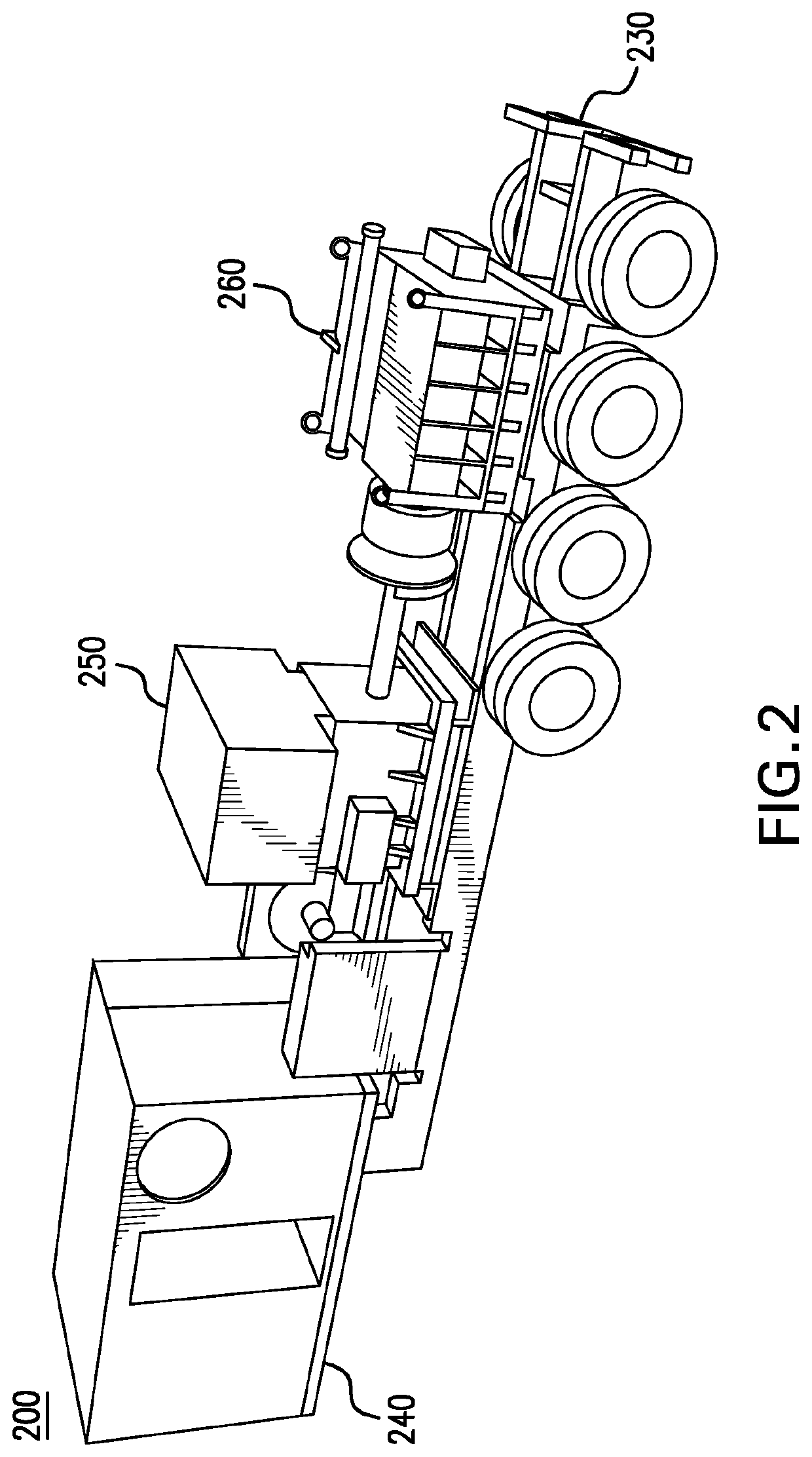
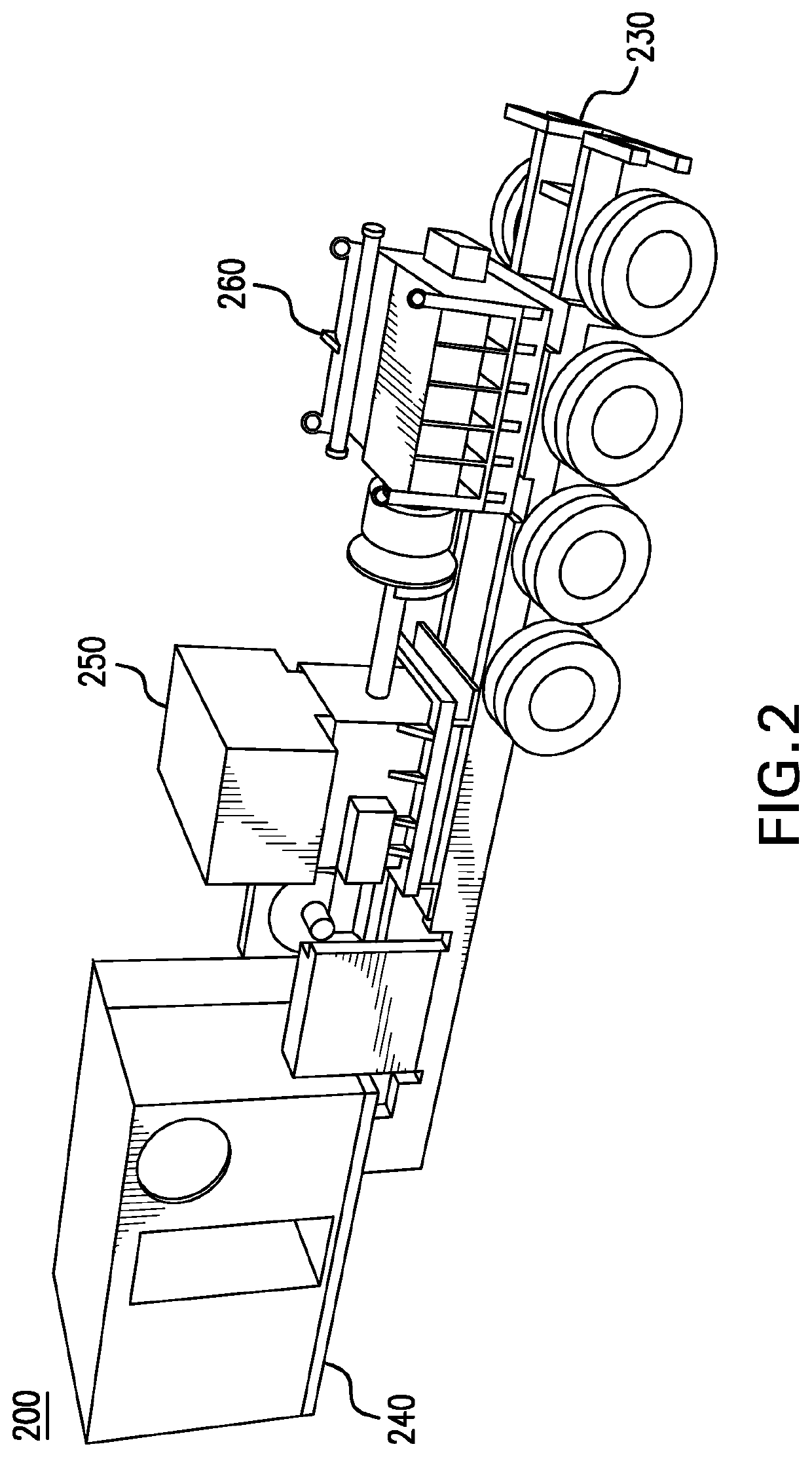
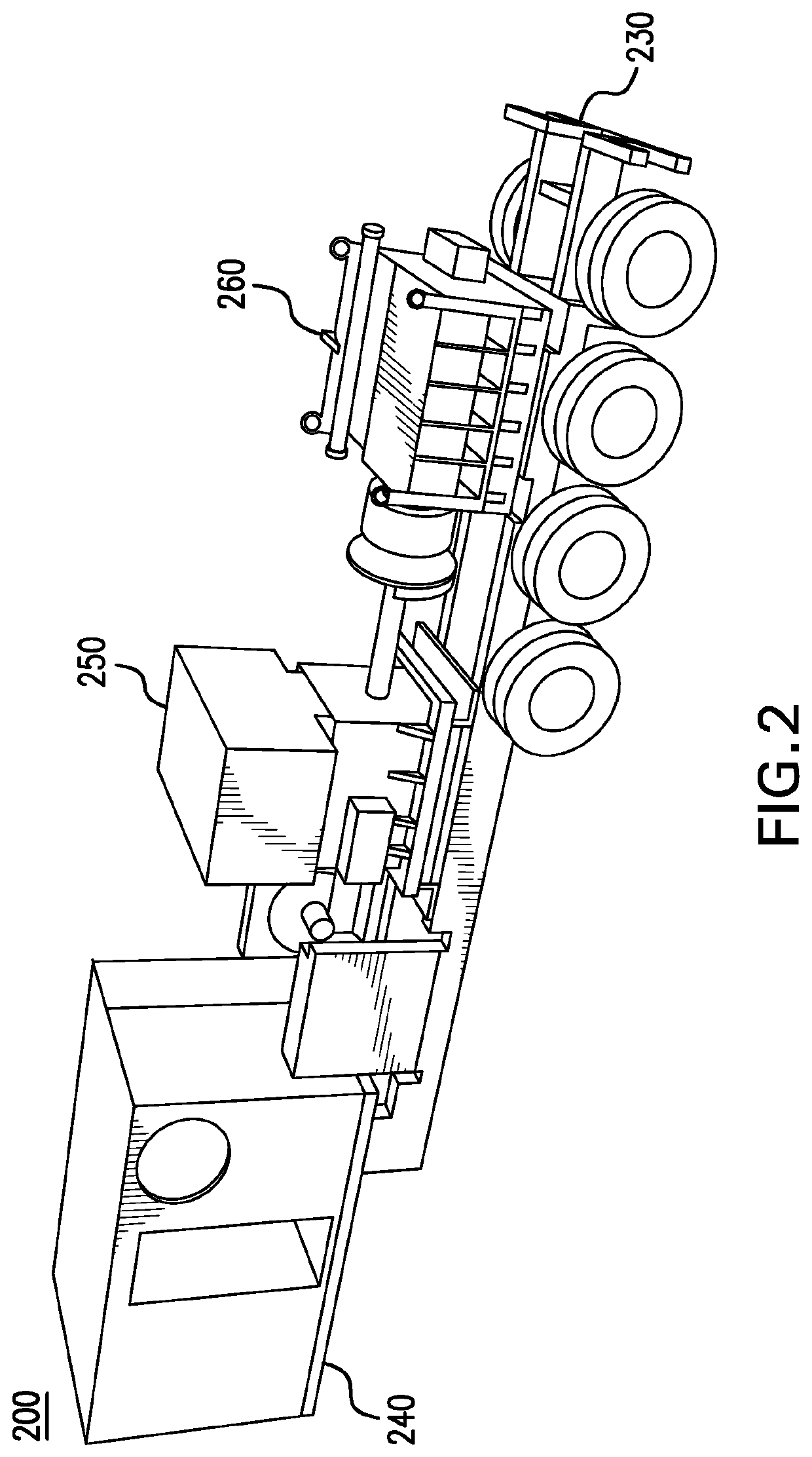
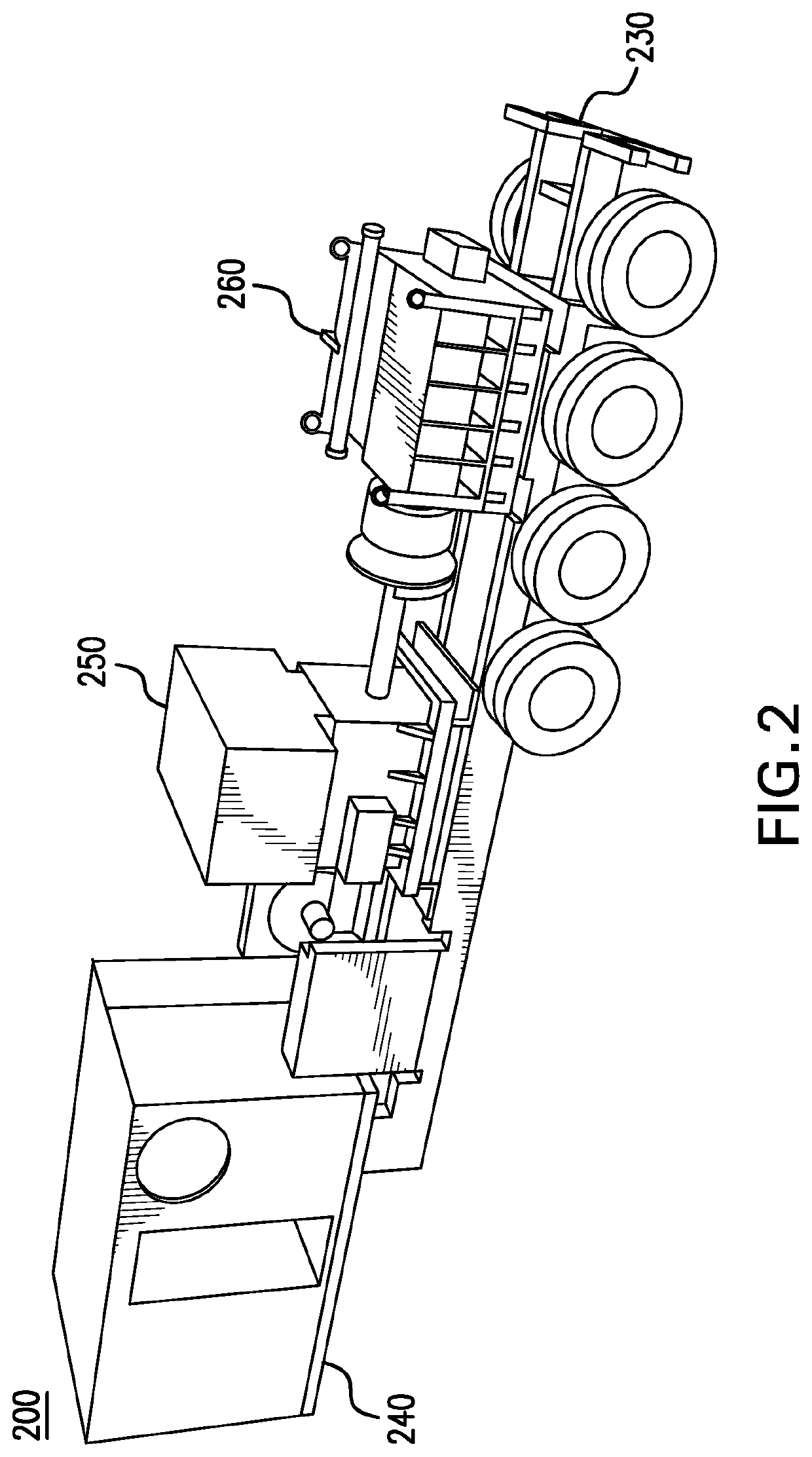
Slide out pump stand for hydraulic fracturing equipment
A hydraulic fracturing system has a pump driven by an electrically powered motor. The pump pressurizes fluid which is piped into a wellbore to fracture a subterranean formation. The pump and motor are mounted on a trailer that is hitched to a tractor. A platform assembly is mounted onto the trailer, and which is selectively moveable between deployed and stowed configurations. The platform assembly includes a platform, a lateral rail assembly mounted to the platform, and gates on the forward and aft ends of the platform. The rail assembly and gates define a safety barrier to prevent operations personnel from falling off the platform. In the stowed configuration the platform assembly is anchored in place over wheels on the trailer. In the deployed configuration, the platform assembly provides work surface so that operations personnel can readily access the pump on the trailer.
