Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
179 results about "Word count" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The word count is the number of words in a document or passage of text. Word counting may be needed when a text is required to stay within certain numbers of words. This may particularly be the case in academia, legal proceedings, journalism and advertising. Word count is commonly used by translators to determine the price for the translation job. Word counts may also be used to calculate measures of readability and to measure typing and reading speeds (usually in words per minute). When converting character counts to words, a measure of 5 or 6 characters to a word is generally used for English.
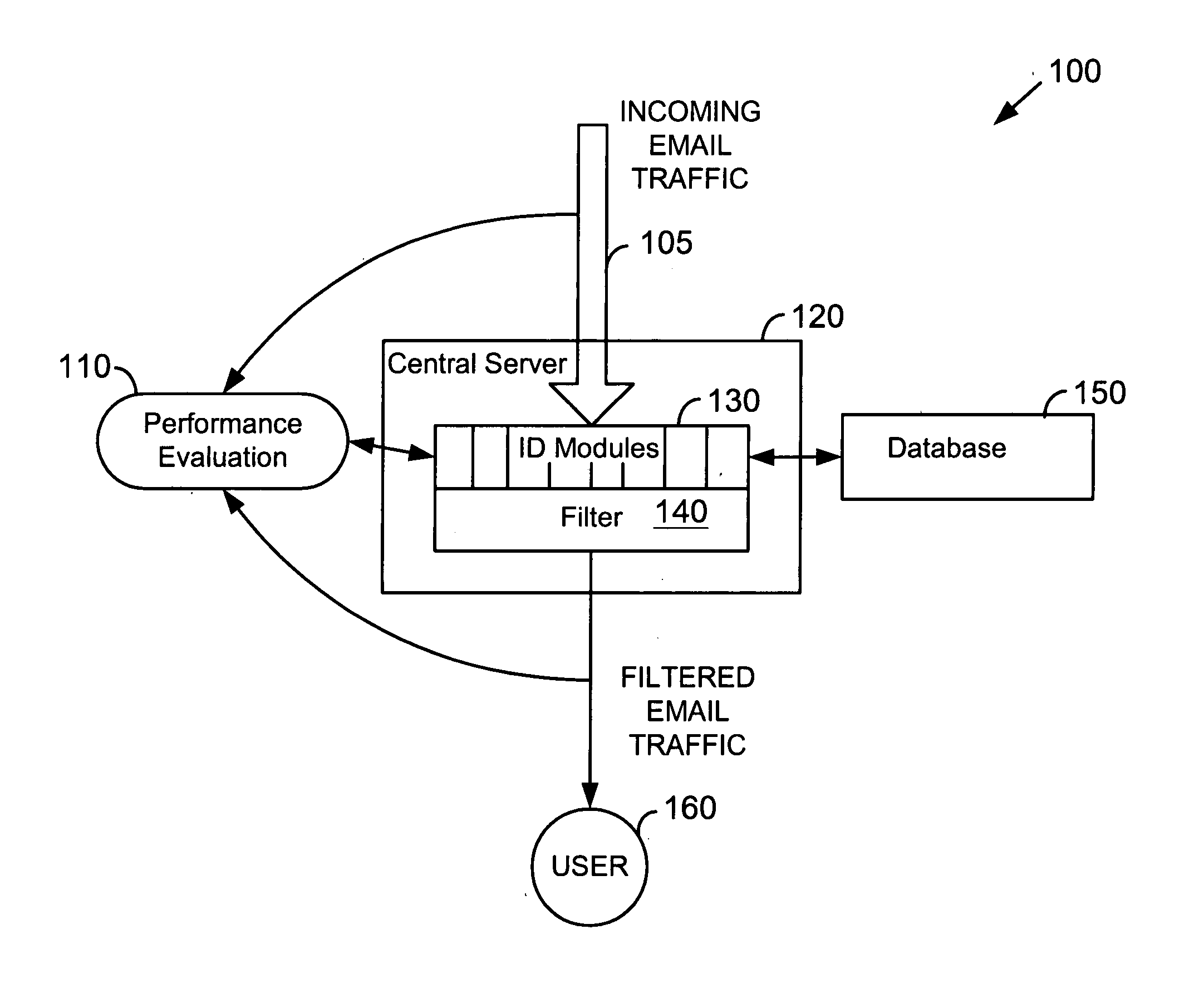
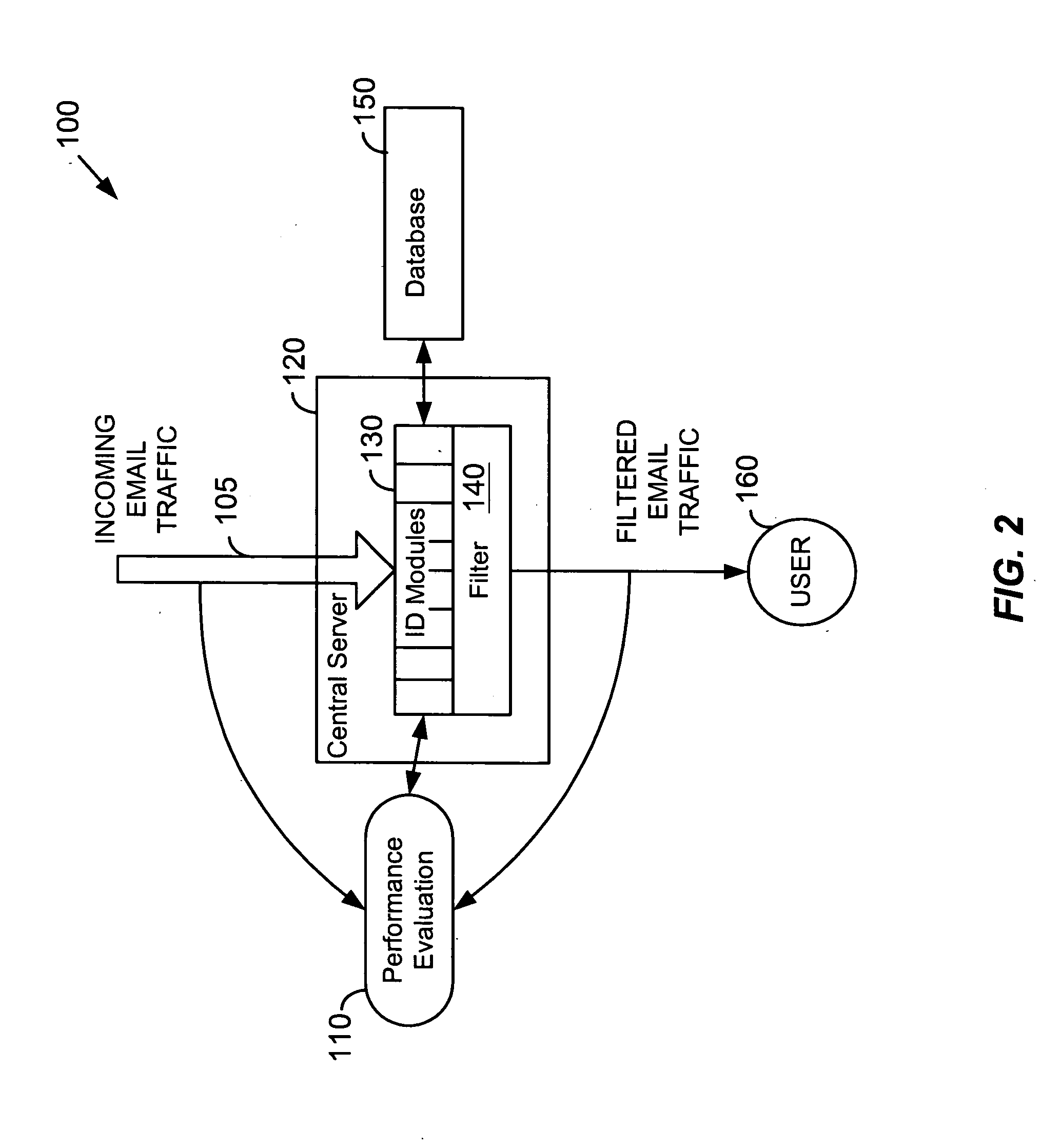
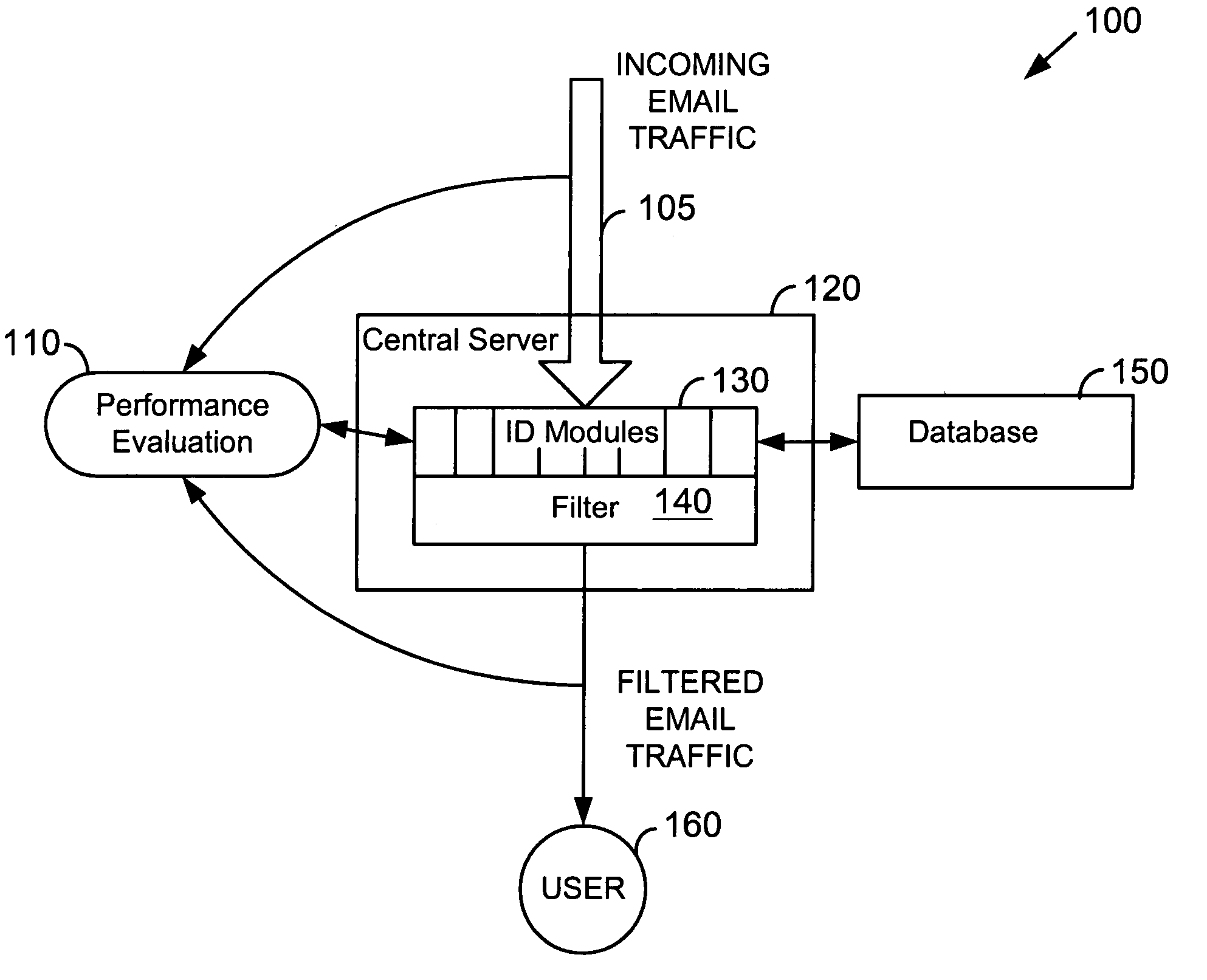
System for determining degrees of similarity in email message information
InactiveUS20050160148A1Improve reliabilityImprove performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksSpammingWord count
Similarity of email message characteristics is used to detect bulk and spam email. A determination of “sameness” for purposes of both bulk and spam classifications can use any number and type of evaluation modules. Each module can include one or more rules, tests, processes, algorithms, or other functionality. For example, one type of module may be a word count of email message text. Another module can use a weighting factor based on groups of multiple words and their perceived meanings. In general, any type of module that performs a similarity analysis can be used. A preferred embodiment of the invention uses statistical analysis, such as Bayesian analysis, to measure the performance of different modules against a known standard, such as human manual matching. Modules that are performing worse than other modules can be valued less than modules having better performance. In this manner, a high degree of reliability can be achieved. To improve performance, if a message is determined to be the same as a previous message, the previous computations and results for that previous message can be re-used. Users can be provided with options to customize or regulate bulk and spam classification and subsequent actions on how to handle the classified email messages.
Owner:GOZOOM COM
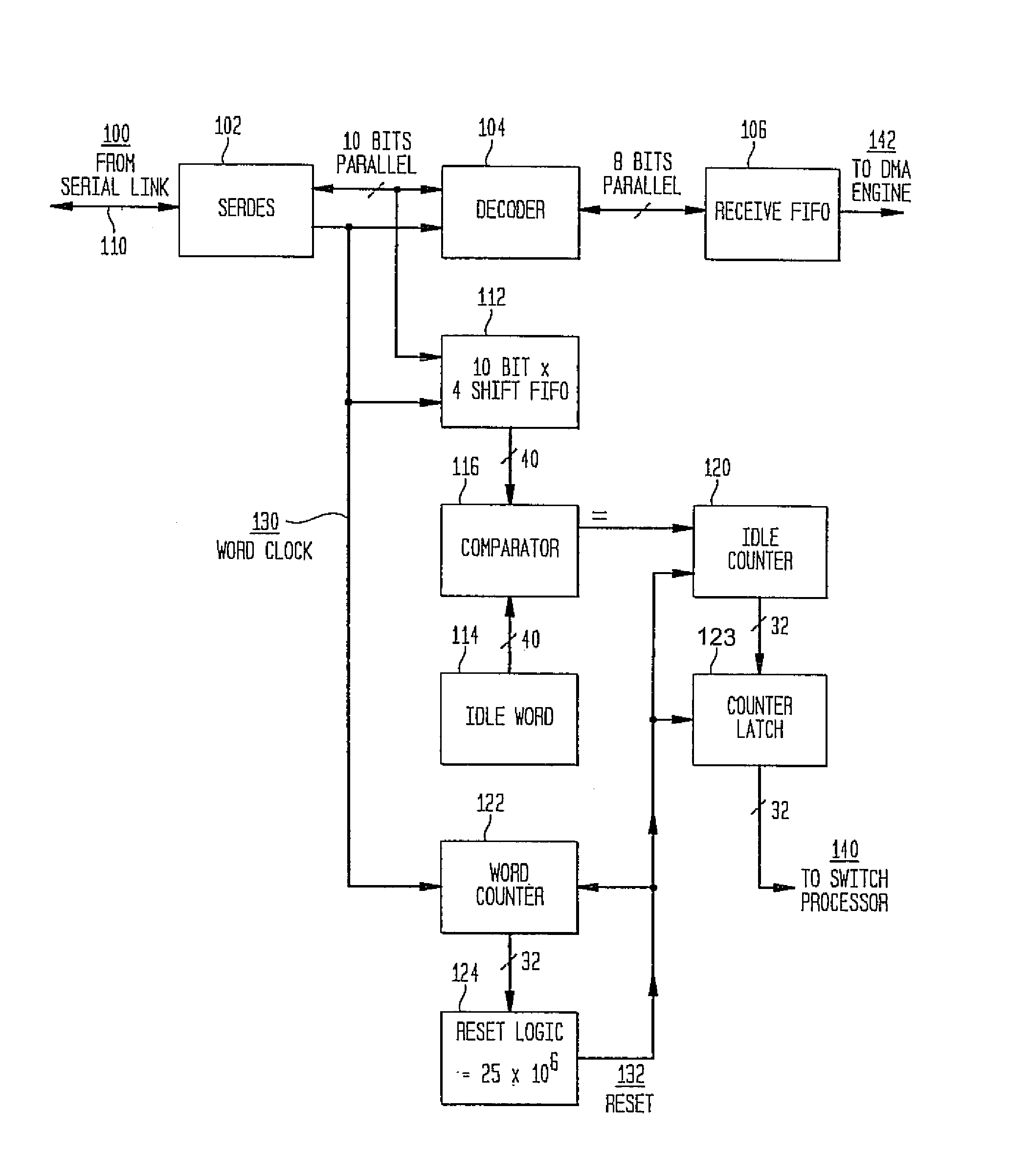
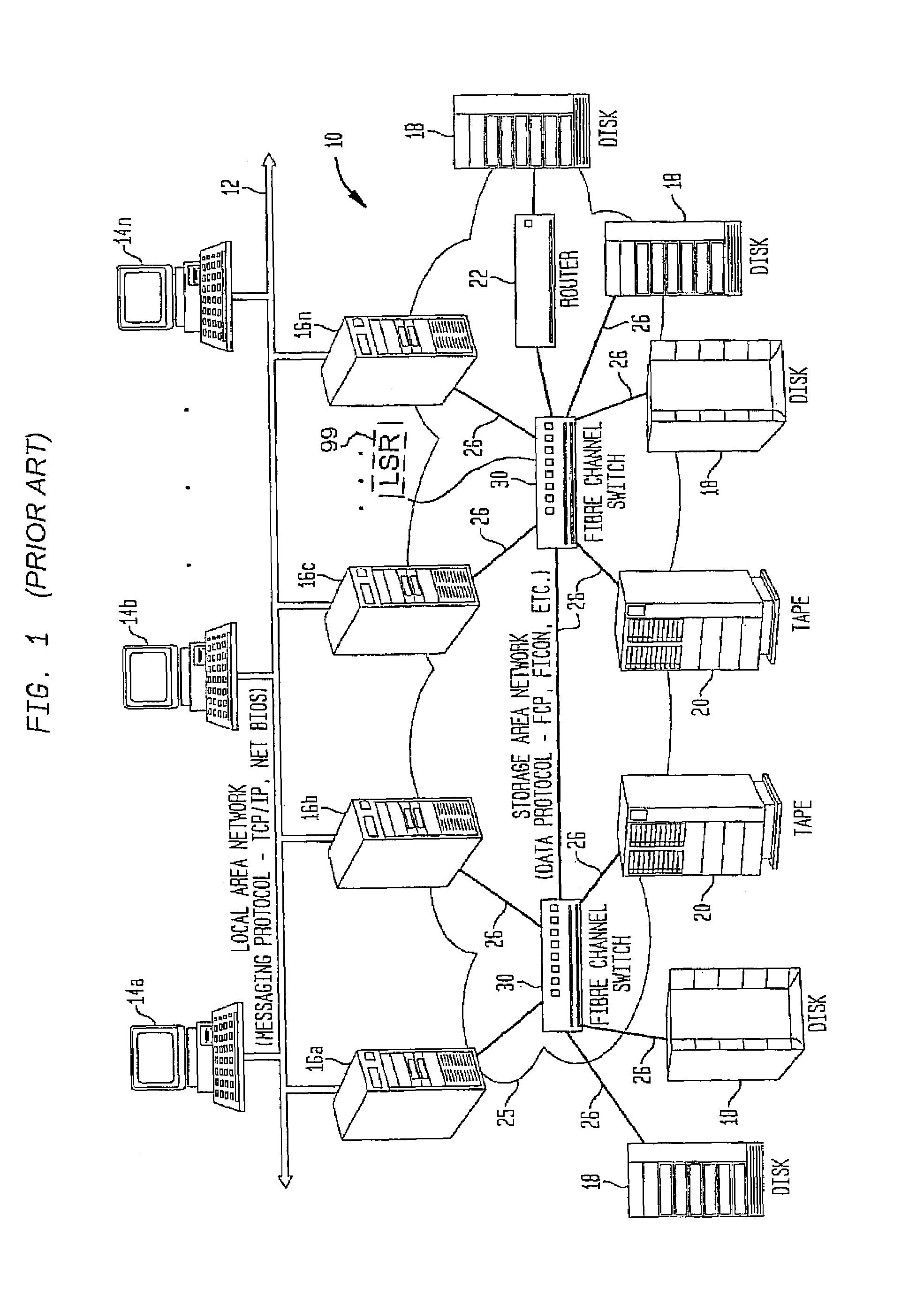
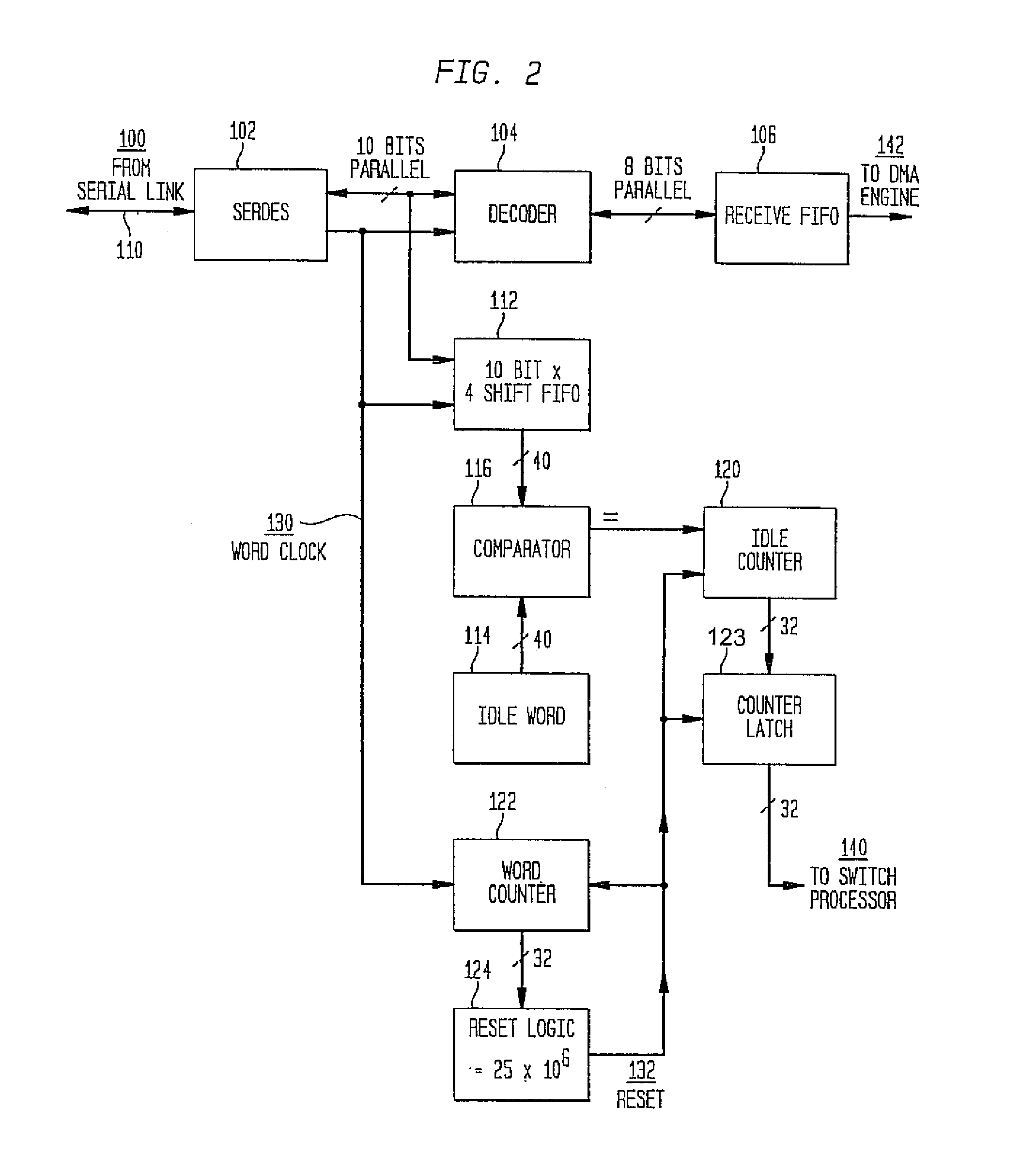
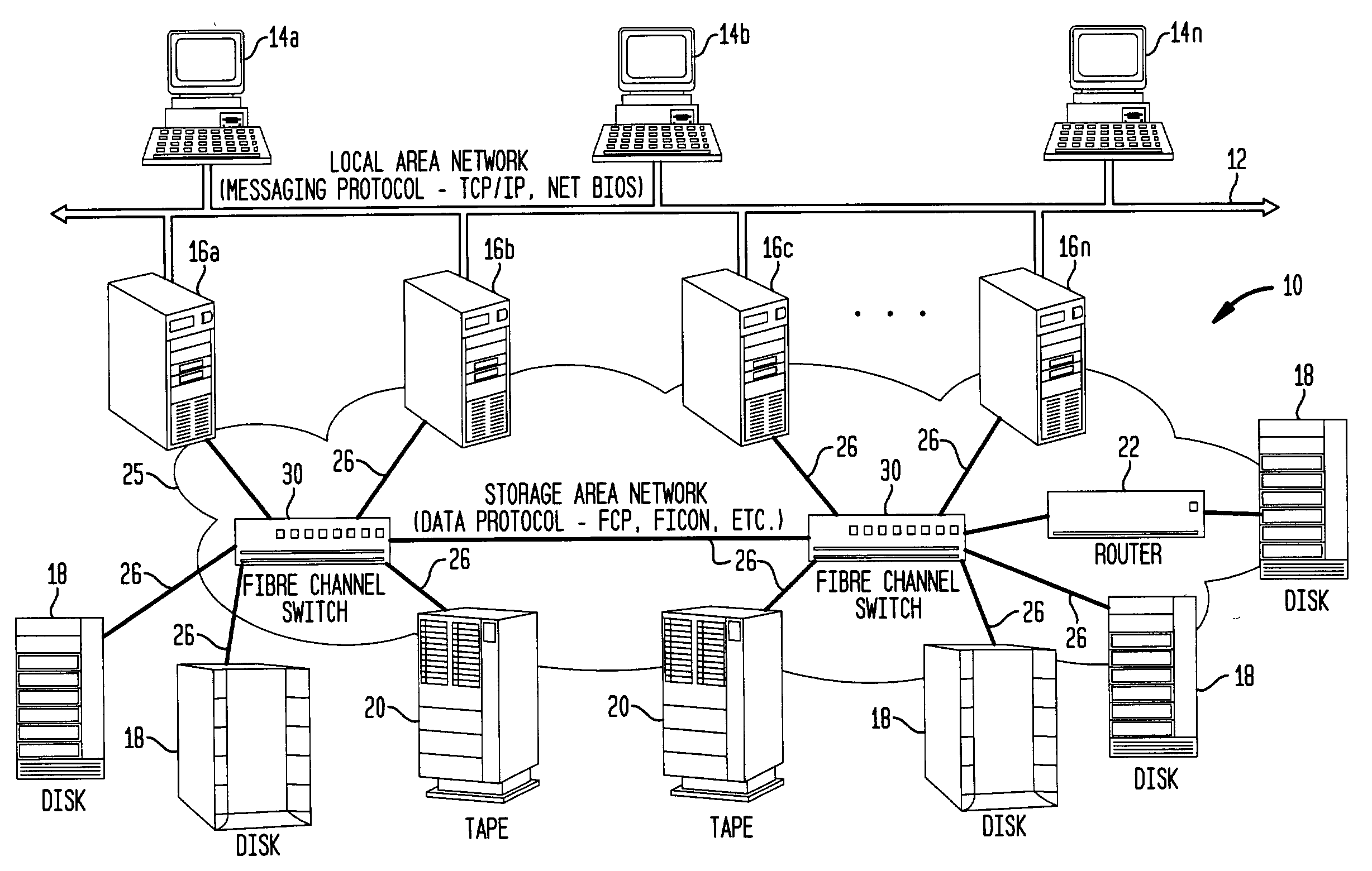
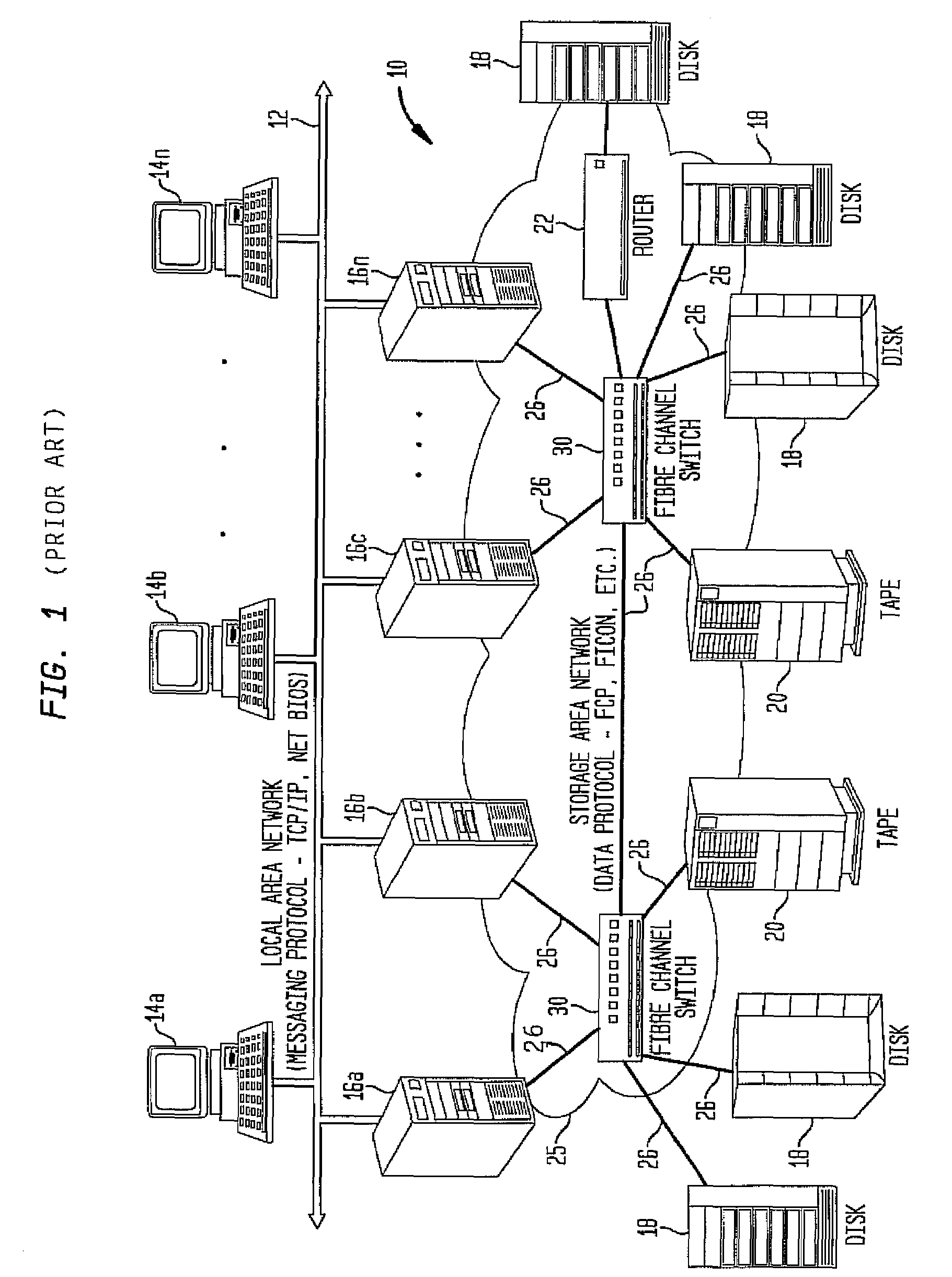
System and method for selecting fibre channel switched fabric frame paths
InactiveUS7327692B2Proper selectionFacilitate decision-makingError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsStorage area networkWord count
A system and method for measuring data transmission activity through a port of a switch device interconnecting nodes of a storage area network, the port transmitting data as words of predetermined length, one data word indicating idle port activity. The method includes steps of: counting a number of transmitted words received from the port in a first counter device; and, for each word counted, comparing that word with a predetermined word indicating no (idle) port transmission activity. In response to the comparing, a number of matches are counted in a second counter device. In this manner, a ratio of a number of counted matches with a total amount of words counted indicates available bandwidth for transmitting additional data over that link. Preferably, this available bandwidth information is included in a link state record that the switch communicates to other switch devices interconnecting that link. Processing devices at the switches determine a link cost factor, based on the available bandwidth of that link and, in addition, the link speed, the cost factor being used to optimize path selection over links in the network according to a path routing algorithm.
