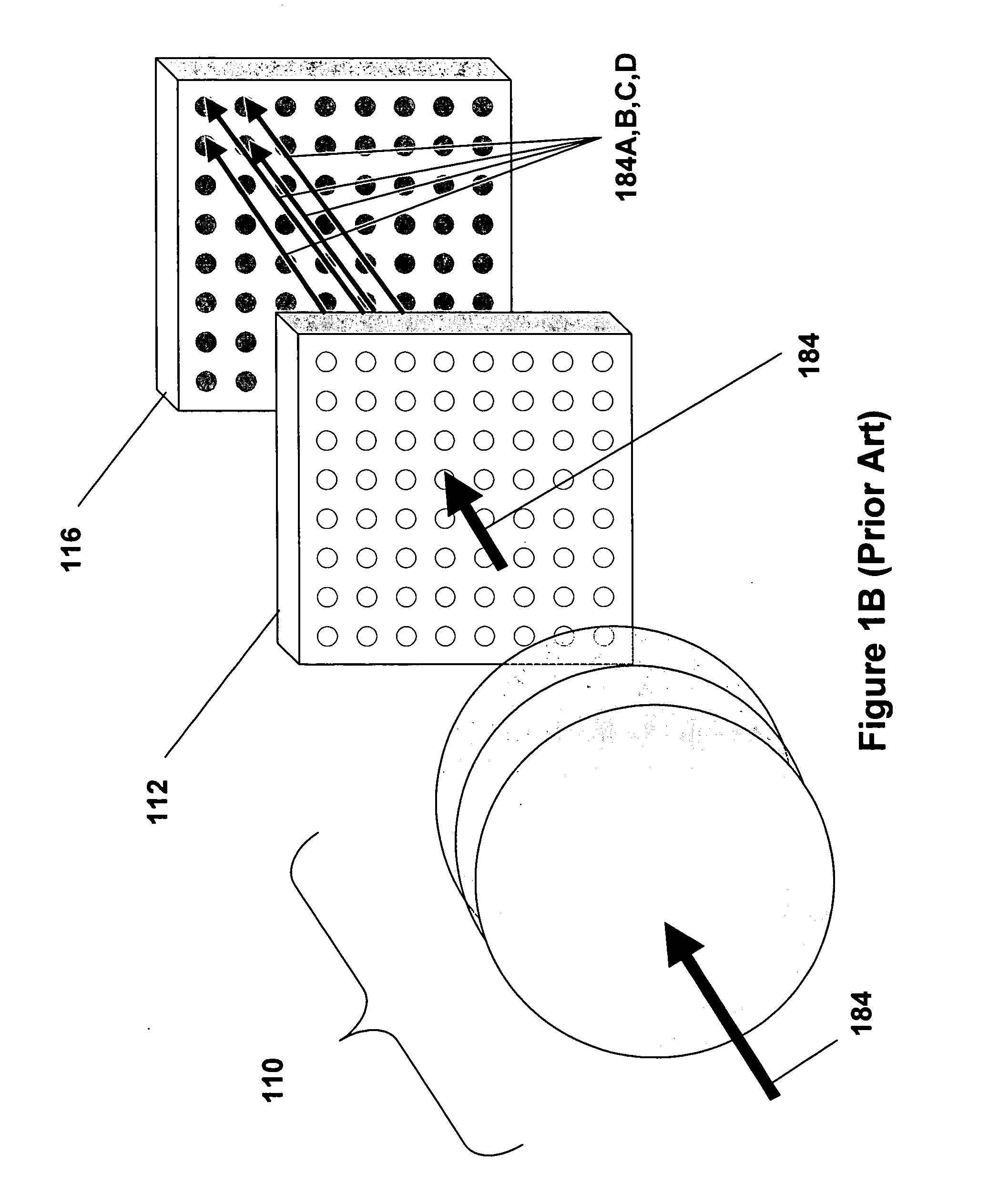
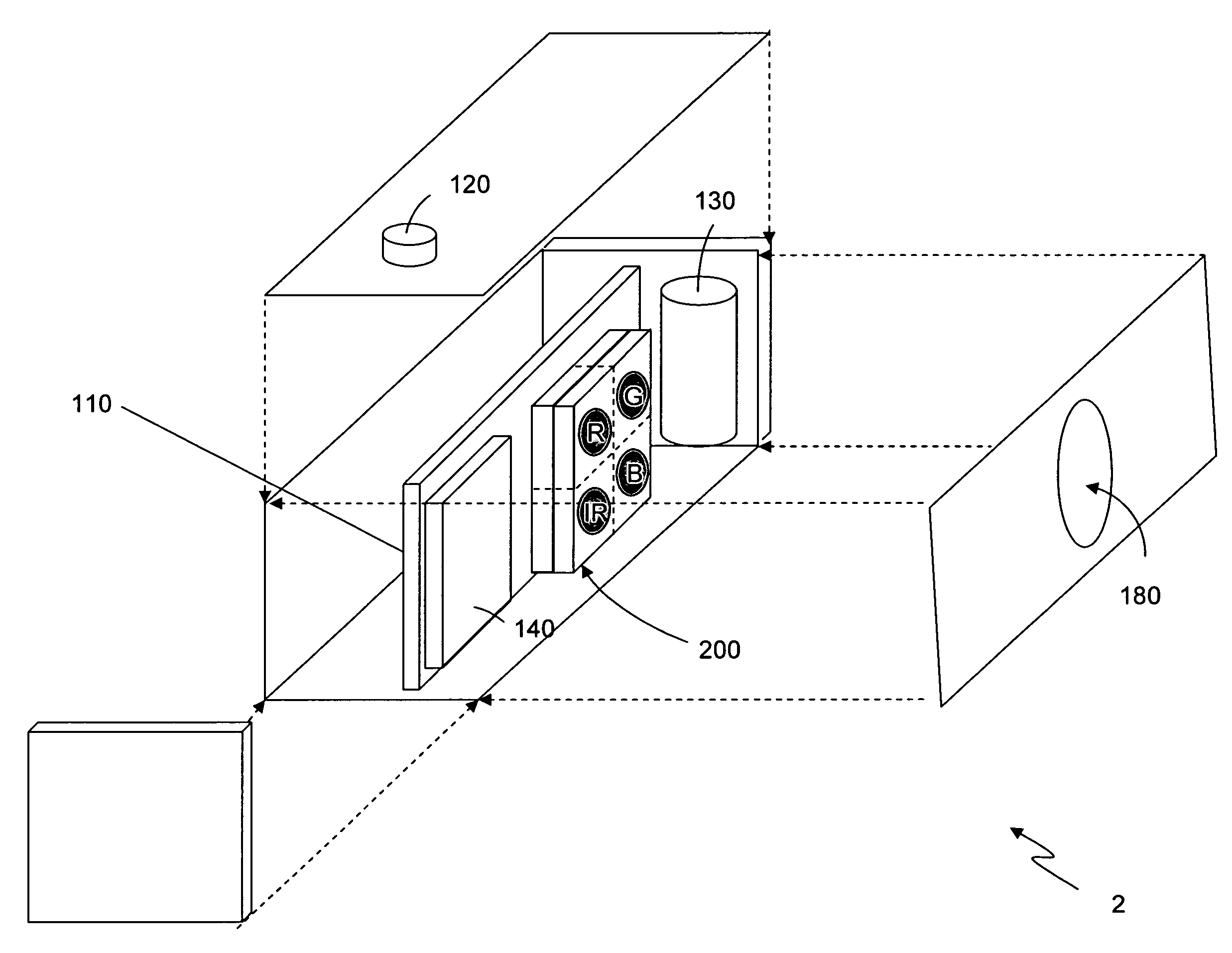
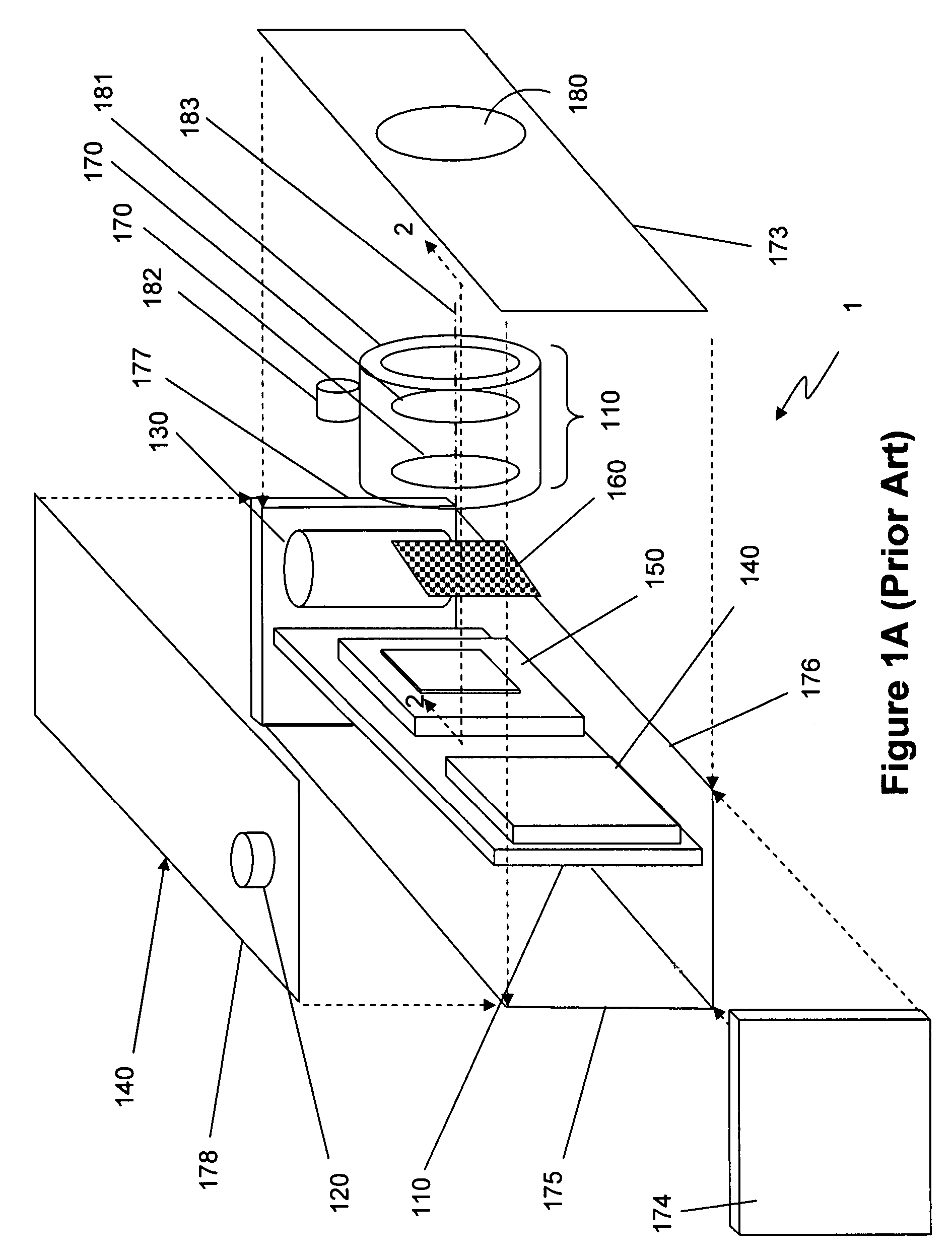
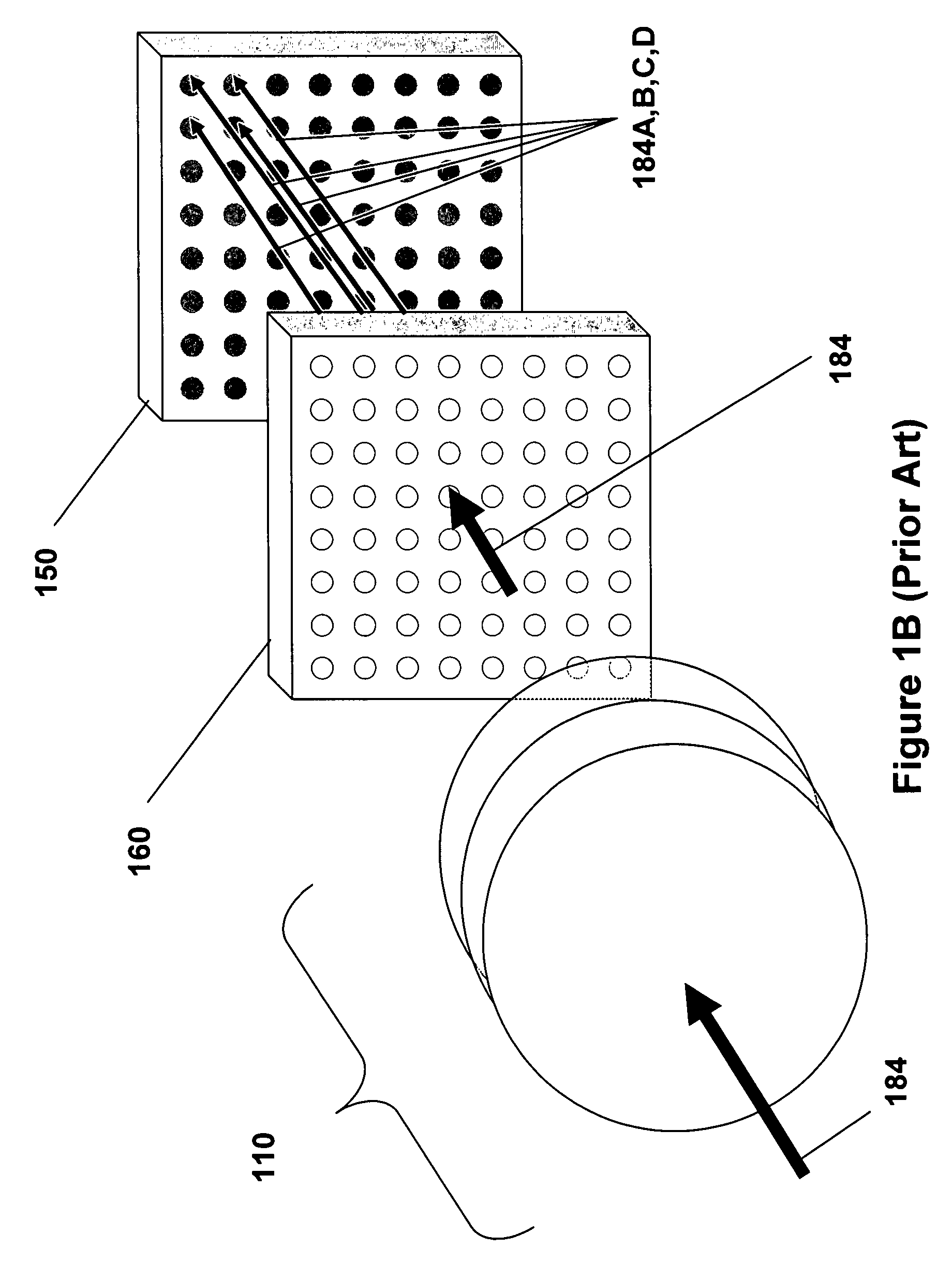
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8314results about "Focusing aids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
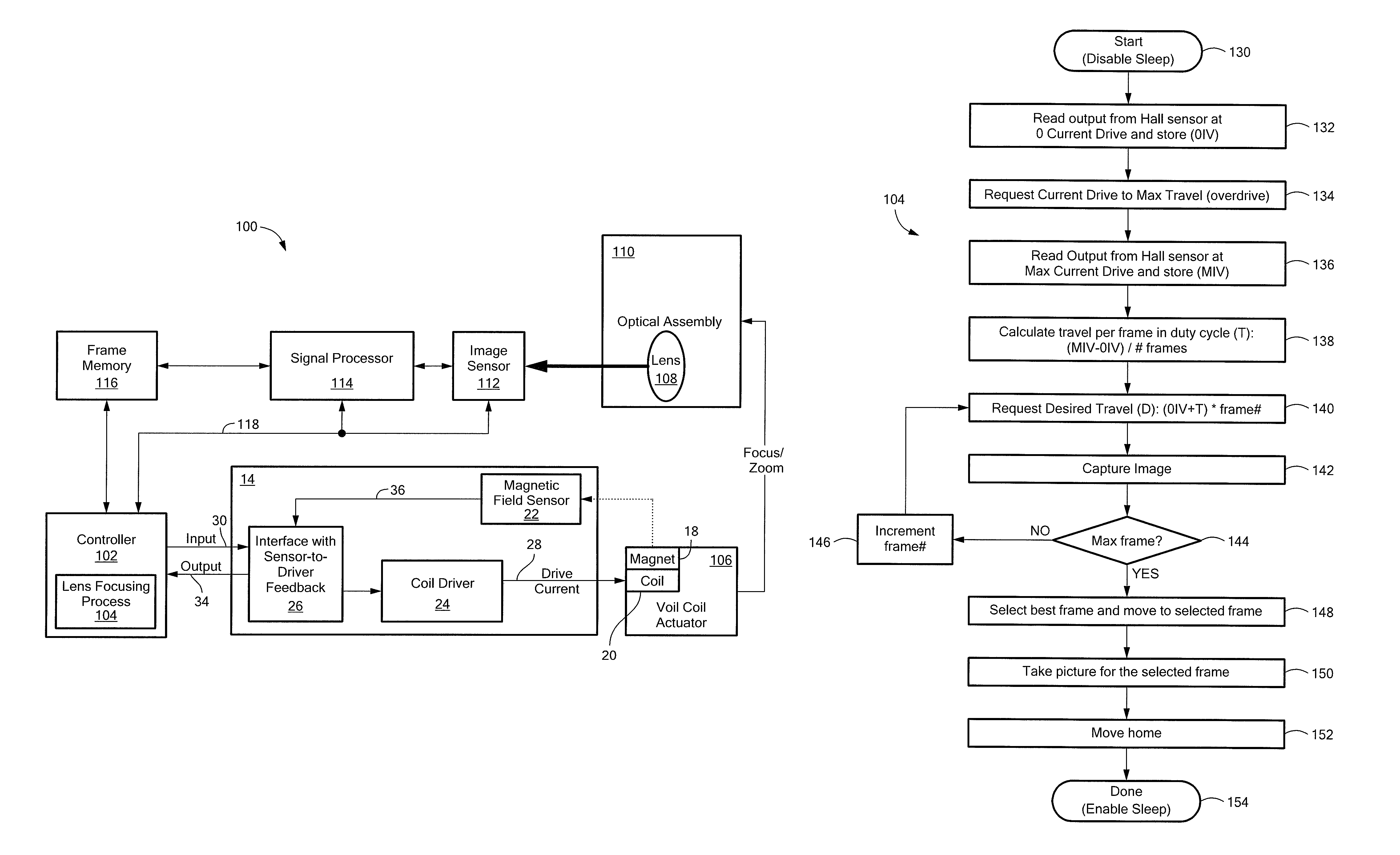
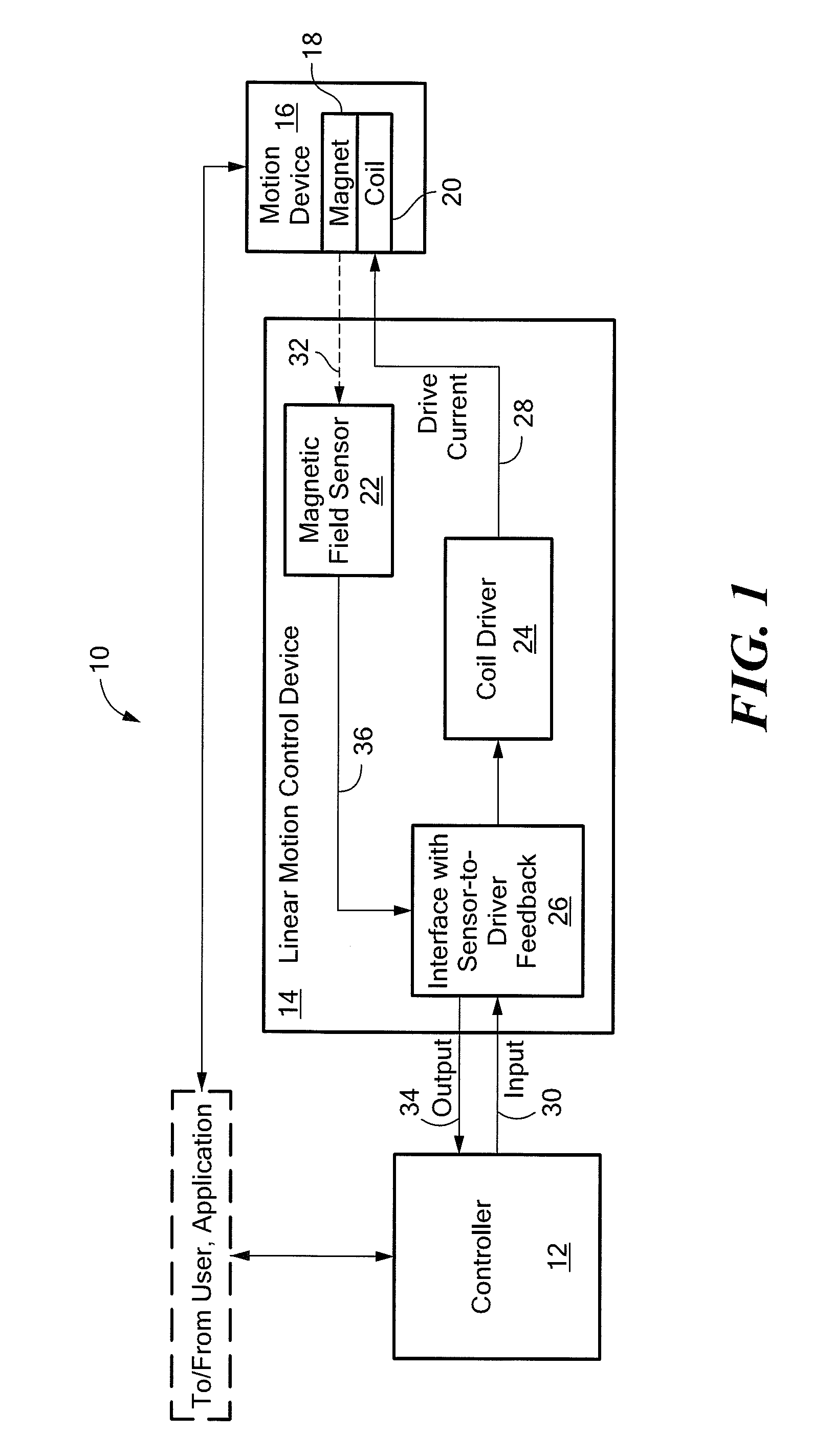
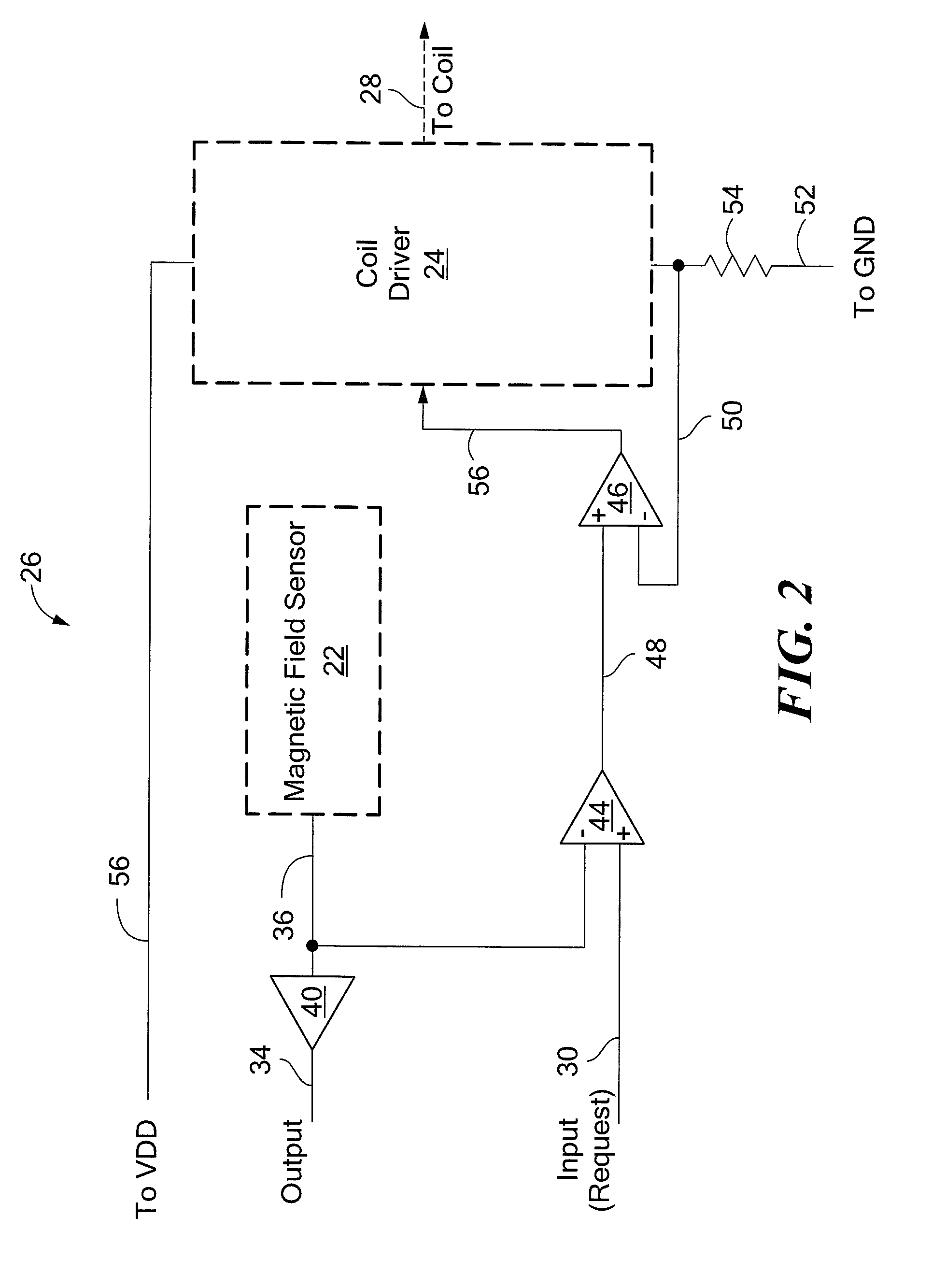
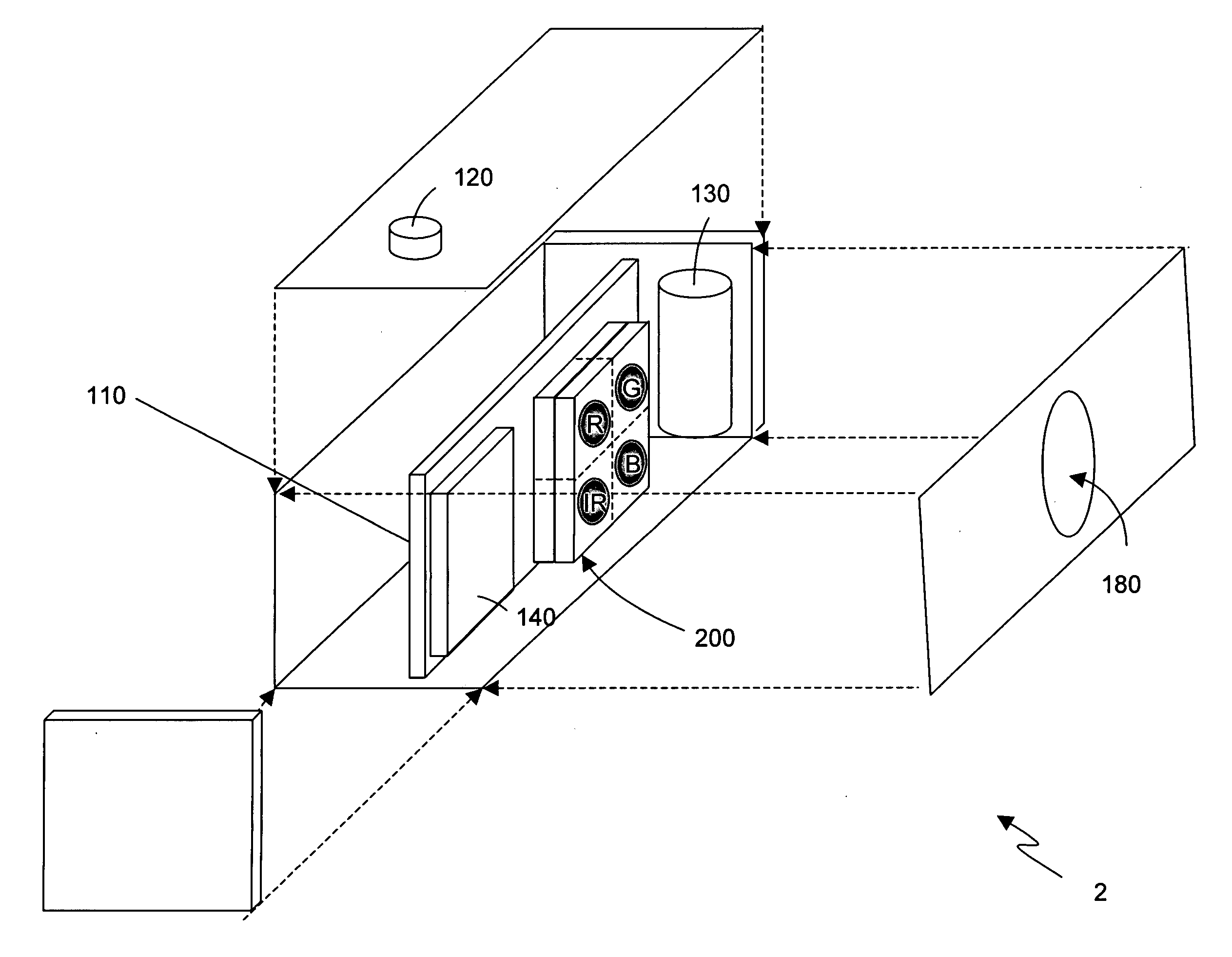
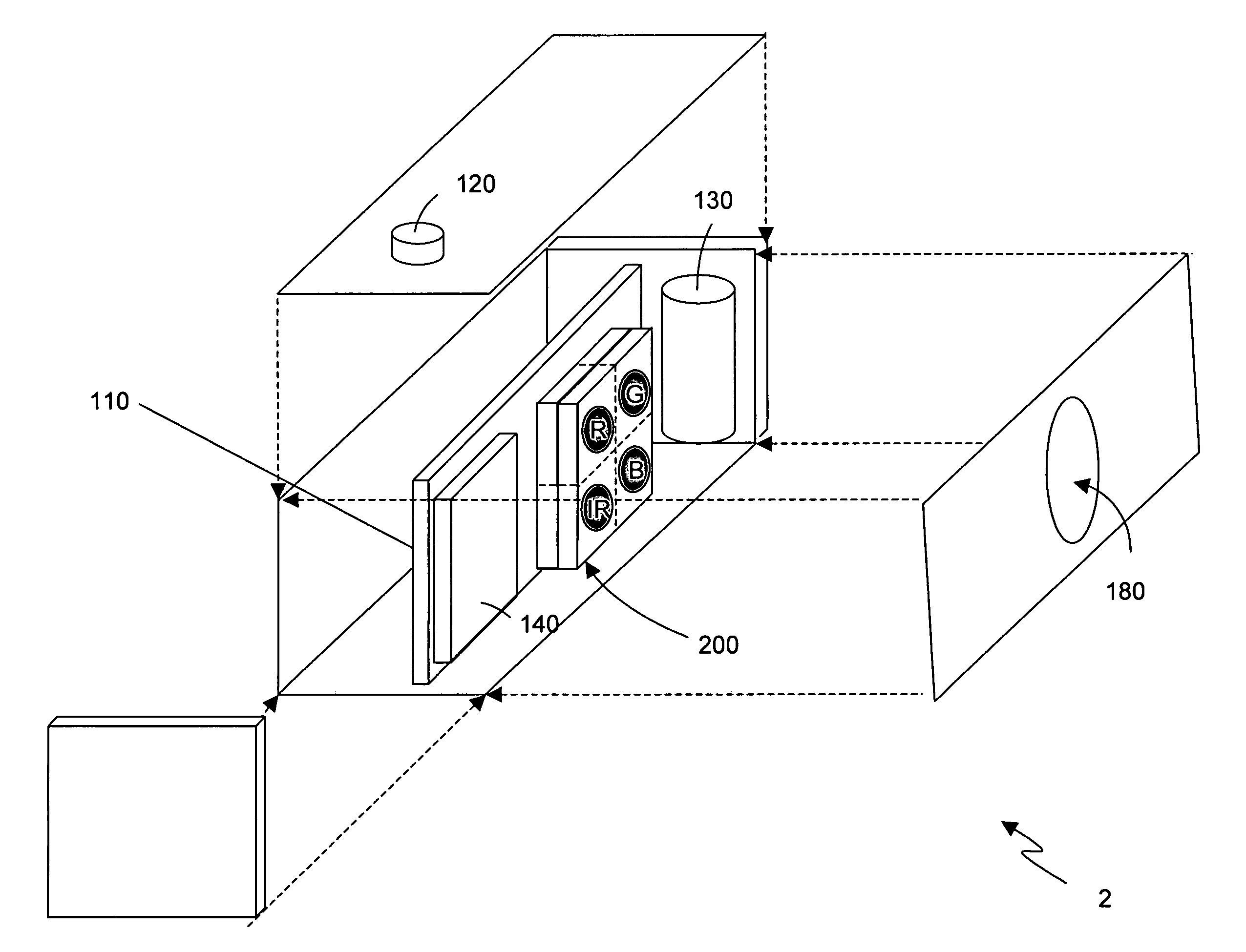
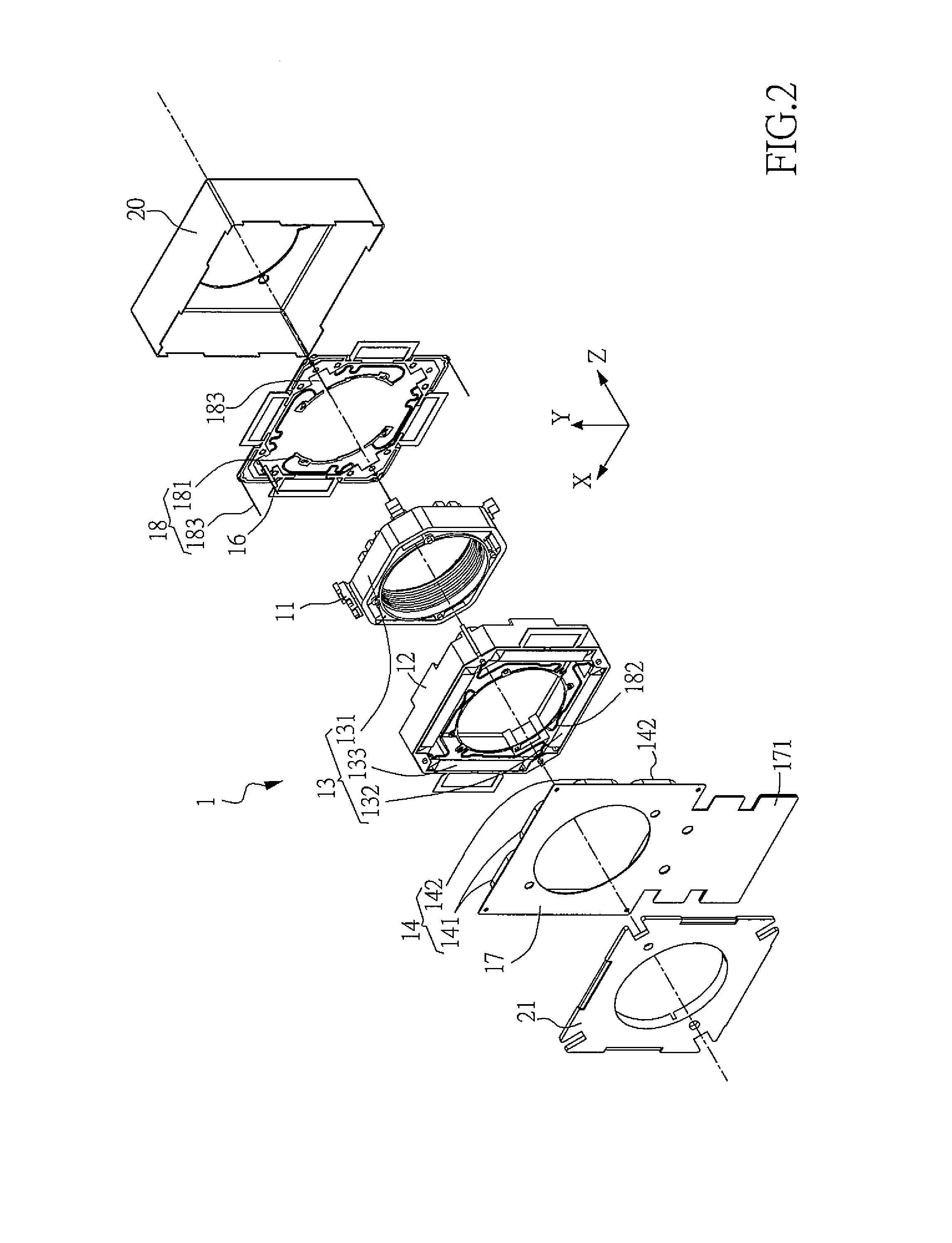
Hall-effect based linear motor controller
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
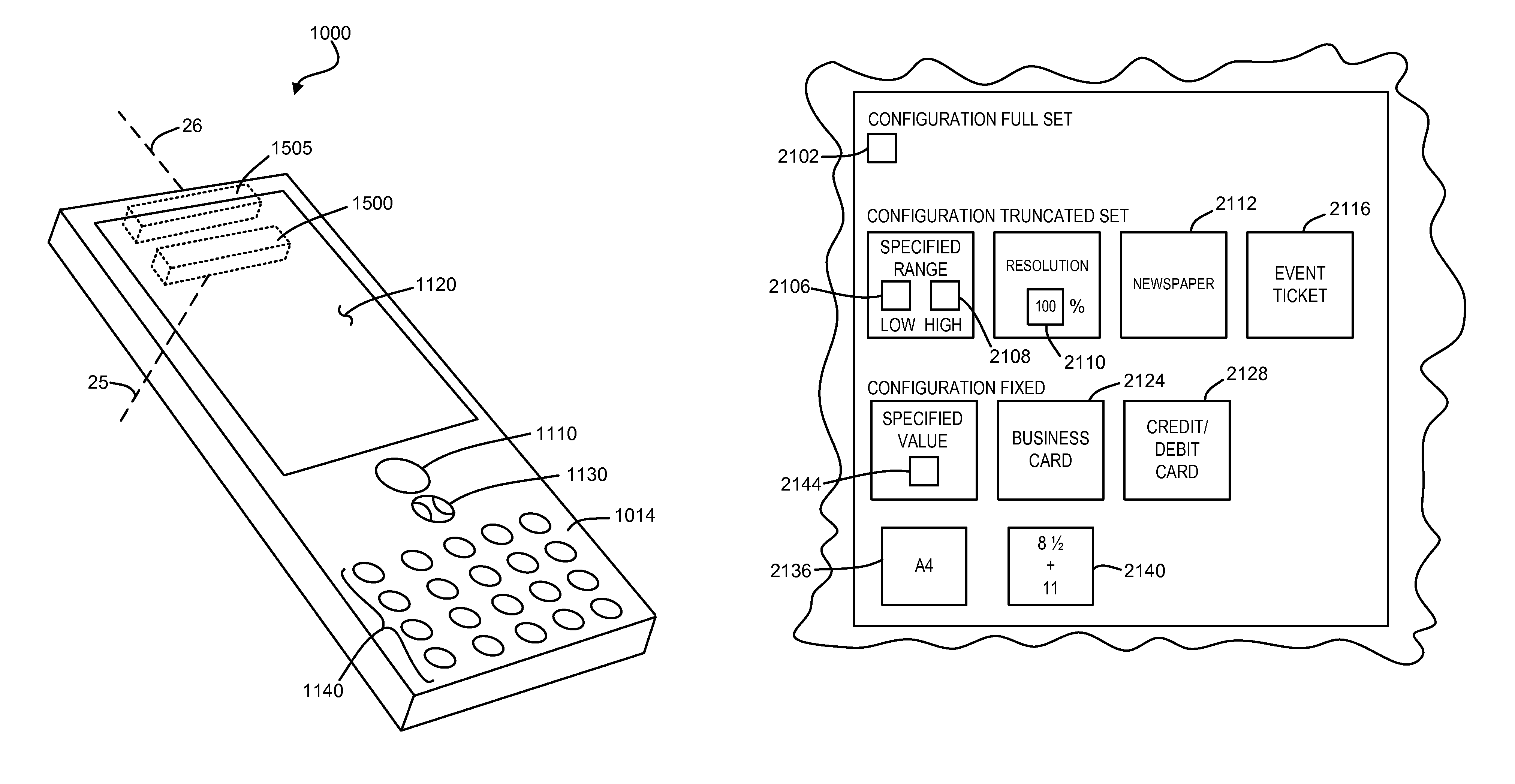
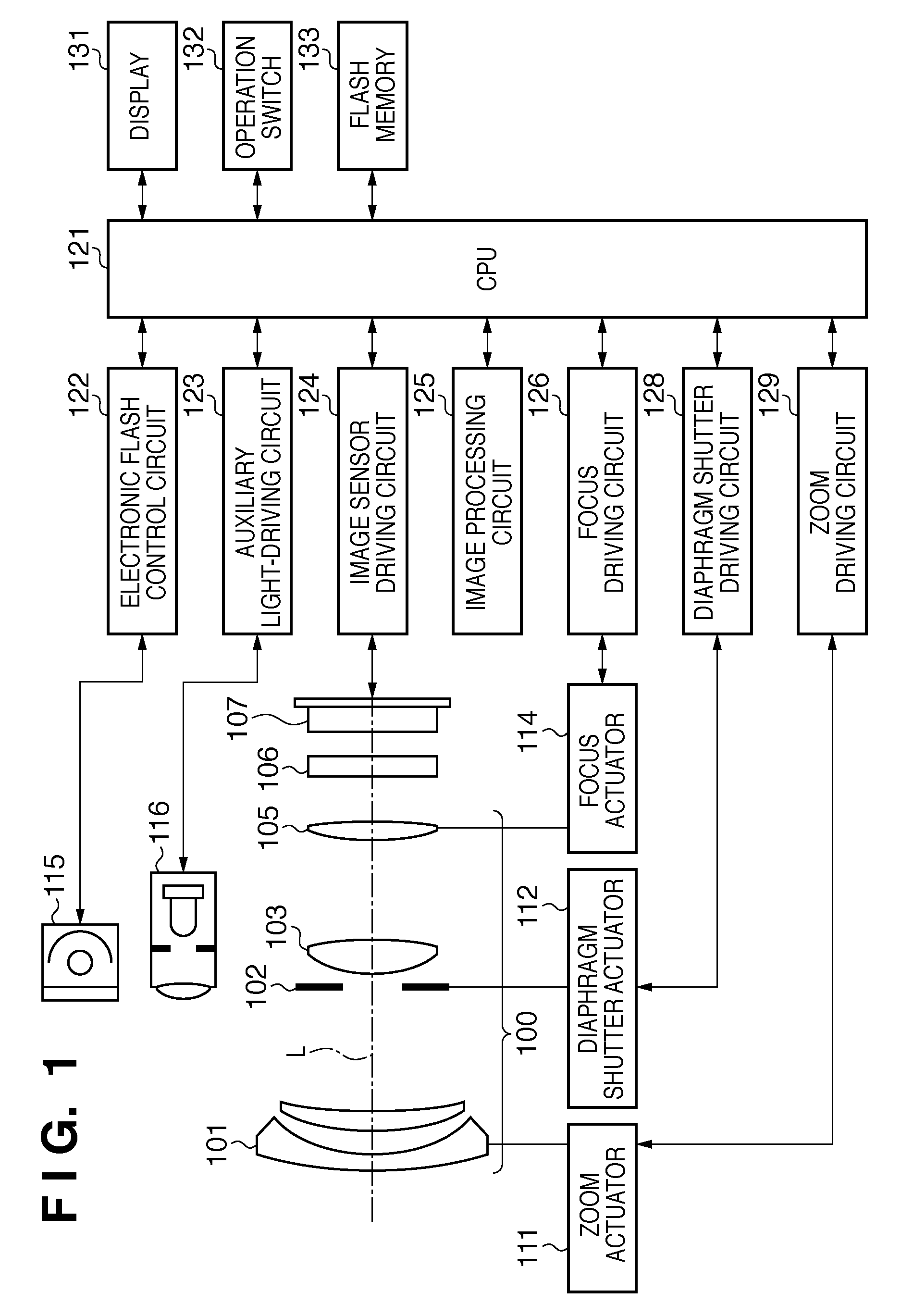
Imaging terminal having focus control
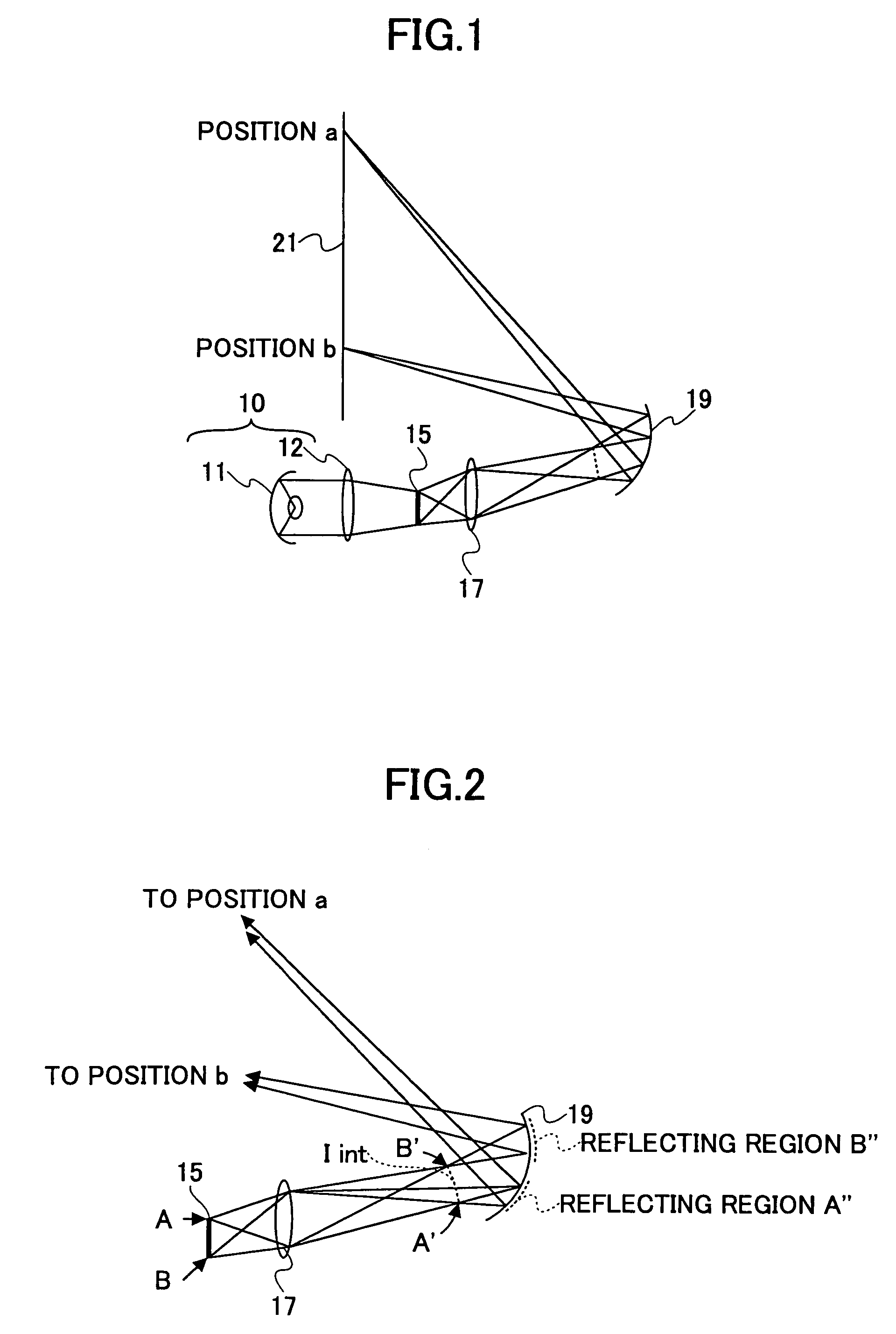
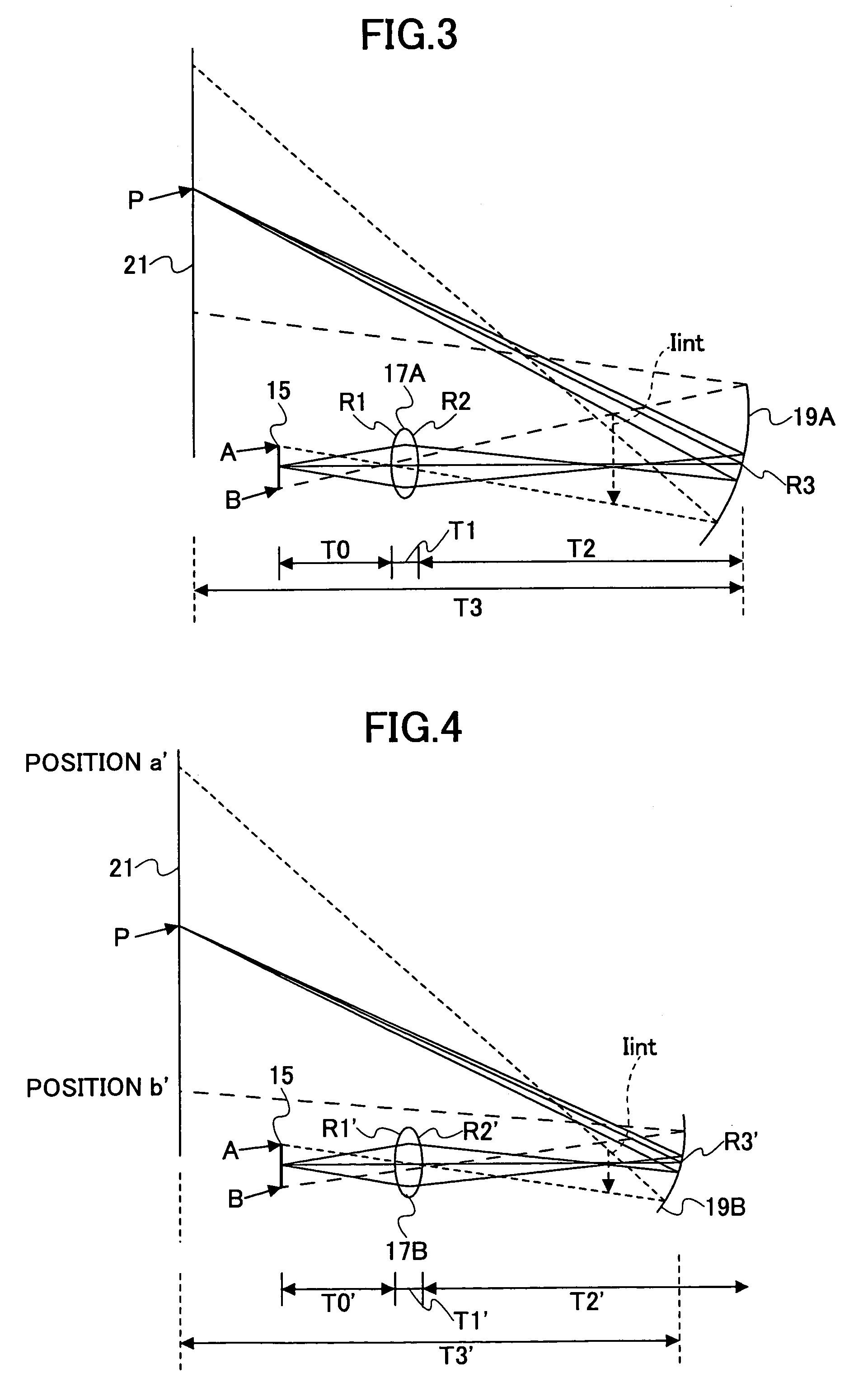
ActiveUS8692927B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging lensBiological activation
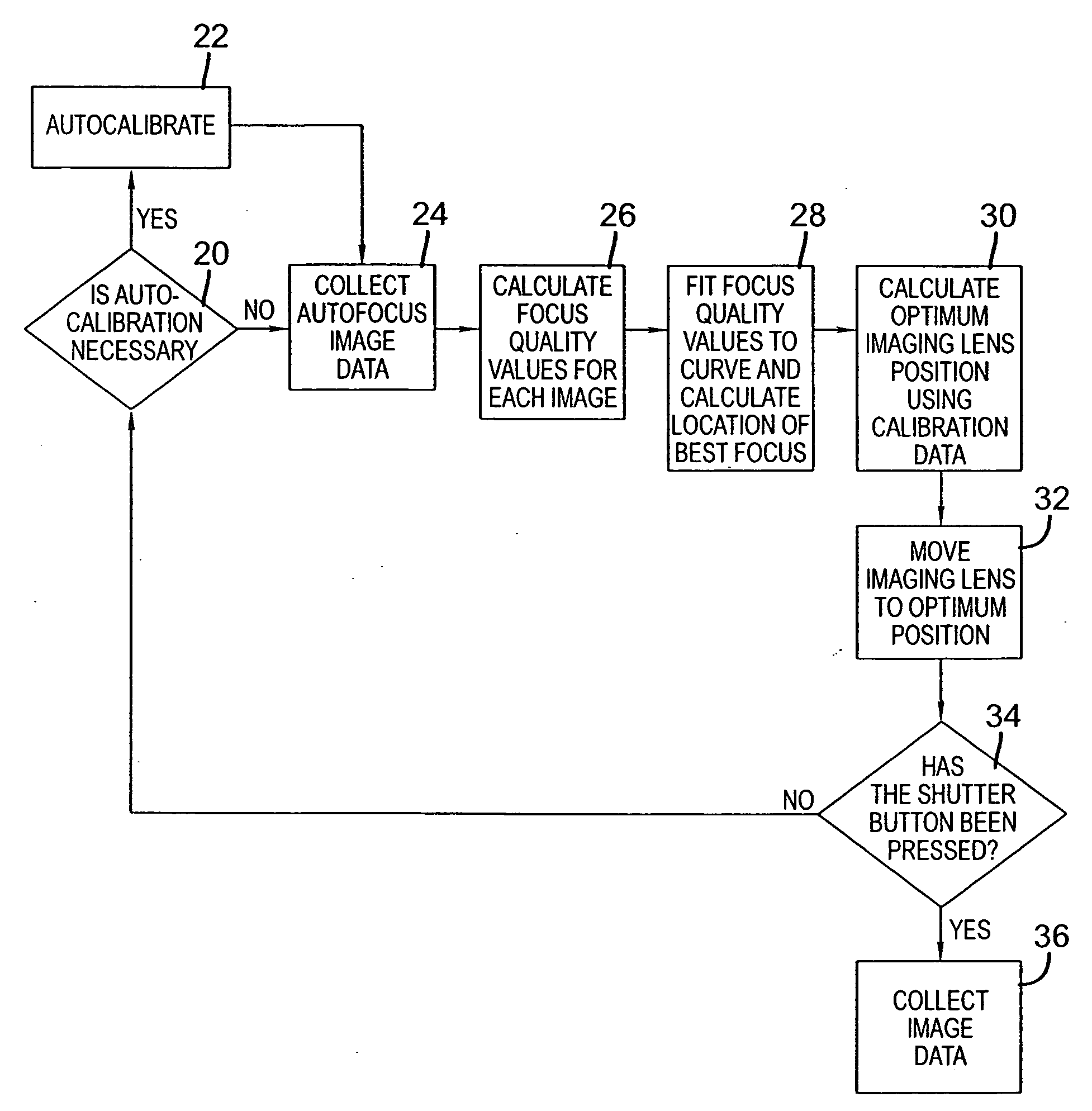
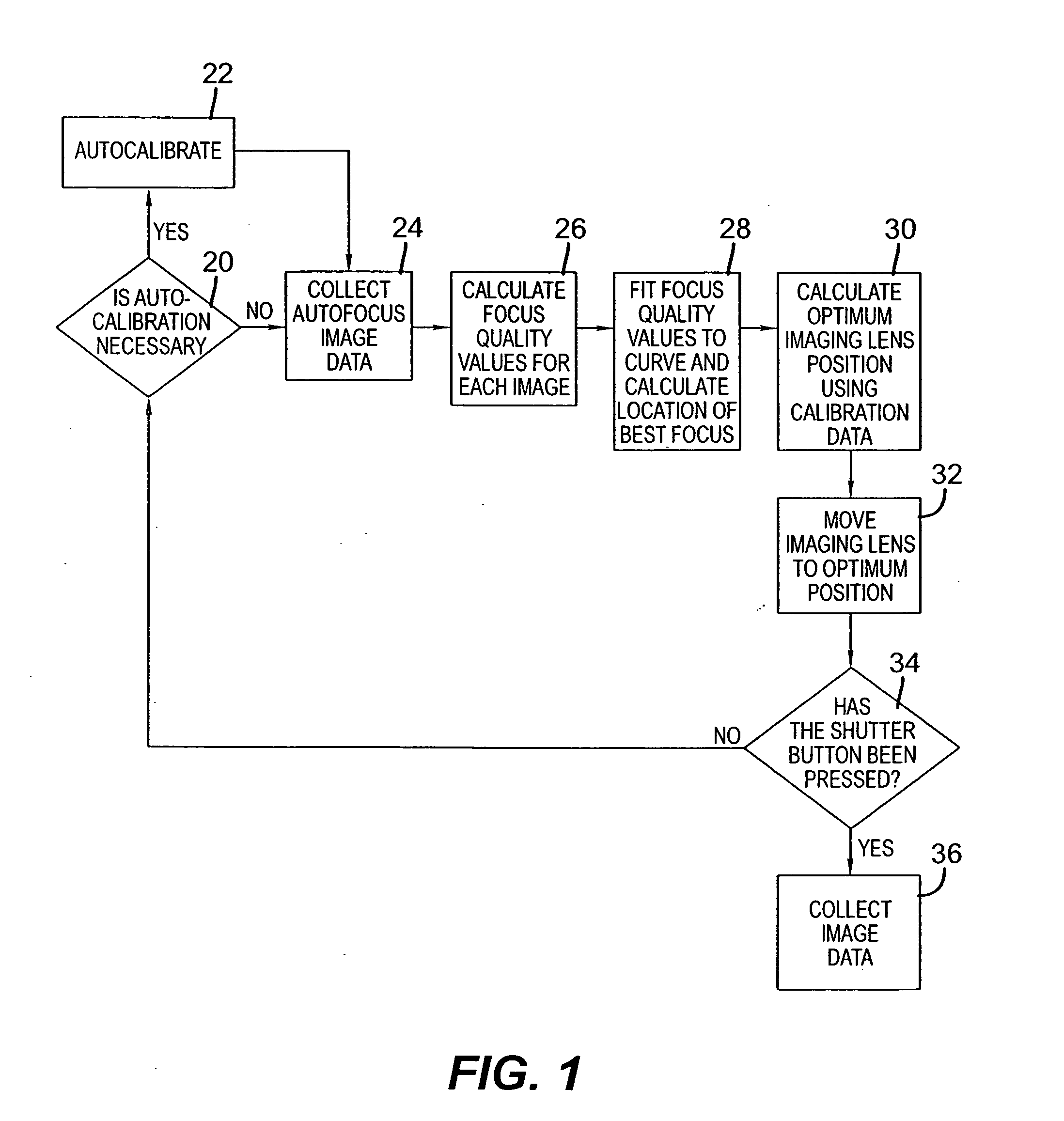
There is set forth herein an imaging terminal having an image sensor array and a variable lens assembly for focusing an image onto the image sensor array. In one embodiment, an imaging terminal can include one or more focusing configuration selected from the group comprising a full set focusing configuration, a truncated set focusing configuration and a fixed focusing configuration. When a full set focusing configuration is active, a full set of candidate focus settings can be active when the imaging terminal determines a focus setting of the terminal responsively to a trigger signal activation. When a truncated set focusing configuration is active, a truncated range of candidate focus settings can be active when the imaging terminal determines a focus setting of the terminal responsively to a trigger signal activation. When a fixed focusing configuration is active, the focus setting of the imaging lens assembly can be fixed so that a predetermined lens assembly focus setting is active when a trigger signal is active.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
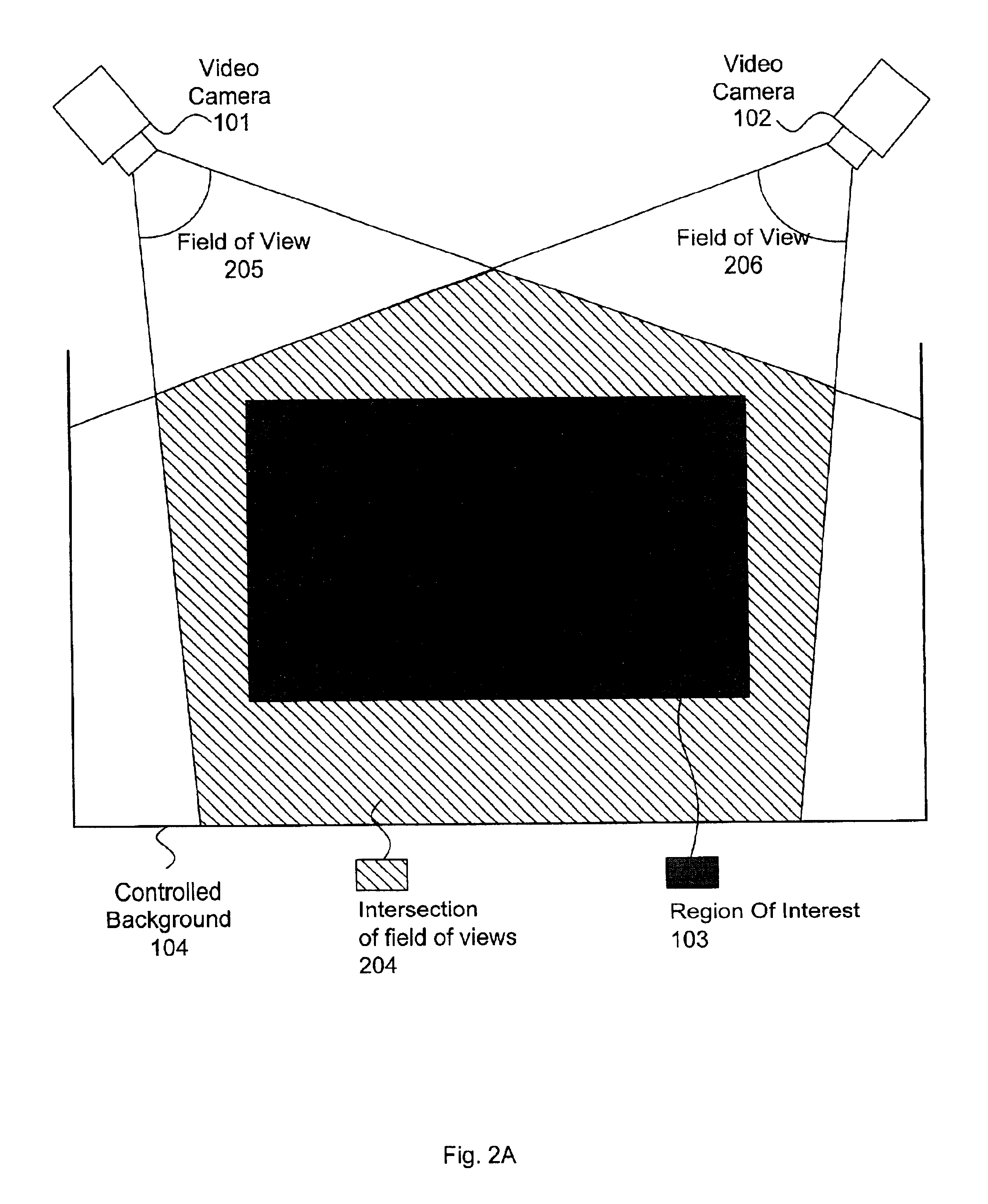
Multiple camera control system
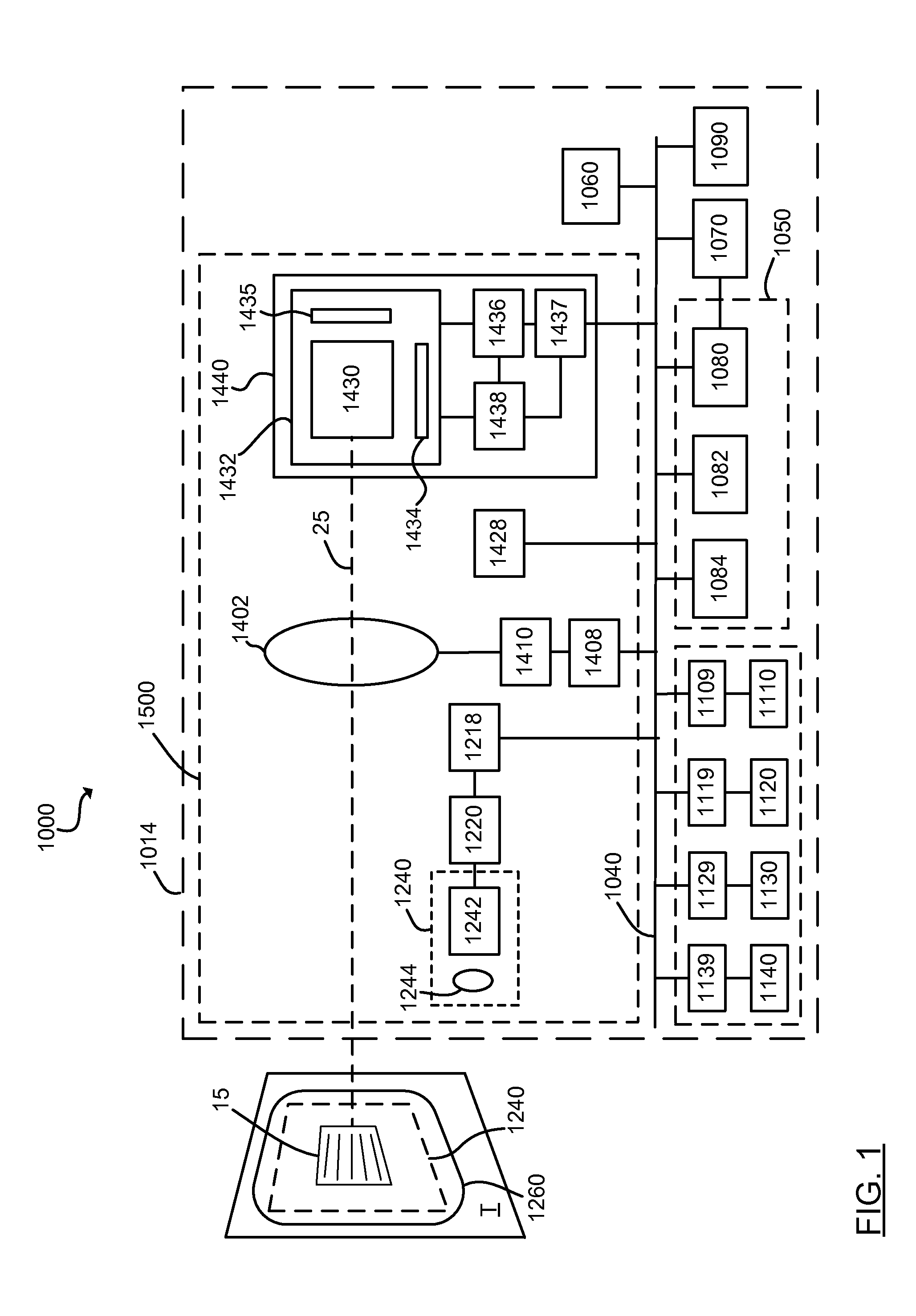
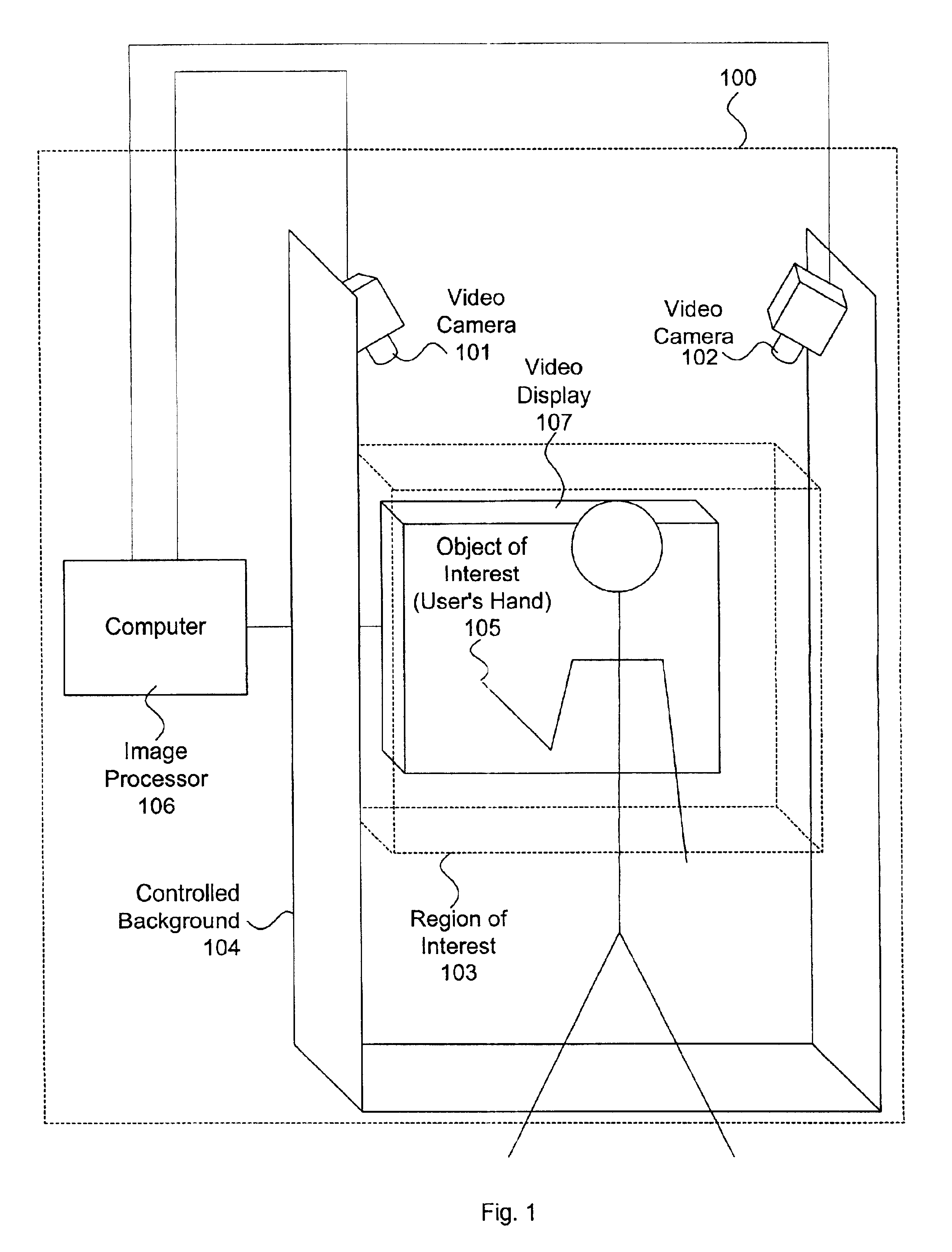
A multiple camera tracking system for interfacing with an application program running on a computer is provided. The tracking system includes two or more video cameras arranged to provide different viewpoints of a region of interest, and are operable to produce a series of video images. A processor is operable to receive the series of video images and detect objects appearing in the region of interest. The processor executes a process to generate a background data set from the video images, generate an image data set for each received video image, compare each image data set to the background data set to produce a difference map for each image data set, detect a relative position of an object of interest within each difference map, and produce an absolute position of the object of interest from the relative positions of the object of interest and map the absolute position to a position indicator associated with the application program.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