Owner:US WELL SERVICS LLC
Remotely controlled apparatus for downhole applications and methods of operation
An apparatus for use downhole is disclosed that, in one configuration includes a downhole tool configured to operate in an active position and an inactive position and an actuation device, which may include a control unit. The apparatus includes a telemetry unit that sends a first pattern recognition signal to the control unit to move the tool into the active position and a second pattern recognition signal to move the tool into the inactive position. The apparatus may be used for drilling a subterranean formation and include a tubular body and one or more extendable features, each positionally coupled to a track of the tubular body, and a drilling fluid flow path extending through a bore of the tubular body for conducting drilling fluid therethrough. A push sleeve is disposed within the tubular body and coupled to the one or more features. A valve assembly is disposed within the tubular body and configured to control the flow of the drilling fluid into an annular chamber in communication with the push sleeve; the valve assembly comprising a mechanically operated valve and / or an electronically operated valve. Other embodiments, including methods of operation, are provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES OILFIELD OPERATIONS LLC
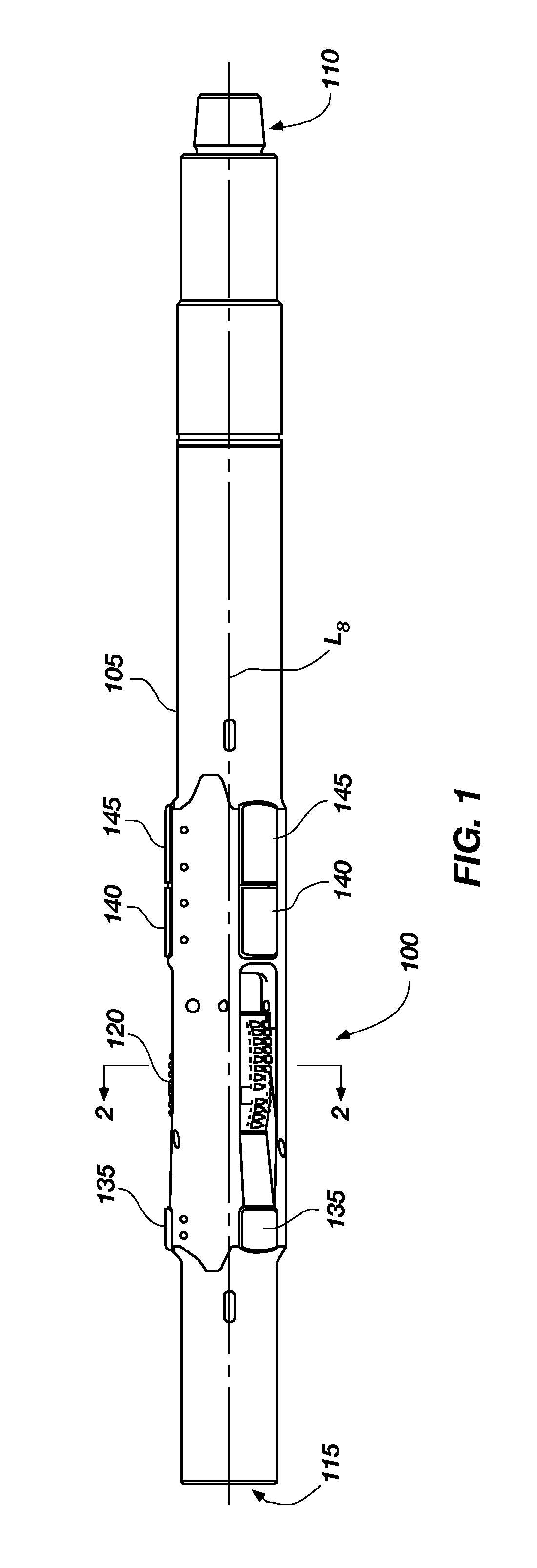
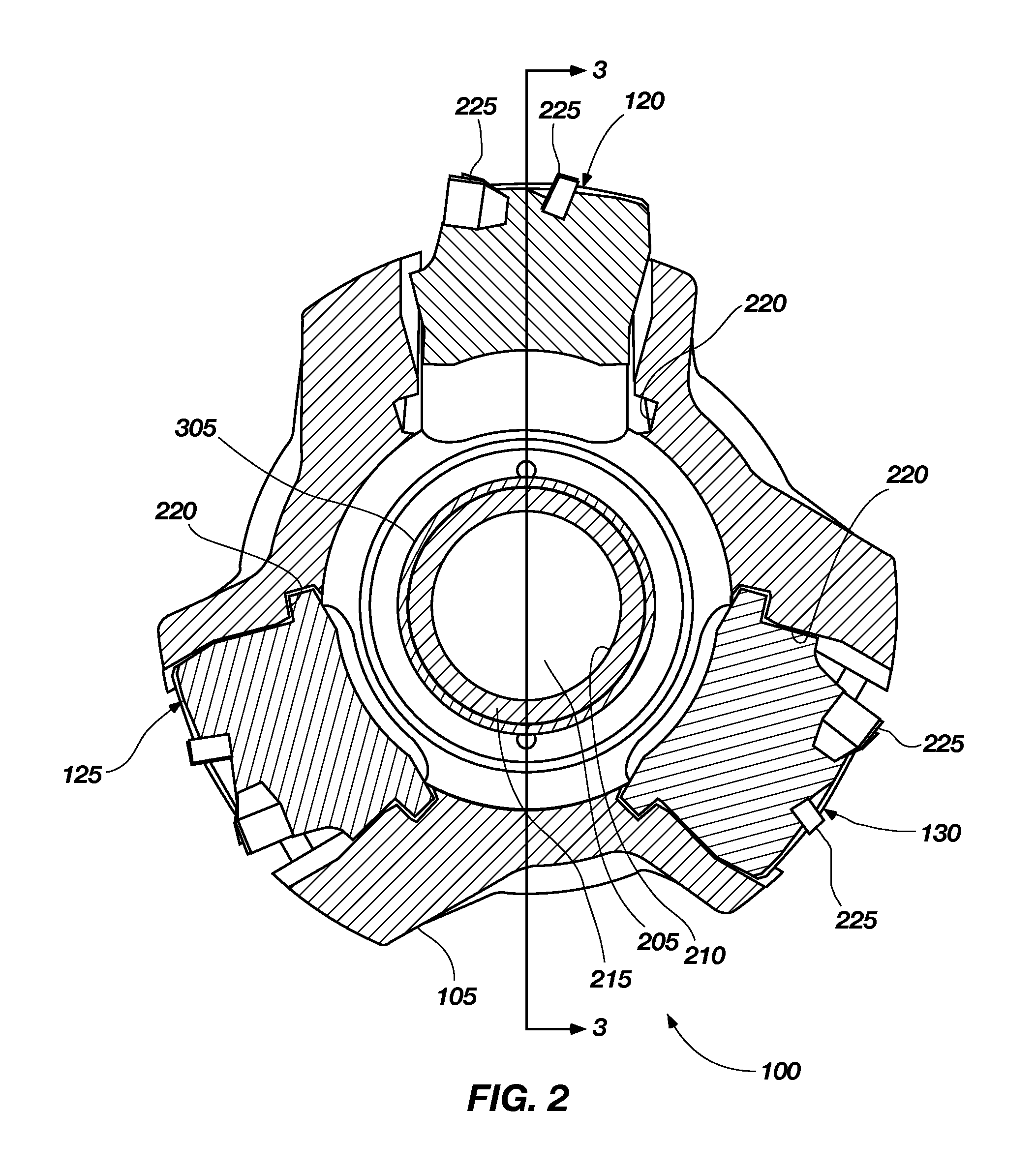
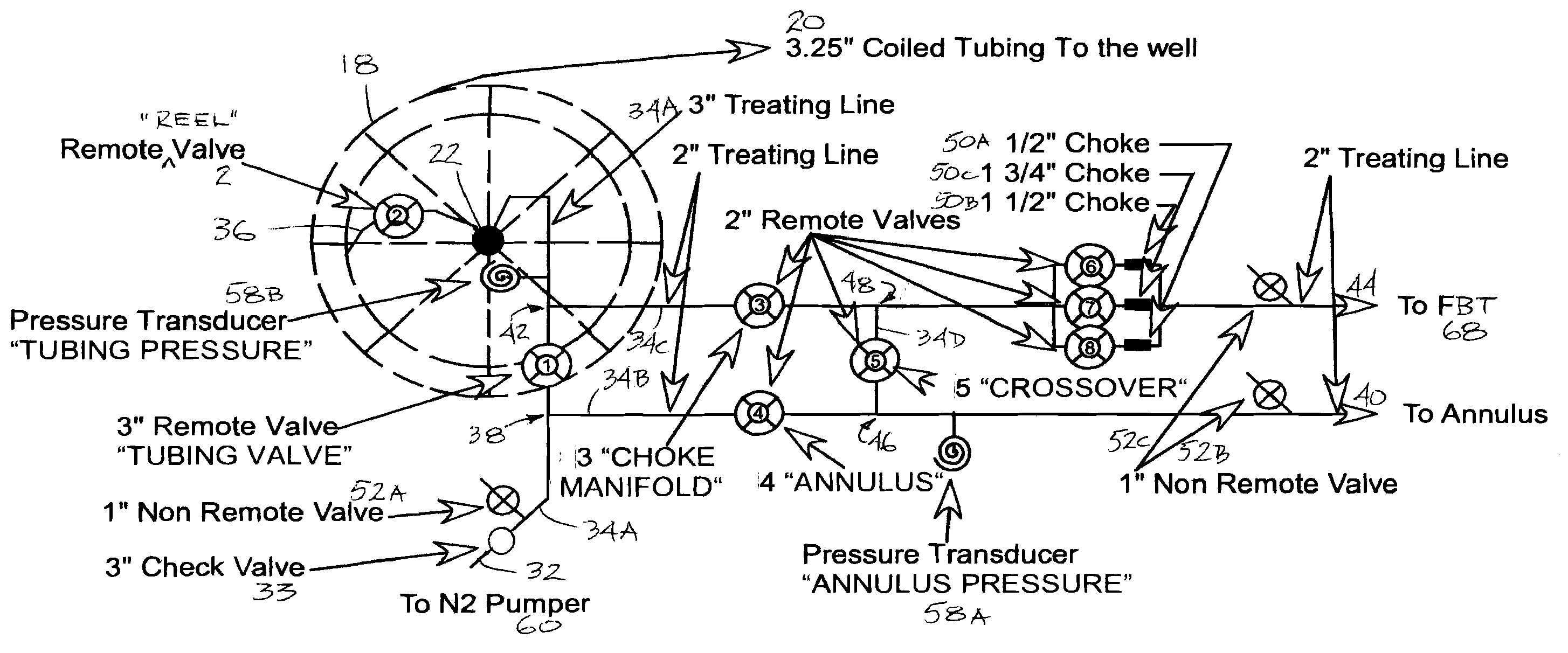
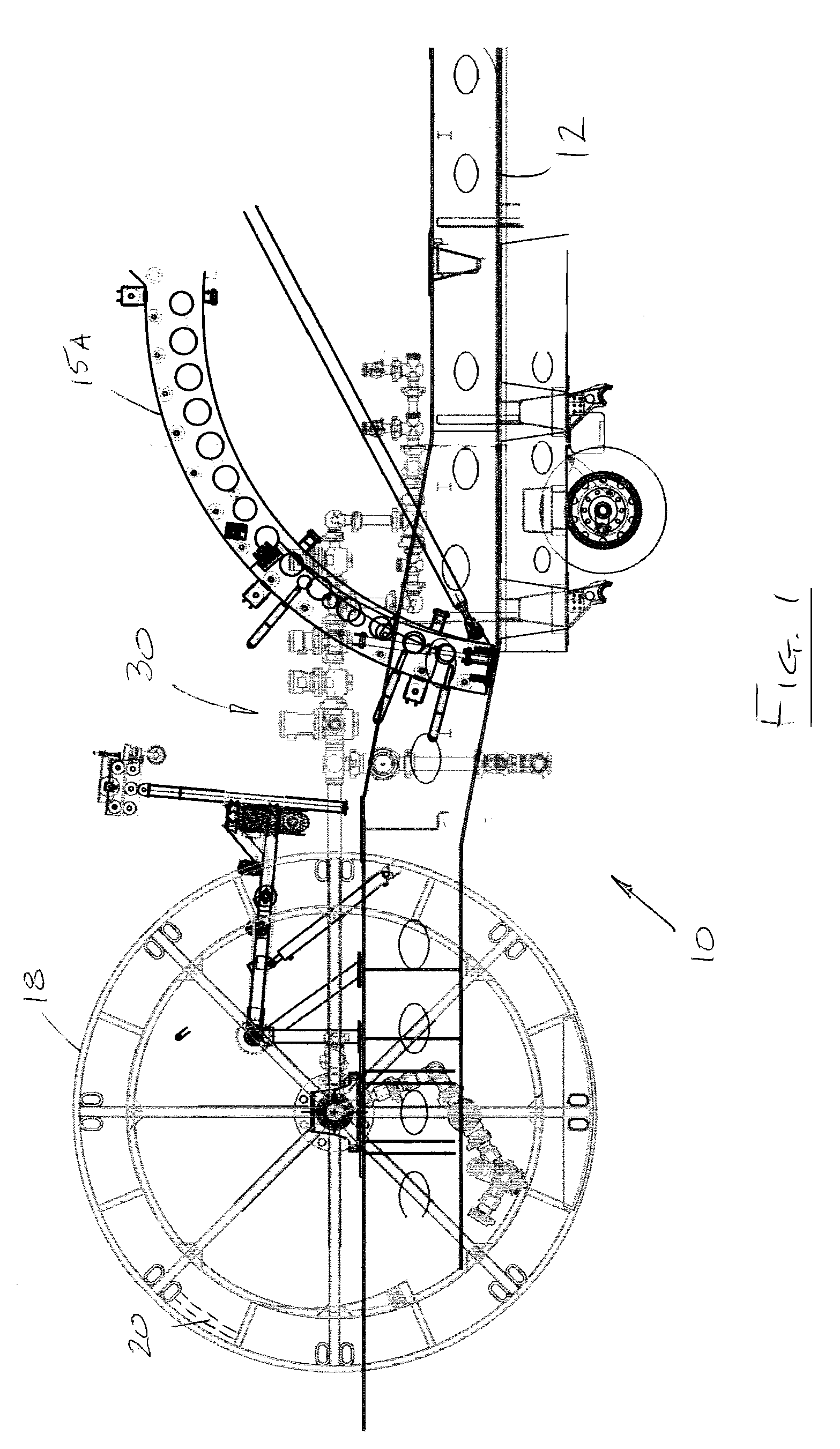
Well Servicing Rig and Manifold Assembly
A well servicing rig for communicating with a fluid source and an effluent reservoir (such as a flow back tank) has an apparatus for holding and dispensing coiled tubing. A manifold assembly is advantageously located on the rig for routing the pressurized fluid (such as nitrogen gas mixed with proppant) from the fluid source between the coiled tubing apparatus, the well and the effluent reservoir. The manifold assembly controls the flow of the fluid to perform fracturing operations, for reverse fluid circulation, for a common coiled tubing operation, for pressure testing, and the like. The assembly includes remotely controlled valves and pressure transducers for controlling the fluid flow, and chokes for diffusing fluid energy prior to entering the effluent reservoir. The rig, fluid source, effluent reservoir and a fluid pumper provide a novel method of servicing an underground formation (such as a coal bed) for natural gas.
