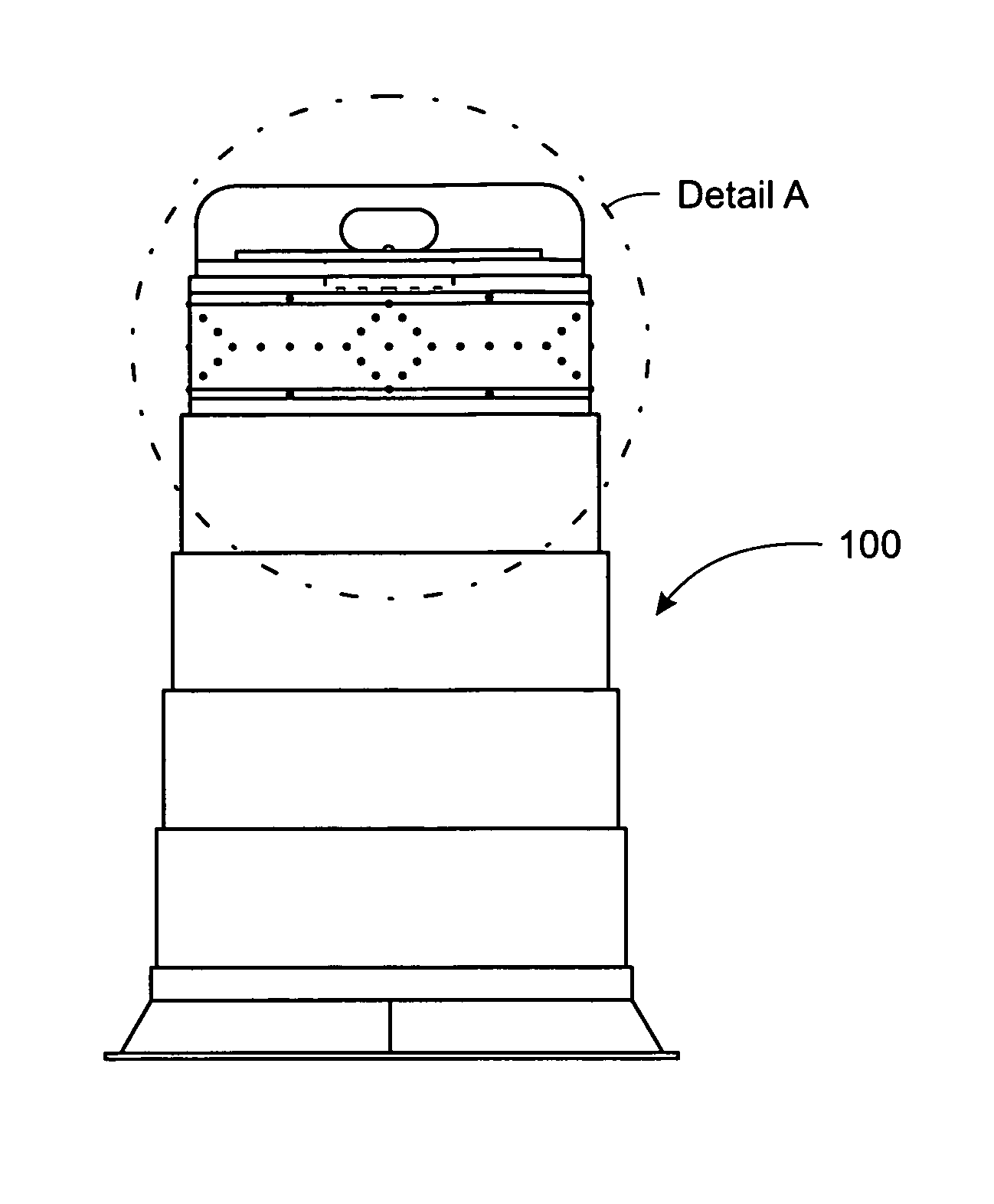
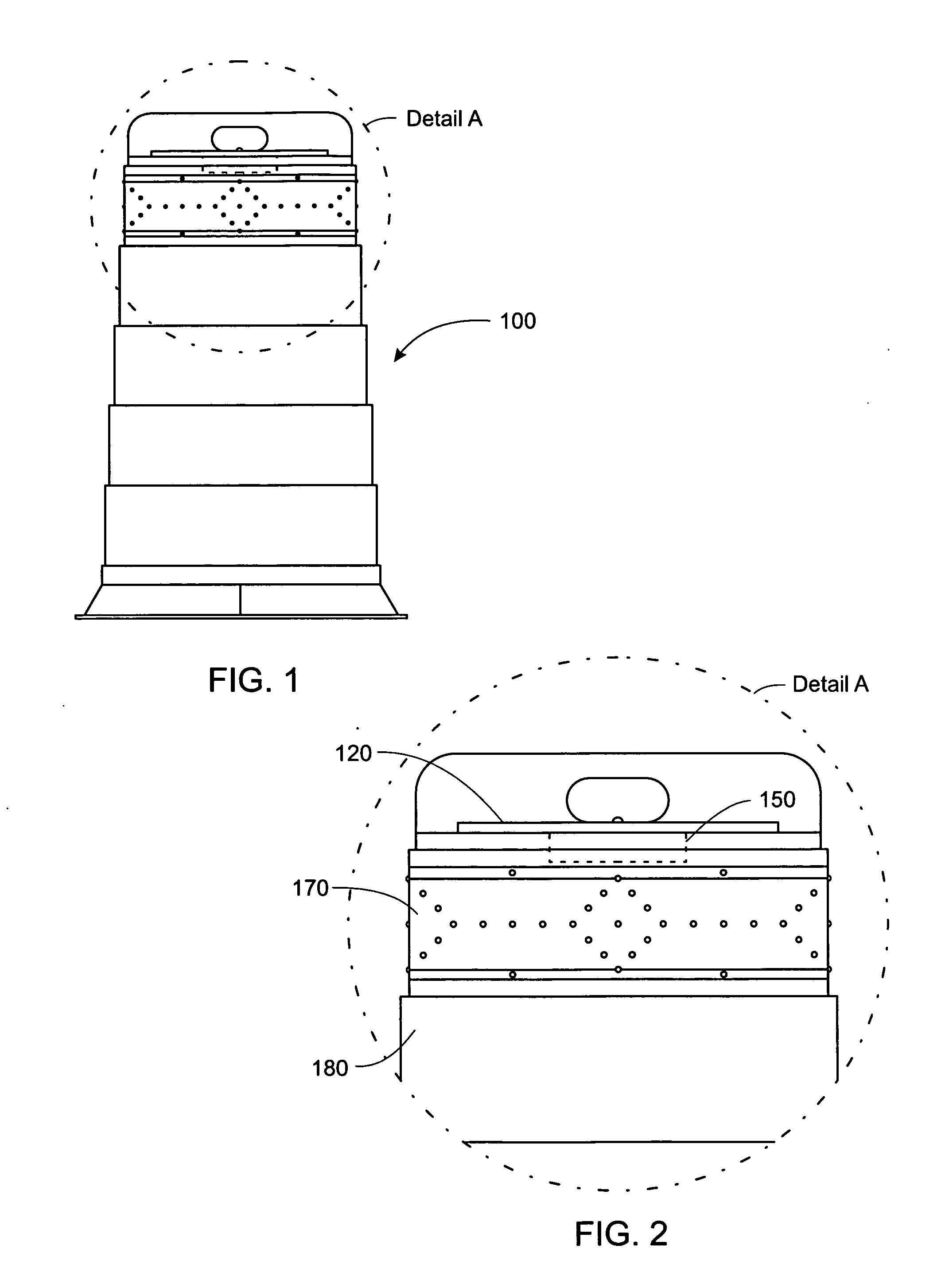
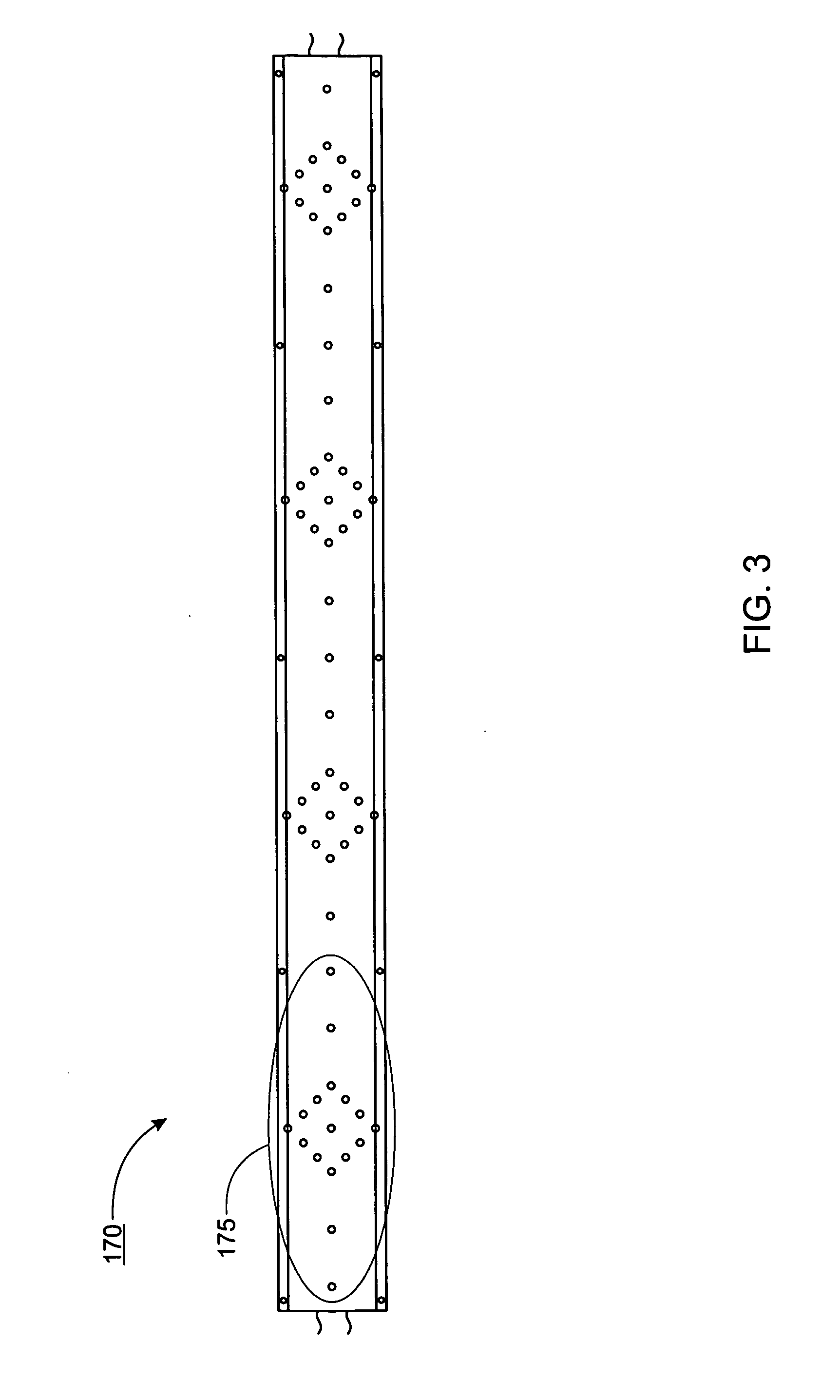
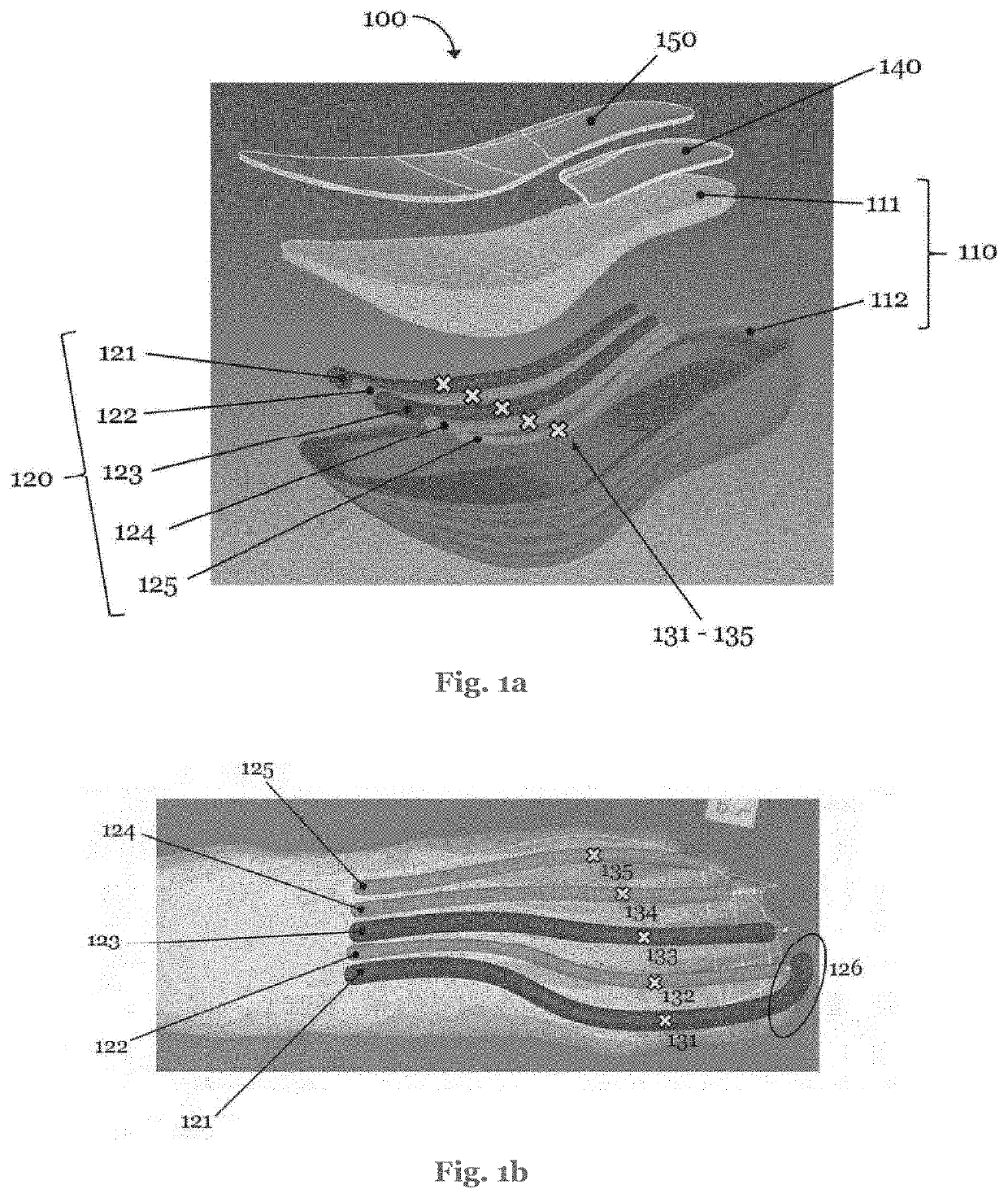
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Low risk of injury" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
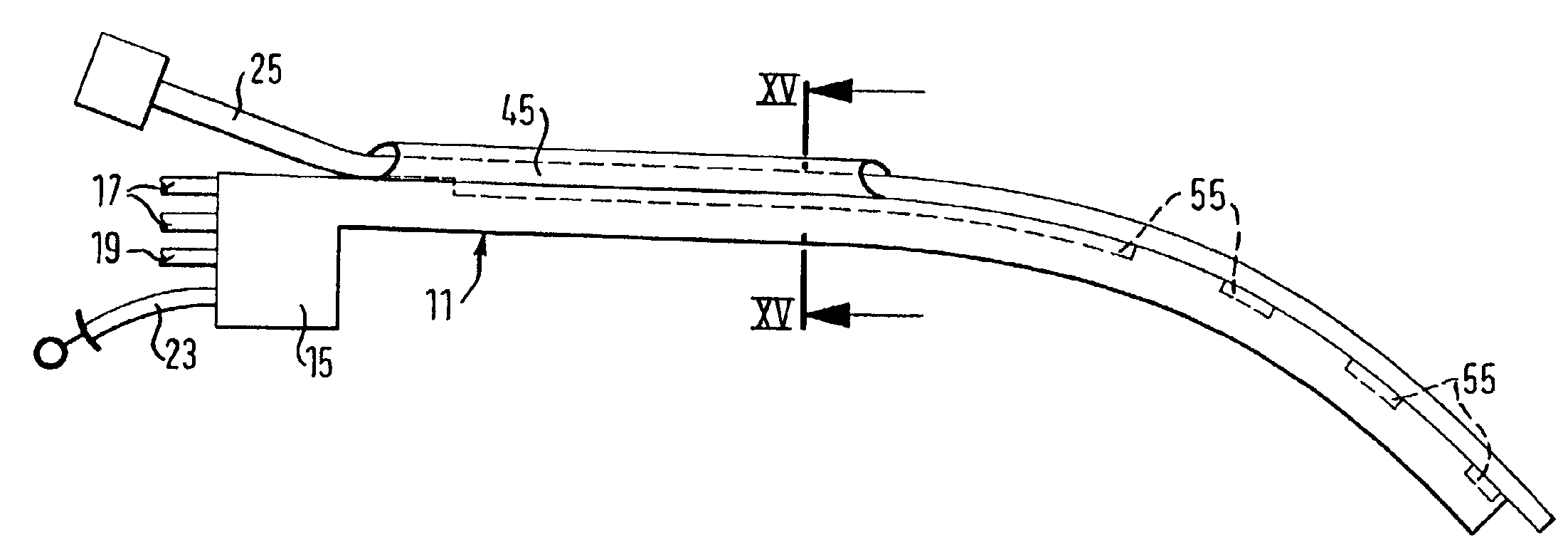
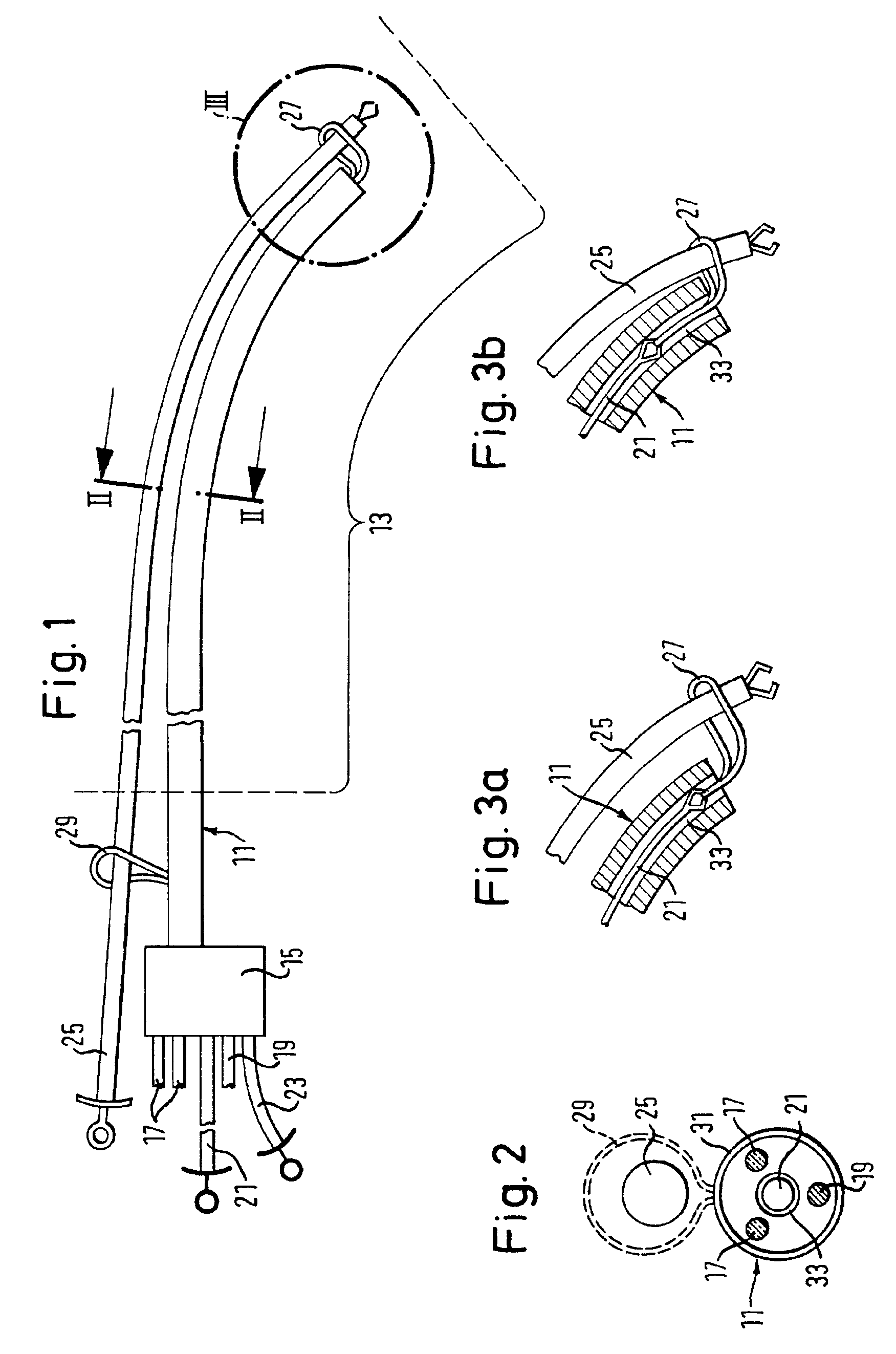
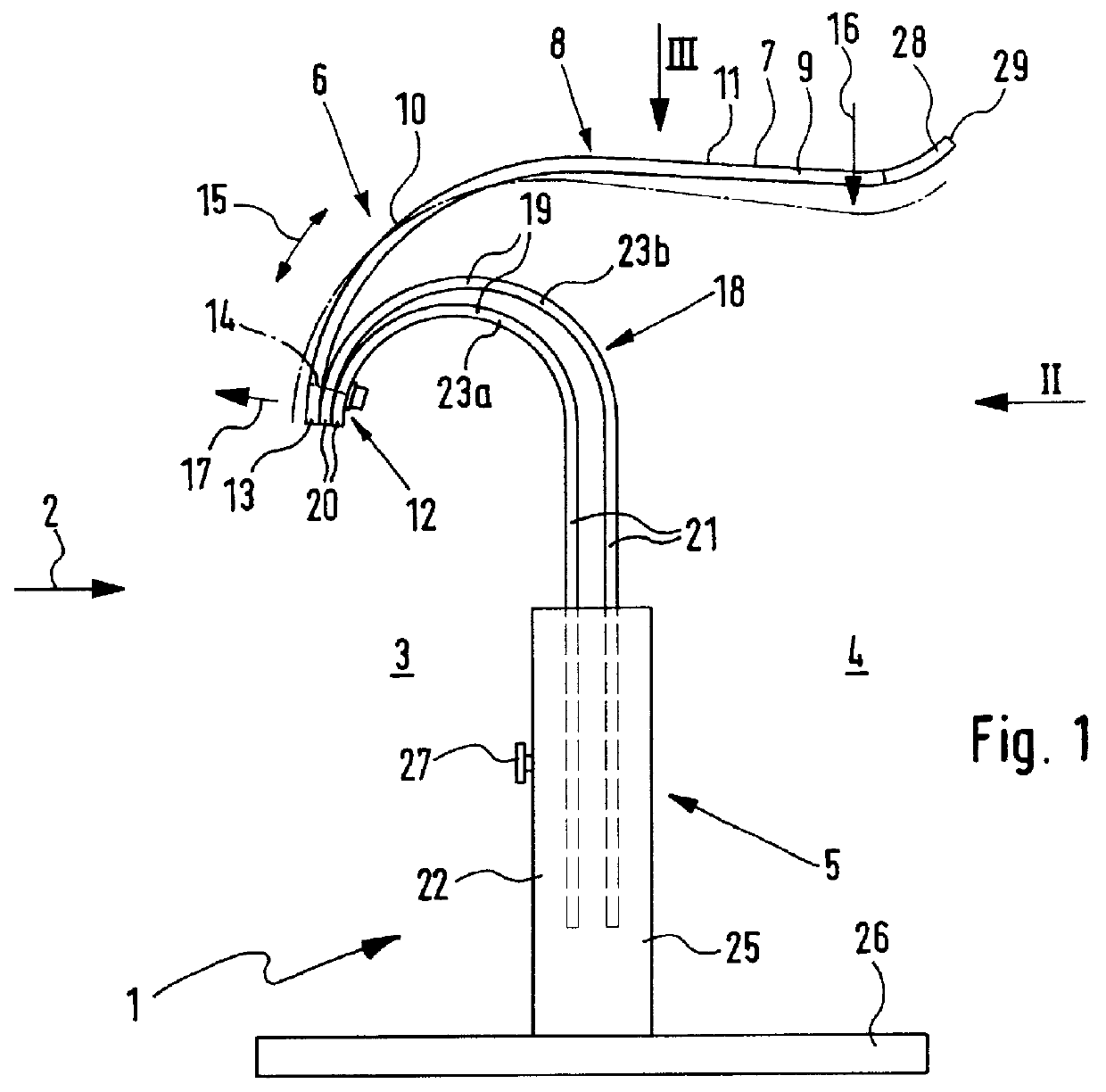
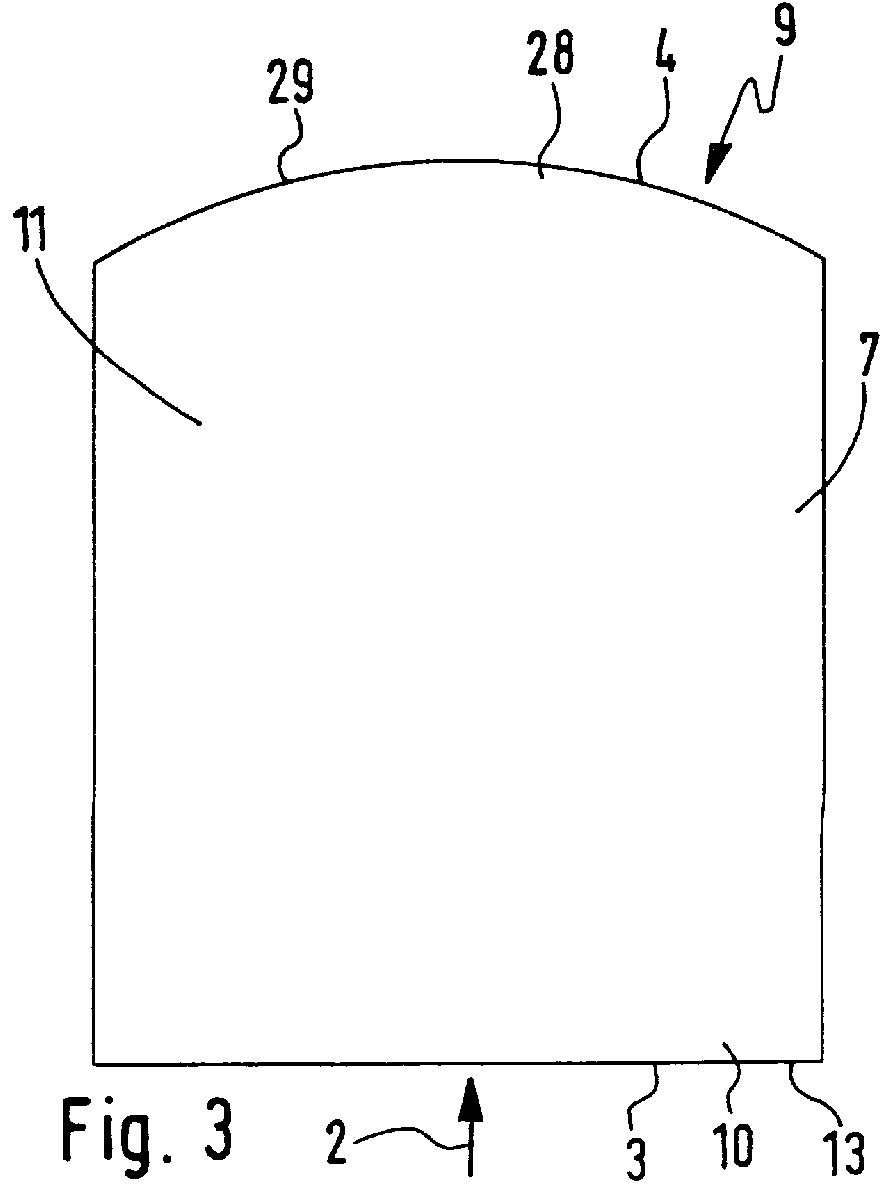
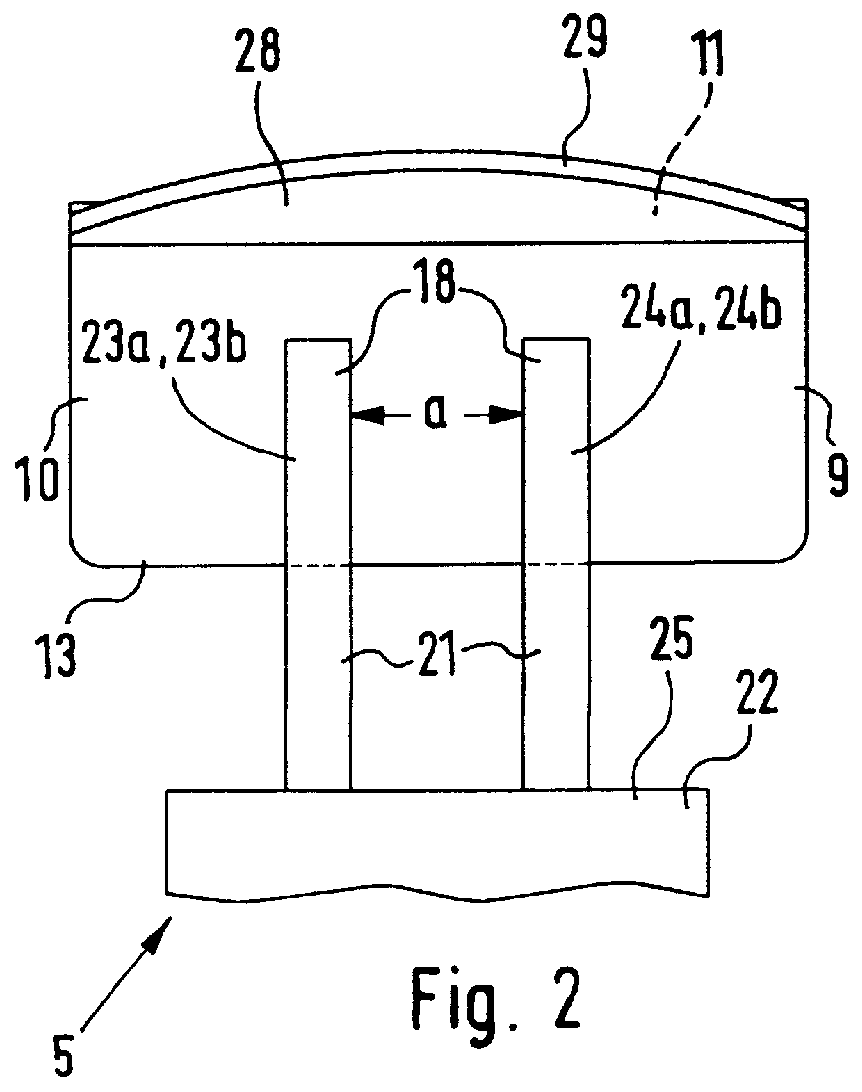
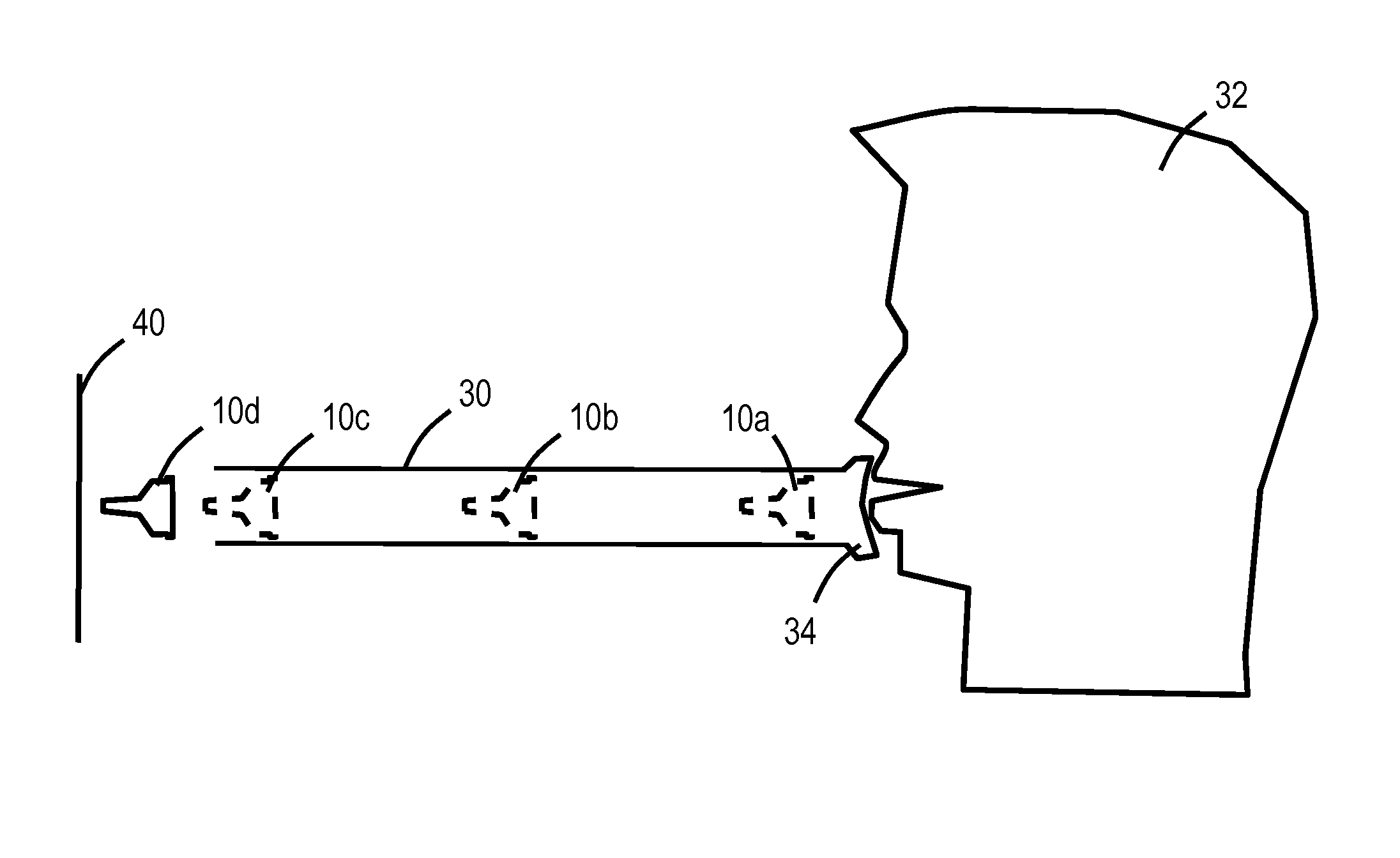
Deformable fiberscope with a displaceable supplementary device
InactiveUS6878106B1Reduce the risk of injuryPleasant subjective perceptionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesFiberscopeAnimal body
The invention relates to a deformable endoscope that has one or more light / image transmission passages and in which at least one additional instrument is provided, wherein the unit of endoscope and additional instrument has a non-round cross-section along a longitudinal section (insertion section) to be inserted into a human or animal body orifice. The light / image transmission passage or the plurality of light / image transmission passages form—in particular together with at least one work passage—a closed unit (fiberscope part) which can be separated from the additional instrument. The fiberscope part and the additional instrument can be displaced relatively relative to one another along their longitudinal directions. A holding unit is provided for the holding and / or guiding of the fiberscope part and the additional instrument relative to one another.