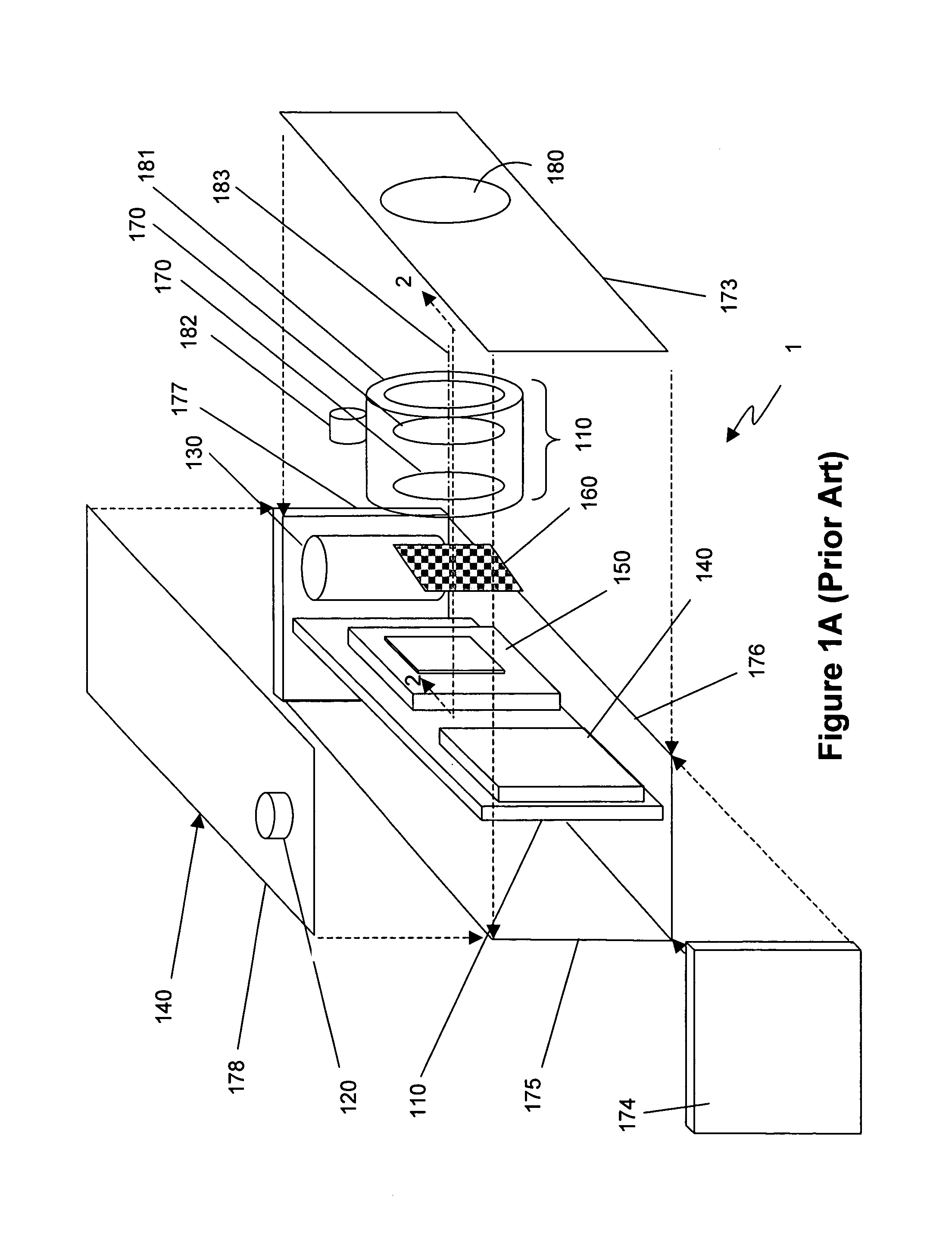
Camera using multiple lenses and image sensors to provide improved focusing capability
InactiveUS20080219654A1Increasing sizeIncreasing costTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensImage signal
An electronic camera for producing an output image of a scene from a captured image signal includes: (a) a first imaging stage comprising a first image sensor for generating a first sensor output; a first lens for forming a first image of the scene on the first image sensor; and a first lens focus adjuster for adjusting focus of the first lens responsive to a first focus detection signal; and (b) a second imaging stage comprising a second image sensor for generating a second sensor output; a second lens for forming a second image of the scene on the second image sensor; and a second lens focus adjuster for adjusting focus of the second lens responsive to a second focus detection signal. A processing stage either (a) selects the sensor output from the first imaging stage as the captured image signal and uses the sensor output from the second imaging stage to generate the first focus detection signal for the selected imaging stage, or (b) selects the sensor output from the second imaging stage as the captured image signal and uses the sensor output from the first imaging stage to generate the second focus detection signal for the selected imaging stage.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
Apparatus for multiple camera devices and method of operating same
InactiveUS20060054782A1Additional imaging capabilityHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsSignal processing circuits
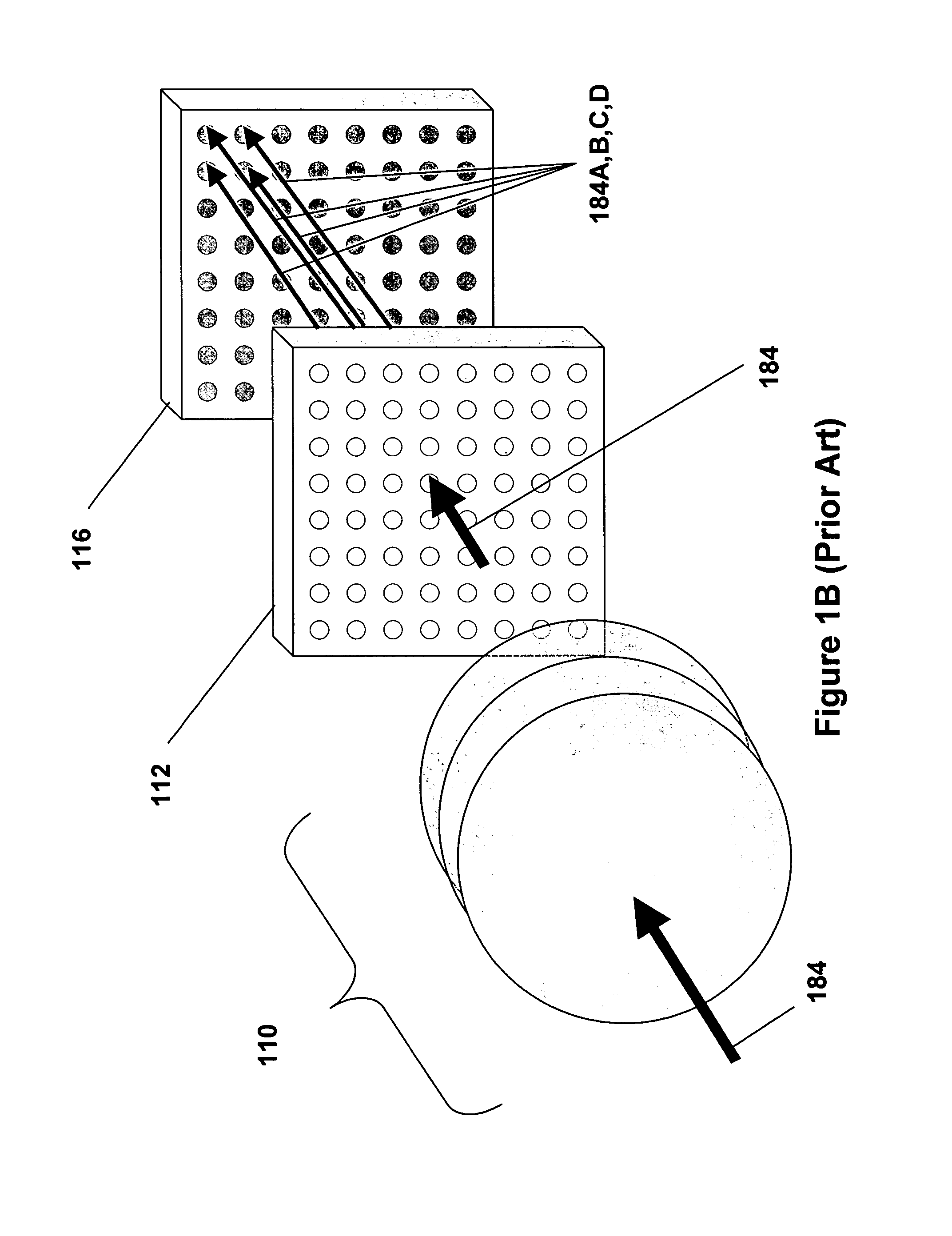
There are many, many inventions described herein. In one aspect, what is disclosed is a digital camera including a plurality of arrays of photo detectors, including a first array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a first wavelength and a second array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a second wavelength. The digital camera further may also include a first lens disposed in an optical path of the first array of photo detectors, wherein the first lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the first wavelength, and a second lens disposed in with an optical path of the second array of photo detectors wherein the second lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the second wavelength. In addition, the digital camera may include signal processing circuitry, coupled to the first and second arrays of photo detectors, to generate a composite image using (i) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the first array of photo detectors, and (ii) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the second array of photo detectors; wherein the first array of photo detectors, the second array of photo detectors, and the signal processing circuitry are integrated on or in the same semiconductor substrate.