Owner:IBM CORP
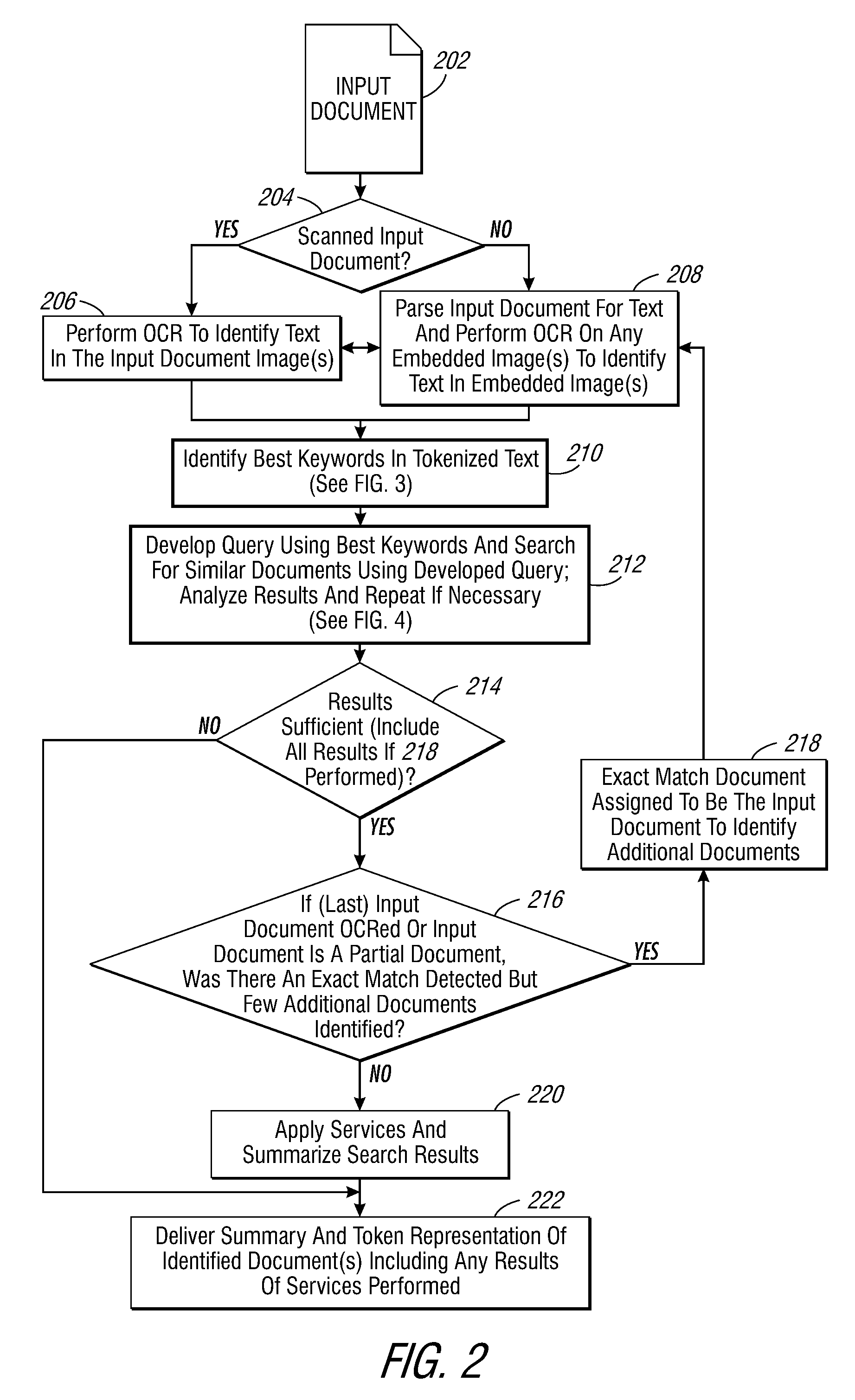
System and method for performing electronic information retrieval using keywords
ActiveUS7370034B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsA domainDocument preparation
Output documents similar to an input document are identified. A query is formulated using a list of best keywords from the input document to search for a first set of output documents. The list of best keywords is defined with a maximum number of keywords less than the total number of keywords in the list of best keywords that are identified as belonging to a domain specific dictionary of words and as having no measurable linguistic frequency. Lists of keywords are identified for each output document in the first set of documents. A second set of similar documents is determined using a measure of similarity that is computed between keywords identified in the input document and each output document in the first set of documents.
Owner:XEROX CORP
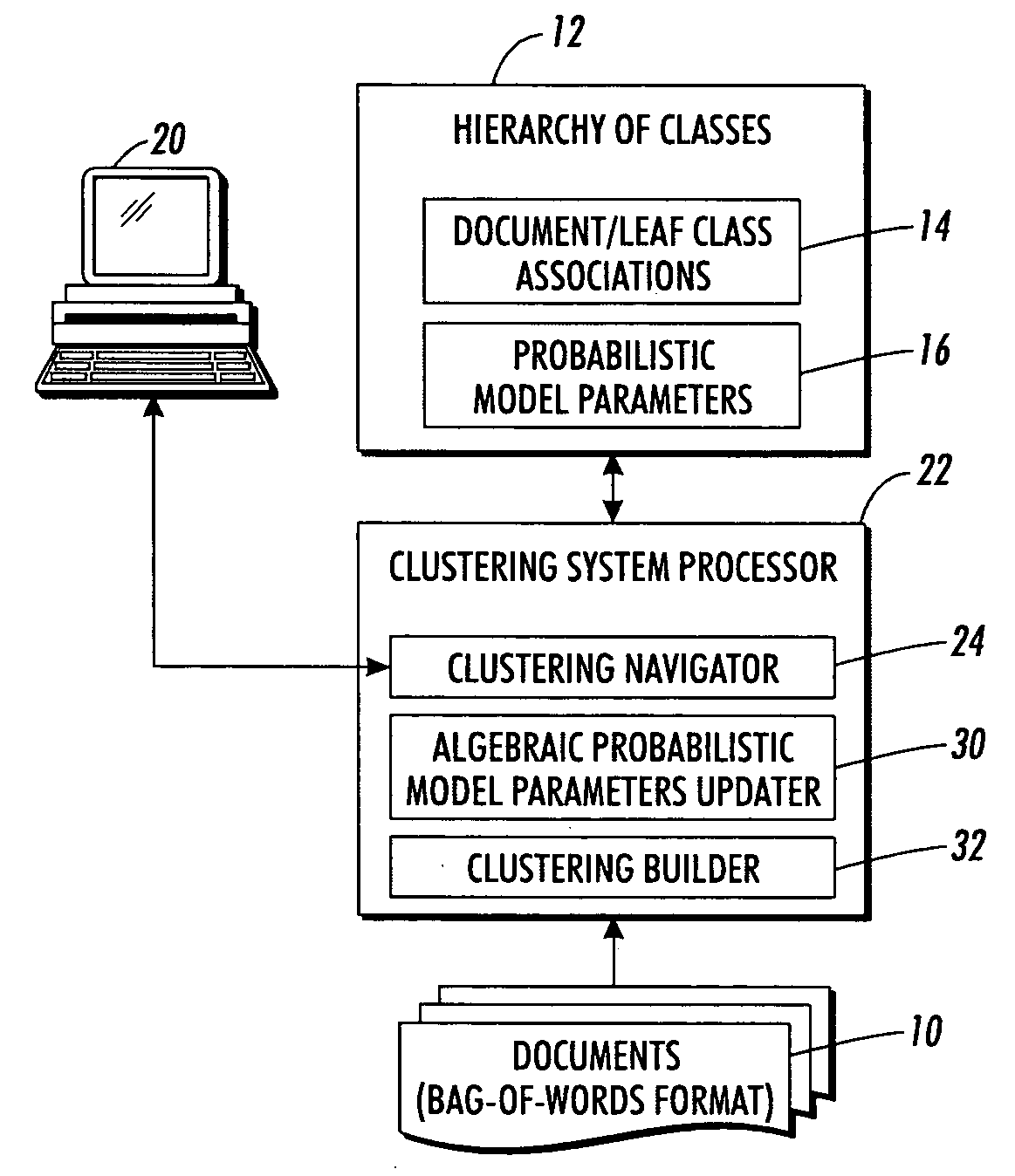
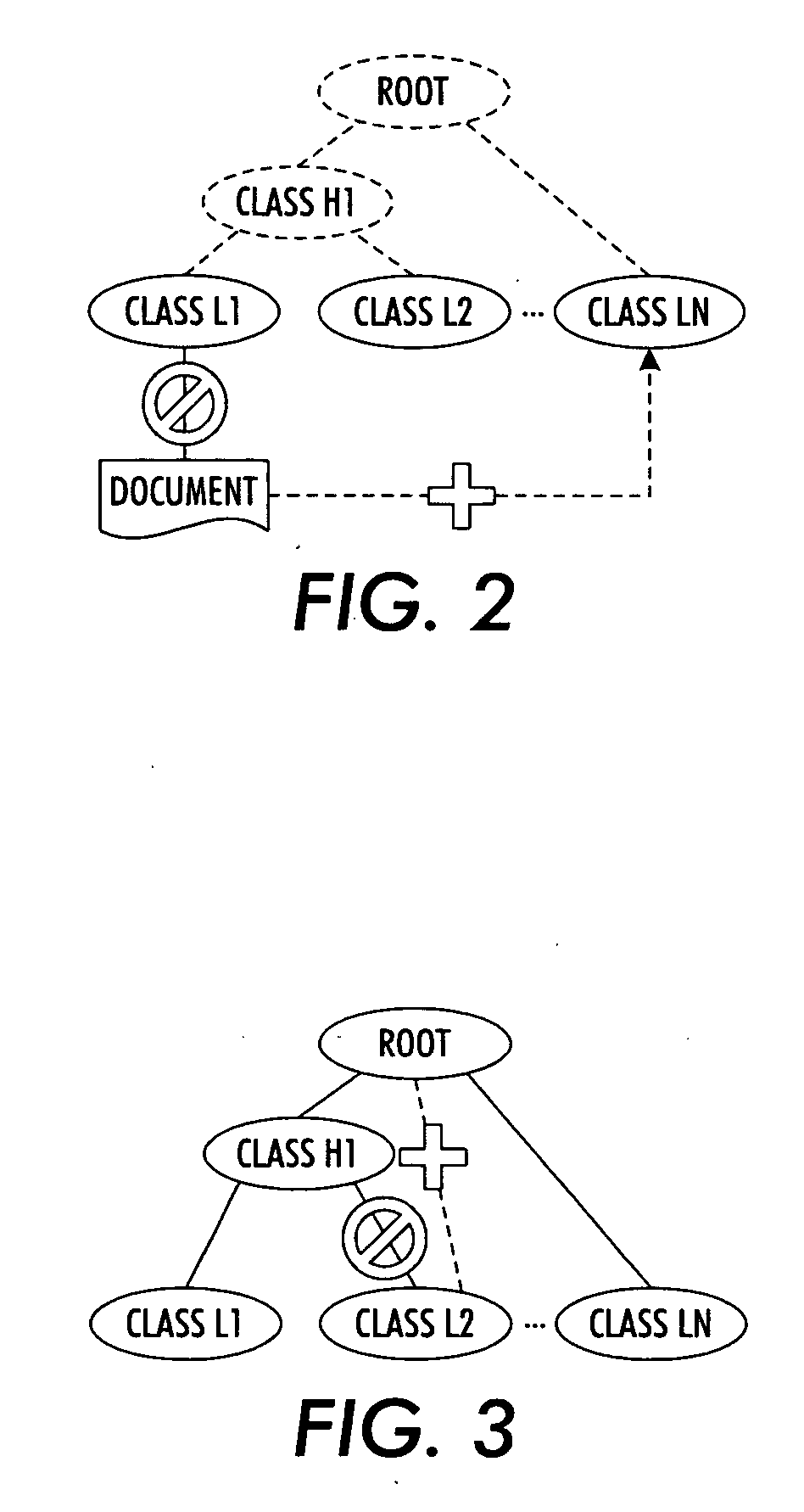
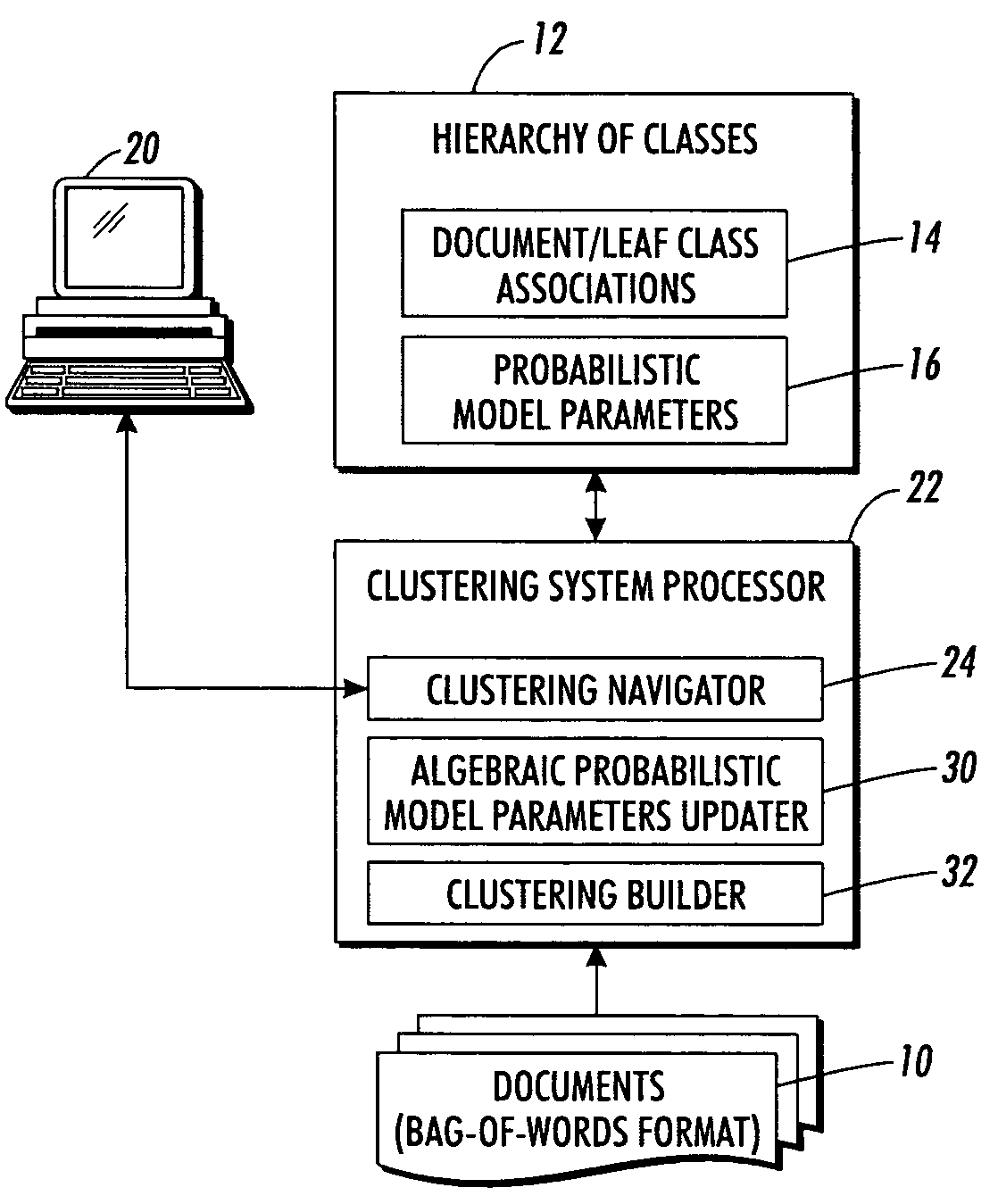
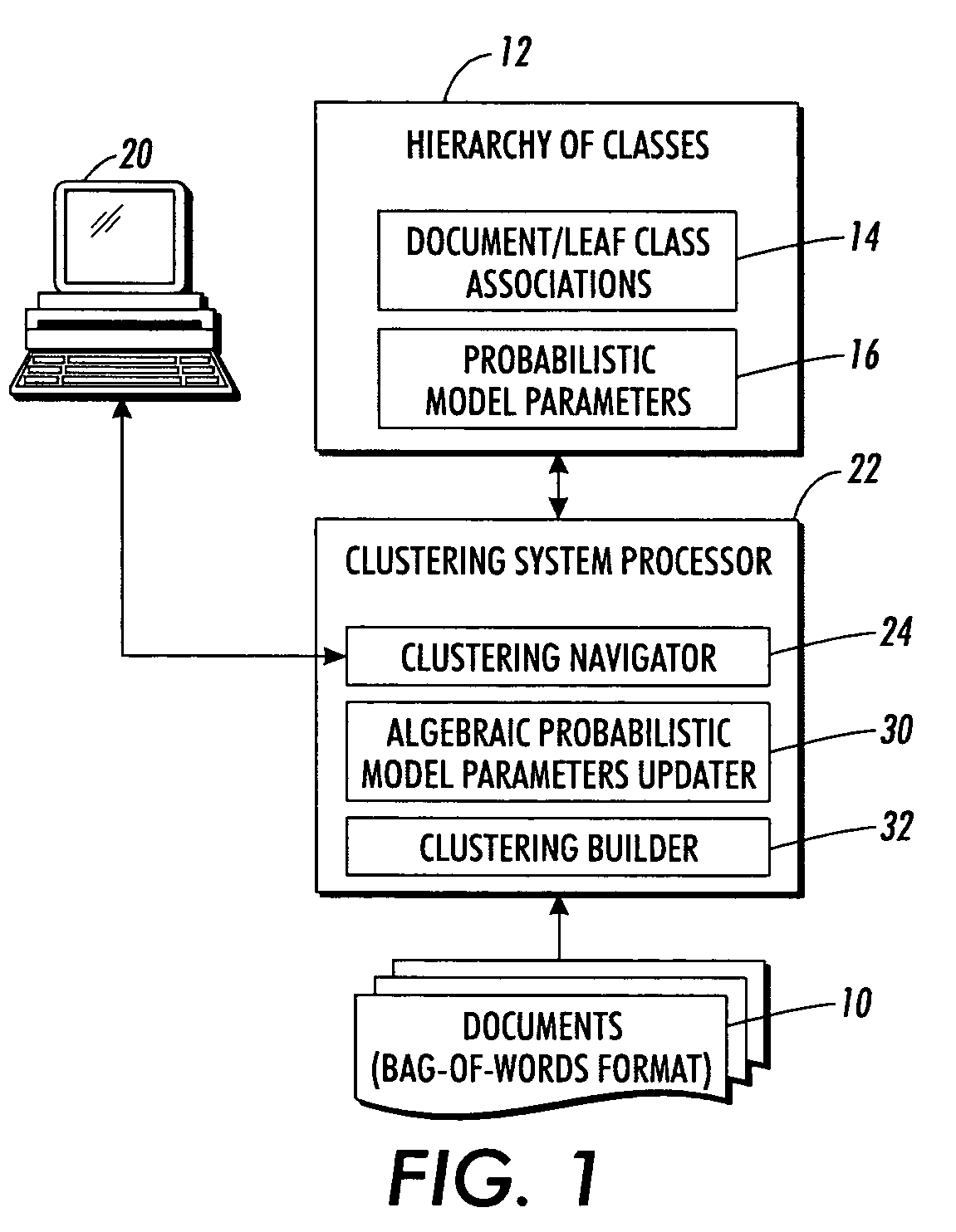
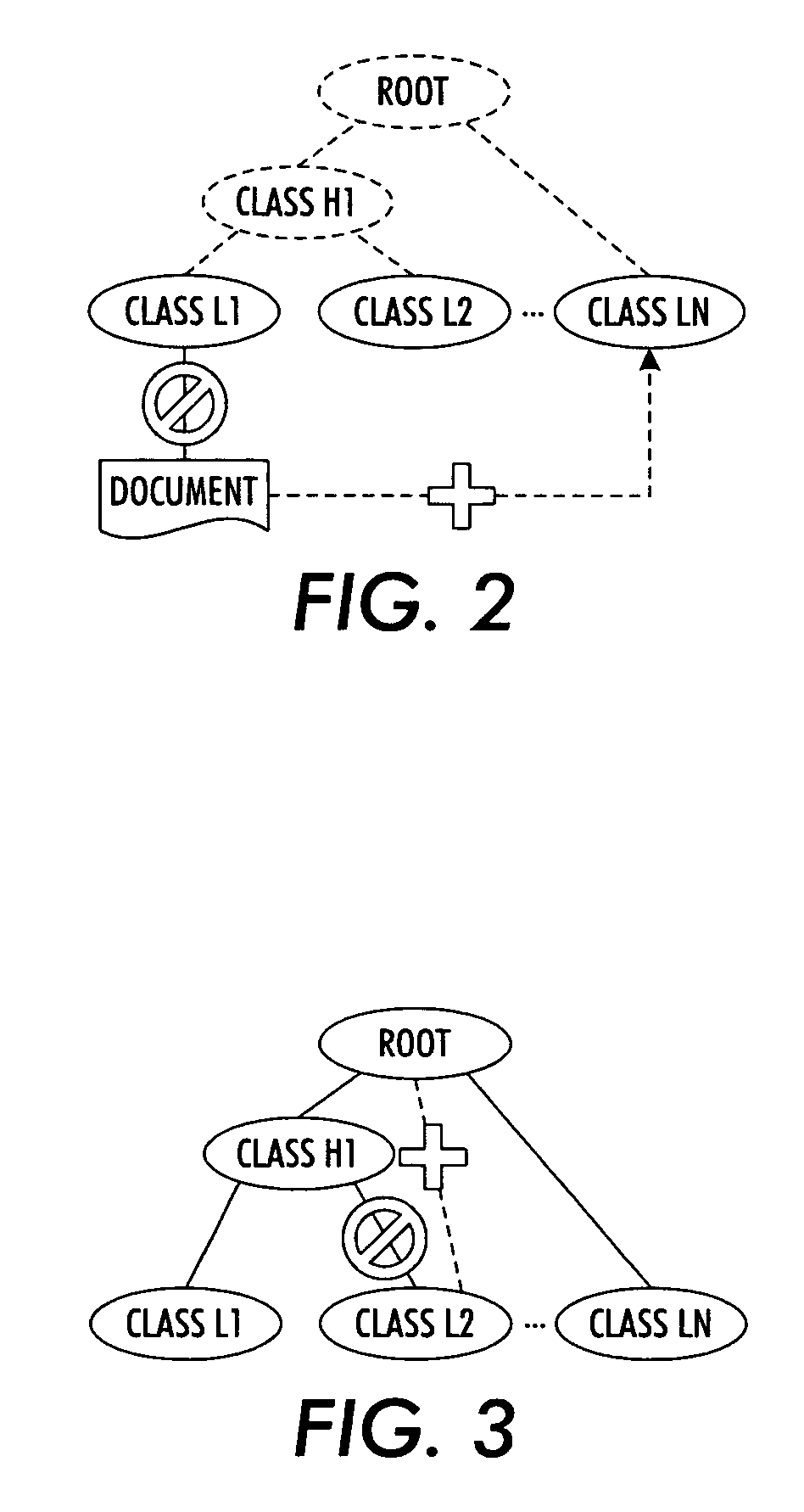
Hierarchical clustering with real-time updating
InactiveUS20070239745A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsAlgorithmCluster systems
A probabilistic clustering system is defined at least in part by probabilistic model parameters indicative of word counts, ratios, or frequencies characterizing classes of the clustering system. An association of one or more documents in the probabilistic clustering system is changed from one or more source classes to one or more destination classes. Probabilistic model parameters characterizing classes affected by the changed association are locally updated without updating probabilistic model parameters characterizing classes not affected by the changed association.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Application translation cost estimator
ActiveUS20090241115A1Estimated costMultiprogramming arrangementsMarketingWord countArtificial intelligence
The invention provides a computer-implemented method for estimating the cost of translating a body of text associated with a software application, wherein the software application is configured to perform one or more tasks. In particular the method comprises: determining one or more content types associated with the body of text, wherein each content type has an average word count per content unit; assigning a number of tasks associated with the software application to each content type, wherein each task has an associated number of content units; generating an estimated word count for each content type based on the number of tasks assigned to each content type and the average word count per unit for each content type; summing the estimated word count for each content type to generate an estimated word count for the body of text; and calculating an estimated translation cost based on the estimated word count.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
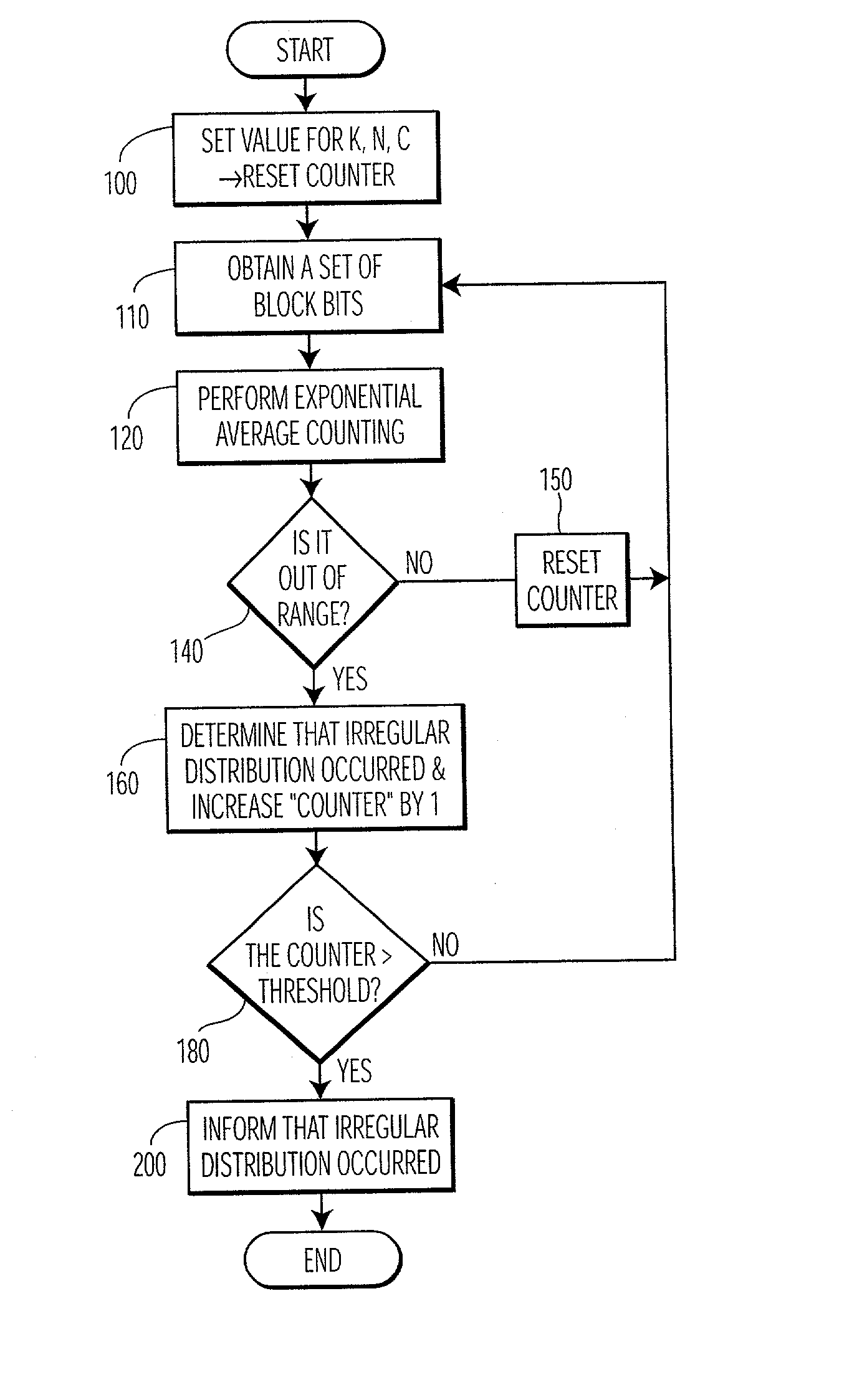
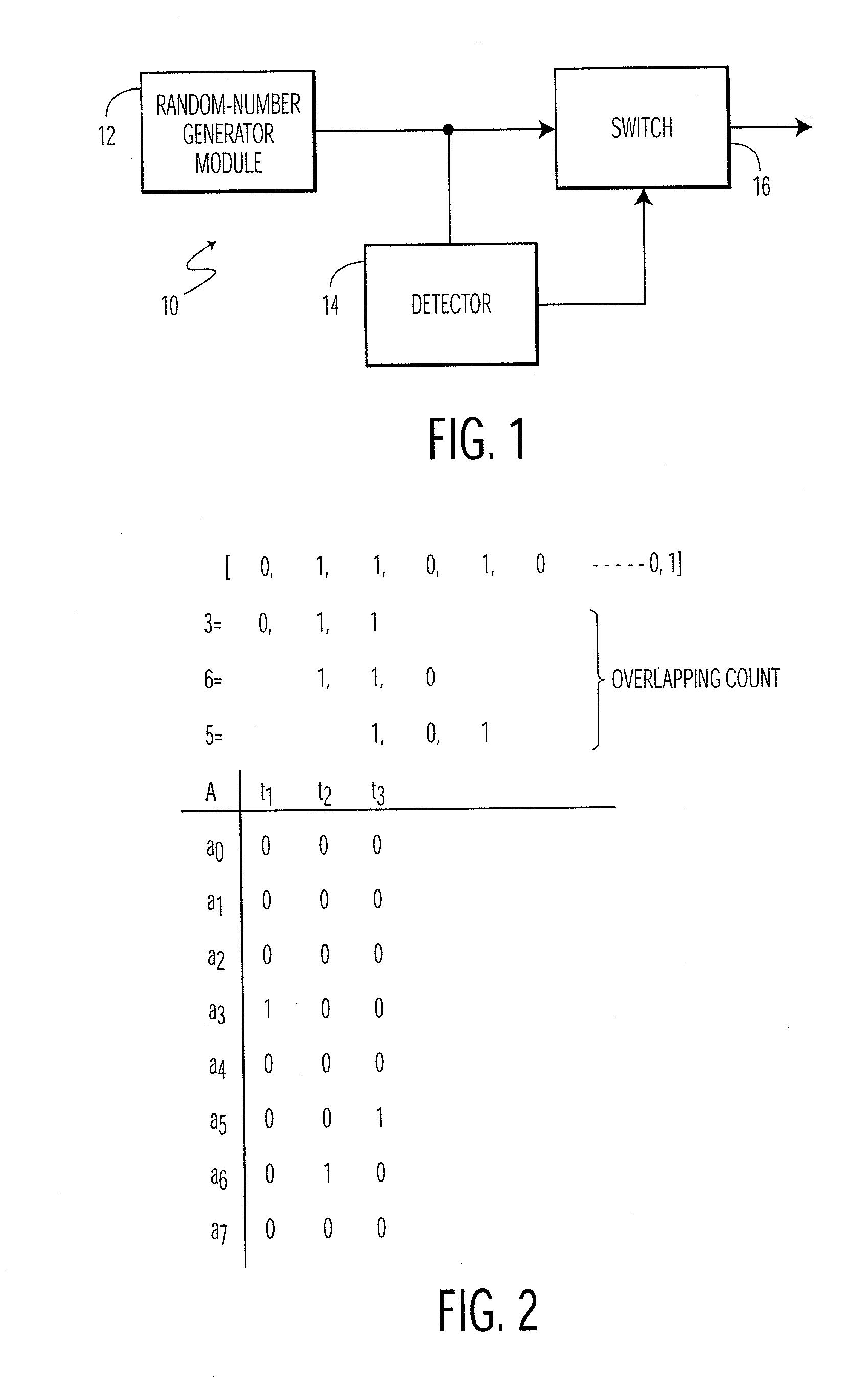
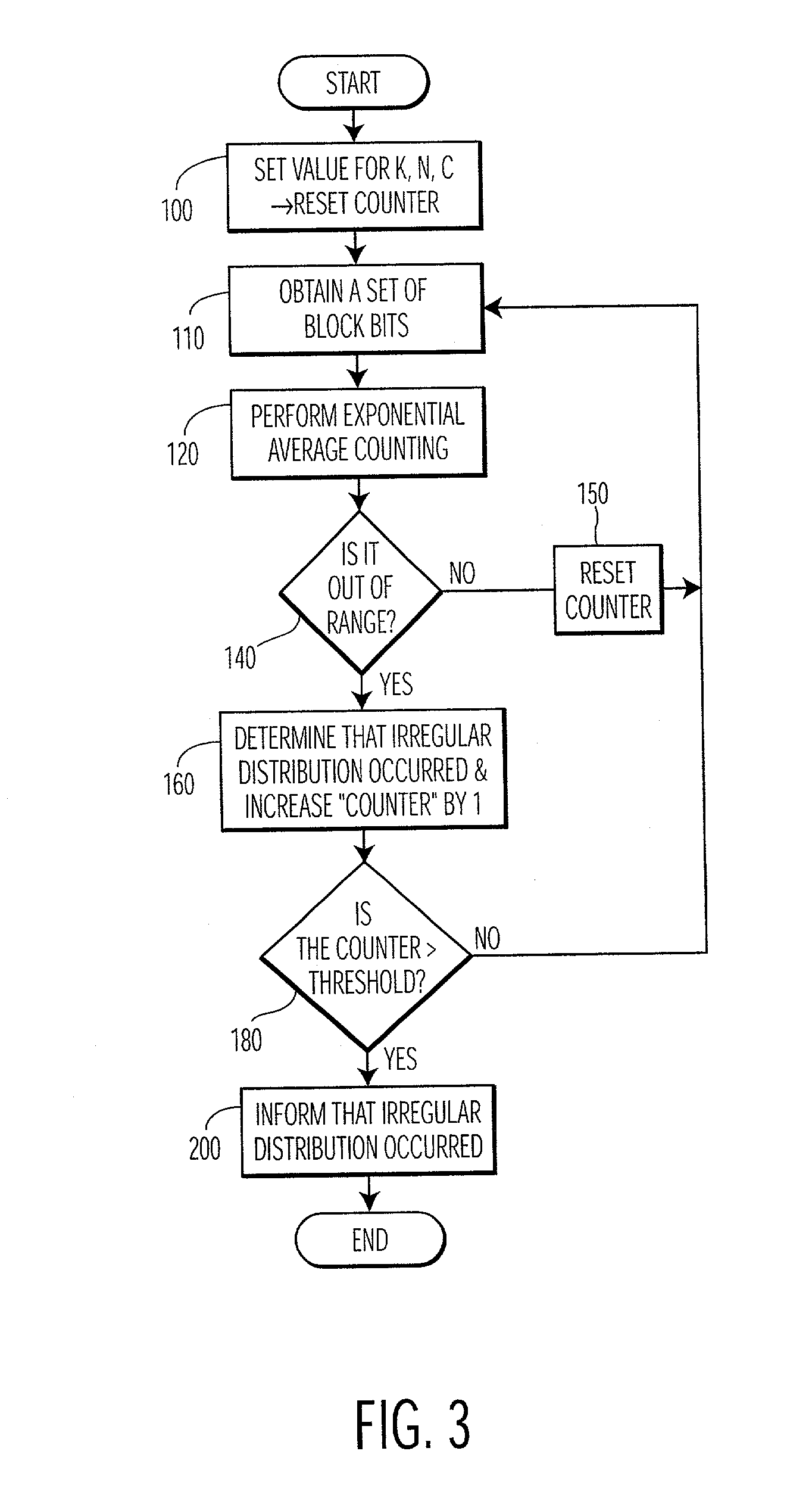
On-line randomness test through overlapping word counts
InactiveUS20030158876A1Improve securityRandom number generatorsCoding/ciphering apparatusWord countNumber generator
The present invention is a method and apparatus for testing random numbers generated by a random number generator in real time. As random numbers are generated, overlapping blocks of k bits undergo an exponential count operation one at a time, in which the count operation is performed by dropping the leftmost bit from the previous k bit block and appending a new random bit to the right of it to form a new k bit block, thus maintaining the size of the block. The binary value of this k bit block is used for performing the accumulator selection during the overlapping count operation. All of the outputs of the exponential averaging are compared to a predetermined acceptance range to determine whether the bits generated by the random number generator is sufficiently random.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
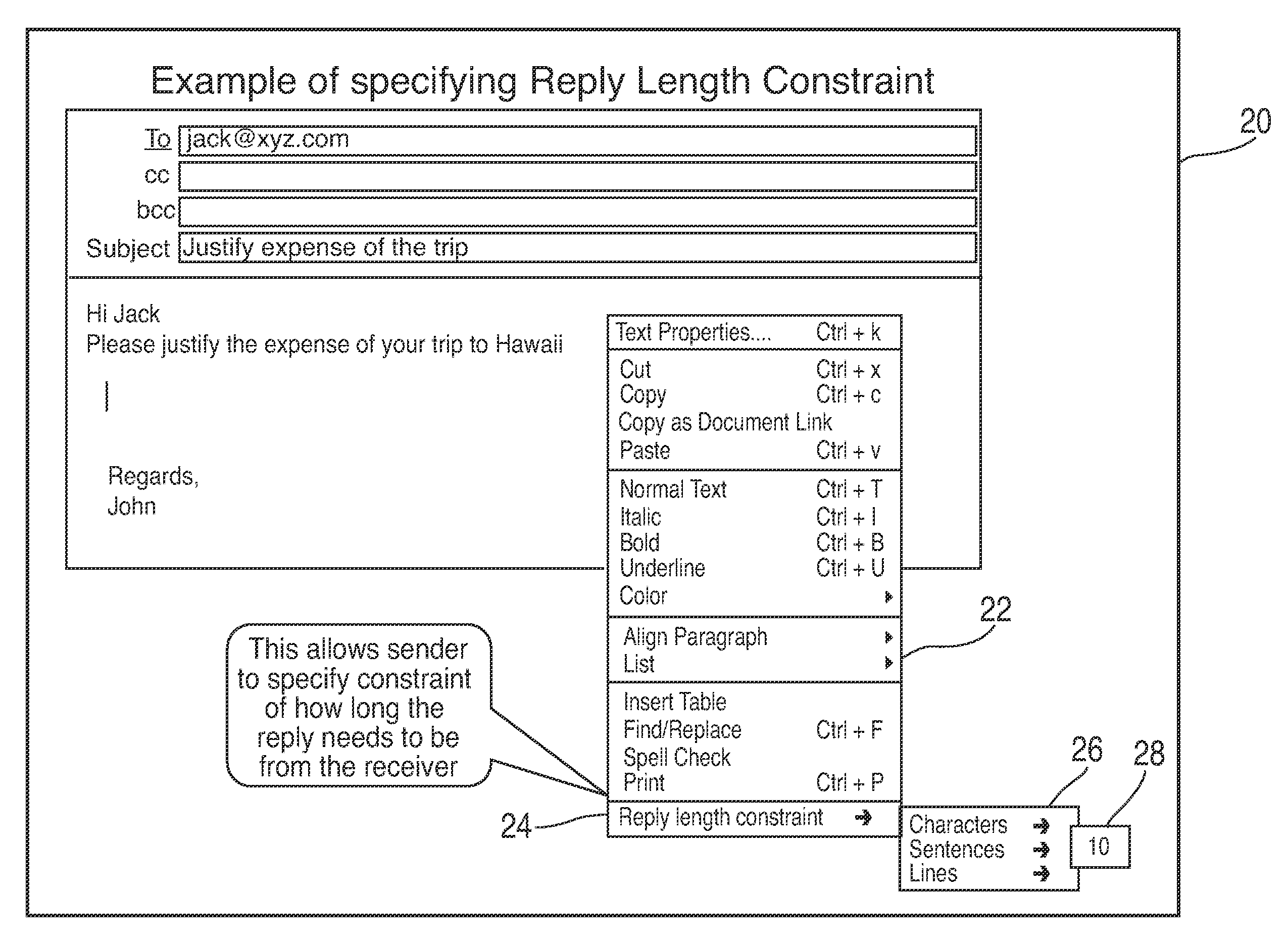
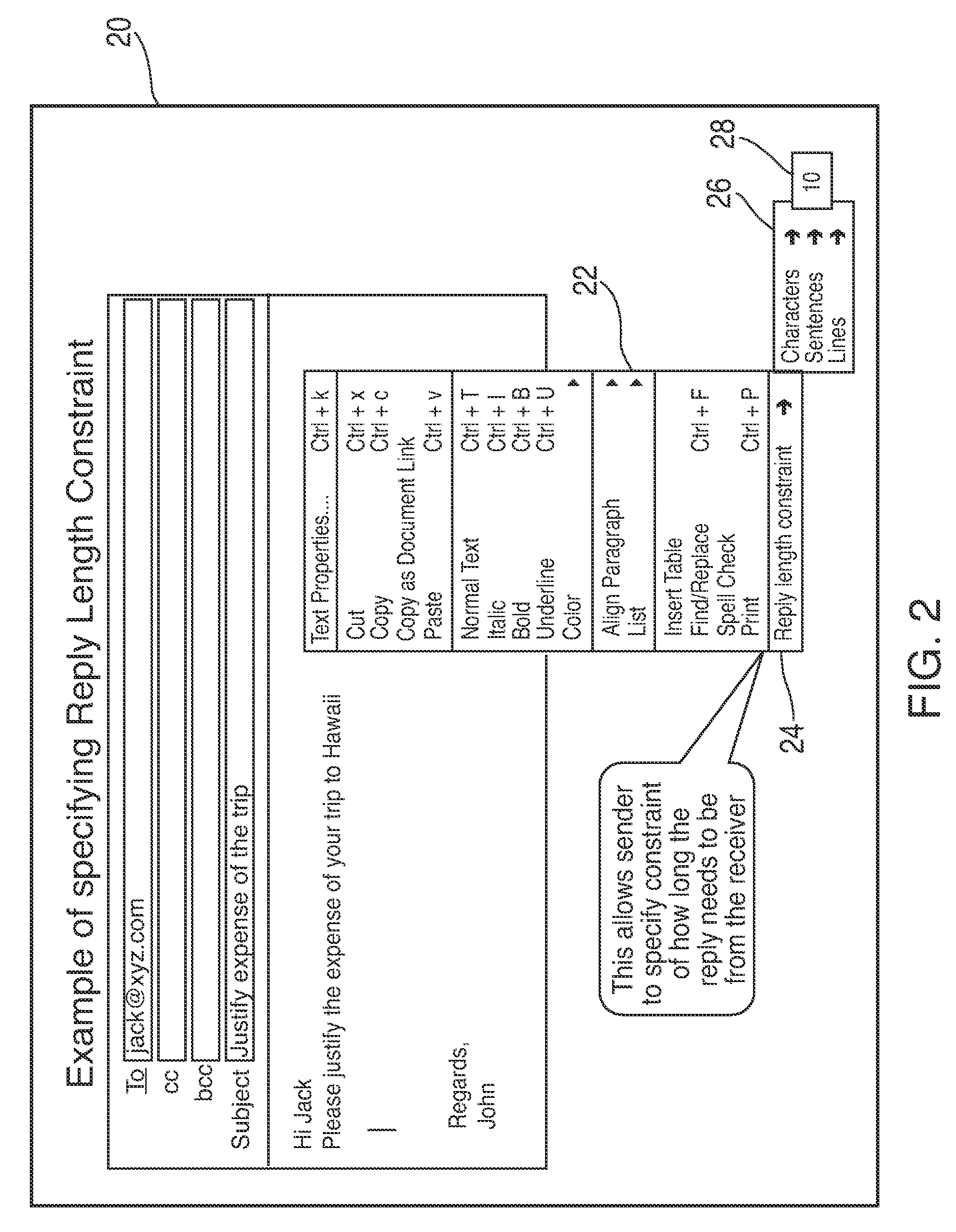
Electronic mail message replay constraints