Owner:HERRMANN INGO F
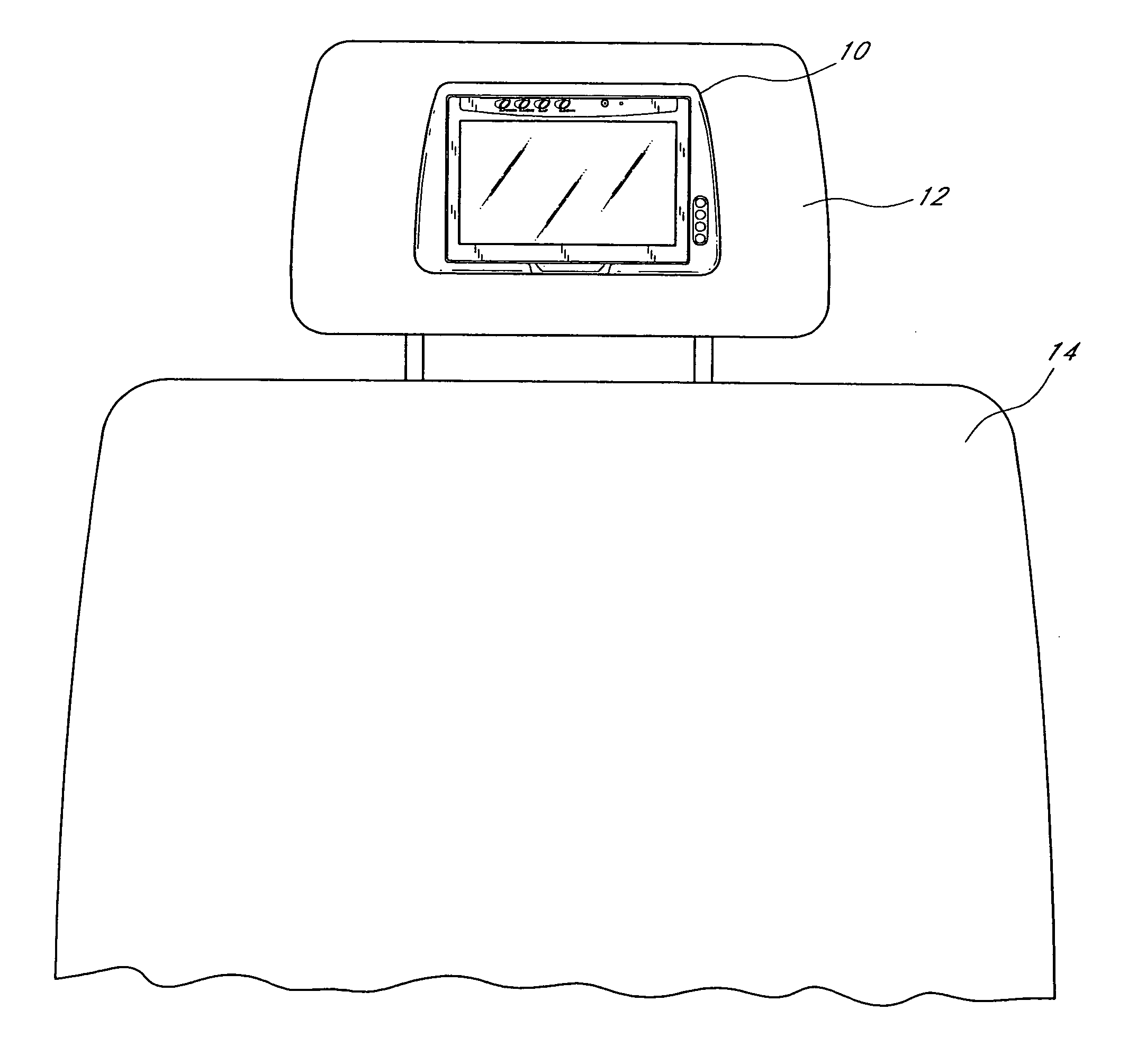
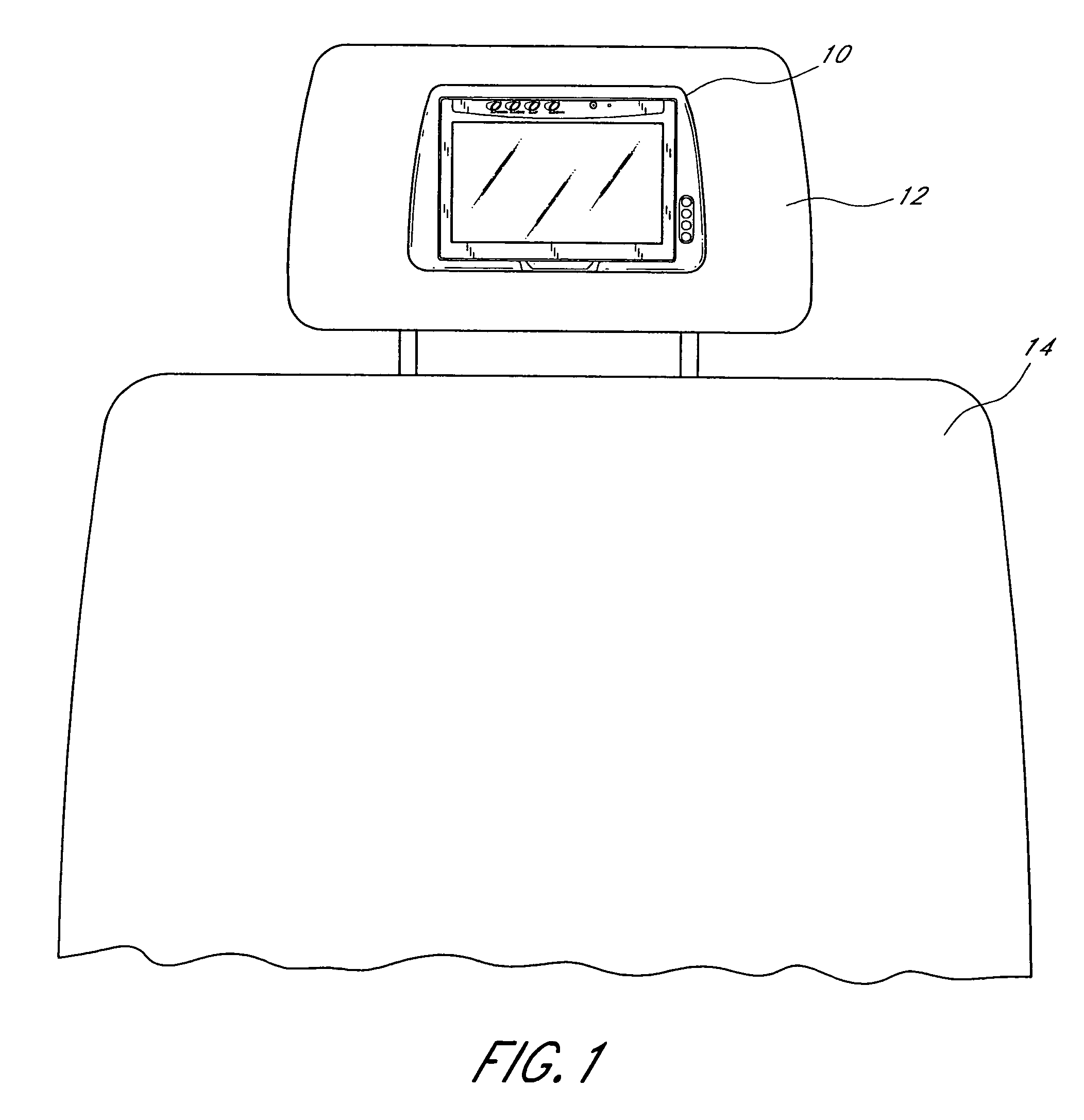
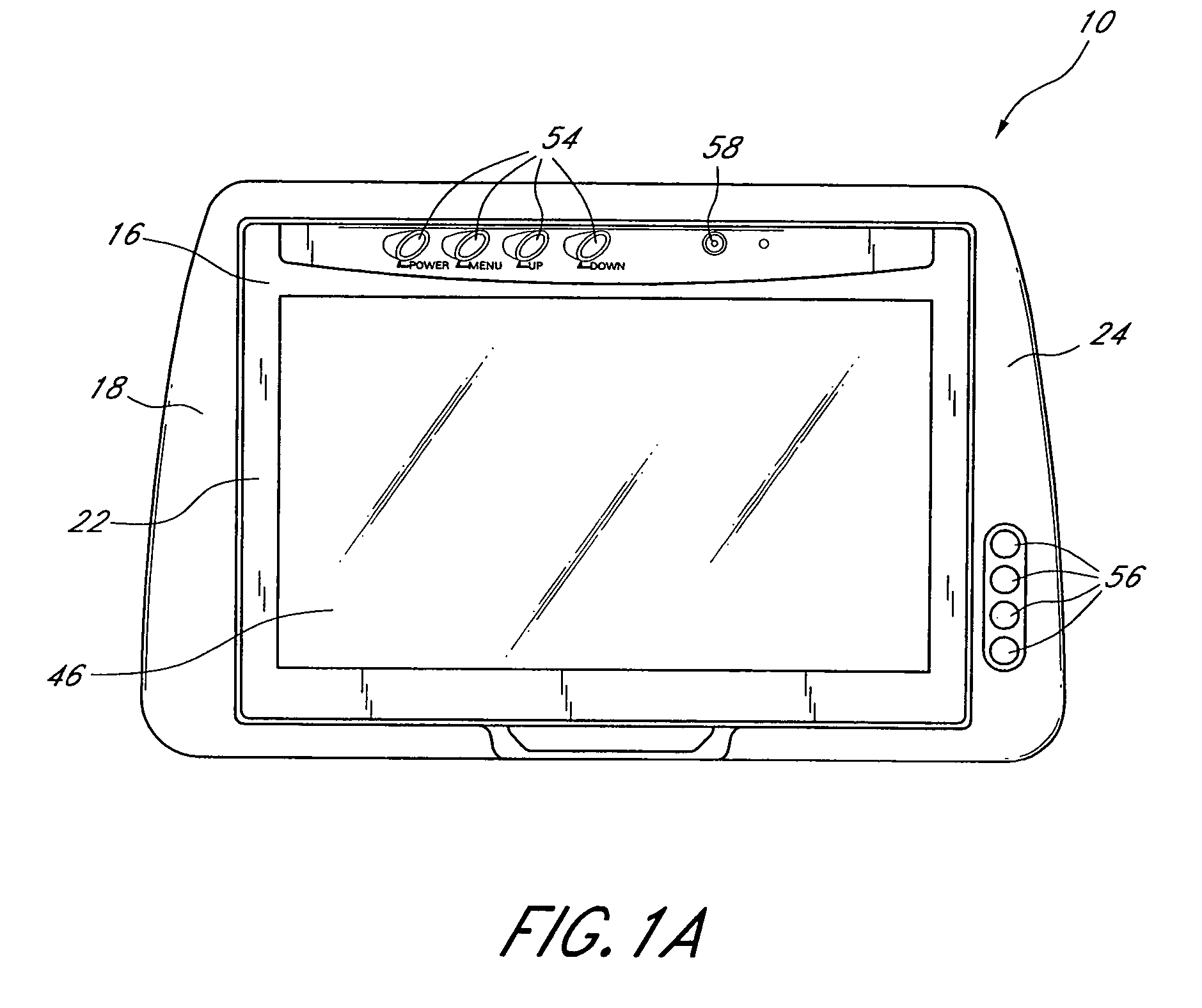
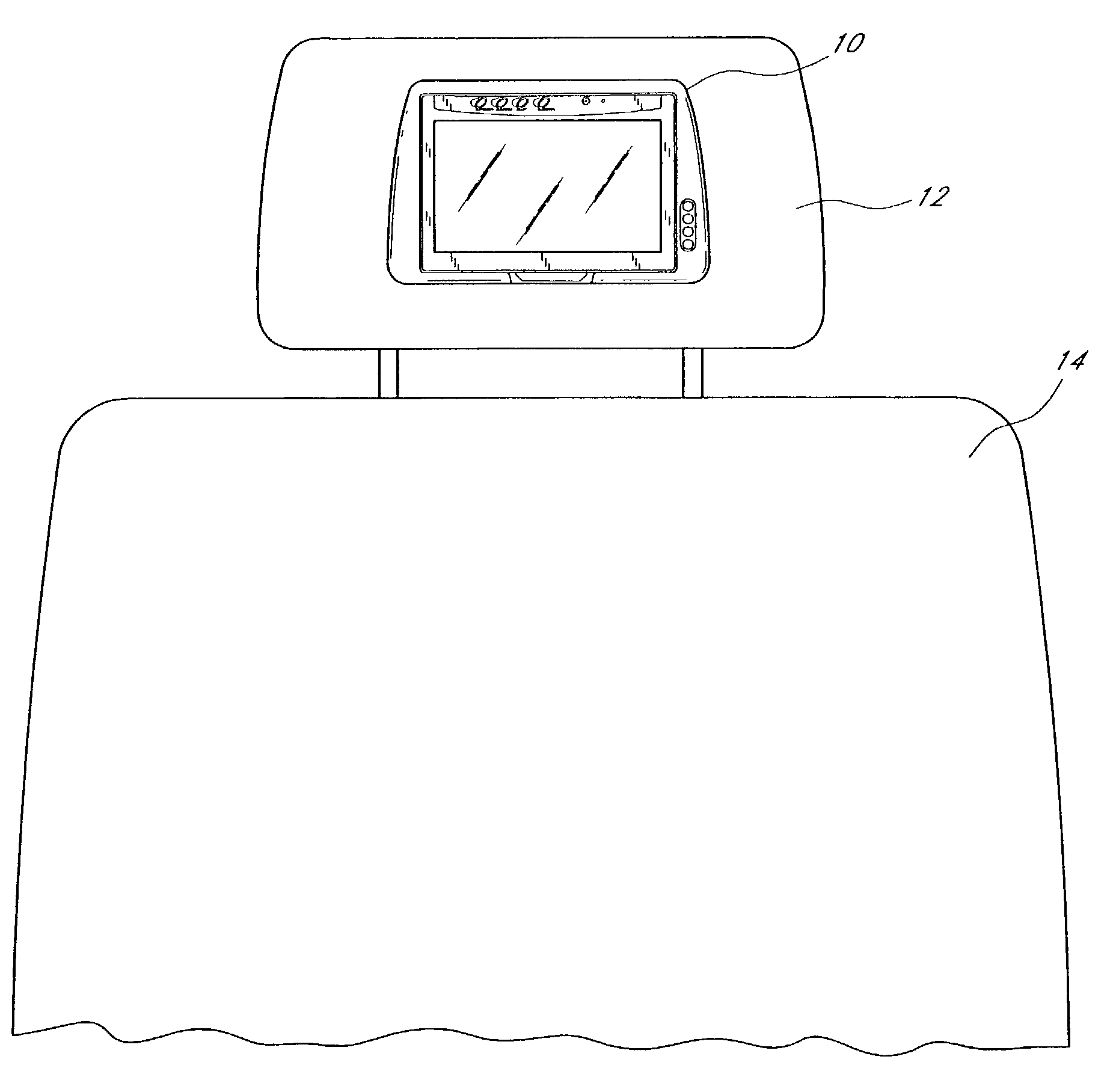
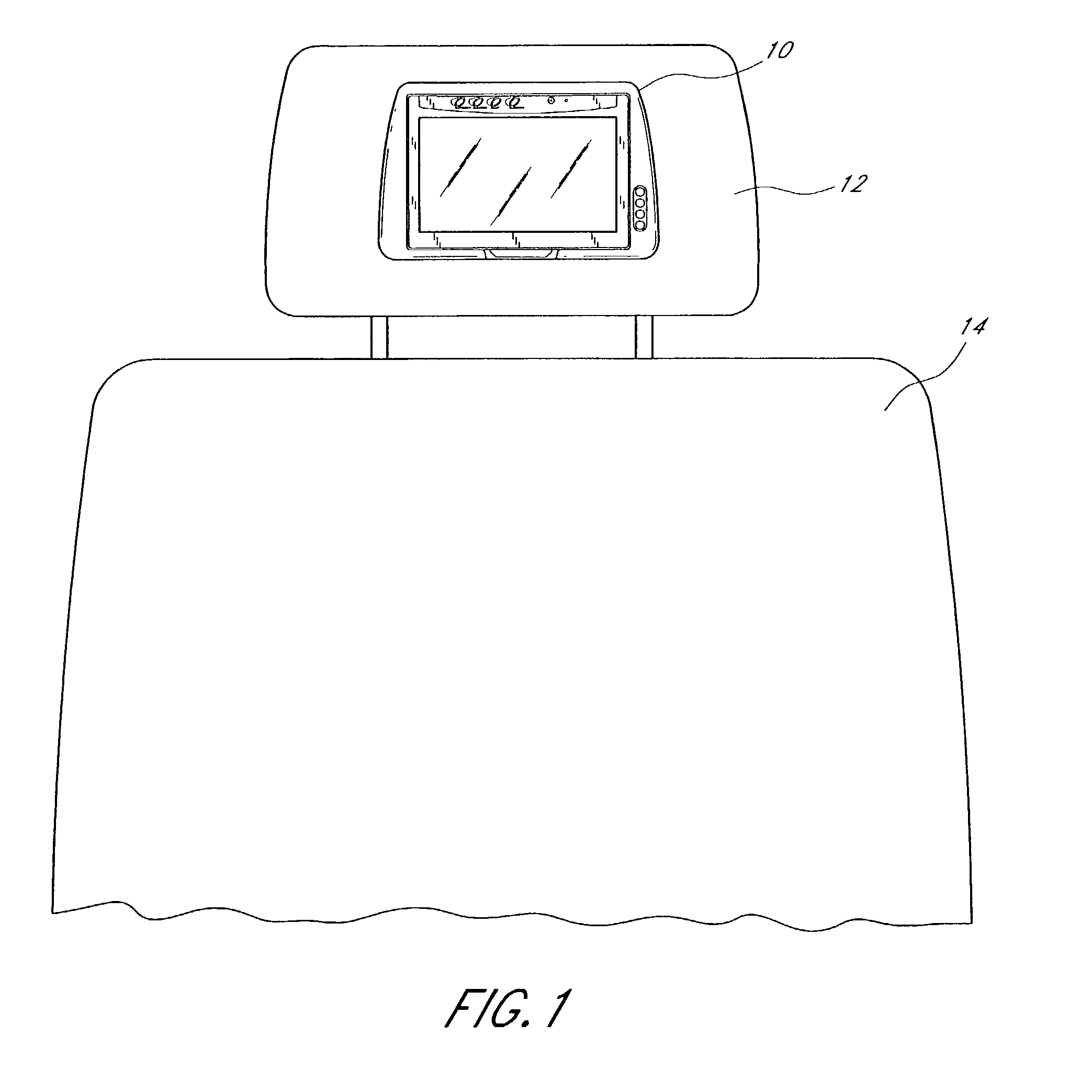
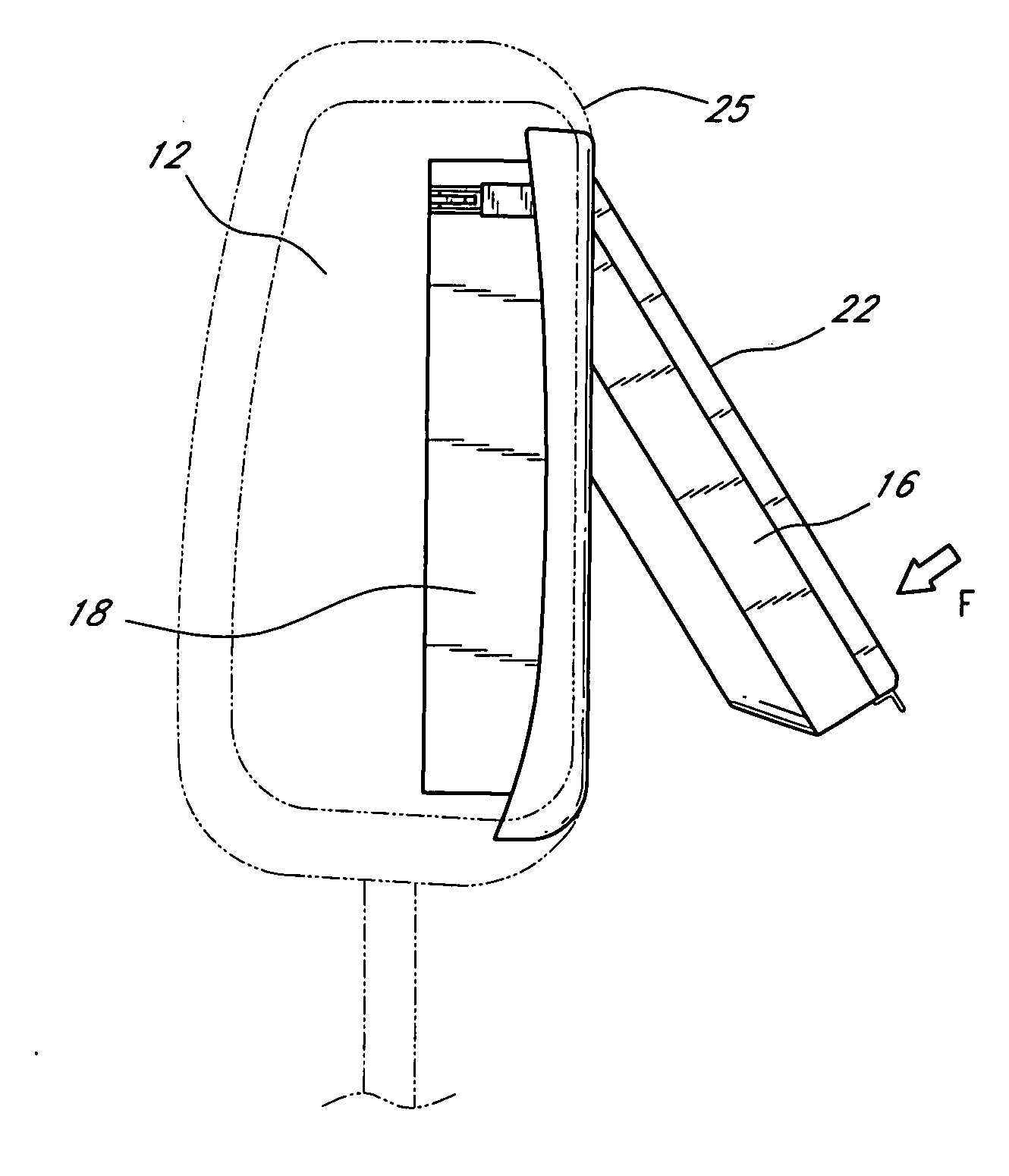
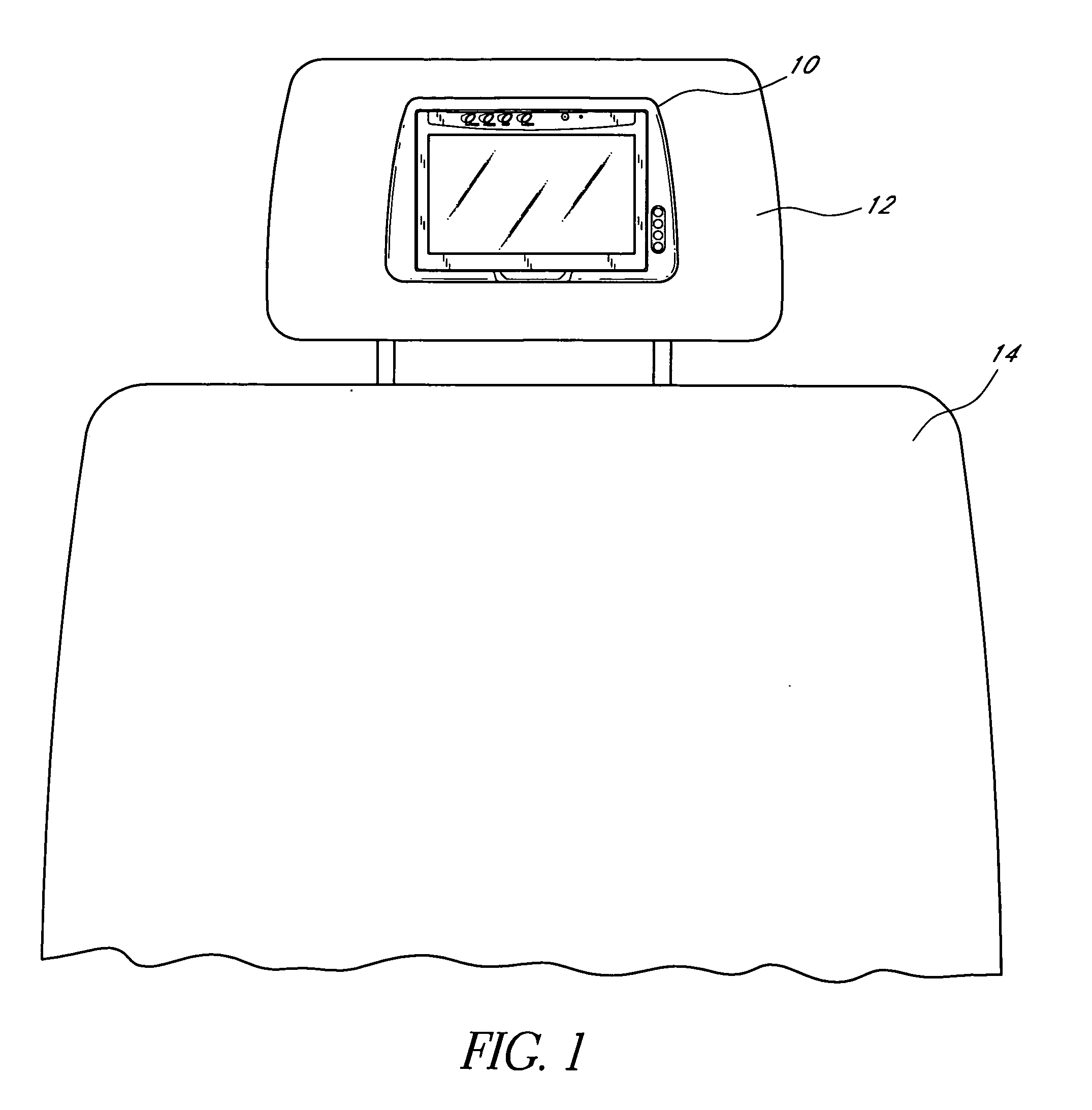
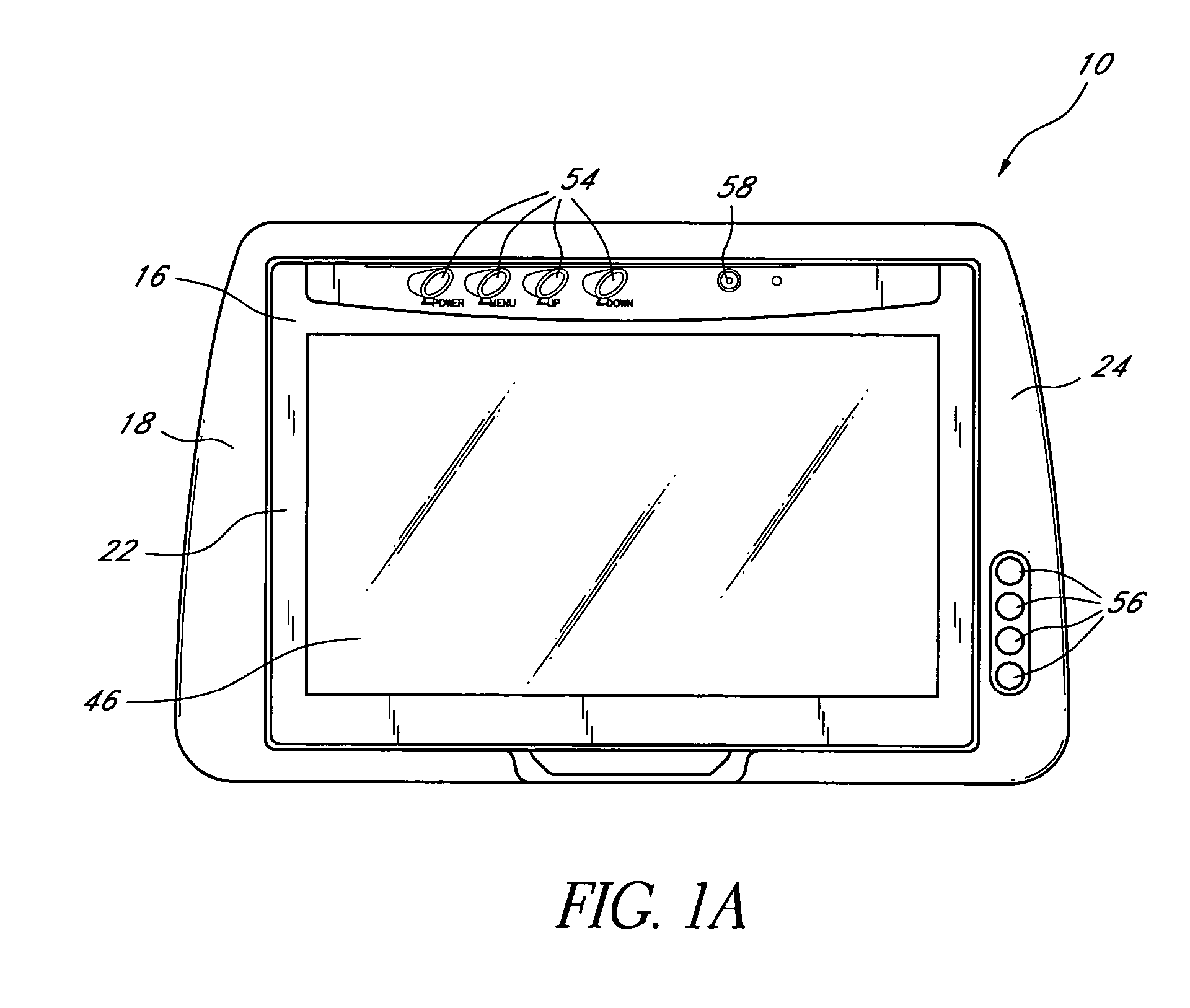
Headrest-mounted monitor
InactiveUS7044546B2Low risk of injuryVehicle seatsTelevision system detailsHead restraintElectrical and Electronics engineering
A monitor adapted for mounting in an automobile headrest is provided. A screen structure of the monitor is pivotable about an upper edge thereof, such that the monitor occupies little volume within the headrest. A viewing angle of the screen structure is independently adjustable by a viewer, such that the viewer can continuously select the optimum viewing angle with changing conditions inside the automobile. The screen structure automatically retracts into a housing when struck. Thus, the monitor poses little risk of injury to passengers. The housing of the monitor is attachable to the headrest with screws, which provides a very sturdy connection and reduces the chances of the housing becoming detached from the headrest during a vehicle collision. The hinged connection between the screen structure and the housing is preferably constructed of interconnected components made from sturdy materials, such as metals. Hinge components are optionally secured with metal fastening members and fastening apertures made of metal and strong plastics. The hinges are thus unlikely to break during a vehicle collision.
Owner:VOXX INT CORP
Headrest-mounted monitor
ActiveUS7036879B2Low risk of injuryTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHead restraintView angle
Owner:VOXX INT CORP
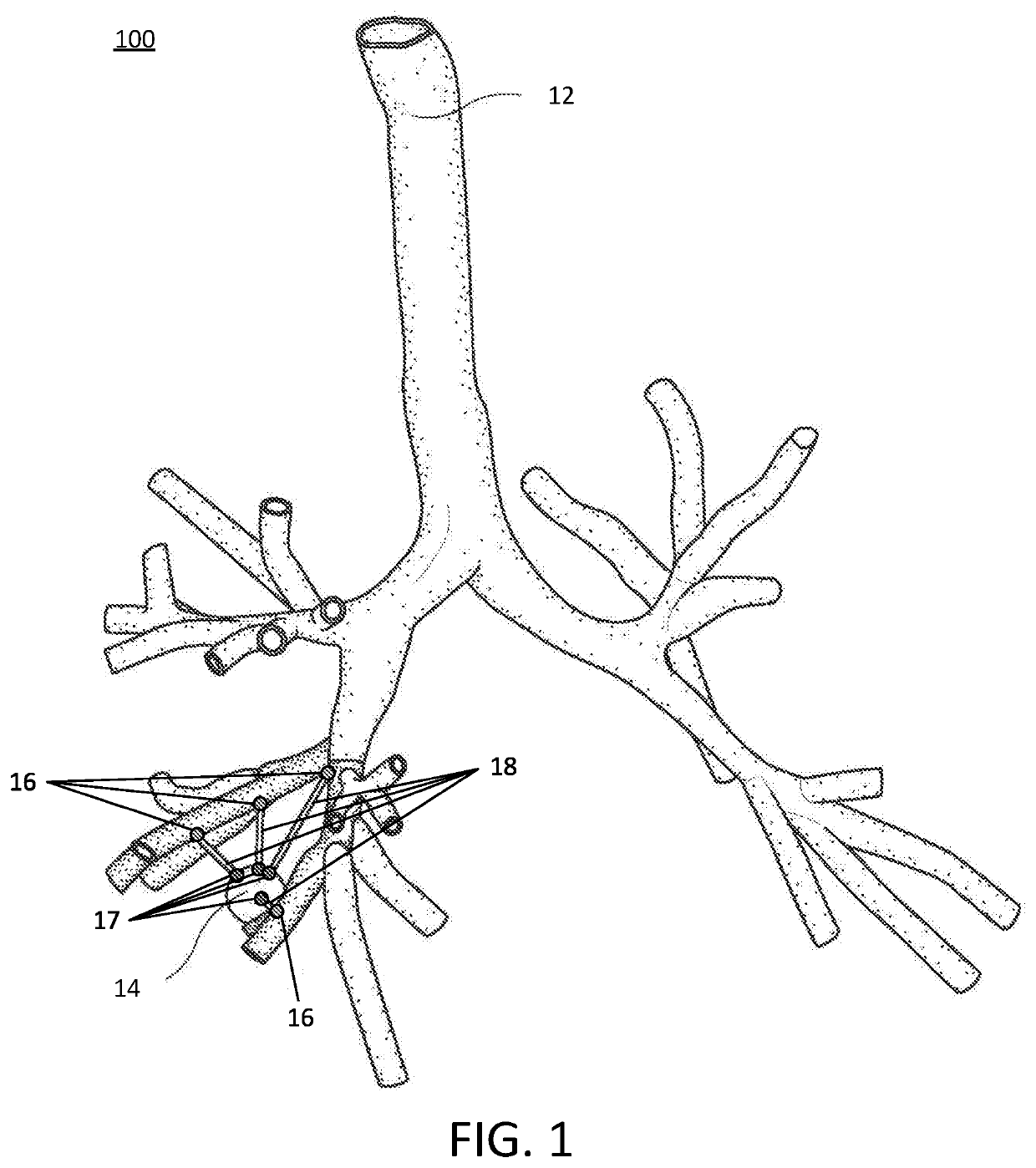
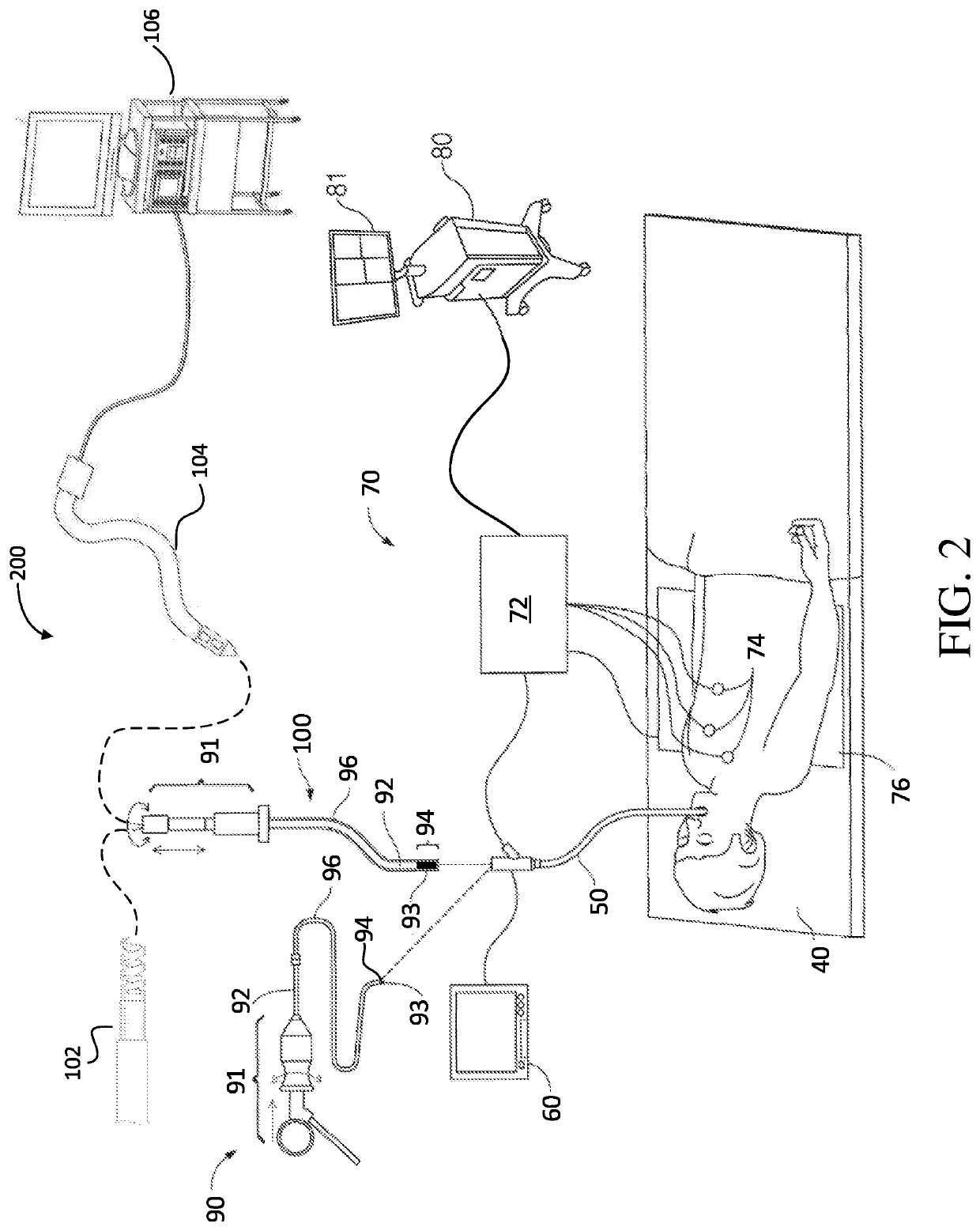
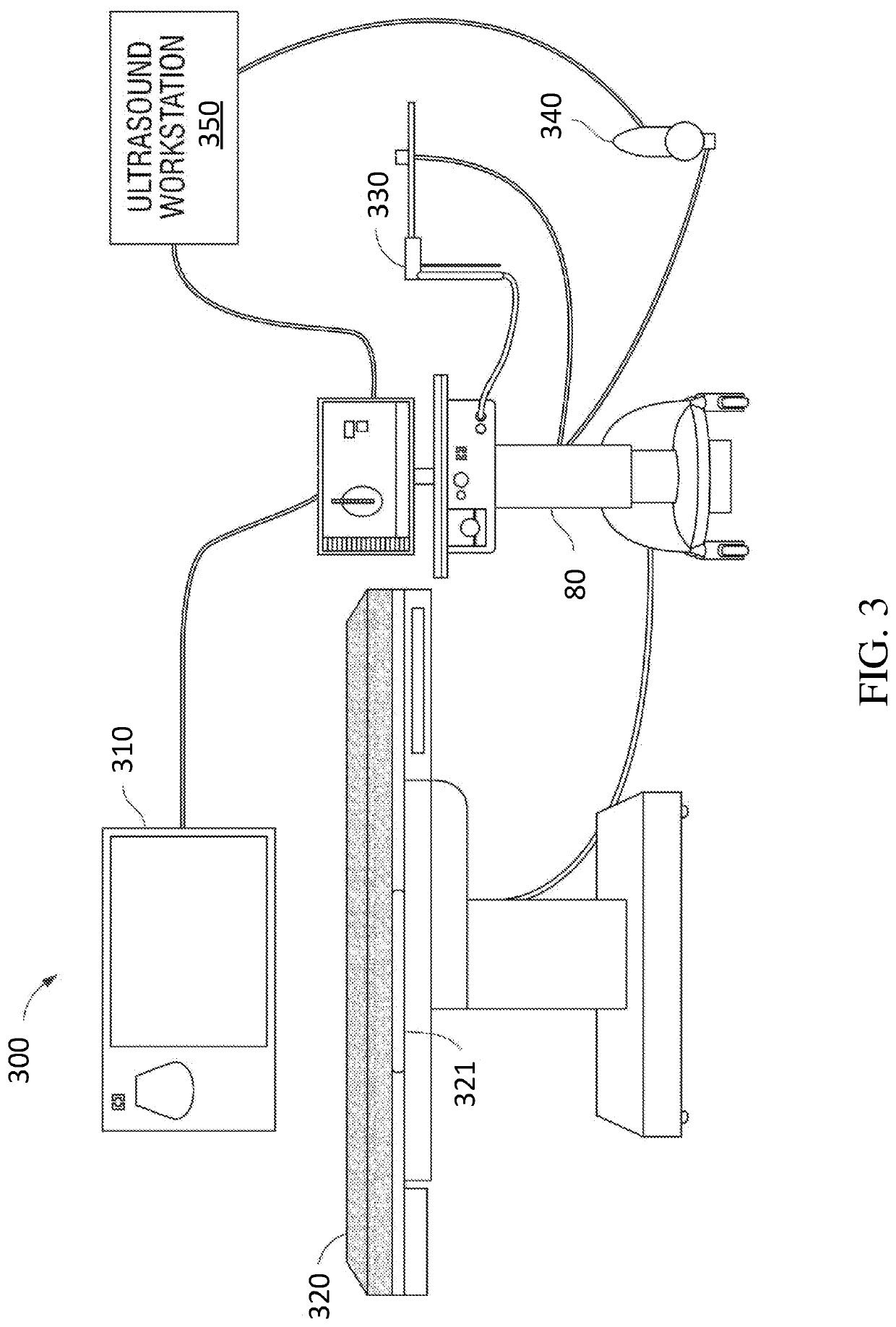
Pathway planning for use with a navigation planning and procedure system
ActiveUS20180055582A1Low risk of injuryMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesProgram planningLung tissue
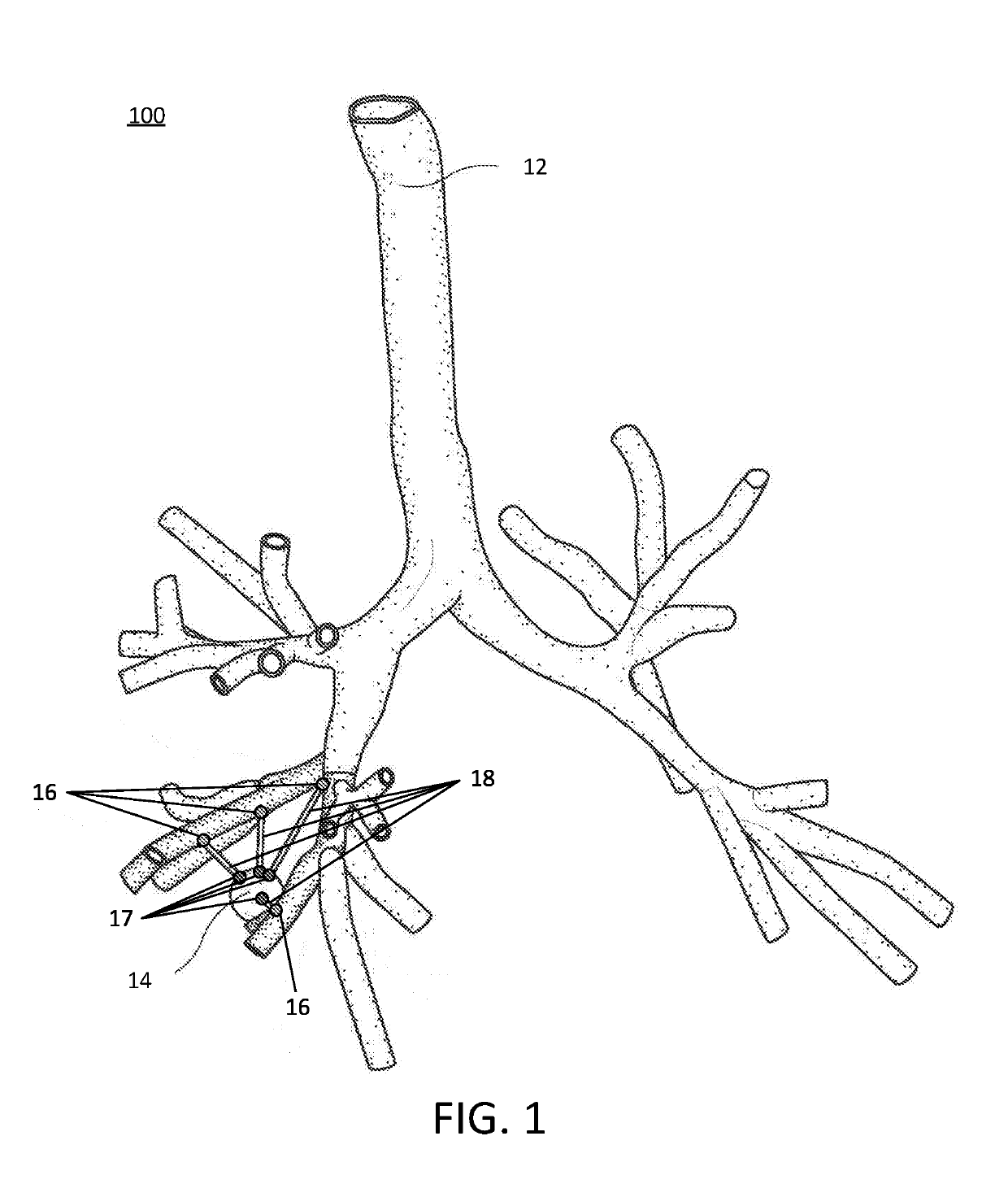
Disclosed are systems, devices, and methods for planning a procedure for treatment of lung tissue. An exemplary method includes generating a three-dimensional (3D) model of the luminal network, displaying the 3D model of the luminal network, selecting a target location in the tissue adjacent to the luminal network as displayed on the 3D model, identifying a point in the luminal network which is proximate to or at the target location, determining an access path between the target location and the identified point in the luminal network, calculating a risk of injury to intervening structures between the target location and the identified point in the luminal network, based on the determined access path, and displaying the access path and the calculated risk of injury for the access path on the 3D model.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Headrest-mounted monitor
