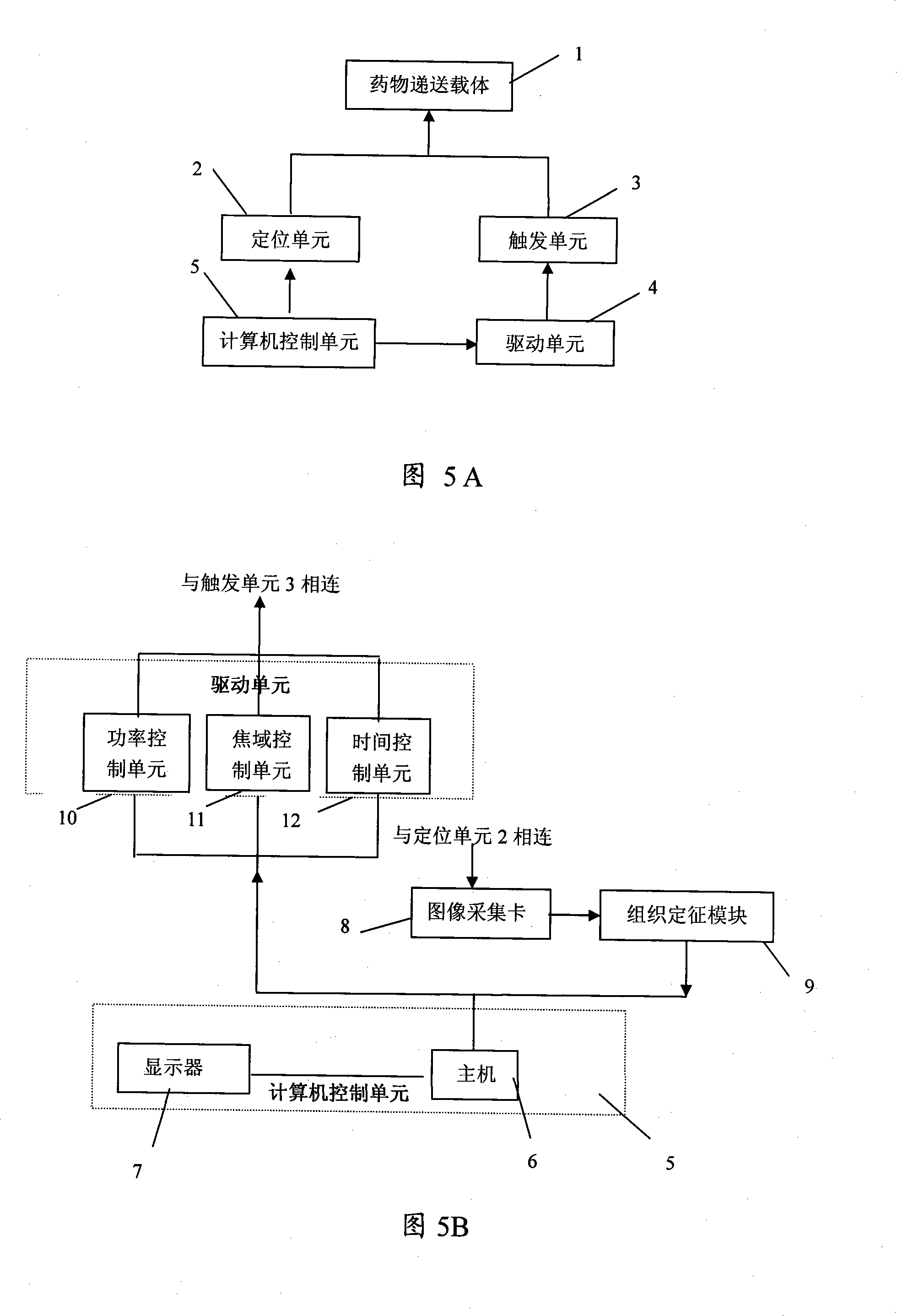
System for positioning delivery of medicament and quantitatively controlling and releasing
A drug and delivery carrier technology, applied in the field of biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of small cavitation effect, unfavorable microbubble reperfusion, and reduced cavitation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0028] Example 1: Preparation of drug-microbubble conjugate
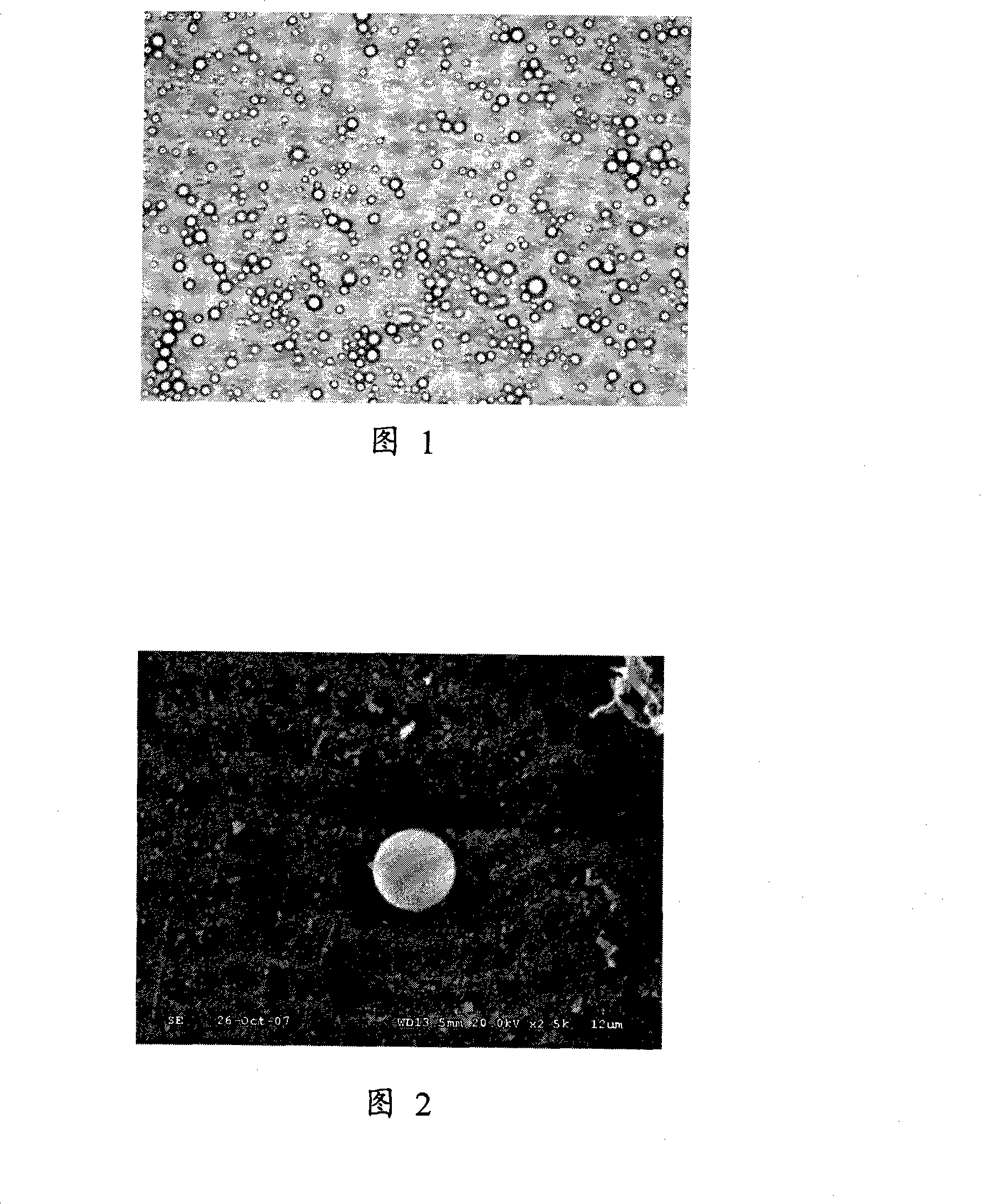
[0029] Mix phosphatidylcholine (DPPC), phosphatidylethanolamine (DPPE), dipalmitoylphosphatidic acid (DPPA) and hypocretin 2 mg into 400 μl of soybean oil in a mass ratio of 5:2:1, and add poloxa The drug-microbubble combination was obtained after 50 μl of mol, 0.5 mg of glycerol and perfluoropropane gas were shaken mechanically for 60 seconds. The prepared drug-microbubble combination was rinsed several times with phosphate buffer, and the particle size distribution was measured with a Malvern measuring instrument, and the morphology and structure of the drug-microbubble combination were observed under light and electron microscopes. The test results showed that the concentration was 1.4×10 9 ~4.5×10 9 / ml, 90% of its particle size is between 1 and 5 μm, and the size distribution of the drug-microbubble combination is uniform and stable as observed by light and electron microscopes. (Figure 1, Figure 2)
example 2
[0030] Example 2: Determination of drug entrapment efficiency in drug-microbubble conjugates
[0031] Adopt density gradient centrifugation to separate free drug and encapsulated drug, use blank soybean oil microbubble as control group, adopt density gradient centrifugation, use 10%-20% sucrose to dilute the drug and microbubble combination to 4ml, 3000 Centrifuge at rpm for 5 minutes, take 40 μl of the gradient layer and dilute it to 2 ml with double distilled water to detect the free drug content by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. (2) Calculation of Encapsulation Efficiency: Calculate Encapsulation Efficiency as follows: Encapsulation Efficiency (%)=[(input drug amount-free drug amount) / input drug amount]×100; (3) drug loading Calculation: The following formula is used to calculate the drug loading: drug loading=(Wt-Wi) / Vc×100%, where Wt is the total drug content in the drug-microbubble complex, Wi is the free drug amount, and Vc is the total solution amount. The results sho...
