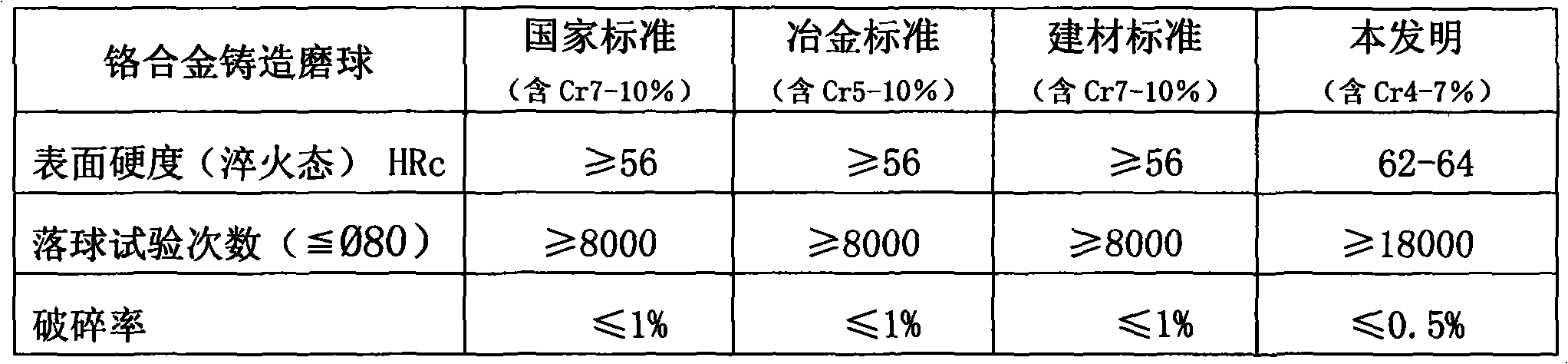
Production process method of high-carbon multi-element alloy casting grinding ball
A technology for alloy casting and casting grinding balls, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, quenching agents, heat treatment process control, etc., can solve the problems of increased cost of chromium alloy casting grinding balls, large investment in production equipment, complex production processes, etc., and achieves reduction of precious metal chromium. content, reducing operating costs, and huge social benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] diameter High-carbon multi-element alloy casting grinding ball, its chemical composition is as follows:
[0048] Carbon (C): 2.5%, Silicon (Si): 0.75%, Manganese (Mn): 0.46%,
[0049] Chromium (Cr): 4.5%, Phosphorus (P): 0.051%, Sulfur (S): 0.054%;
[0050] Copper (Cu): 0.061%, Molybdenum (Mo): 0.032%, Nickel (Ni): 0.026%,
[0051] Tungsten (W): 0.02%, composite heavy rare earth modifier (Y-Re): 0.15%,
[0052] Iron (Fe): 91.4%.
[0053] The manufacturing process of high carbon multi-element alloy casting grinding ball is as follows:
[0054] Firstly, the steel scrap is melted in an intermediate frequency induction furnace, and the temperature is raised to 1480-1520°C, and then Cr, Cu, Mo, Ni, W alloys are added to achieve the required chemical composition. Then put the massive composite heavy rare earth modifier into the molten iron ladle, melt it with molten iron and let it stand for 7 minutes to carry out the modification and inoculation treatment of the molt...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The chemical composition of the high-carbon multi-element alloy casting grinding ball with a diameter of 50mm is as follows:
[0064] Carbon (C): 2.3%, Silicon (Si): 0.82%, Manganese (Mn): 0.60%,
[0065] Chromium (Cr): 5.1%, Phosphorus (P): 0.06%, Sulfur (S): 0.05%;
[0066] Copper (Cu): 0.04%, Molybdenum (Mo): 0.04%, Nickel (Ni): 0.03%,
[0067] Tungsten (W): 0.02%, composite heavy rare earth modifier (Y-Re): 0.13%,
[0068] Iron (Fe): 90.8%.
[0069] The manufacturing process of high-carbon multi-element alloy casting grinding ball with a diameter of 50mm is as follows:
[0070] Firstly, the steel scrap is melted in an intermediate frequency induction furnace, and the temperature is raised to 1480-1520°C, and then Cr, Cu, Mo, Ni, W alloys are added to achieve the required chemical composition. Then put the composite heavy rare earth modifier into the molten iron ladle, melt it with molten iron and let it stand for 6 minutes to carry out the modification and inocu...
Embodiment 3
[0079] The chemical composition of the high-carbon multi-element alloy casting grinding ball with a diameter of 120mm is as follows:
[0080] Carbon (C): 1.4%, Silicon (Si): 0.8%, Manganese (Mn): 0.9%,
[0081] Chromium (Cr): 6.0%, Phosphorus (P): 0.04%, Sulfur (S): 0.04%;
[0082] Copper (Cu): 0.05%, Molybdenum (Mo): 0.03%, Nickel (Ni): 0.02%,
[0083] Tungsten (W): 0.02%, composite heavy rare earth modifier (Y-Re): 0.13%,
[0084] Iron (Fe): 90.7%.
[0085] The manufacturing process of high-carbon multi-element alloy casting grinding ball with a diameter of 100mm is as follows:
[0086] First, the steel scrap is melted in an intermediate frequency induction furnace, and the temperature is raised to 1510-1560°C, and then Cr, Cu, Mo, Ni, W alloys are added to achieve the required chemical composition. Then put the composite heavy rare earth modifier into the molten iron ladle, melt it with molten iron and let it stand for 5 minutes to carry out modification and inoculation...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com