InactiveUS20070001492A1Low risk of injuryTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDisplay deviceHead restraint
Owner:VOXX INT CORP
Retrofit Kit for a Training Device and Training Device
InactiveUS20070298941A1Low possible risk of injuryGuaranteed detection effectDumb-bellsEngineeringCounterforce
The invention generally relates to a retrofit kit for a training device and to a training device. The training device includes a moving actuating element via which a training force produced by an individual who is training can be introduced into the training device. The training device also includes a force producing device via which a counterforce that works against the training force can be produced by a training weight. The training weight can be composed of one or more individual weights. In order to increase the training effect of the training device, an oscillation producing device is provided via which an oscillation can be produced that influences and modulates the counterforce. The oscillation producing device is provided in the form of an individual weight.
Owner:EGGER NORBERT
Headrest-mounted monitor
InactiveUS20070001493A1Low risk of injuryTelevision system detailsVehicle seatsDisplay deviceEngineering
A monitor adapted for mounting in an automobile headrest is provided. A screen structure of the monitor is pivotable about an upper edge thereof, such that the monitor occupies little volume within the headrest. A viewing angle of the screen structure is independently adjustable by a viewer, such that the viewer can continuously select the optimum viewing angle with changing conditions inside the automobile. The screen structure automatically retracts into a housing when struck. Thus, the monitor poses little risk of injury to passengers. The housing of the monitor is attachable to the headrest with screws, which provides a very sturdy connection and reduces the chances of the housing becoming detached from the headrest during a vehicle collision. The hinged connection between the screen structure and the housing is preferably constructed of interconnected components made from sturdy materials, such as metals. Hinge components are optionally secured with metal fastening members and fastening apertures made of metal and strong plastics. The hinges are thus unlikely to break during a vehicle collision.