A method, article, and system for providing a sender of an electronic mail message (hereafter referred to as email) a means to specify to a recipient a reply length constraint for the text body of the reply message, as well as criteria for the size, number, and type of allowed attachments associated with the reply message. The sender specified reply length constraints for the text message body can be stated in terms of number of lines, number of sentences, and / or by word count. The sender reply attachment constraints can be specified in terms of number of attachment files, maximum size per attachment, and / or receiver supported file types. The method includes having the sender determine the desired reply message constraints or parameters prior to sending out a message, and appending the constraint parameters to the outgoing email. At a receiving terminal that supports the novel features of the present invention, the email will have additional marked text that may be highlighted, italicized, colorized, placed in boxes, etc. to alert the reader that the sender prefers the reply to be constrained within the specified limits. If the reply from the receiving terminal does not meet the specified constraints, the reply will not be sent and appropriate warning will be displayed to the reader. For a receiving terminal that does not support the novel features of the present invention, a simple text message will appear with the sender reply constraint parameters.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hierarchical clustering with real-time updating
InactiveUS7720848B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsAlgorithmCluster systems
A probabilistic clustering system is defined at least in part by probabilistic model parameters indicative of word counts, ratios, or frequencies characterizing classes of the clustering system. An association of one or more documents in the probabilistic clustering system is changed from one or more source classes to one or more destination classes. Probabilistic model parameters characterizing classes affected by the changed association are locally updated without updating probabilistic model parameters characterizing classes not affected by the changed association.
Owner:XEROX CORP
System for determining degrees of similarity in email message information
InactiveUS7590694B2Improve reliabilityImprove performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTechnical standardWord count
Similarity of email message characteristics is used to detect bulk and spam email. A determination of “sameness” for purposes of both bulk and spam classifications can use any number and type of evaluation modules. Each module can include one or more rules, tests, processes, algorithms, or other functionality. For example, one type of module may be a word count of email message text. Another module can use a weighting factor based on groups of multiple words and their perceived meanings. In general, any type of module that performs a similarity analysis can be used. A preferred embodiment of the invention uses statistical analysis, such as Bayesian analysis, to measure the performance of different modules against a known standard, such as human manual matching. Modules that are performing worse than other modules can be valued less than modules having better performance. In this manner, a high degree of reliability can be achieved. To improve performance, if a message is determined to be the same as a previous message, the previous computations and results for that previous message can be re-used. Users can be provided with options to customize or regulate bulk and spam classification and subsequent actions on how to handle the classified email messages.
Owner:GOZOOM COM
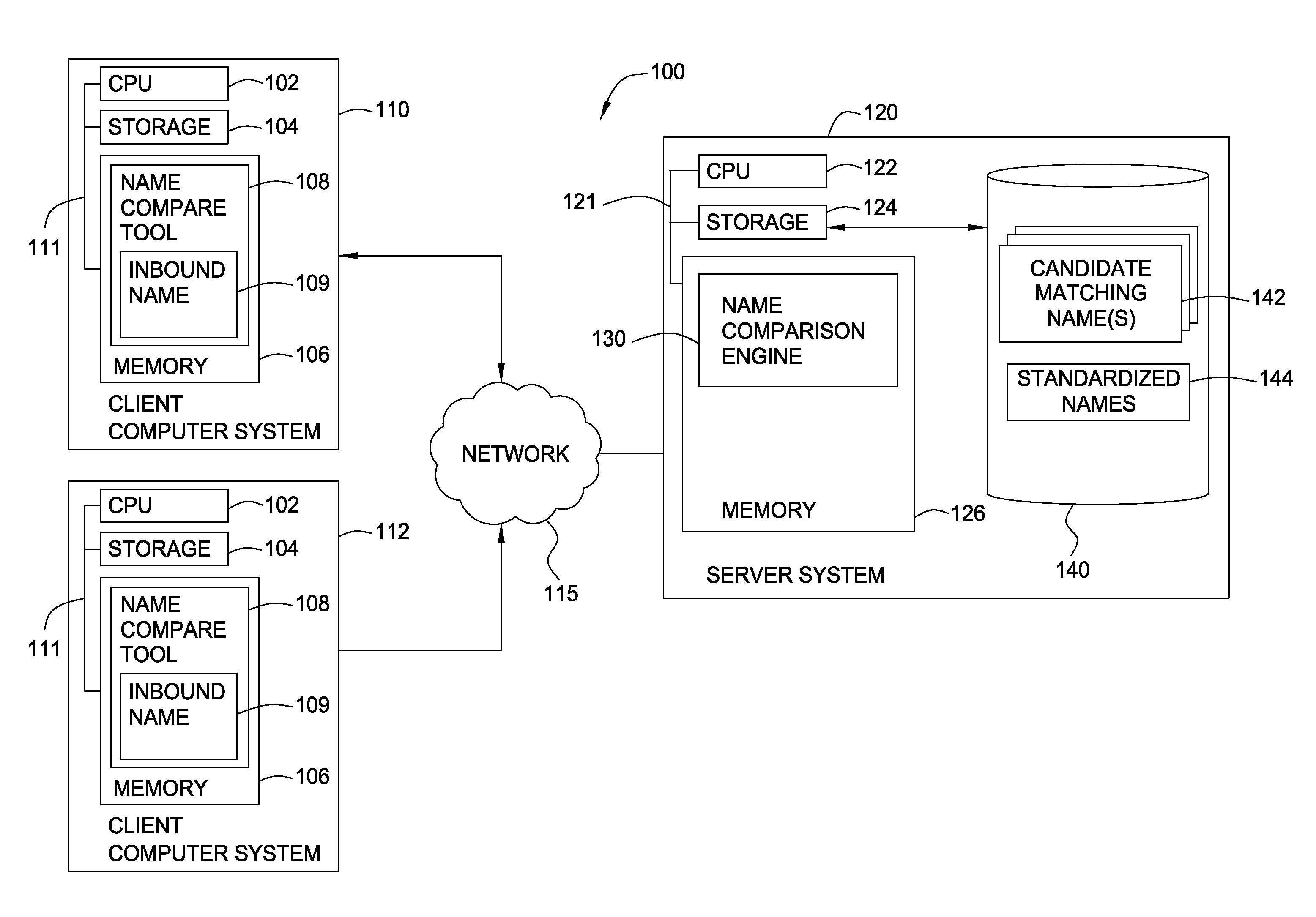
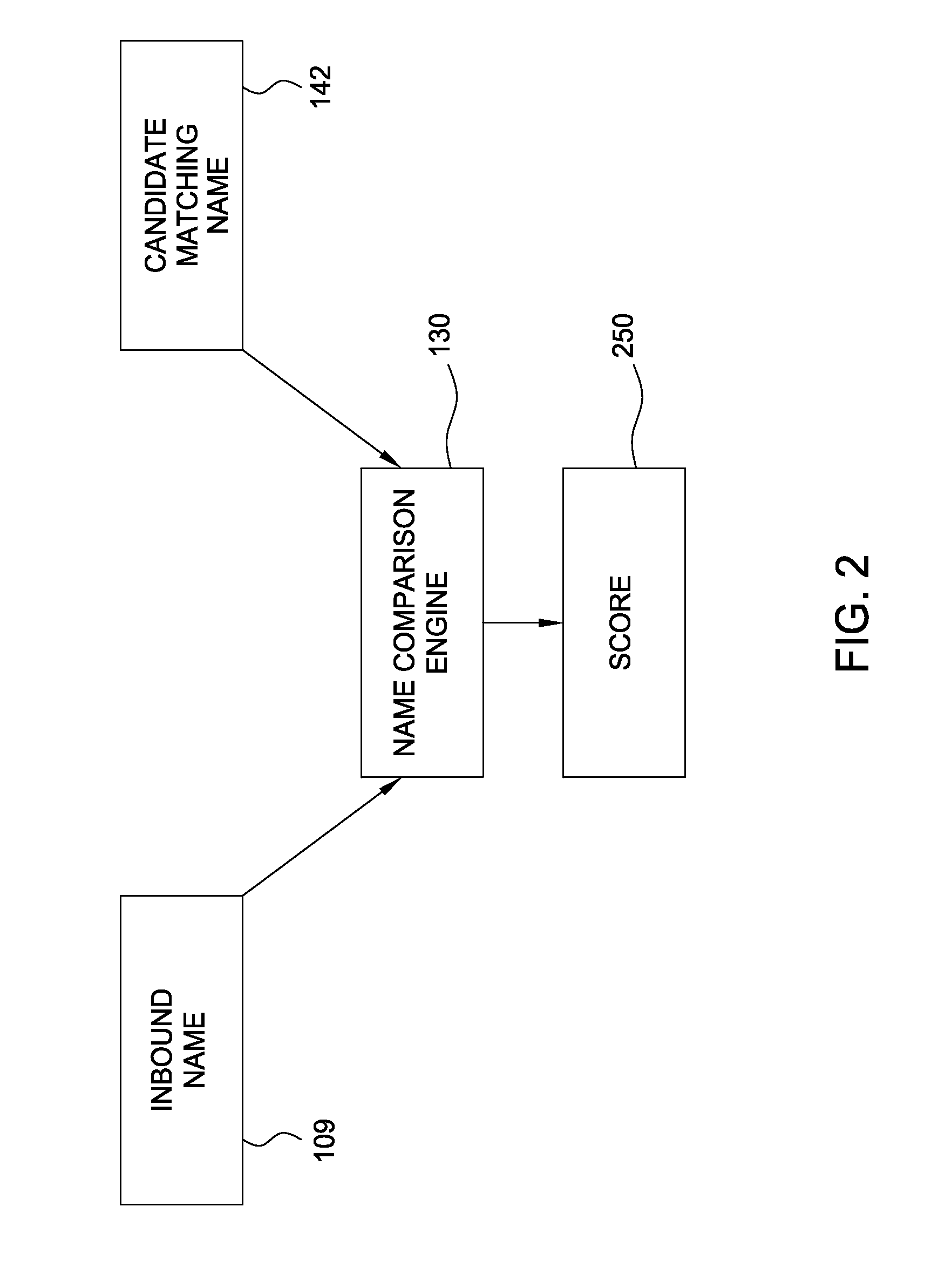
Method, apparatus and article for assigning a similarity measure to names
ActiveUS20080091674A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmWord count
A method, article and apparatus for calculating a measure of similarity between names is disclosed. Generally, name elements from an inbound name may be matched to name elements in a candidate matching name. A measure of similarity for the inbound name and candidate matching name may be calculated based on the number of matching name elements, an inbound name word count, a candidate name word count, and the number of transpositions that occur in matching name elements with one another.