Owner:FRAC SOURCE
Expandable reamer apparatus for enlarging boreholes while drilling and methods of use
ActiveUS7036611B2Reduce capacityReduce the cross-sectional areaSurveyDrill bitsFixed bearingWell drilling
An expandable reamer apparatus and methods for reaming a borehole, wherein a laterally movable blade carried by a tubular body may be selectively positioned at an inward position and an expanded position. The laterally movable blade, held inwardly by blade-biasing elements, may be forced outwardly by drilling fluid selectively allowed to communicate therewith by way of an actuation sleeve disposed within the tubular body. Alternatively, a separation element may transmit force or pressure from the drilling fluid to the movable blade. Further, a chamber in communication with the movable blade may be pressurized by way of a downhole turbine or pump. A ridged seal wiper, compensator, movable bearing pad, fixed bearing pad preceding the movable blade, or an adjustable spacer element to alter expanded blade position may be included within the expandable reamer. In addition, a drilling fluid pressure response indicating an operational characteristic of the expandable reamer may be generated.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES OILFIELD OPERATIONS LLC
Apparatus identification systems and methods
Owner:VARCO I P INC
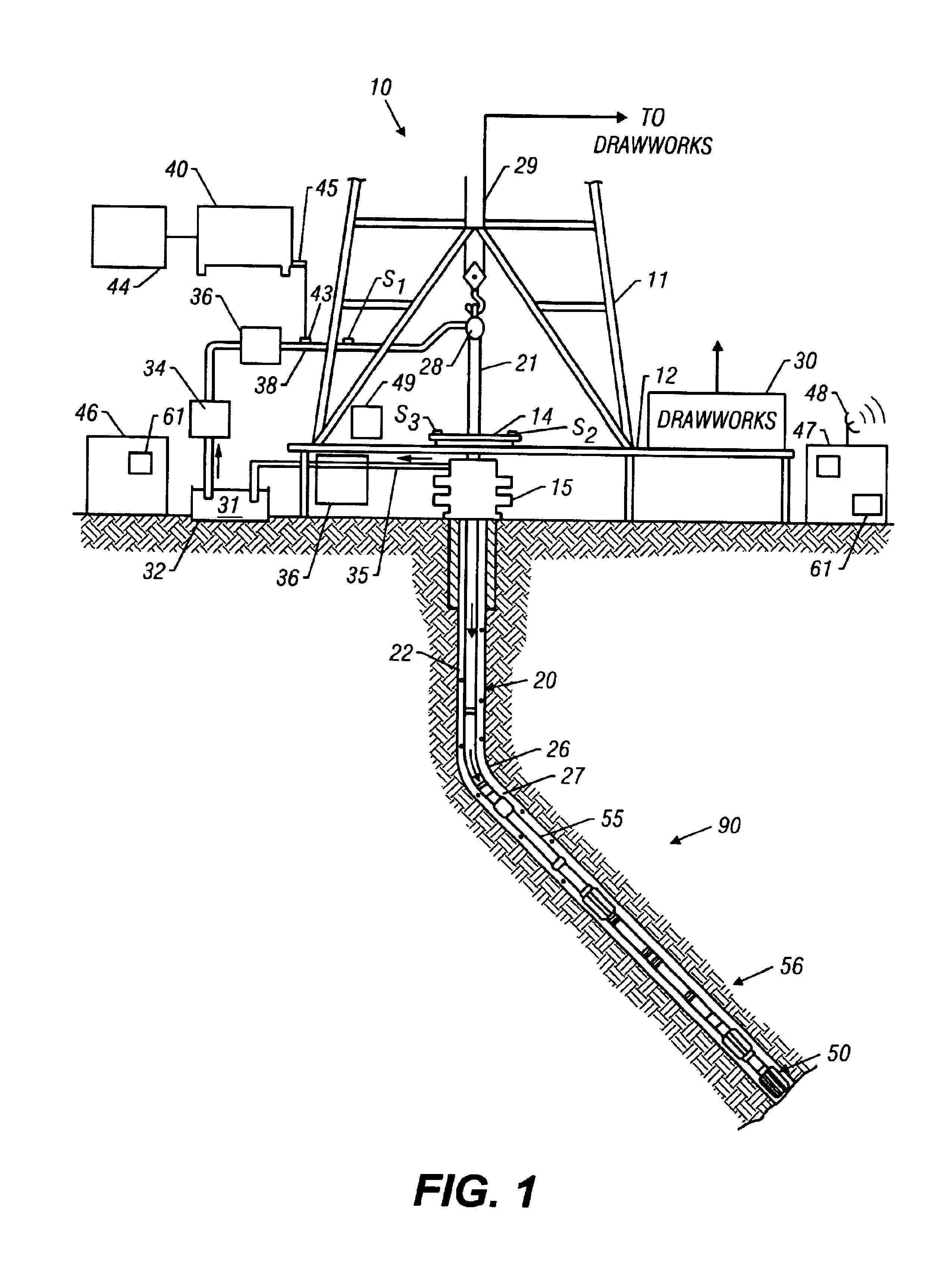
Downhole telemetry system and method
A cabled communication link for a drill string includes spaced apart adapter subs within the drill string and a cable connecting the adapter subs for communication of a signal therebetween. The cabled communication link may be drill pipe joints are interconnected within the drill string between adapter subs to form a piped communication link, whereby the cabled communication link establishes a pathway to the piped communication link for transmitting a signal through the drill string. The cabled communication link may also be in a non-wired section of the drill string is disposed between adapter subs, whereby the cabled communication link establishes a pathway for transmitting a signal through the non-wired section of the drill string. Inductive couplings are preferably used for communication across the adapter subs and wired drill pipe joints. Another aspect of the cabled communication employs wireless transceivers at or near the surface of the wellbore.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
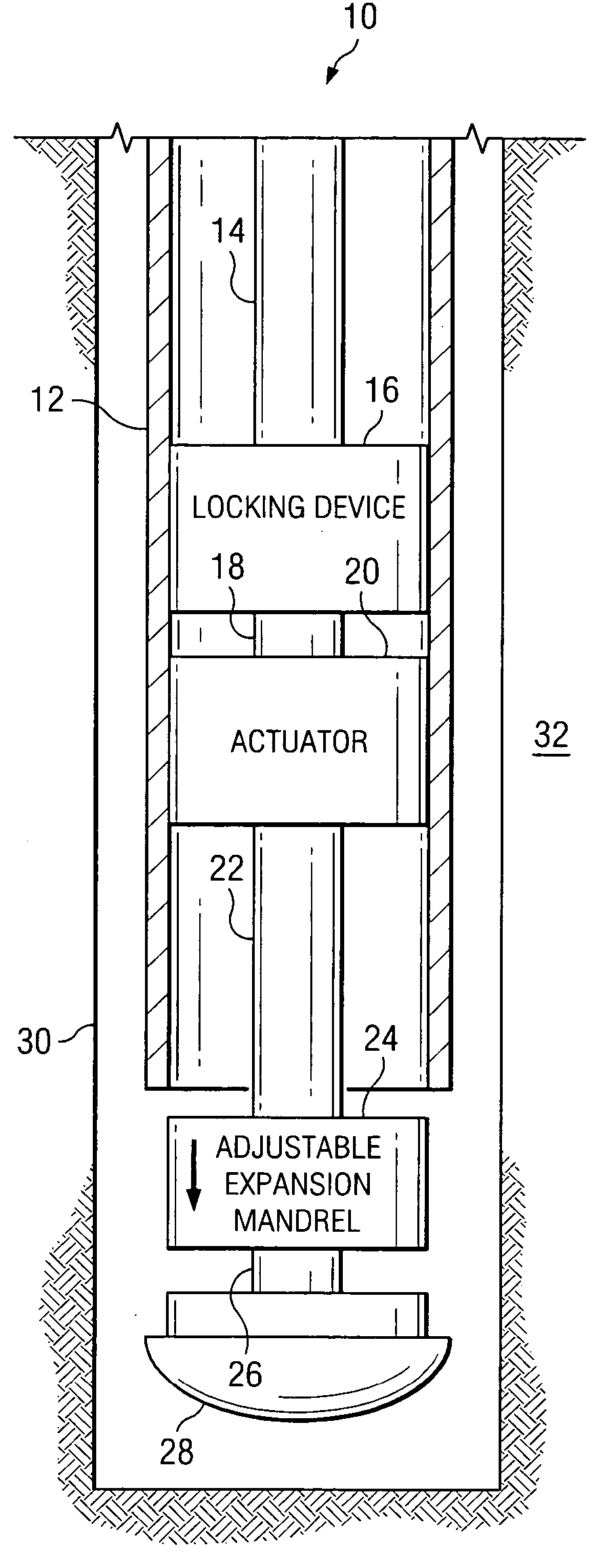
Tools and methods for hanging and/or expanding liner strings
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to tools and methods for hanging and / or expanding liner strings. In one embodiment, a method of hanging a liner assembly from a previously installed tubular in a wellbore includes running the liner assembly and a setting tool into the wellbore using a run-in string. The setting tool includes an isolation valve and the liner assembly includes a liner hanger and a liner string. The method further includes sending an instruction signal from the surface to the isolation valve, wherein the isolation valve closes in response to the instruction signal and isolates a setting pressure in the setting tool from the liner string; and increasing fluid pressure in the setting tool, thereby setting the liner hanger.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Methods and systems for improved drilling operations using real-time and historical drilling data
ActiveUS20140116776A1Maximized drilling rateLower Drilling CostsEarth drilling toolsMathematical modelsLithologyReal-time data
Methods and systems are described for improved drilling operations through the use of real-time drilling data to predict bit wear, lithology, pore pressure, a rotating friction coefficient, permeability, and cost in real-time and to adjust drilling parameters in real-time based on the predictions. The real-time lithology prediction is made by processing the real-time drilling data through a multilayer neural network. The real-time bit wear prediction is made by using the real-time drilling data to predict a bit efficiency factor and to detect changes in the bit efficiency factor over time. These predictions may be used to adjust drilling parameters in the drilling operation in real-time, subject to override by the operator. The methods and systems may also include determining various downhole hydraulics parameters and a rotary friction factor. Historical data may be used in combination with real-time data to provide expert system assistance and to identify safety concerns.