Owner:NEWPORT IMAGING CORP
Apparatus for multiple camera devices and method of operating same
ActiveUS7199348B2High resolutionExcellent color renditionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectrical conductorPhotovoltaic detectors
There are many, many inventions described herein. In one aspect, what is disclosed is a digital camera including a plurality of arrays of photo detectors, including a first array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a first wavelength and a second array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a second wavelength. The digital camera further may also include a first lens disposed in an optical path of the first array of photo detectors, wherein the first lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the first wavelength, and a second lens disposed in with an optical path of the second array of photo detectors wherein the second lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the second wavelength. In addition, the digital camera may include signal processing circuitry, coupled to the first and second arrays of photo detectors, to generate a composite image using (i) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the first array of photo detectors, and (ii) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the second array of photo detectors; wherein the first array of photo detectors, the second array of photo detectors, and the signal processing circuitry are integrated on or in the same semiconductor substrate.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
Camera using multiple lenses and image sensors in a rangefinder configuration to provide a range map
ActiveUS20080218612A1Increasing size and costPrecise and rapid autofocusTelevision system detailsPrintersComputer graphics (images)Radiology
An electronic camera for producing an output image of a scene from a captured image signal includes a first imaging stage comprising a first image sensor for generating a first sensor output and a first lens for forming a first image of the scene on the first image sensor, and a second imaging stage comprising a second image sensor for generating a second sensor output and a second lens for forming a second image of the scene on the second image sensor, where the lenses have different focal lengths. A processing stage uses the sensor output from one of the imaging stages as the captured image signal and uses the images from both imaging stages to generate a range map identifying distances to the different portions of the scene.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
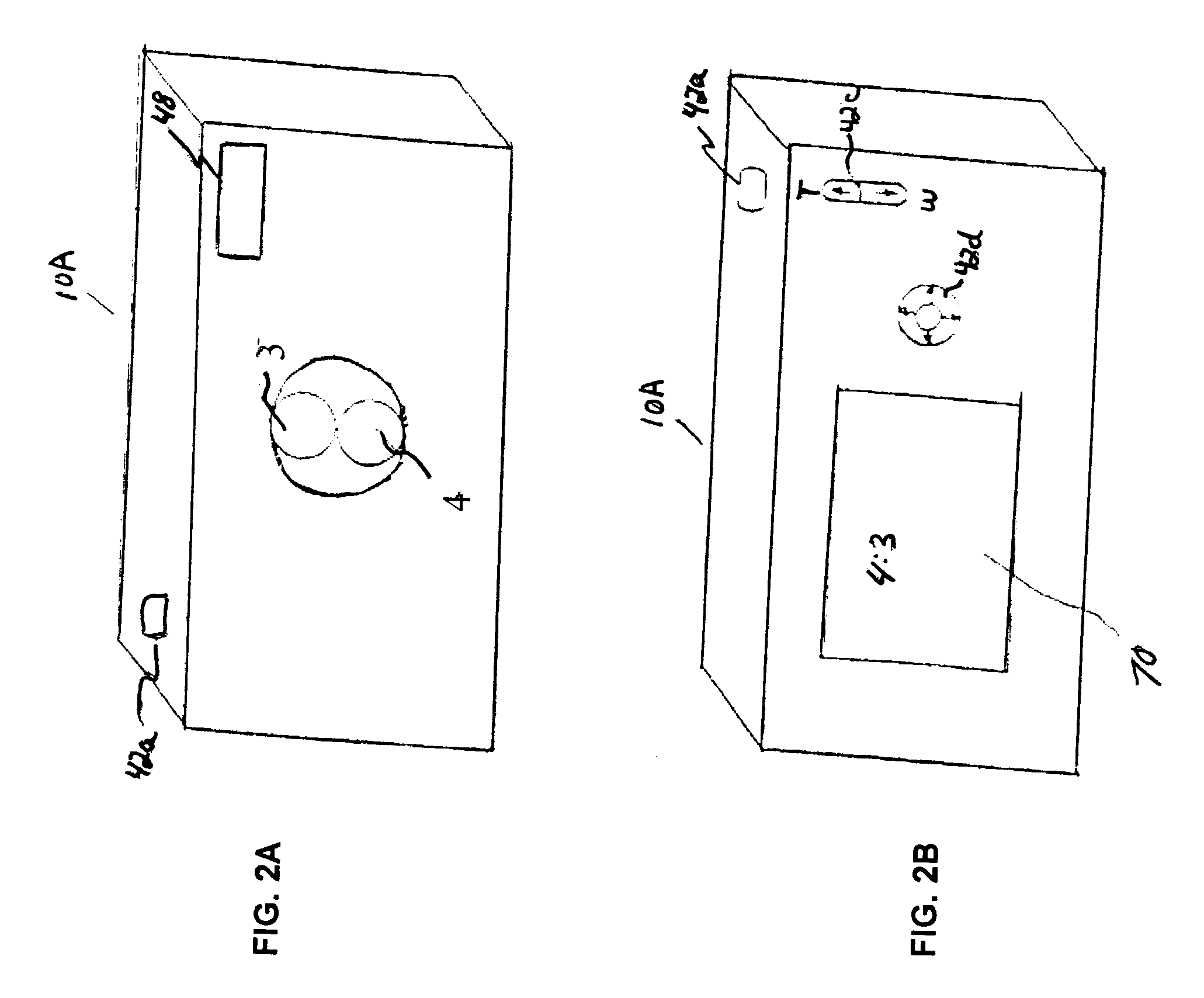
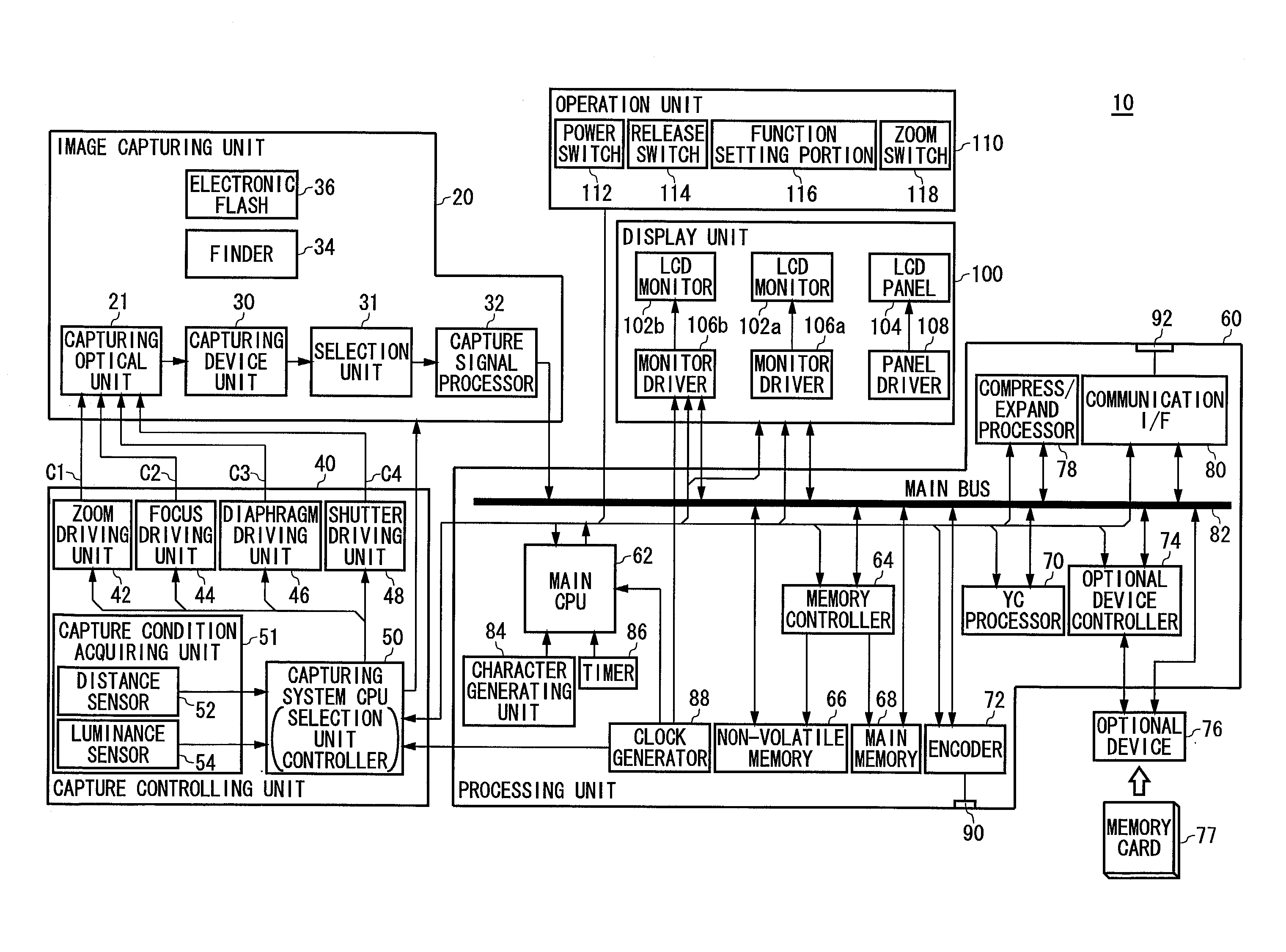
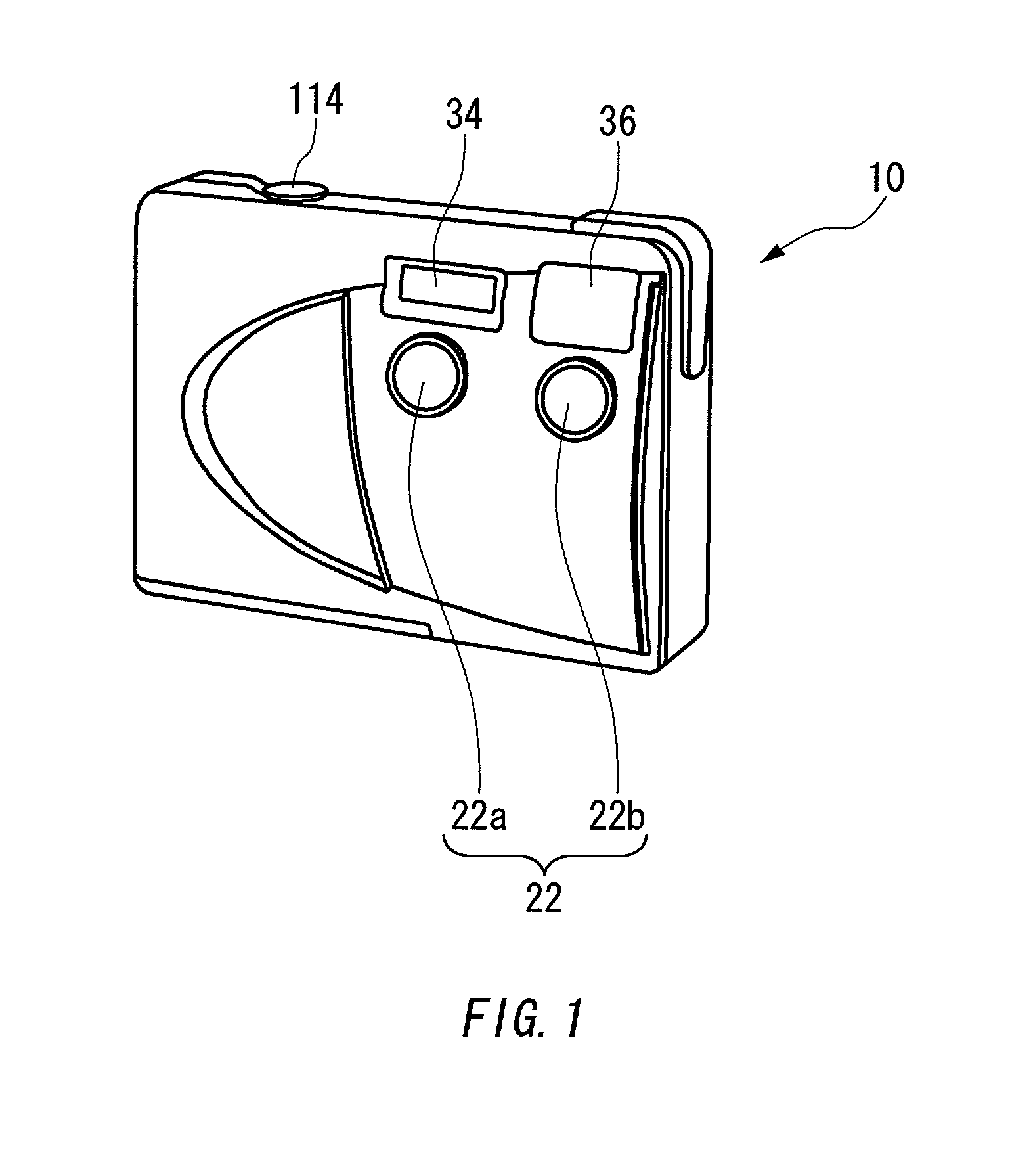
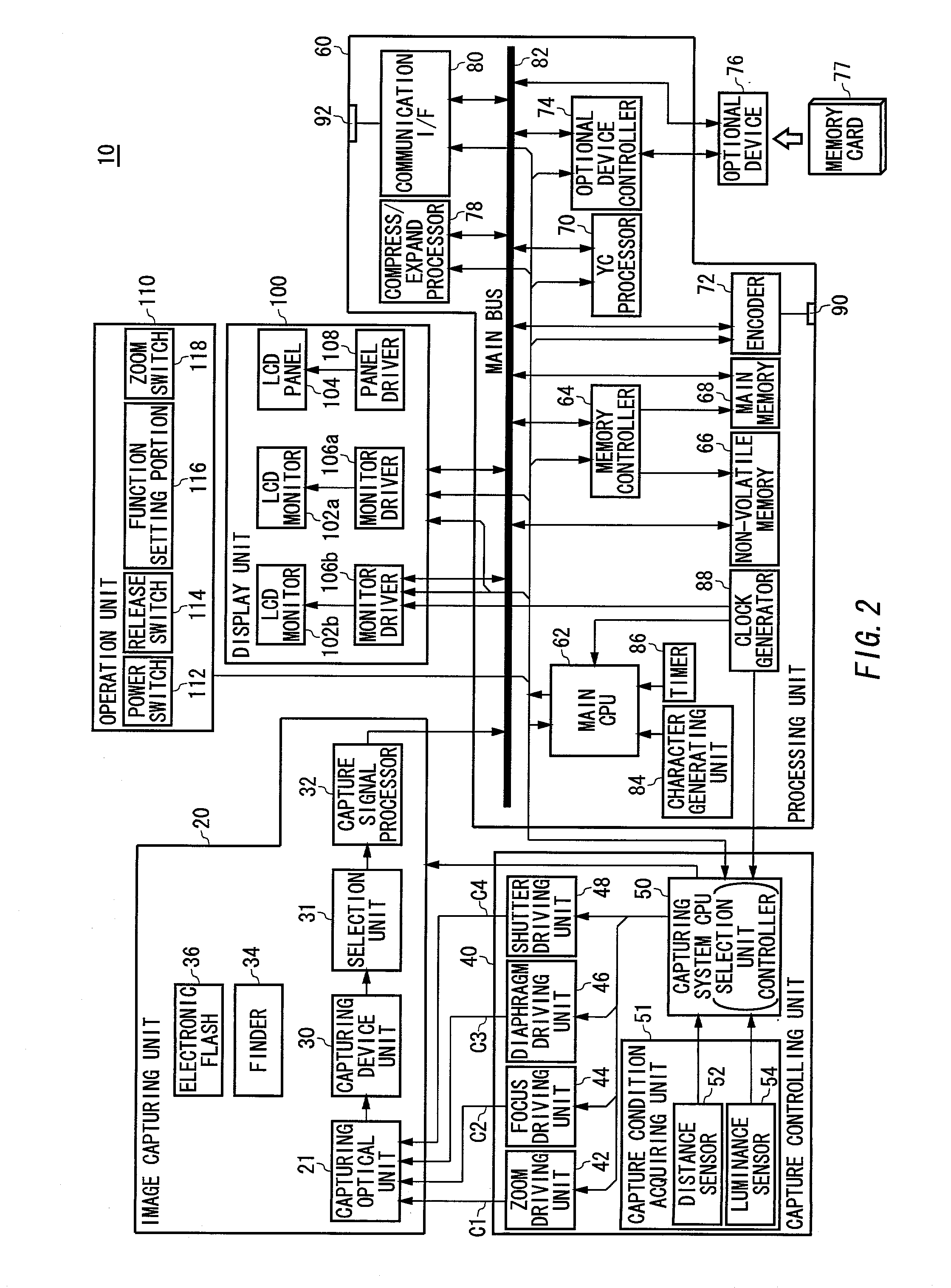
Image capturing apparatus
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Camera-shake correction device
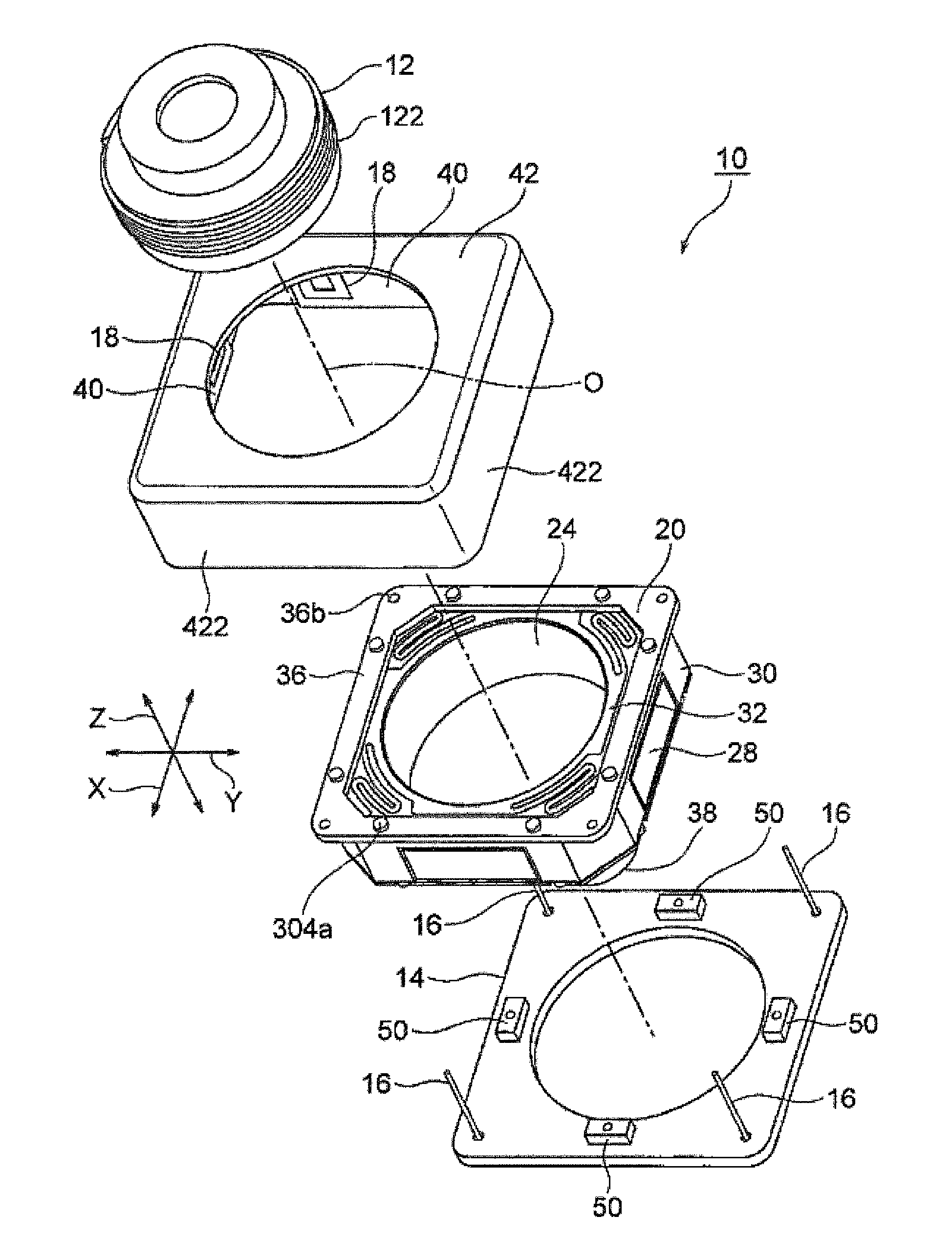
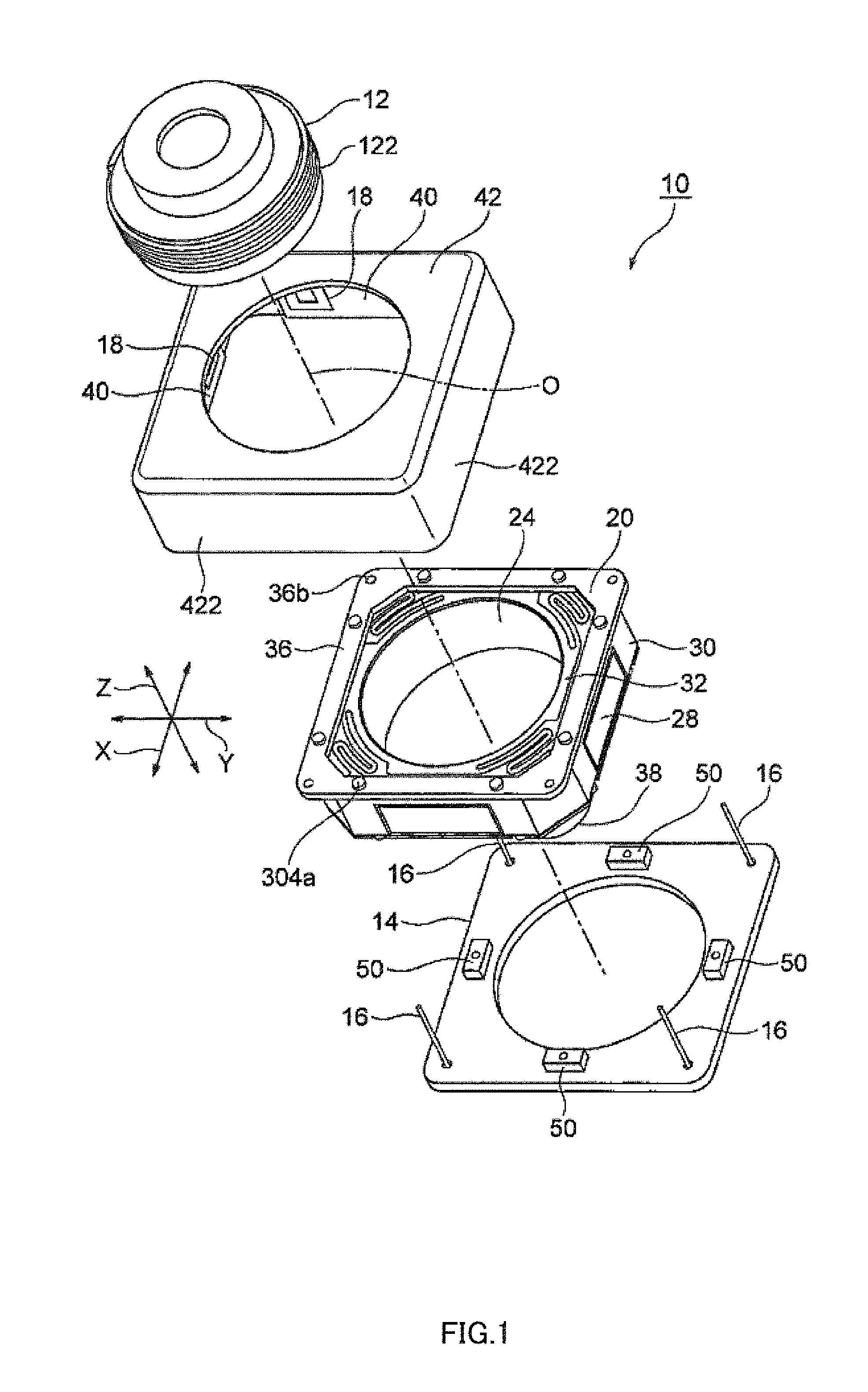
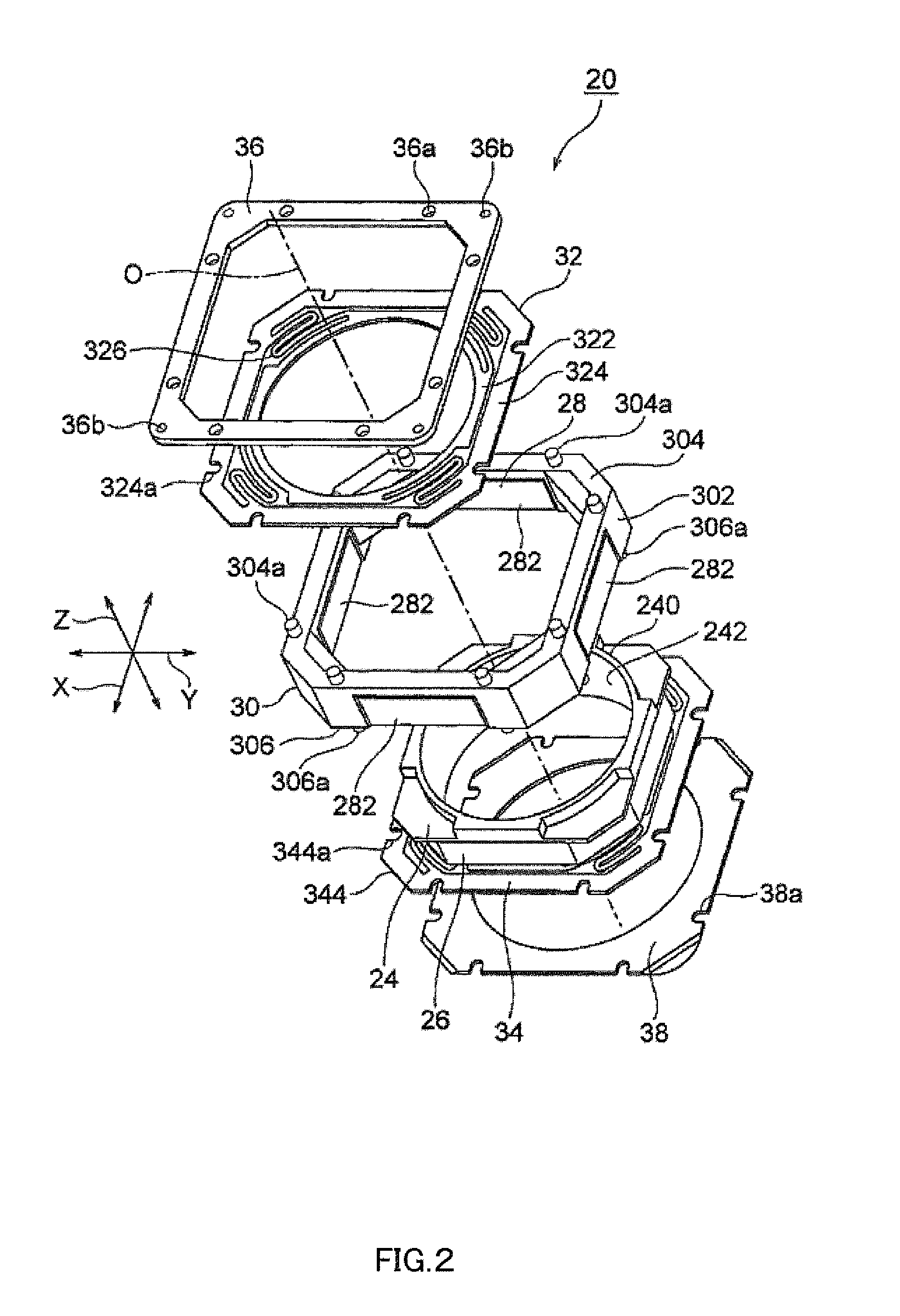
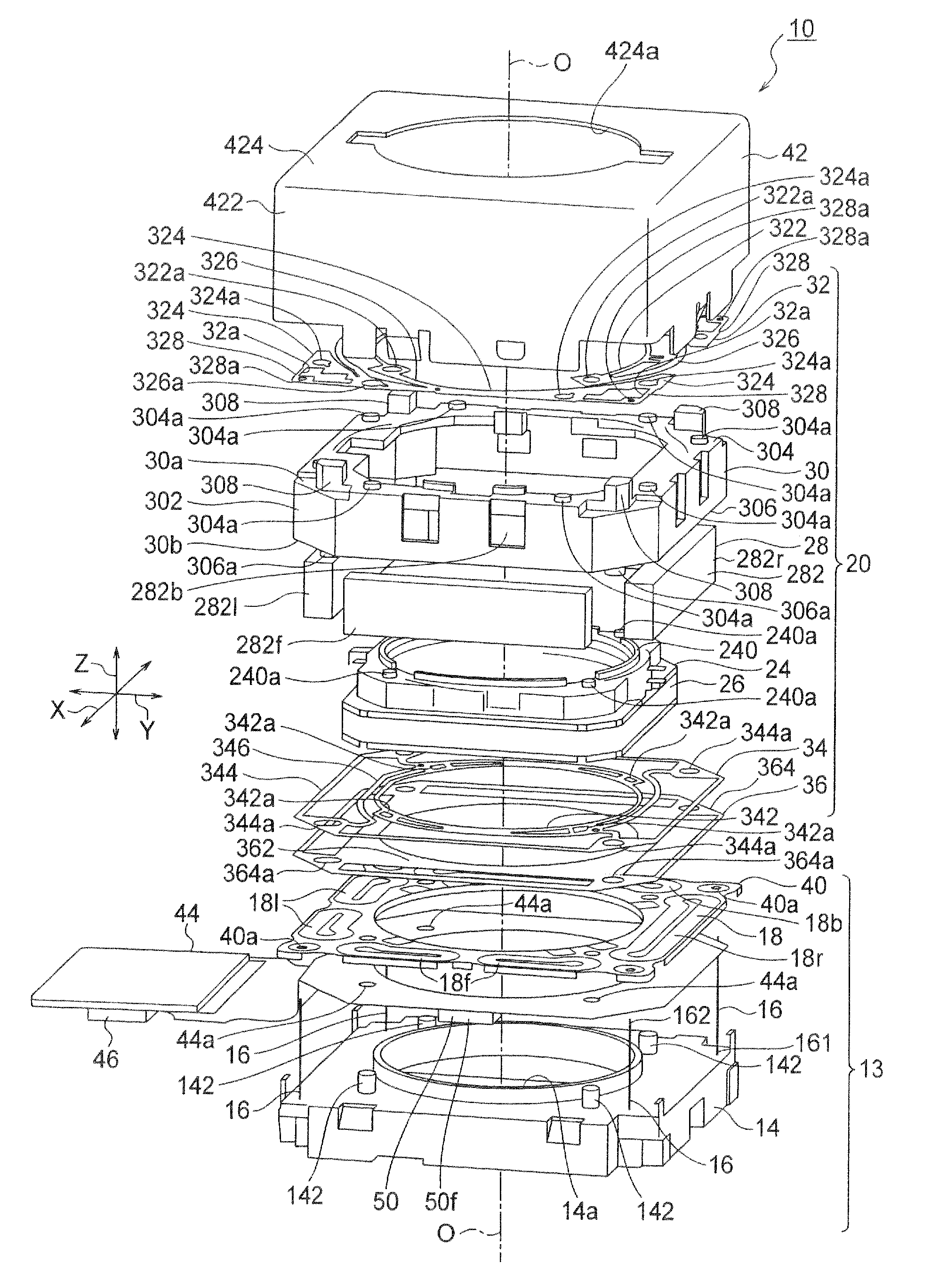
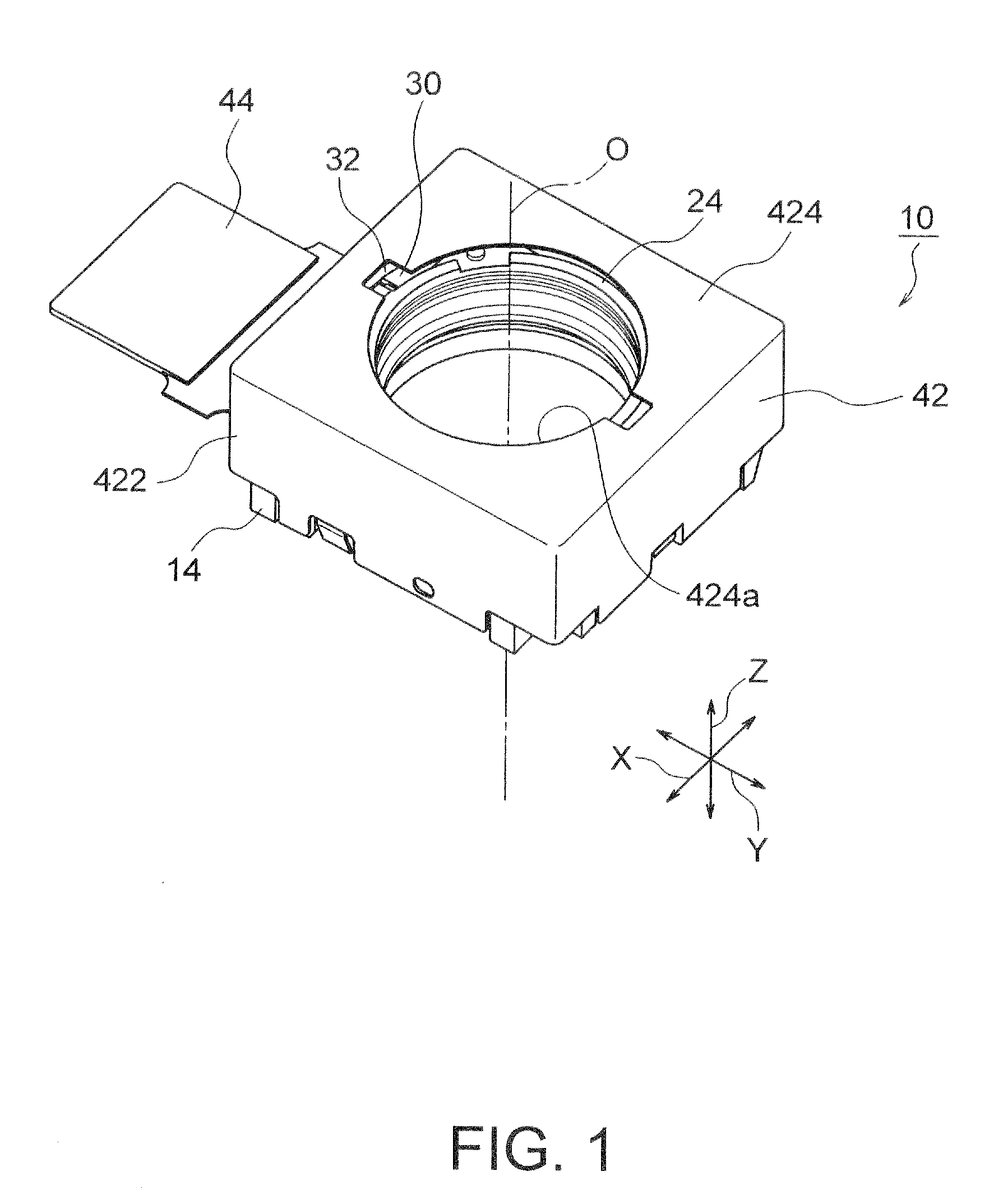
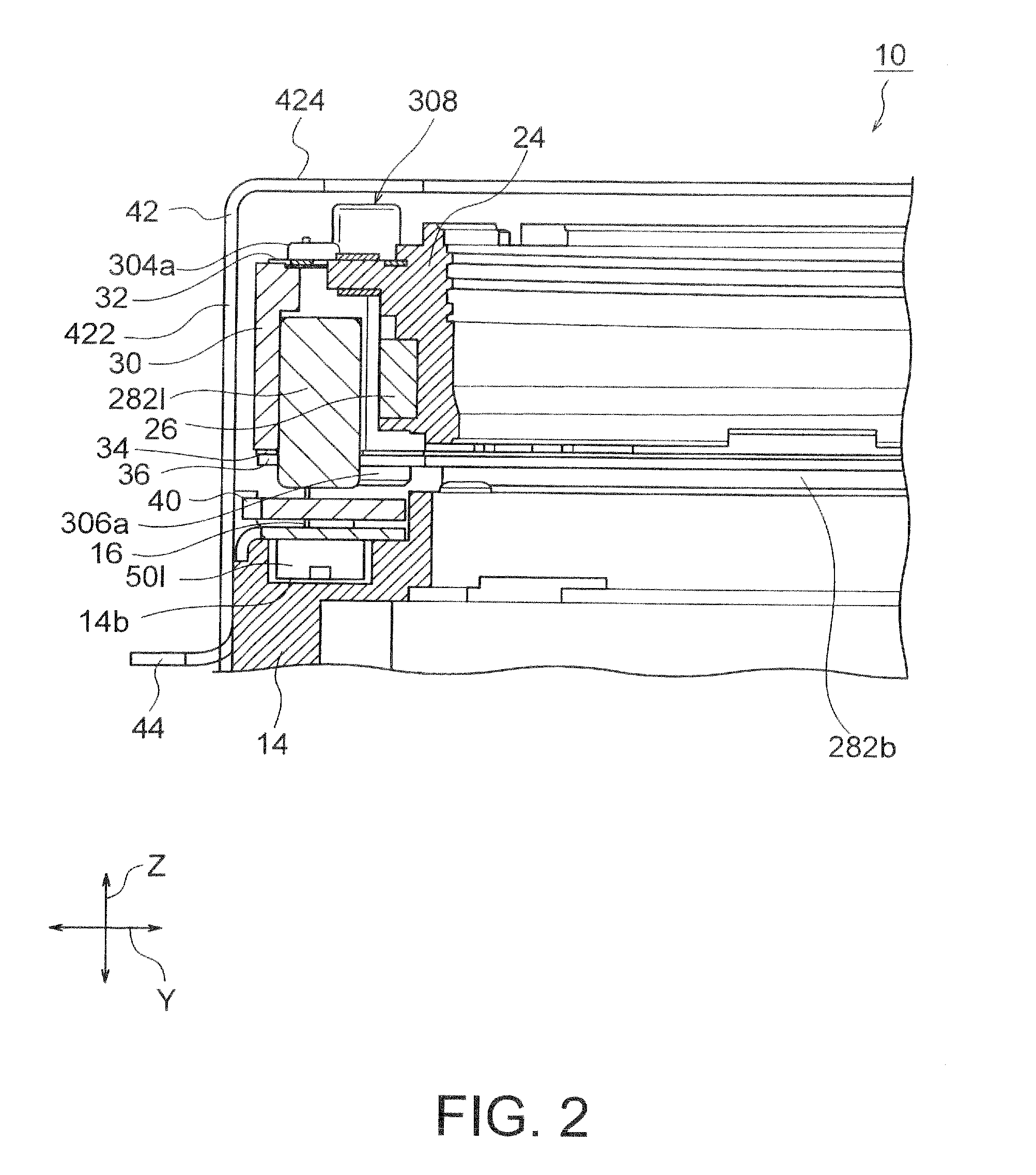
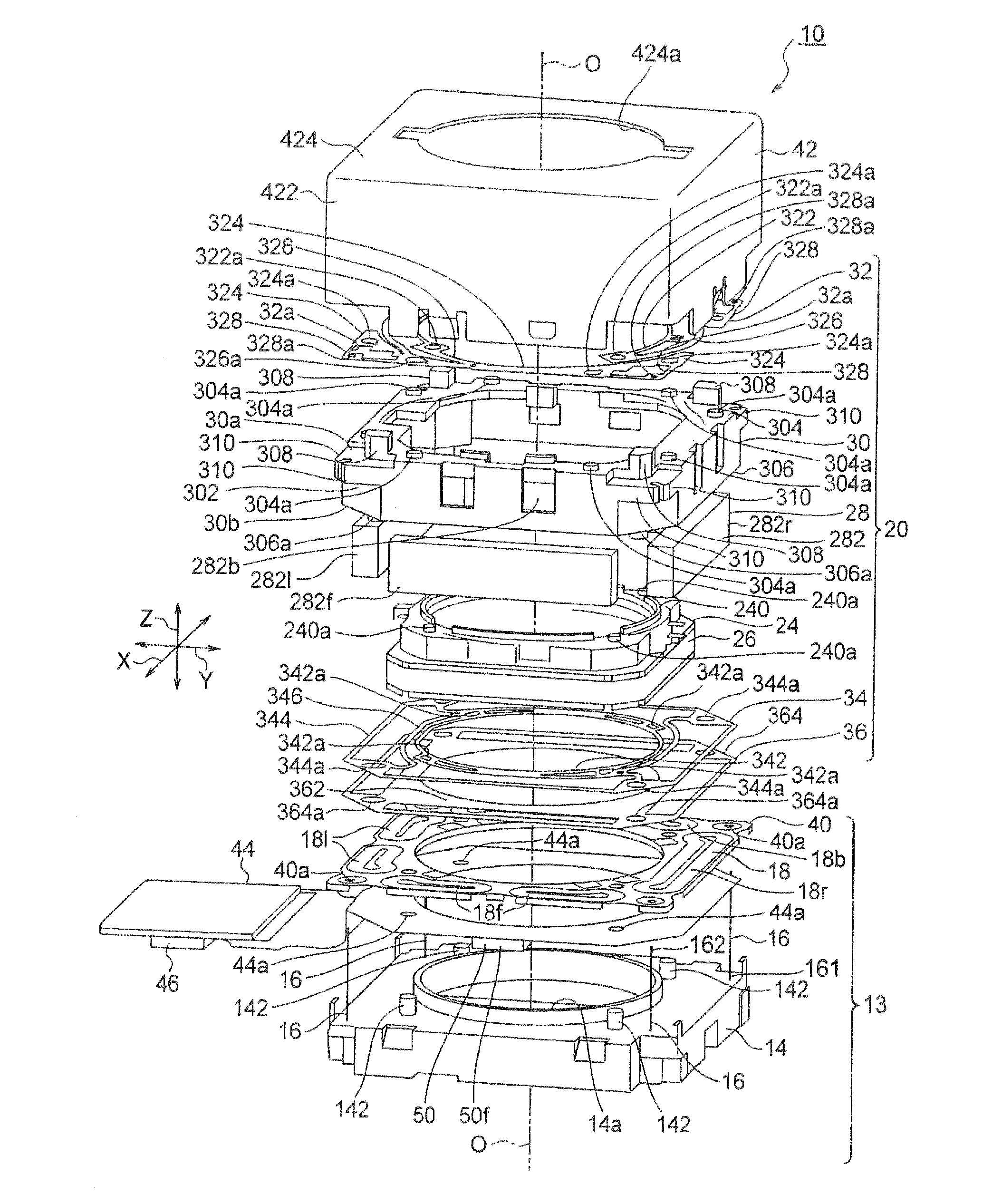
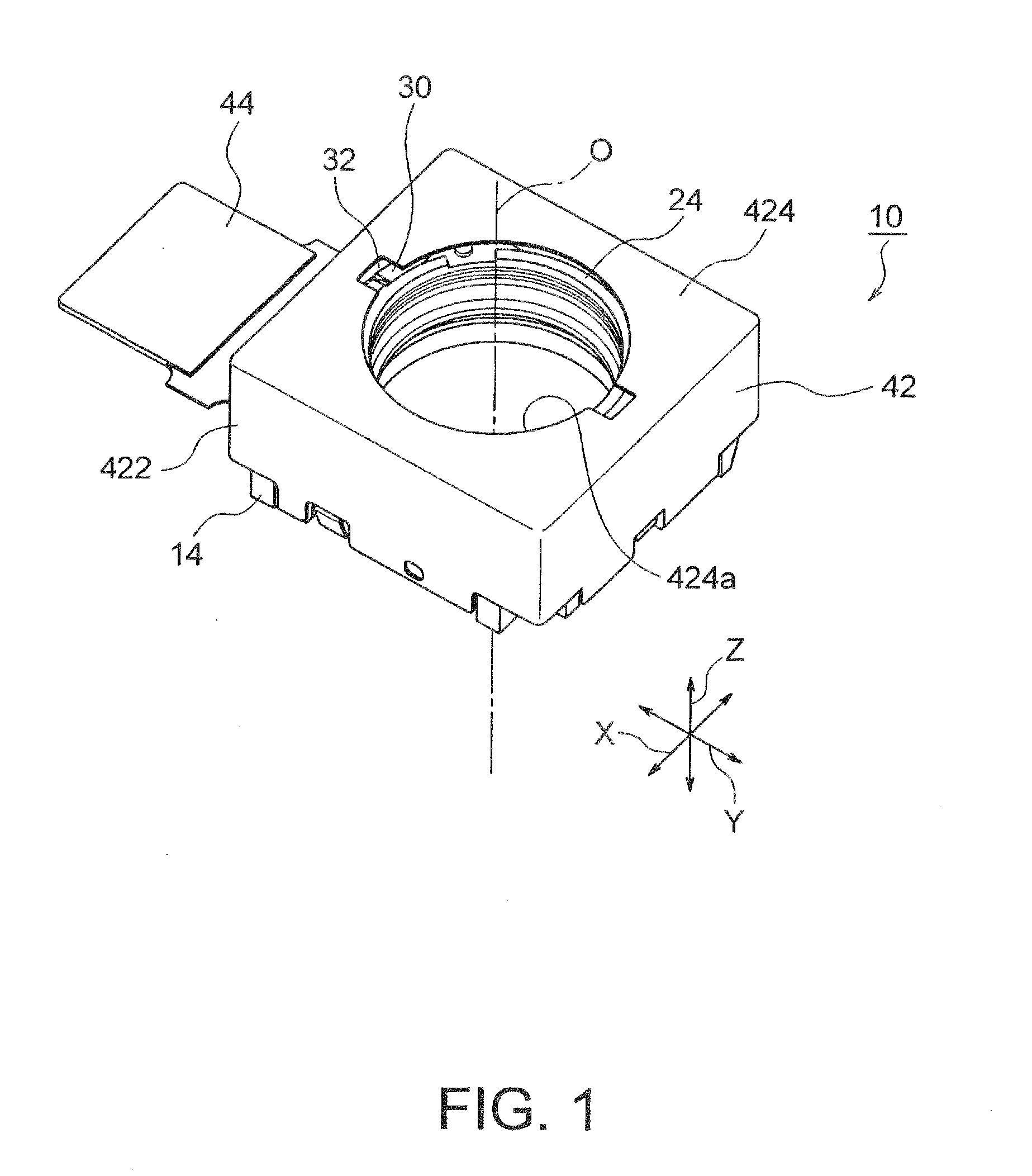
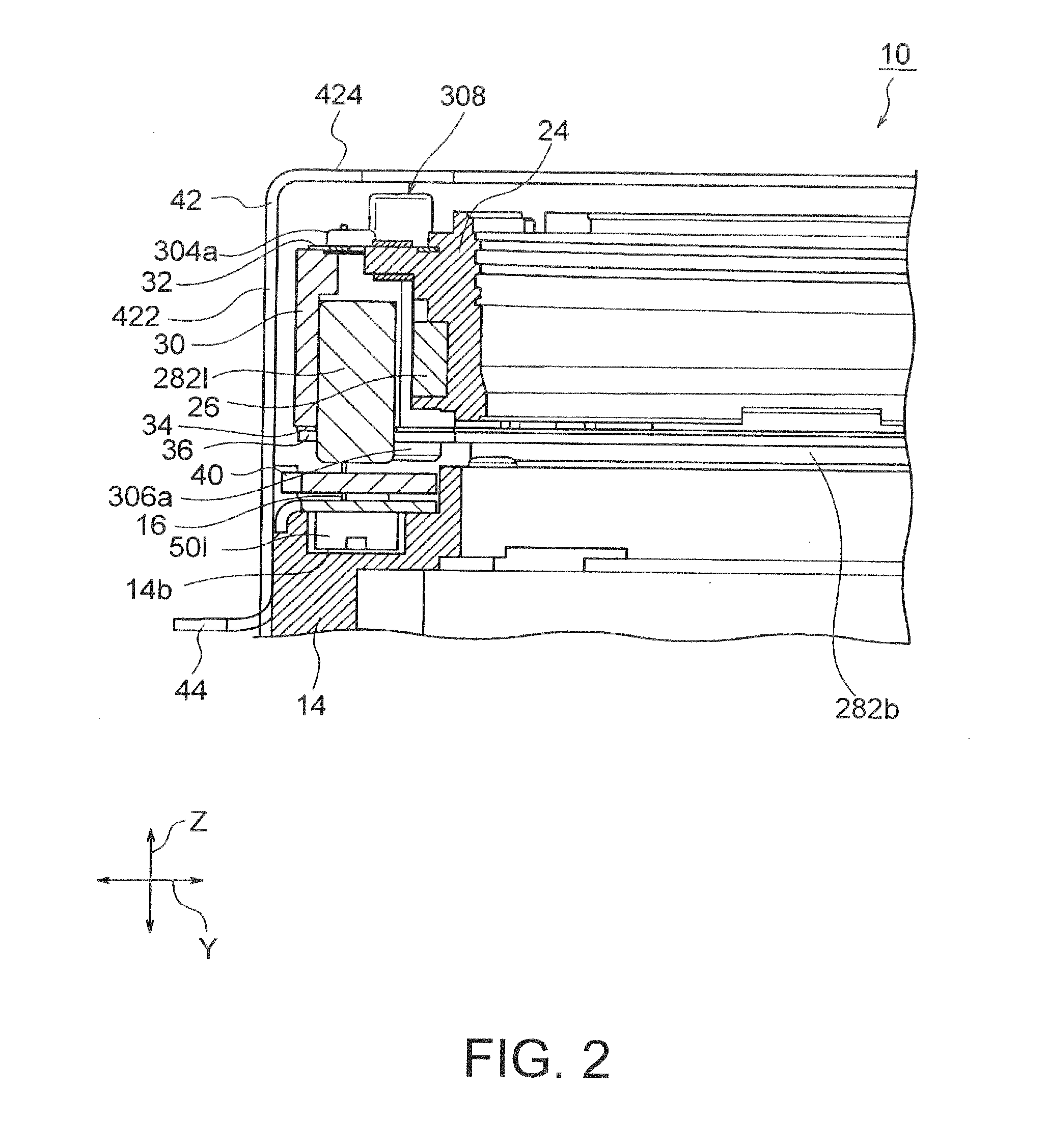
InactiveUS20120154614A1Small sizeLow profileTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisMagnet
A small size, low profile camera-shake correction device. A camera-shake correction device (10) corrects camera shake by moving the entire auto-focusing lens drive device (20) in a first direction (X) and a second direction (Y) which are perpendicular to the optical axis (O) and are perpendicular to each other, the auto-focusing lens drive device (20) being provided with a focusing coil (26) and a permanent magnet (28) which is disposed on the outside of the focusing coil. The camera-shake correction device (10) includes: a base (14) disposed so as to be spaced from the bottom surface of the auto-focusing lens drive device (20); suspension wires (16) which each have one end affixed to the outer peripheral section of the base, which extend along the optical axis (O), and which support the entire auto-focusing lens drive device (20) in such a manner that the auto-focusing lens drive device (20) is rockable in the first direction (X) and the second direction (Y); and a camera-shake correcting coil (18) disposed so as to face the permanent magnet (28).
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
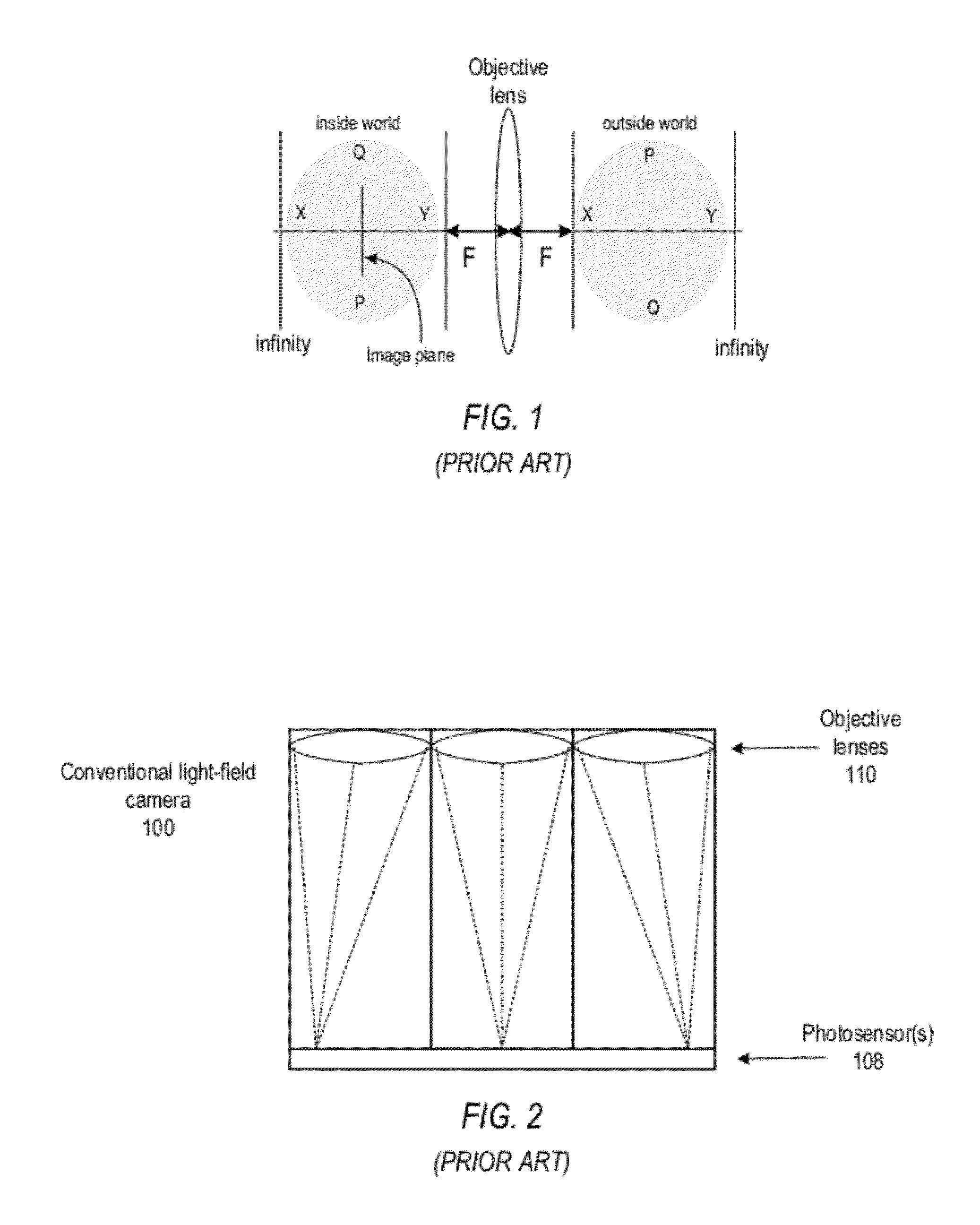
4D light field cameras
InactiveUS20080187305A1Simple attenuating maskSuppress unwanted occludersProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensUltrasound attenuation
A camera acquires a 4D light field of a scene. The camera includes a lens and sensor. A mask is arranged in a straight optical path between the lens and the sensor. The mask including an attenuation pattern to spatially modulate the 4D light field acquired of the scene by the sensor. The pattern has a low spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the lens, and a high spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the sensor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method and apparatus for use in camera and systems employing same
ActiveUS20070002159A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesControl signalImage resolution
There are many inventions described herein. Some aspects are directed to methods and / or apparatus to provide relative movement between optics, or portion(s) thereof, and sensors, or portion(s) thereof, in a digital camera. The relative movement may be in any of various directions. In some aspects, relative movement between an optics portion, or portion(s) thereof, and a sensor portion, or portion(s) thereof, are used in providing any of various features and / or in the various applications disclosed herein, including, for example, but not limited to, increasing resolution, optical and electronic zoom, image stabilization, channel alignment, channel-channel alignment, image alignment, lens alignment, masking, image discrimination, range finding, 3D imaging, auto focus, mechanical shutter, mechanical iris, multi and hyperspectral imaging, and / or combinations thereof. In some aspects, movement is provided by actuators, for example, but not limited to MEMS actuators, and by applying appropriate control signal thereto.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
Lens holder driving device capable of avoiding deleterious effect on hall elements
ActiveUS20130016427A1Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisHall element