Owner:HCL TECH LTD
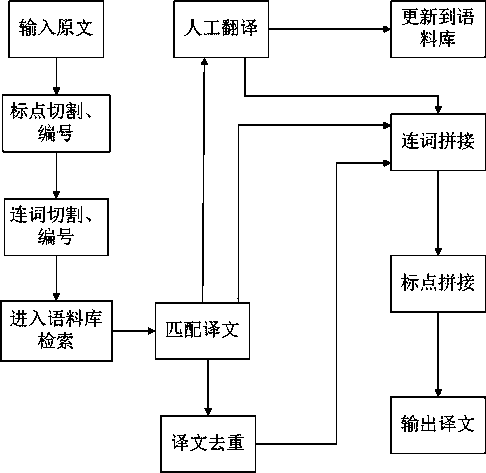
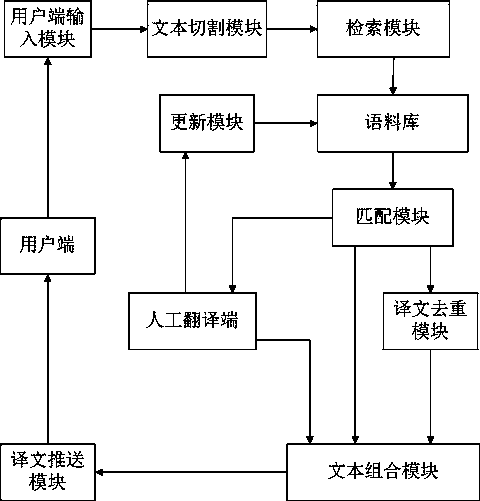
Translation system and translation method
InactiveCN103838718AImprove the efficiency of human translationReduce labor costsSpecial data processing applicationsWord countTranslation system
The invention discloses a translation system and a translation method. The translation method is characterized by comprising steps: original texts required to be translated are input through the user side, the user side transmits the original texts required to be translated to a server, the server judges whether cutting is required or not according to the situation whether the original text word number is larger than a number threshold value, performs punctuation cutting and primary marking, performs judgment again, conjunction cutting and secondary marking, retrieves cut fragments in a language database and matched translation and returns the translation to the user side, artificial translation is adopted to perform splicing if the matched translation is not retrieved, and spliced translation is transferred to the user side. The matching efficiency of linguistic database is improved, and labor cost is further reduced.
Owner:IOL WUHAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
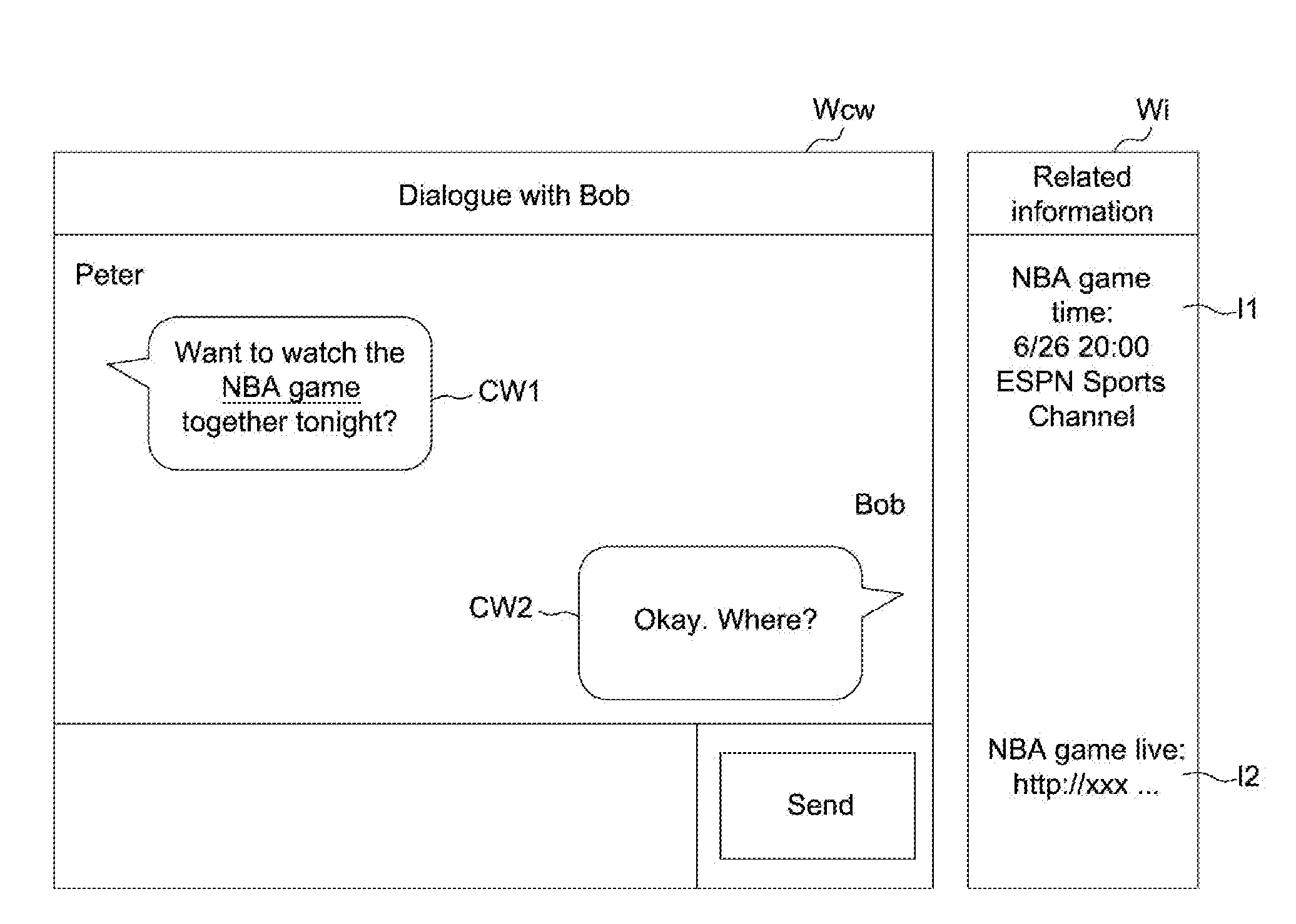
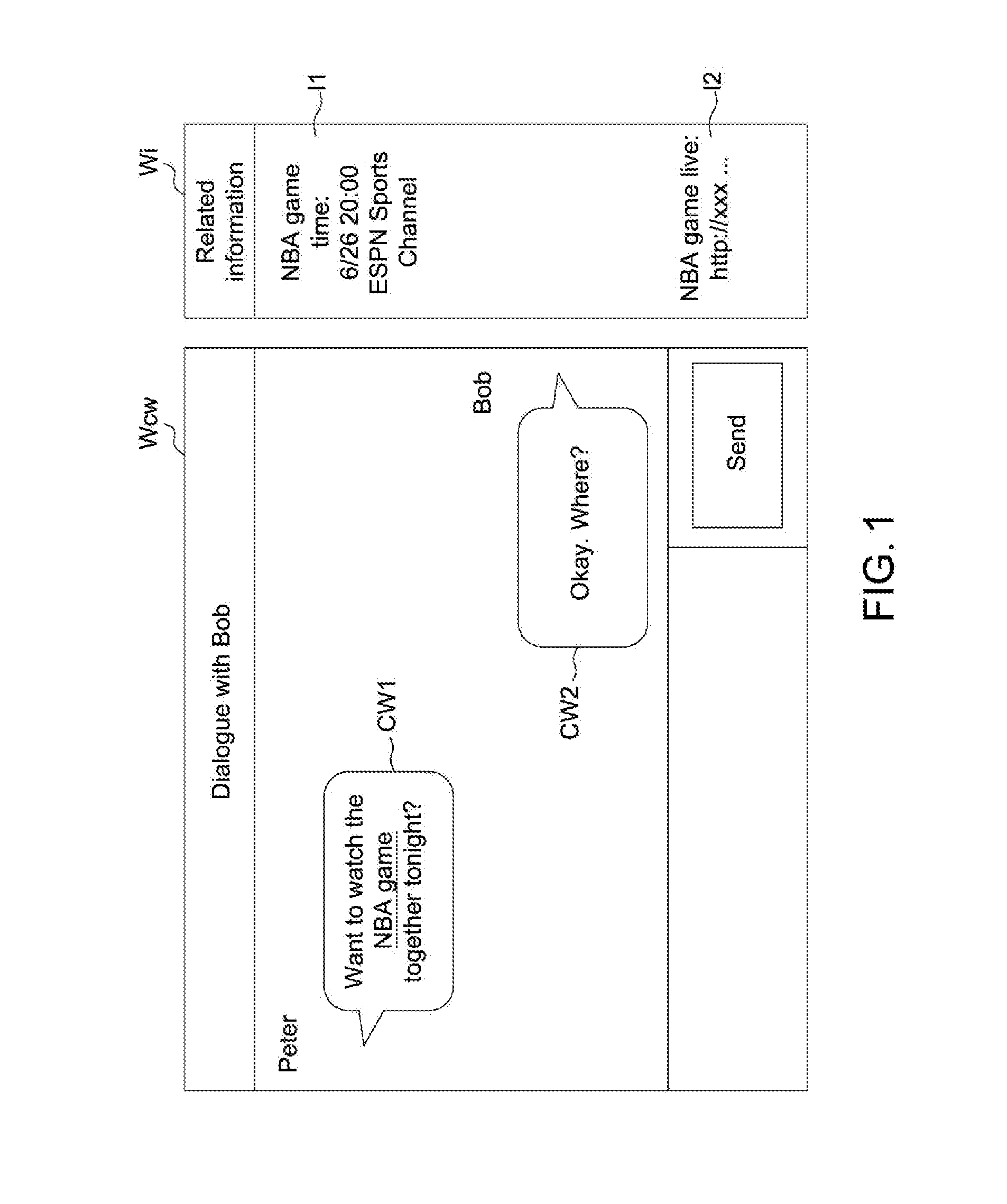
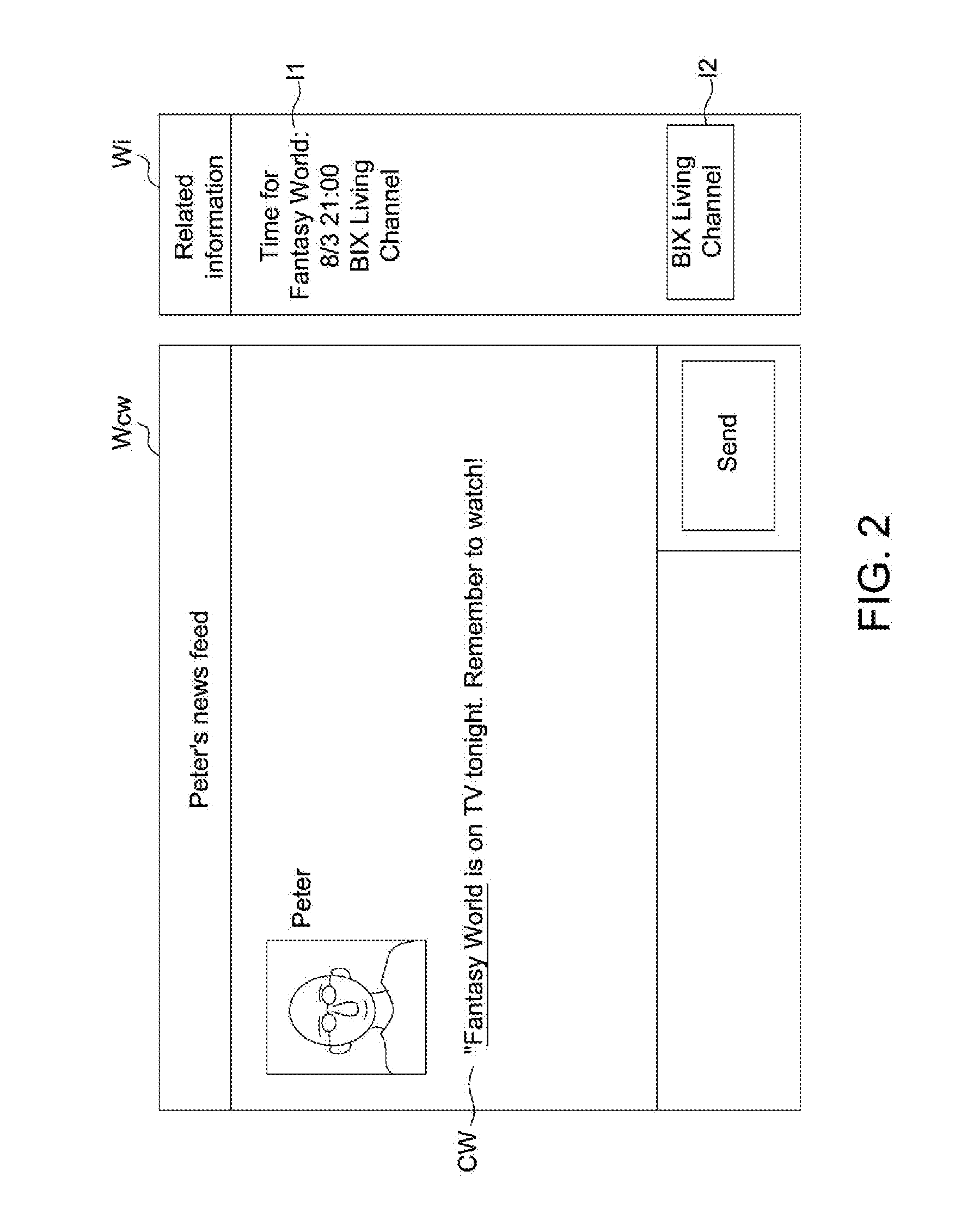
Related information display method and electronic device capable of automatically displaying related information
InactiveUS20160179833A1Easy to learnAccurate informationWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsRelevant informationWord count
A related information display method includes following steps. In step (a), a maximum word count of consecutive same words between a candidate text paragraph and a target text string to determine a similarity level. In step (b), it is determined whether to display related information of the target text string according to the similarity level. The related information is a website link associated with the target text string. The candidate text string may be dialogues in a communication software interface, text on a webpage, or text of a document in an electronic device. The target text string may be a name of a television program, a name of a place, a name of a movie, a name of a song, a name of a person, or a name of an object.
Owner:MSTAR SEMICON INC
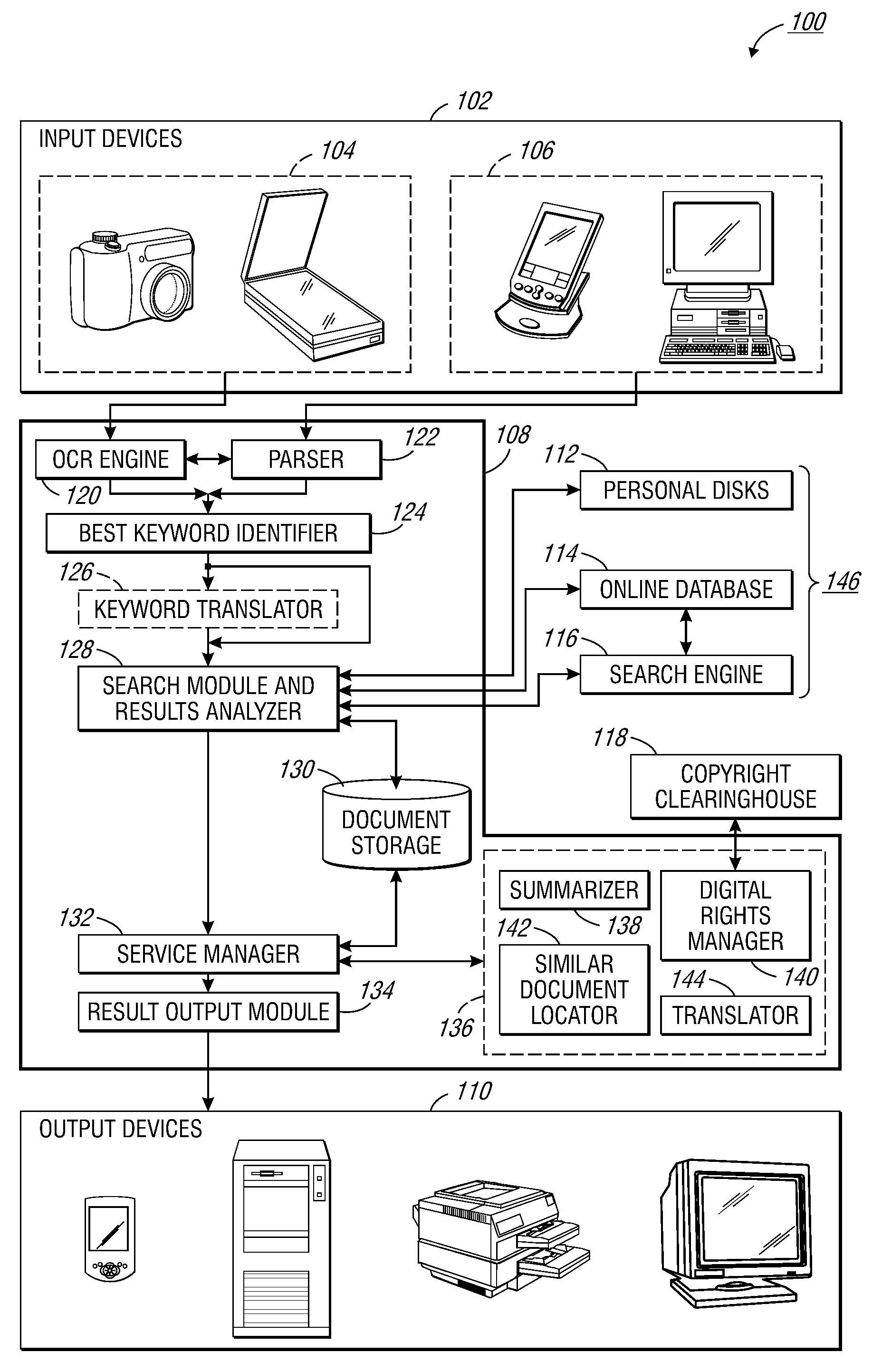
Methods and apparatus for document management
InactiveUS20060095841A1Special data processing applicationsDocument management systemsWord countPaper document
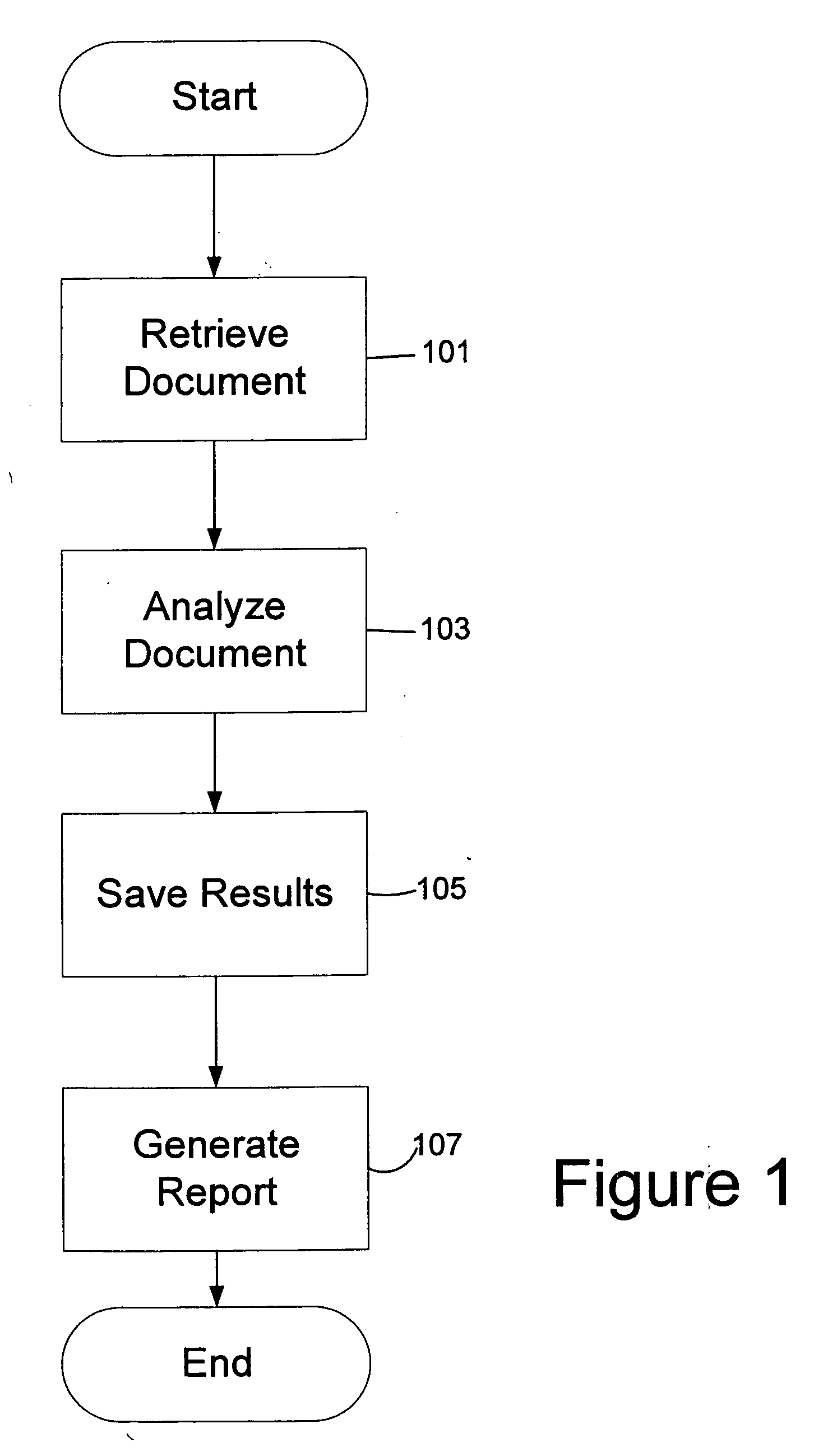
One embodiment of the invention is directed to the analysis of a document. The document may be retrieved and automatically analyzed to measure quality metrics defined for the document. A quality metric is any attribute of the document and may be, for example, a word count, a sentence count, a paragraph count, or any other suitable attribute. A set of results based on the act of analyzing the document may be generated and stored and a report based, at least in part, on the set of results that indicates measurements of the quality metrics over a period of time.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and device for realizing internet propaganda monitoring target evaluations
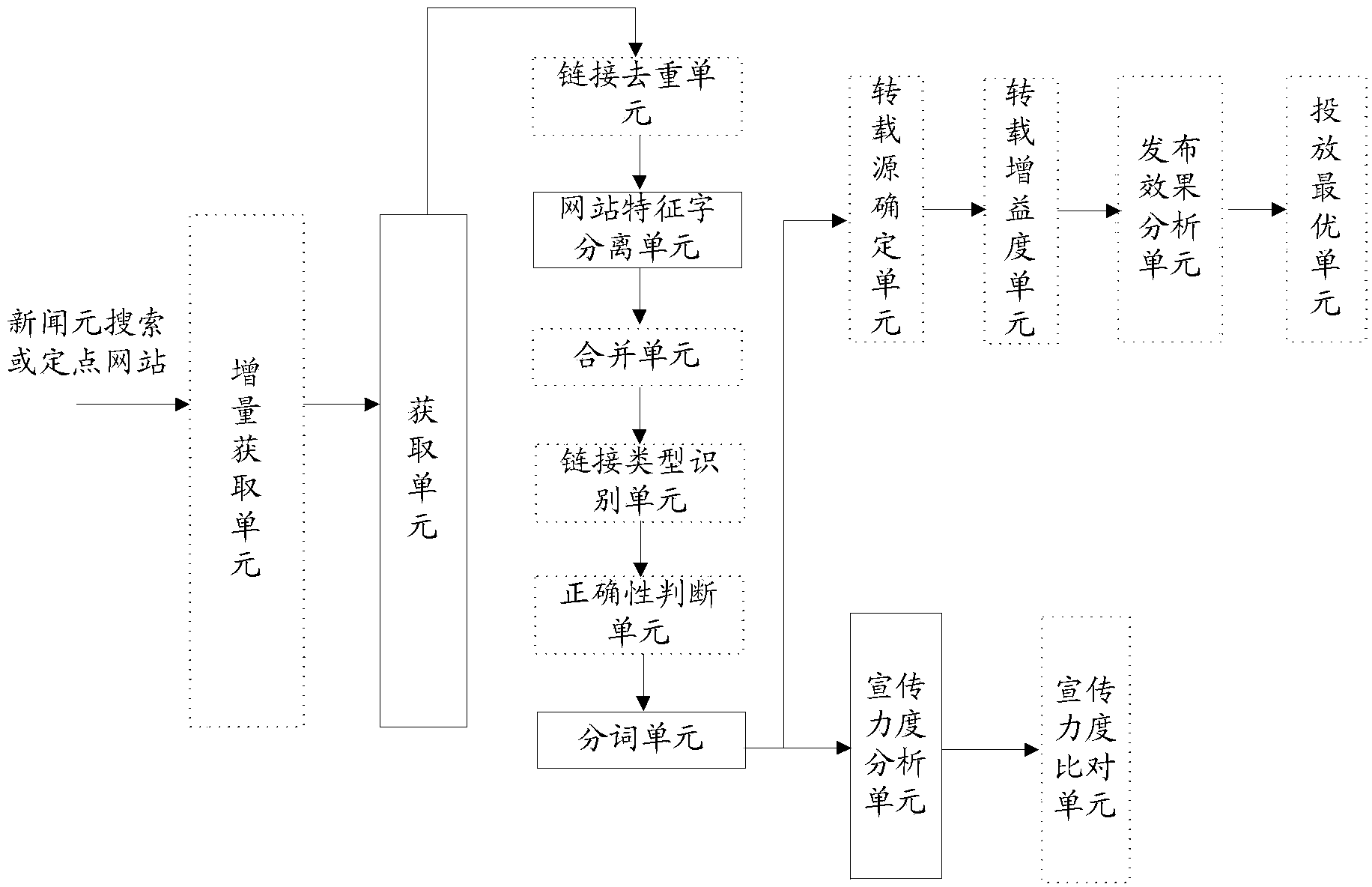
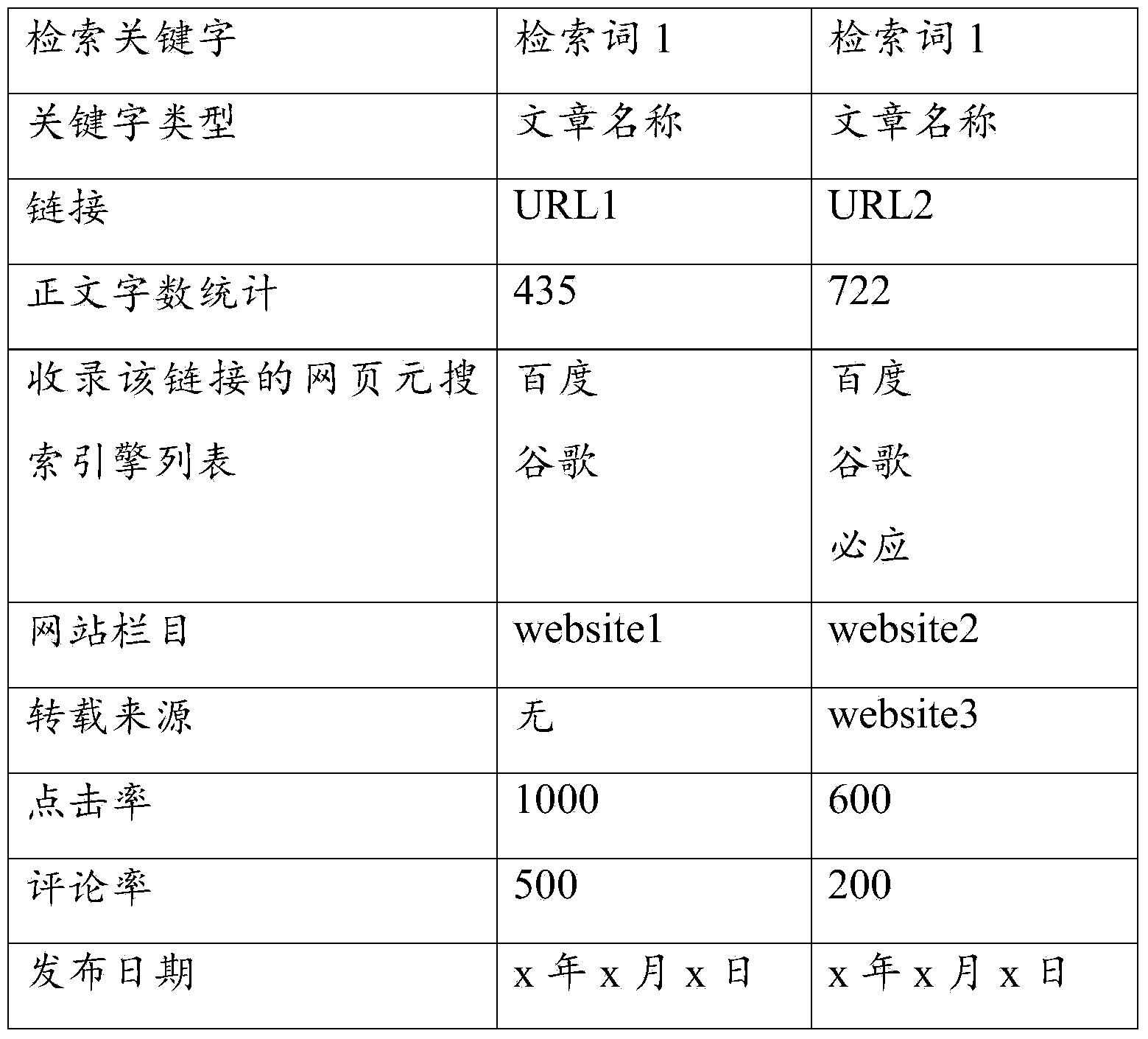
ActiveCN103646078AAnalyzing data powerfullyWebsite content managementSpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis dataWeb page
The invention discloses a method and a device for realizing internet propaganda monitoring target evaluations. The method comprises the steps as follows: obtaining web page information of a propaganda monitoring target from a selected data source according to configuration information; performing website tagged word separation on each piece of obtained web page information to obtain a corresponding title, a text and statistic text word number information; performing segmentation and extraction of keywords on the title and the text of each piece of obtained web page information, and calculating the information amount of each piece of web page information of the propaganda monitoring target; and determining propaganda force information of the propaganda monitoring target according to the information amount of each piece of web page information. According to the method and the device, the web page information of the selected data source is obtained, the website tagged word separation and the segmentation are performed on the web page information of the propaganda monitoring target, the propaganda force information is obtained through processing the obtained information, and powerful analytical data can be provided to enterprises for article release through analysis of the propaganda force information.