Owner:VOXX INT CORP
Multi-purpose driver assist system for a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6856874B2Improve securityLow risk of injuryVehicle fittingsBelt retractorsMobile vehicleDriver/operator
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Board-like sliding device in the form of a ski or snowboard
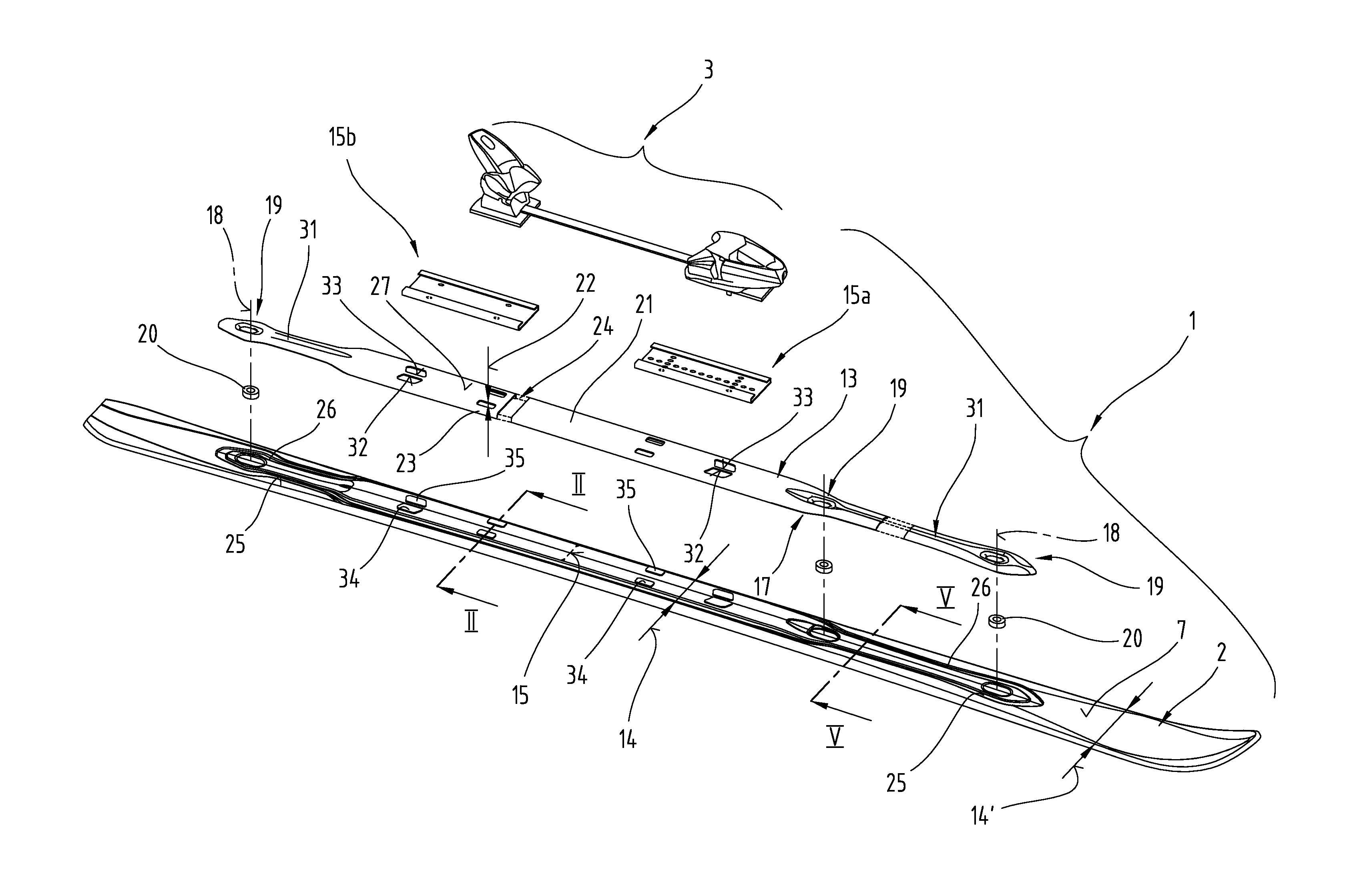
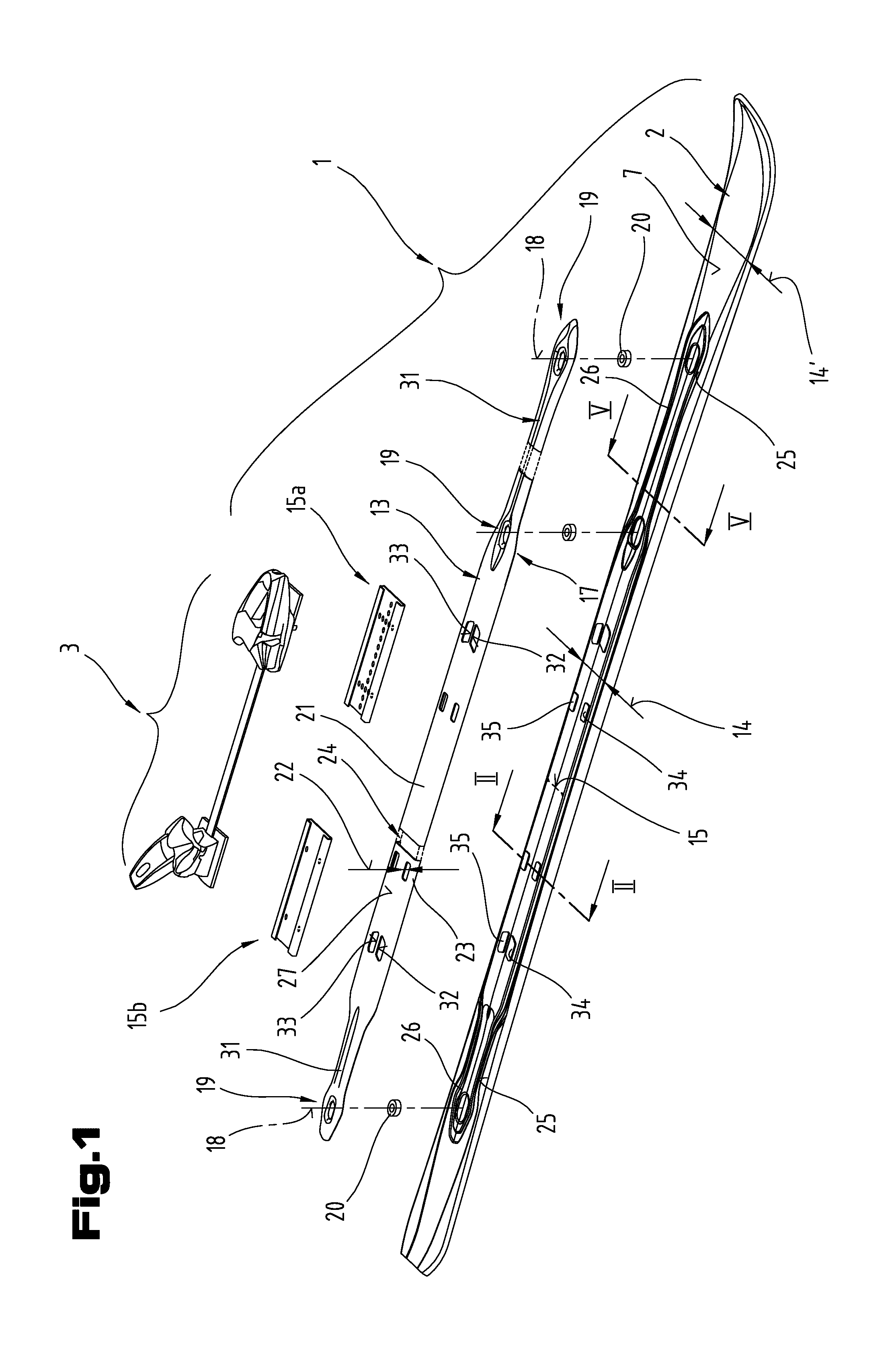
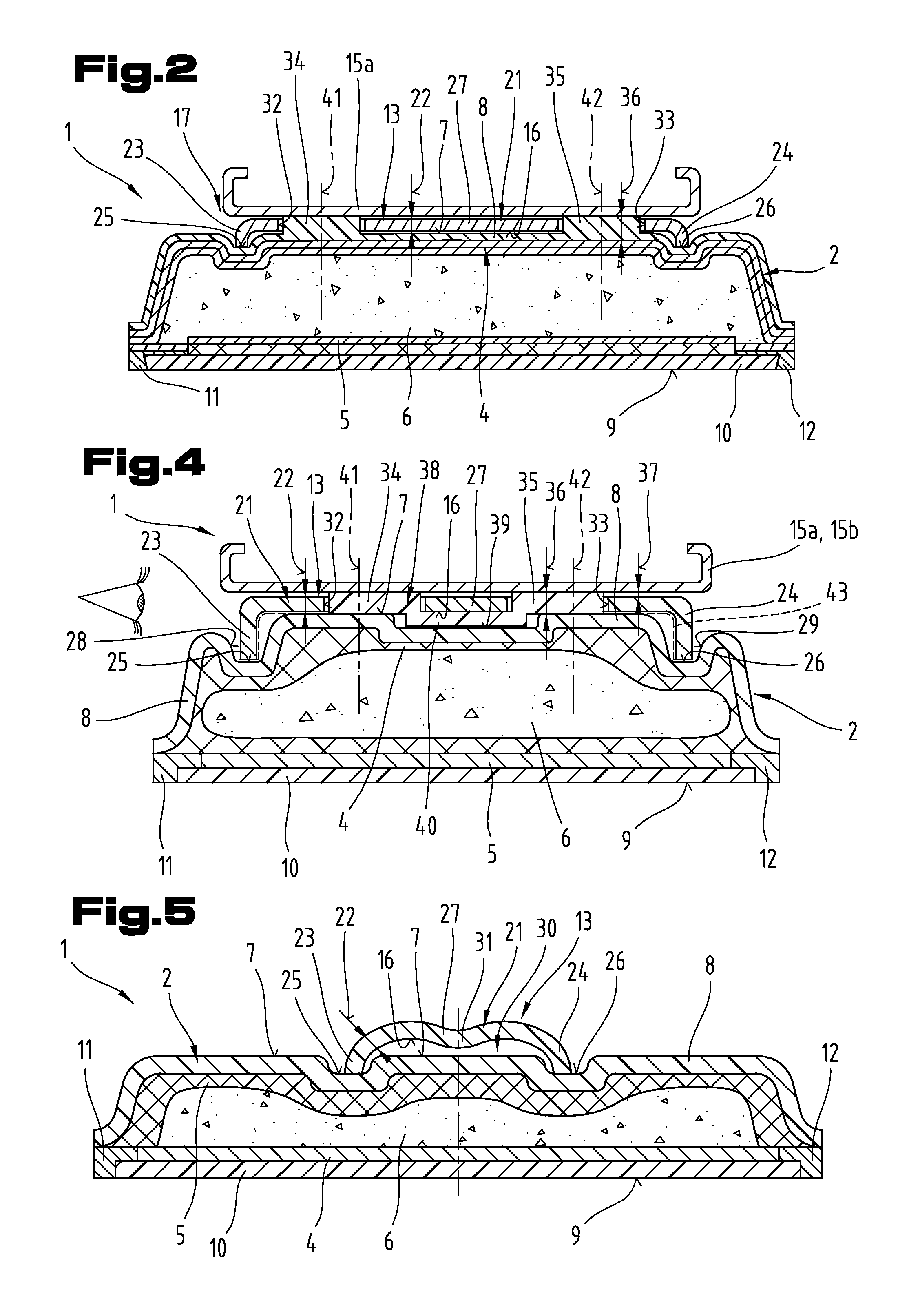
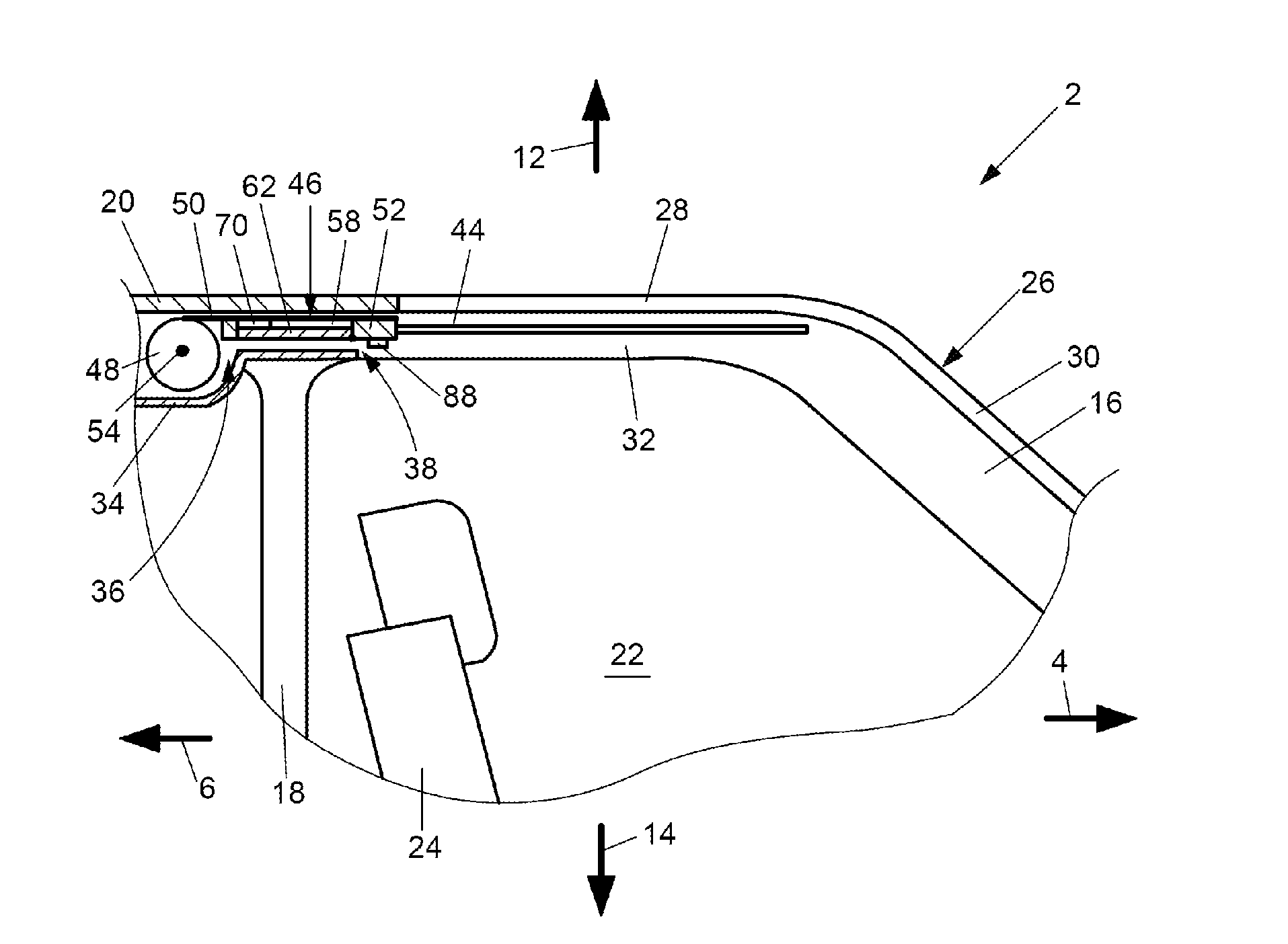
InactiveUS20110001305A1Low production costExcellent functionality and performanceSki bindingsSki-brakesThin walledEngineering
The invention relates to a board-like sliding device in the form of a ski or snowboard. Said board-like sliding device comprises a multilayered sliding board body and at least one elongated force-transmitting element supported on the upper side of the sliding board body for influencing the bending resistance or the vibrational behaviour of the sliding board body as well as a binding device for a potentially detachable connection with a sports shoe. Between the lower side of the force-transmitting element and the upper side of the sliding board body at least one engaging coupling means is formed. The force-transmitting element is designed in this case as a thin-walled shell body with a wall thickness of less than 5 mm, which at least over the main part of its longitudinal extension has a substantially U-shaped cross section. At least part sections of the side arms of the force-transmitting element run at least partly in groove-like depressions on the upper side of the sliding board body.
Owner:ATOMIC AUSTRIA
Motor vehicle with a protective sunscreen for the windowpane
A motor vehicle is provided that includes, but is not limited to a windowpane and a protective sunscreen for the windowpane, and the protective sunscreen exhibits a cover that can be moved from a non-use position into a use position, in which the cover at least partially covers the windowpane. The cover exhibits a rigid load-bearing section that accommodates at least one sun visor, which can be moved from a non-use position into a use position.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Releasable segment in the working members of an agricultural harvesting machine
InactiveUS7137882B2Little structural elaboratenessWithout risk of injuryMowersThreshersMechanical engineeringAgriculture
An agricultural harvesting machine includes a first rotating working member rotating about an axis; a non-rotating working member cooperatively associated with the first working member; and at least one releasable segment associated with the first rotating working member, forming an assembly and dismounting opening when the releasable segment is removed and wherein the assembly and dismounting opening creates an access to the non-rotating working member and additional adjacent working members.
Owner:CLAAS SELBSTFAHRENDE ERNTEMASCHINEN GMBH
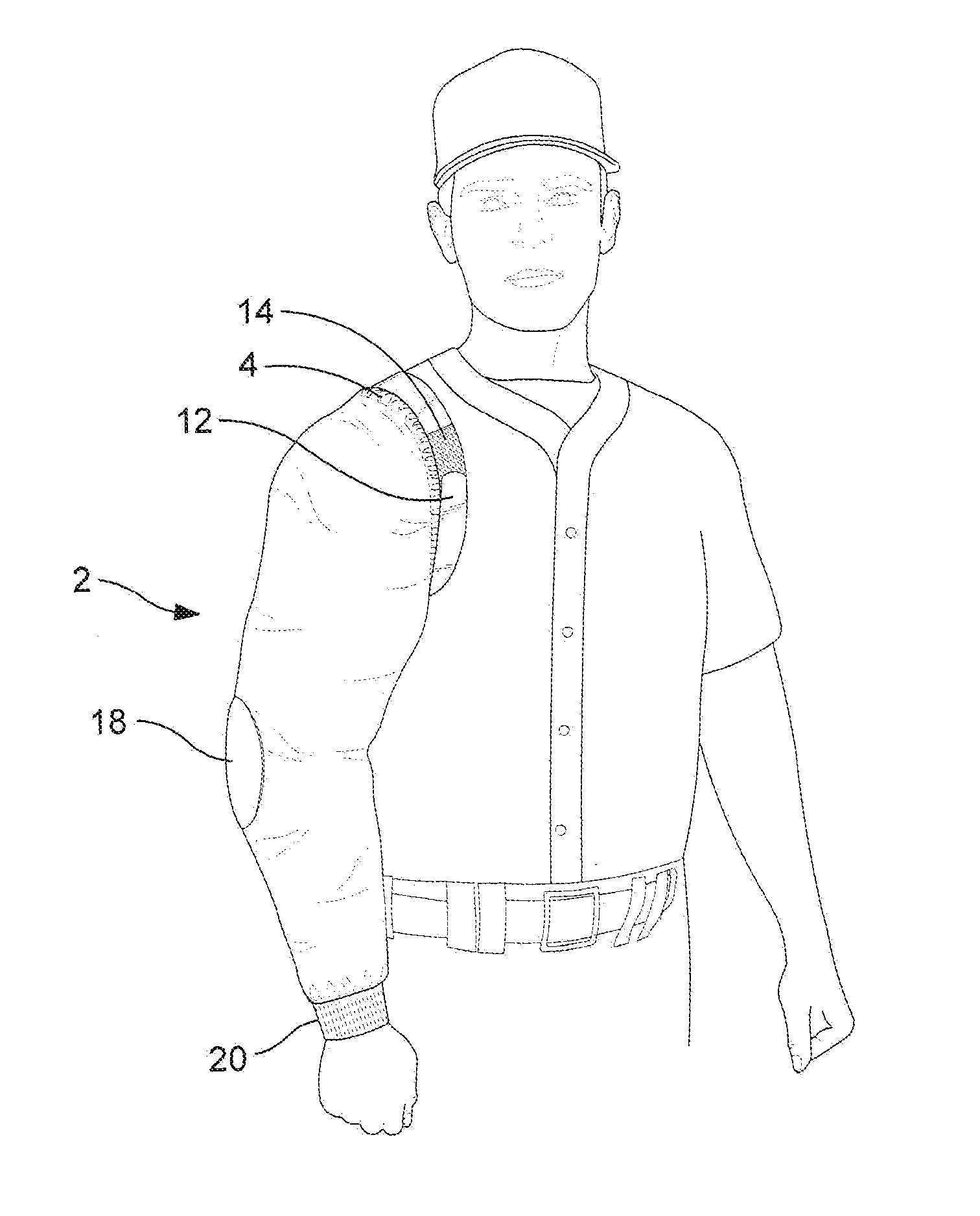
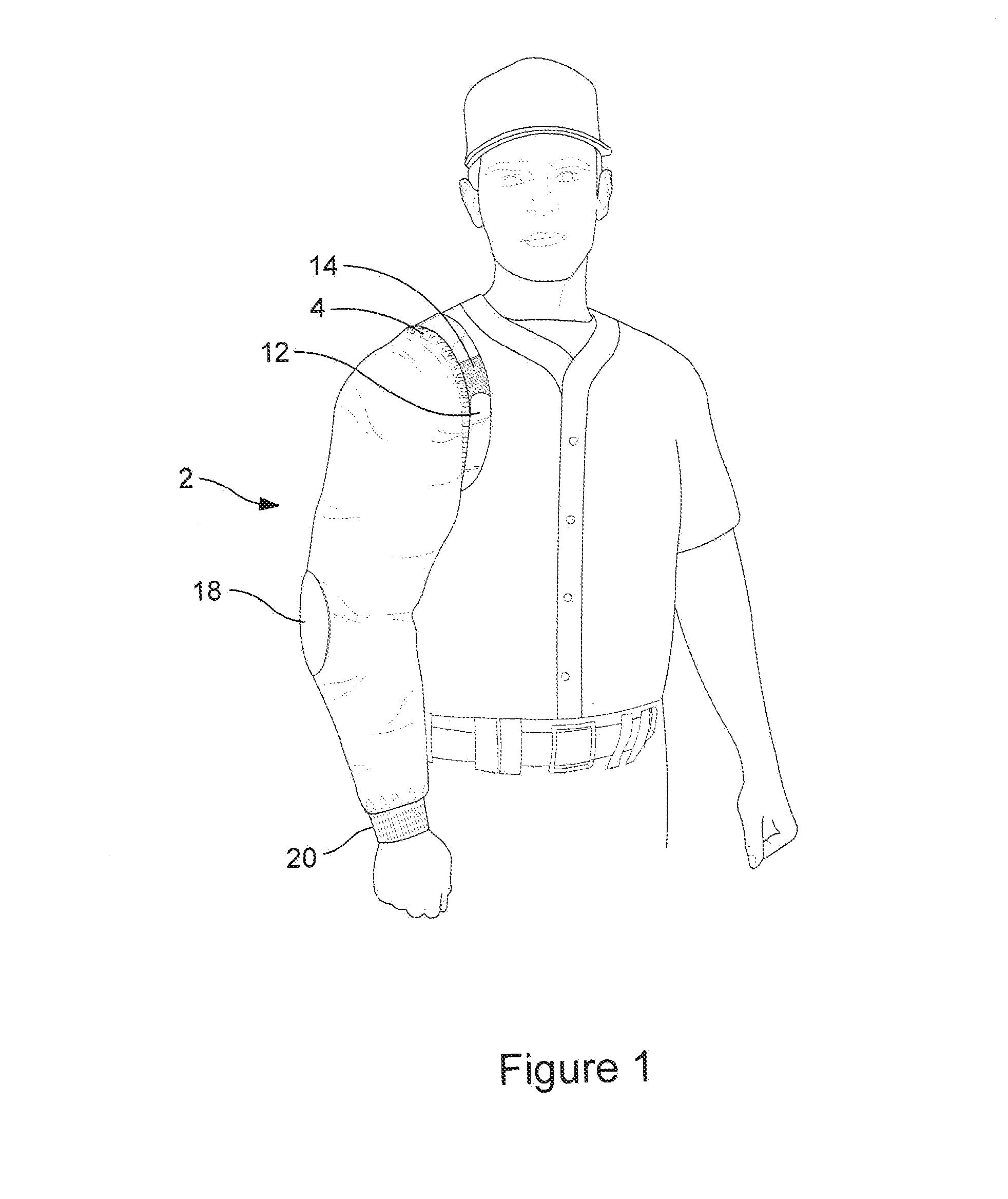
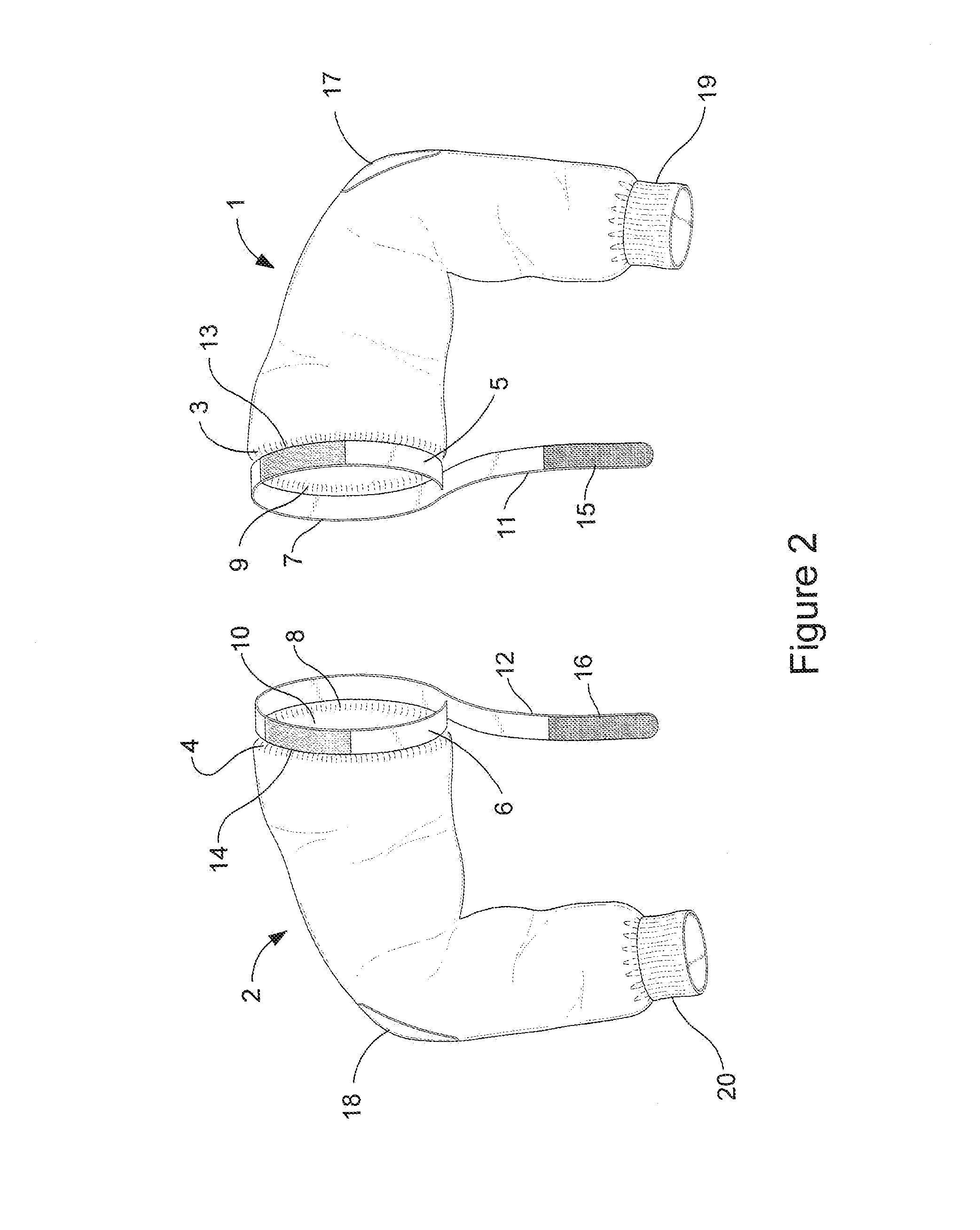
Pitcher's mini-jacket
InactiveUS20130318674A1Minimizes its contractionRapid coolingConvertible garmentEye treatmentPull forceEngineering
Disclosed is a quick-donning mini-jacket with matching left and right segments, either one of which may independently be used to cover and / or protect a baseball pitcher's throwing arm. Upon insertion of the pitcher's arm into either segment, the wearer may experience a snug, comfortable fit of the garment about the perimeter of the wearer's shoulder and arm, by virtue of an inner elastic band. Should the inner elastic band be insufficient for a close and comfortable fit, an adjustment strap is provided, typically of a hook-and-felt fastening mechanism. By adjusting tightness of the strap, the tensile force about the shoulder joint may be increased a comfortable amount. In this manner, a pitcher's arm can be kept warm, relaxed, and relatively free from muscle tightening or tension that might result from a just-completed pitching session.
Owner:BANKS JOSEPH
Traffic safety system
InactiveUS20120120640A1Lower riskLow risk of injuryPoint-like light sourceWith electric batteriesArchitectural engineeringThin film solar cell
A traffic safety system includes an enhanced reflective strip made from a flat, elongated flexible material having a plurality of layers. Preferably, the enhanced reflective strip includes a back layer having a plurality of LED's arranged in a pattern; a middle layer including weatherproofing material; and a front layer including a reflective material. Preferably, the enhanced reflective strip is installed in place of the top reflective band on a round construction drum or a construction barricade, though it could also be installed on any flat or round surface such as lane dividers, guardrails or water barriers. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention the enhanced reflective strip is installed on a construction drum and is solar powered. Preferably, a thin-film solar panel is attached to the top surface of the construction drum and the other components are placed inside the drum.