example 3
[0032] Example 3: In Vitro Ultrasound Imaging of Drug-Microbubble Conjugates
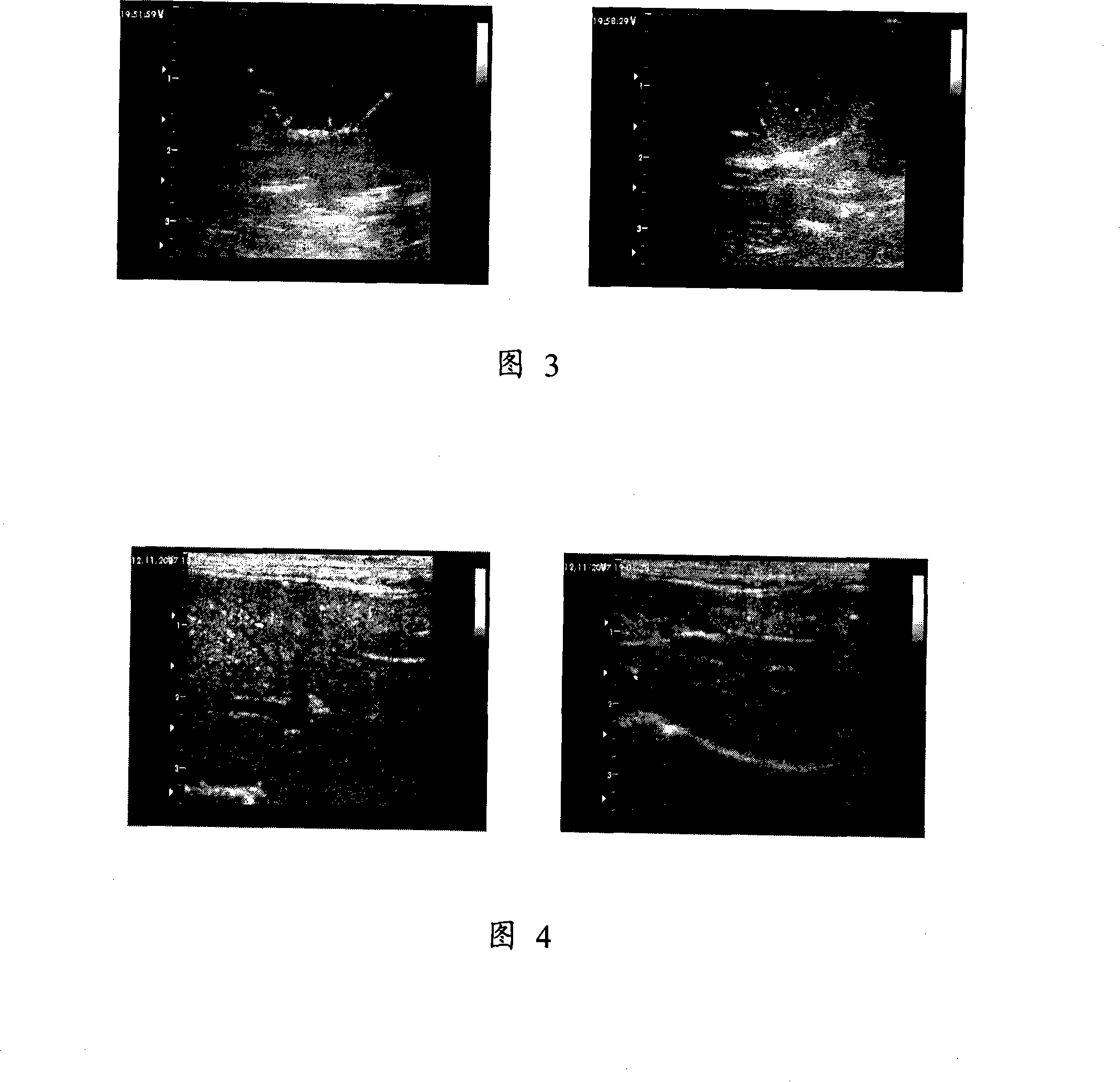
[0033] Add 0.2ml of drug and microbubble combination into degassed water and mix well, use GEVivid 7 color ultrasonic diagnostic instrument, 12L linear array probe. All conditions of the instrument are set to the same standard: the mechanical index (MI) is set to 0.24 for the second harmonic, the gain is -14dB, the imaging depth is fixed at 3cm, and parameters such as TGC and focus range are adjusted to the best state. Use the internal workstation of the ultrasonic instrument to store the imaging data before and after adding the combination of drugs and microbubbles. It was found that there was a significant difference before and after contrast (Figure 3).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com