Owner:BEIJING VENUS INFORMATION SECURITY TECH +1
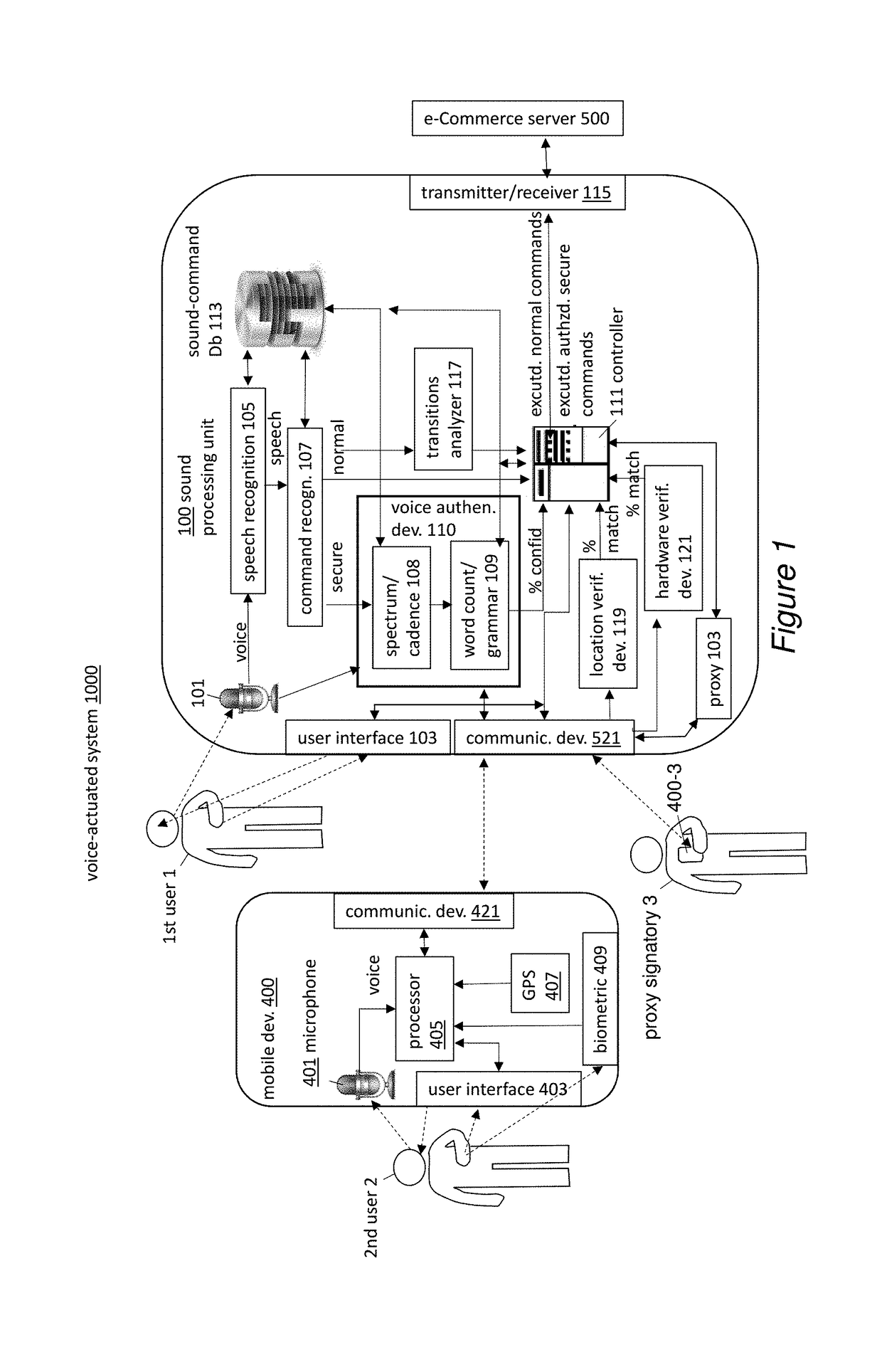
Voice activated payment
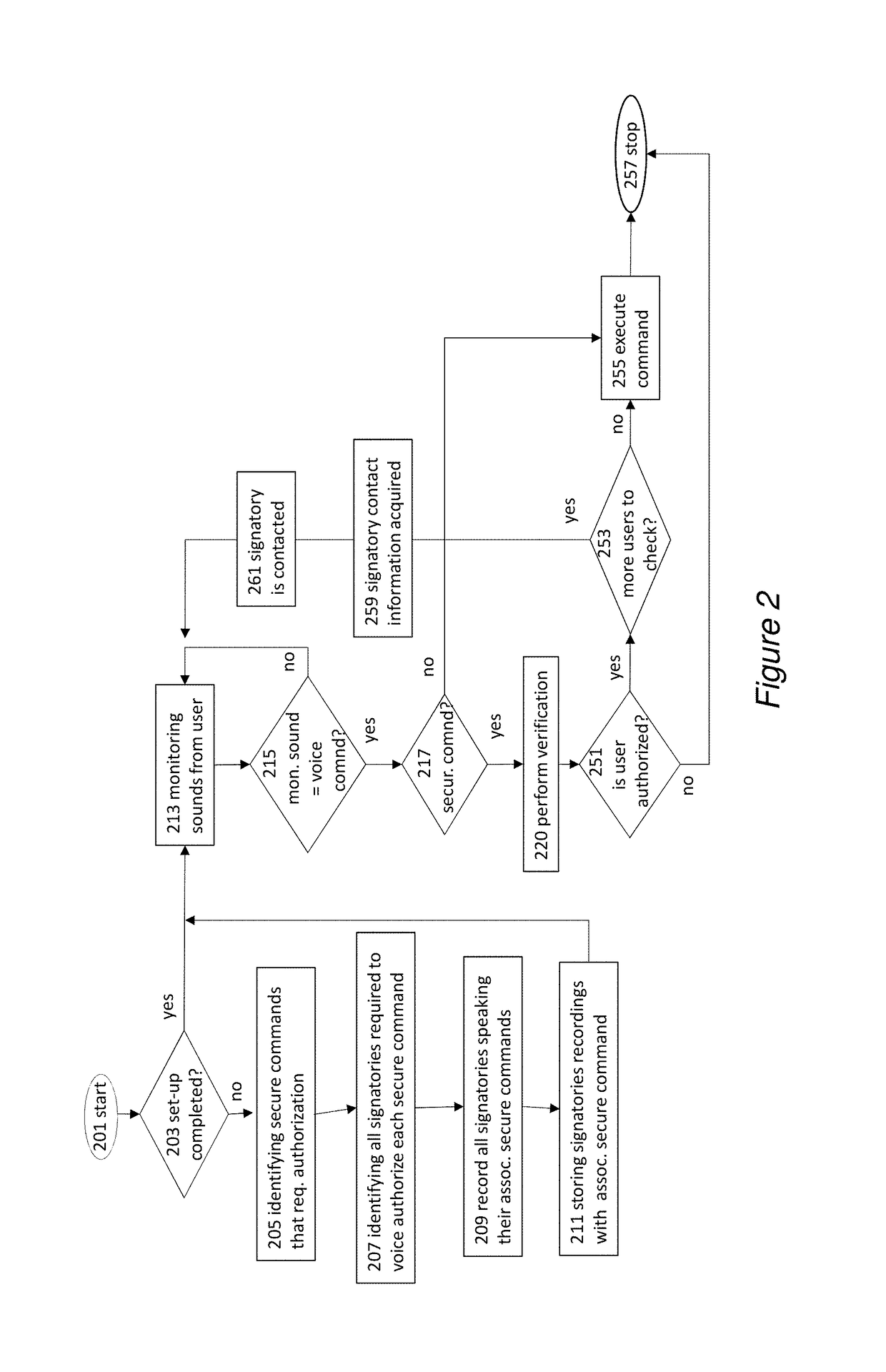
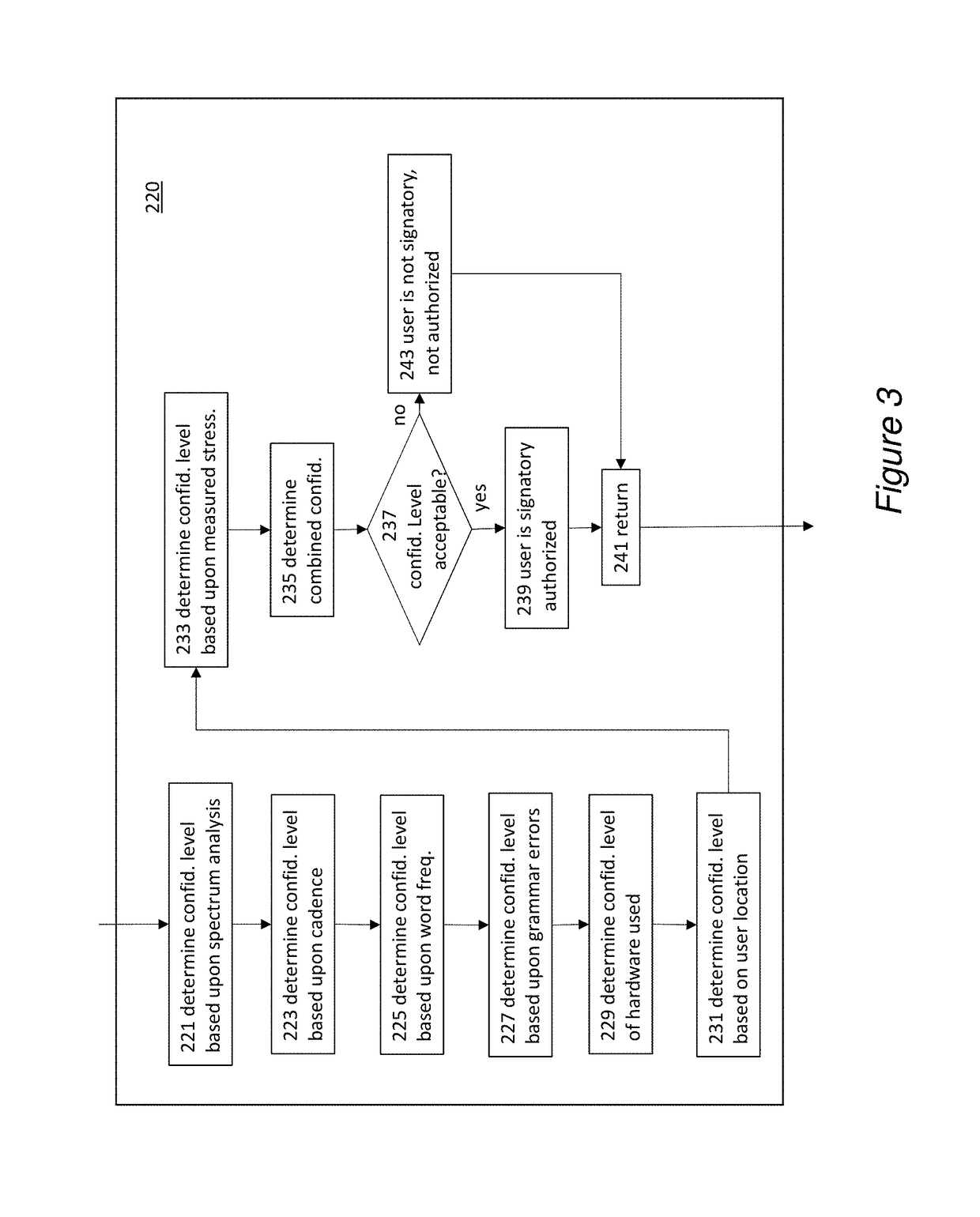
A voice-actuated system is described that allows voice authentication of on-line secure commands, such as purchases, by one or more designated users. It allows for an account to have multiple signatories that are required to approve a secure command. A user speaks commands into a local microphone, or in another embodiment, into a mobile device. A command recognition device identifies a secure command and sends it to a spectrum / cadence device to analyze spectrum and / or cadence. Also, the voice input may be sent to a word count / grammar device to analyze word counts and grammar errors to identify the user. Once identified, the account of user may be found and contact information for other signatories is acquired. The signatories are contacted and their identities are verified by comparison of their voices to pre-stored voice samples of the signatories.
Owner:WALMART APOLLO LLC
Method for displaying textbox in navigation system and navigation system
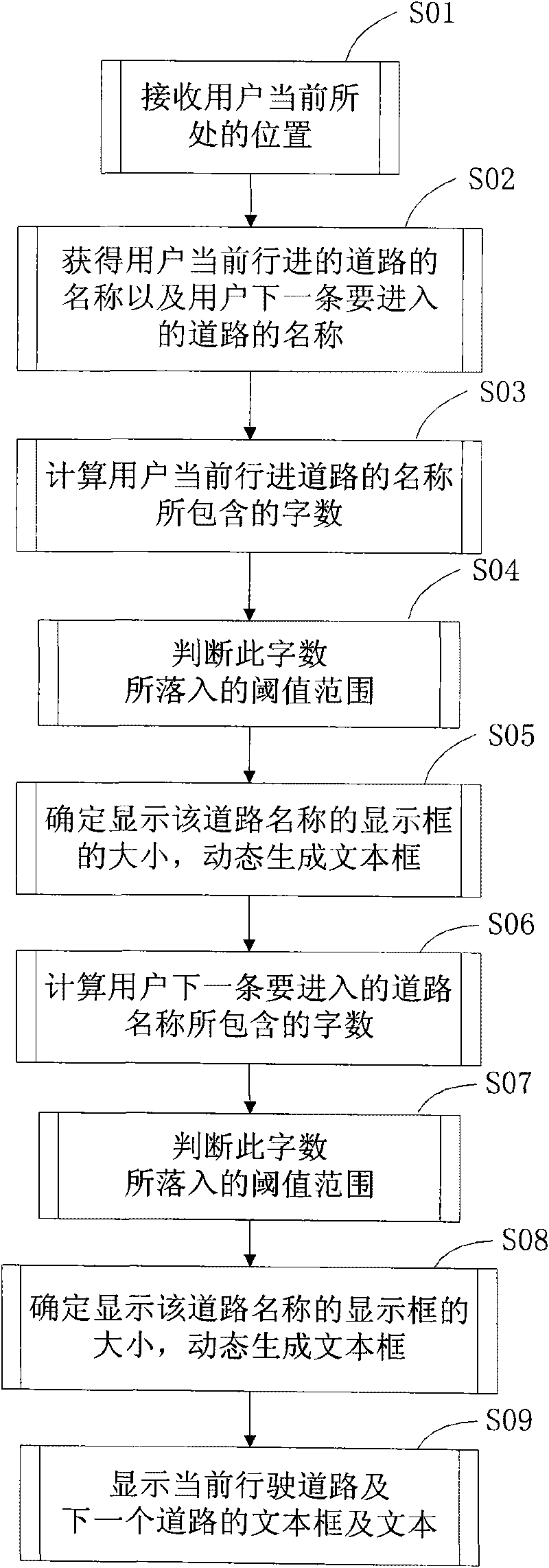
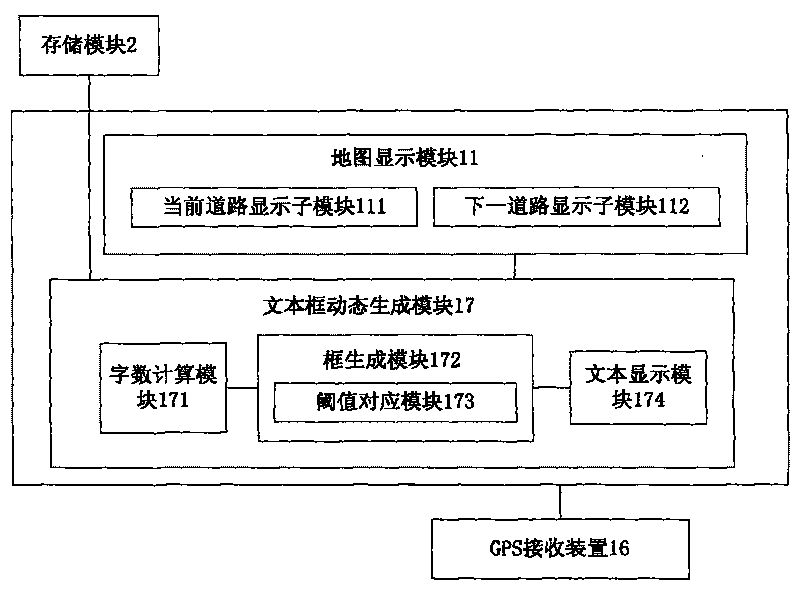
InactiveCN101713663ADoes not waste display spaceReduce computing burdenInstruments for road network navigationSatellite radio beaconingComputer graphics (images)Word count
The invention discloses a method for displaying a textbox in a navigation system and the navigation system. The method for displaying the textbox comprises the following steps of: firstly, acquiring and calculating the word count of a text to be displayed of the textbox; secondly, determining the length of the textbox according to the acquired word count; and thirdly, dynamically generating the textbox, and displaying the textbox namely the text. The method for displaying the textbox in the navigation system can determine the length of the textbox according to the word count of the text to be displayed and dynamically generate the textbox, so the method not only can well display the content of the text of the textbox but also cannot cause the problem that the blank part in the textbox can occupy more space of a display screen of a navigation device due to the oversize textbox when the text is short, the display effect is good, and the user can use smoothly and conveniently.
Owner:SHENZHEN CARELAND TECH
Available bandwidth detector for SAN switch ports
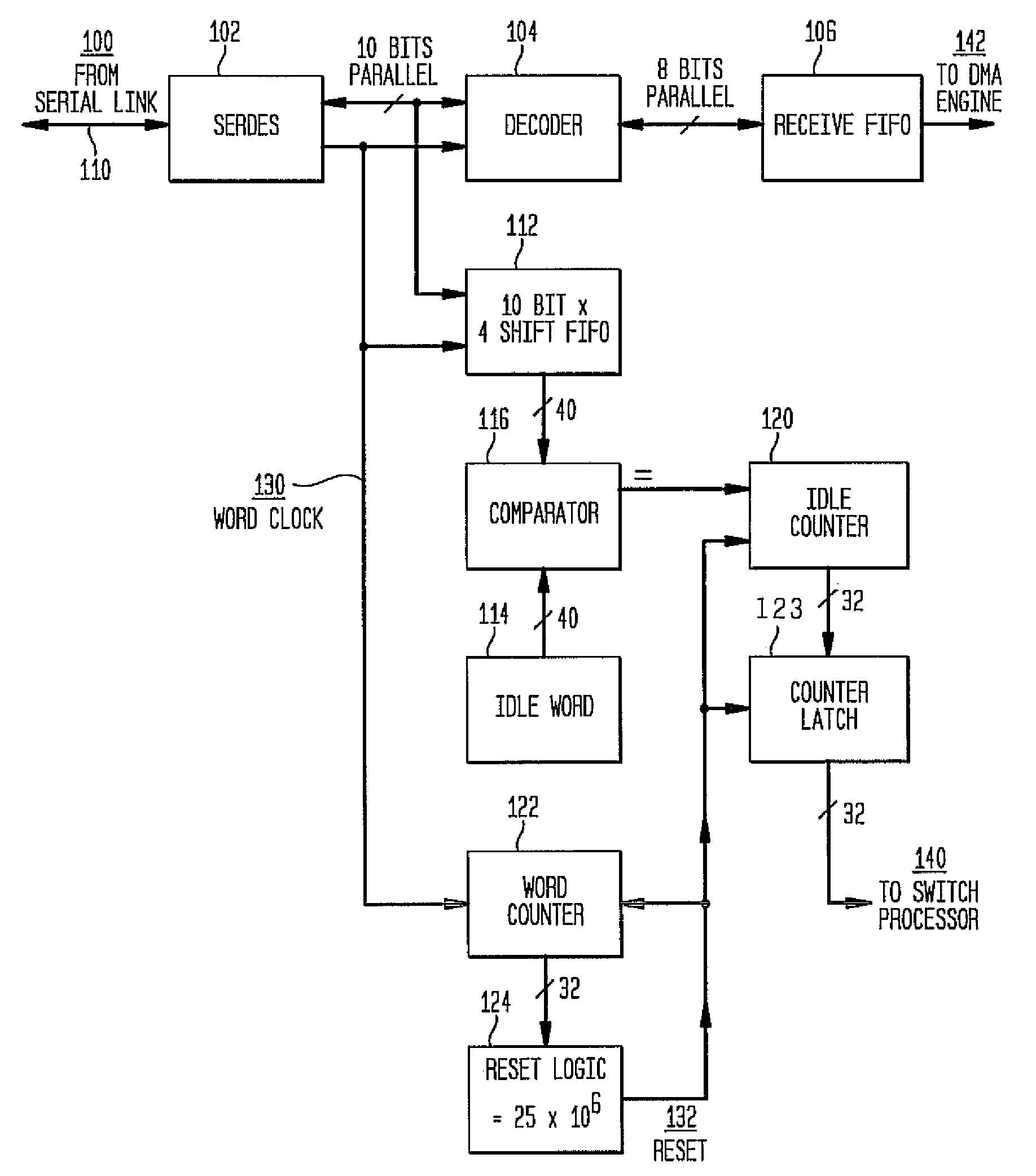
InactiveUS20040047291A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsStorage area networkWord count
A system and method for measuring data transmission activity through a port of a switch device interconnecting nodes of a storage area network, the port transmitting data as words of predetermined length, one data word indicating idle port activity. The method includes steps of: counting a number of transmitted words received from the port in a first counter device; and, for each word counted, comparing that word with a predetermined word indicating no (idle) port transmission activity. In response to the comparing, a number of matches are counted in a second counter device. In this manner, a ratio of a number of counted matches with a total amount of words counted indicates available bandwidth for transmitting additional data over that link. Preferably, this value is communicated to a processor device for controlling bandwidth over the link.