Owner:GRAHAM MATTHEW M
Sole comprising individually deflectable reinforcing members, shoe with such a sole, and method for the manufacture of such items
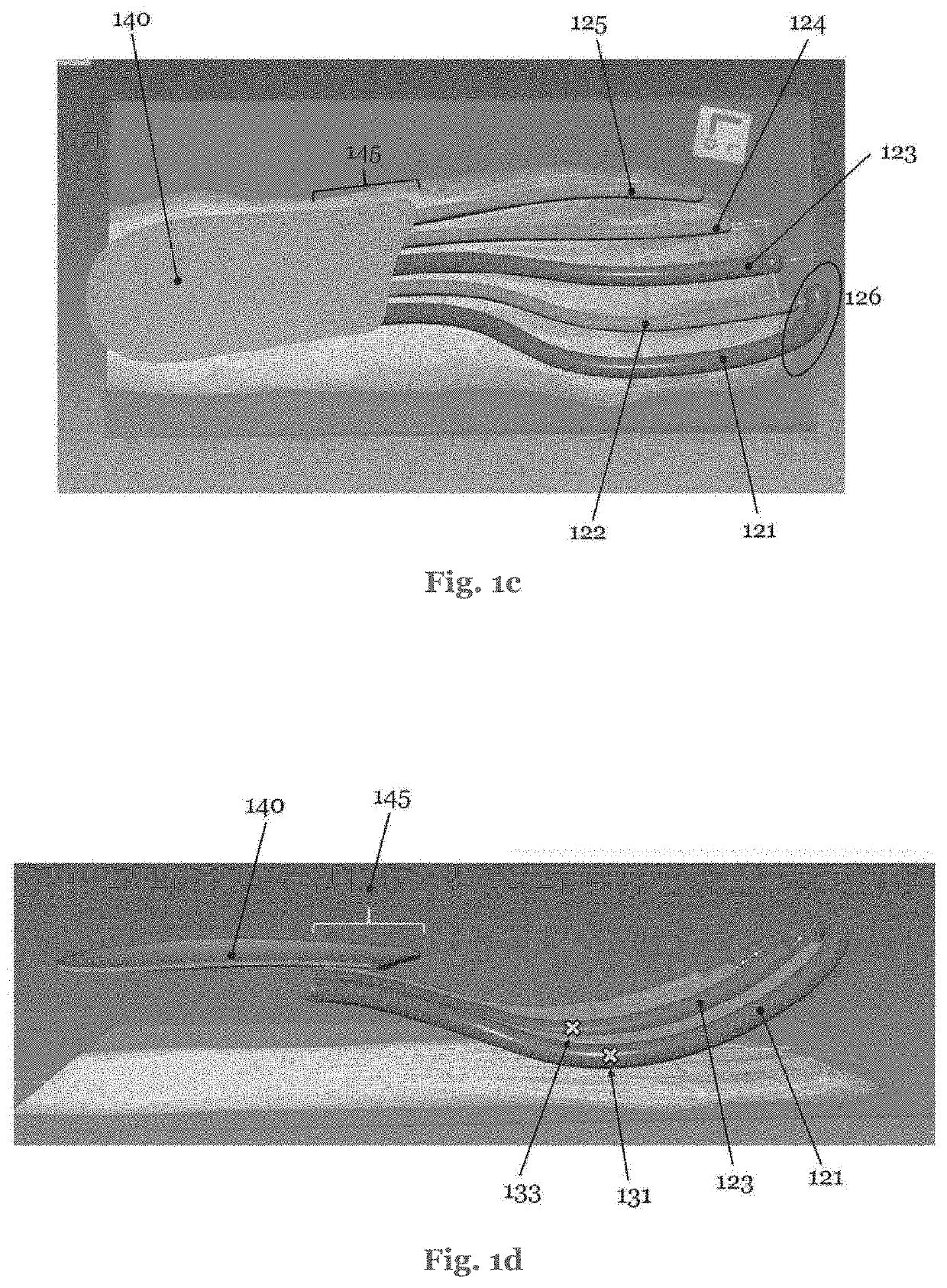
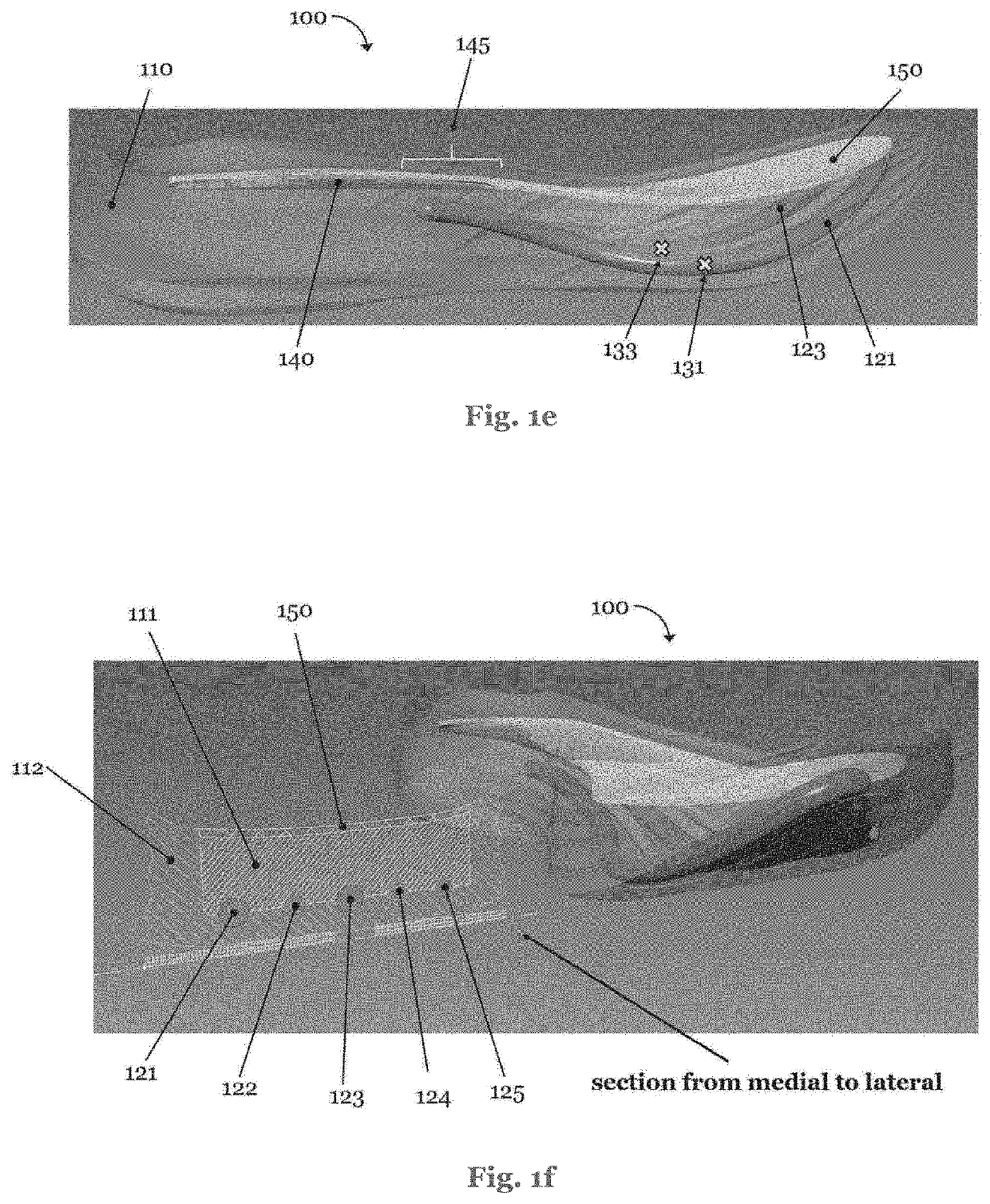
ActiveUS20210259358A1Low risk of injuryPrompt experienceSolesDomestic footwearAnkle regionEngineering
A sole for a shoe, the sole comprising reinforcing members extending in a front half of the sole, wherein at least a first one of the reinforcing members further extends rearwardly beyond a midfoot area and into a heel area of the sole and wraps up to a posterior portion of an ankle region. A shoe, in particular a running shoe, comprising such a sole. A method for the manufacture of such items.
Owner:ADIDAS
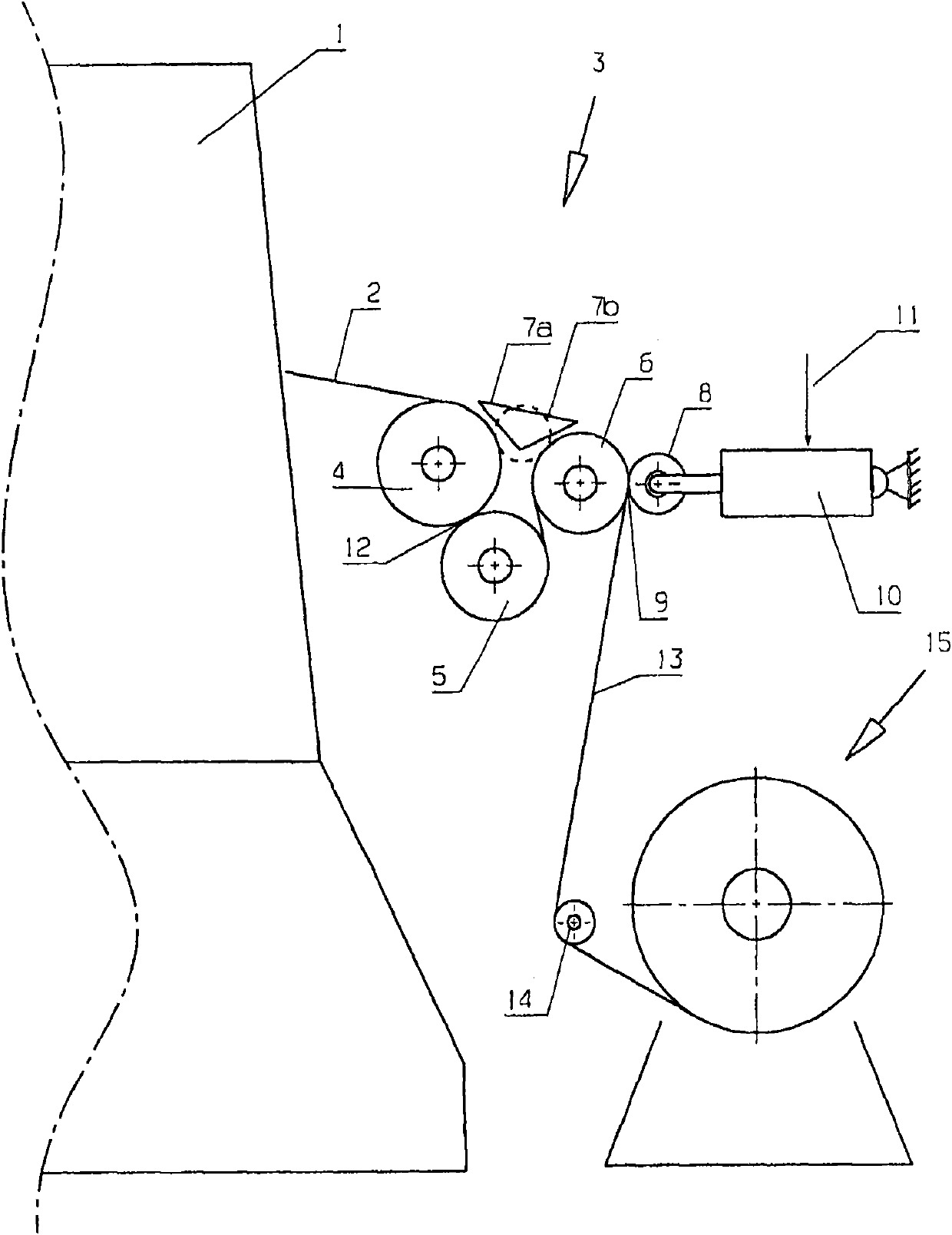
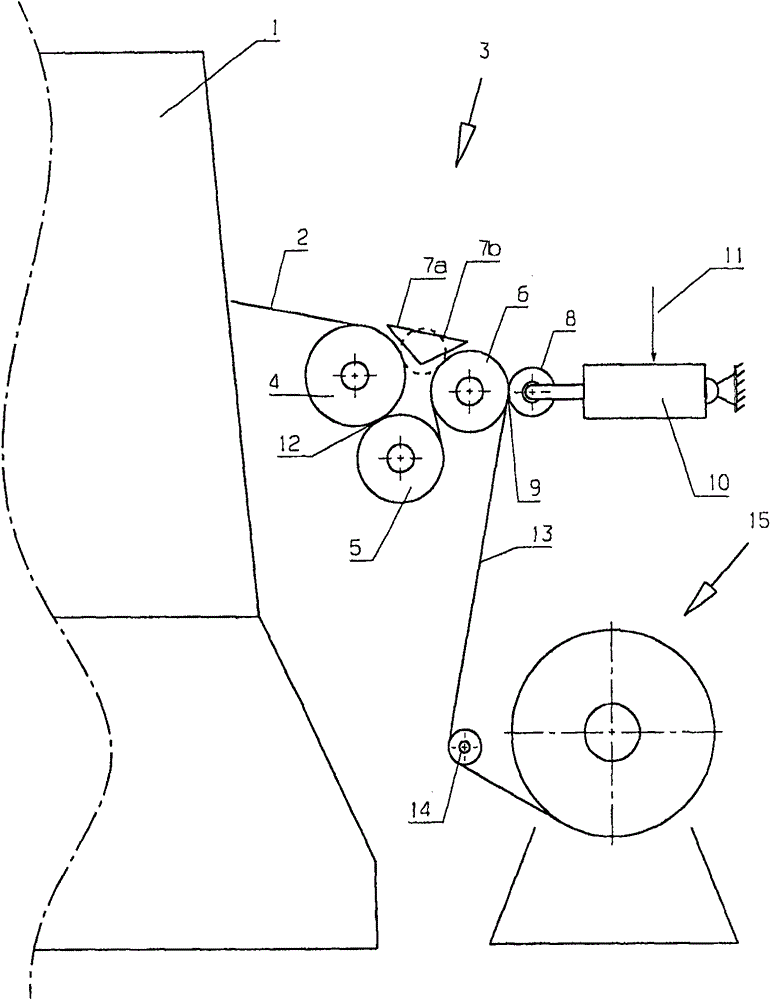
Device for drawing fabric breadth of surface-shaped textile from textile machine, especially tricot machine
The present invention relates to a device for drawing a fabric breadth(2) of a surface-shaped textile from a textile machine(1), especially tricot machine. The device is provided with a plurality of leading-out rollers (4-6), the breadth path of the textile breadth (2) is extended on the surfaces of the leading-out rollers (4-6),and the breadth path is led to a textile accommodating piece (15) in the processing direction after passing the leading-out rollers (4-6).The device is expected to convey textile breadth of elastic textiles with high quality. Clamping equipment is arranged on the last leading-out roller (6) of the processing direction, and a clamping clamp (9) is formed by the clamping equipment and the leading-out roller (6),and the breadth path is extended through the clamping clamp (9).
Owner:KARL MAYER STOLL R&D GMBH
Gymnastic equipment for vaulting exercises
InactiveUS6071212AHandy and space saving structureLow risk of injurySpring boardsPhysical exerciseEngineering
A gymnastic apparatus for performing vaults possesses a lower portion, an upper part arranged on same in a vertically adjustable fashion and constituted by a board arranged in a resilient manner on the lower portion. A gymnast running toward a front side of the apparatus, places his hands on the top side of the board, which forms a support face, applies his weight for an instant and leaps over the apparatus. In such leap he is aided by the resilient board. A front region of the board rises from the front convexly toward the rear in a arcuate manner, the arcuate region merging with an approximately horizontal flat region. The transitional region and / or the flat region serves a support face.
Owner:JANSSEN & FRITSEN HLDG
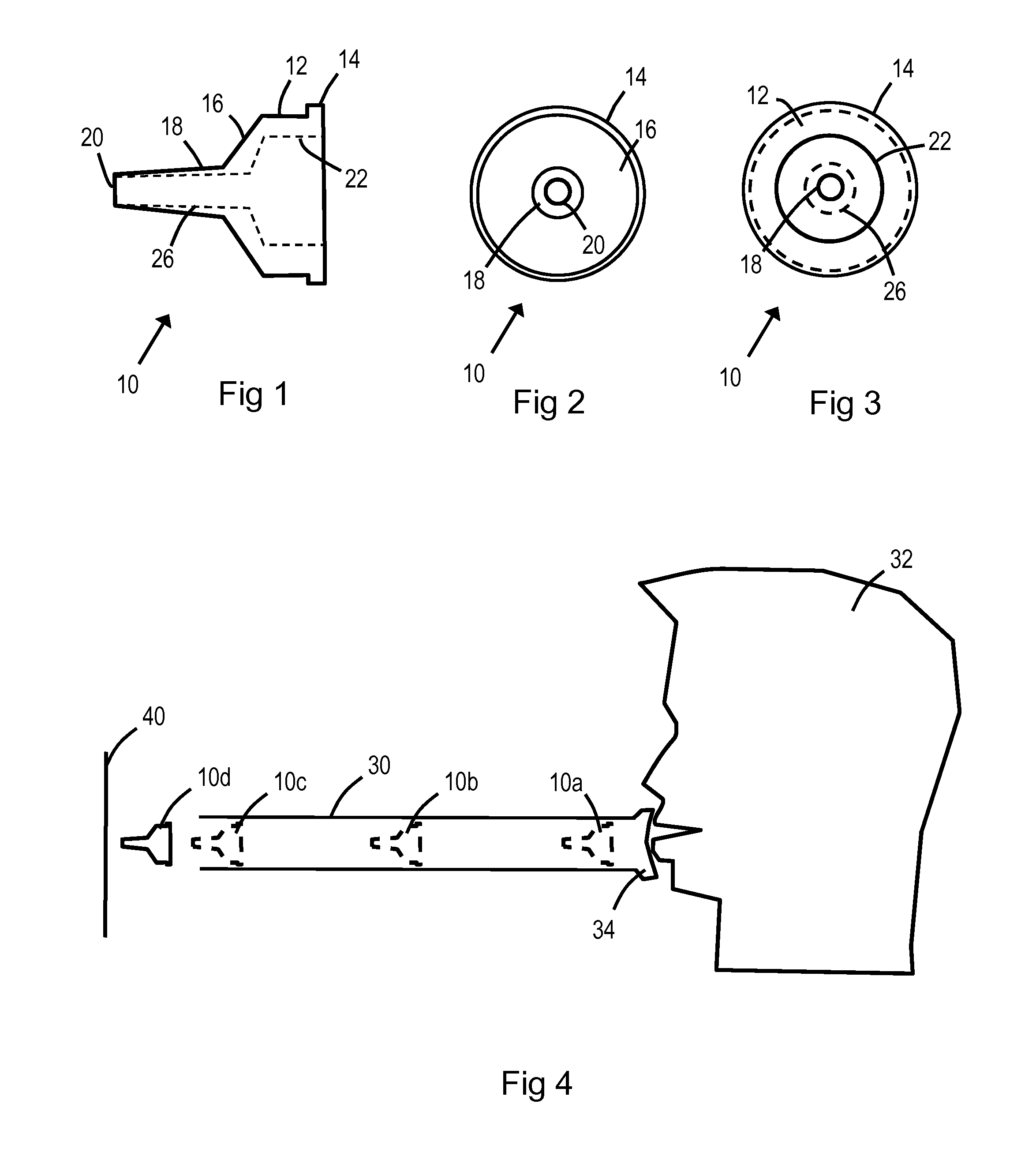
Blow pipe dart
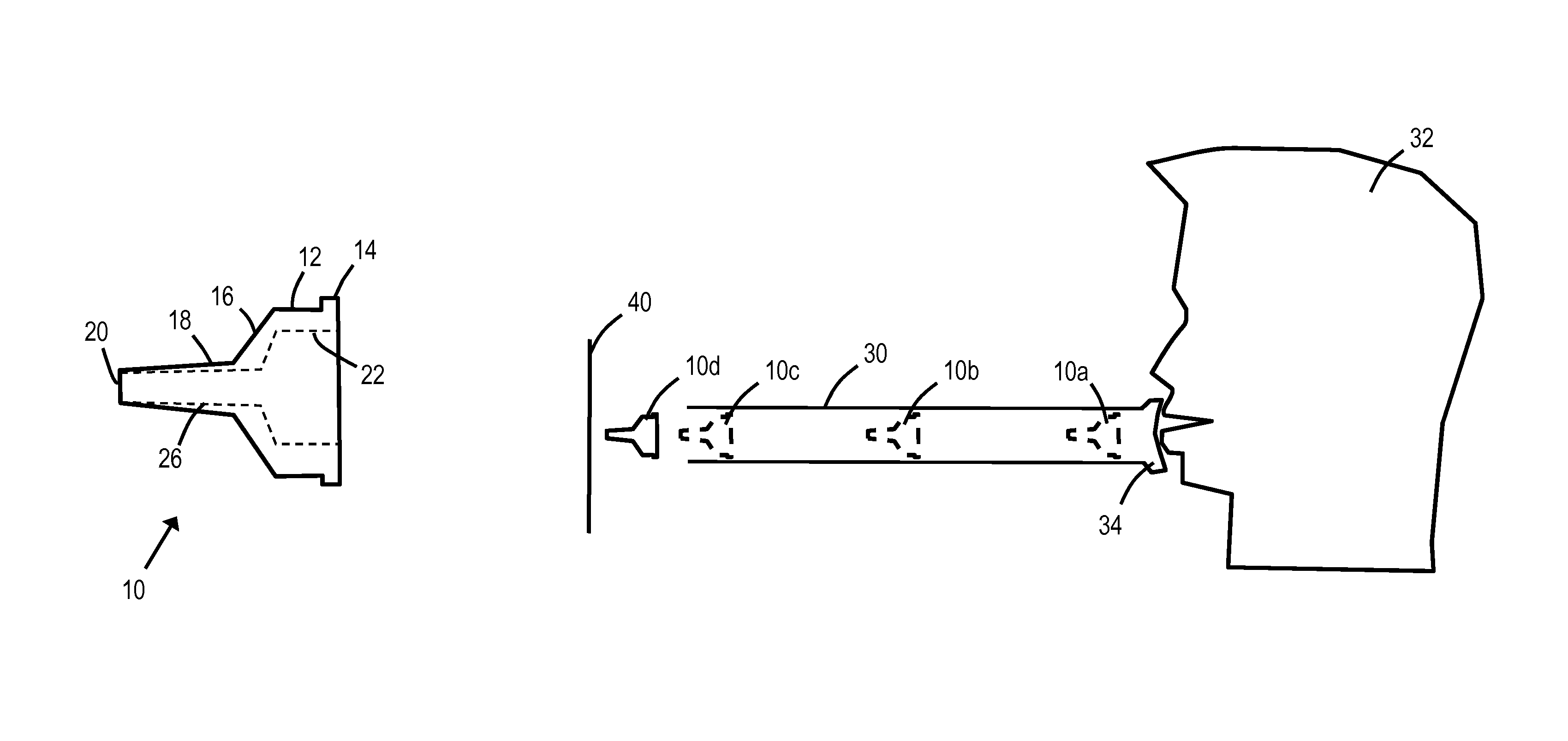
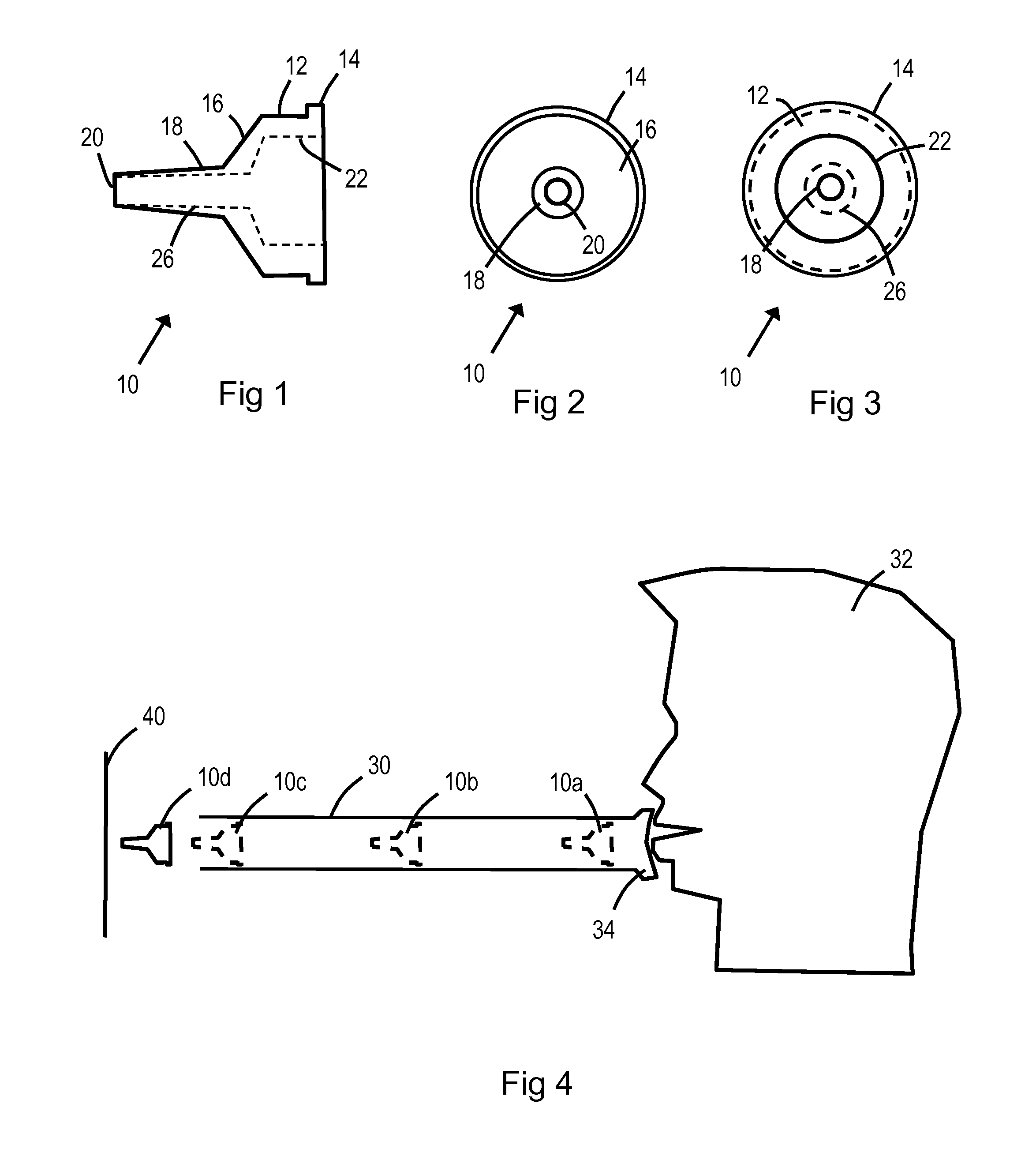
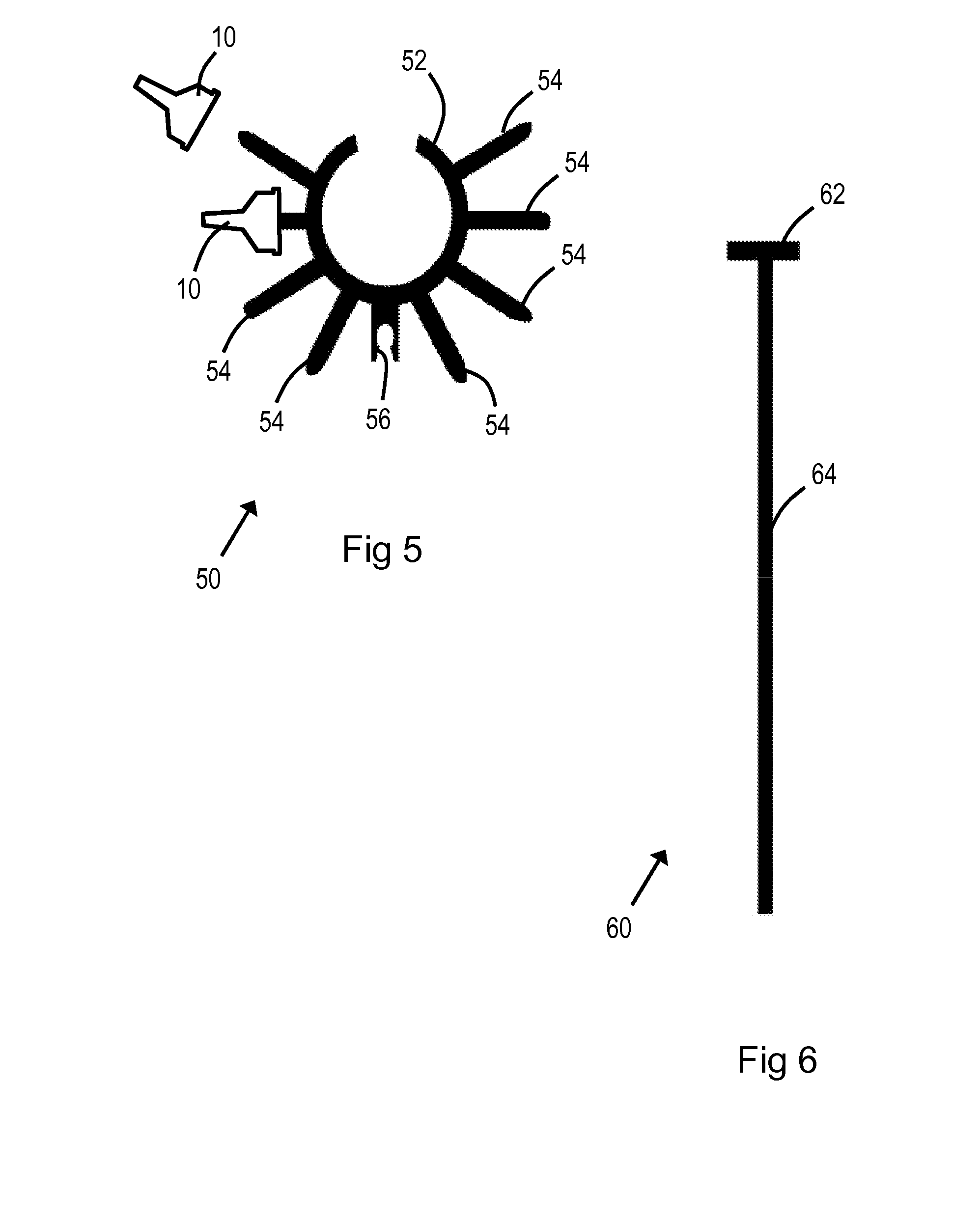
InactiveUS20140261361A1Reduce speedReduce painAmmunition projectilesThrow gamesEngineeringMechanical engineering
An elastomeric blow pipe dart (10) including: a generally circular body portion (12); a tapered portion (16) extending from the generally circular body portion (12); and a nose (18) having a smaller diameter than the tapered portion (16) and extending from the tapered portion (16) to a tip (20). The blow pipe dart (10) may comprise a soft rubber, and the nose (18) may define an end bore (26) so that air passes through the nose (18) when the dart (10) is launched.