Owner:RESOURCE ENERGY SOLUTIONS
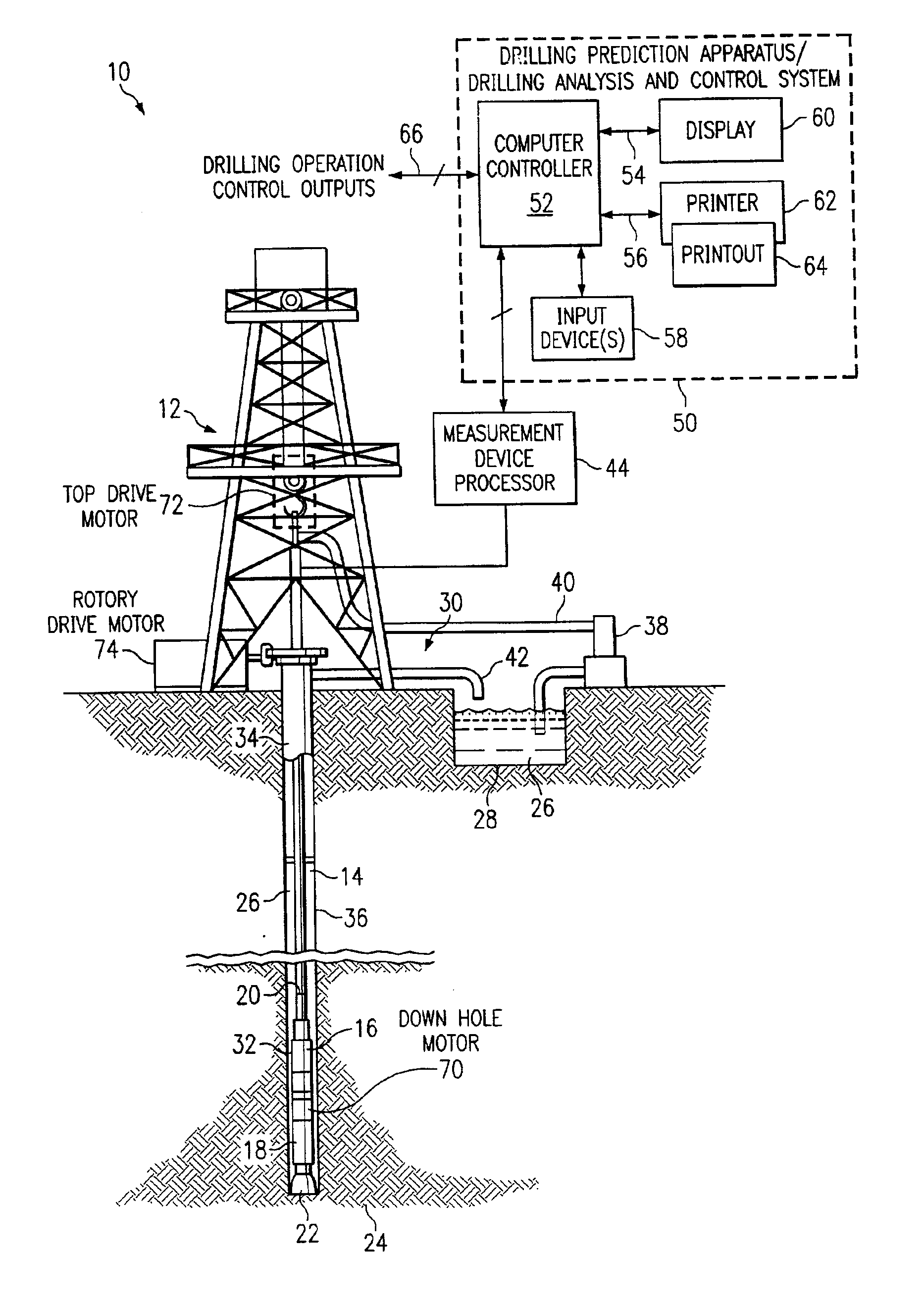
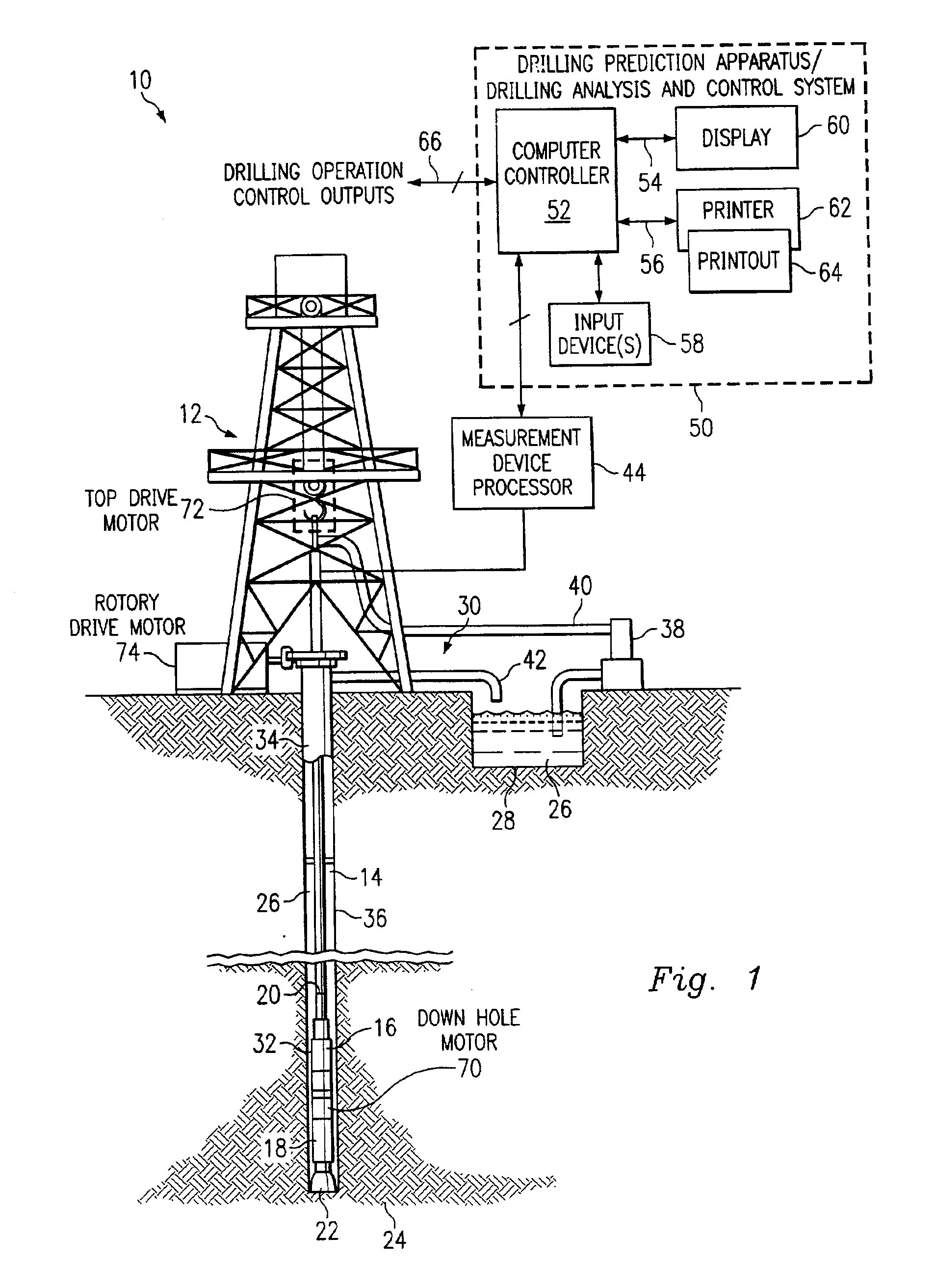
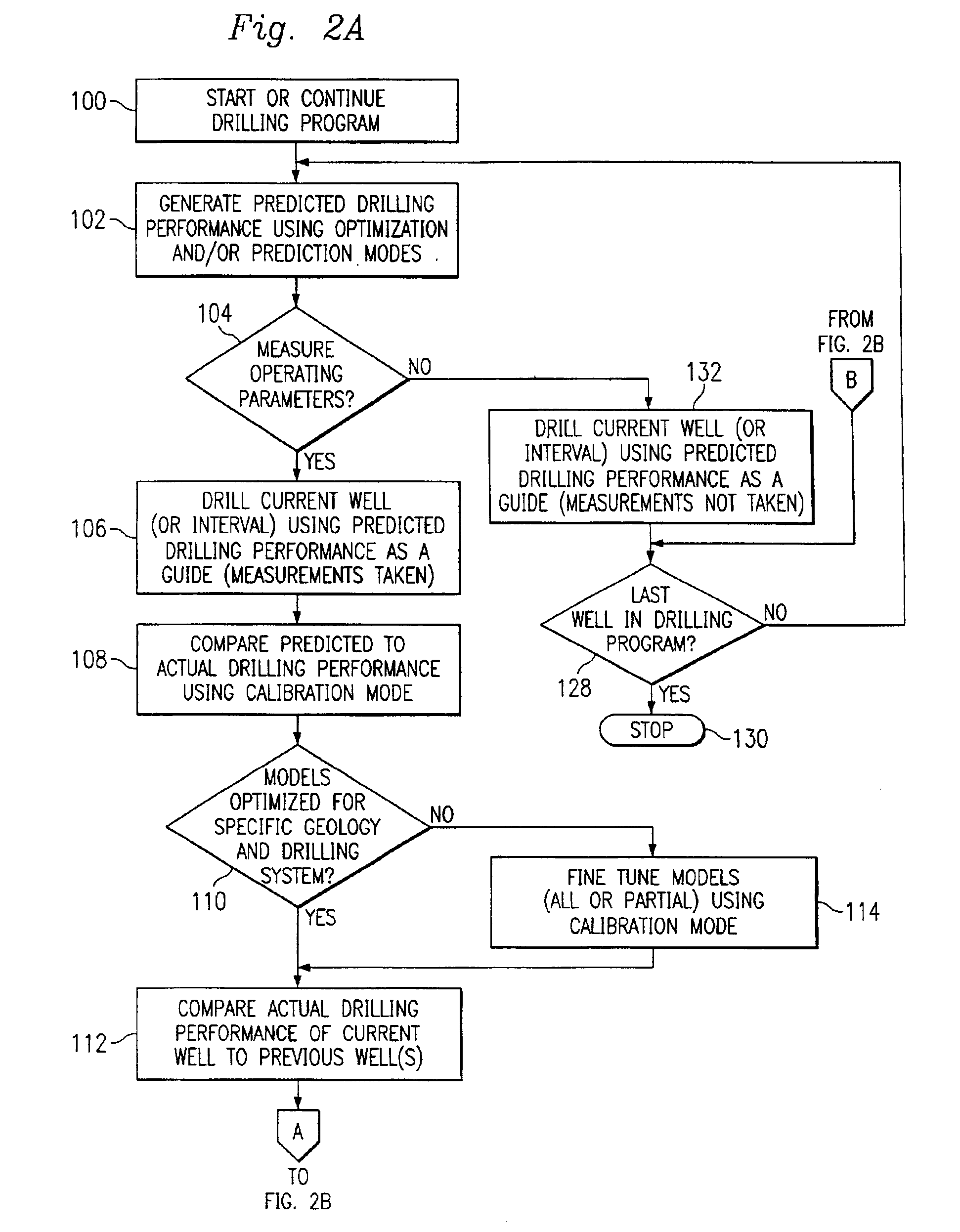
Method and system for predicting performance of a drilling system of a given formation
InactiveUS7032689B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth drilling toolsComputer printingDisplay device
A method and apparatus for predicting the performance of a drilling system for the drilling of a well bore in a given formation includes generating a geology characteristic of the formation per unit depth according to a prescribed geology model, obtaining specifications of proposed drilling equipment for use in the drilling of the well bore, and predicting a drilling mechanics in response to the specifications as a function of the geology characteristic per unit depth according to a prescribed drilling mechanics model. Responsive to a predicted-drilling mechanics, a controller controls a parameter in the drilling of the well bore. The geology characteristic includes at least rock strength. The specifications include at least a bit specification of a recommended drill bit. Lastly, the predicted drilling mechanics include at least one of bit wear, mechanical efficiency, power, and operating parameters. A display is provided for generating a display of the geology characteristic and predicted drilling mechanics per unit depth, including either a display monitor or a printer.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods of well stimulation during drilling operations
The present invention relates to subterranean well stimulation. More particularly, the present invention relates to improved methods of stimulating subterranean formations during drilling operations. In some embodiments, the present invention discloses methods of stimulating a section of a subterranean formation comprising (a) forming at least a portion of a well bore that at least penetrates a section of the subterranean formation using a drilling operation; (b) stimulation a section of the subterranean; and (c) continuing the drilling operation. In other embodiments, the present invention discloses methods of stimulation a section of a subterranean formation comprising (a) forming at least a portion of a well bore that at least penetrates a section of the subterranean formation using a drilling operation; (b) stimulating a section of the subterranean formation; and (c) continuing the drilling operation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Slide out pump stand for hydraulic fracturing equipment
A hydraulic fracturing system has a pump driven by an electrically powered motor. The pump pressurizes fluid which is piped into a wellbore to fracture a subterranean formation. The pump and motor are mounted on a trailer that is hitched to a tractor. A platform assembly is mounted onto the trailer, and which is selectively moveable between deployed and stowed configurations. The platform assembly includes a platform, a lateral rail assembly mounted to the platform, and gates on the forward and aft ends of the platform. The rail assembly and gates define a safety barrier to prevent operations personnel from falling off the platform. In the stowed configuration the platform assembly is anchored in place over wheels on the trailer. In the deployed configuration, the platform assembly provides work surface so that operations personnel can readily access the pump on the trailer.