Owner:IBM CORP
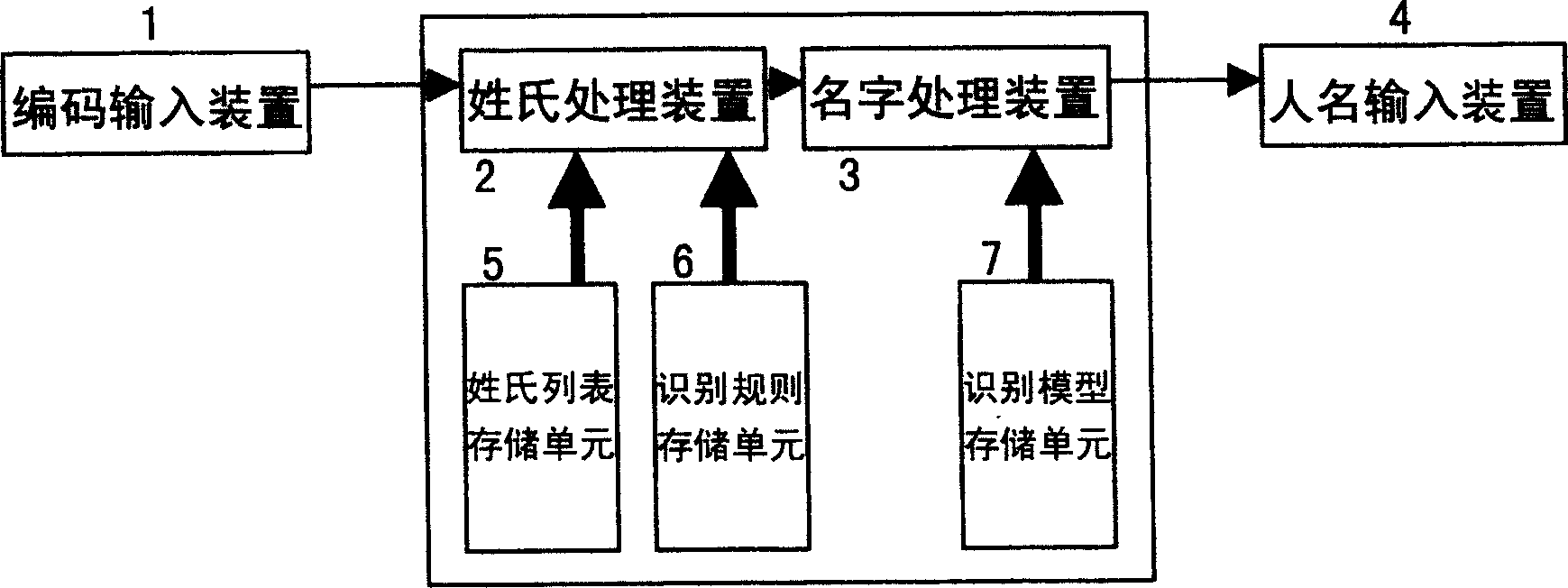
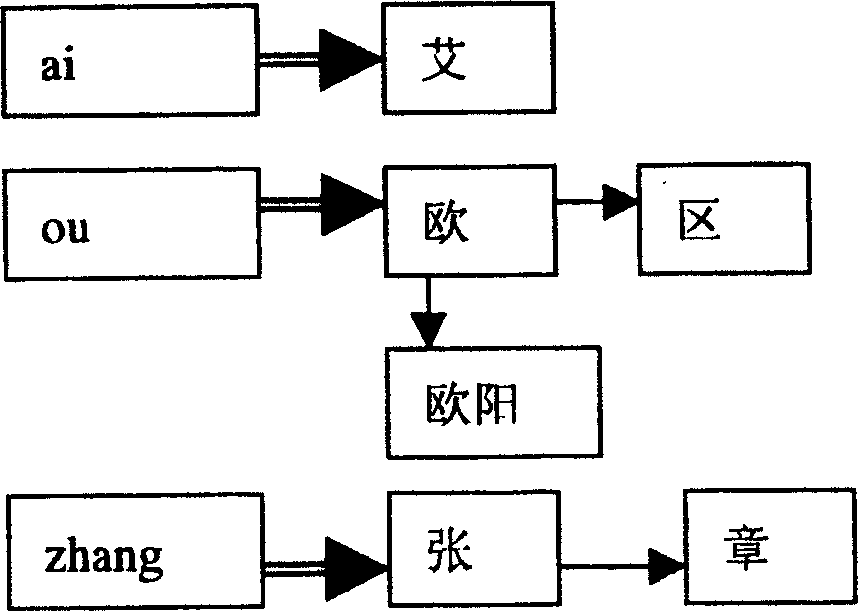
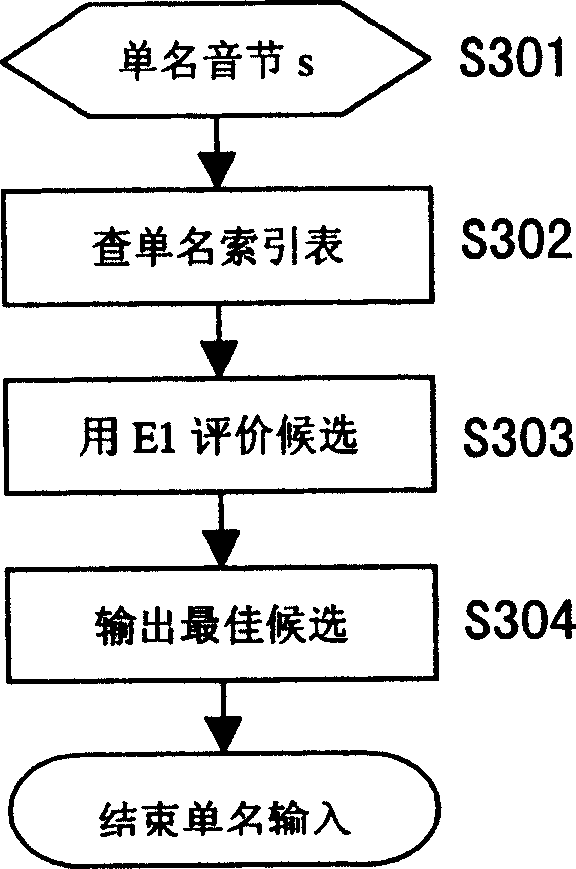
Name input processing method and system
The invention discloses an input method and equipment which can identify the inputted name. The method comprises: checking the surname inputting code in the inputting coded sequence, choosing the candidate character which is corresponding with the surname inputting code in surname listing, acquiring the name's word number from the inputting coded sequence, if the number of the name's word is a single name, calculating the using probability of the single candidate word and doing descend arrangement by the using probability; if the number of the name's word is a double name, calculating the suing probability of the double candidate word and doing descend arrangement by the using probability of the candidate word.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Apparatus, method and program for text mining
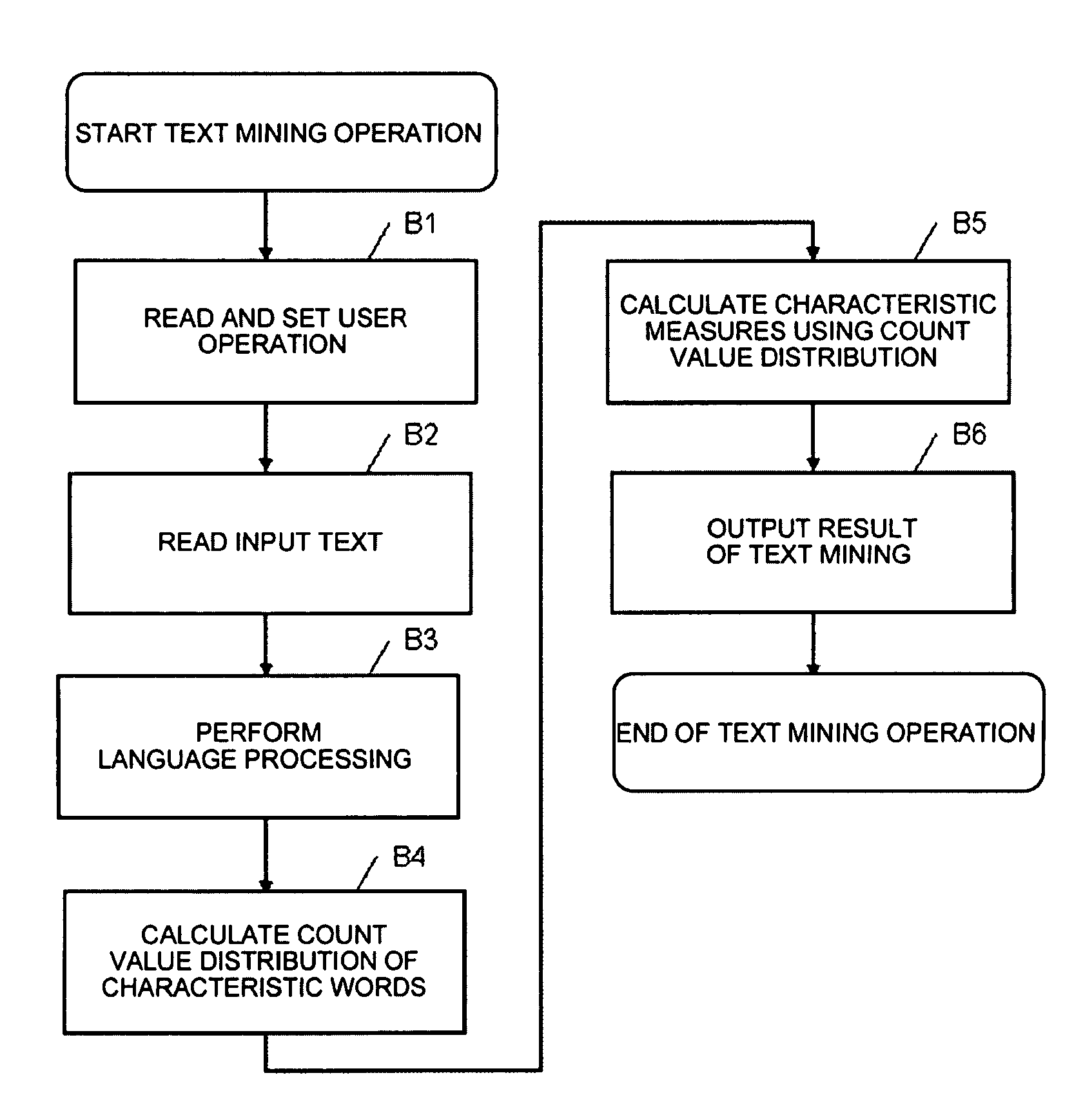
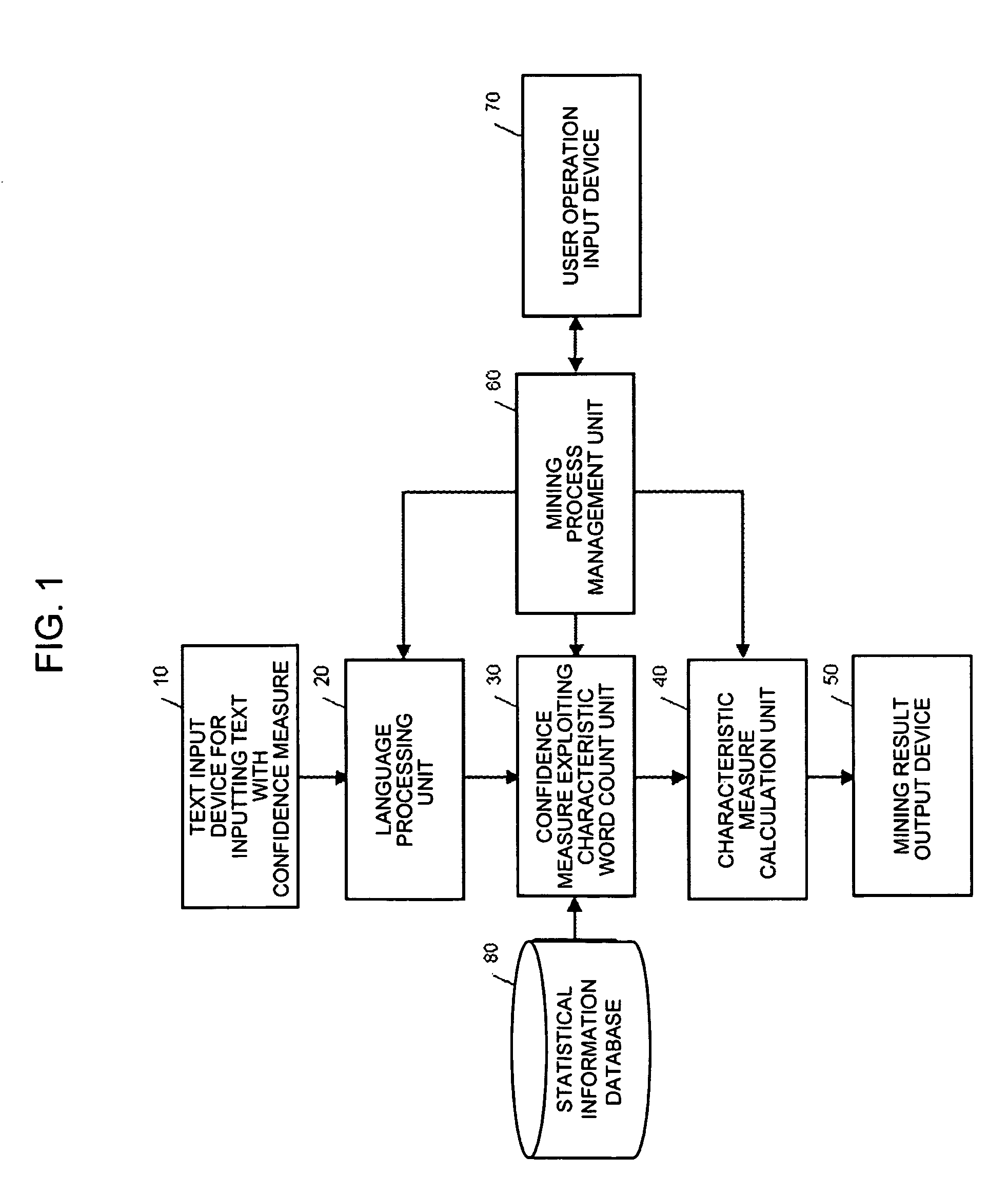
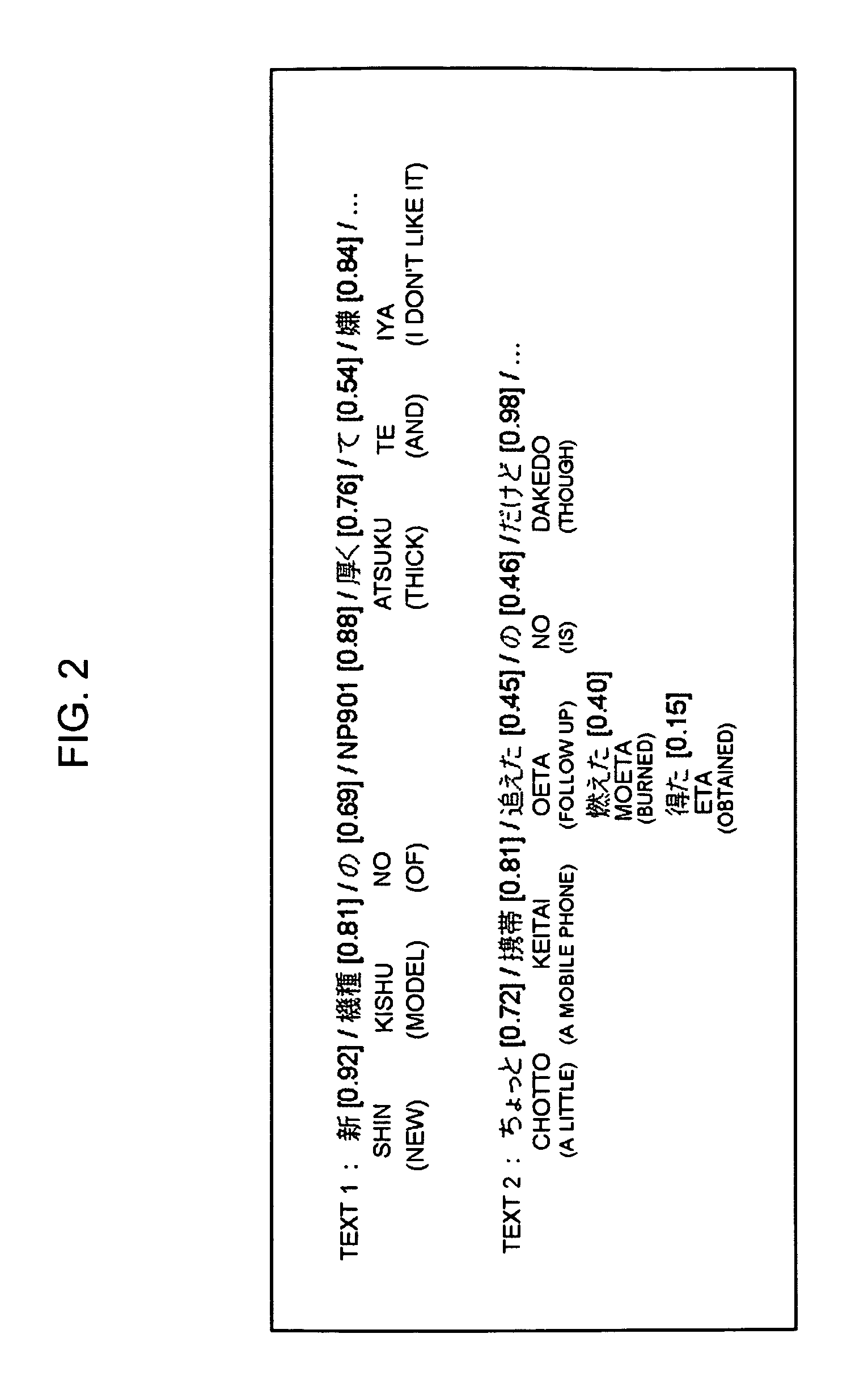
ActiveUS8140337B2Improve accuracyEliminate the effects ofDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsText miningWord count
Disclosed is an apparatus includes a text input device that inputs text data provided with confidence measure, as subject for mining, a language processing unit that performs language analysis of the input text data provided with the confidence measures, a confidence measure exploiting characteristic word count unit that counts the characteristic words in the input text to provide a count result and that exploits the statistical information and the confidence measures provided in the input text to correct the count result obtained, a characteristic measure calculation unit that calculates the characteristic measure of each characteristic word from the corrected count result, a mining result output device that outputs the characteristic measure of each characteristic word obtained, a user operation input device for a user to input setting for language processing of the input text and setting for a technique for calculating the characteristic measure being found, a mining process management unit that transmits a user's command delivered from the user operation input device to respective components, and a statistical information database that records and holds the statistical information representing the property of the input text that may be presupposed.
Owner:NEC CORP
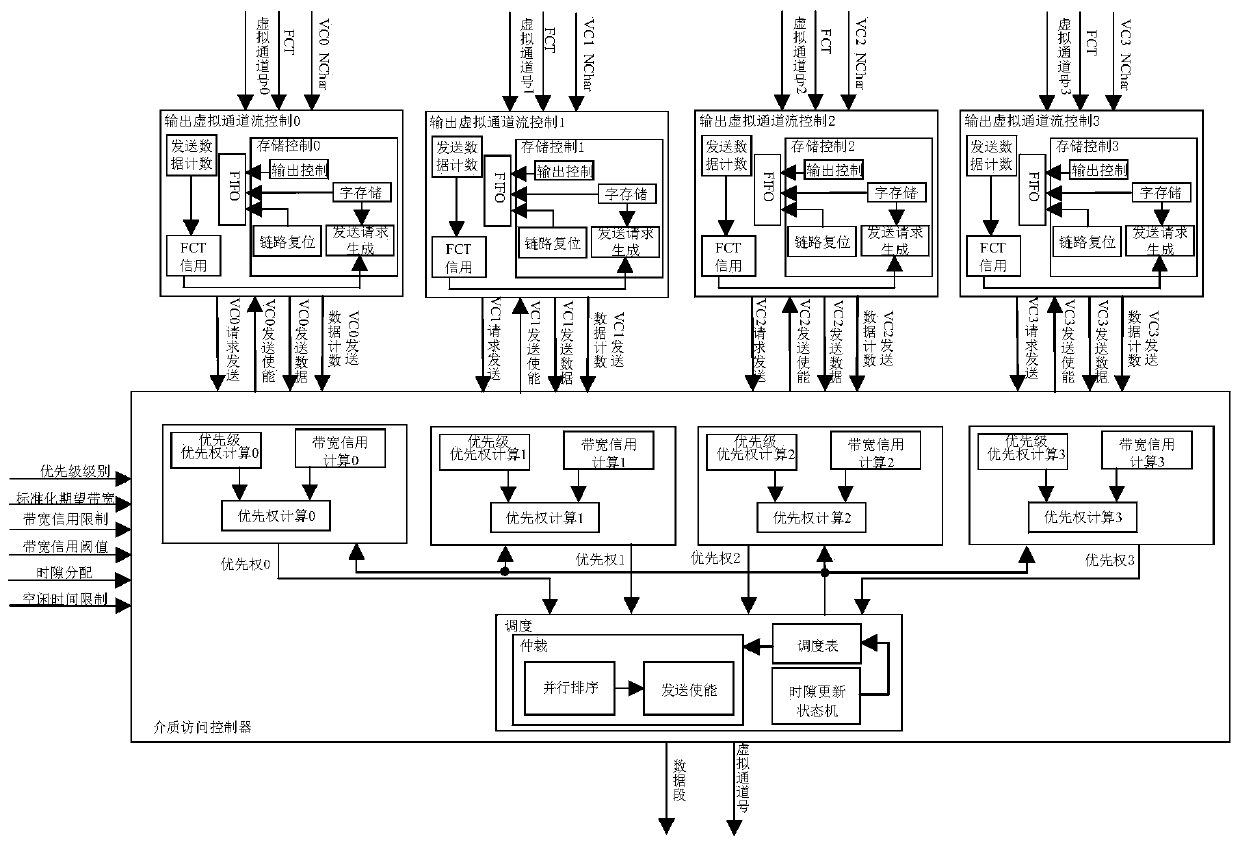
SpaceFibre satellite-borne network service quality control system based on FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
ActiveCN110474670AGuaranteed stabilityImprove reading speedRadio transmissionData switching networksData segmentQuality control system
The invention discloses a SpaceFibre satellite-borne network service quality control system based on an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), which comprises a multi-path virtual channel flow controlmodule and a single-path medium access controller, and is characterized in that the medium access controller is provided with a plurality of priority calculation modules and a scheduling module; a virtual channel flow control module which is used for receiving data of a virtual channel and generating a data sending request, and is also used for sending the data segment and the data word count value output by the buffer area to the media access controller when receiving a sending enable signal of the media access controller; a priority calculation module which is used for calculating the priority and sending the priority to the scheduling module; a scheduling module which is used for carrying out parallel sorting on the received priorities and selecting a scheduled virtual channel from allthe virtual channels according to a sorting result; transmitting and sending a data enabling signal to a virtual channel flow control module corresponding to the scheduled virtual channel; and outputting the number of the scheduled virtual channel and the data segment output by the buffer area of the corresponding virtual channel flow control module.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
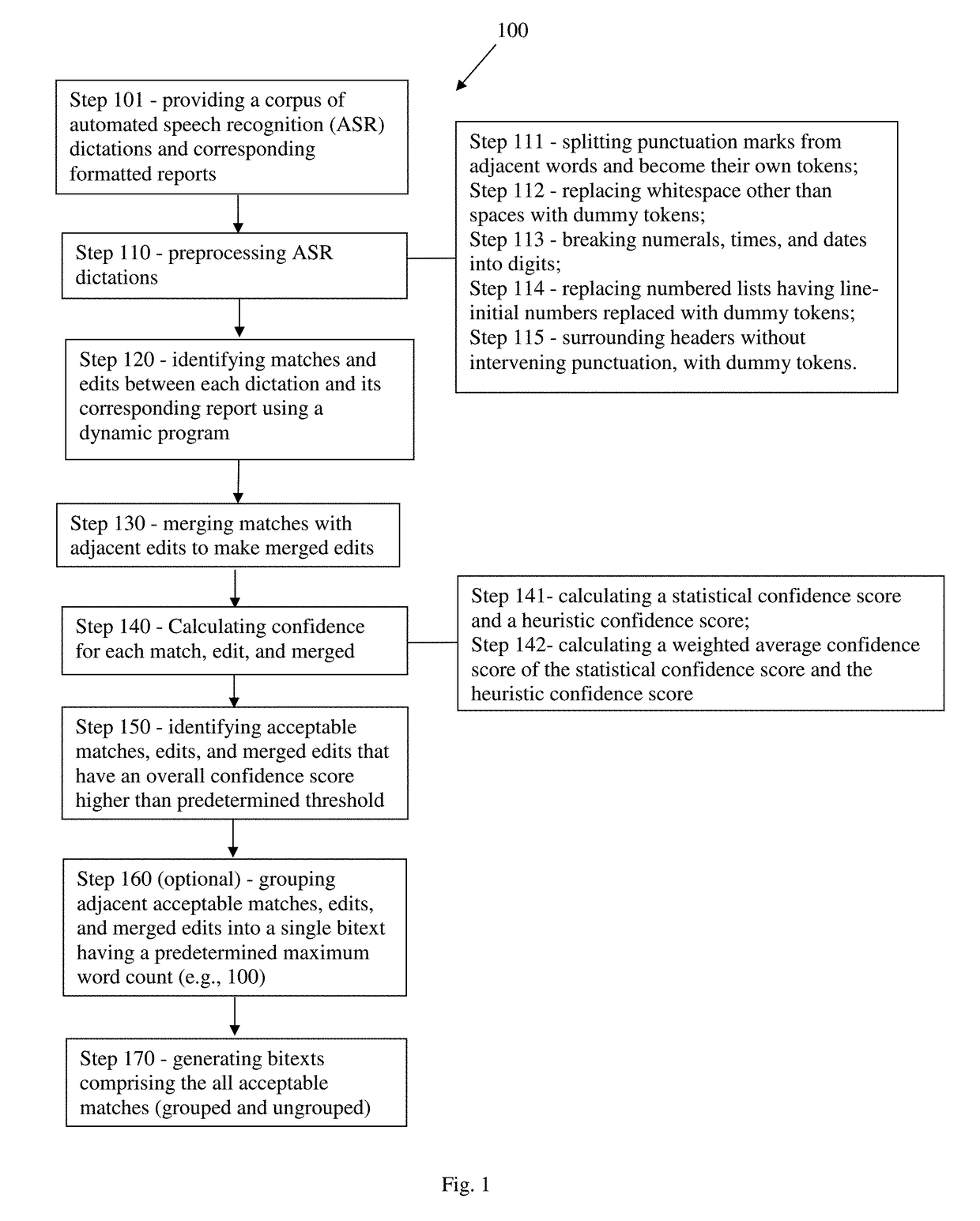
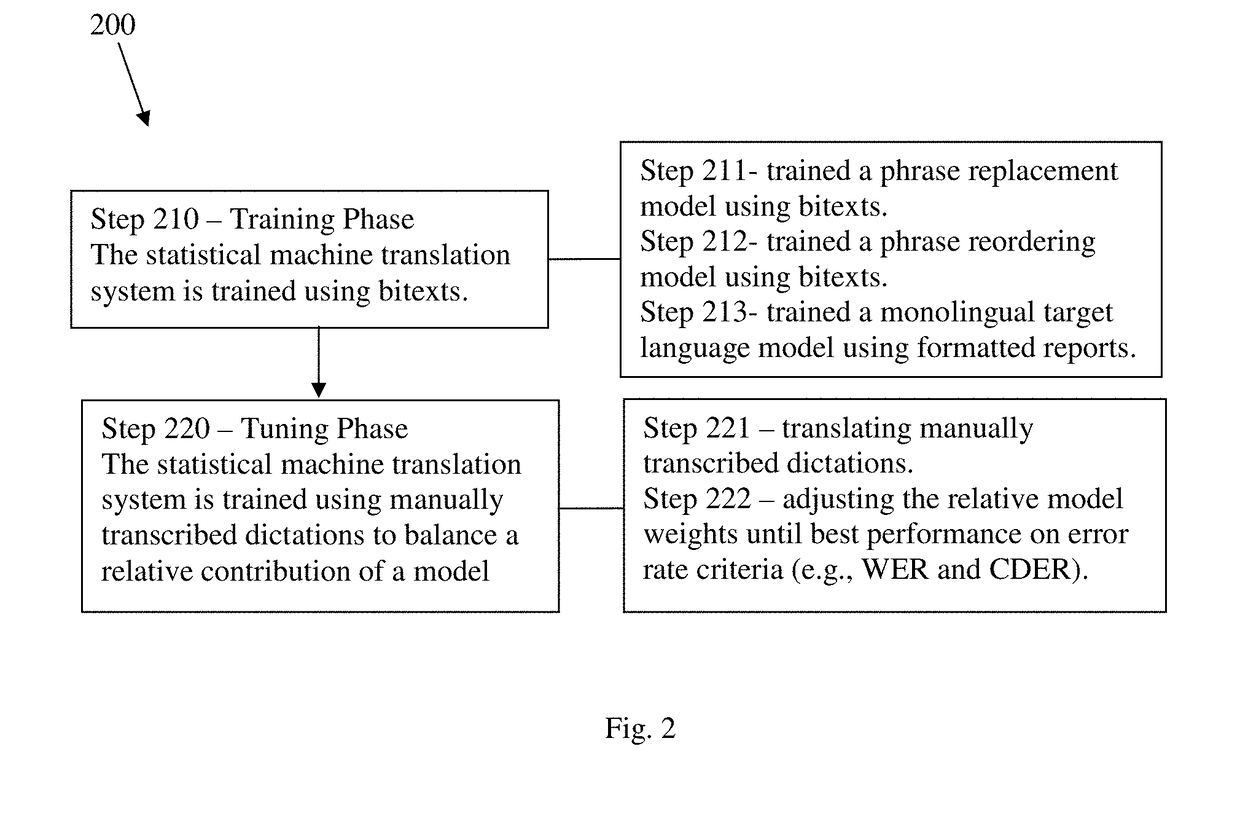
Automated medical report formatting system
Systems, methods, and computer-readable non-transitory storage medium in which a statistical machine translation model for formatting medical reports is trained in a learning phase using bitexts and in a tuning phase using manually transcribed dictations. Bitexts are generated from automated speech recognition dictations and corresponding formatted reports, using a series of steps including identifying matches and edits between the dictations and their corresponding reports using dynamic programming, merging matches with adjacent edits, calculating a confidence score, identifying acceptable matches, edits, and merged edits, grouping adjacent acceptable matches, edits, and merged edits, and generating a plurality of bitexts each having a predetermined maximum word count (e.g., 100 words), preferably with a predetermined overlap (e.g., two thirds) with another bitext. During the tuning phase, the system is trained by iteratively translating manually transcribed dictations and adjusting the relative model weights until best performance on error rate criteria (e.g., WER and CDER).