Owner:HEPBURN RALPH ROBERTSON
Pathway planning for use with a navigation planning and procedure system
ActiveUS10631933B2Low risk of injuryMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPhysical therapy
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
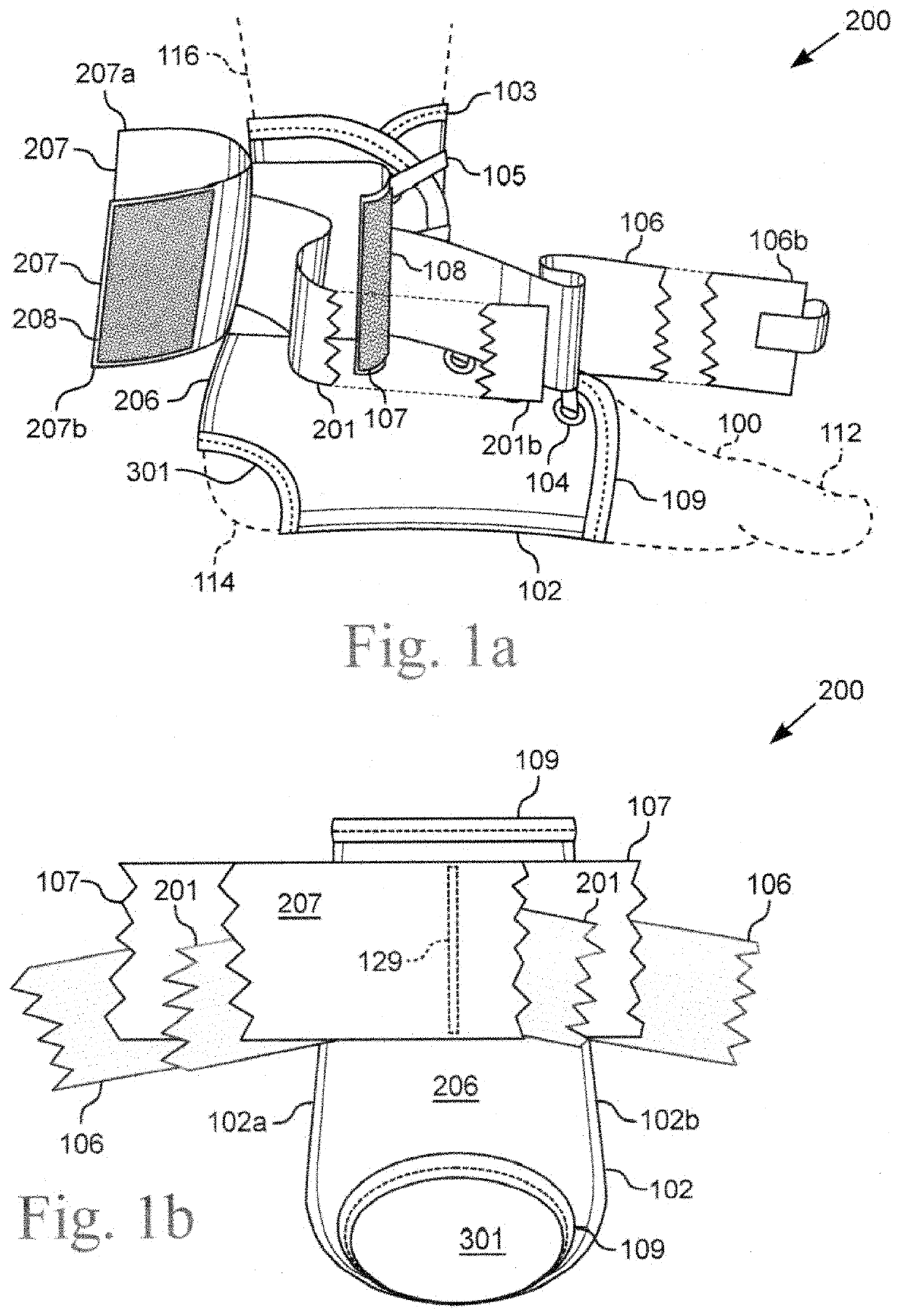
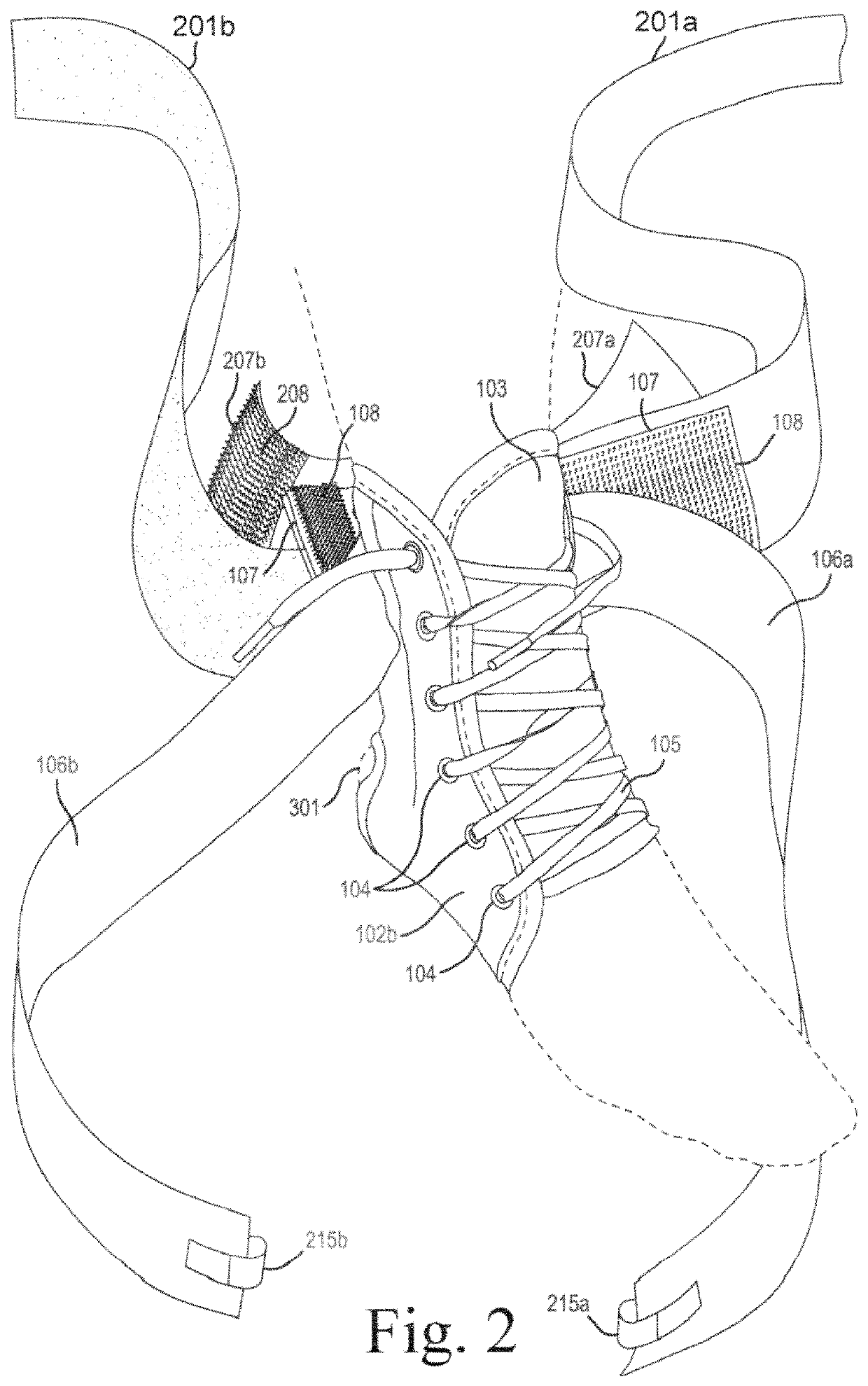
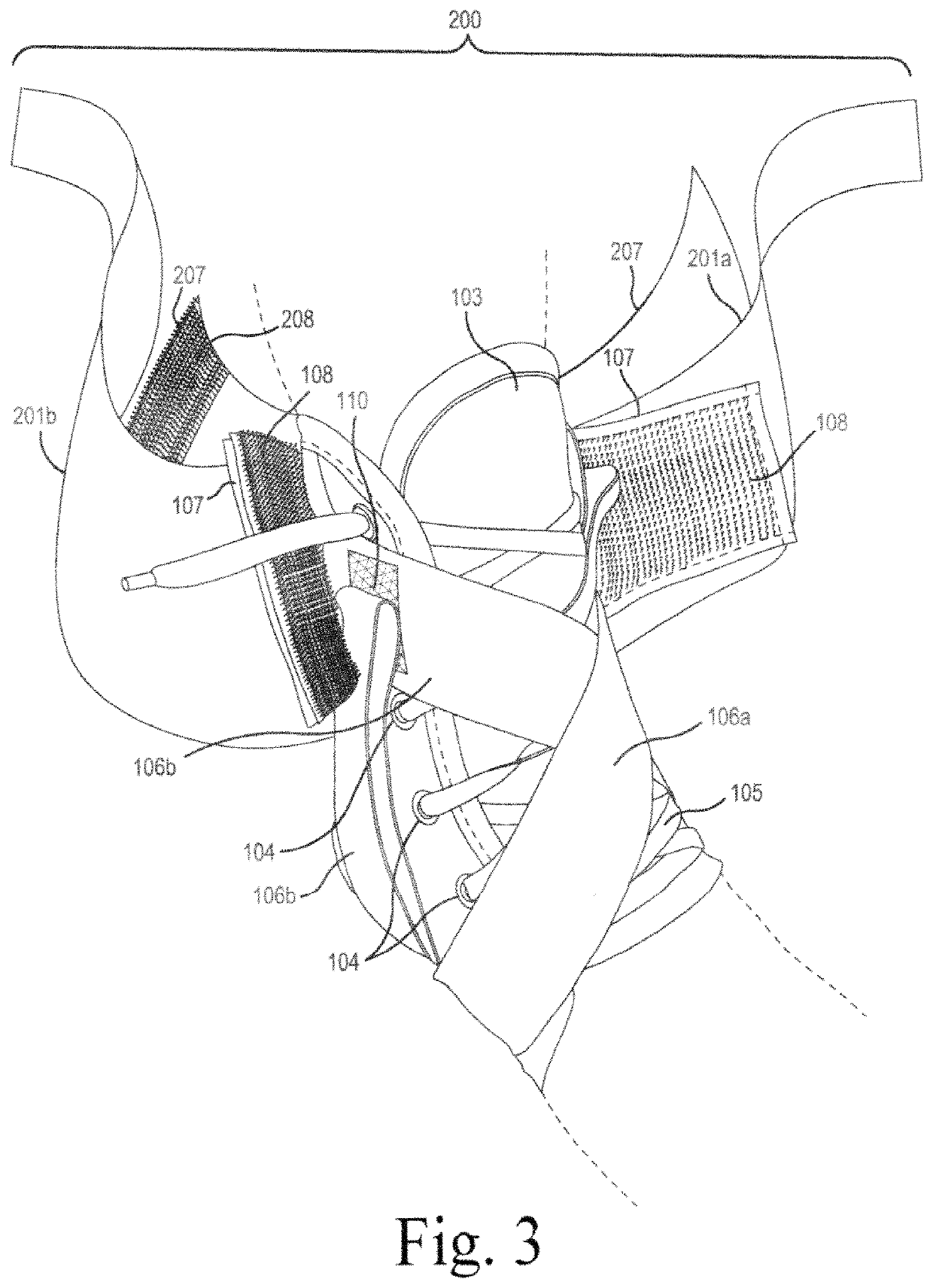
Ankle brace
ActiveUS11344442B1Low risk of injuryHigh utilityFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPhysical therapy
The present general inventive concept, in various embodiments, includes a brace for protective or therapeutic restraint of the ankle and / or foot. In some embodiments, the brace comprises a holding pocket of flexible material for stabilizing the ankle or foot, a means for releasably and adjustably attaching the holding pocket around the foot and ankle, a first support strap including a means for releasably and adjustably binding the first support strap to itself, a first support cuff including a means for releasably and adjustably tightening the first support cuff upon itself, a second support strap including a means for releasably and adjustably binding the second support strap to itself, and a second support cuff including a means for releasably and adjustably tightening the second support cuff upon itself.
Owner:MCVEIGH JASON +1
Skate guard and walking device
ActiveUS8414030B2Improve usabilityLowering potential risk of injurySnowboard bindingsSkisEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention provides a skate guard having an elongated body piece with a longitudinal channel for receiving a skate blade, and an end piece adapted to pivot relative to the body piece. The end piece, which is adapted to receive an end portion of a skate blade, may be pivotally and detachably secured in a closed position whereby a skate blade is held within the guard. In a preferred embodiment, a biased latch member is provided in the end piece to further secure a blade within the guard and to enable a user to install the guard by a step-in process. The end piece is preferably connected to the body piece though an adapter piece that enables the guard to be configured for a variety of skate lengths and shapes. The skate guard preferably includes lateral stabilizing ball and heel segments for added stability when walking and installing the guard.
Owner:QUS DESIGN
Steam cleaning device
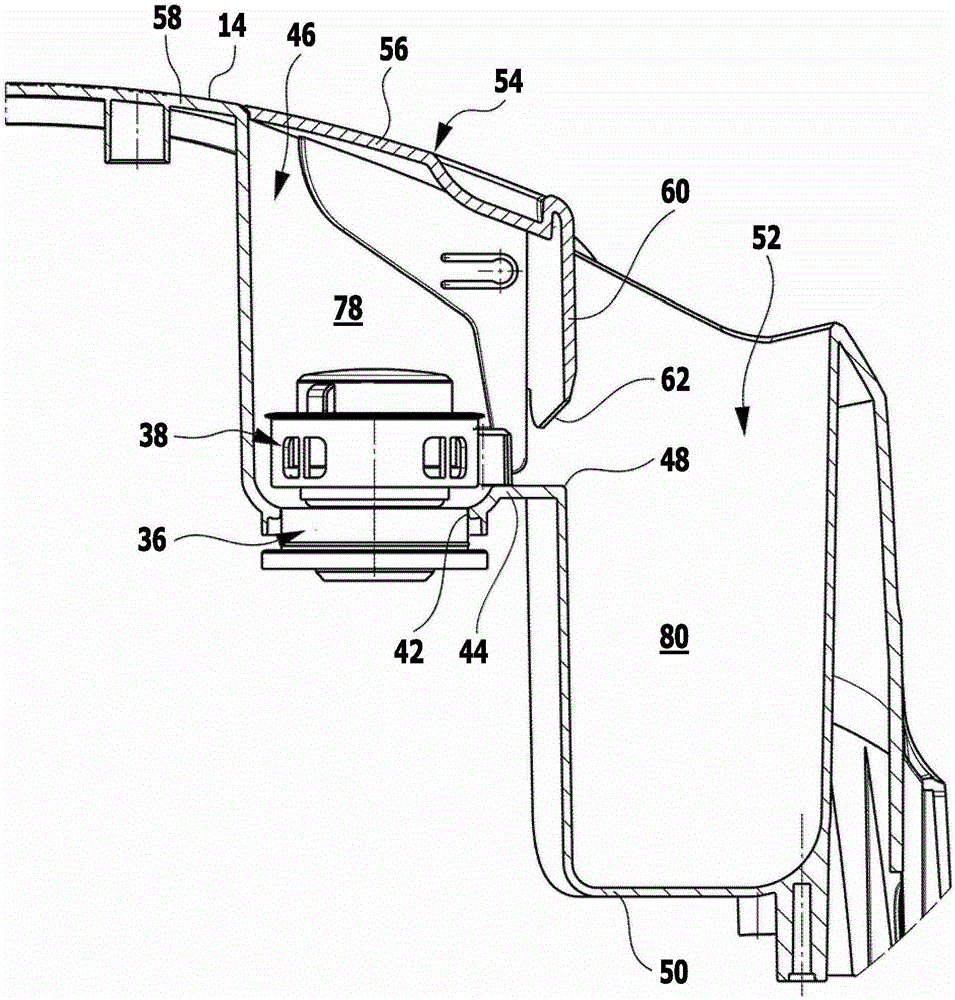
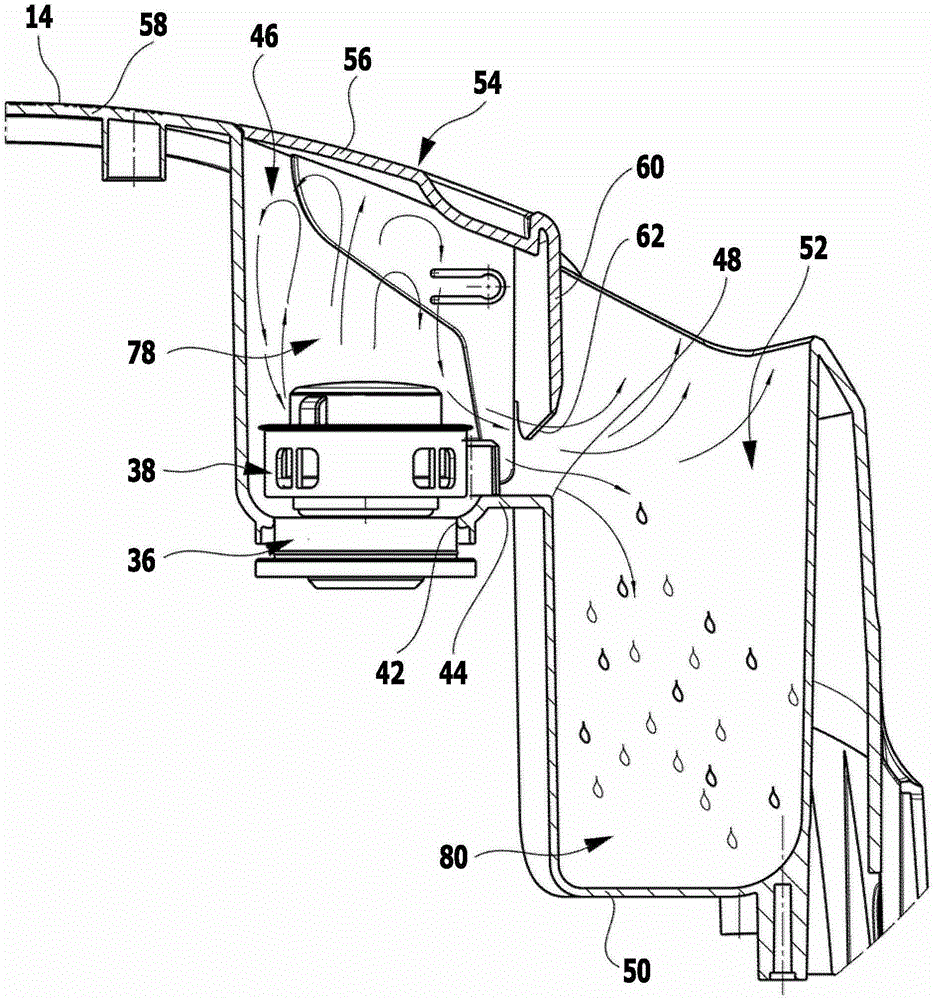
The invention relates to a steam cleaning device (10), comprising a liquid tank (24), which is connected to an electrically heatable steam boiler (26), wherein the steam boiler has a safety valve (38), which opens at an impermissibly high steam pressure in the steam boiler (26). In order to further develop the steam cleaning device (10) in such a way that the danger of the user being adversely affected by steam exiting through the safety valve (38) is reduced and the handling of the steam cleaning device is simplified, the safety valve (38) is integrated into a detachable maintenance closure (36) and can be covered by a covering element (54), which can be moved back and forth between a closed position that covers the maintenance closure (36) and an uncovering position that uncovers the maintenance closure (36).
Owner:ALFRED KARCHER GMBH & CO KG
Pathway planning for use with a navigation planning and procedure system
ActiveUS10238455B2Low risk of injuryMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLung tissueComputer science
Disclosed are systems, devices, and methods for planning a procedure for treatment of lung tissue. An exemplary method includes generating a three-dimensional (3D) model of the luminal network, displaying the 3D model of the luminal network, selecting a target location in the tissue adjacent to the luminal network as displayed on the 3D model, identifying a point in the luminal network which is proximate to or at the target location, determining an access path between the target location and the identified point in the luminal network, calculating a risk of injury to intervening structures between the target location and the identified point in the luminal network, based on the determined access path, and displaying the access path and the calculated risk of injury for the access path on the 3D model.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Display device
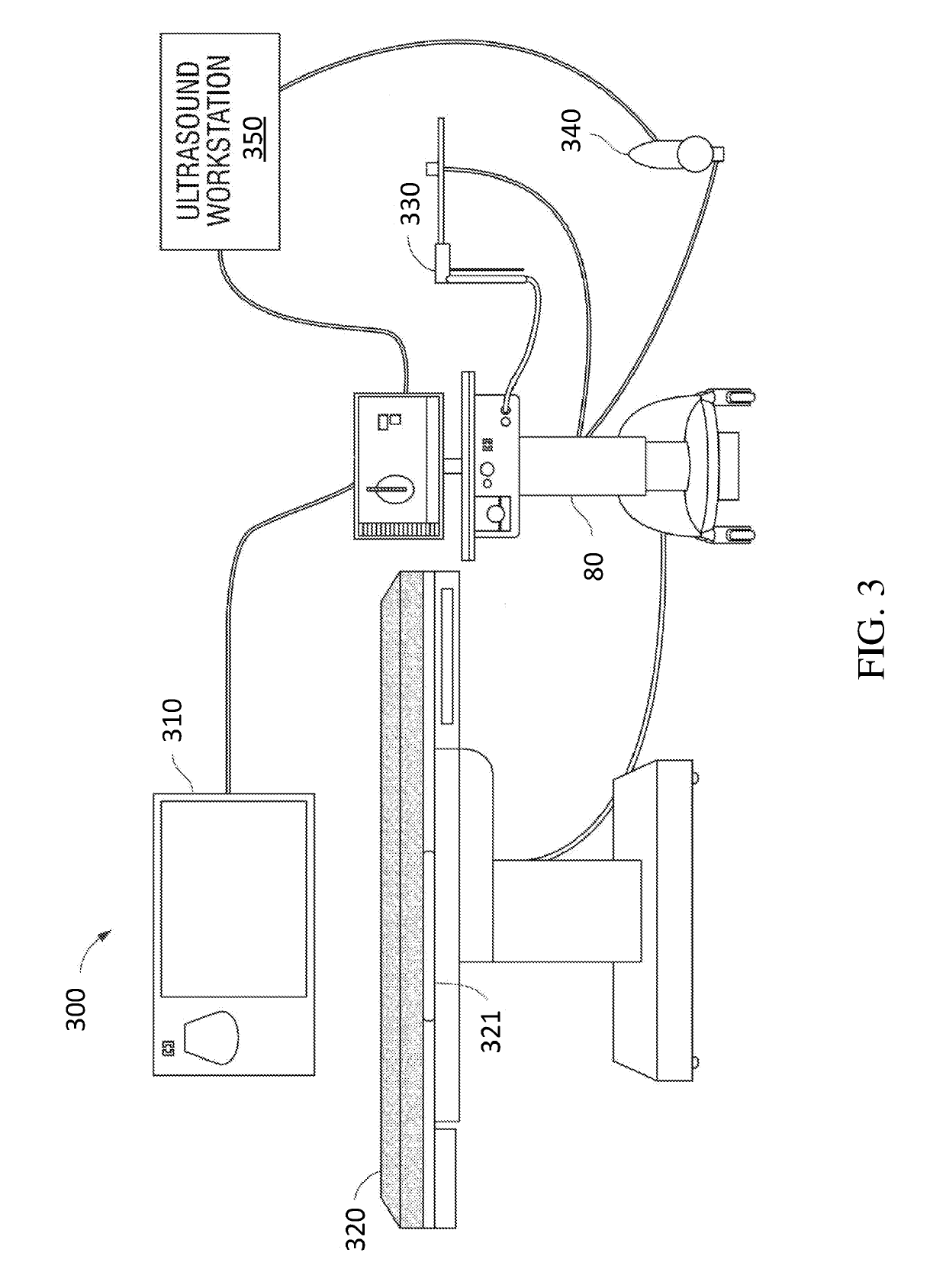
InactiveCN101311795ASetting is validLow risk of injuryCoupling device connectionsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
This invention provides a liquid crystal display device, which includes a vertical backlight source. A connector (50) formed by silicon rubber keeps end parts of a plurality of fluorescent tubes. A slit part (53) is pushed out to the outside along the arrow direction in the picture so as to install fluorescent tubes (37) into an inserting hole (50). A concave part (60) is formed between the inserting hole (51) and the inserting hole (51) of the connector (50) so as to enable the slit part (53) to easily open and prevent the damage to fluorescent tubes (37) or fluorescent tube terminal (371). And a plurality of fluorescent tubes can be effectively installed at the backlight source without damage.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS
Separating device for a livestock cubicle and arrangement thereof, in particular for a dairy farm
A separating device for a dairy farm livestock cubicle having a head region, a rear region, a first vertical separating unit, a second vertical separating unit spaced apart from the first vertical separating unit, and a substantially horizontally arranged crossmember extending through an obliquely arranged guide on one of the vertical separating units.