An AF unit of a lens holder driving device includes a lens holder, a focusing coil, a permanent magnet having a plurality of permanent magnet pieces having first surfaces opposed to the focusing coil, a magnet holder holding the permanent magnet, and first and second leaf springs supporting the lens holder in a direction of an optical axis shiftably. An image stabilizer portion includes a fixed portion disposed near the second leaf spring, a supporting member swingably supporting the AF unit with respect to the fixed portion, an image stabilizer coil having a plurality of image stabilizer coil portions disposed so as to oppose to second surfaces of the plurality of permanent magnet pieces that are perpendicular to the first surfaces, and a plurality of Hall elements. Each Hall element is disposed at a position where the image stabilizer coil portion is separated into a plurality of coil parts.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
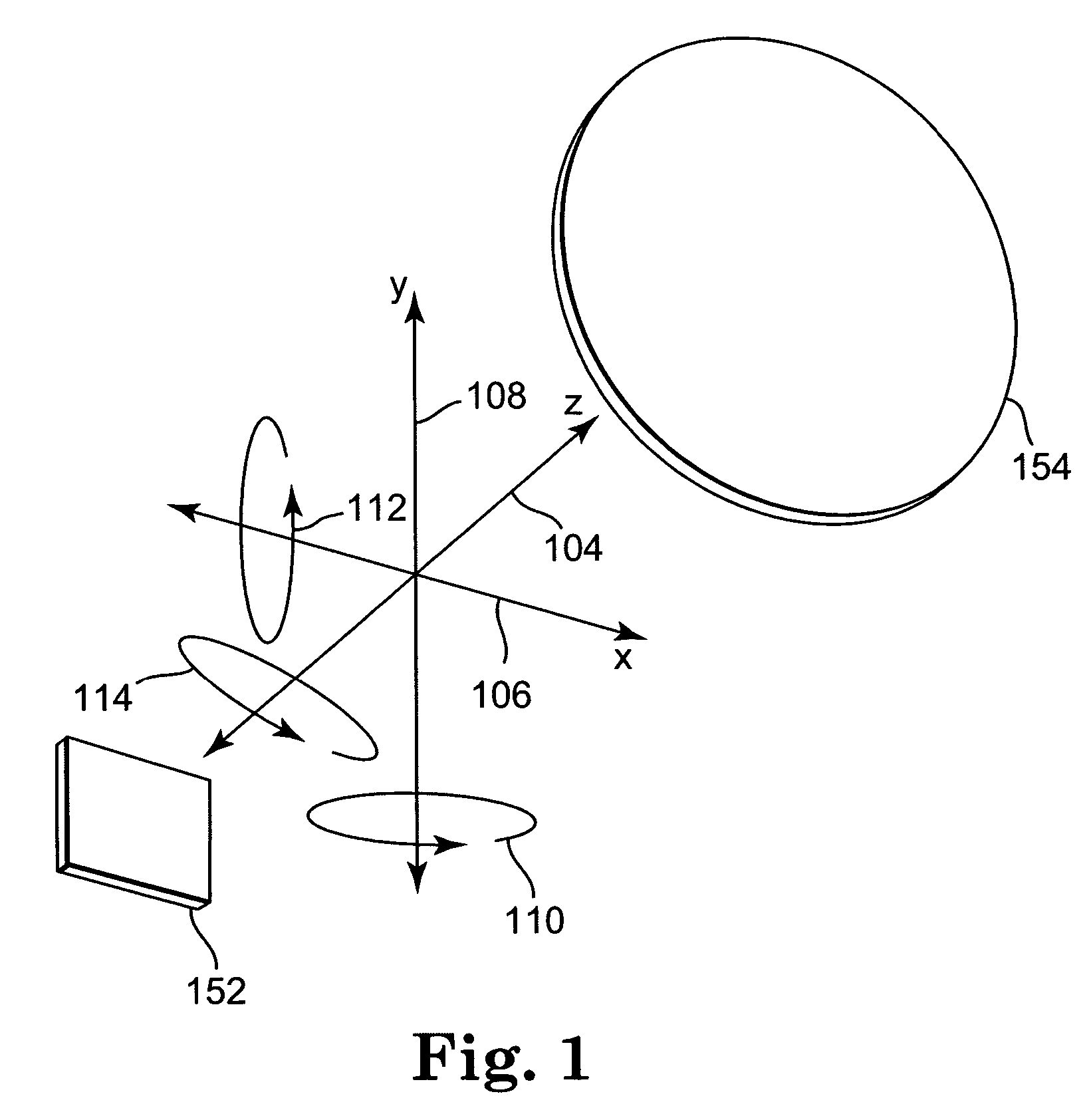
Optical see-through augmented reality modified-scale display
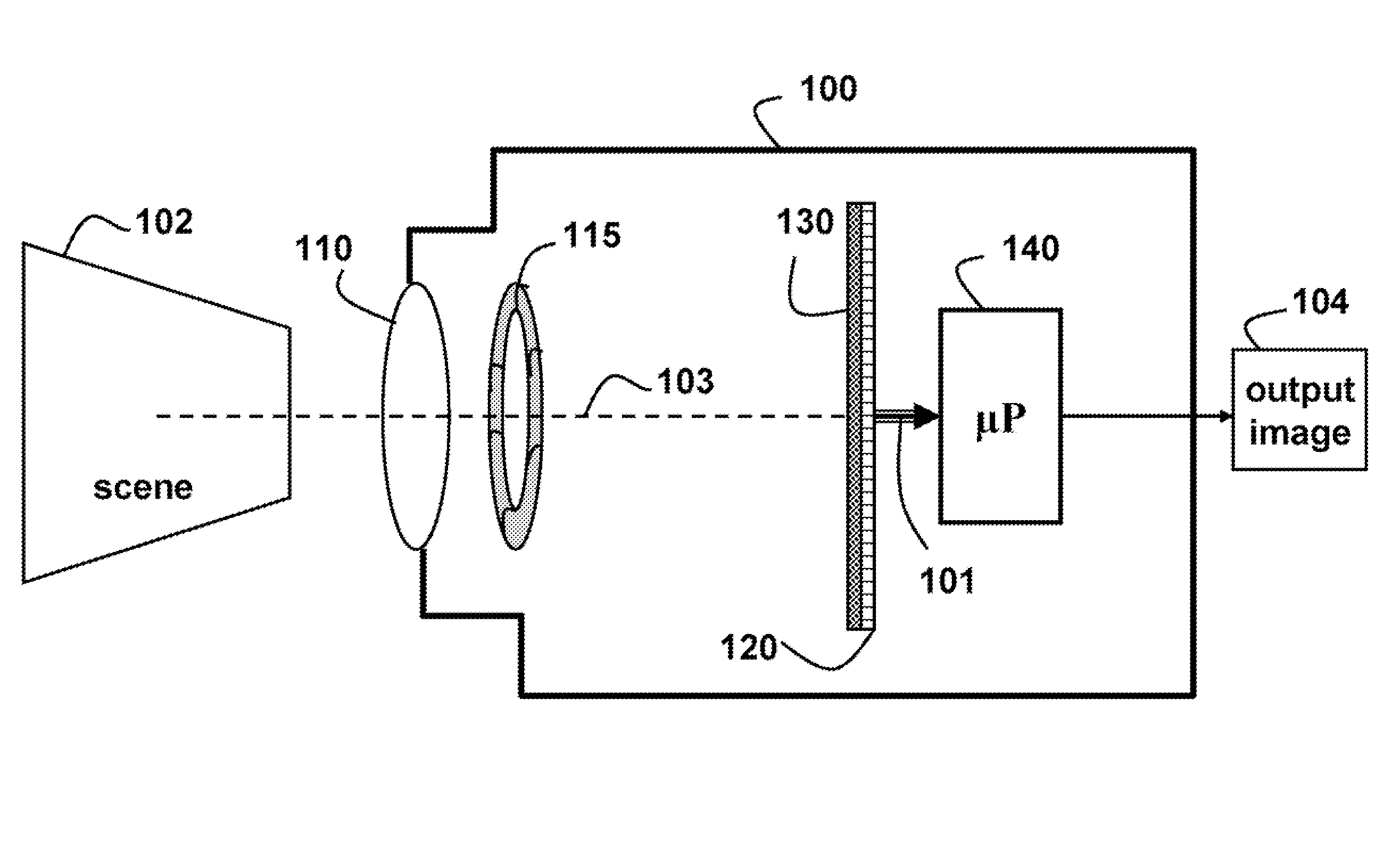
InactiveUS7002551B2Improve accuracyAccurate currentInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsDisplay device
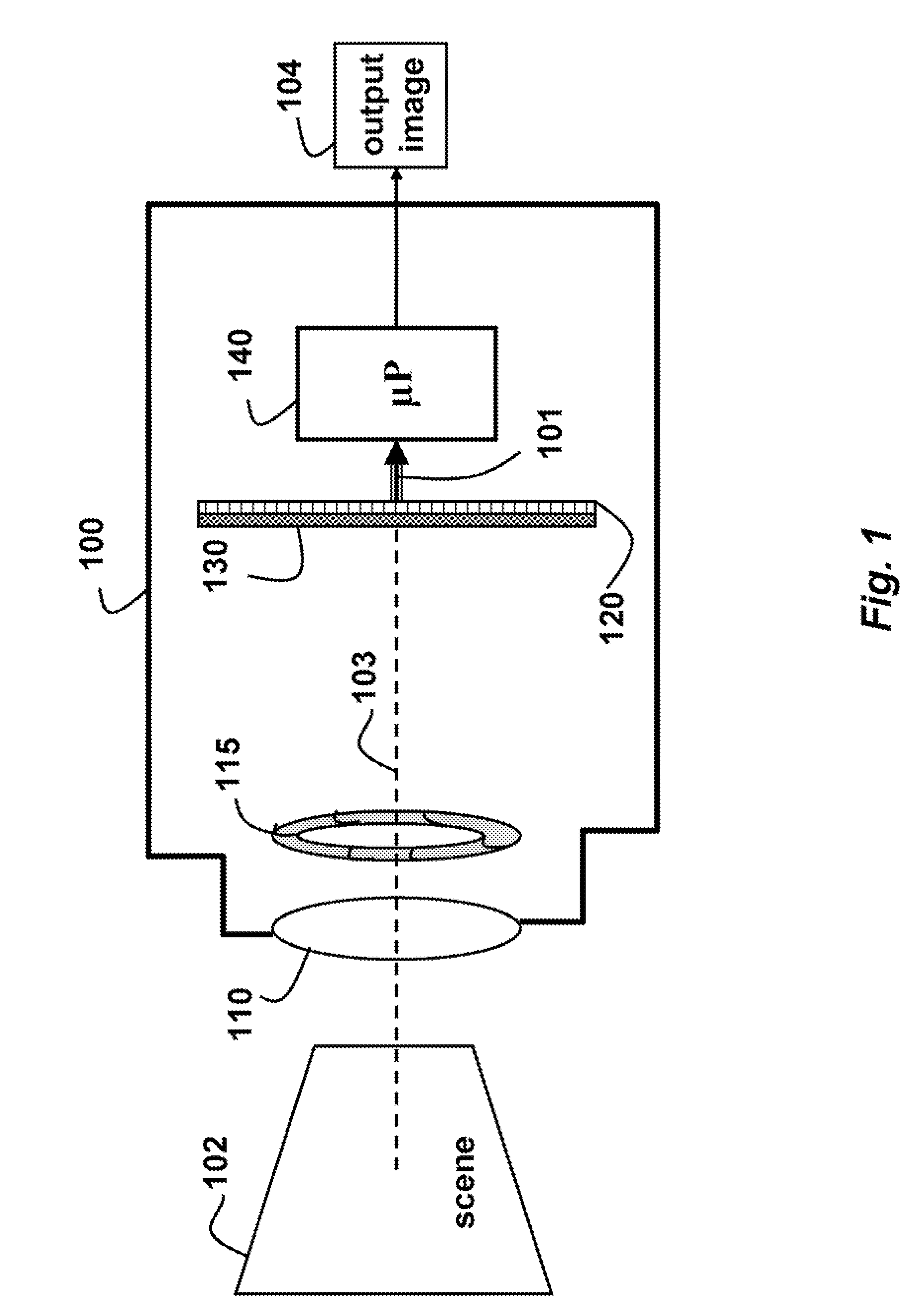
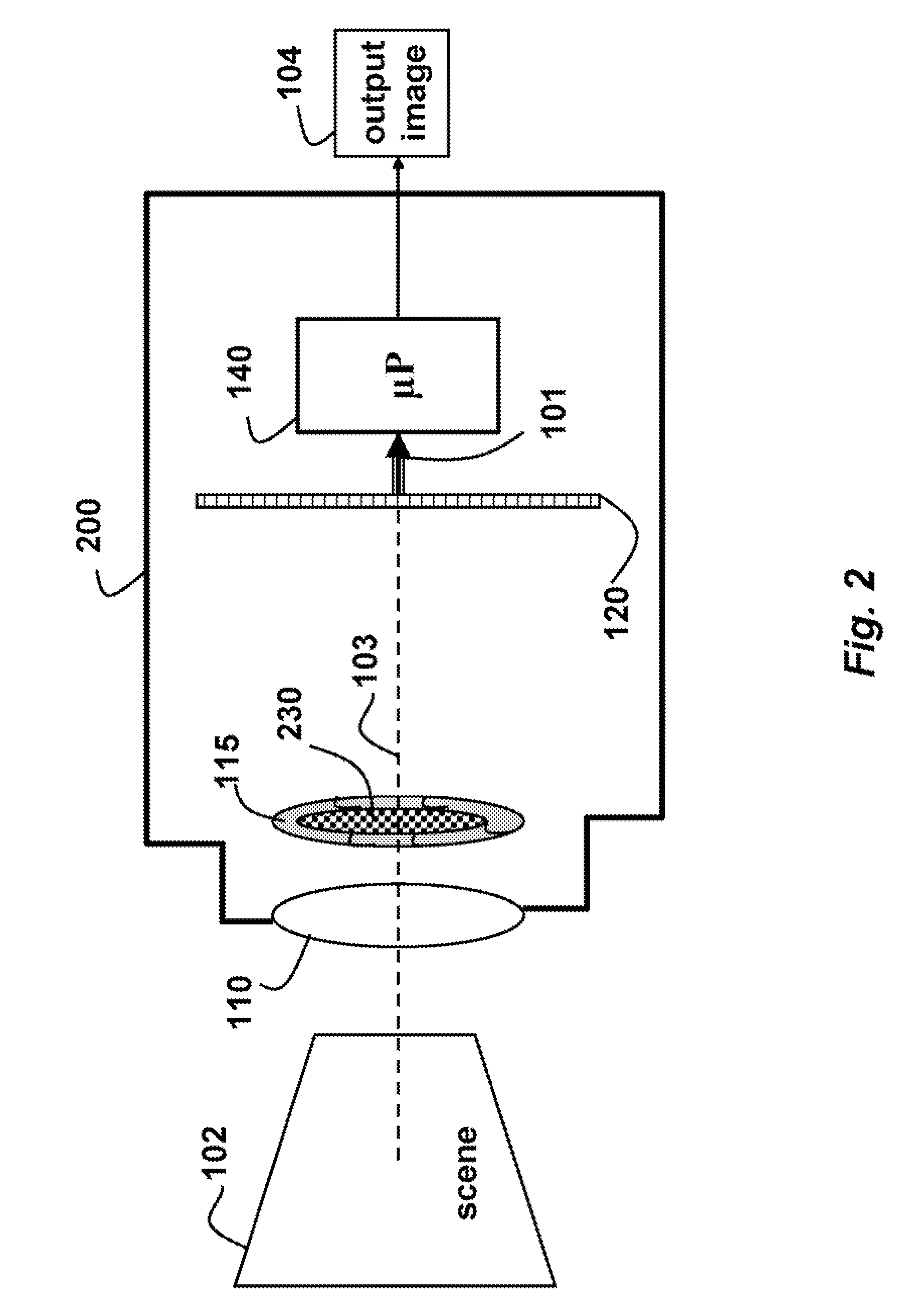
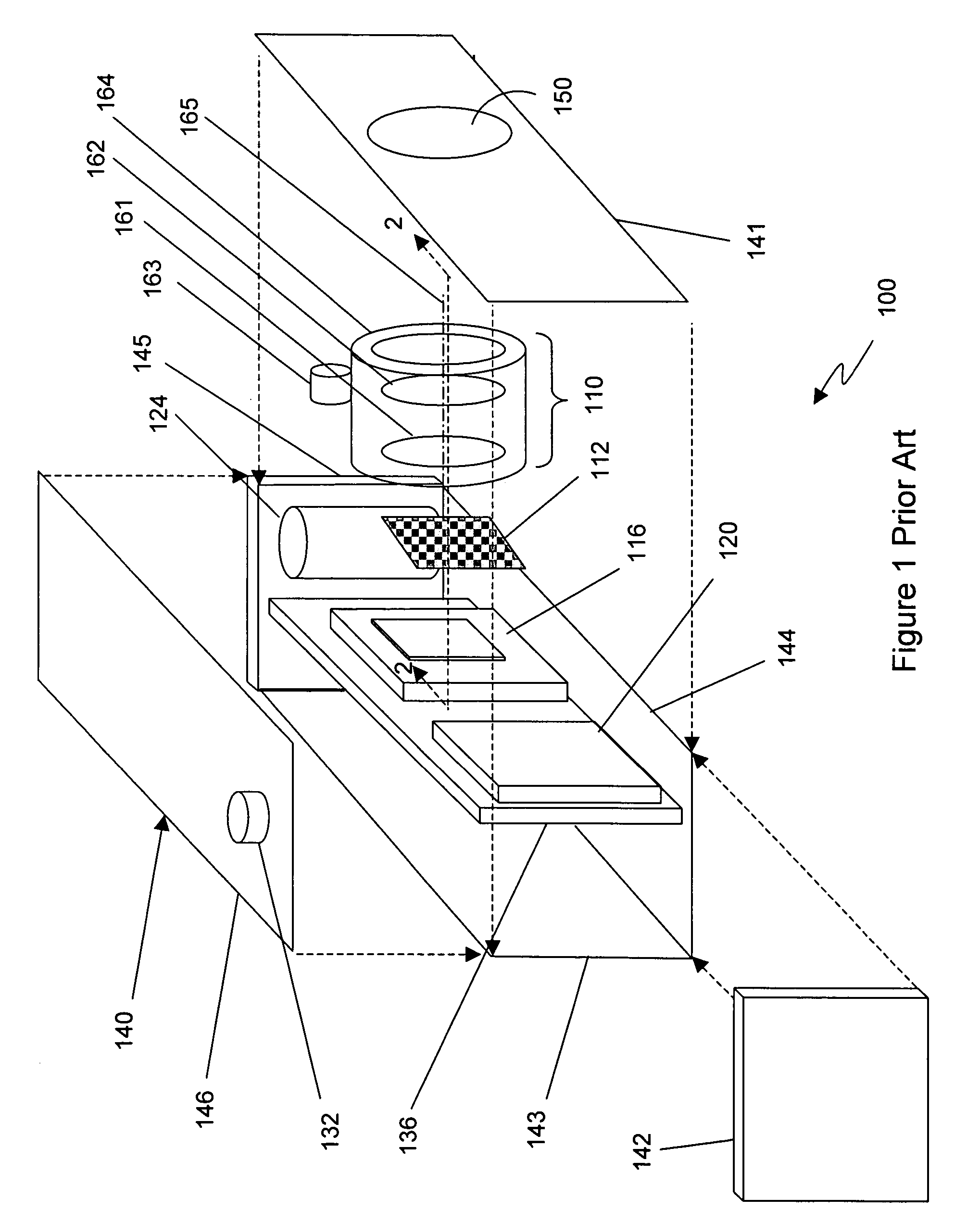
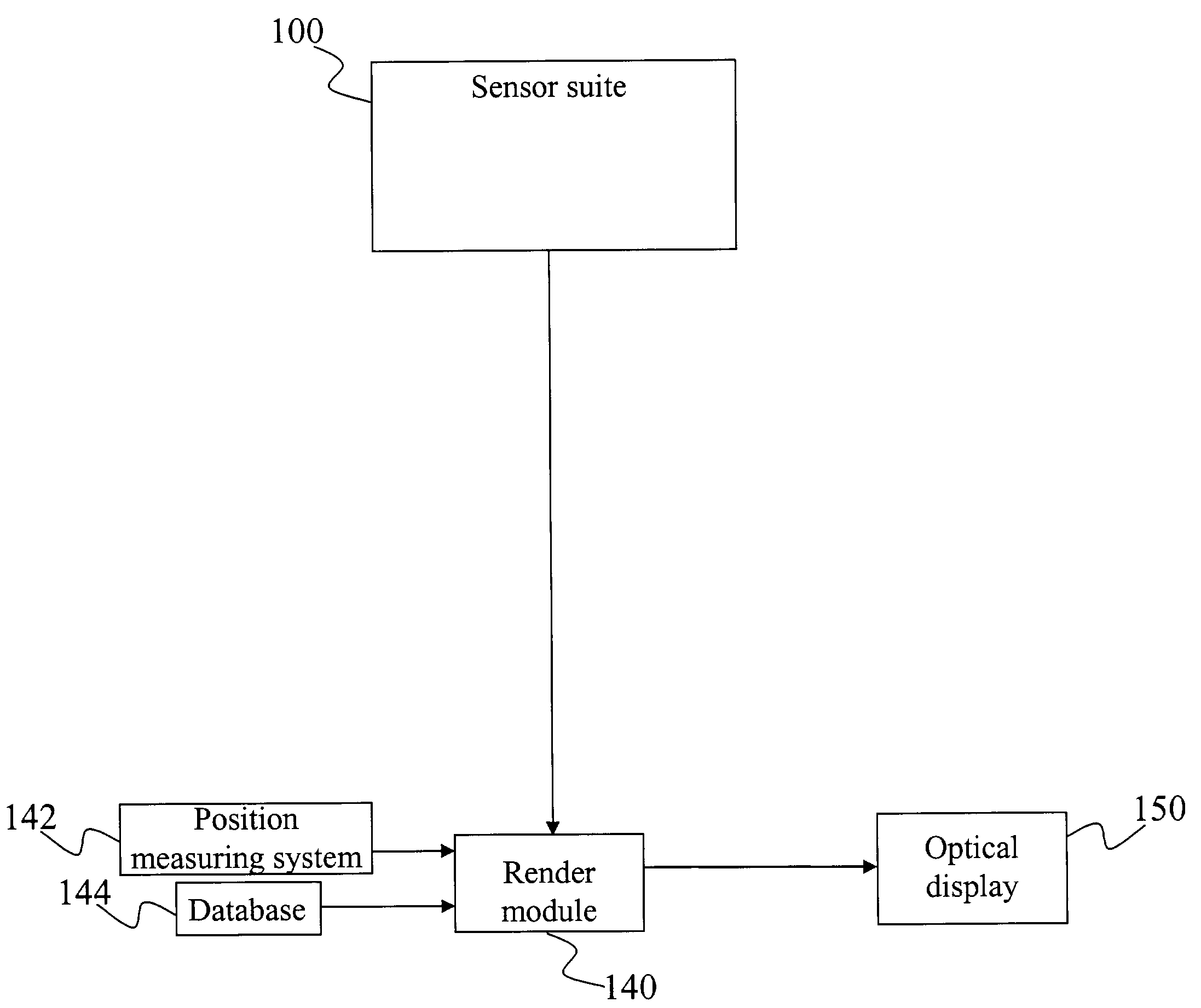
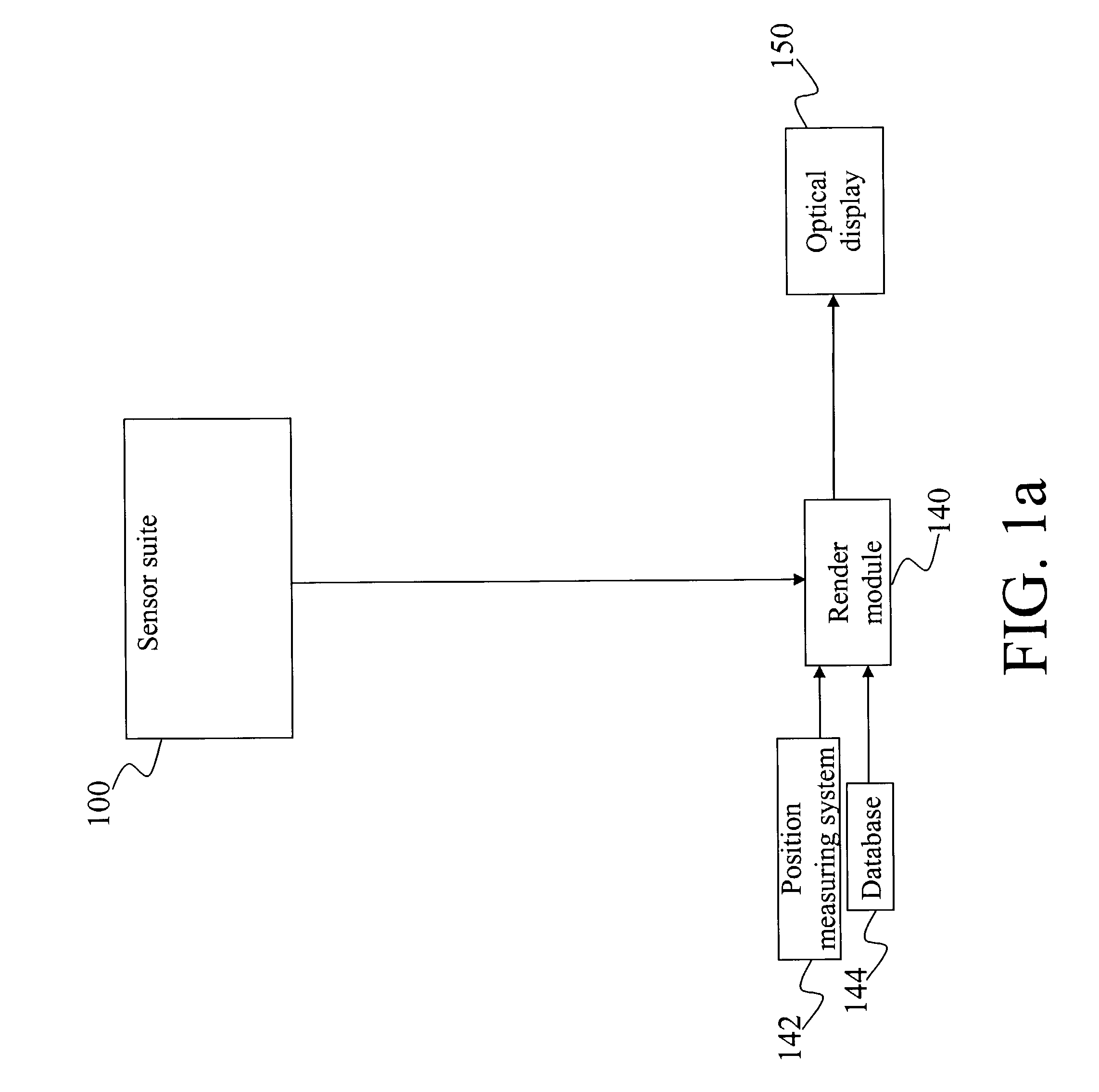
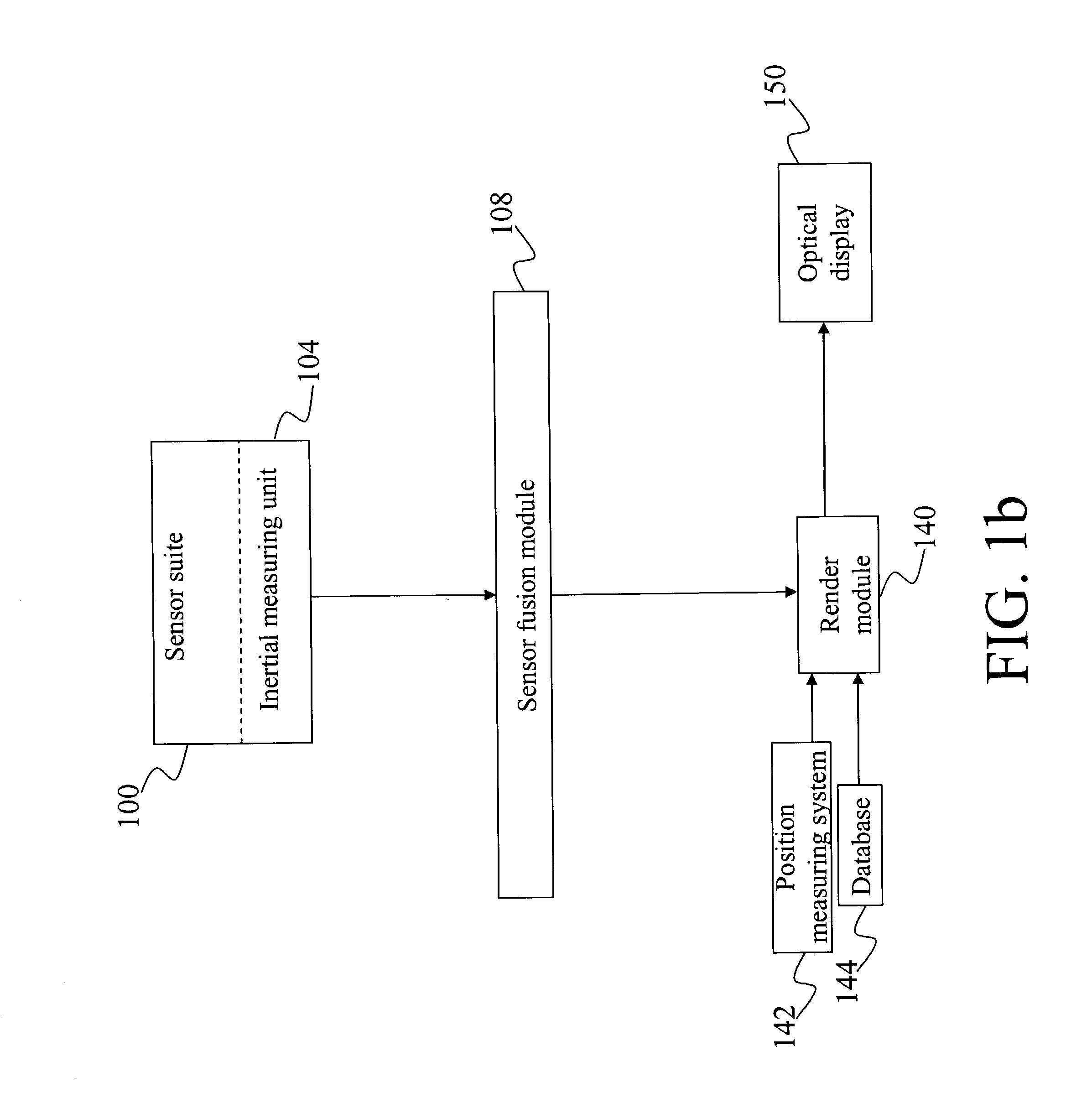
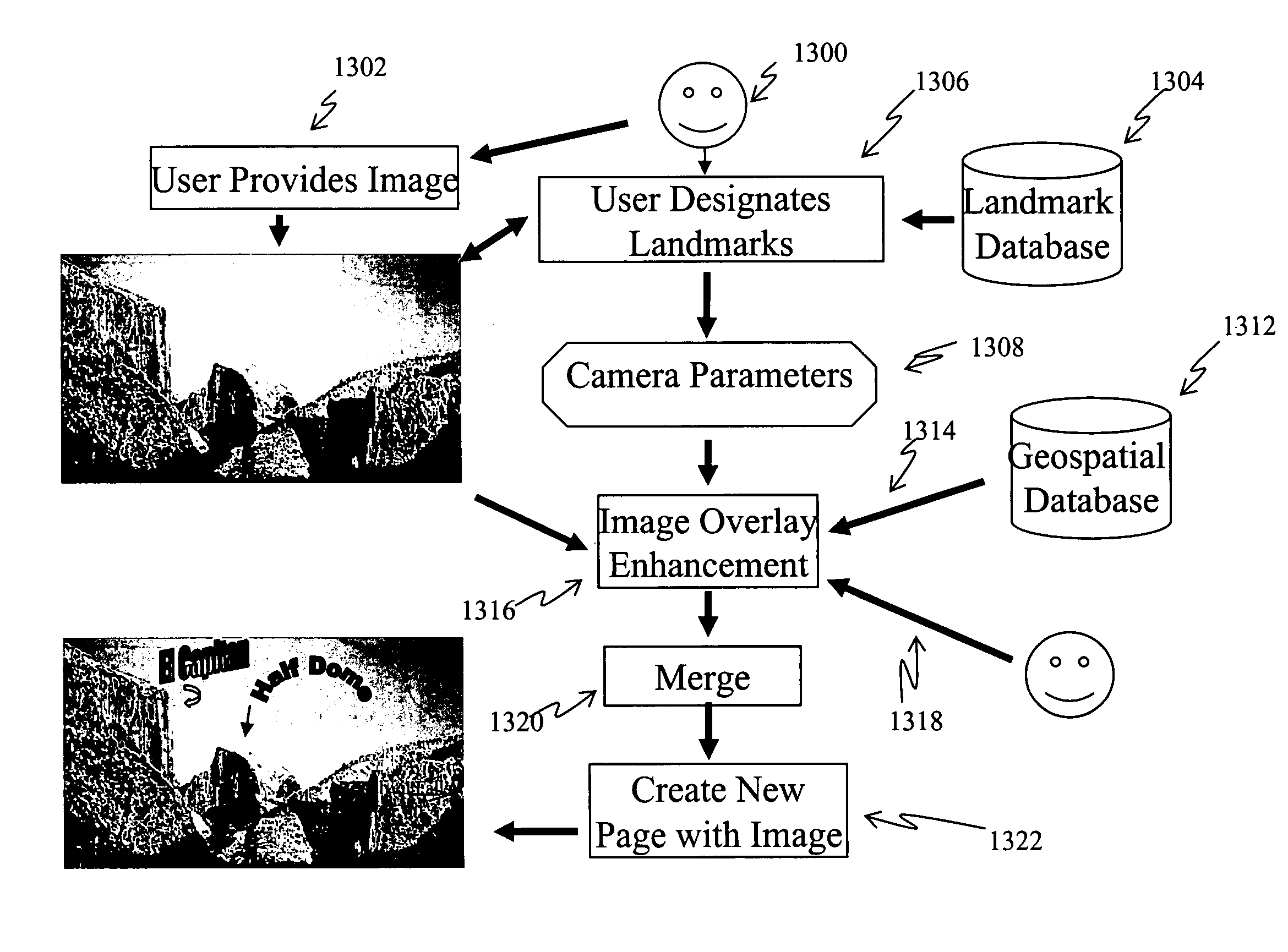
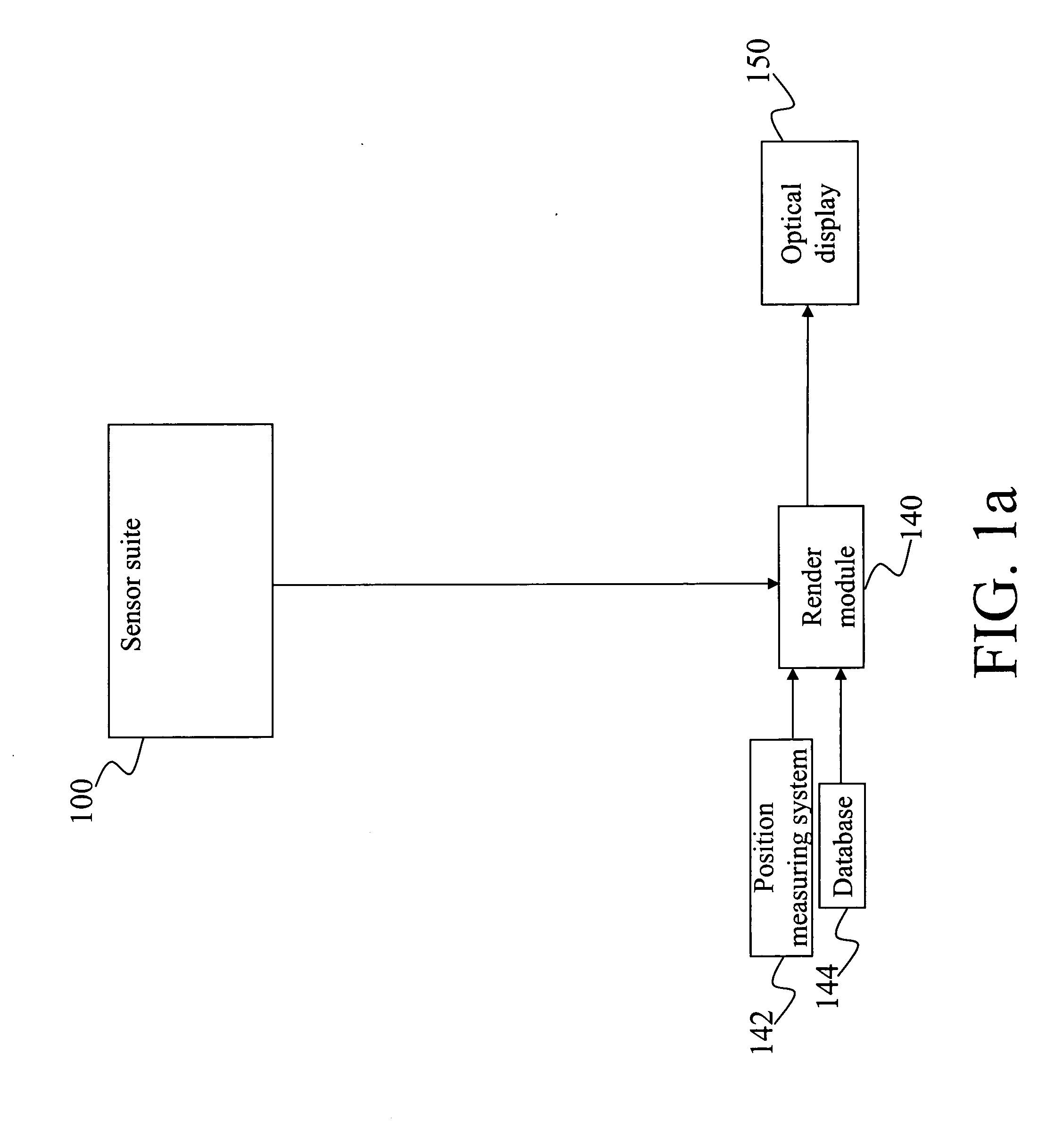
A method and system for providing an optical see-through Augmented Reality modified-scale display. This aspect includes a sensor suite 100 which includes a compass 102, an inertial measuring unit 104, and a video camera 106 for precise measurement of a user's current orientation and angular rotation rate. A sensor fusion module 108 may be included to produce a unified estimate of the user's angular rotation rate and current orientation to be provided to an orientation and rate estimate module 120. The orientation and rate estimate module 120 operates in a static or dynamic (prediction) mode. A render module 140 receives an orientation; and the render module 140 uses the orientation, a position from a position measuring system 142, and data from a database 144 to render graphic images of an object in their correct orientations and positions in an optical display 150.
Owner:HRL LAB
Folded camera lens systems
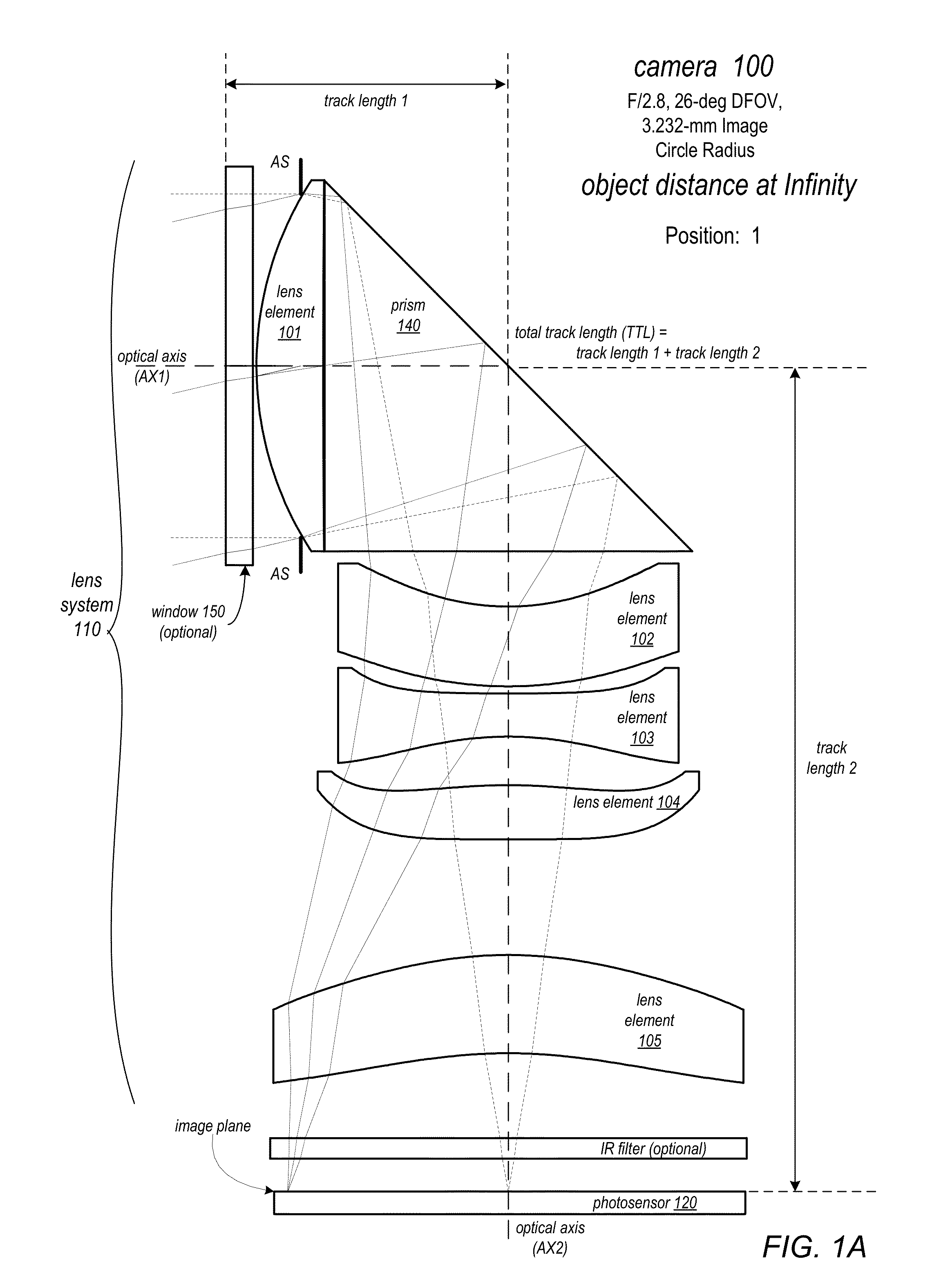
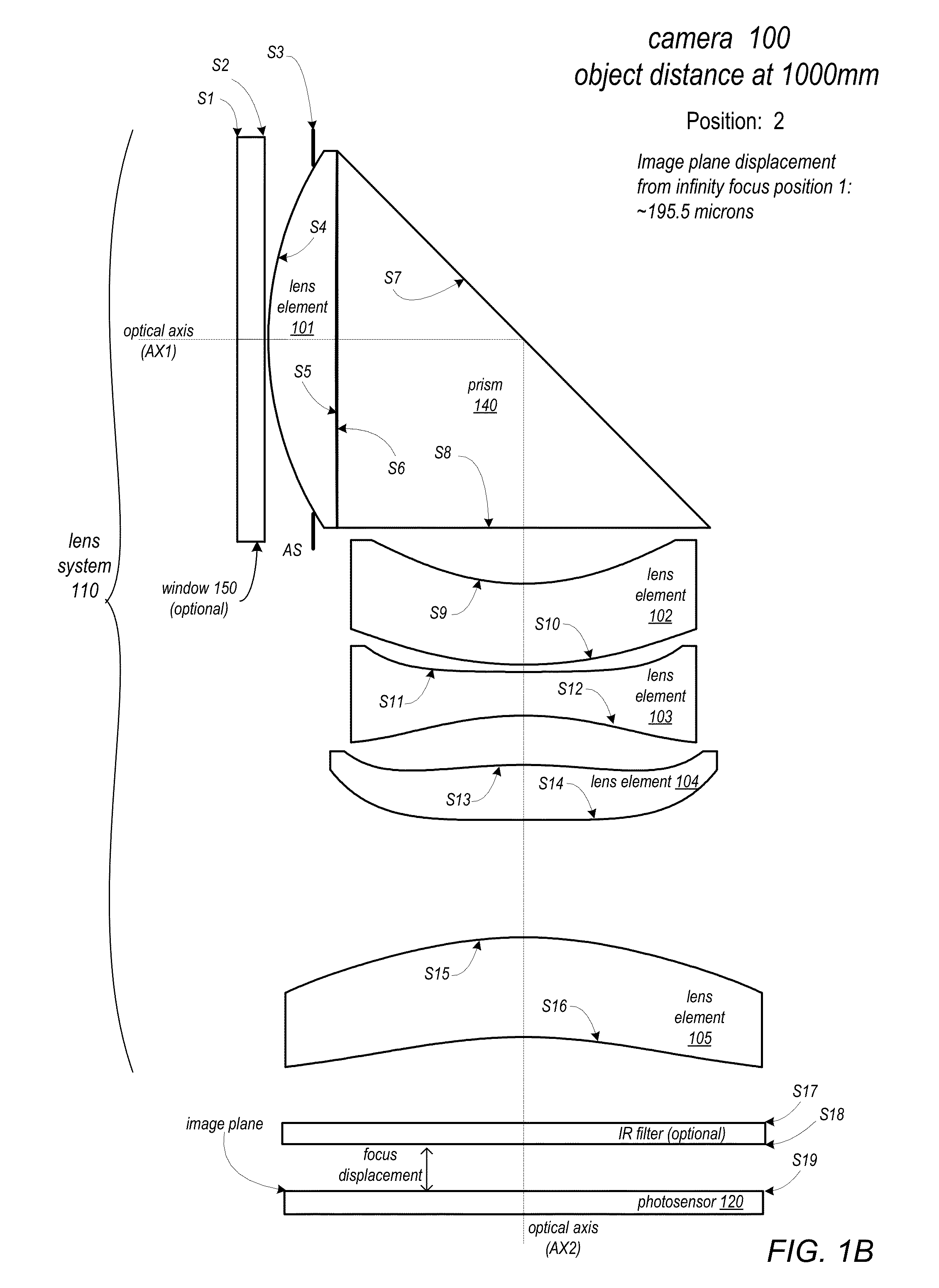
ActiveUS20150253647A1Well-corrected and balanced minimal residual aberrationReduce track lengthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensImage resolution
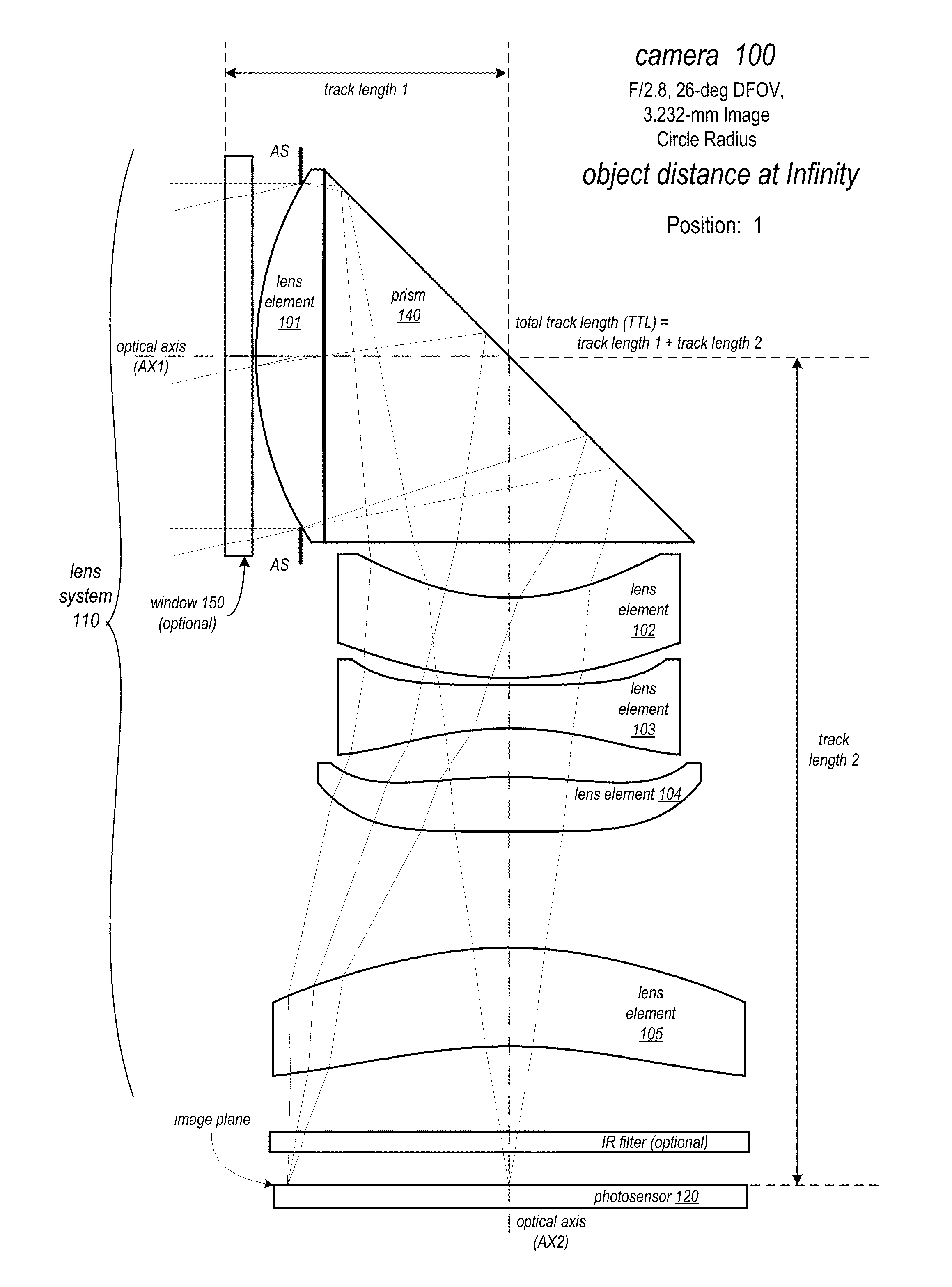
A folded lens system may include multiple lenses with refractive power and a light path folding element. Light entering the camera through lens(es) on a first optical path or axis is refracted to the folding element, which changes direction of the light onto a second optical path or axis with lens(es) that refract the light to form an image plane at a photosensor. At least one of the object side and image side surfaces of at least one of the lens elements may be aspheric. Total track length (TTL) of the lens system may be 16.0 mm or less. The lens system may be configured so that the telephoto ration |TTL / f| is greater than 1.0. Materials, radii of curvature, shapes, sizes, spacing, and aspheric coefficients of the optical elements may be selected to achieve quality optical performance and high image resolution in a small form factor camera.