Owner:US WELL SERVICS LLC
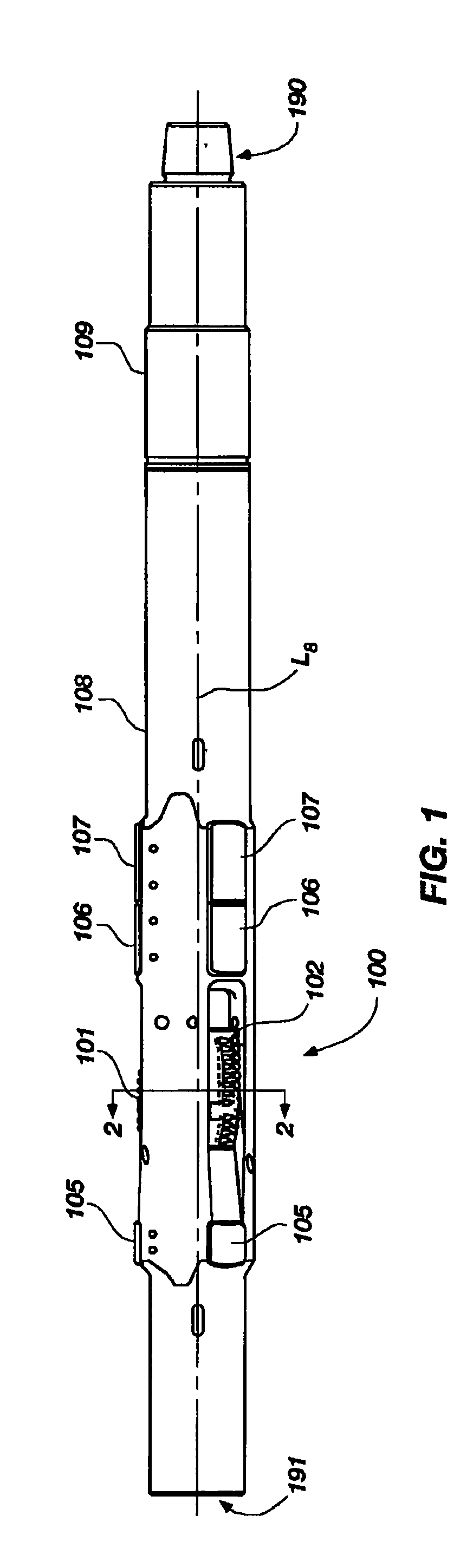
Expandable underreamer/stabilizer
A downhole tool is disclosed that functions as an underreamer, or alternatively, as a stabilizer in an underreamed borehole. An embodiment of the tool includes one or more moveable arms disposed within a body having a flowbore therethrough in fluid communication with the wellbore annulus. The tool alternates between collapsed and expanded positions in response to differential fluid pressure between the flowbore and the wellbore annulus. In one embodiment, the tool moves automatically in response to differential pressure. In a second embodiment, the tool must be selectively actuated before it is moveable. When the tool expands, the arms are preferably translated axially upwardly, while simultaneously being extended radially outwardly from the body. The expanded tool diameter is adjustable at the surface without changing components. The arms may include borehole engaging pads that comprise cutting structures or wear structures or both, depending upon the function of the tool.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Expandable bit with secondary release device
The present invention generally relates to an apparatus and method of forming a wellbore. In one aspect, an expandable bit for use in a wellbore is provided. The expandable bit includes a body and a blade assembly disposed on the body. The blade assembly is movable between a closed position whereby the expandable bit has a smaller outer diameter and an open position whereby the expandable bit has a larger outer diameter. The expandable bit further includes a release assembly for providing a secondary means to move the blade assembly from the open position to the closed position. In another aspect, a method of forming a wellbore is provided. In yet another aspect, an expandable apparatus for use in forming a wellbore is provided.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Mono diameter wellbore casing
ActiveUS20050056433A1Add dimensionIncrease in sizeDrilling rodsConstructionsWellboreEnvironmental geology
Owner:ENVENTURE GLOBAL TECH LLC
Continuous flow drilling systems and methods
In one embodiment, a method for drilling a wellbore includes injecting drilling fluid into a top of a tubular string disposed in the wellbore at a first flow rate. The tubular string includes: a drill bit disposed on a bottom thereof, tubular joints connected together, a longitudinal bore therethrough, and a port through a wall thereof. The drilling fluid exits the drill bit and carries cuttings from the drill bit. The cuttings and drilling fluid (returns) flow to the surface via an annulus defined between the tubular string and the wellbore. The method further includes rotating the drill bit while injecting the drilling fluid; remotely removing a plug from the port, thereby opening the port; and injecting drilling fluid into the port at a second flow rate while adding a tubular joint or stand of joints to the tubular string. The injection of drilling fluid into the tubular string is continuously maintained between drilling and adding the joint or stand to the drill string. The method further includes remotely installing a plug into the port, thereby closing the port. The first and second flow rates may be substantially equal or different.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