Owner:ROYAL DE BOER STALINRICHTINGEN
Pneumatic thread tensioner and thread handling system
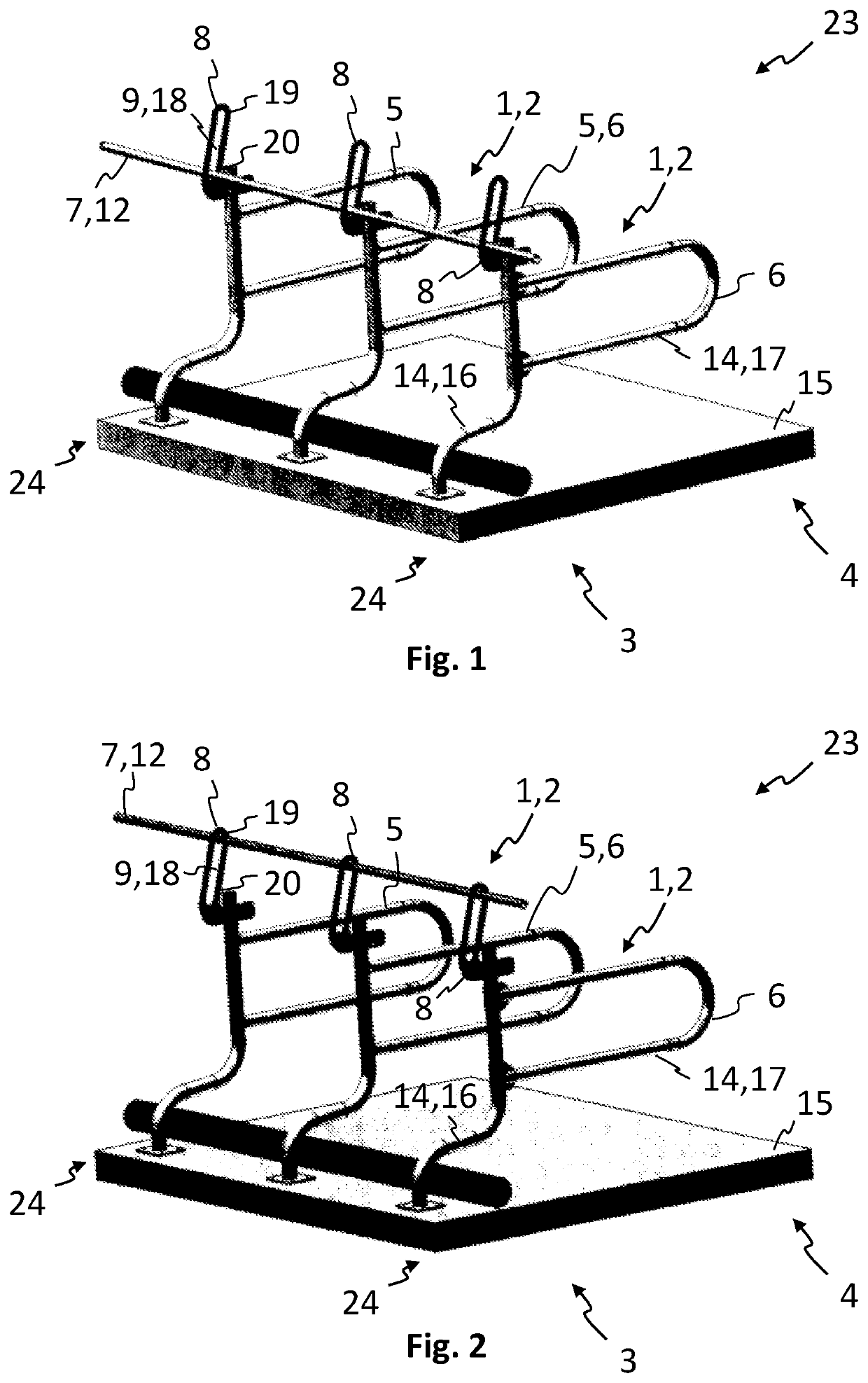
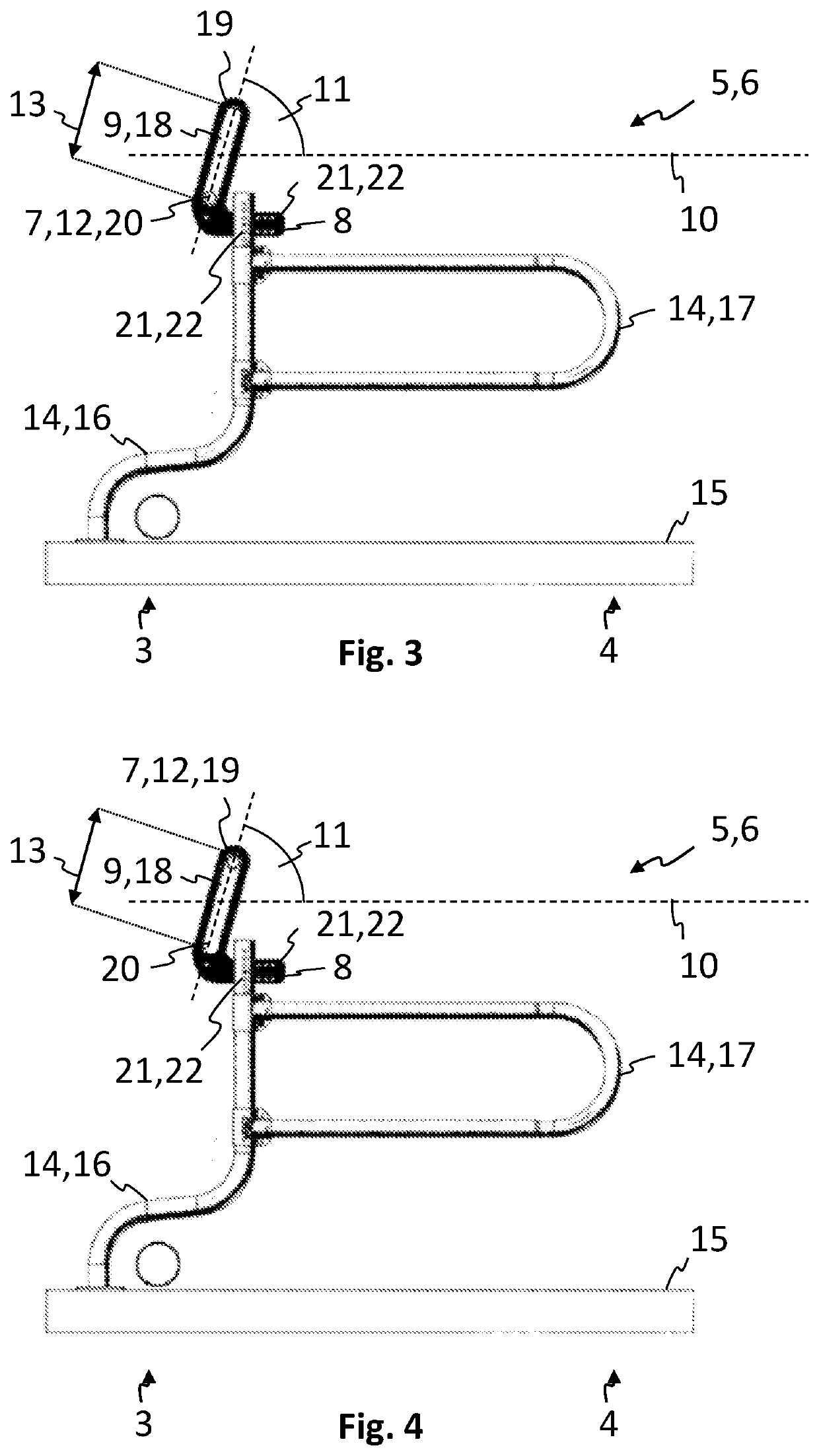
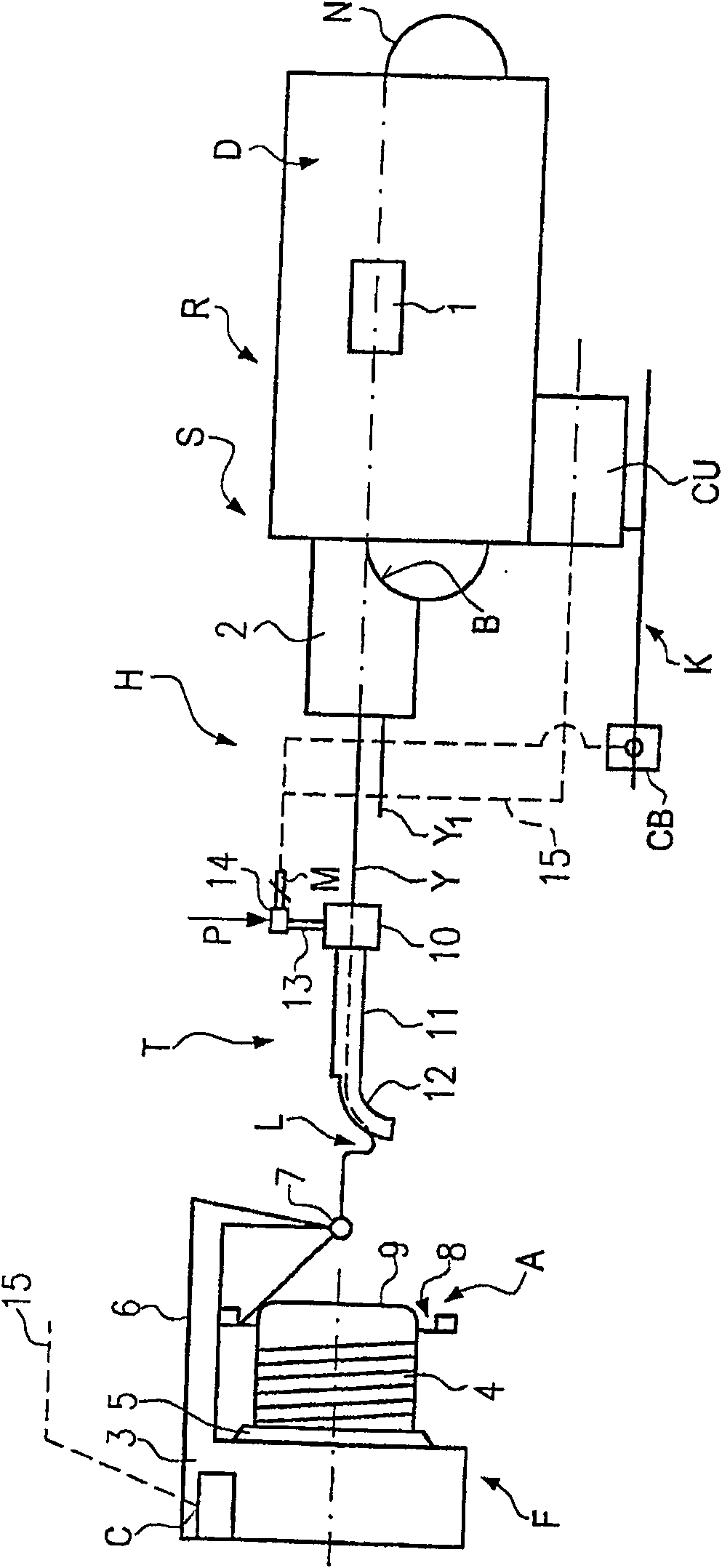
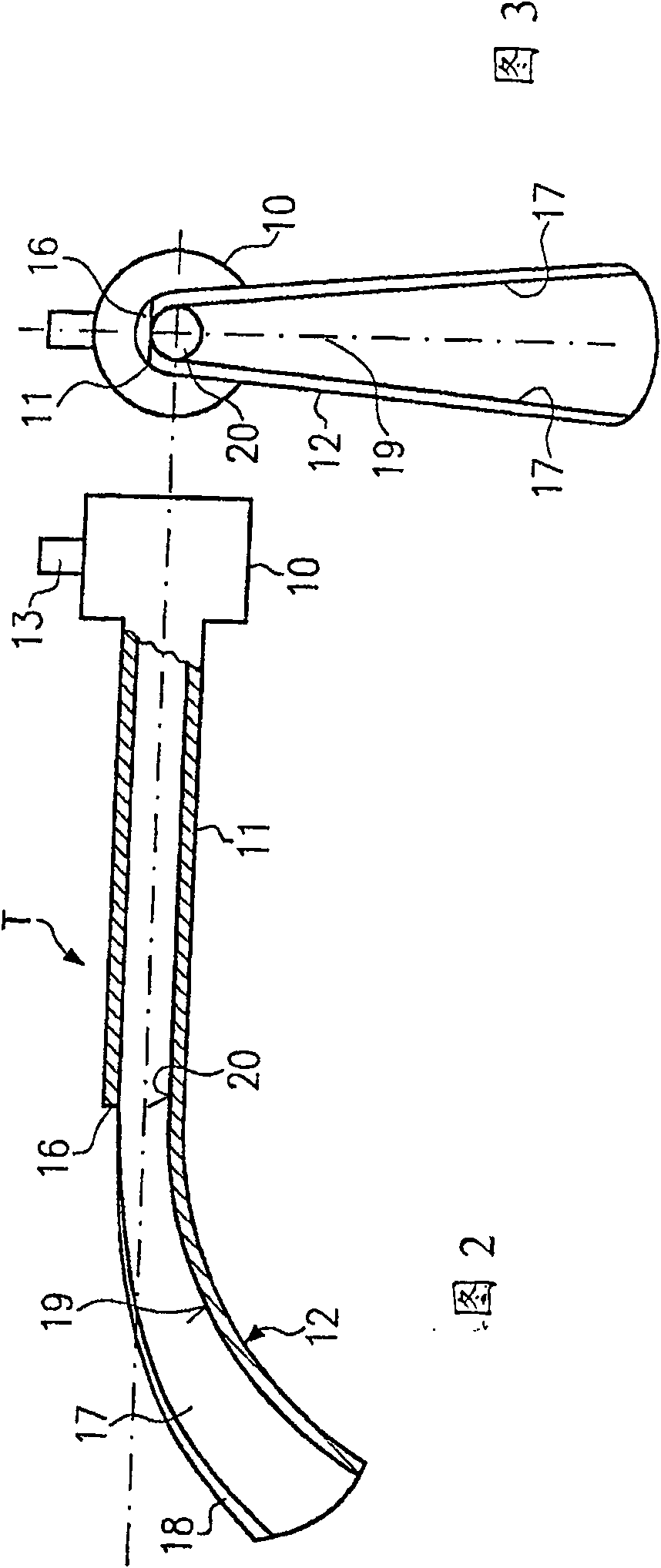
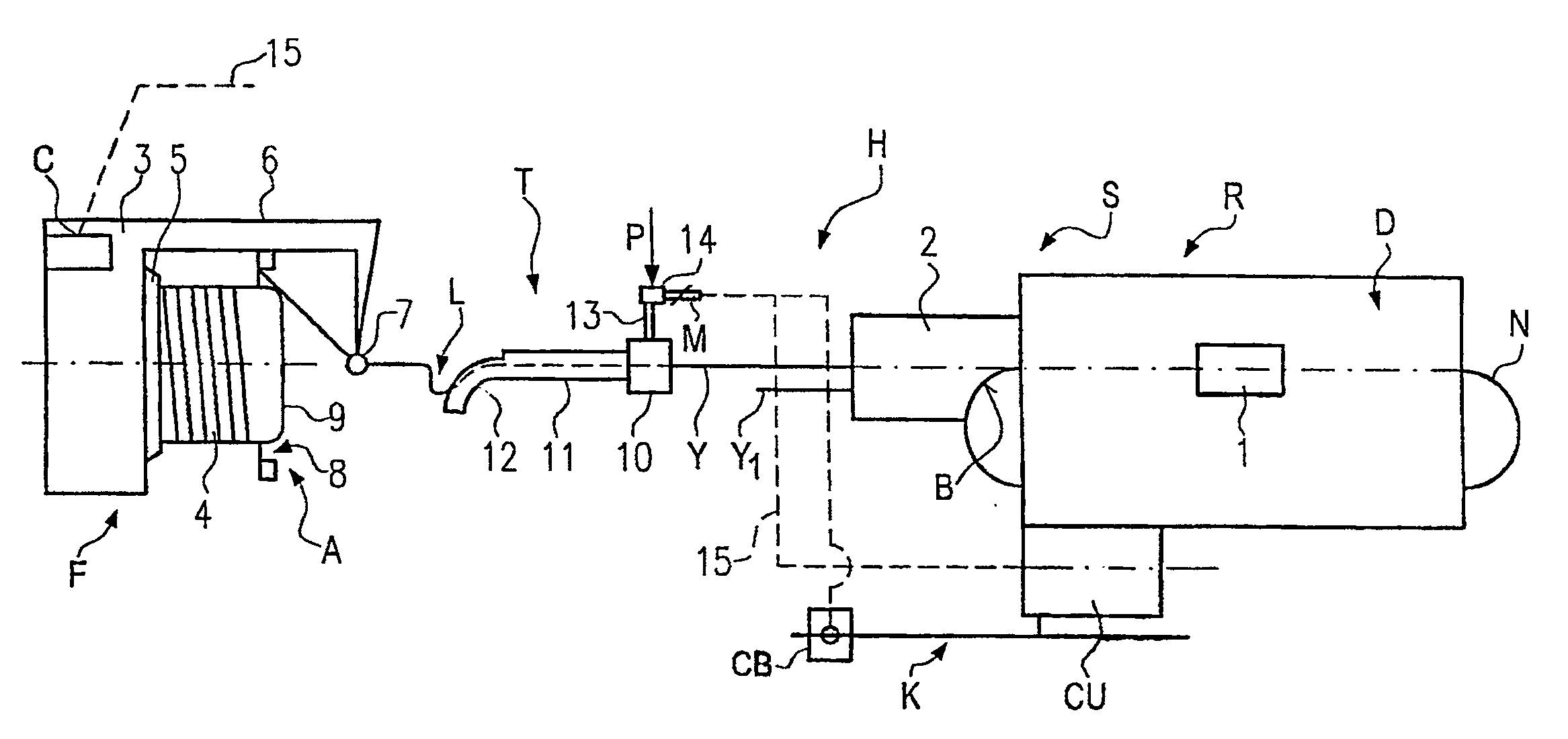
The invention relates to a pneumatic yarn tensioner (T) for rapier looms or knitting machines, wherein the airflow deflection surface (19) for deflecting the yarn (Y, Y1) forms the inner wall of the linear channel A seamless extension (12) through which the yarn passes. The invention also relates to a device (H) for varying the flow rate or pressure of the air flow along the deflection plane (19 )flow.
Owner:IROPA AG (CH)
Yaw rate control with simultaneous maximum deceleration
ActiveUS20120022758A1Decrease in severityPrevent timeCarriage/perambulator accessoriesAnalogue computers for trafficAutomotive engineeringBrake force
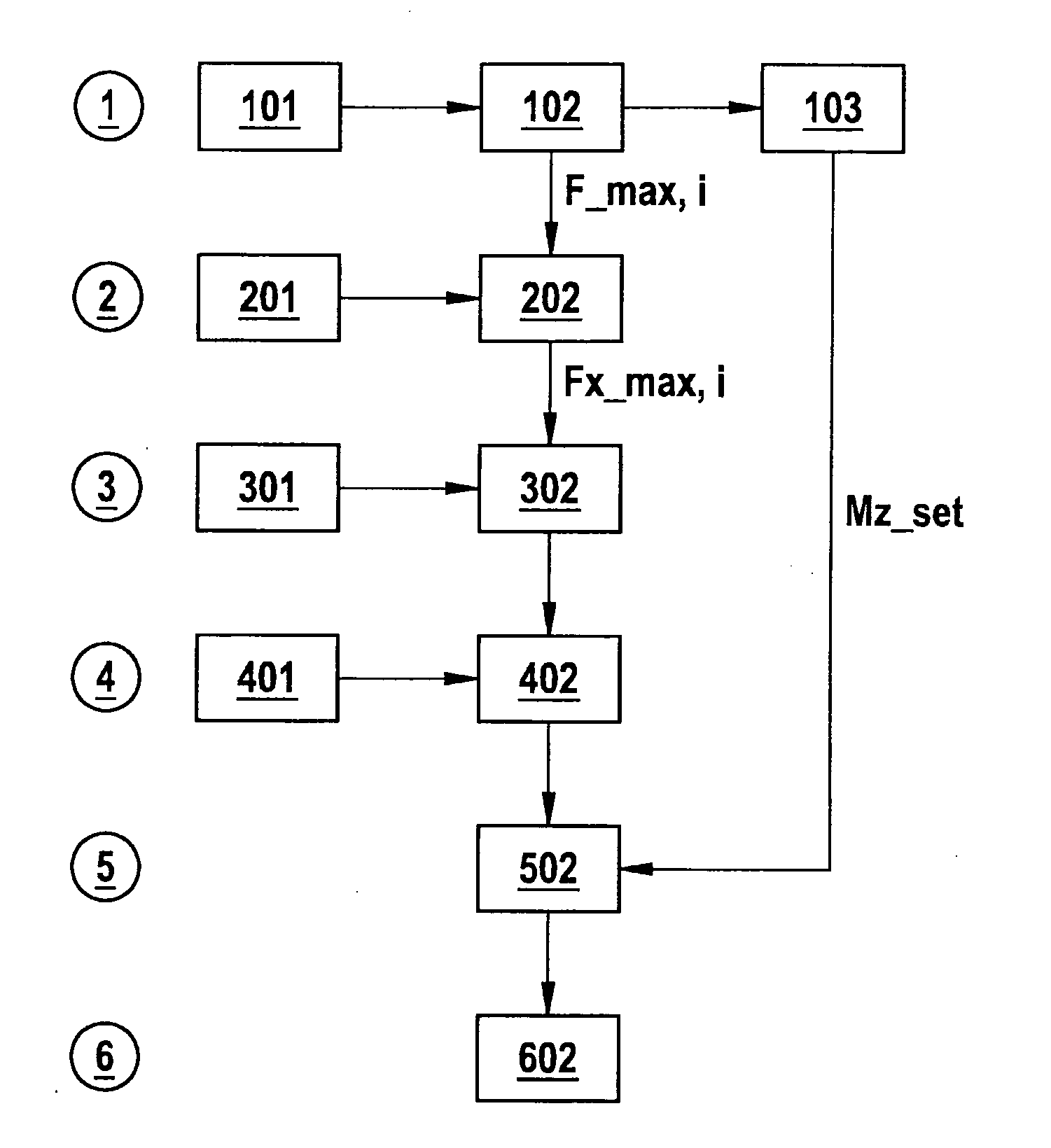
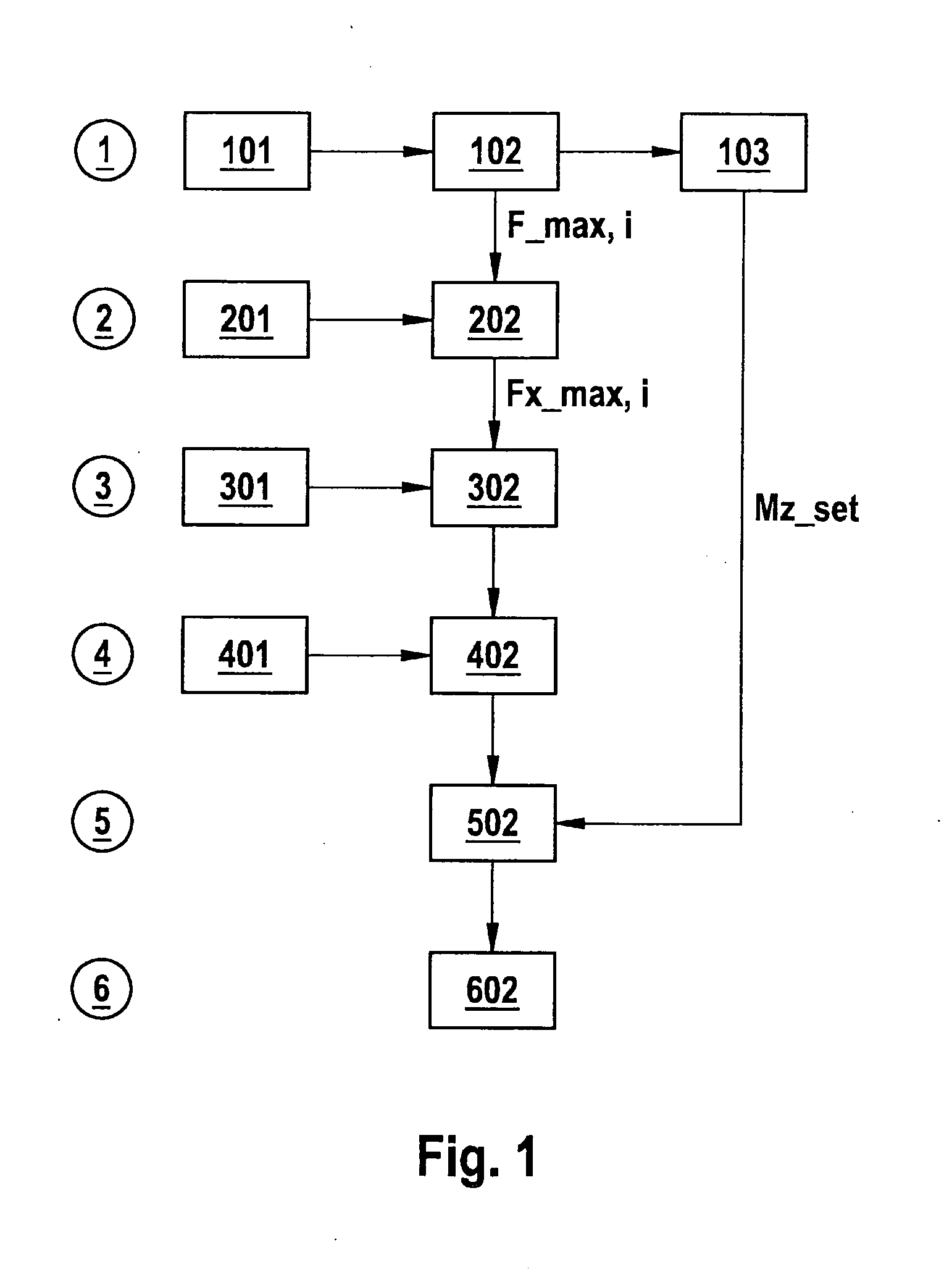
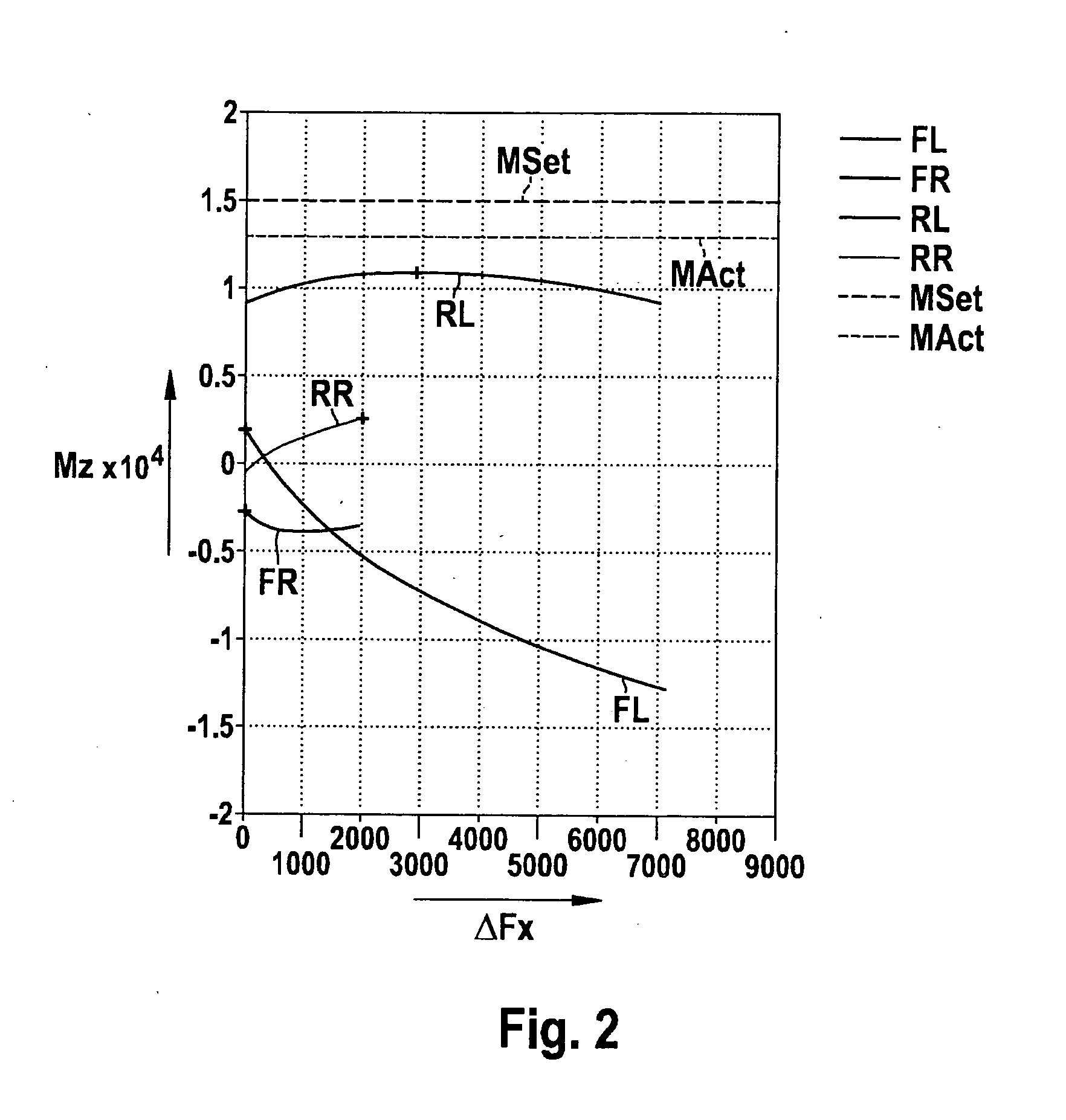
A method for stabilizing a vehicle in a transverse direction, in which: for a first braking force distribution in which each vehicle wheel is braked using the maximum braking force transmittable to the road surface in the current driving situation, the yawing moment acting on the vehicle is ascertained; for at least a second braking force distribution that differs from the first braking force distribution in that at least one wheel is not braked using the maximum braking force, the yawing moment acting on the vehicle is ascertained; a setpoint yawing moment is ascertained; and from at least the first and second braking force distributions, the braking force distribution whose associated yawing moment comes closest to the setpoint yawing moment is set at the vehicle.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
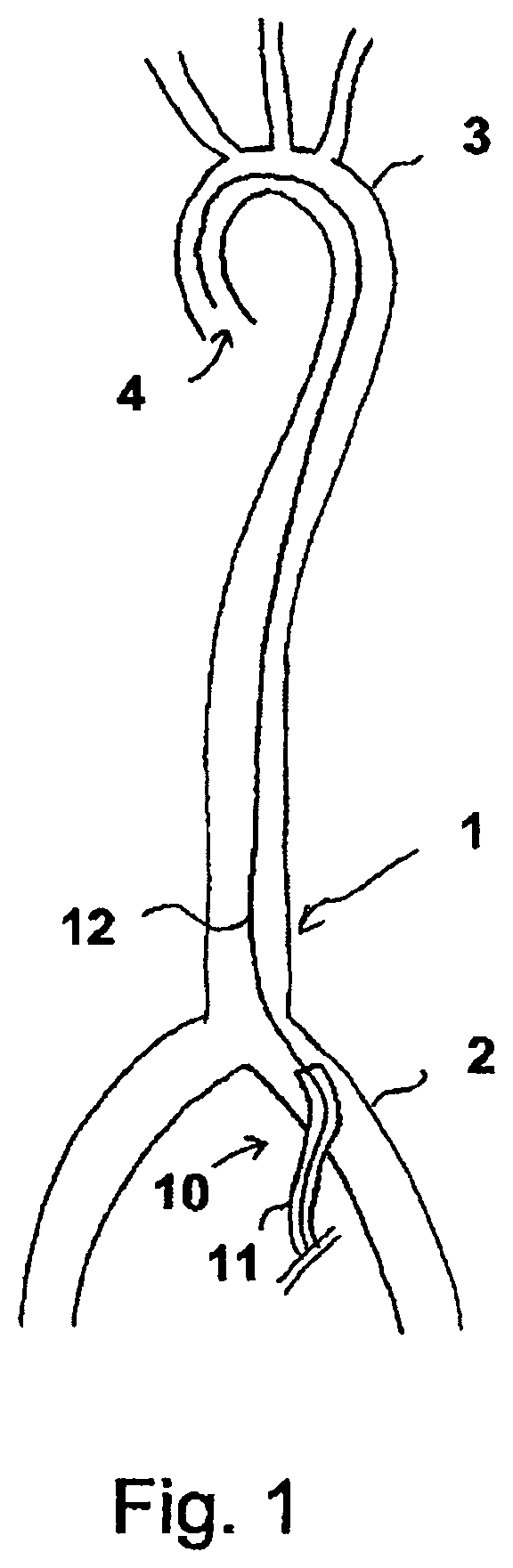
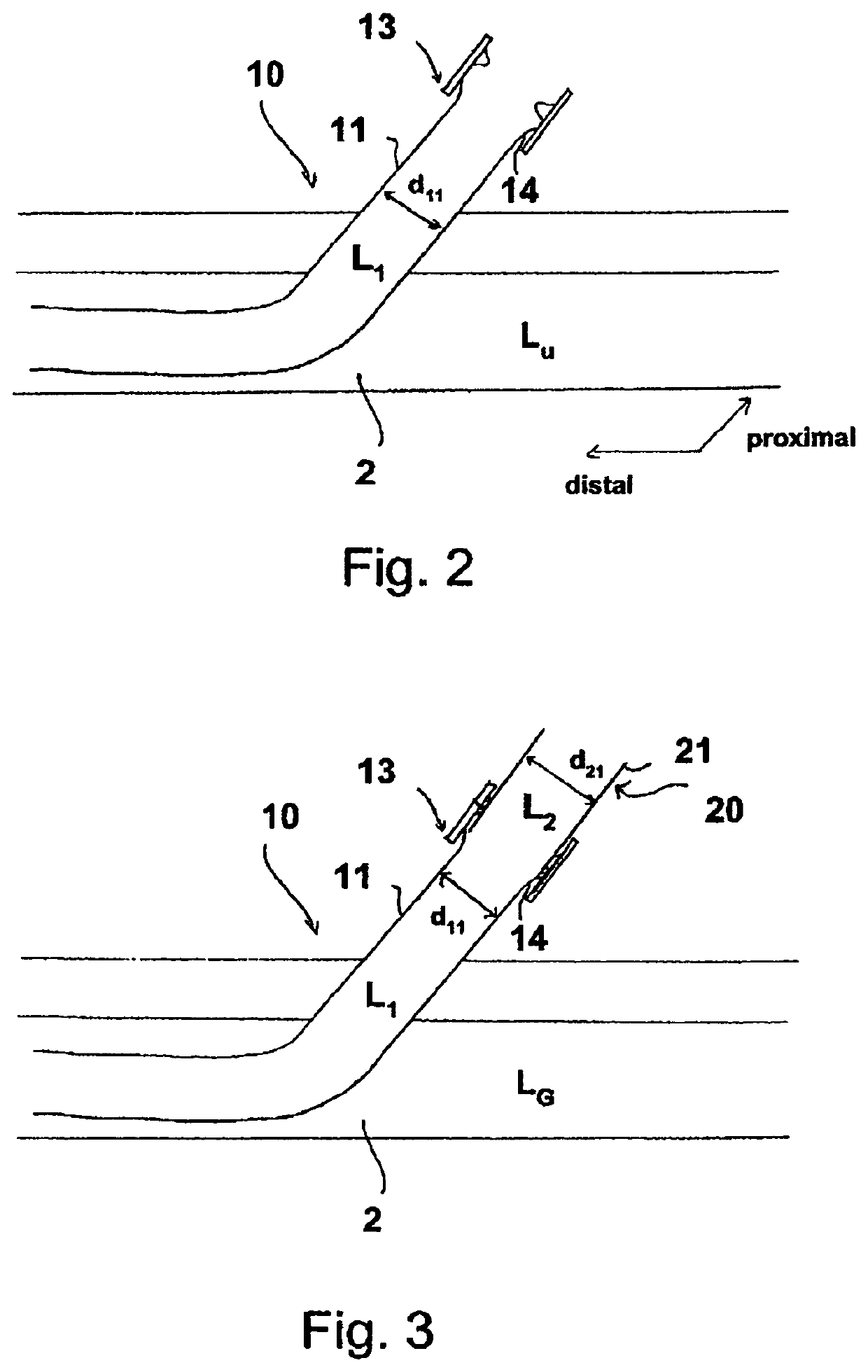
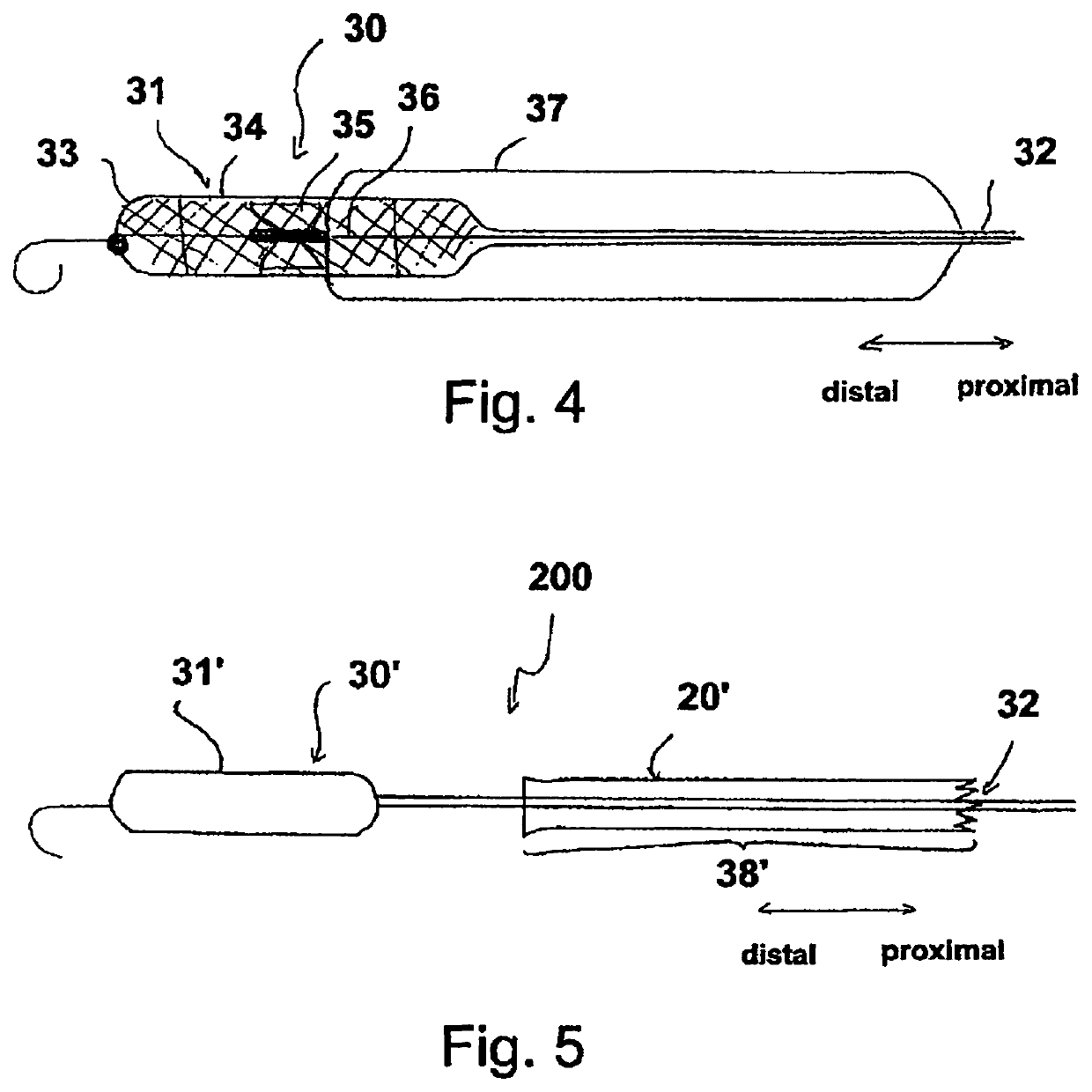
Sheath device for inserting a catheter
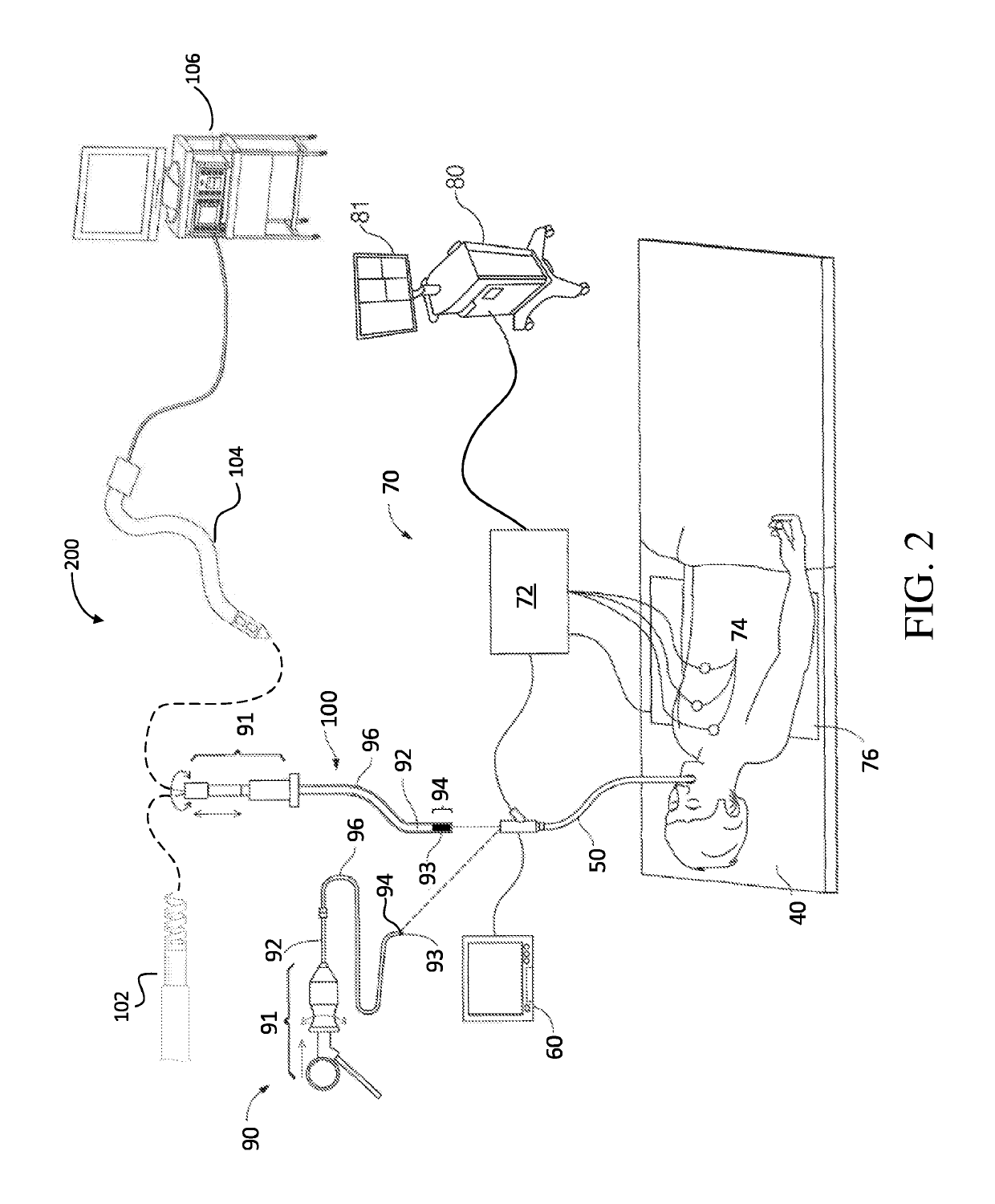
A sheath device for inserting a catheter into a patient's body is described. The device has a first sheath with a proximal end and a distal end. When the device is used as intended, the distal end of the first sheath is provided for arrangement in the patient's body and the proximal end of the first sheath is provided for arrangement outside the patient's body. The first sheath comprises a tubular section and a sheath housing, which is disposed at the proximal end of the section and has a receiving channel for a strand-shaped body. The device solves the problem of reliably fixing a second sheath or a catheter with respect to the first sheath by providing a clamping element on the receiving channel for fixing a strand-shaped body in the receiving channel by way of clamping.