Owner:APPLE INC
Apparatus for multiple camera devices and method of operating same
InactiveUS20070102622A1High resolutionExcellent color renditionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSignal processing circuitsPhotovoltaic detectors
There are many, many inventions described herein. In one aspect, what is disclosed is a digital camera including a plurality of arrays of photo detectors, including a first array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a first wavelength and a second array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a second wavelength. The digital camera further may also include a first lens disposed in an optical path of the first array of photo detectors, wherein the first lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the first wavelength, and a second lens disposed in with an optical path of the second array of photo detectors wherein the second lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the second wavelength. In addition, the digital camera may include signal processing circuitry, coupled to the first and second arrays of photo detectors, to generate a composite image using (i) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the first array of photo detectors, and (ii) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the second array of photo detectors; wherein the first array of photo detectors, the second array of photo detectors, and the signal processing circuitry are integrated on or in the same semiconductor substrate.
Owner:OLSEN RICHARD IAN +8
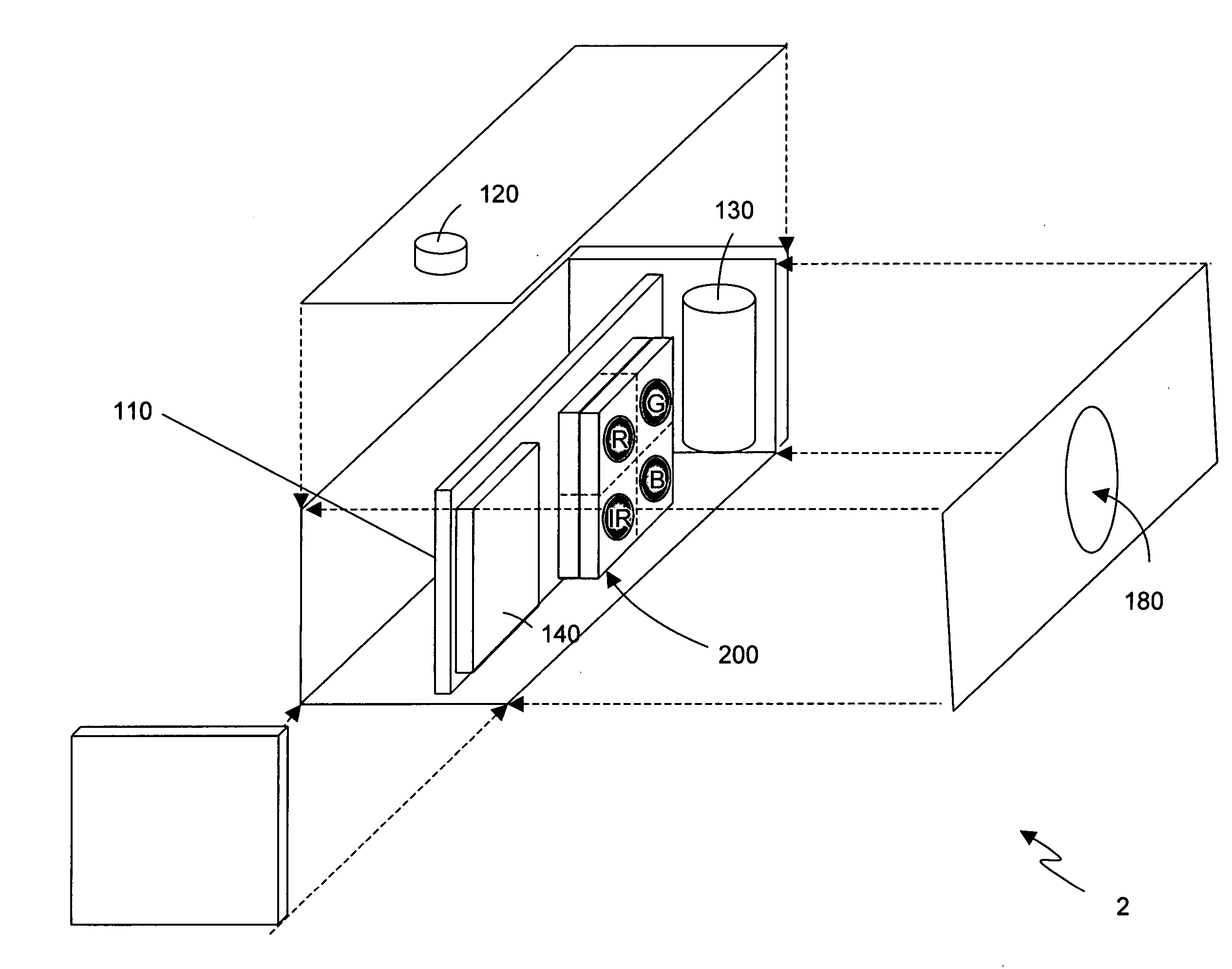
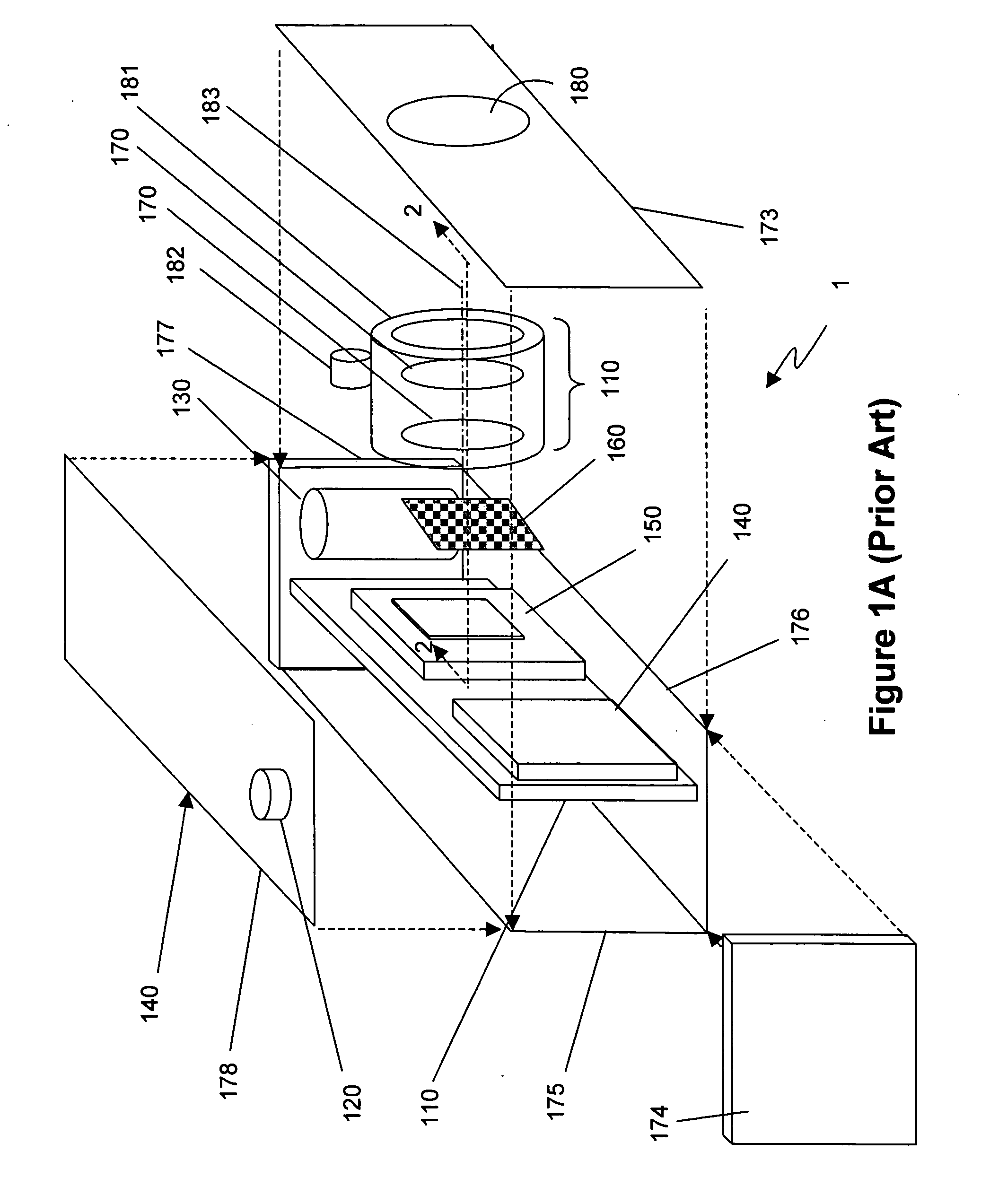
Digital camera with integrated infrared (IR) response
ActiveUS7566855B2High resolutionExcellent color renditionTelevision system detailsX-ray/infra-red processesSignal processing circuitsElectrical conductor
There are many, many inventions described herein. In one aspect, what is disclosed is a digital camera including a plurality of arrays of photo detectors, including a first array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a first wavelength and a second array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a second wavelength. The digital camera further may also include a first lens disposed in an optical path of the first array of photo detectors, wherein the first lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the first wavelength, and a second lens disposed in with an optical path of the second array of photo detectors wherein the second lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the second wavelength. In addition, the digital camera may include signal processing circuitry, coupled to the first and second arrays of photo detectors, to generate a composite image using (i) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the first array of photo detectors, and (ii) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the second array of photo detectors; wherein the first array of photo detectors, the second array of photo detectors, and the signal processing circuitry are integrated on or in the same semiconductor substrate.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
Lens holder driving device including damper compound suppressing undesired resonance
ActiveUS20130050828A1Carrying out operation with stabilityTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensOptical axis
A lens holder driving device includes a lens holder moving portion, a fixed member, suspension wires, and a damper compound. In the lens holder moving portion, a lens holder moves in an optical axis and in first and second directions which are orthogonal to the optical axis and which are perpendicular to each other. The fixed member is disposed apart from the lens holder moving portion in the direction of the optical axis. The suspension wires have first end portions fixed to the fixed member at outer regions thereof, extending along the optical axis, having second end portions fixed to an elastic member mounted to the lens holder moving portion, and swingably supporting the lens holder moving portion in the first direction and the second direction. The damper compound is disposed so as to enclose at least one suspension wire and suppresses undesired resonance in the lens holder moving portion.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
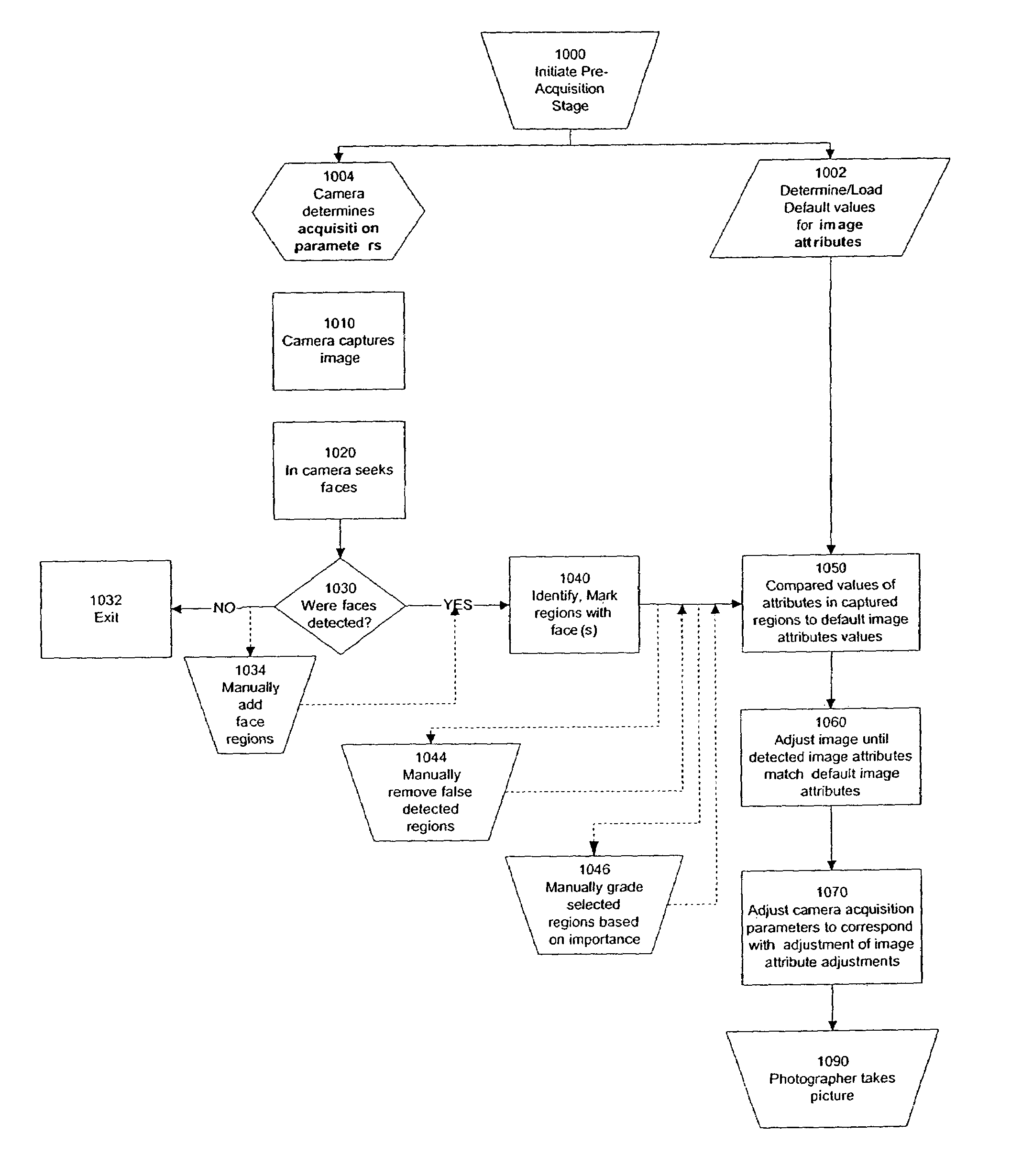
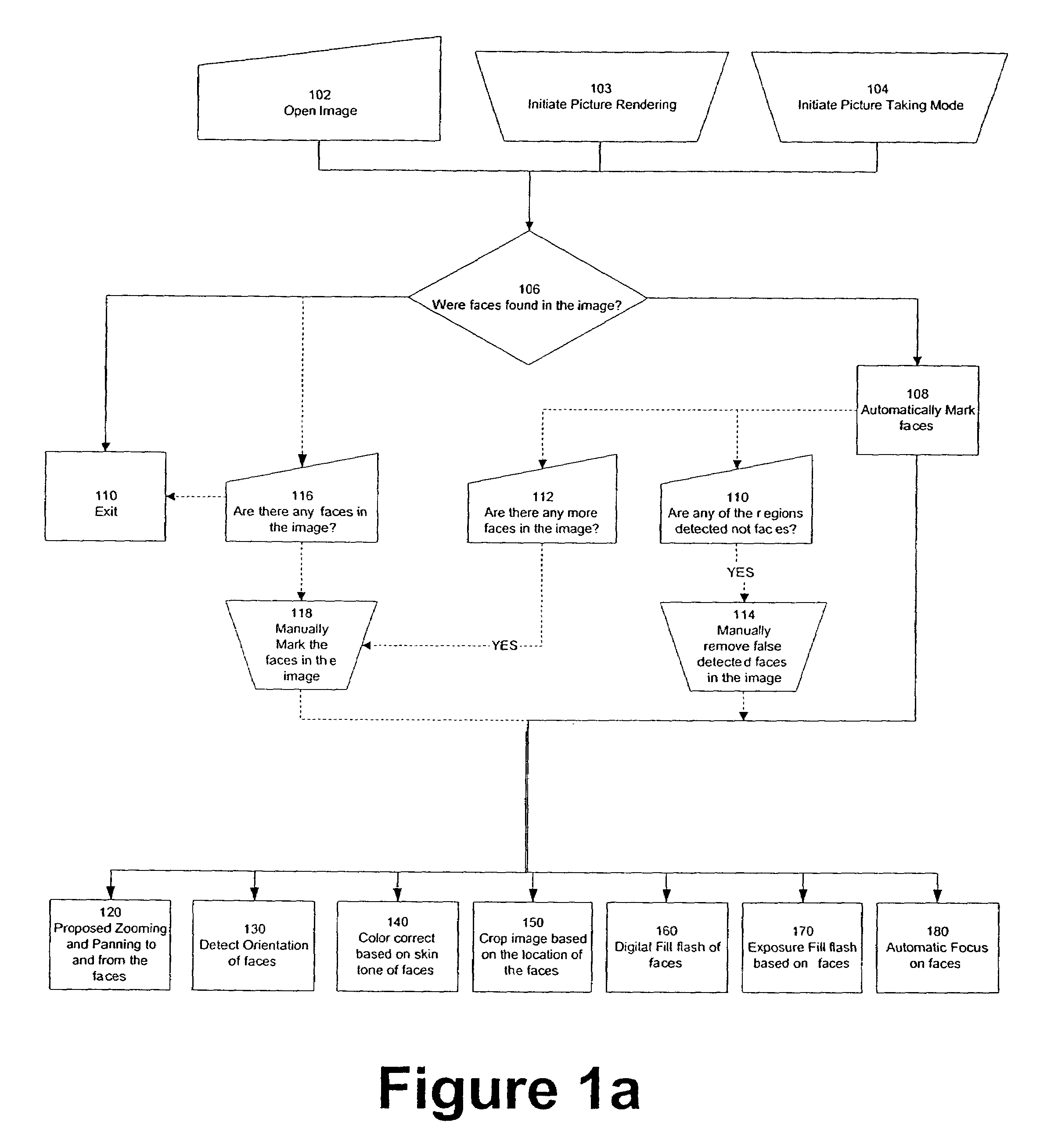
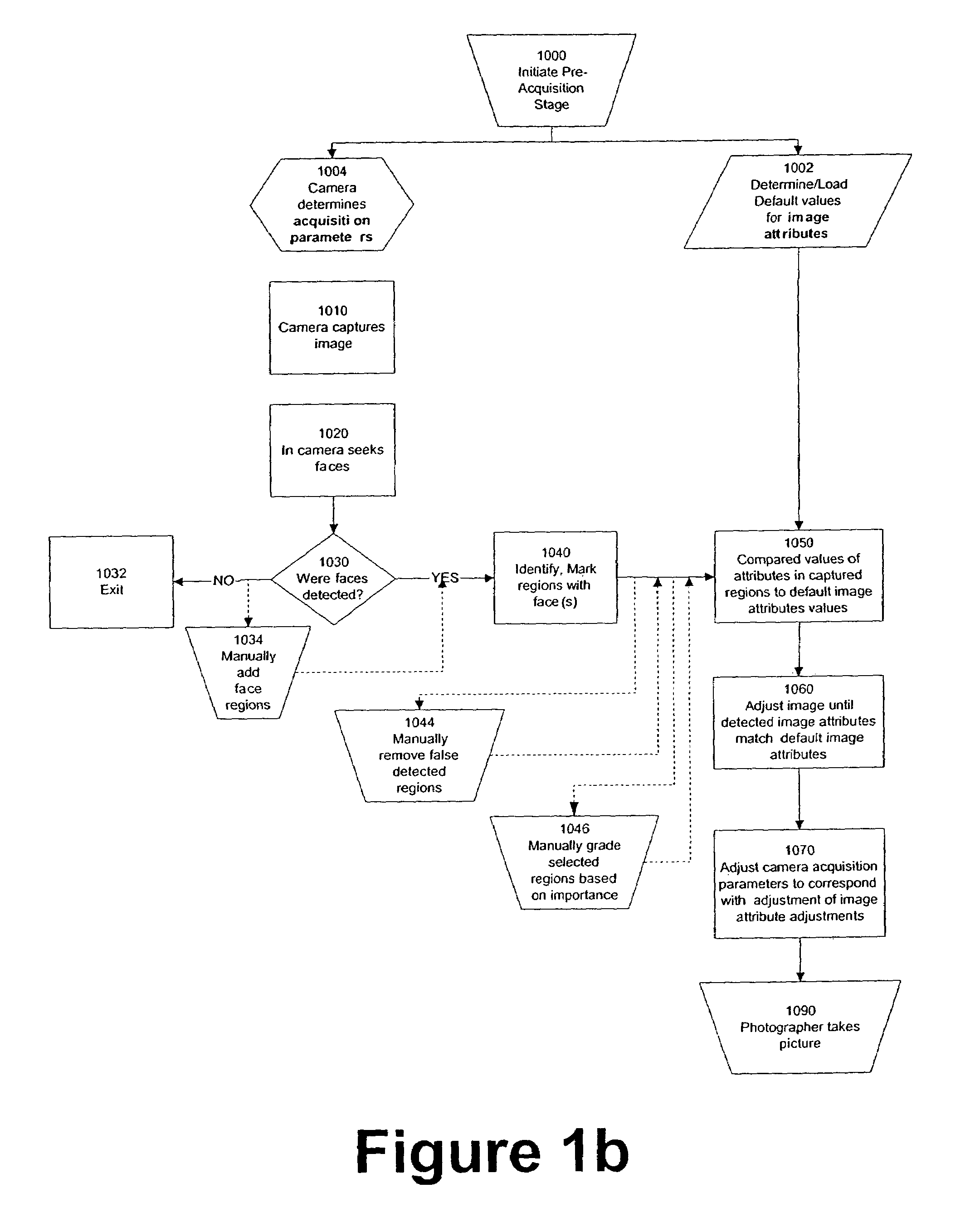
Perfecting the optics within a digital image acquisition device using face detection
ActiveUS7362368B2Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementFace detectionAcquisition apparatus
Within a digital acquisition device, acquisition parameters of a digital image are perfected as part of an image capture process using face detection within said captured image to achieve one or more desired image acquisition parameters. Default values are determined of one or more image attributes of at least some portion of the digital image. Values of one or more camera acquisition parameters are determined. Groups of pixels are identified that correspond to an image of a face within the digitally-captured image. Corresponding image attributes to the groups of pixels are determined. One or more default image attribute values are compared with one or more captured image attribute values based upon analysis of the image of the face. Camera acquisition parameters are then adjusted corresponding to adjusting the image attribute values.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
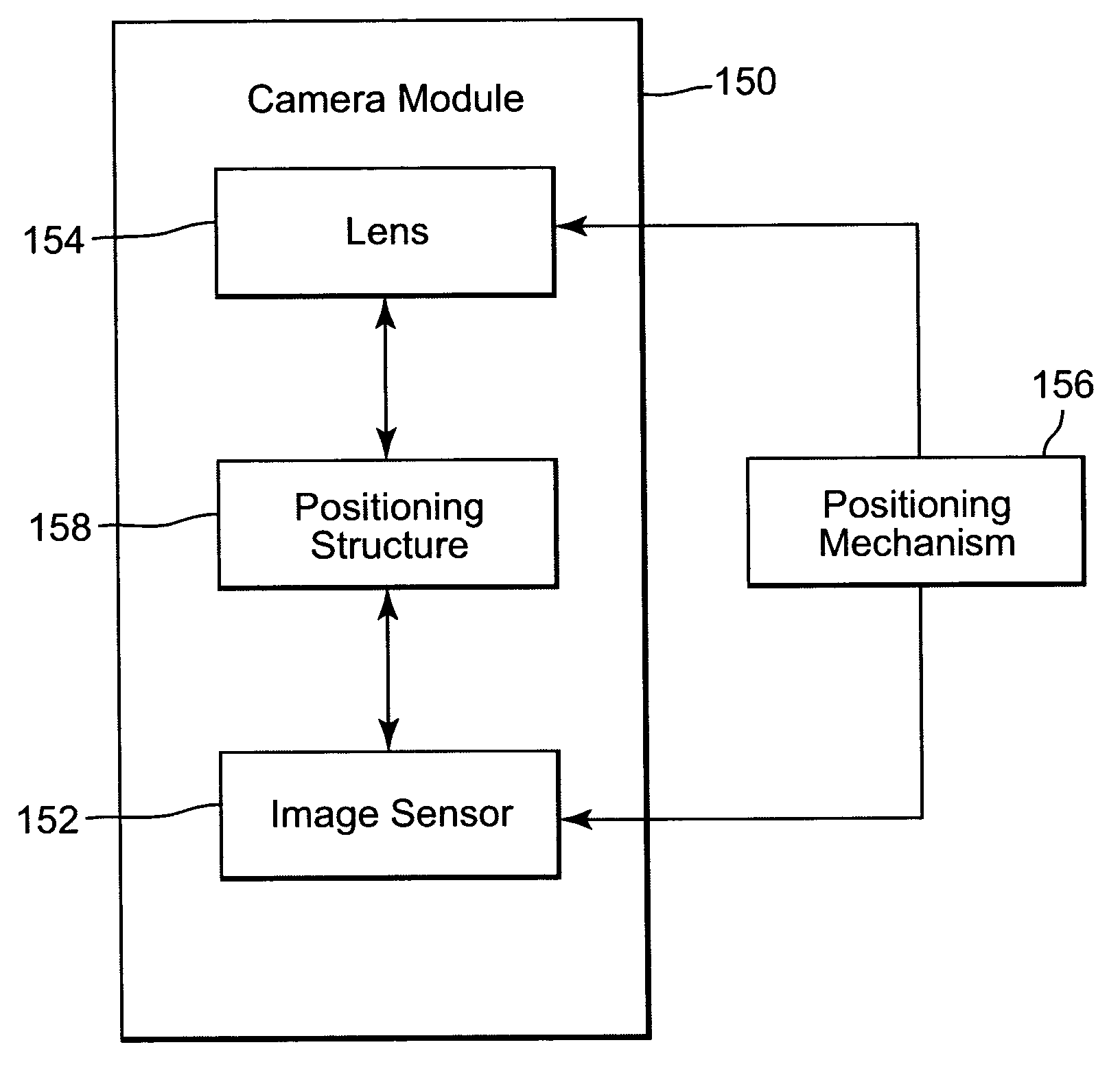
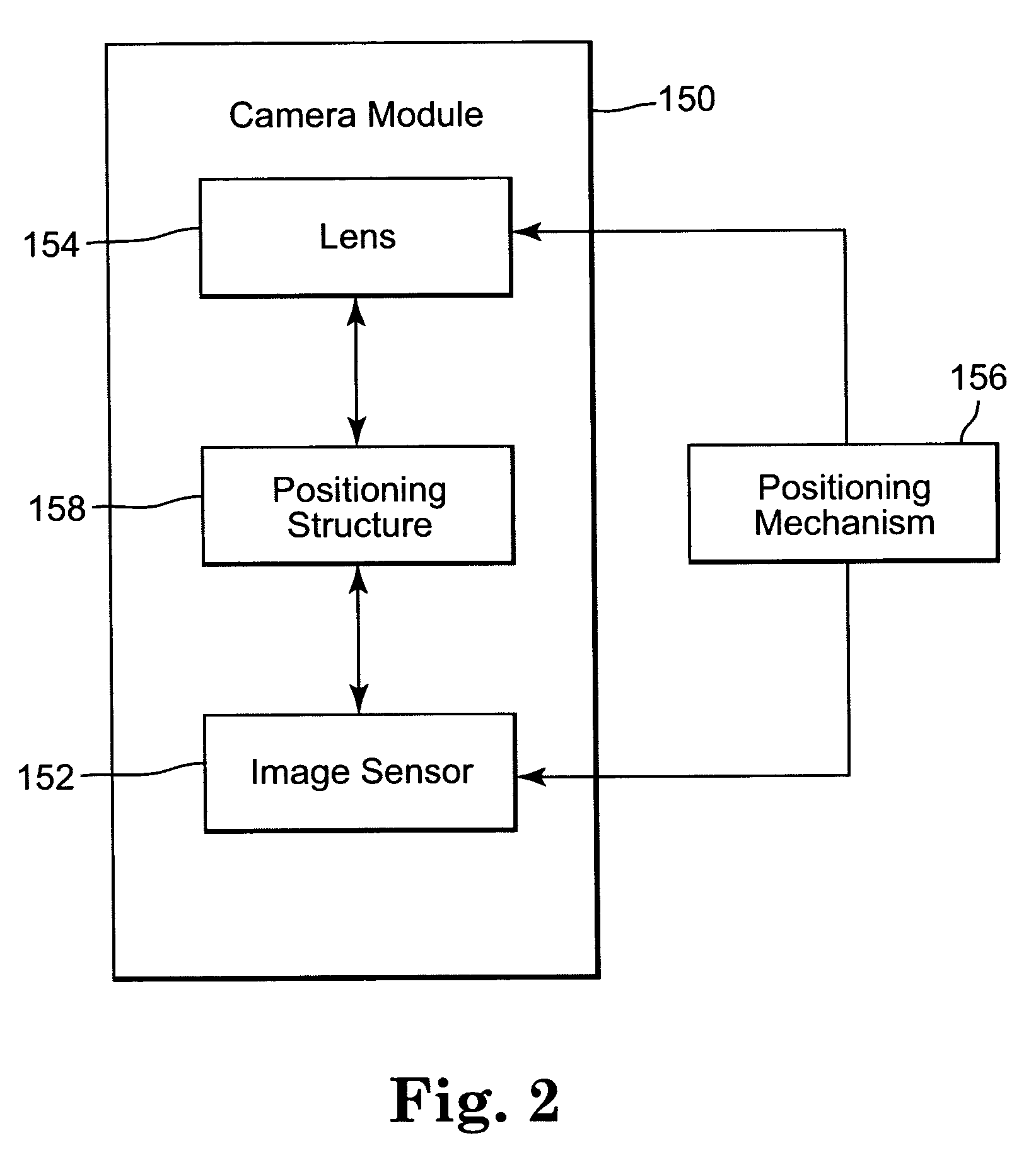
Fixed-focus camera module and associated method of assembly
InactiveUS20050036778A1Maintain alignmentTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementImaging qualityCamera module
A fixed-focus camera module includes an image sensor, a lens for focusing an image onto the image sensor, and a positioning structure for maintaining an alignment of the lens and image sensor. The alignment provides a desired image quality of the image focussed onto the image sensor. The positioning structure includes a first unthreaded member coupled to the lens and a second unthreaded member coupled to the image sensor. One of the first and the second members is configured to be inserted into the other of the members to provide an adjustable relative position of the lens and the image sensor.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
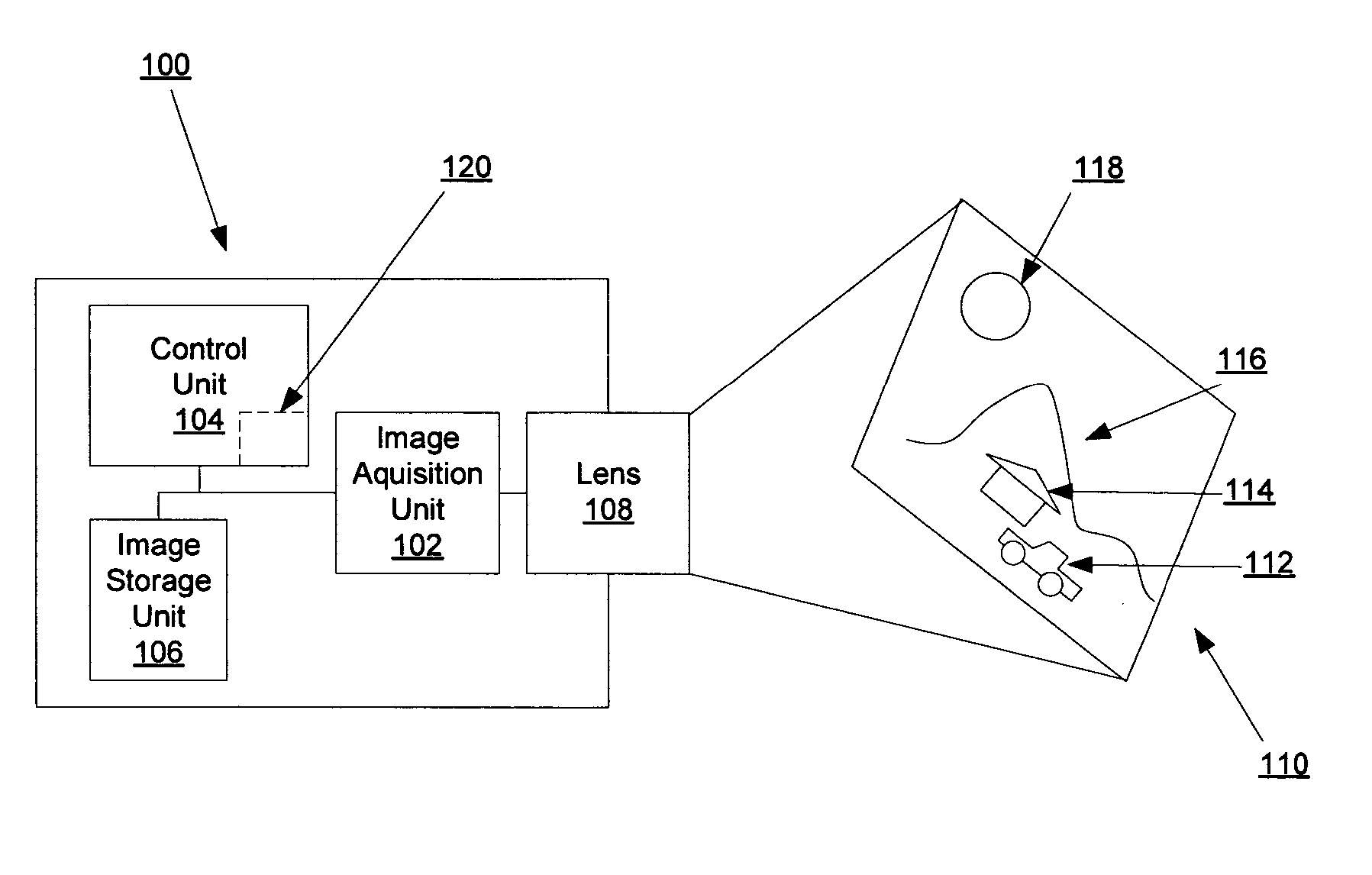
Simple method for calculating camera defocus from an image scene
ActiveUS20070216765A1Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementThree-dimensional spaceAutofocus
An imaging acquisition system that generates a picture depth from an auto focus curve generated from picture of a three dimensional spatial scene is described. The auto focus curve comprises a step edge. The system generates the depth based on the step edge and a reference auto focus normalization curve.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
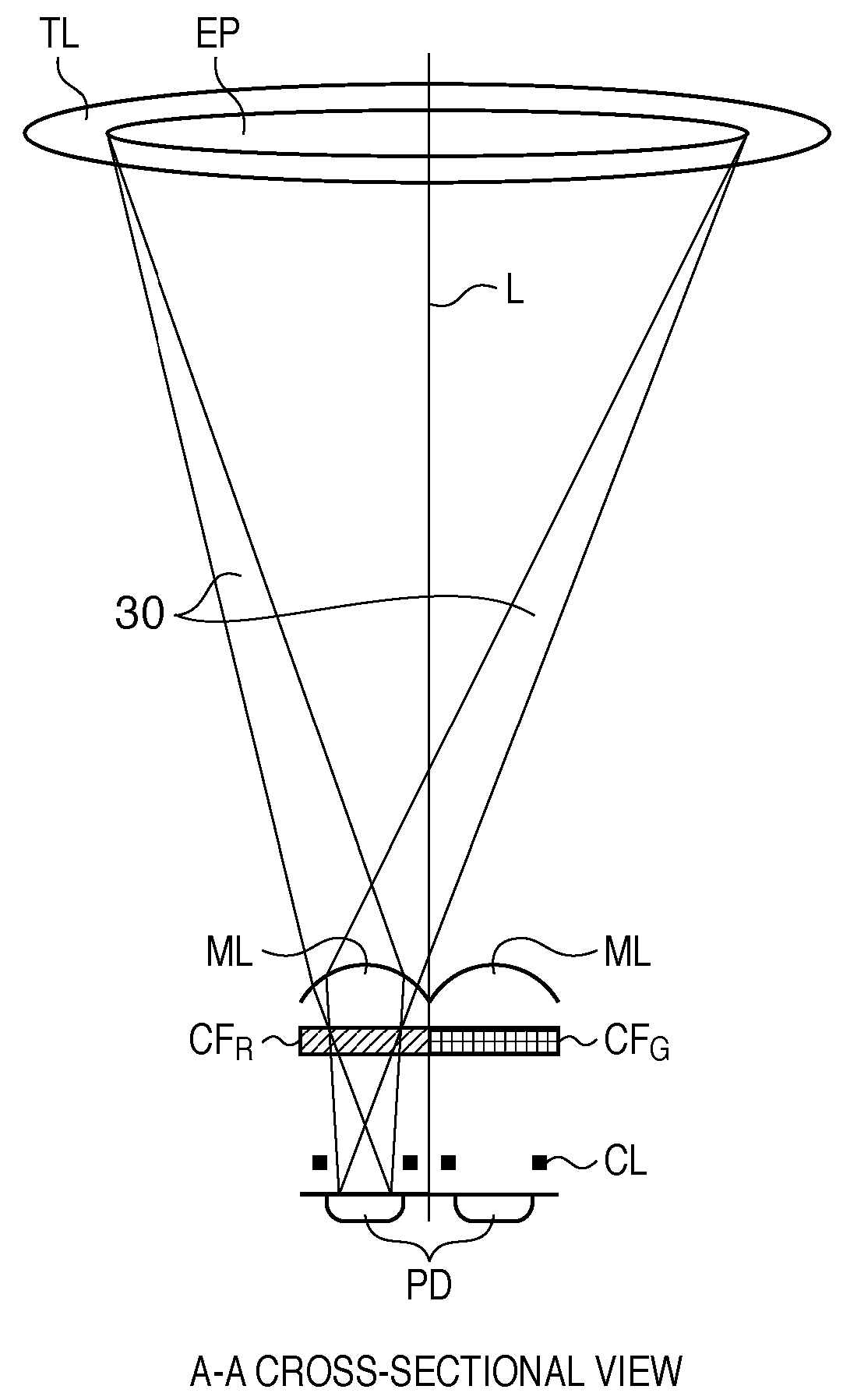
Image sensing apparatus, image sensing system and focus detection method
InactiveUS20100045849A1Improve accuracyMethod can be usedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCamera lensRelative shift
An image sensing apparatus including: an image sensor including a plurality of focus detection pixel pairs that perform photoelectric conversion on each pair of light beams that have passed through different regions of a photographing lens and output an image signal pair; a flash memory that stores shift information on relative shift between an optical axis of the photographing lens and a central axis of the focus detection pixel pairs; a correction unit that corrects a signal level of the image signal pair based on the shift information and exit pupil information of the photographing lens so as to compensate for an unbalanced amount of light that enters each of the focus detection pixel pairs; and a focus detection unit that detects a focus of the photographing lens using the image signal pair corrected by the correction unit.