Owner:EMR AI INC
Man-machine combined translation batch processing translation method containing artificial intelligence
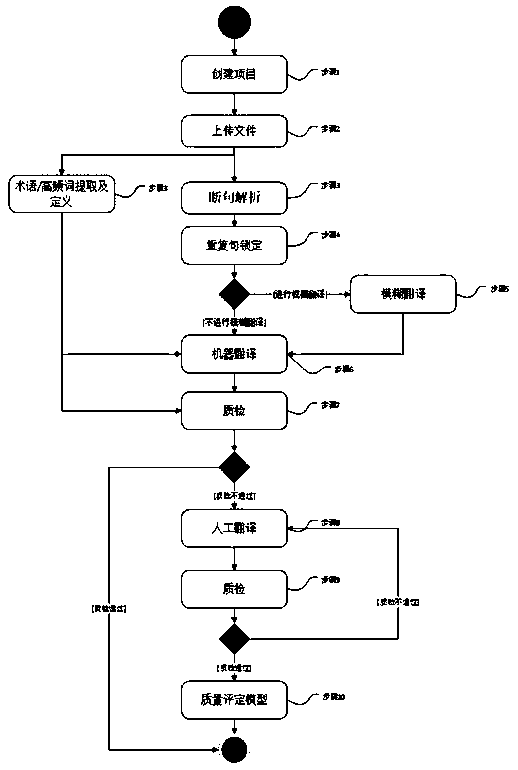
PendingCN110837742AImprove translation speedImprove translation efficiencyNatural language translationResourcesSentence segmentationBatch processing
The invention discloses a man-machine combined translation batch processing translation method containing artificial intelligence. The method comprises the following steps of 1, creating a translationitem; 2, uploading a file to be translated; 3, the system performing sentence segmentation analysis and extraction on the file and defines high-frequency words and terms; 4, locking the repeated sentences of the original text; 5, the system automatically translating the matched original text in a fuzzy manner according to the translation memory corpus; 6, the system calling machine translation totranslate the remaining original text according to the translation direction and specialty; 7, performing quality inspection on translations of fuzzy translation and machine translation; 8, manuallychecking and modifying the fuzzy translation and the machine translation on line; 9, conducting the quality inspection on the result of manual translation; and 10, counting related parameters such asmanual editing modification amplitude and word number, and generating a quality evaluation model report. The translation efficiency is improved, the translation quality is ensured, and the translationcost is reduced.
Owner:广州市汇泉翻译服务有限公司
Available bandwidth detector for SAN switch ports
InactiveUS7339896B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsStorage area networkWord count
A system and method for measuring data transmission activity through a port of a switch device interconnecting nodes of a storage area network, the port transmitting data as words of predetermined length, one data word indicating idle port activity. The method includes steps of: counting a number of transmitted words received from the port in a first counter device; and, for each word counted, comparing that word with a predetermined word indicating no (idle) port transmission activity. In response to the comparing, a number of matches are counted in a second counter device. In this manner, a ratio of a number of counted matches with a total amount of words counted indicates available bandwidth for transmitting additional data over that link. Preferably, this value is communicated to a processor device for controlling bandwidth over the link.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Data format and data transfer
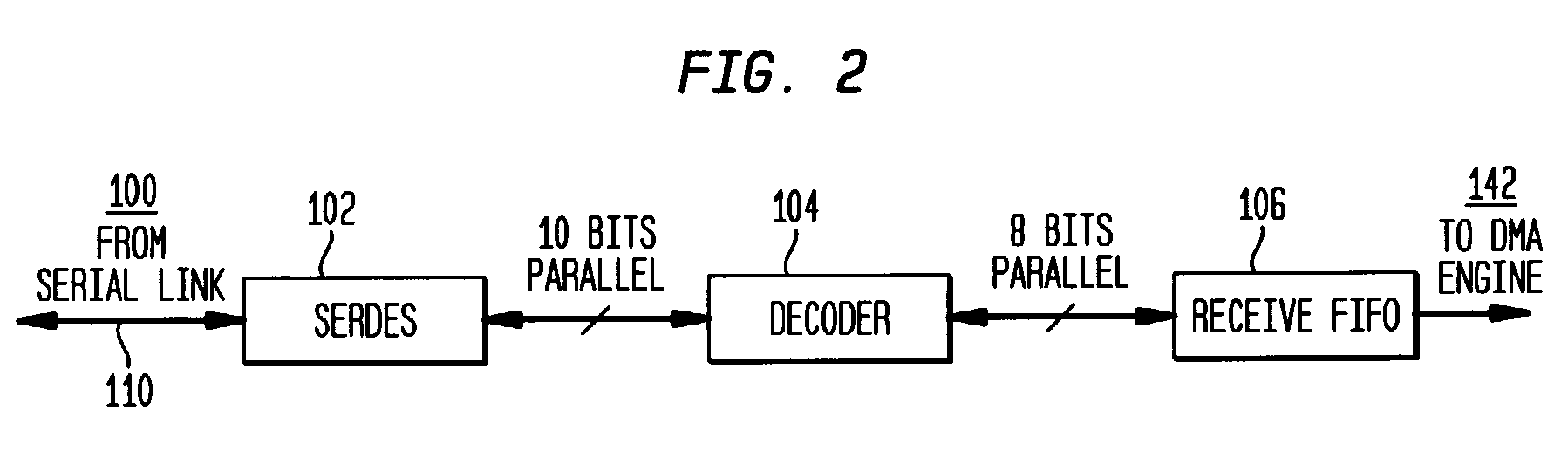
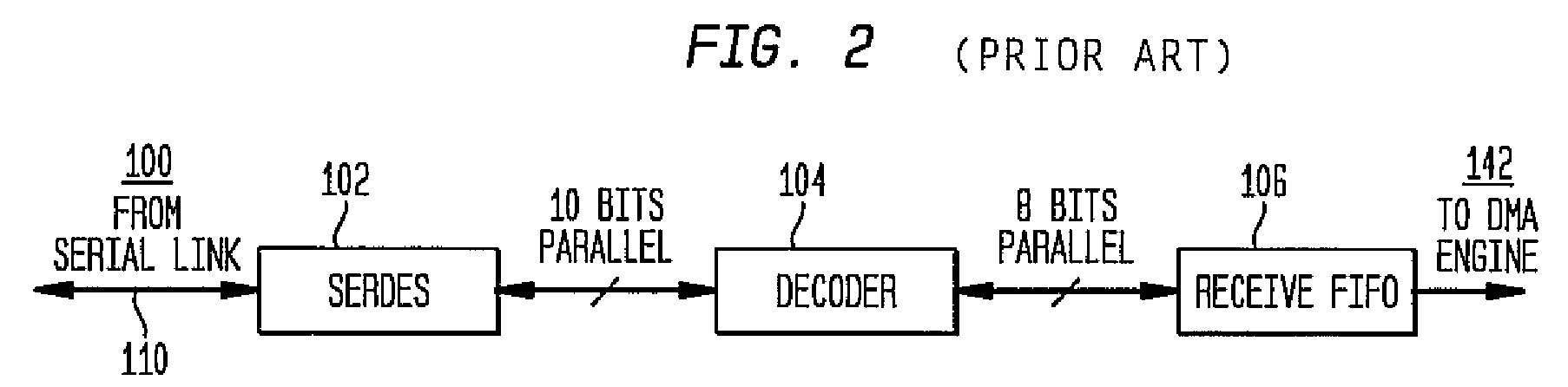
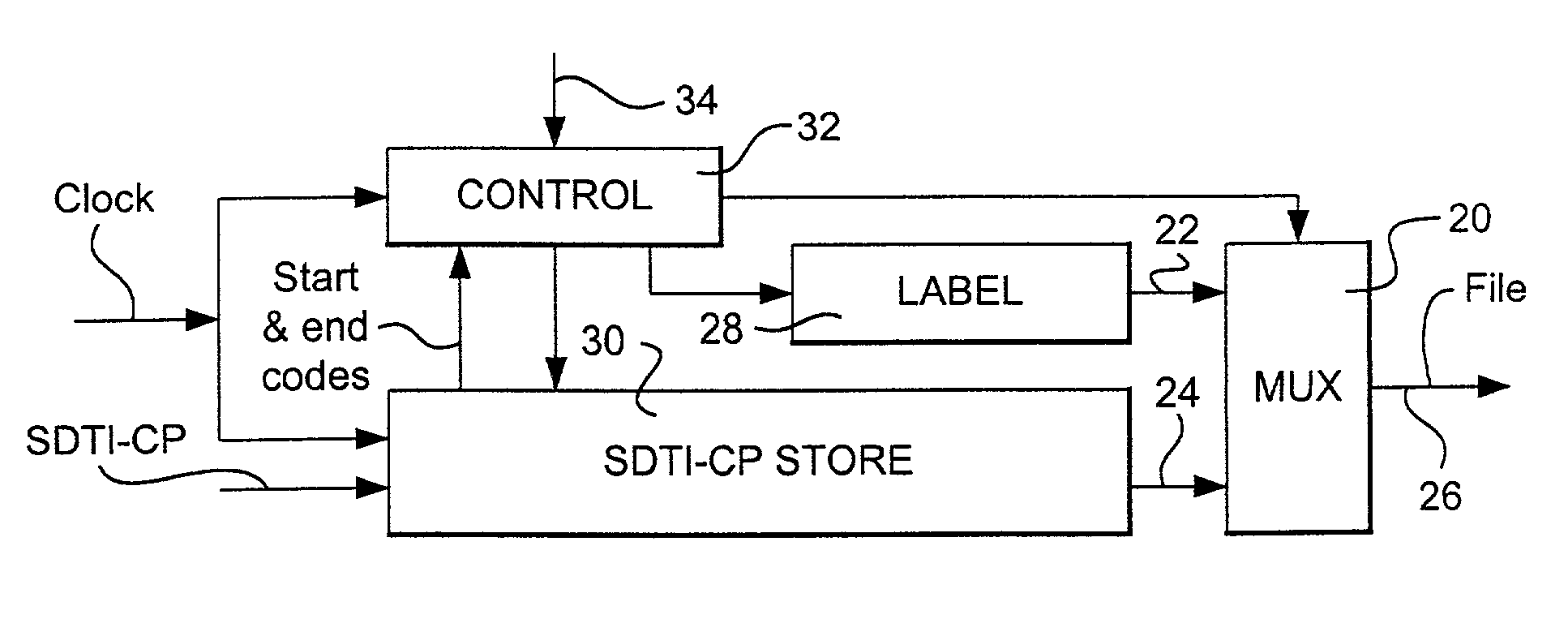
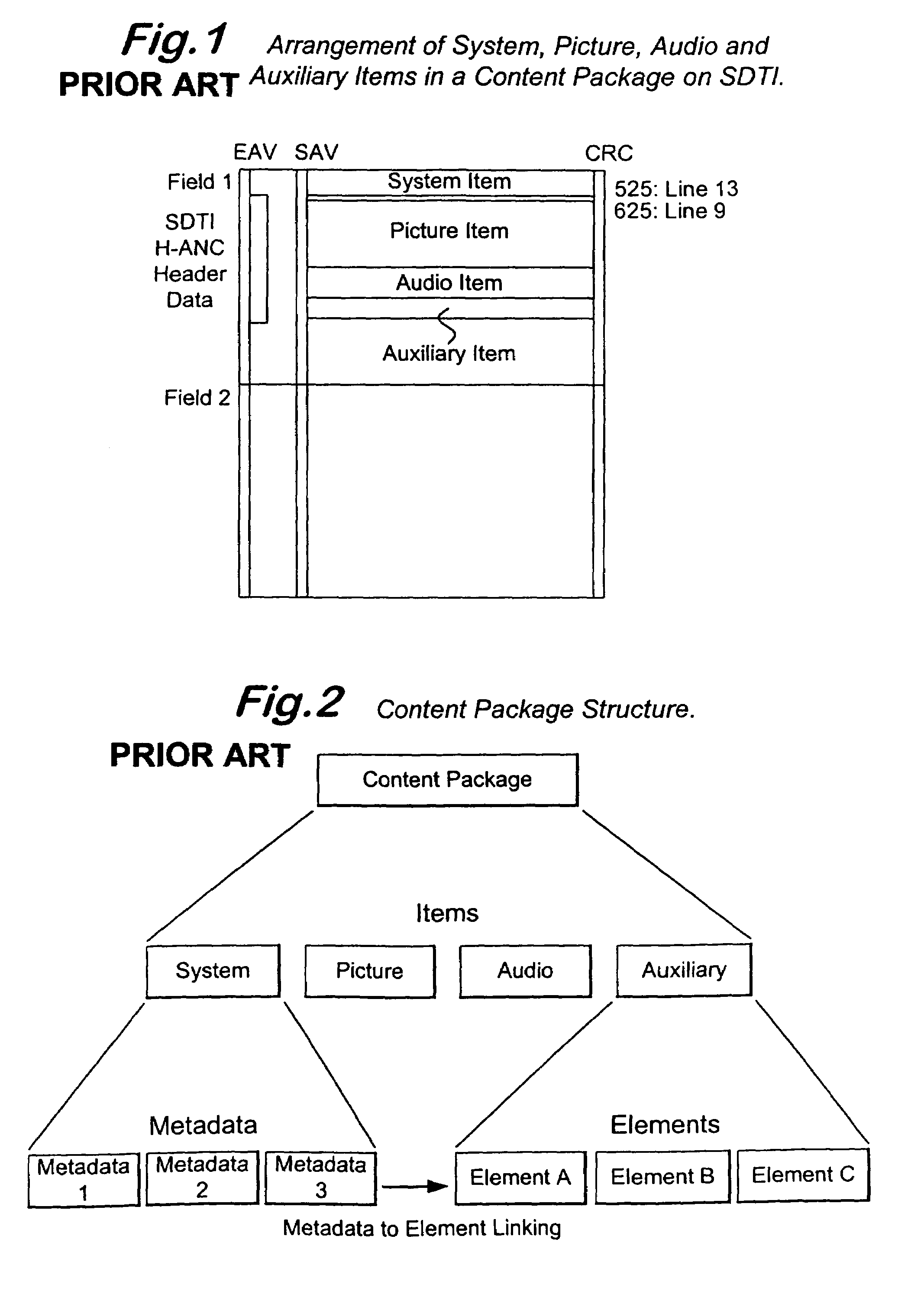
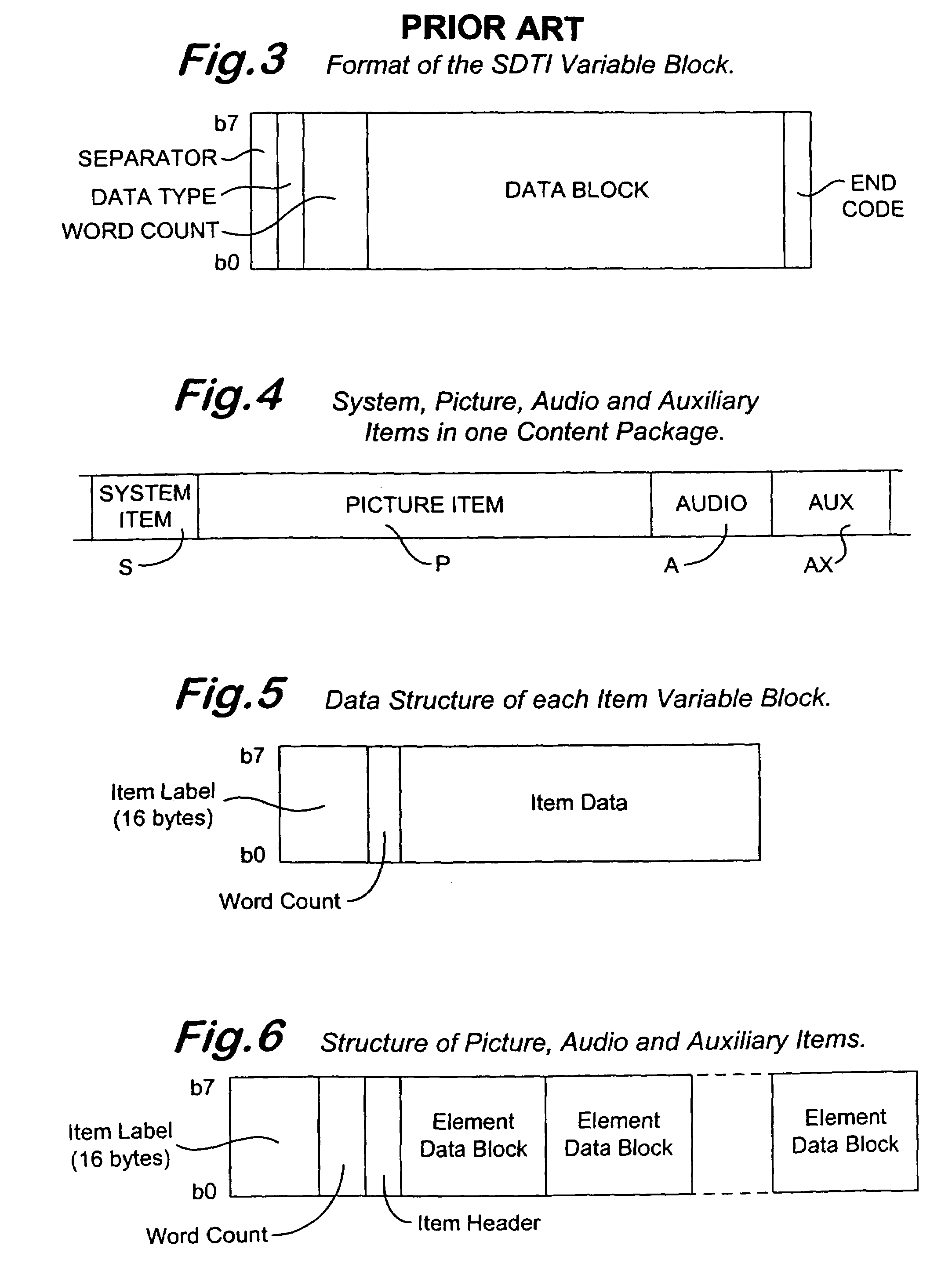
InactiveUS7336681B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionWord countByte
A signal format that can be accessed, as a file, by the computer on which it is stored is provided with a plurality of concatenated content packages. The content package comprises System, Picture, Audio and Auxiliary Items. The System, Picture, Audio and Auxiliary Items have a common format including a 16 byte SMPTE Universal Label, a Word Count, and Data. The Item Label has a predetermined length which is set to fixed value except for the byte identifying the Item to which the label belongs. The data of the System Item includes a set of Metadata blocks, which has an initial Metadata Count byte defining the number of blocks in the set. A metadata block may include a metadata Link which links the metadata of that block to the essence of the element of the Auxiliary Item with which element it is associated.
Owner:SONY UK LTD
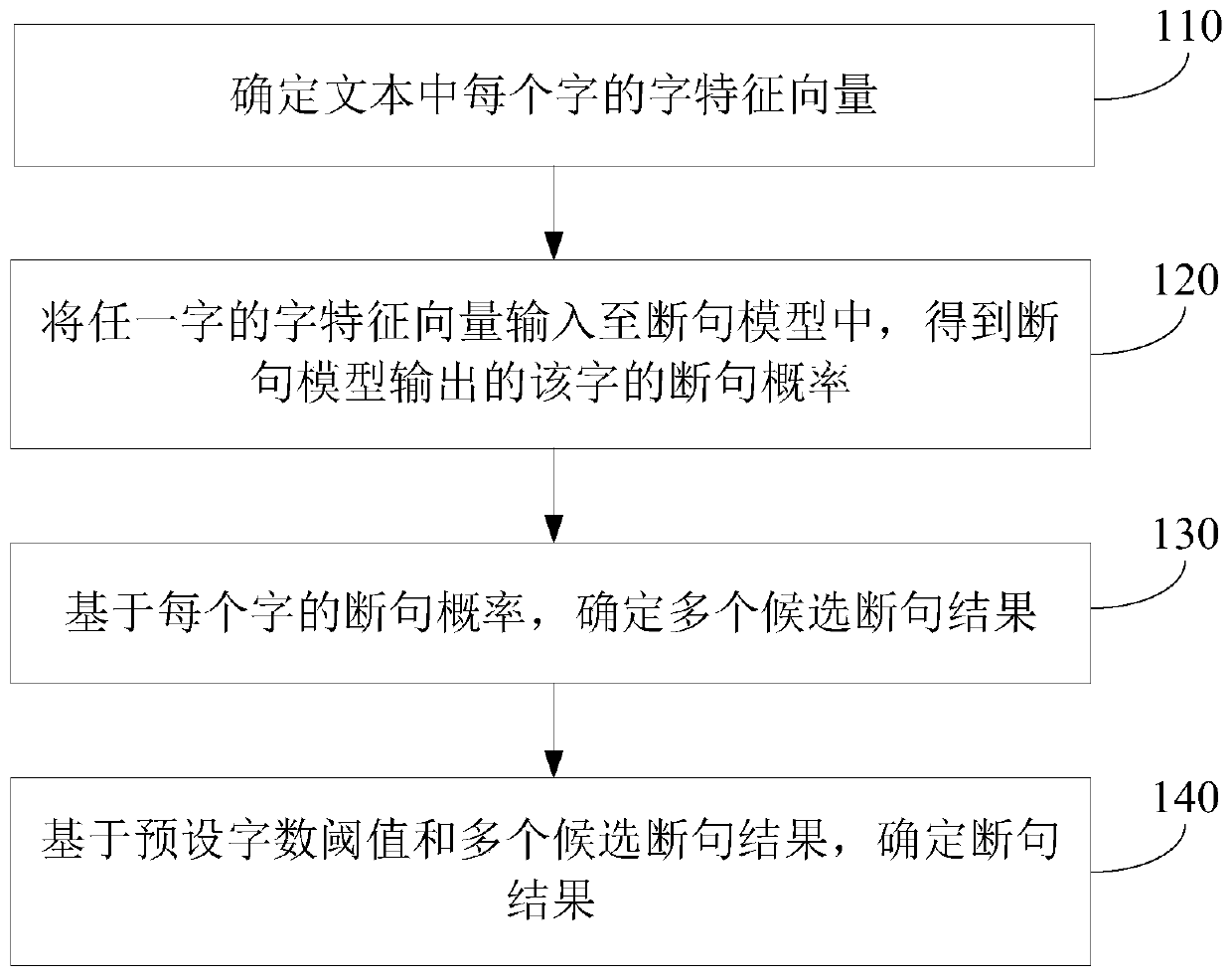
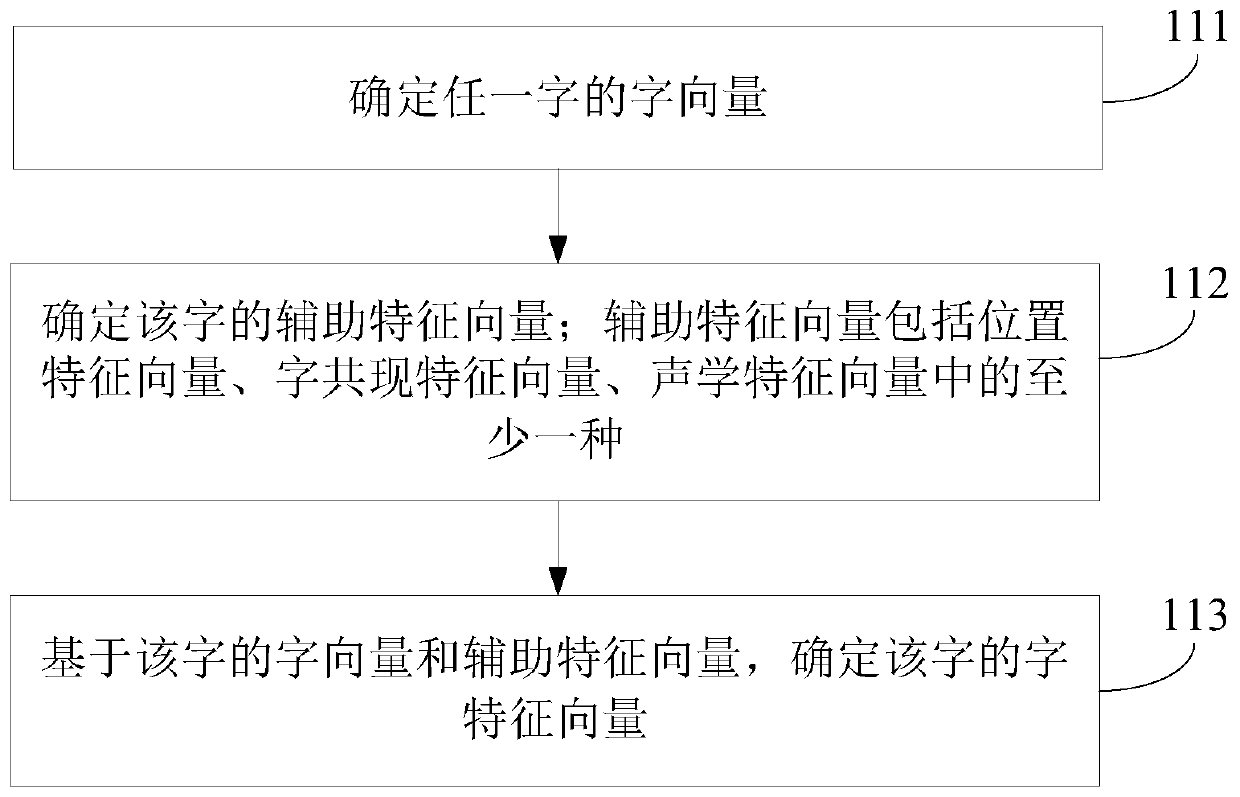
Text sentence segmentation method and device, electronic device and storage medium
ActiveCN110705254AEfficient text segmentationAccurate text segmentationNatural language data processingPattern recognitionSentence segmentation
Embodiments of the invention provide a text sentence segmentation method and device, an electronic device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of determining a character feature vectorof each character in a text; inputting the character feature vector of each character into a sentence segmentation model to obtain a sentence segmentation probability of each character output by thesentence segmentation model; wherein the sentence segmentation model is obtained by training based on a sample word feature vector and a sentence segmentation identifier of a sample word in the sampletext; determining a plurality of candidate sentence segmentation results based on the sentence segmentation probability of each character; and determining a sentence segmentation result based on a preset word number threshold and the plurality of candidate sentence segmentation results. According to the method and device, the electronic device and the storage medium provided by the embodiment ofthe invention, the sentence segmentation result that the length of each clause is smaller than or equal to the preset word number threshold value is obtained while the local semantics are not cut off,so that efficient and accurate text sentence segmentation is realized, and the loss of labor cost and time cost is avoided.
