Medical apparatus carrying gene and/or medicament and preparation method thereof
A medical device and gene technology, applied in the field of medical devices carrying genes and/or drugs and their preparation, can solve the problems of limited gene quantity, weakened gene therapy effect, and treatment gene loss, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1 Preparation of gene drug-loaded stent
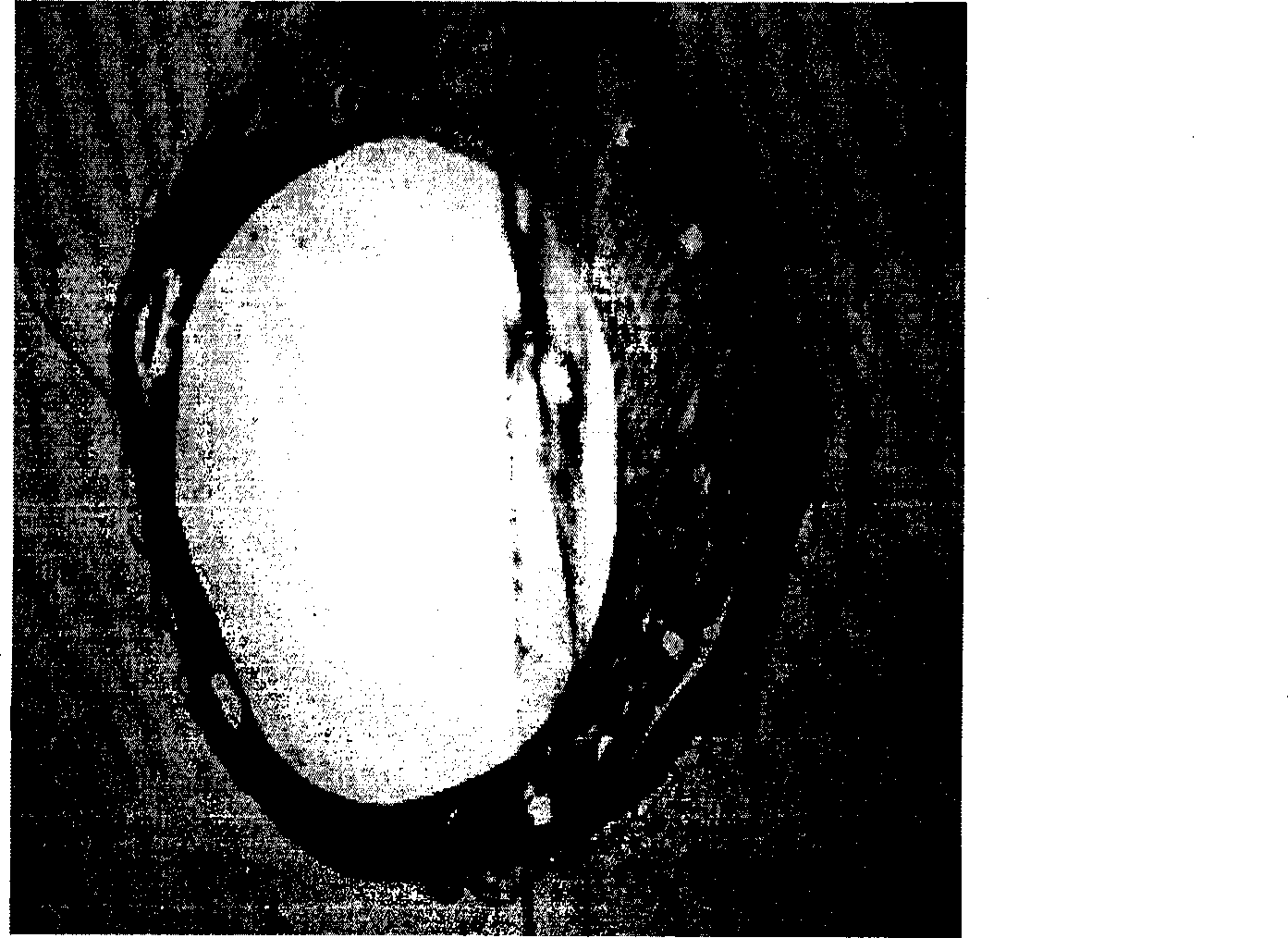
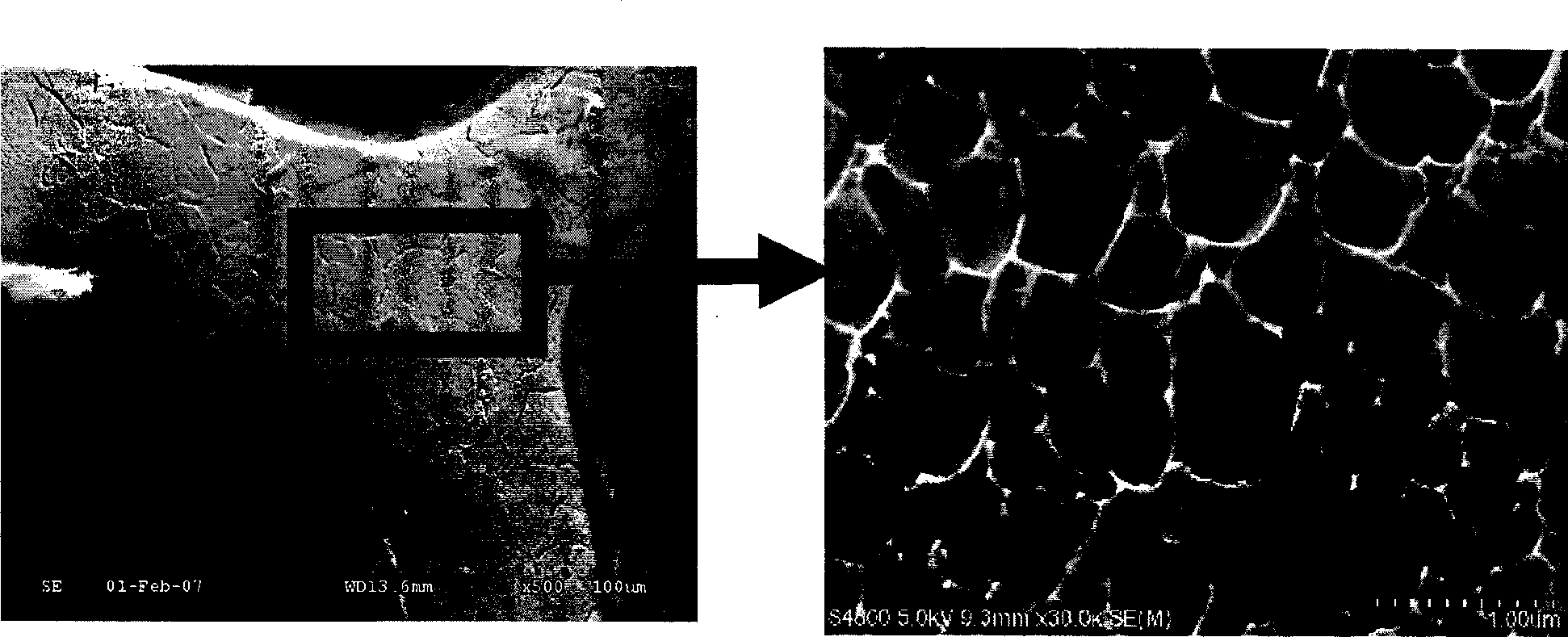
[0050](1) The bare 316L stainless steel stent was cut, slag-removed, polished, placed in 75% medical alcohol, cleaned with ultrasonic waves at a frequency of 30khz for 15 minutes, set at 40°C, dried for 60 minutes, and then taken out. Then place the bracket in ~38% hydrochloric acid for 12 hours of corrosion, connect the bracket body as the anode to the positive pole of the pulse power supply, connect the titanium metal sheet to the negative pole of the pulse power supply as the cathode, and place the bracket body and the cathode metal sheet at the same time. In 28% hydrochloric acid, the current is set to 20A, the frequency is 2000 Hz, and the time is 5 minutes, and holes are prepared on the surface of the 316L bare metal stent body ( figure 1 ).
[0051] (2) Add 0.2g rapamycin to 10ml tetrahydrofuran solution, protect the blood flow side surface of the stent body with holes with a balloon, and disperse the prepared ra...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2 Preparation of gene drug-loaded stent and experimental study of implantation into porcine coronary artery