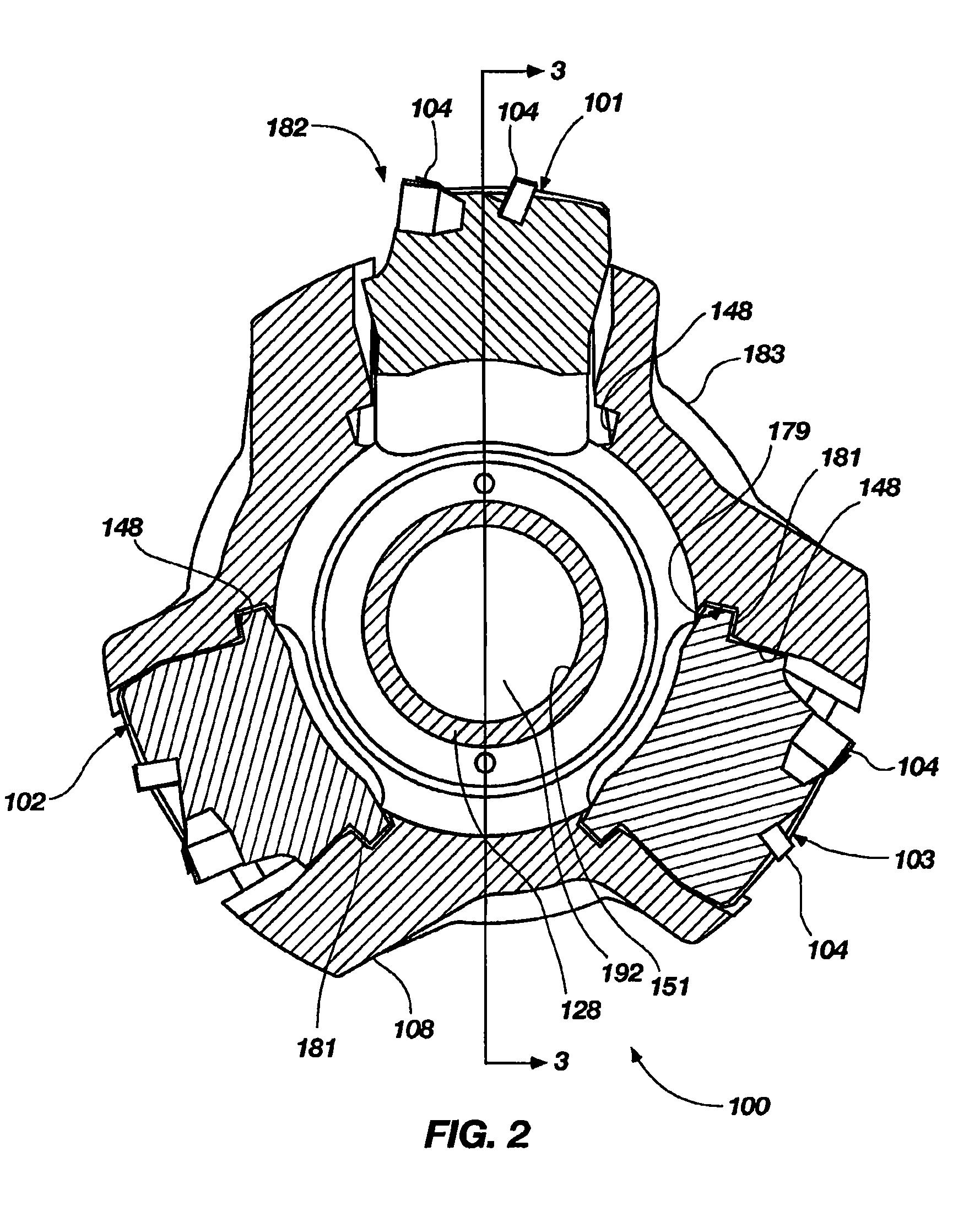
Expandable reamers for earth boring applications
An expandable reamer apparatus for drilling a subterranean formation includes a tubular body, one or more blades, each blade positionally coupled to a sloped track of the tubular body, a push sleeve and a drilling fluid flow path extending through an inner bore of the tubular body for conducting drilling fluid therethrough. Each of the one or more blades includes at least one cutting element configured to remove material from a subterranean formation during reaming. The push sleeve is disposed in the inner bore of the tubular body and coupled to each of the one or more blades so as effect axial movement thereof along the track to an extended position responsive to exposure to a force or pressure of drilling fluid in the flow path of the inner bore. Other embodiments of the expandable reamer apparatus are provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Expandable stabilizer with roller reamer elements
An expandable reamer apparatus for drilling a subterranean formation may include a tubular body, one or more blades, each blade positionally coupled to a sloped track of the tubular body, a push sleeve and a drilling fluid flow path extending through an inner bore of the tubular body for conducting drilling fluid therethrough. Each of the one or more blades may be configured to ream a subterranean formation. The push sleeve may be disposed in the inner bore of the tubular body and coupled to each of the one or more blades so as effect axial movement thereof along the track to an extended position responsive to exposure to a force or pressure of drilling fluid in the flow path of the inner bore. Each blade may include one or more roller elements for reaming a wellbore.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
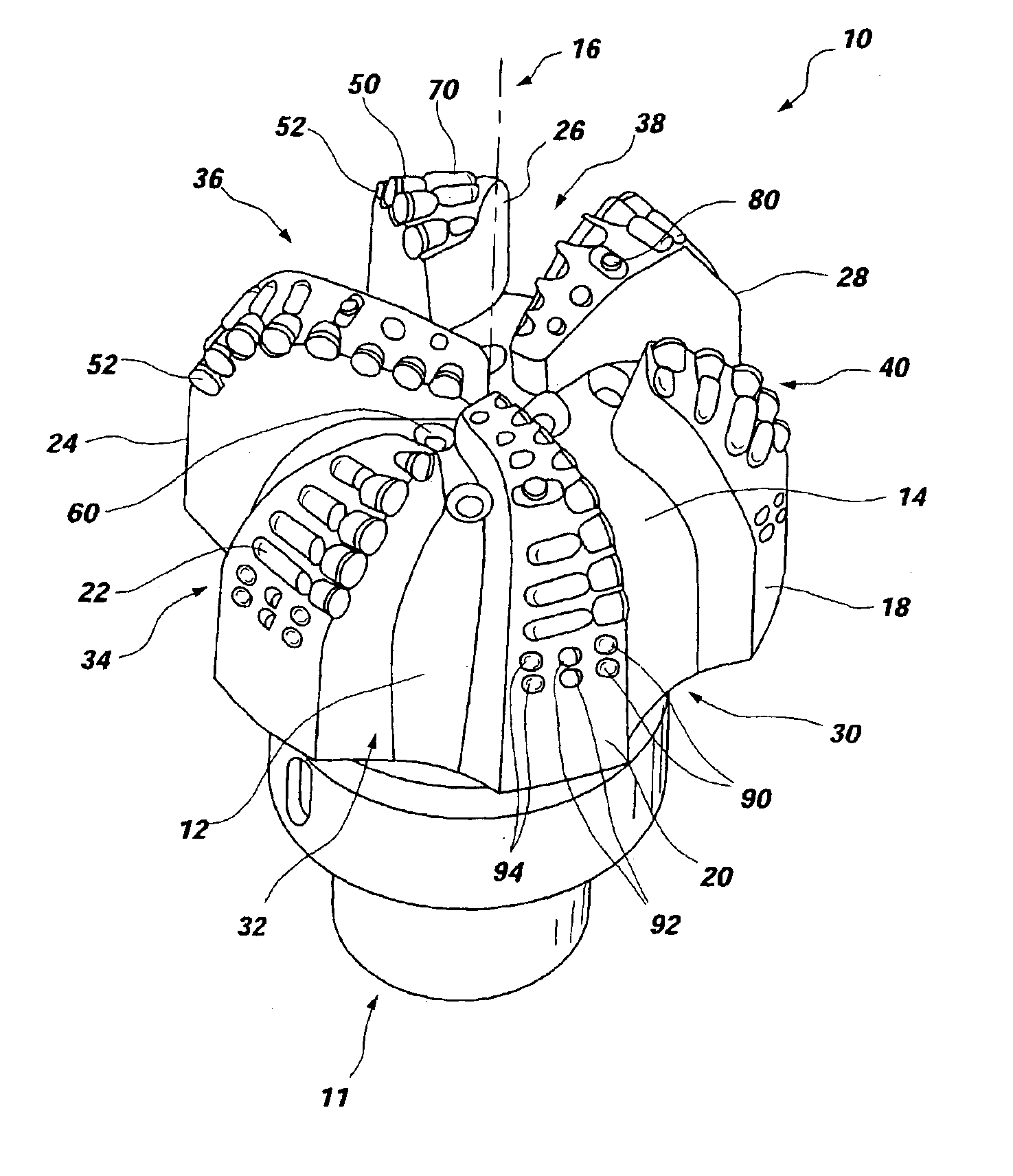
Earth boring apparatus and method offering improved gage trimmer protection
InactiveUS6883623B2Less wear resistantWear down quicklyDrill bitsDrilling rodsLeading edgeEngineering
A rotary drill bit for drilling subterranean formations configured with at least one protective structure proximate to the rotationally leading and trailing edges of a gage trimmer, wherein the at least one protective structure is positioned at substantially the same exposure as its associated gage trimmer. Particularly, the apparatus of the present invention may provide protection for gage trimmers during drilling, tripping, and / or rotation within a casing; i.e., when changing a drilling fluid. Protective structures may be configured and located according to anticipated drilling conditions including helix angles. In addition, a protective structure may be proximate to more than one gage trimmer while having a substantially equal exposure to each associated gage trimmer. Methods of use and a method of rotary bit design are also disclosed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for treating a productive zone while drilling