Owner:CANON KK
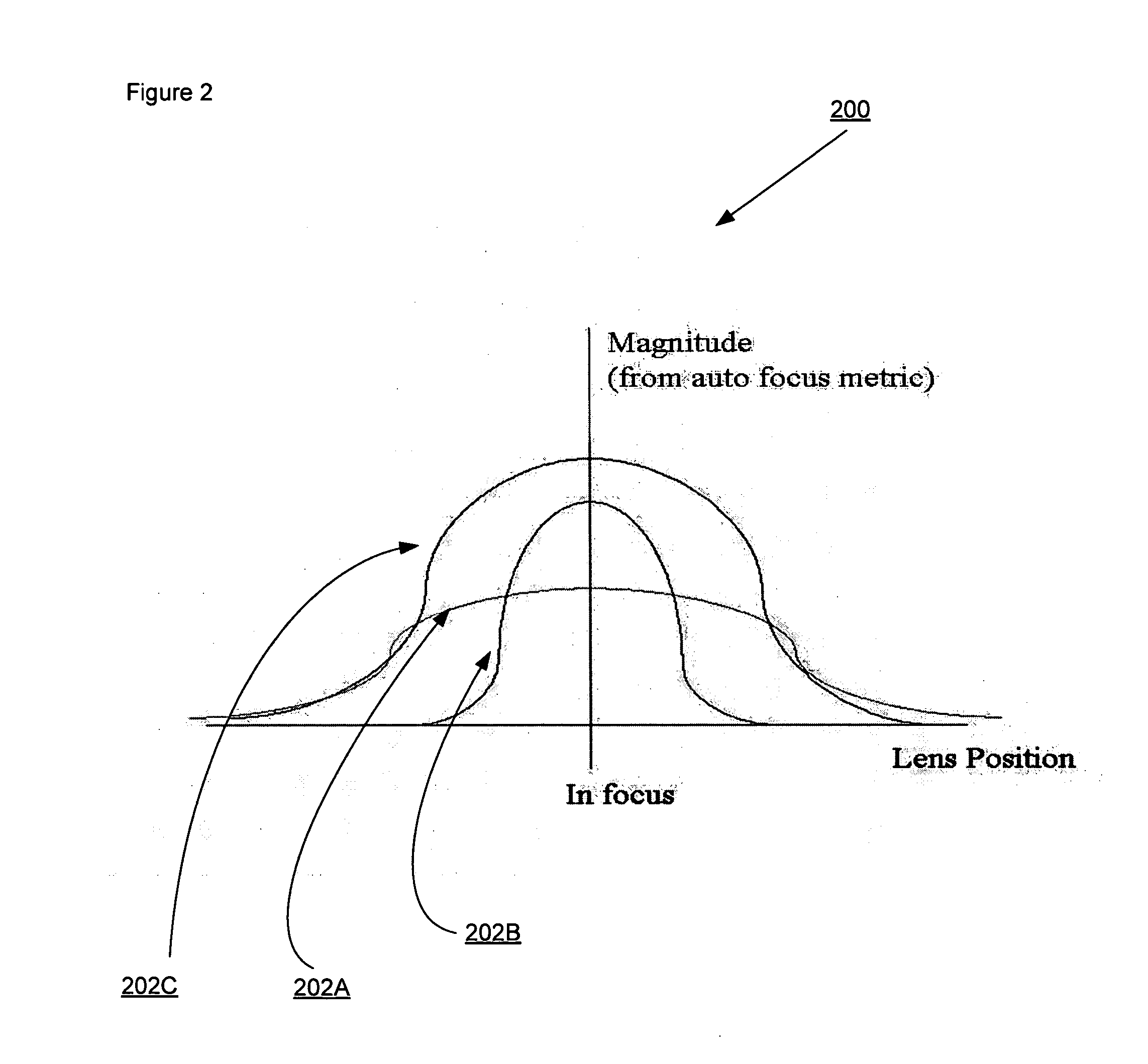
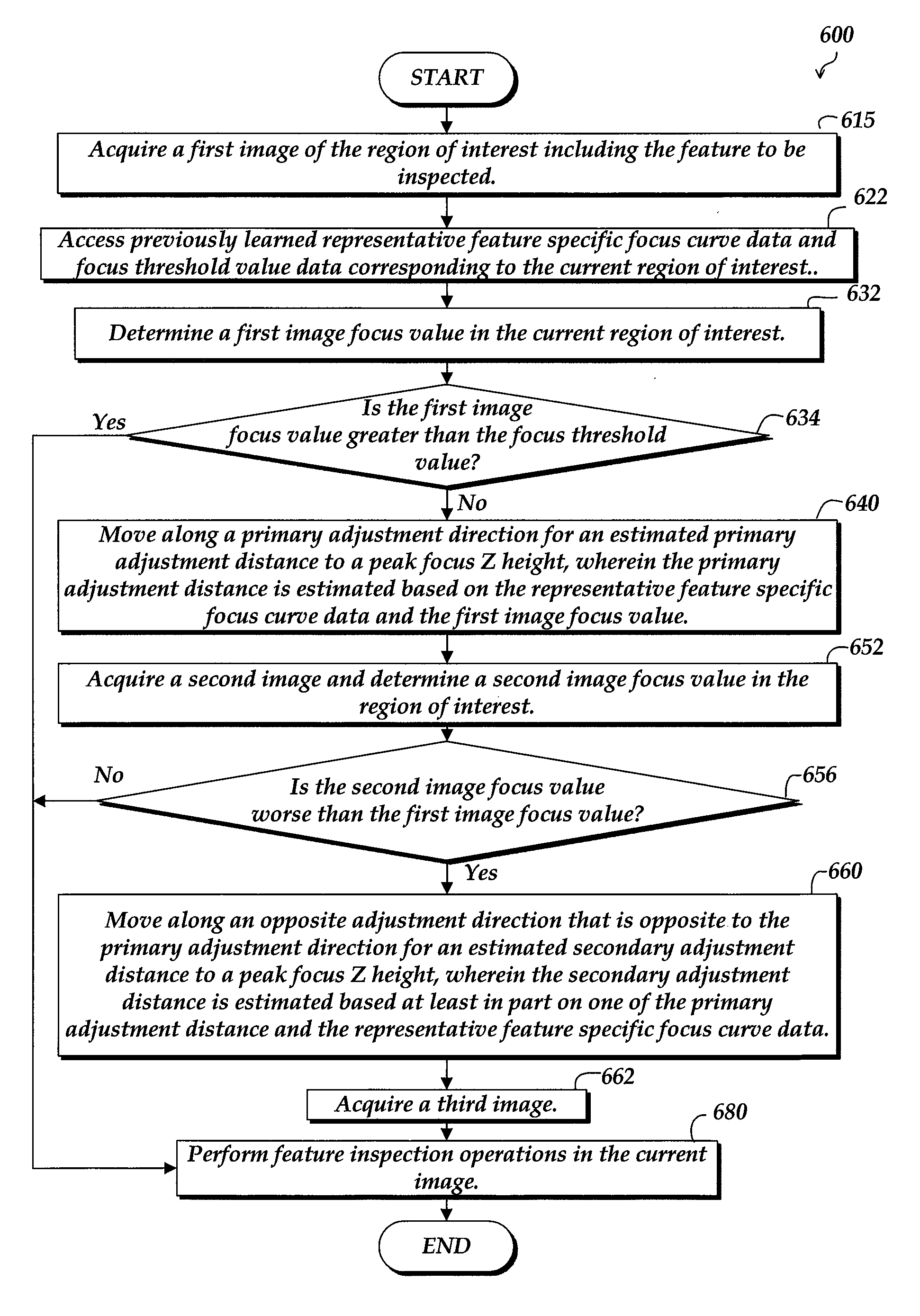
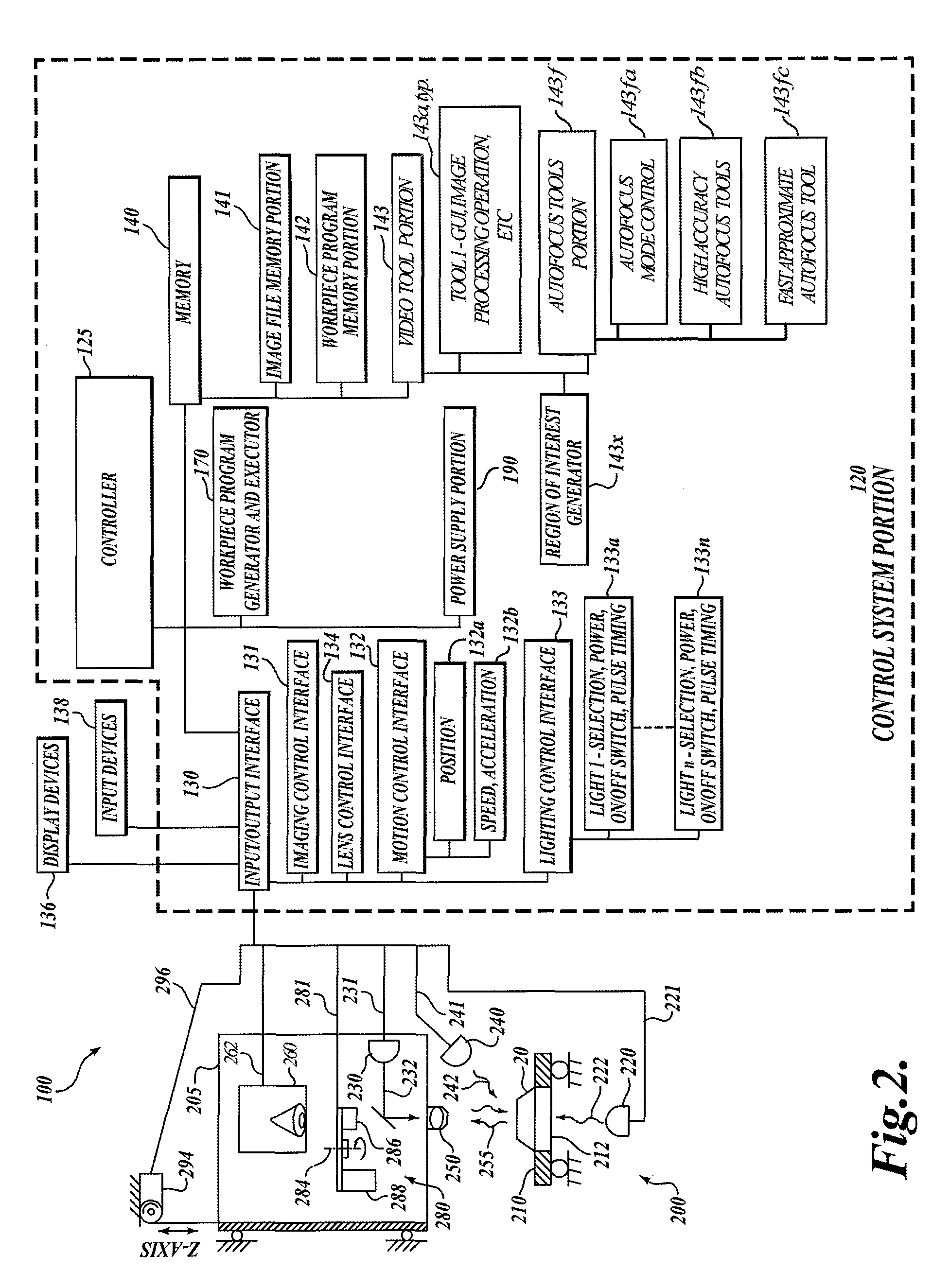
System and method for fast approximate focus
ActiveUS8111938B2Improve throughputQuick focusTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Engineering
Fast approximate focus operations providing an approximately focused image that is sufficiently focused to support certain subsequent inspection operations. The operations are particularly advantageous when used to provide images for successive inspection operations that predominate when inspecting planar workpieces. Improved inspection throughput is provided because, in contrast to conventional autofocus operations, the fast approximate focus operations do not acquire an image stack during a run mode as a basis for determining a best focused image. Rather, during learn mode, a representative feature-specific focus curve and a focus threshold value are determined and used during run mode to provide an approximately focused image that reliably supports certain inspection operations. In one embodiment, an acceptable approximately focused inspection image is provided within a limit of two focus adjustment moves that provide two corresponding images. The adjustment moves are based on the representative feature-specific focus curve provided in learn mode.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Method and apparatus for image enhancement
InactiveUS20070035562A1Improve accuracyAccurate currentInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsImage enhancement
The present invention is generally related to image enhancement and augmented reality (“AR”). More specifically, this invention presents a method and an apparatus for static image enhancement and the use of an optical display and sensing technologies to superimpose, in real time, graphical information upon a user's magnified view of the real world.
Owner:HRL LAB
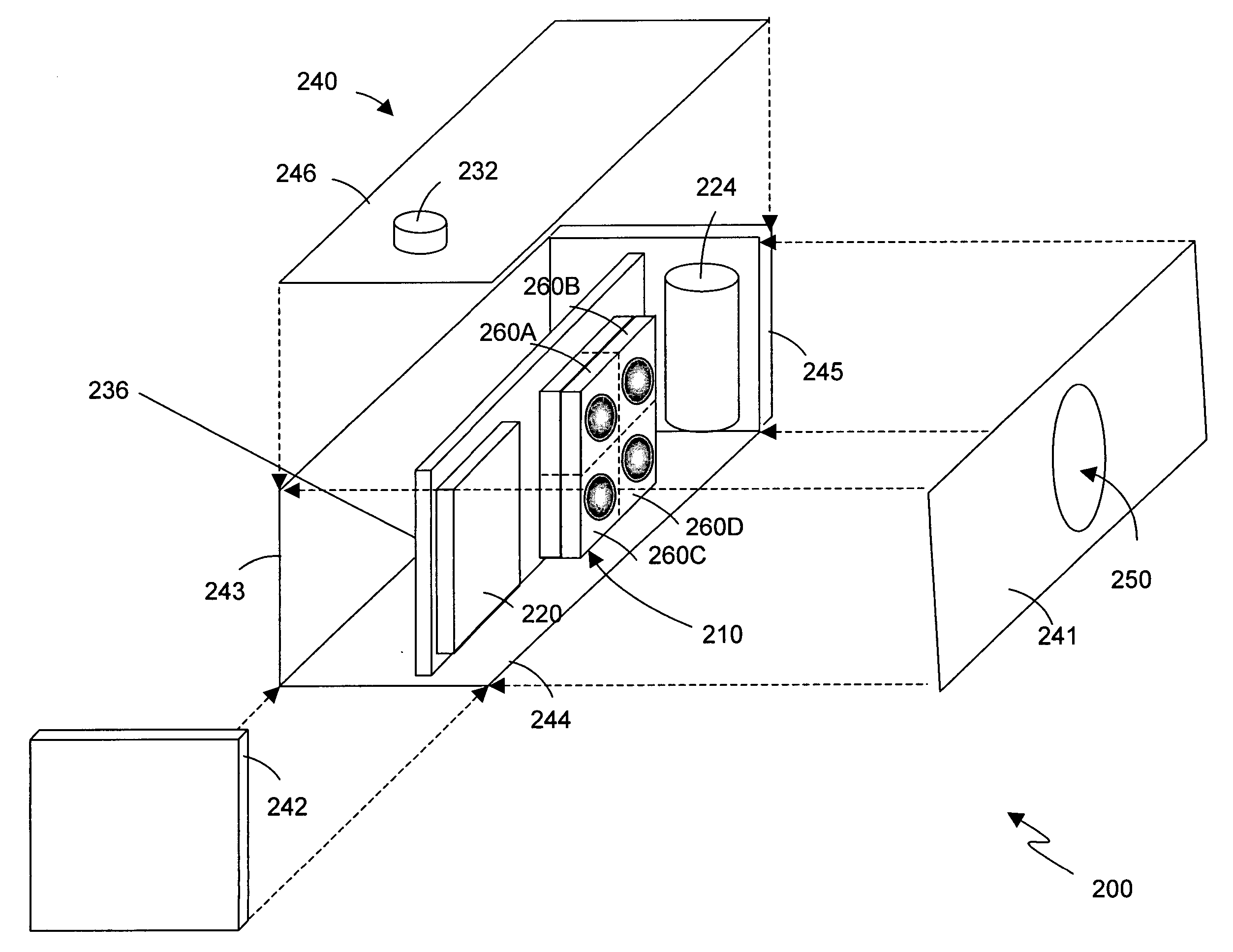
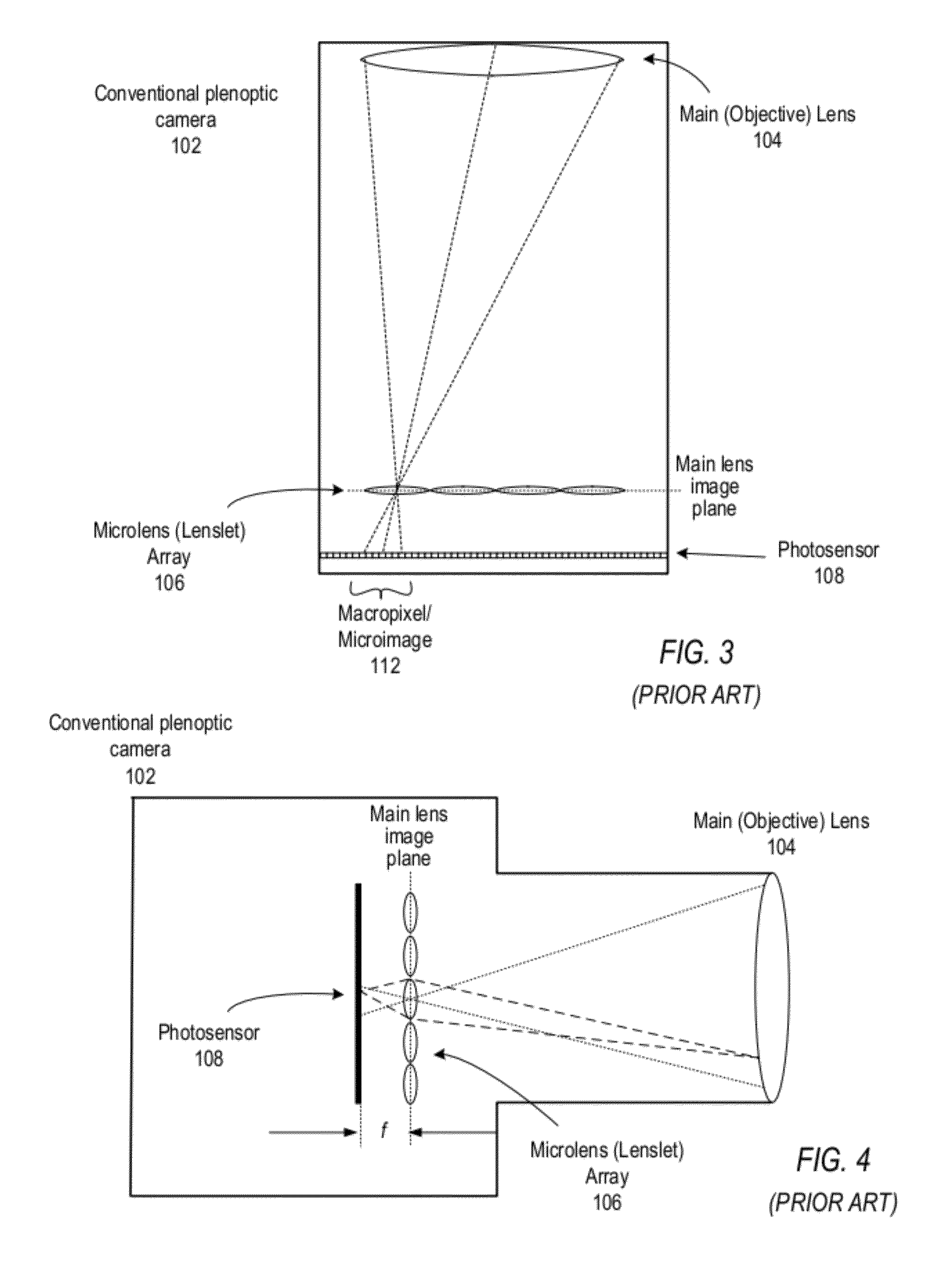
Focused plenoptic camera employing different apertures or filtering at different microlenses
ActiveUS8228417B1Increase and maximize spatial resolutionSharper and high spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensMicro lens array
Owner:ADOBE INC
Tri-Axis Close Loop Feedback Controlling Module for Electromagnetic Lens Driving Device
The tri-axis close-loop feedback controlling module for electromagnetic lens driving device comprises a 6-pin Hall element. Two pins of the Hall element are coupled to an auto-focus module for providing a current to drive the auto-focus module to conduct auto-focusing operations along the Z-axis; while other four pins of the Hall element are coupled to a control unit. The control unit detects the X-Y axial positions of the auto-focus module relative to an OIS module and generates a control signal which is then sent to the Hall element. Therefore, the Hall element not only can provide its own feedback controlling function according to the Z-axial position of lens, but also can drive the auto-focus module based on the control signal corresponding to the X-Y axial positions of the auto-focus module, so as to achieve the goal of tri-axis close-loop feedback controlling for the electromagnetic lens driving device.
Owner:TDK TAIWAN
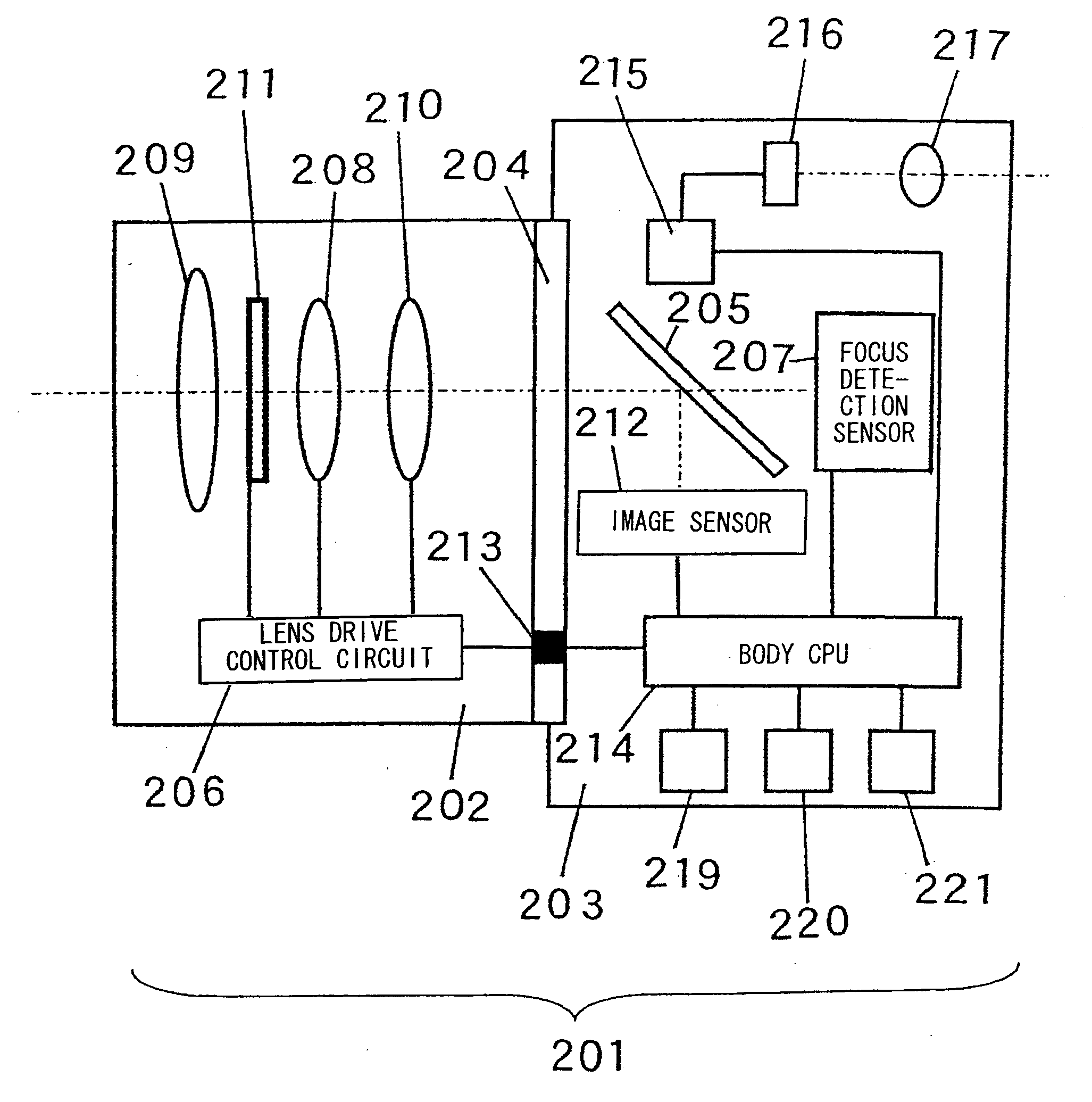
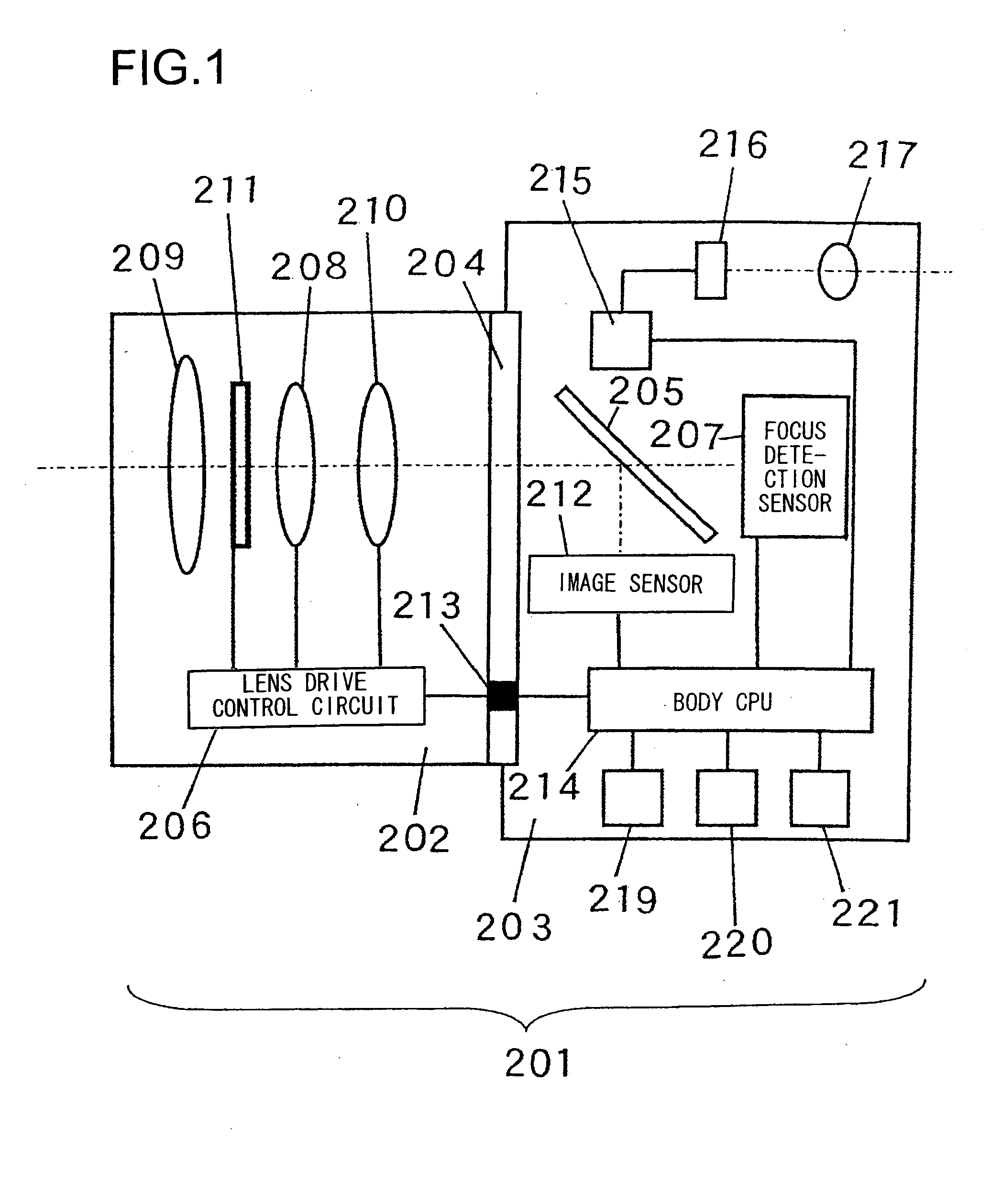
Focus adjustment device, imaging device and focus adjustment method
A focus adjustment device includes an image sensor that includes imaging pixels for capturing an image formed via an imaging optical system and focus detection pixels for detecting a focus adjustment state at the imaging optical system through a first pupil division-type image shift detection method, a focus detector that detects a focus adjustment state at the imaging optical system through a second pupil division-type image shift detection method different from the first pupil division-type image shift detection method, and a focus adjustment controller that executes focus adjustment for the imaging optical system based upon the focus adjustment states detected by the image sensor and the focus detector.
Owner:NIKON CORP
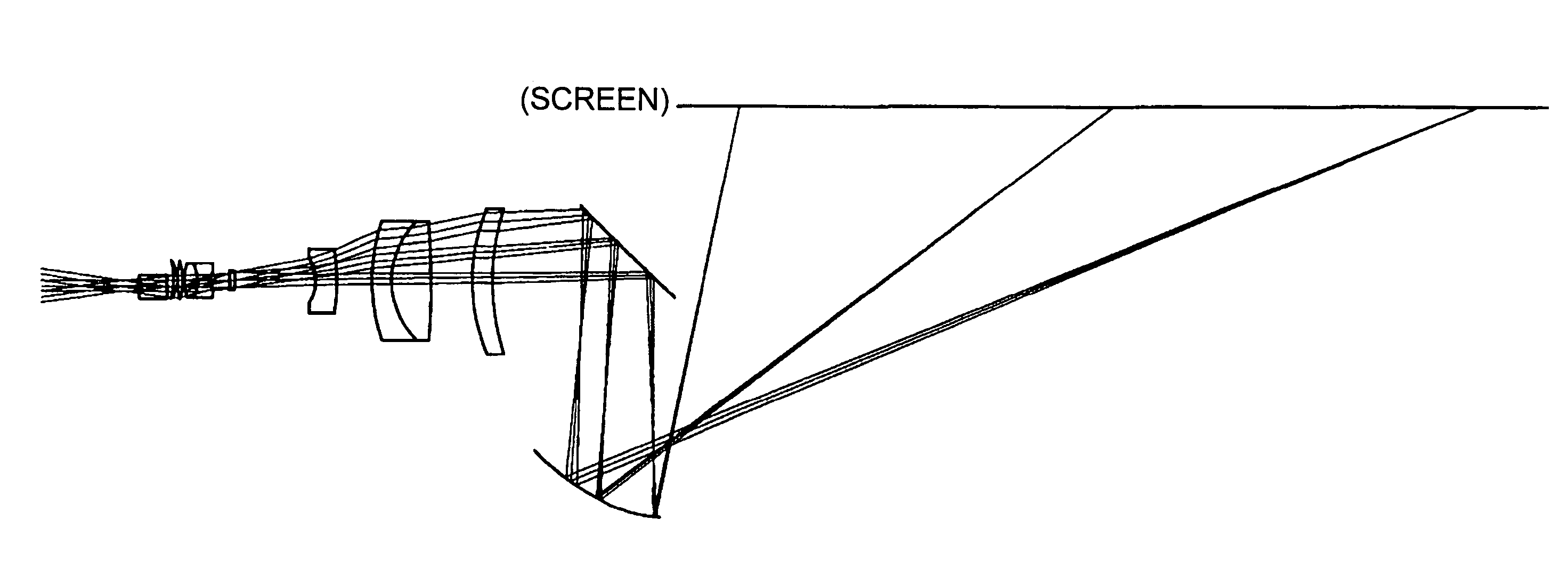
Projection optical system, magnification projection optical system, magnification projection apparatus, and image projection apparatus
ActiveUS7048388B2Increase in sizeReduce spacingProjectorsNon-linear opticsProjection opticsIntermediate image
A projection optical system guiding and projecting a light beam from a projected object surface onto a projection surface in an upstream-downstream direction through a transmission dioptric system and a reflection dioptric system. An intermediate image surface of the projected object surface is positioned closer to the reflection dioptric system than to the transmission dioptric system, and an intermediate image on the intermediate image surface is formed as the final image on the projection surface via the reflecting mirrors, which include at least one anamorphic polynomial free-formed surface having different vertical and lateral powers. A light beam from the reflection dioptric system to the projection surface is guided at an angle to a normal of the projection surface and the transmission dioptric system is decentered with respect to a normal of the projected object surface, the transmission refractive elements prevented from being decentered with respect to each other.