[0054] The gene drug-loaded stent prepared as described in Example 1 was randomly implanted into the anterior descending artery (LAD), the circumflex artery (LCX) and the right coronary artery (RCA) of the porcine coronary artery. Mycin drug stent was used as a control. Coronary angiography (QCA) was performed on the animals in each group at 7 days, 14 days and 28 days after implantation, and the corresponding animals were sacrificed for histomorphological observation and electron microscope observation.
[0055] The results of QCA and histomorphology showed that 28 days after the operation, the implanted gene drug-loaded scaffold ( Figure 3b ) animal lumen loss and neointimal area compared to bare stent ( Figure 3a ) was significantly reduced, and its effect was comparable to that of rapamycin-drug stents ( Figure 3c ) are roughly equivalent.
[...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3 Preparation of dual gene (NOS and VEGF) scaffolds
[0059] (1) A pure titanium bare stent with holes was prepared according to the method of Example 1.
[0060] (2) Preparation of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene plasmids:
[0061] The target gene VEGF was obtained from human leukemia cells HL-60 by reverse transcription method, and the target gene NOS was obtained from human umbilical vein endothelial cell genomic DNA, and the vector therapeutic genes of VEGF and NOS were respectively constructed with plasmid vector pcDNA3.1. Transfected into Escherichia coli DH5α, stored at -70°C. Finally, the endotoxin-free plasmid purification kit and method of Qiagene Company were used to purify the plasmid.
[0062] (3) Dissolve pcDNA3.1-iNOS gene plasmid and pcDNA3.1-VEGF gene plasmid in TAE buffer at the same time, the concentration is 1mg / ml, and then put the bracket with holes prepared according to (1) into the prepared...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com