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for delivering a well treatment fluid to a productive zone of a subterranean formation at the same time that a well bore is being drilled. The method includes the steps of delivering a drill-in fluid to a drill bit drilling a well bore in, or adjacent to, the productive zone; removing drill cuttings from the well bore; and simultaneous with these steps injecting the treatment fluid into the productive zone. The apparatus includes at least three nested tubes, which form one internal flow path and two annuluses. The drill-in fluid and drill cuttings are delivered to, and removed from, the drill bit, respectively, through the internal flow path and one of the two annuluses. The treatment fluid is delivered to the subterranean formation through the remaining annulus and an expandable bladder mounted to the intermediate and outer tubes.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
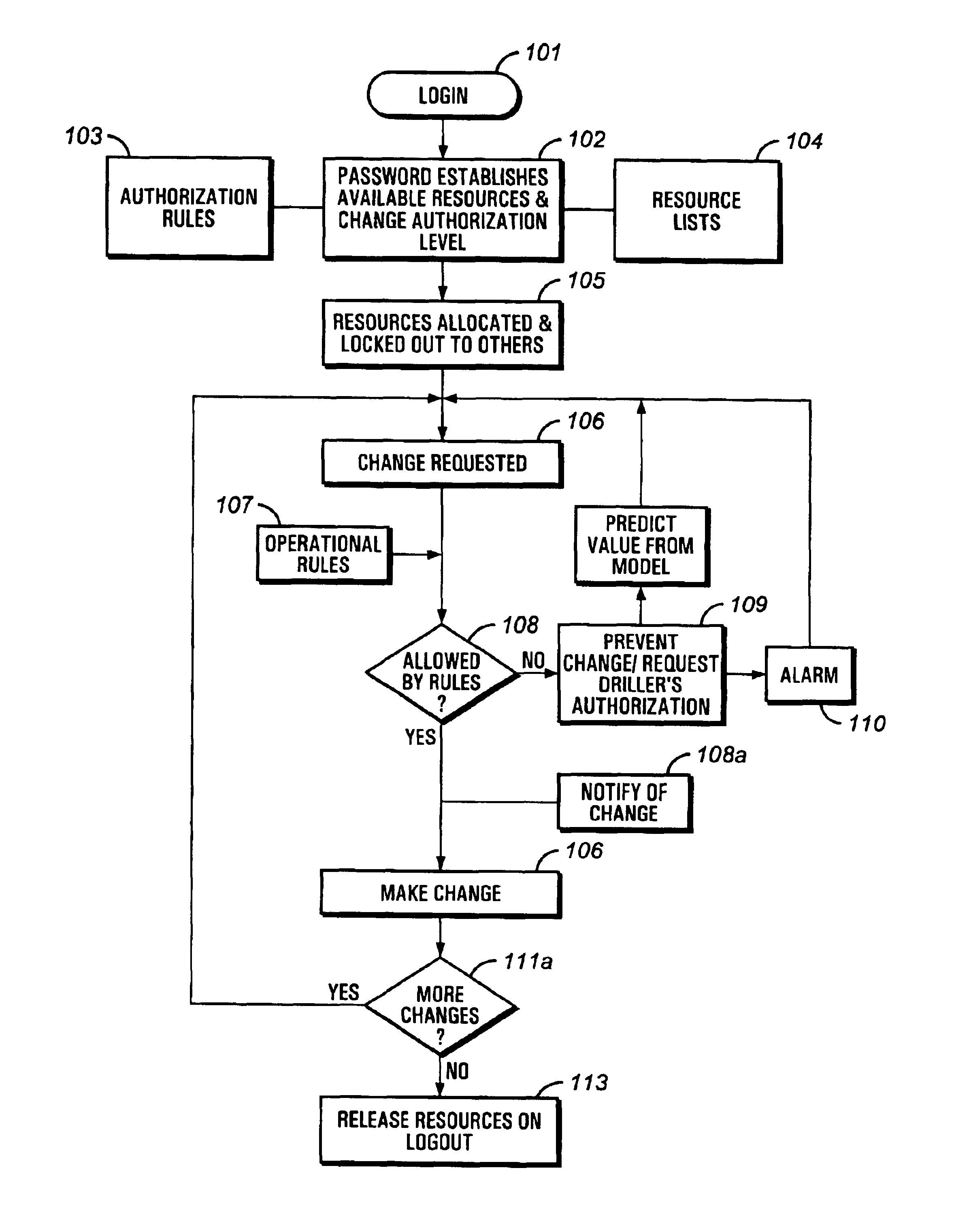
Automated rig control management system
ActiveUS6944547B2Overcome disadvantagesElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingControl systemControl engineering
A system and method for controlling operation of a drilling rig having a control management system, comprises programming the control system with at least one resource module, the at least one resource module having at least one operating model having at least one set of programmed operating rules related to at least one set of operating parameters. In addition, the system and method provide an authenticating hierarchical access to at least one user to the at least one resource module.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
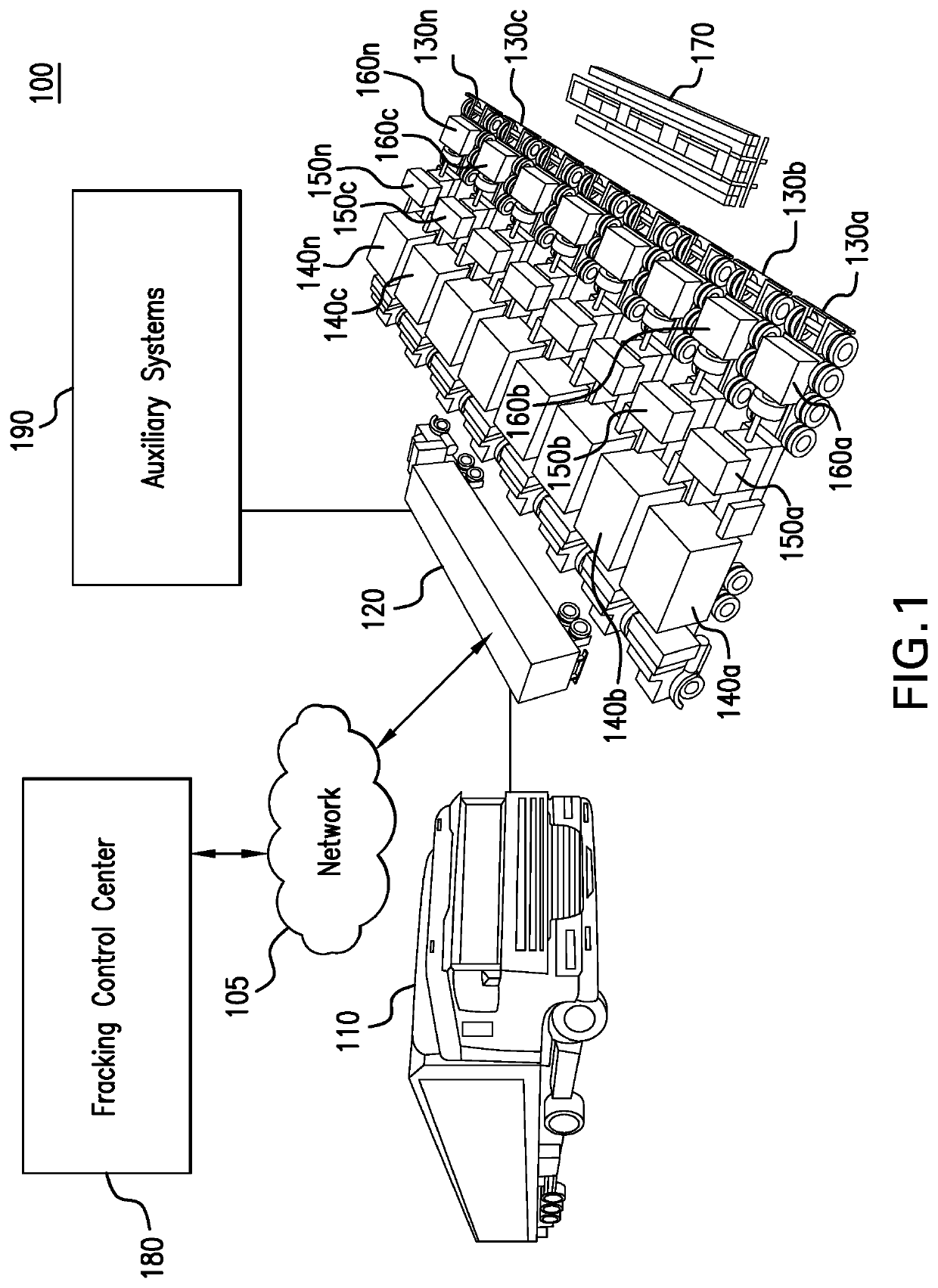
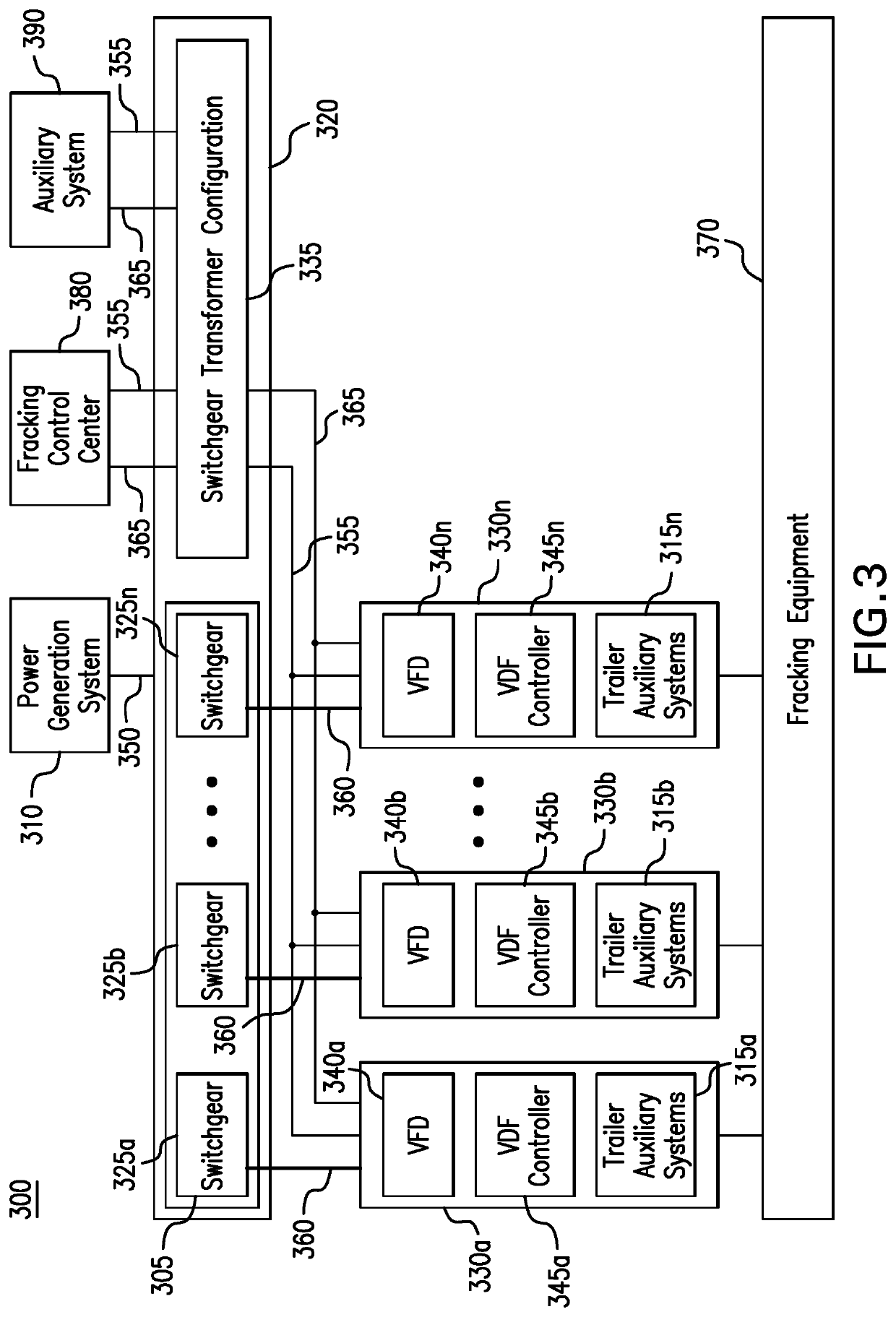
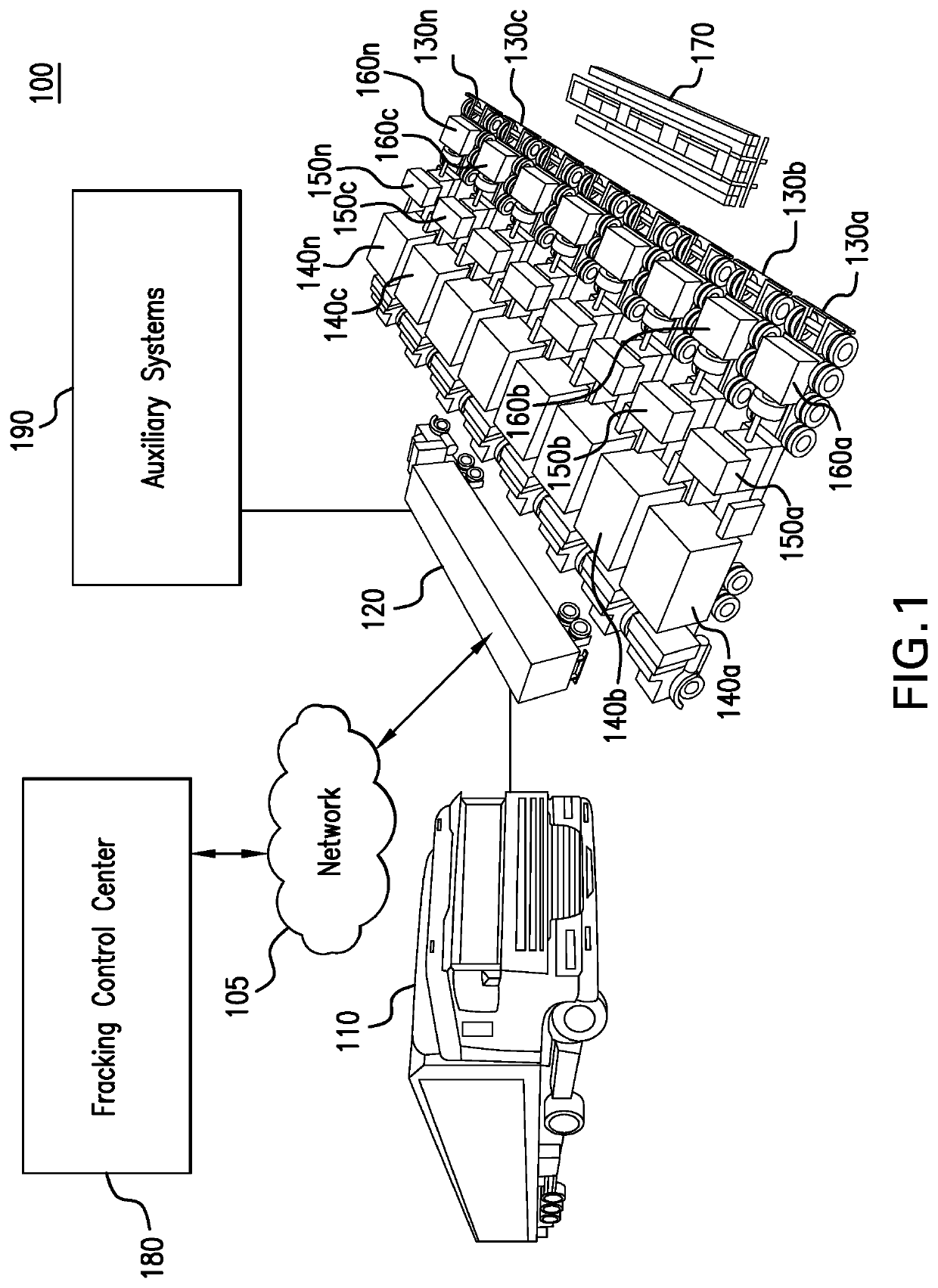
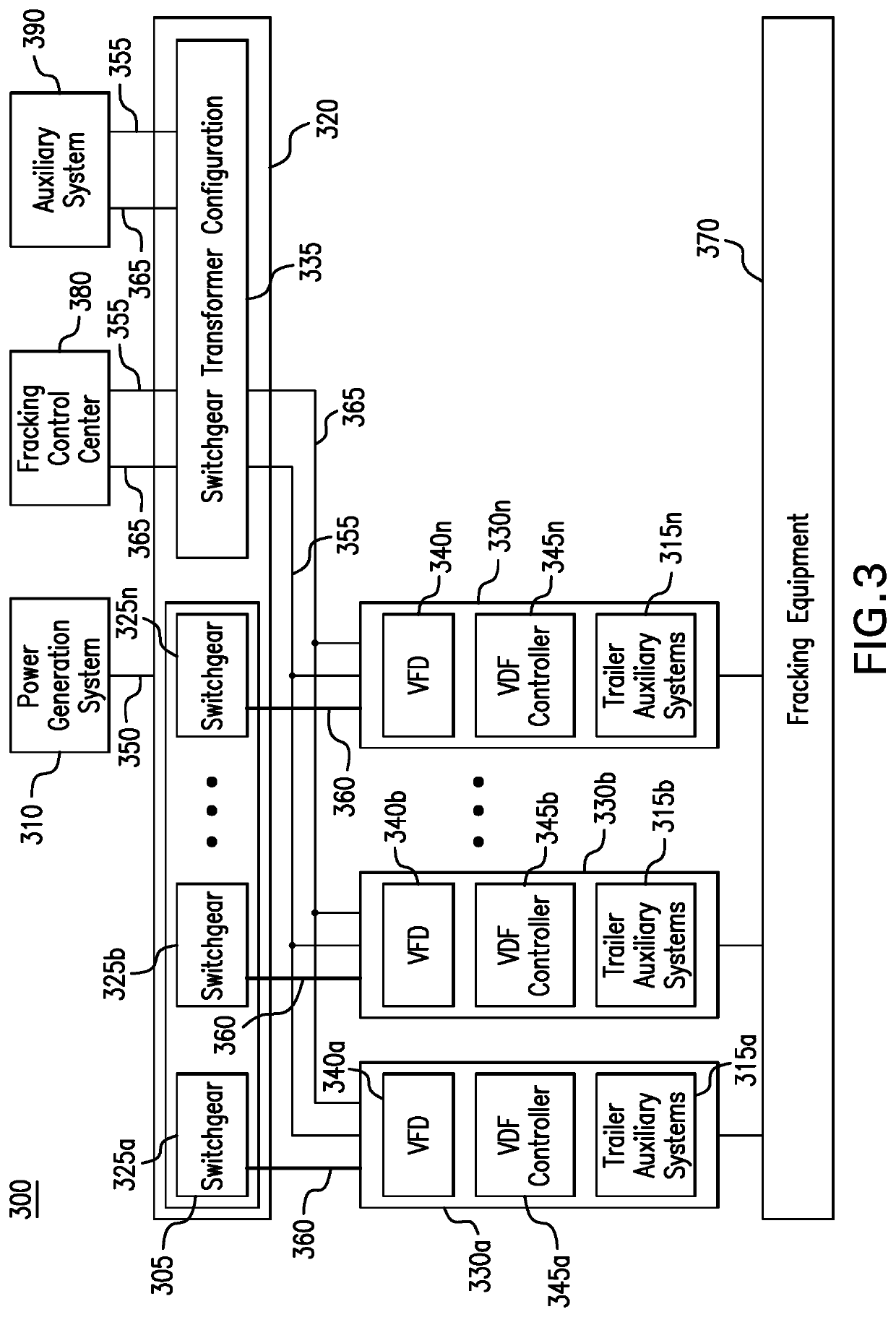
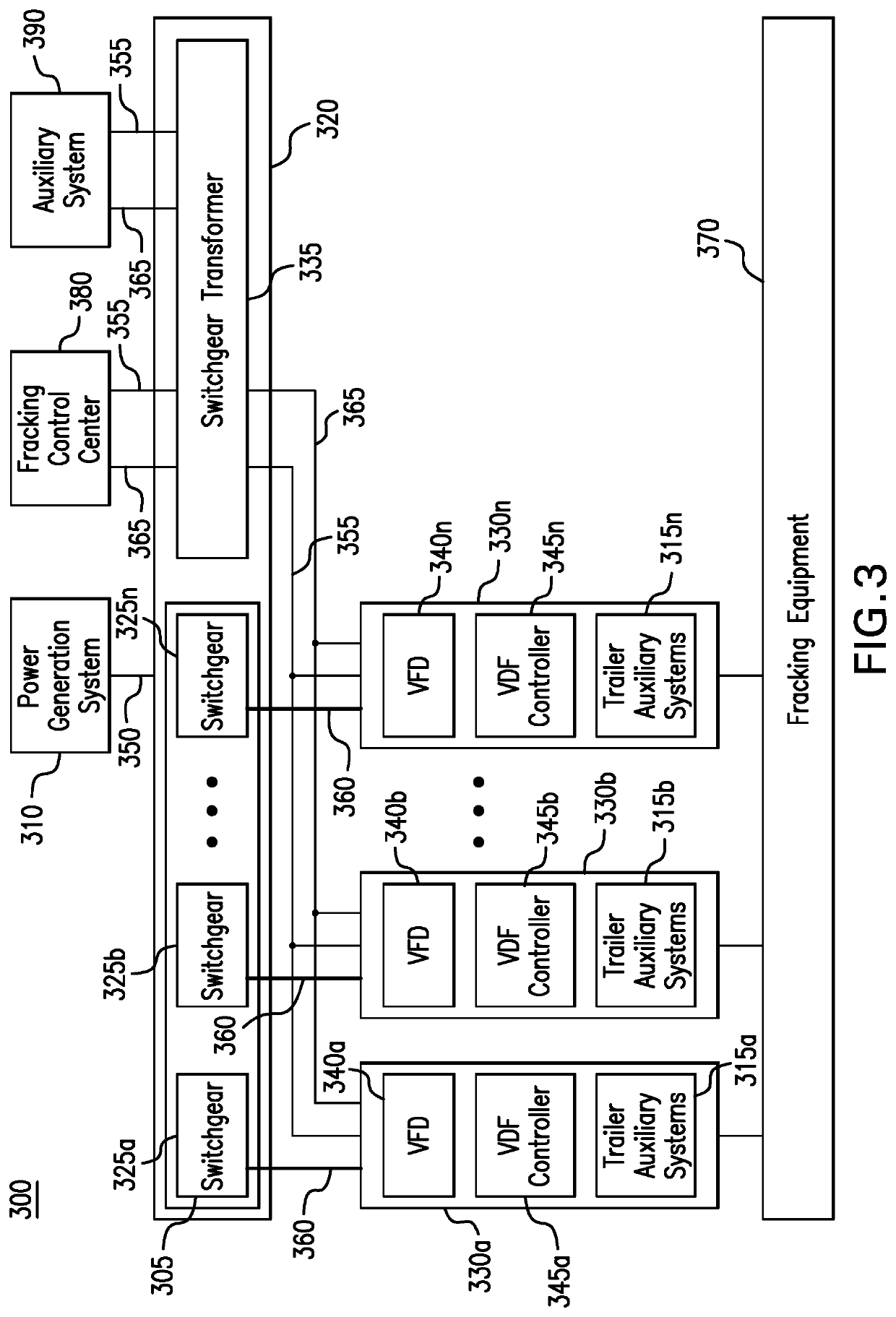
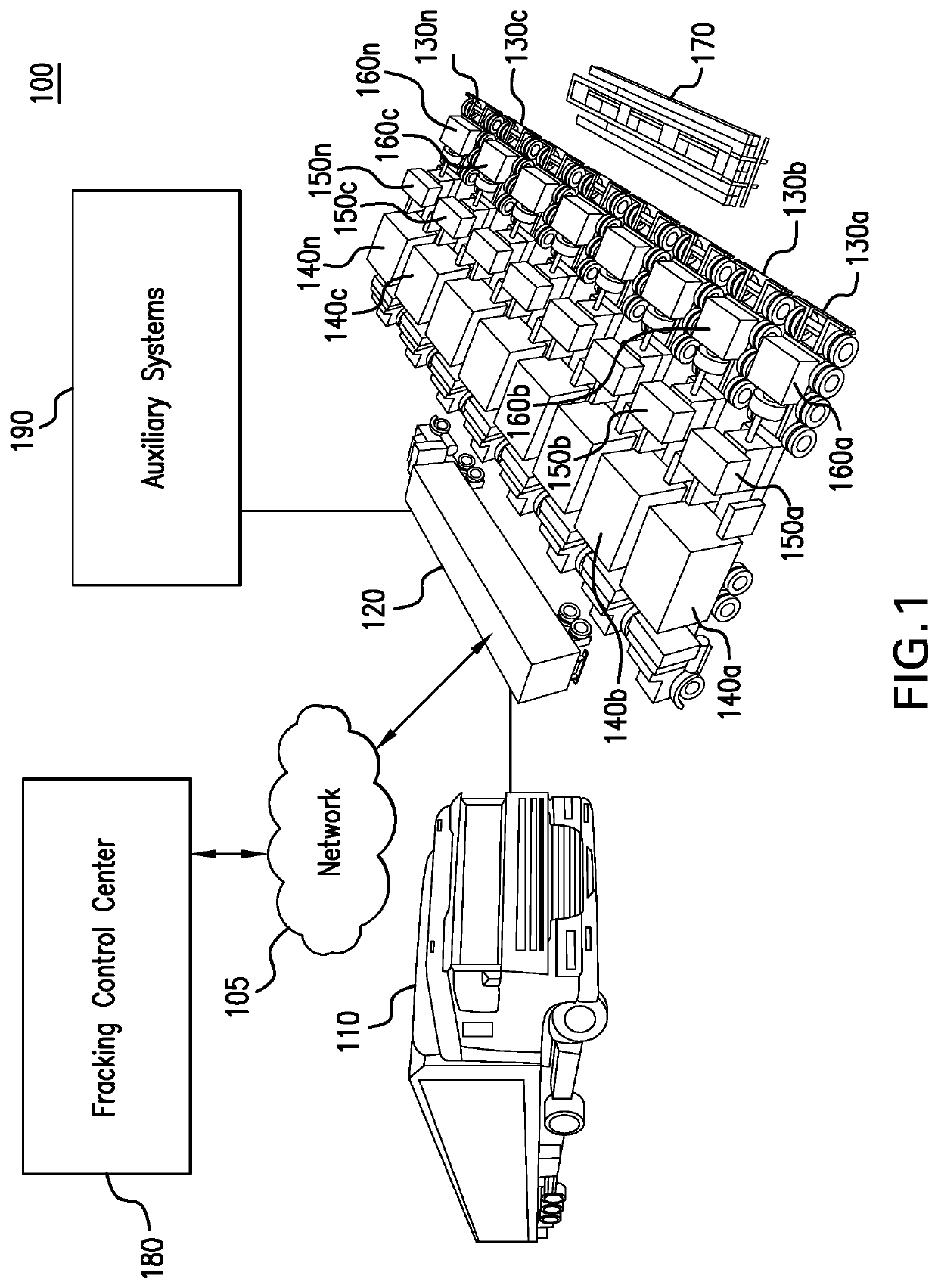
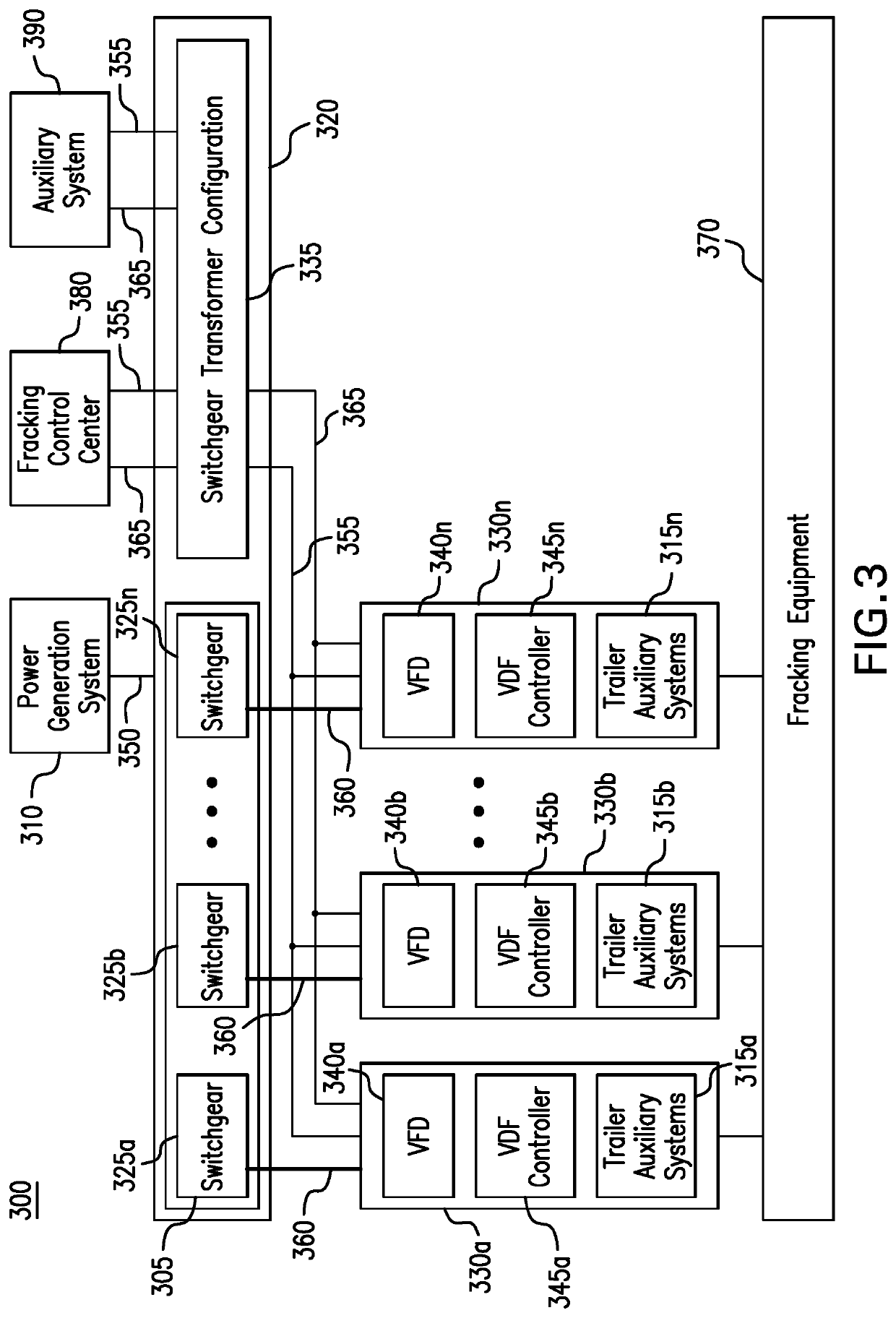
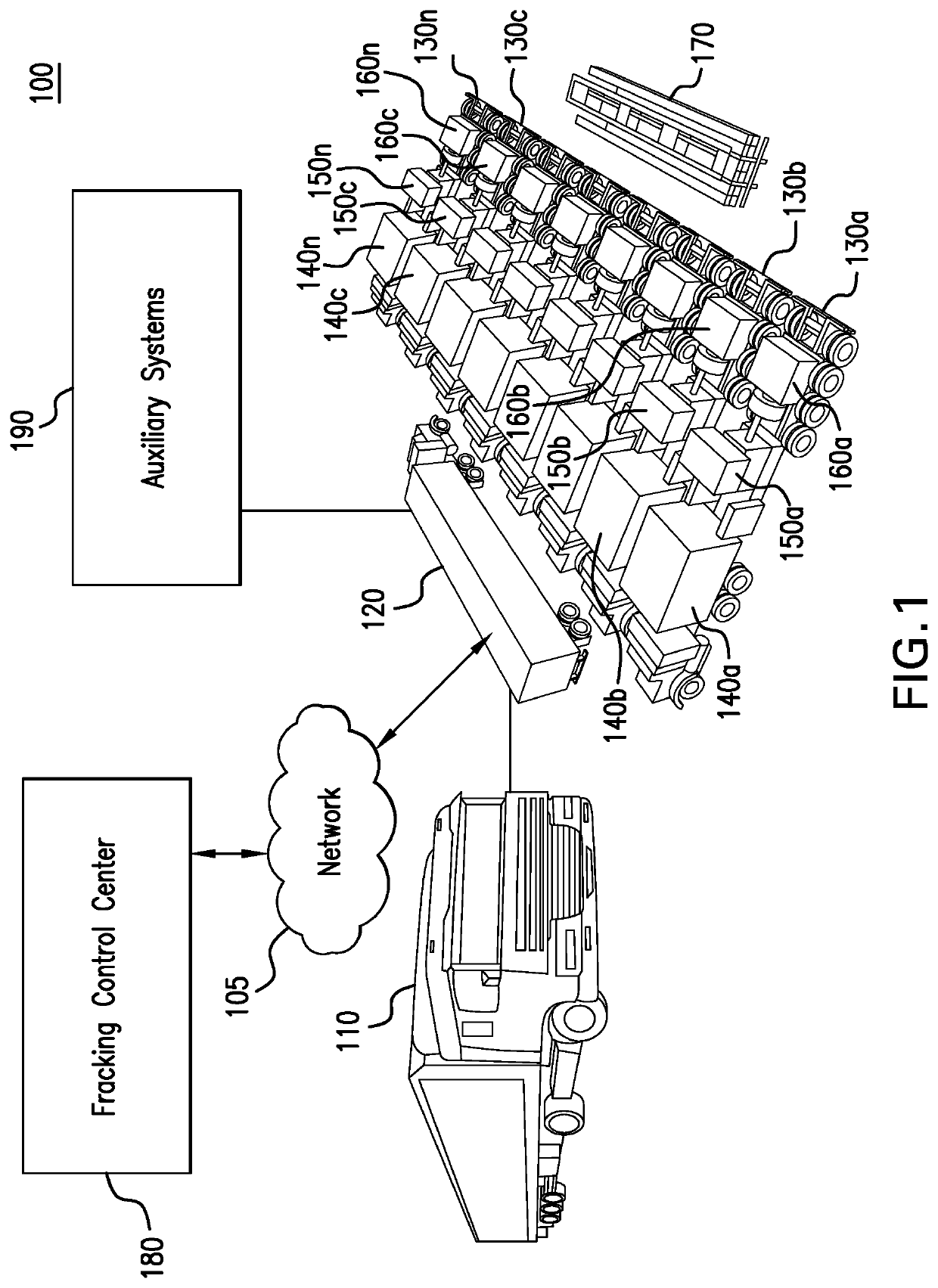
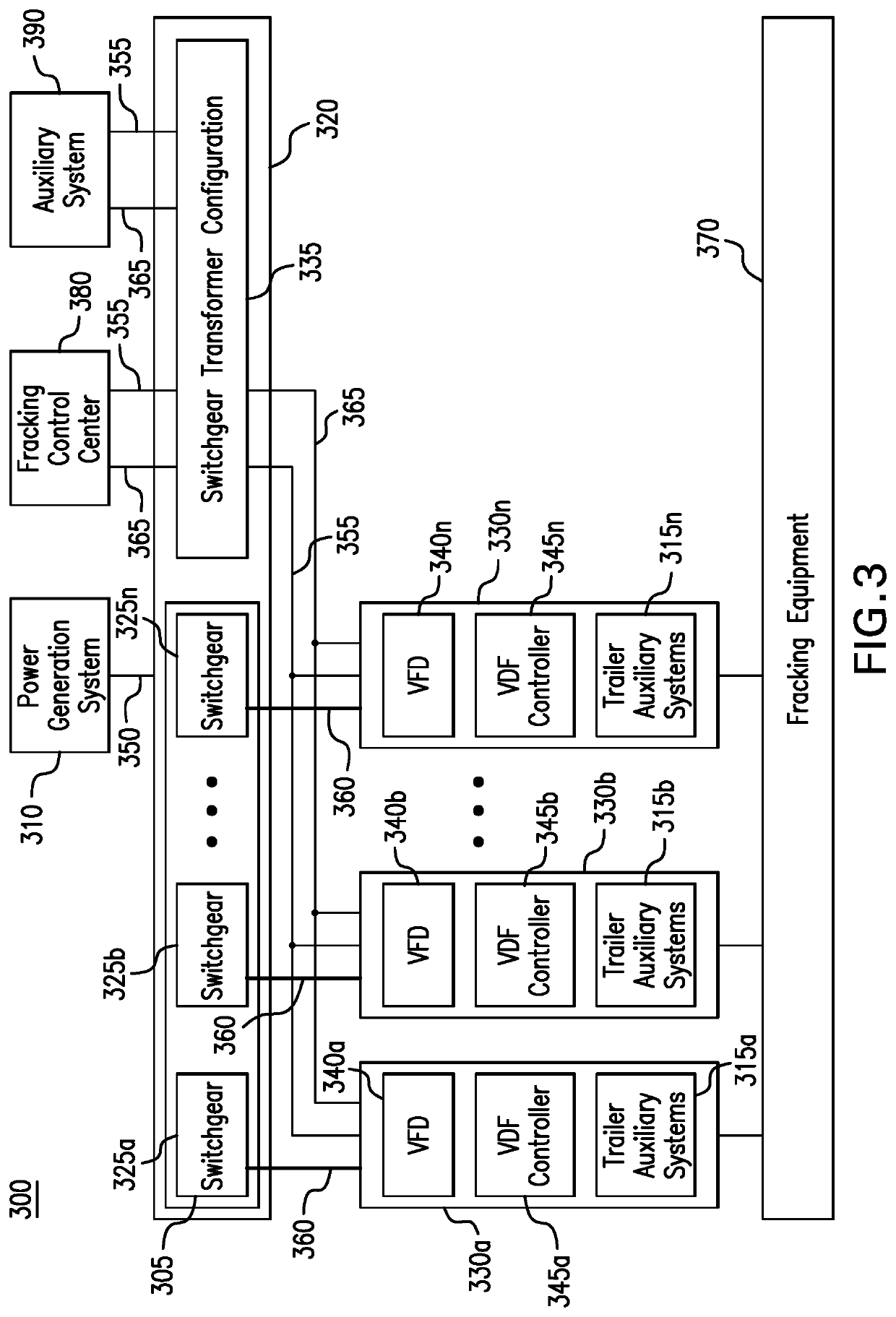
Parameter monitoring and control for an electric driven hydraulic fracking system
An electric driven hydraulic fracking system is disclosed. A pump configuration includes the single VFD, the single shaft electric motor, and the single hydraulic pump mounted on the single pump trailer. A controller associated with the single VFD and is mounted on the single pump trailer. The controller monitors operation parameters associated with an operation of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system as each component of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system operates to determine whether the operation parameters deviate beyond a corresponding operation parameter threshold. Each of the operation parameters provides an indicator as to an operation status of a corresponding component of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system. The controller initiates corrected actions when each operation parameter deviates beyond the corresponding operation threshold. Initiating the corrected actions when each operation parameter deviates beyond the corresponding operation threshold maintains the operation of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Parameter monitoring and control for an electric driven hydraulic fracking system