Owner:RICOH KK
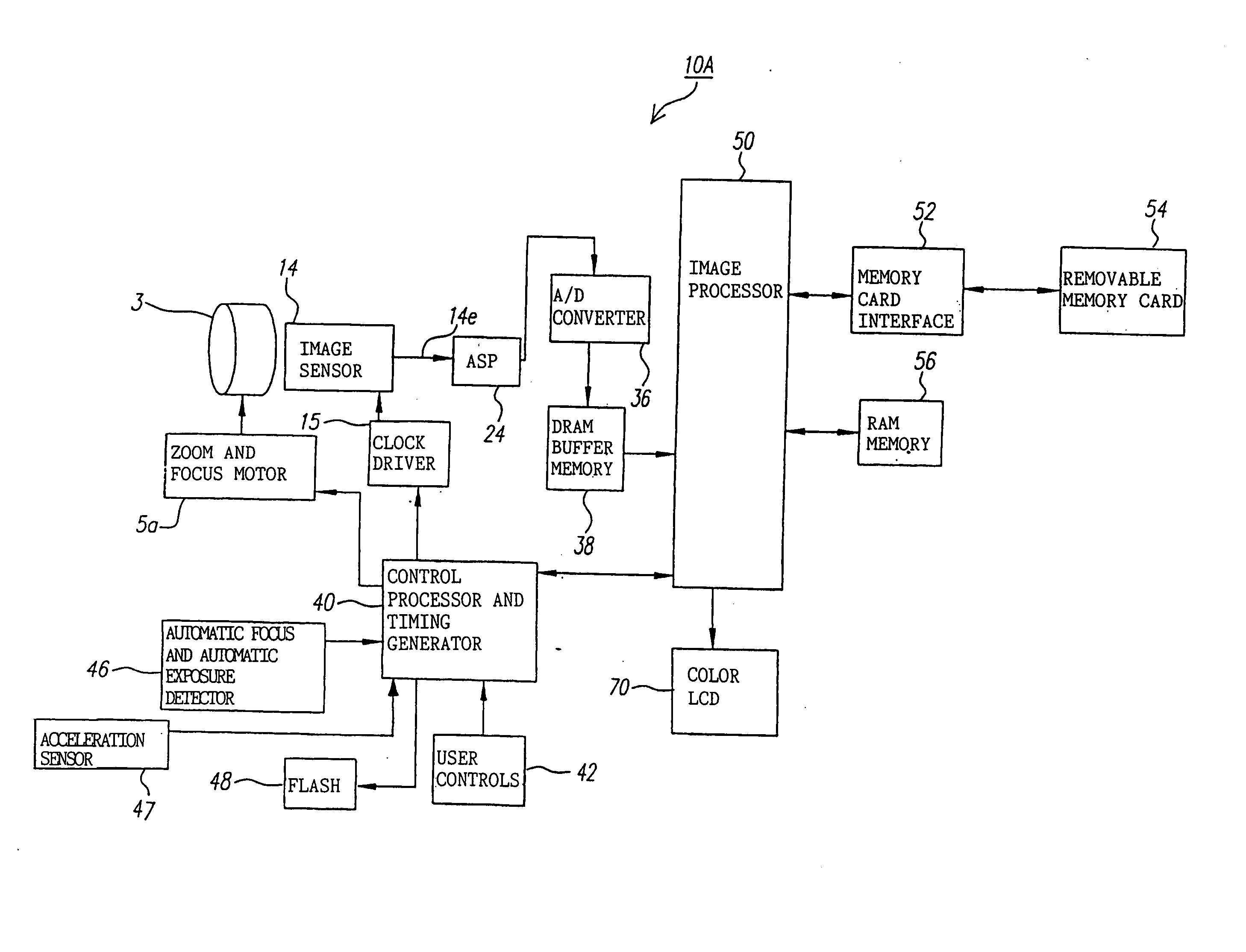
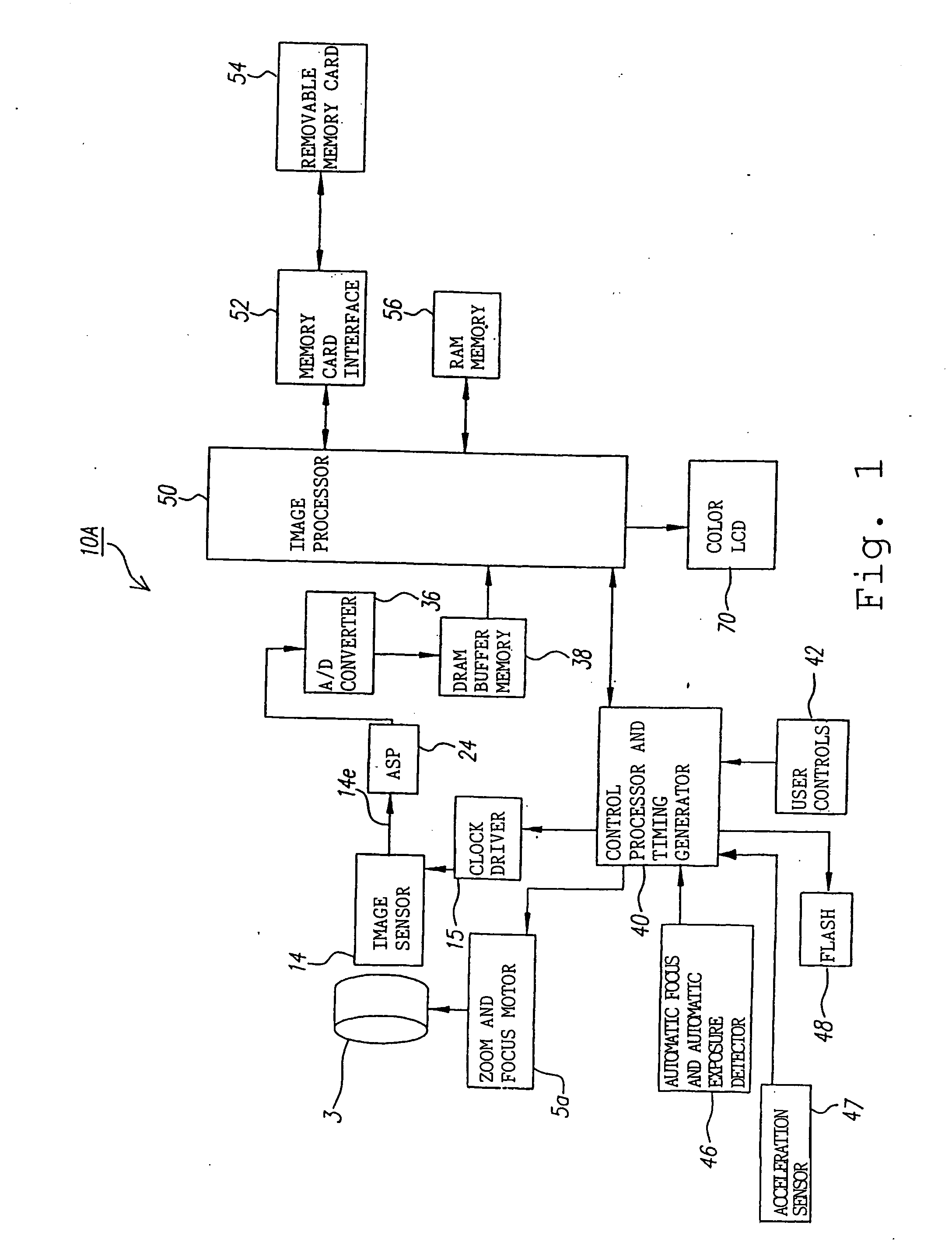
Image capturing apparatus
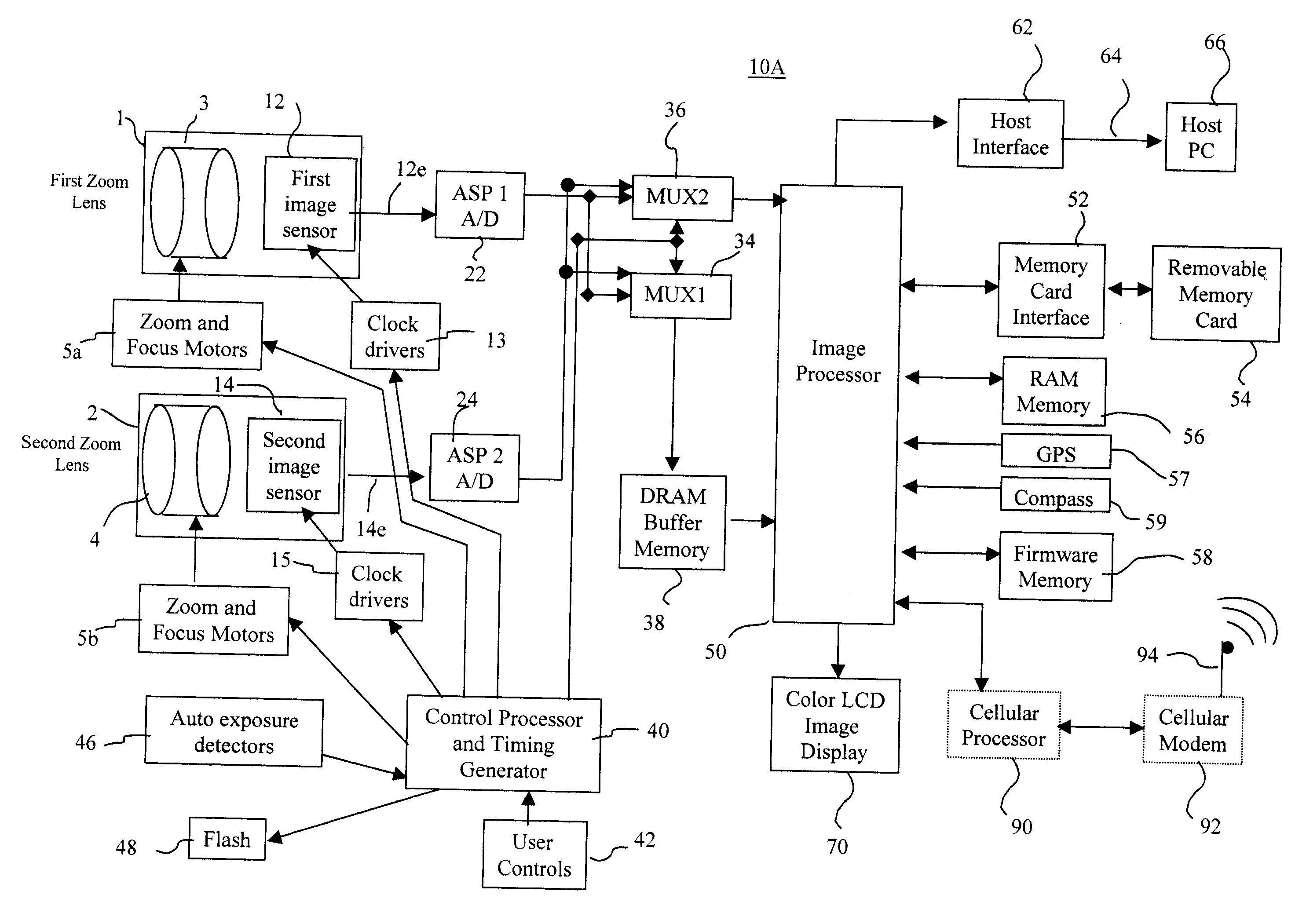
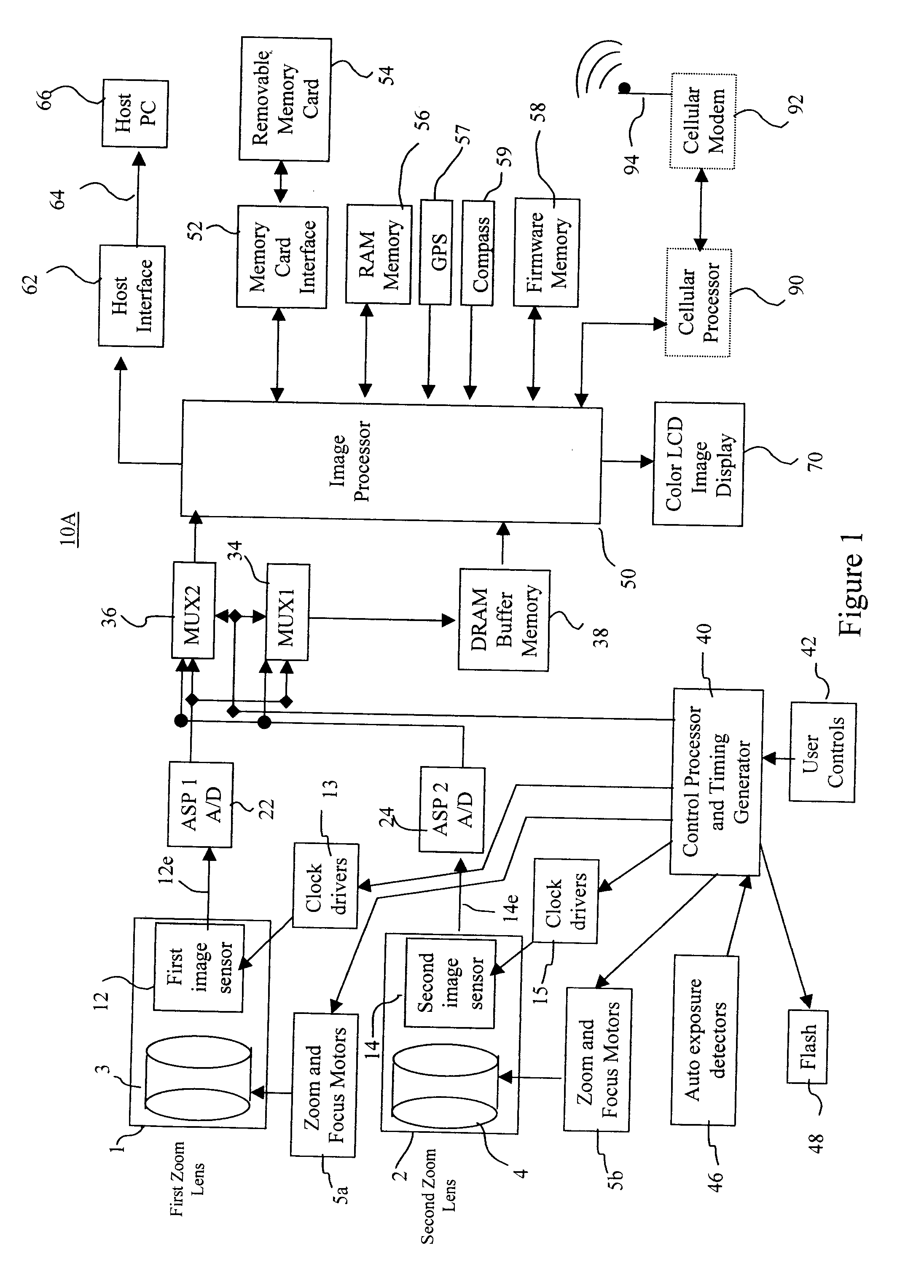
InactiveUS20070025714A1Easy to handleInappropriate exposureTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsImaging conditionTiming generator
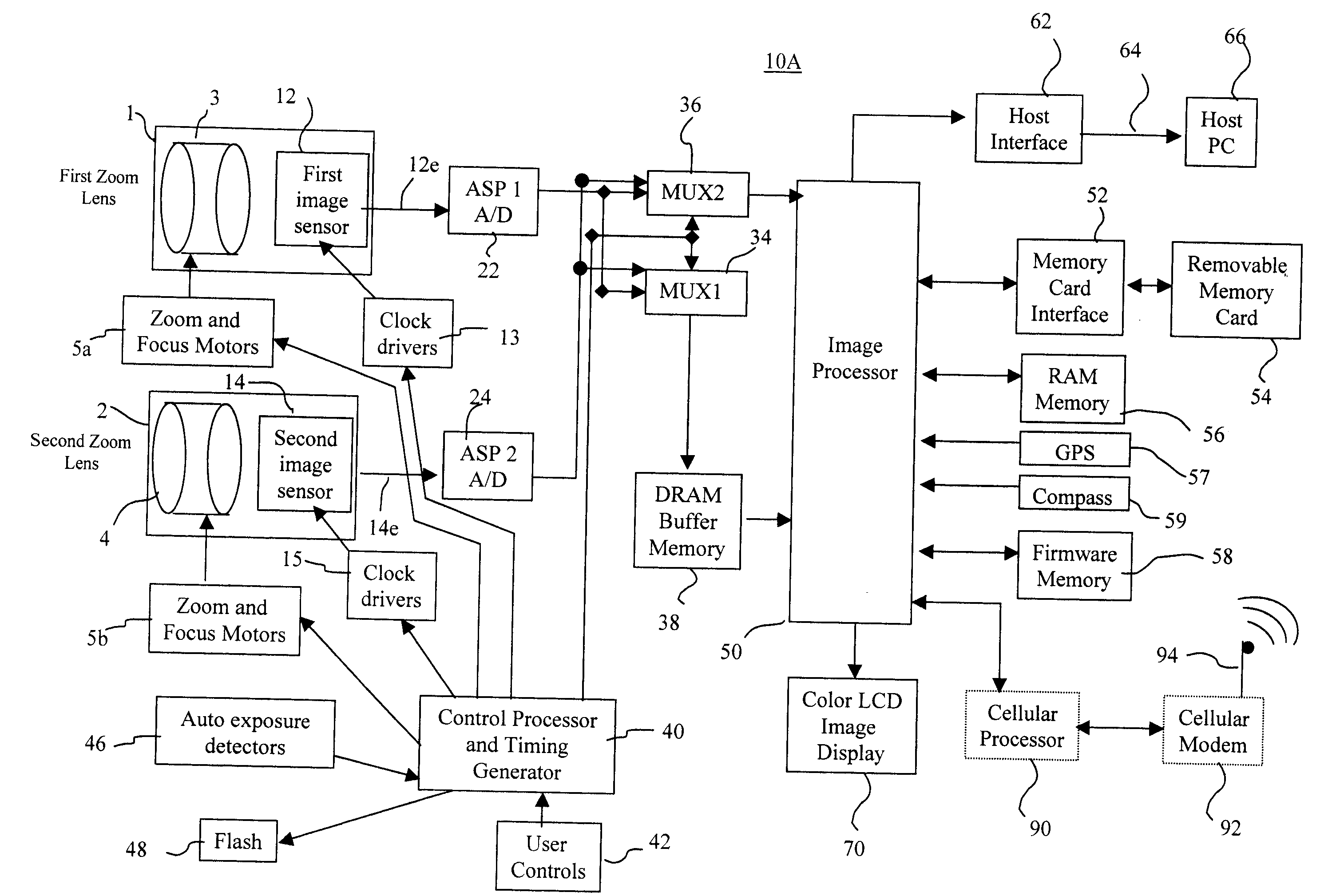
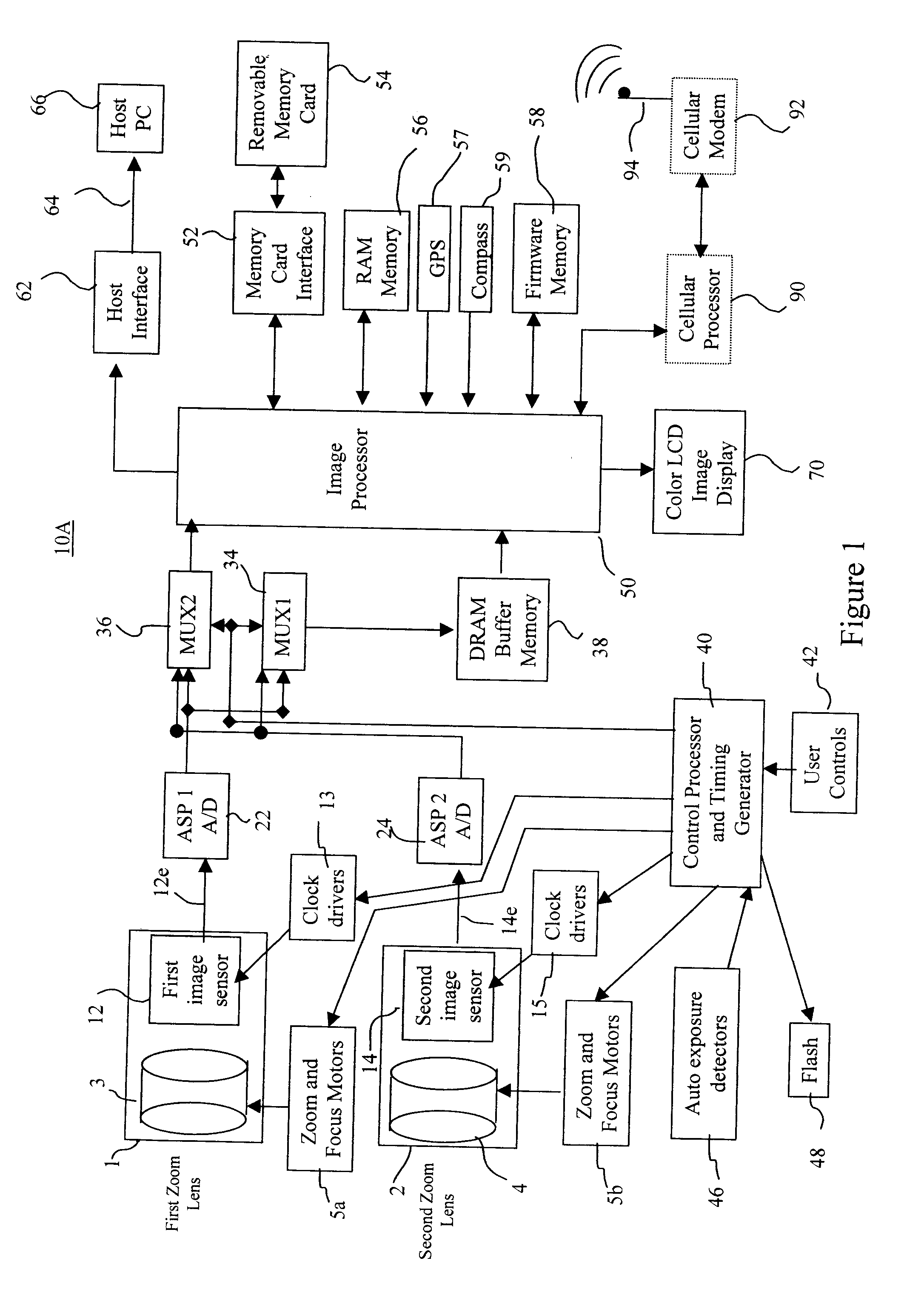
In a digital camera, control operations, such as an AF (automatic focusing) operation which is performed immediately after zooming or panning of the camera, can be performed quickly in an appropriate manner. When a zoom lens 3 is driven to zoom “up”(“in”), a control processor and timing generator 40 uses, of imaging conditions data, such as distance measuring data and photometering data, which are obtained at a wide viewing angle before zooming up, a portion of the imaging conditions data corresponding to a “tele” (telephoto) viewing angle after zooming up, to thereby perform AF, AE, and / or AWB operations after zooming up. When the user pans the camera to shift the viewing angle out of the range of the original wide viewing angle, the data of an area of the image plane of the wide viewing angle closest to the image plane of a new post-panning viewing angle is reused. In a digital camera having a plurality of image capturing optical systems which are switched in response to a zoom position, data obtained by the pre-switching image capturing optical system is reused by a selected post-switching image capturing optical system.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
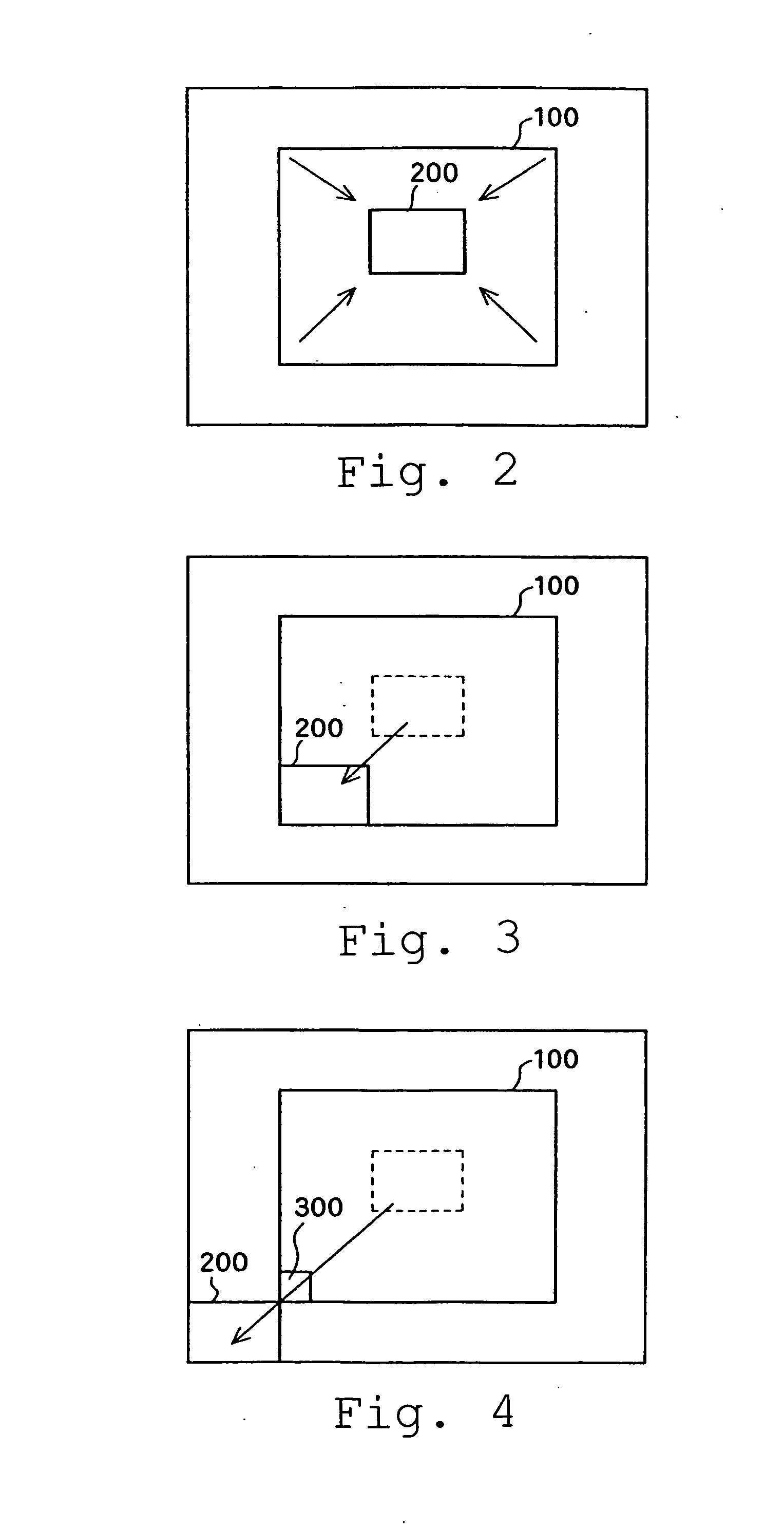
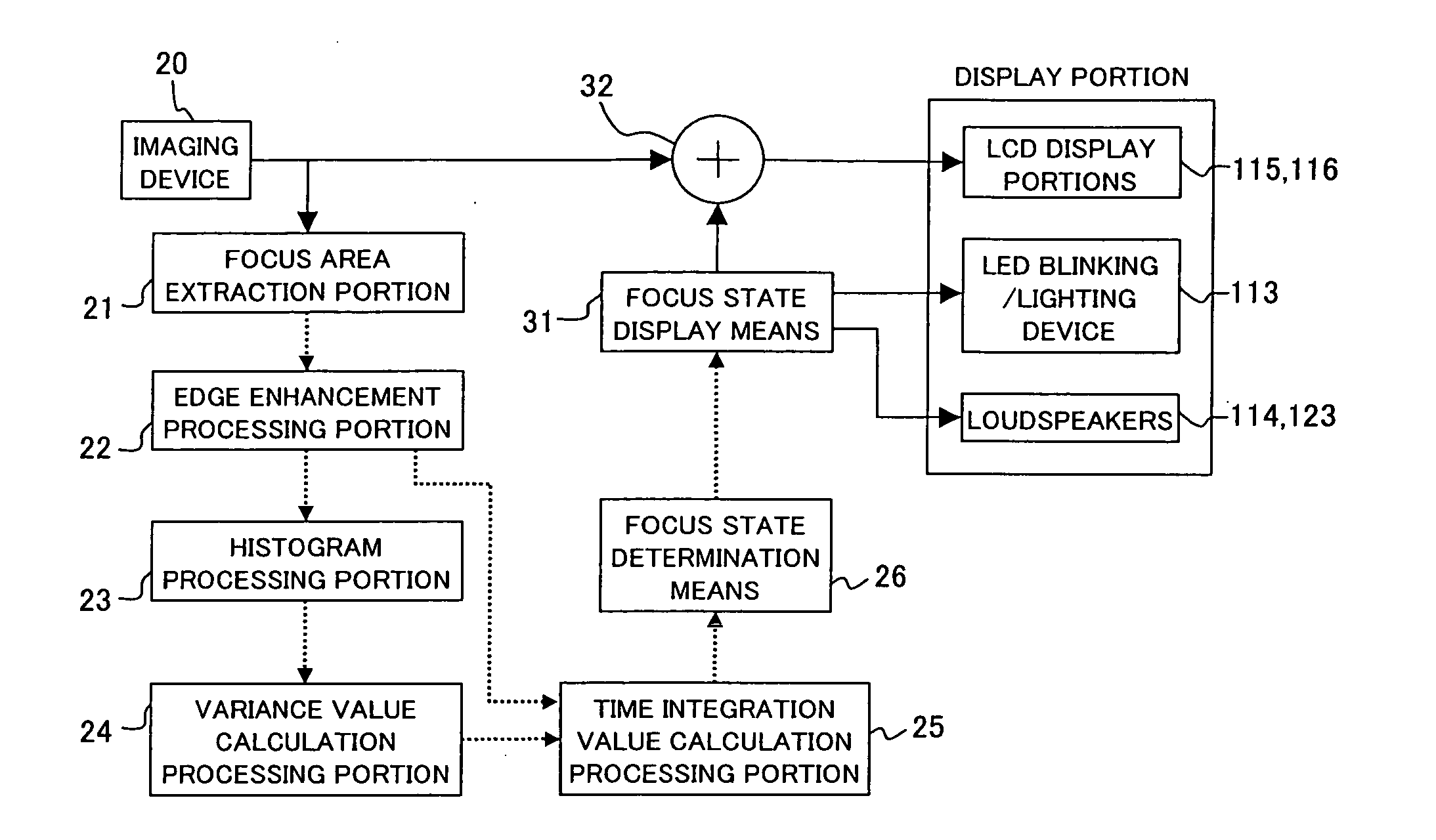
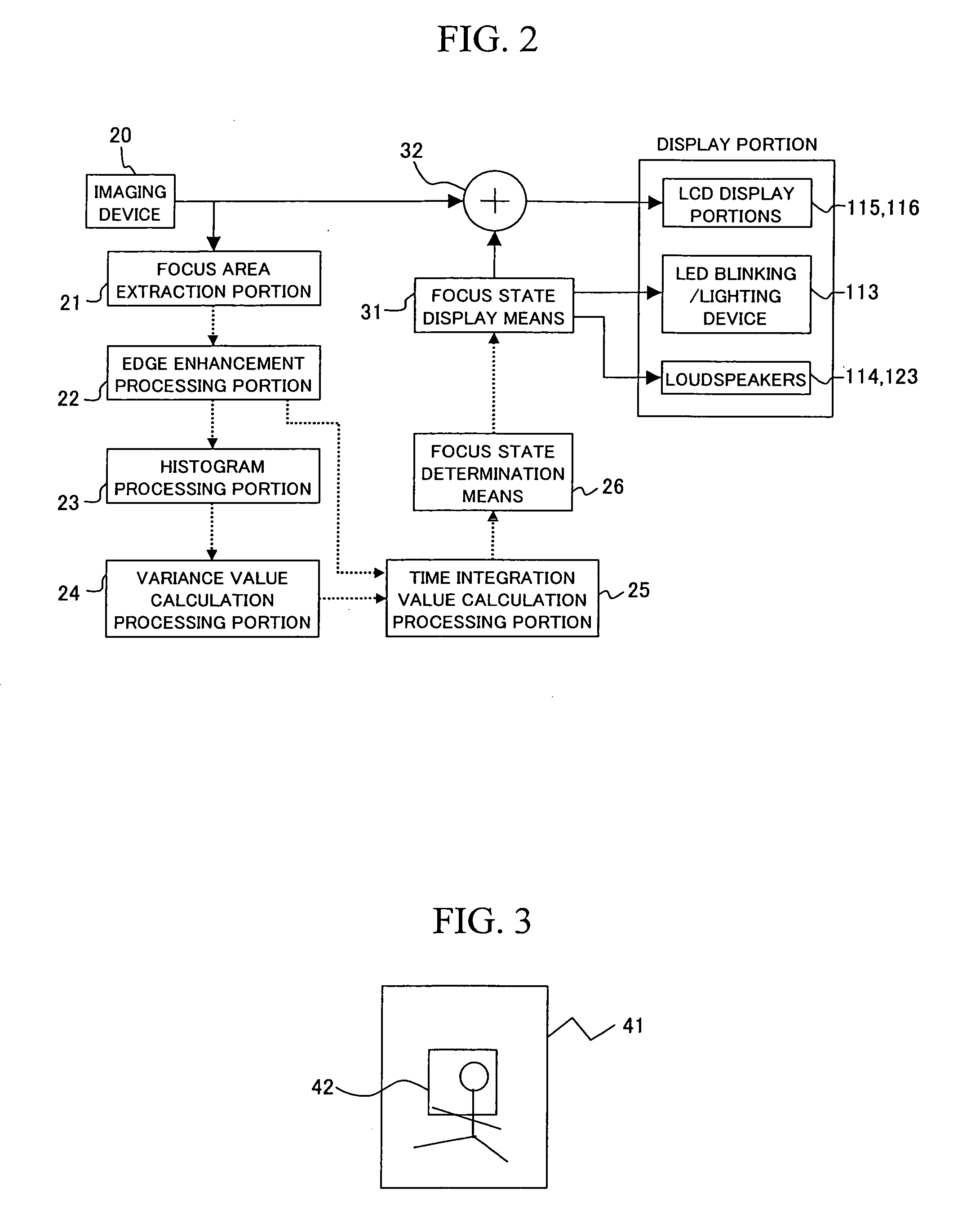
Focused state display device and focused state display method
ActiveUS20060146174A1Edge exclusionInhibition effectTelevision system detailsPrintersTime segmentImage resolution
A focus state display apparatus comprising focus area extraction means for extracting the image signals of a predetermined area from photographed image signals, edge enhancement processing means for enhancing the edge of the extracted image signals, time integration value calculation means for calculating an integration value of the edge-enhanced image signals in a certain period of time, focus state determination means for determining the focus state of the photographed image signals on the basis of the calculated integration value, and focus state display means for displaying the determined focus state. A user is capable of readily determining the focus state of a camera and confirming and adjusting the focus thereof with accuracy even in a display apparatus of a camera-equipped portable terminal device, where the size and resolution thereof are limited.
Owner:SHARP KK
Lens array assisted focus detection
InactiveUS20080095523A1Fast analysisQuick captureTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCamera lensComputer science
A focus detection device includes an image sensor and a plurality of lenslets. Each of the plurality of lenslets has a distinct conjugate length and is associated with a distinct portion of the image sensor.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com