Owner:ECP ENTWICKLUNGSGMBH
Medical suturing needle
InactiveCN101835429AImprove the piercing effectLow risk of injurySurgical needlesBiological bodySuturing needle
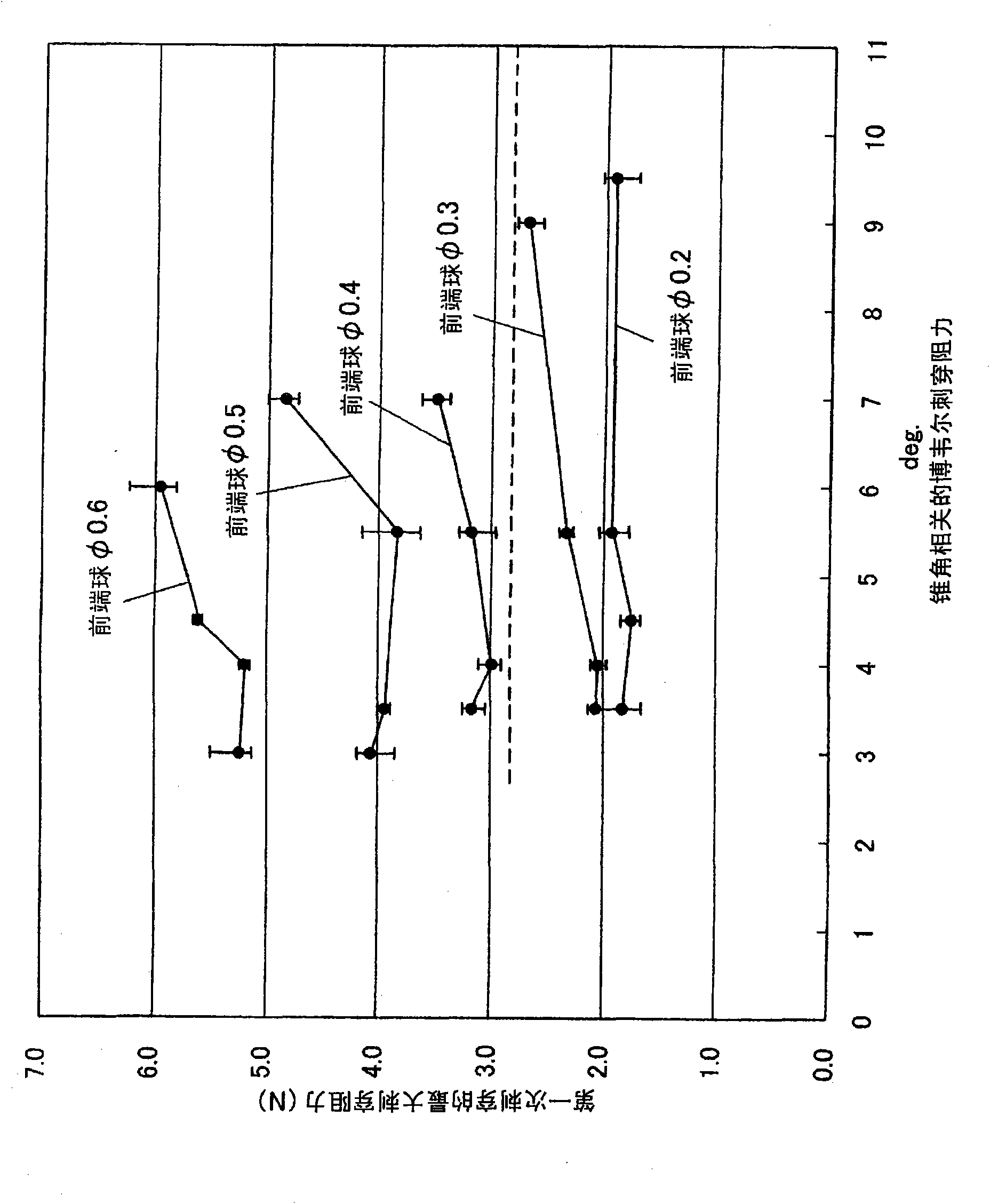
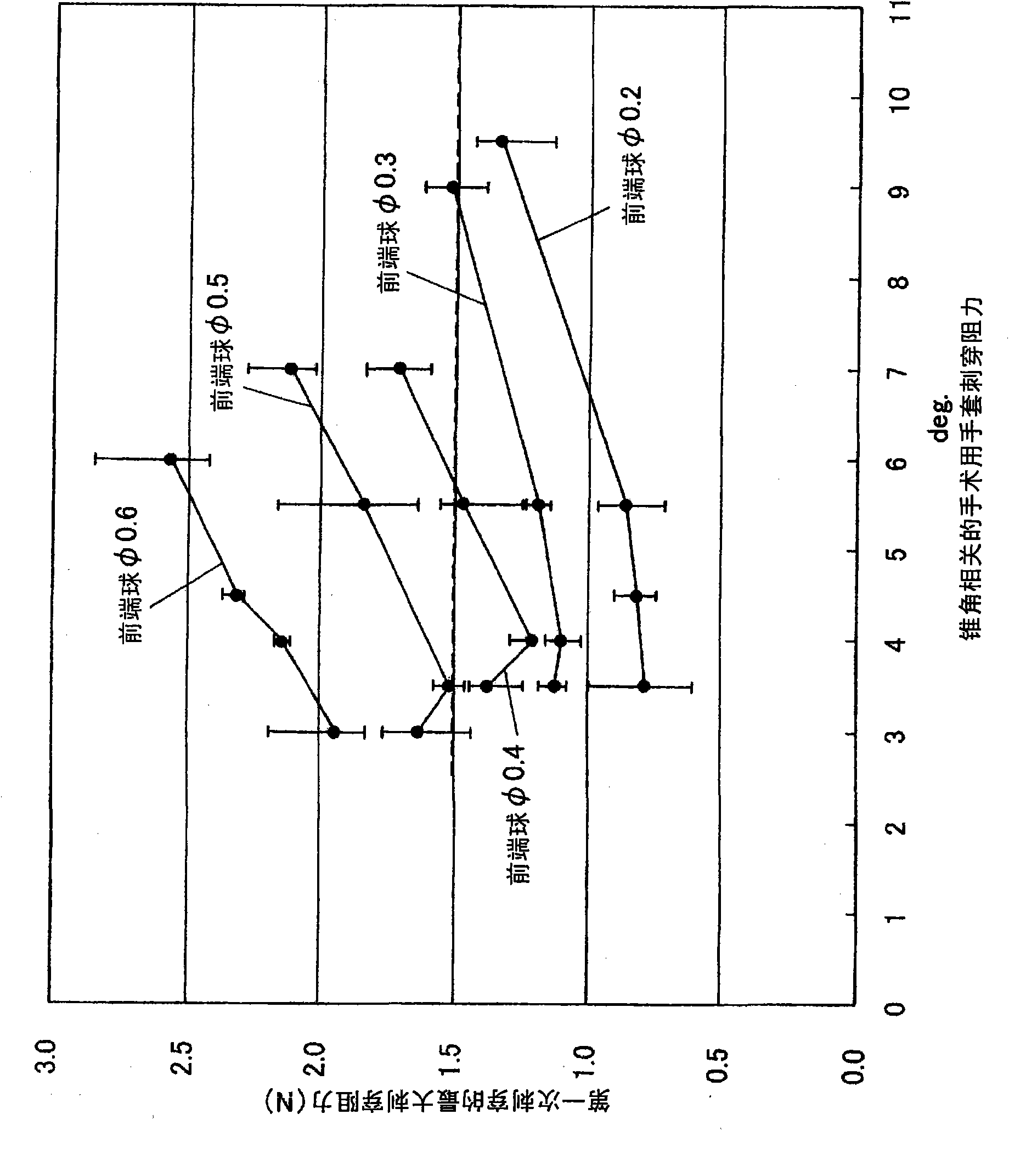
Provided is a medical suturing needle or a round needle having a circular section, which is balanced between the magnitude of an insertion resistance to living tissues and the difficulty in damaging gloves, thereby to improve the safety. The medical suturing needle (A) comprises a ball-shaped needle tip (1), a tapered portion (2) continuing to the needle tip (1), and a trunk portion (3) continuing to the tapered portion (2). The ball of the needle tip (1) has a diameter of 0.25 mm to 0.34 mm, and the tapered portion (2) has a tapering angle of 8.5 degrees to 9.4 degrees.
Owner:MATSUTANI SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
Blow pipe dart
InactiveUS9541358B2Easy to useShorten speedAmmunition projectilesBlow gunsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An elastomeric blow pipe dart (10) including: a generally circular body portion (12); a tapered portion (16) extending from the generally circular body portion (12); and a nose (18) having a smaller diameter than the tapered portion (16) and extending from the tapered portion (16) to a tip (20). The blow pipe dart (10) may comprise a soft rubber, and the nose (18) may define an end bore (26) so that air passes through the nose (18) when the dart (10) is launched.
Owner:HEPBURN RALPH ROBERTSON
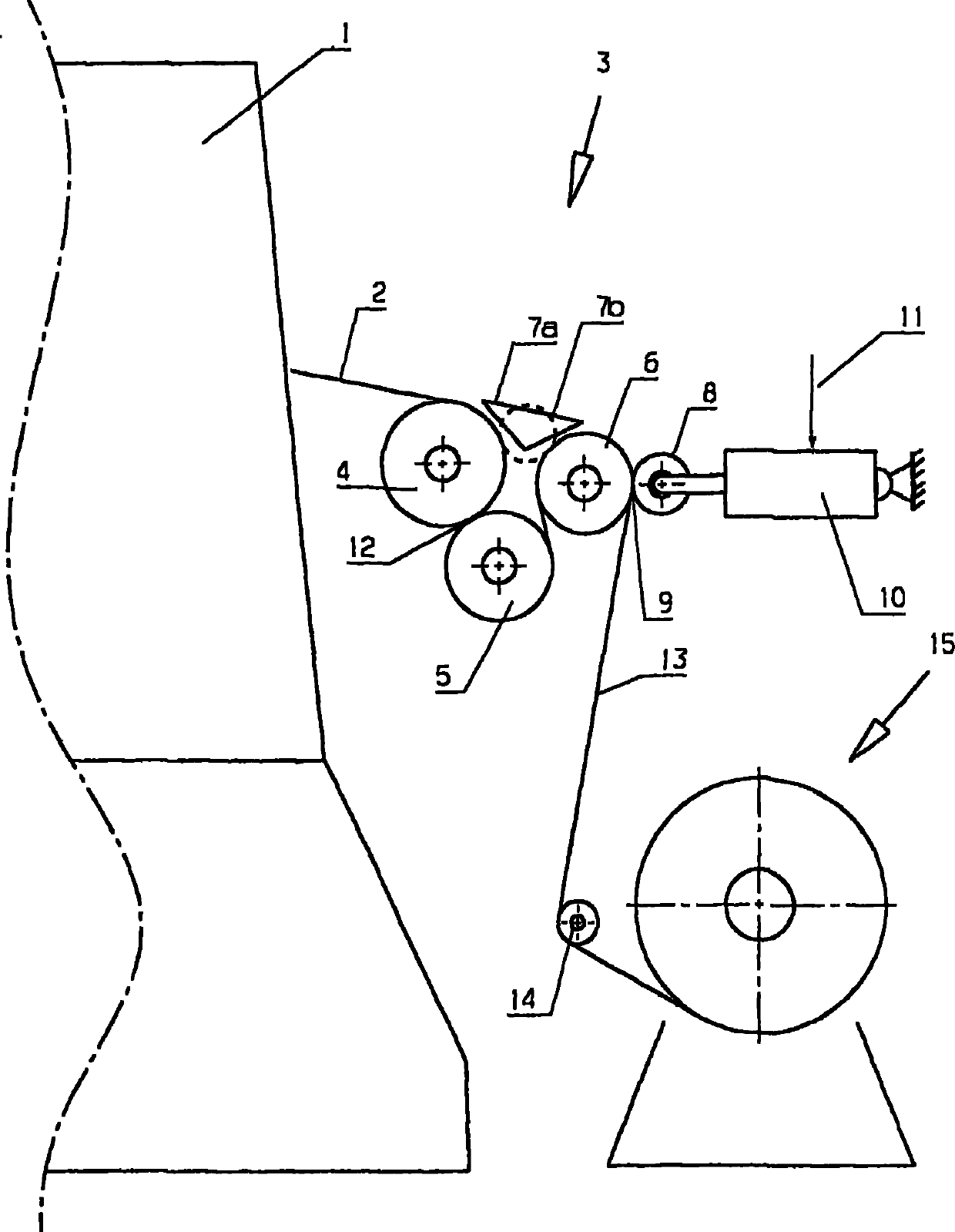
Device for drawing out planar woven fabric webs from textile machines, especially warp knitting machines
The present invention relates to a device for drawing a fabric breadth(2) of a surface-shaped textile from a textile machine(1), especially tricot machine. The device is provided with a plurality of leading-out rollers (4-6), the breadth path of the textile breadth (2) is extended on the surfaces of the leading-out rollers (4-6),and the breadth path is led to a textile accommodating piece (15) in the processing direction after passing the leading-out rollers (4-6).The device is expected to convey textile breadth of elastic textiles with high quality. Clamping equipment is arranged on the last leading-out roller (6) of the processing direction, and a clamping clamp (9) is formed by the clamping equipment and the leading-out roller (6),and the breadth path is extended through the clamping clamp (9).
Owner:KARL MAYER STOLL R&D GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com