An electric driven hydraulic fracking system is disclosed. A pump configuration includes the single VFD, the single shaft electric motor, and the single hydraulic pump mounted on the single pump trailer. A controller associated with the single VFD and is mounted on the single pump trailer. The controller monitors operation parameters associated with an operation of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system as each component of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system operates to determine whether the operation parameters deviate beyond a corresponding operation parameter threshold. Each of the operation parameters provides an indicator as to an operation status of a corresponding component of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system. The controller initiates corrected actions when each operation parameter deviates beyond the corresponding operation threshold. Initiating the corrected actions when each operation parameter deviates beyond the corresponding operation threshold maintains the operation of the electric driven hydraulic fracking system.
Owner:NAT SERVICE ALLIANCE HOUSTON LLC
Variable frequency drive configuration for electric driven hydraulic fracking system
ActiveUS10753153B1Non-enclosed substationsSubstation/switching arrangement detailsHydraulic pumpElectric drive
An electric driven hydraulic fracking system is disclosed. A pump configuration that includes the single VFD, the single shaft electric motor, and the single hydraulic pump that is mounted on the single pump trailer. A pump configuration includes a single VFD configuration, the single shaft electric motor, and the single shaft hydraulic pump mounted on the single pump trailer. The single VFD configuration converts the electric power at the power generation voltage level distributed from the power distribution trailer to a VFD voltage level and drives the single shaft electric motor to control the operation of the single shaft electric motor and the single hydraulic pump. The VFD voltage level is a voltage level that is required to drive the single shaft electric motor. The VFD configuration also controls operation of the auxiliary systems based on the electric power at the auxiliary voltage level.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Electric driven hydraulic fracking system
ActiveUS10738580B1Non-enclosed substationsSubstation/switching arrangement detailsHydraulic pumpElectro hydraulic
An electric driven hydraulic fracking system is disclosed. A pump configuration that includes the single VFD, the single shaft electric motor, and the single hydraulic pump that is mounted on the single pump trailer. The single VFD converts the electric power of at least 13.8 kV to a VFD rated voltage level of at least 4160V and drives the single shaft electric motor at the VFD voltage level of up to 4160V to control the operation of the single shaft electric motor and the single hydraulic pump. The single shaft electric motor drives the single hydraulic pump with the rotation at the rated RPM level of at least 750 RPM. The single hydraulic pump continuously pumps the fracking media into the well at the HP level of at least 5000 HP. The single hydraulic pump operates on a continuous duty cycle to continuously pump the fracking media at the HP level of at least 5000 HP.
Owner:NAT SERVICE ALLIANCE HOUSTON LLC
Expandable stabilizer with roller reamer elements
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Electric driven hydraulic fracking system
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com