Owner:IFLYTEK CO LTD
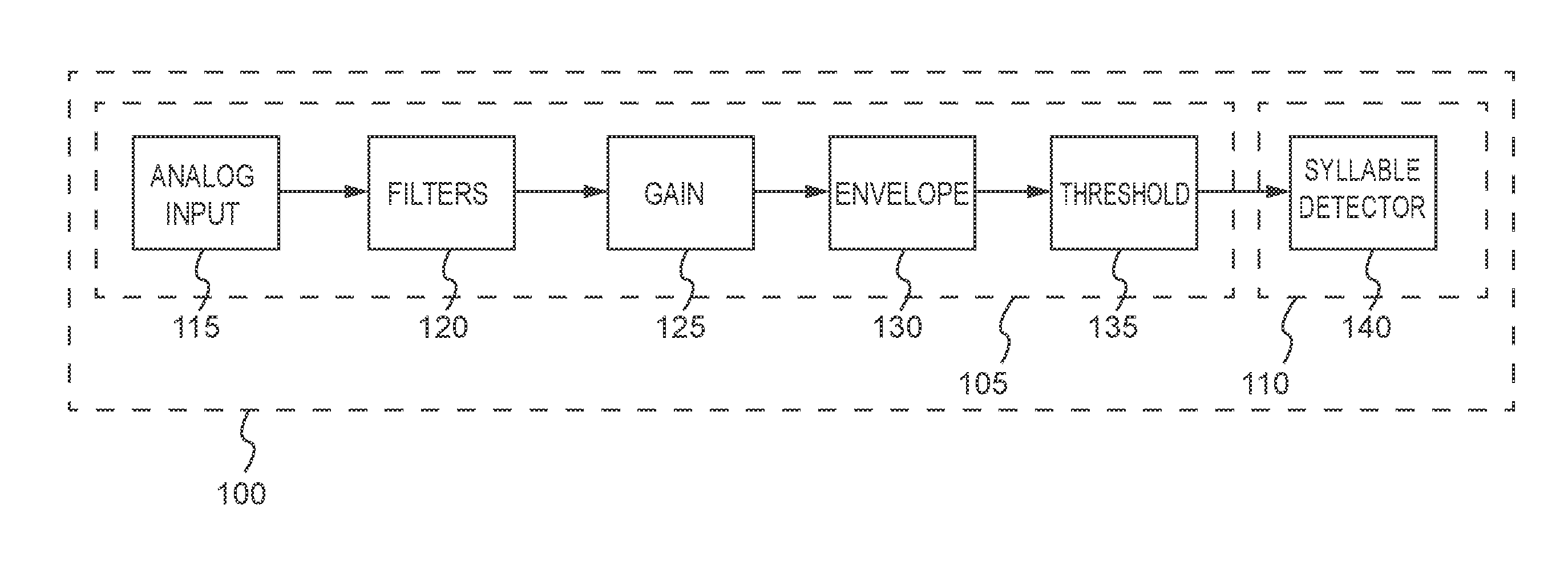
Wearable word counter
This disclosure generally relates to a portable device. Specifically, this disclosure generally relates to a portable word counter device. The portable word counter device includes a digital microcontroller circuit. The digital microcontroller circuit includes a syllable detector detecting syllables in spoken speech. The syllable detector aggregates a number of detected syllables and applies a syllable to word counted ratio. Based on the syllable to word counted ratio, the syllable detector determines a number of words spoken, and transmits the number of words spoken to a mobile device.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
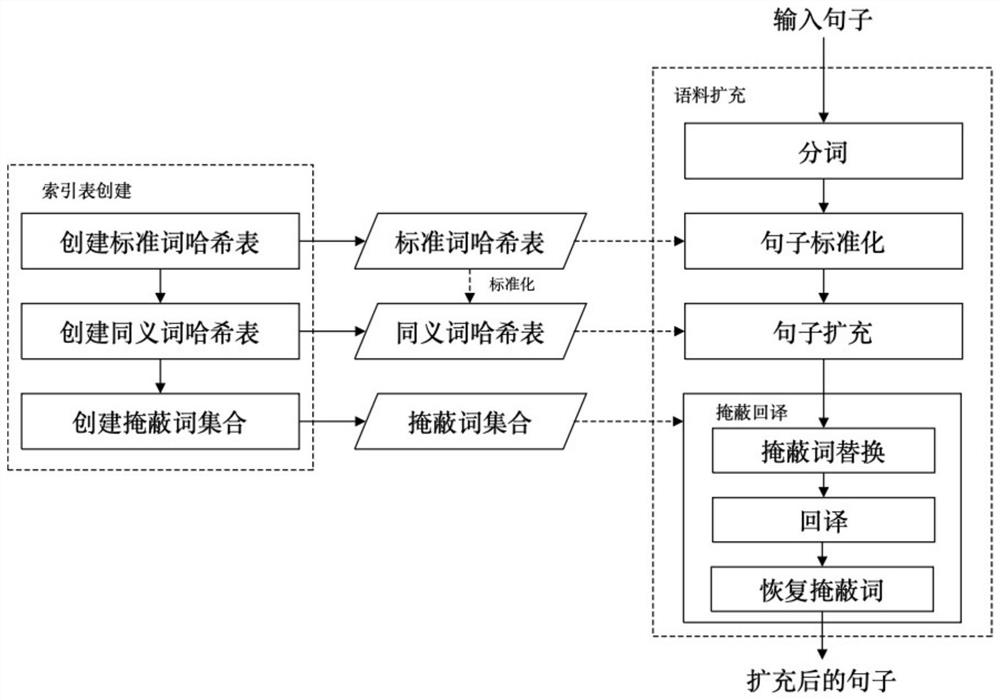
Text corpus expansion method
ActiveCN112446213AImprove the problem of inaccurate translationReduce the impact of back-translation effectsSemantic analysisNeural architecturesWord countText enhancement
The invention belongs to the technical field of natural language processing, and particularly provides a text corpus expansion method which is used for overcoming the defects of an existing text enhancement method in sentence pattern diversity and semantic fidelity of corpus generation. According to the method, a word replacement method and a translation method are combined, and the defects causedby combined use of the two methods are overcome; firstly, synonym hash tables, input sentences and the like are subjected to standardization processing, and meanwhile, a strategy of performing one-way replacement in the direction that the number of words is not reduced is adopted in word replacement, so that the influence of words with wrongly written characters and spoken words on the back-translation effect is reduced; in addition, by introducing masking translation, the problem of inaccurate translation of the professional noun by a translation method is improved; the corpus generated by the method gives consideration to sentence pattern diversity and semantic fidelity, and is particularly suitable for text corpus expansion application under the condition that the initial corpus is insufficient.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
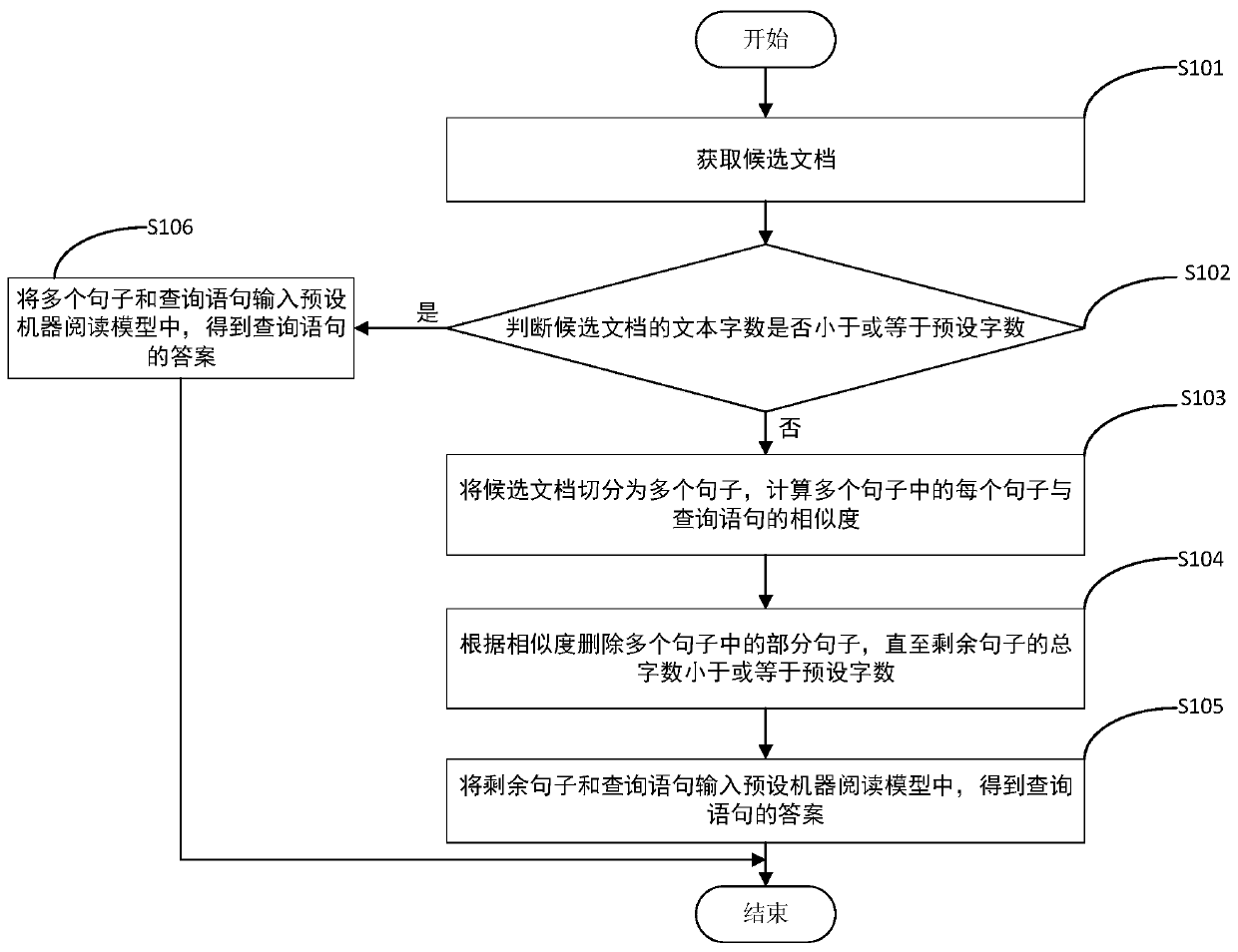
Document retrieval method and device and computer readable storage medium
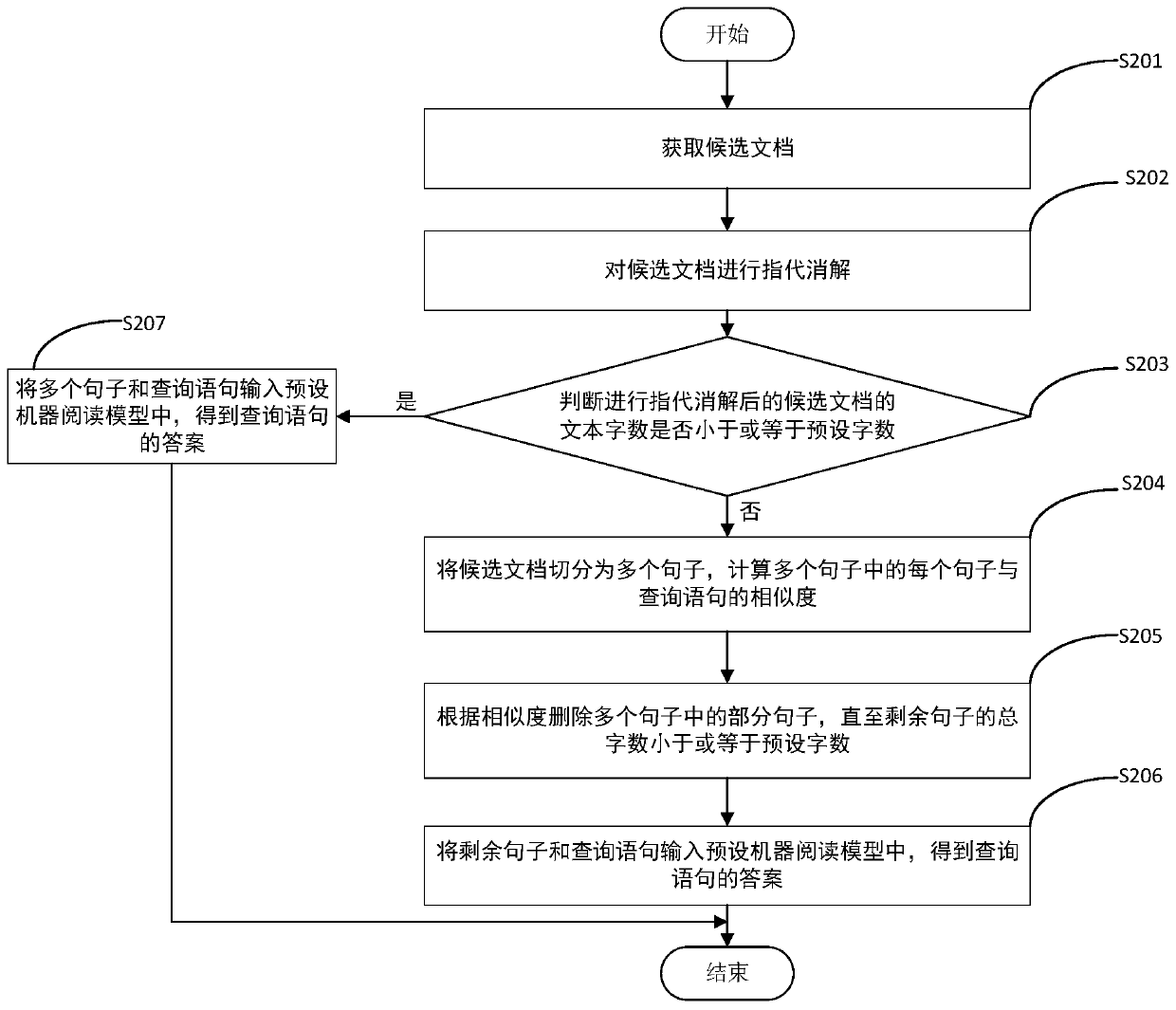
ActiveCN111159359AImprove accuracyReduce the difficulty of readingCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingUser inputWord count
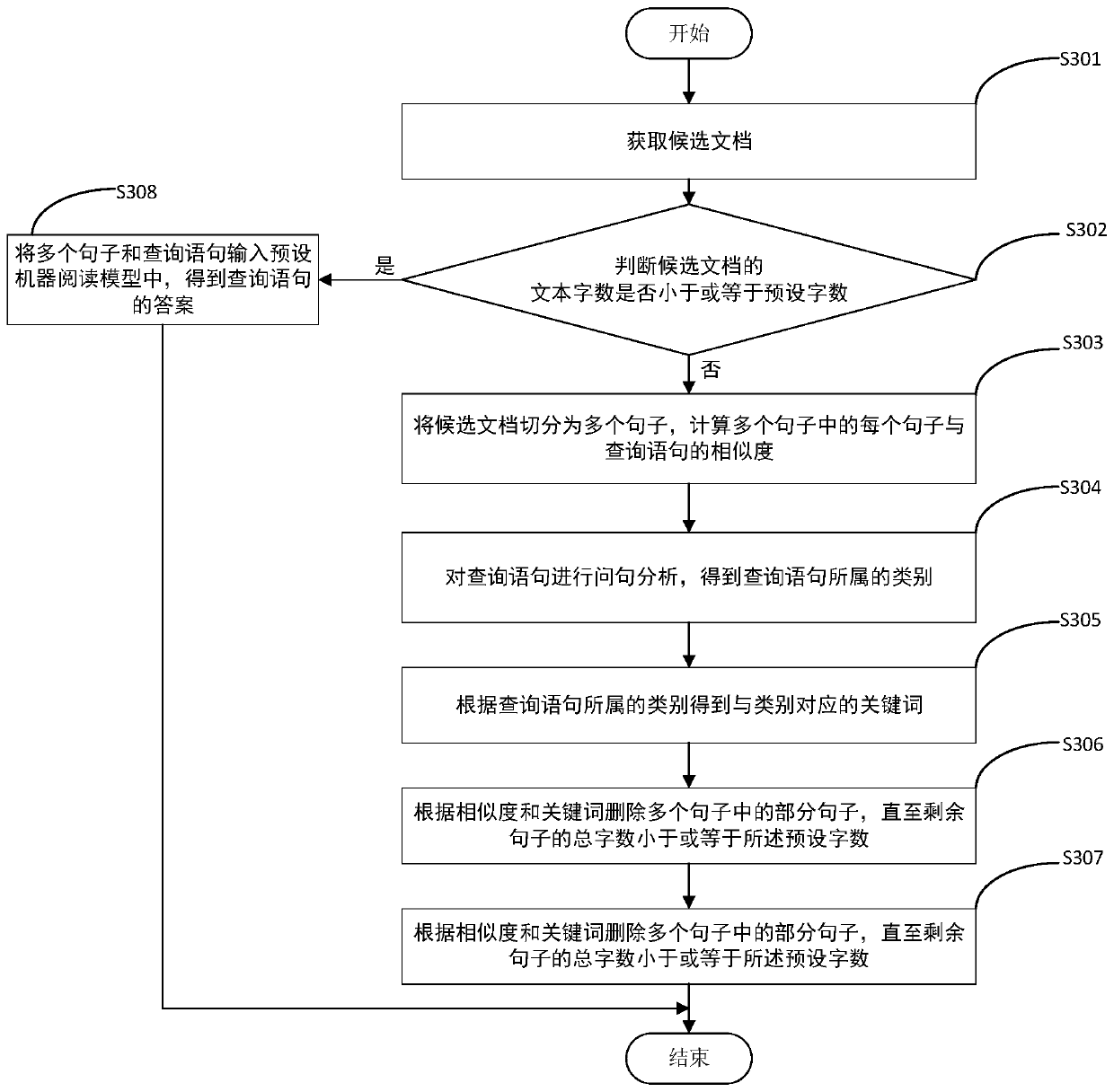
The embodiment of the invention relates to the field of natural language processing, and discloses a document retrieval method and device and a computer readable storage medium. The document retrievalmethod comprises the steps of acquiring candidate documents, wherein the candidate documents are determined by query statements input by a user, judging whether the text word number of the candidatedocument is smaller than or equal to a preset word number or not, if not, segmenting the candidate document into a plurality of sentences, calculating the similarity between each sentence in the plurality of sentences and the query sentence, deleting a part of sentences in the plurality of sentences according to the similarity until the total word number of the remaining sentences is smaller thanor equal to the preset word number, and inputting the remaining sentences and the query statement into a preset machine reading model to obtain an answer of the query statement. According to the document retrieval method and device and the computer readable storage medium provided by the invention, the reading difficulty of the machine reading model can be reduced, and meanwhile, the document retrieval accuracy is improved.
Owner:CLOUDMINDS SHANGHAI ROBOTICS CO LTD
Method of providing input method and electronic device using the same
ActiveUS20150187358A1Natural language data processingSpeech recognitionProgramming languageWord count
A method of providing an input method for an electronic device includes receiving a command for switching a display image of the electronic device; determining whether at least two words correspond to at least two languages when at least the two words are in the display determining a word count of a first language and a word count of a second language when the two words correspond to the two languages; and enabling a first input method corresponding to the first language when the word count of the first language is greater than the word count of the second language, or enabling a second input method corresponding to the second language when the word count of the second language is greater than the word count of the first language.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
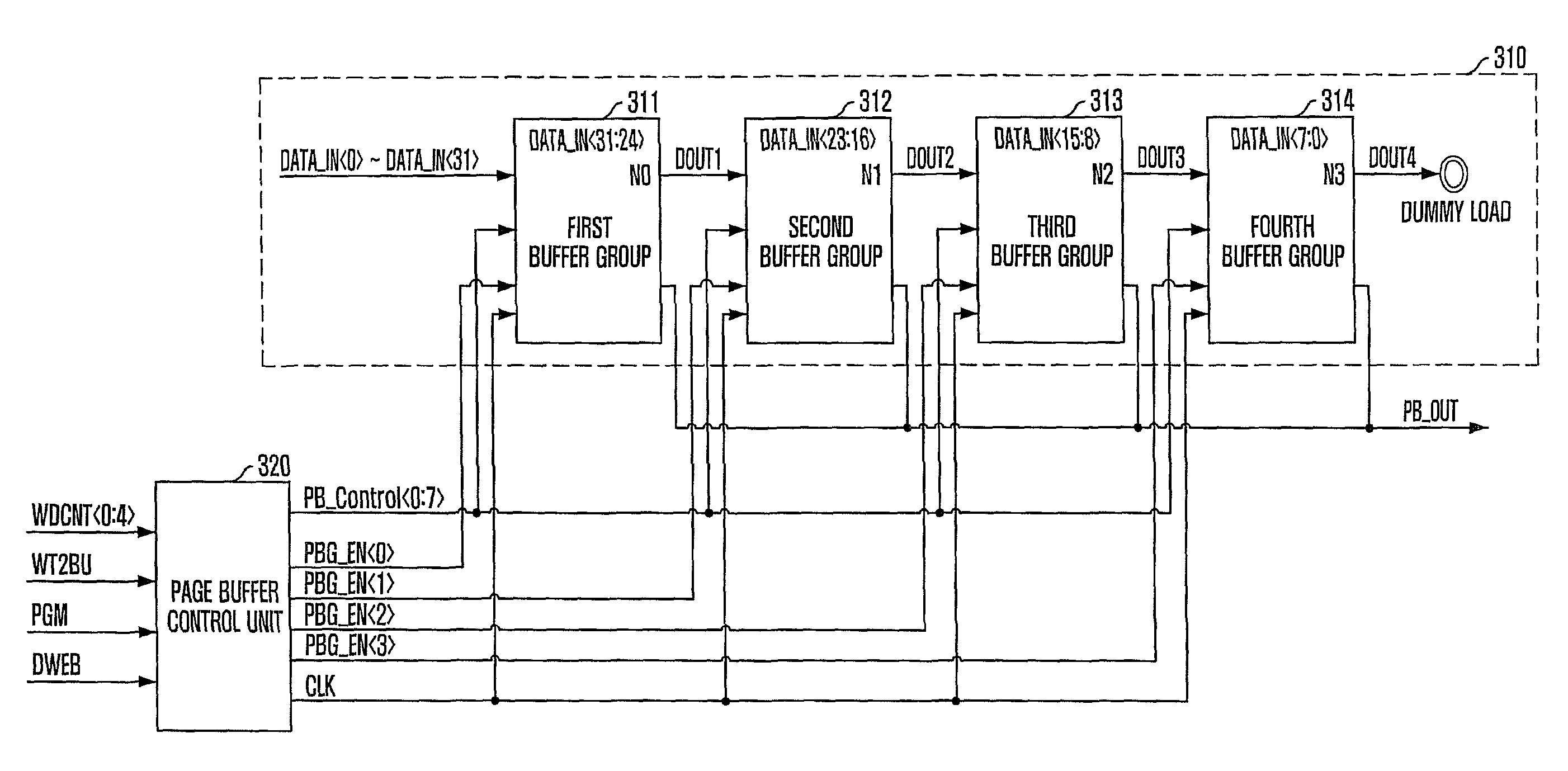
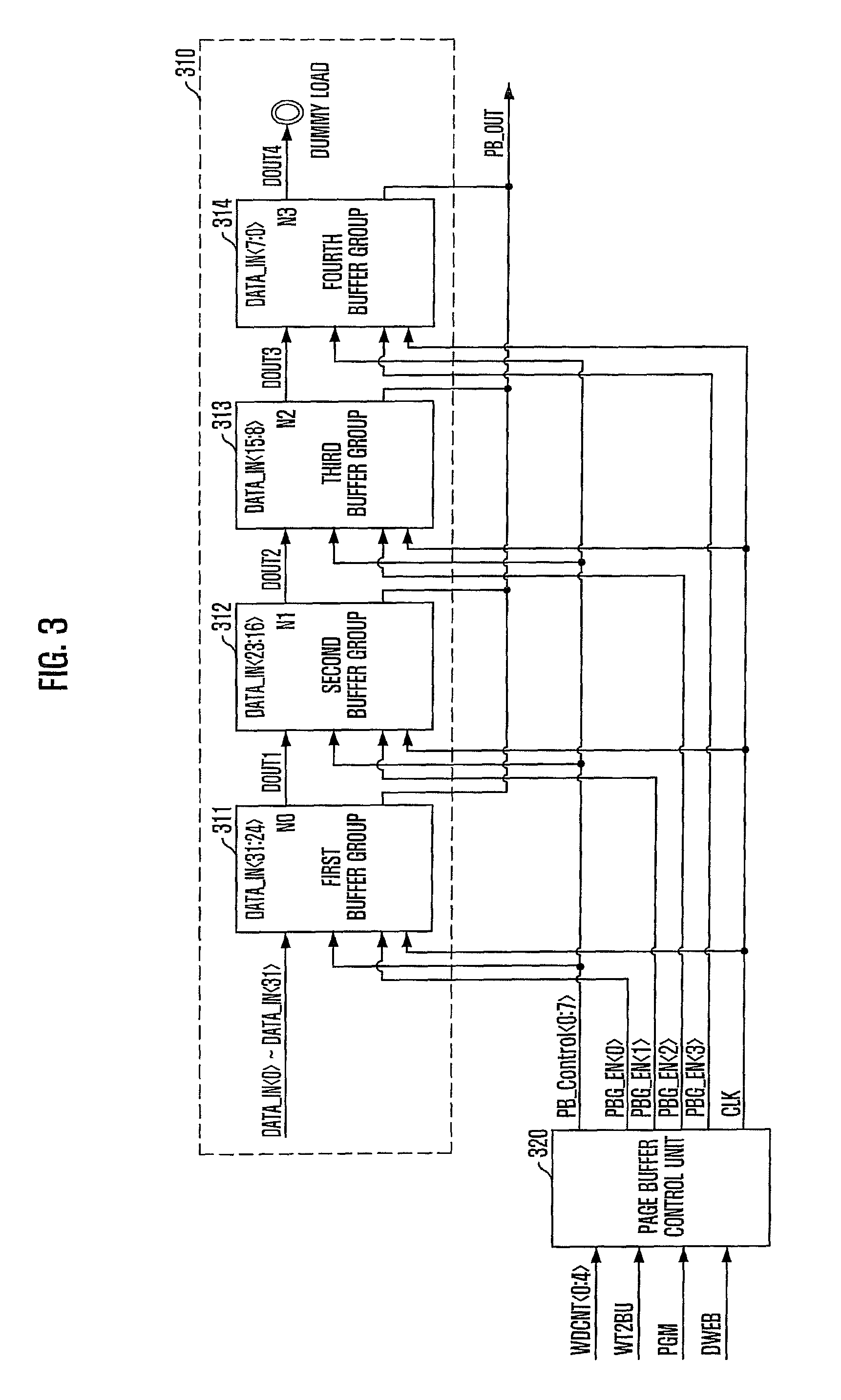
Phase-change memory device
A phase-change memory device performs a buffer program operation in response to a buffer program command sequence. The phase-change memory device includes a page buffer unit configured to store a plurality of input data corresponding to a word count value of a buffer program command sequence and selectively output the stored input data in response to a selection signal, and a page buffer control unit configured to generate the selection signal determined by counting a value representing the word count value.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com