Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89 results about "Vascular access port" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
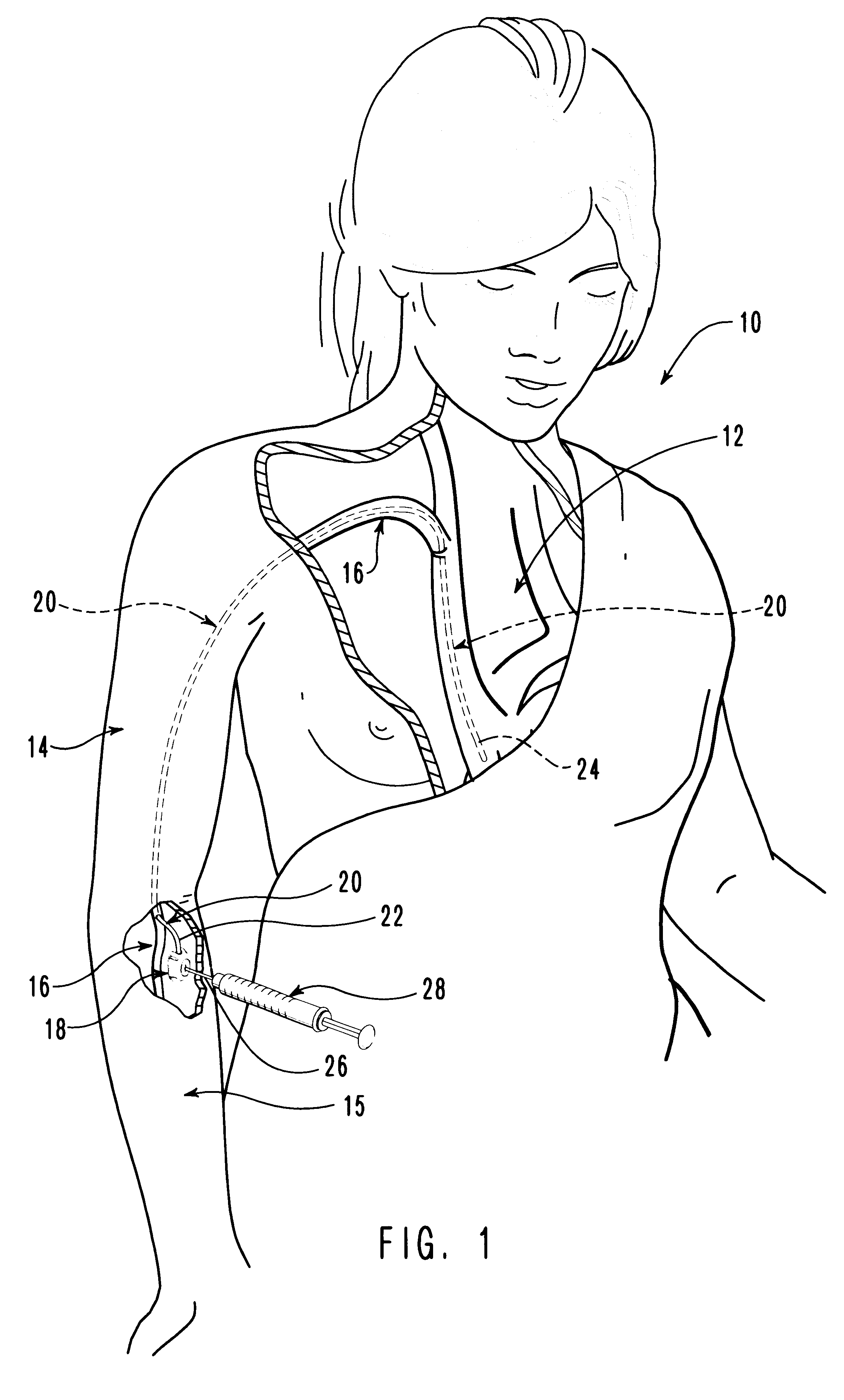
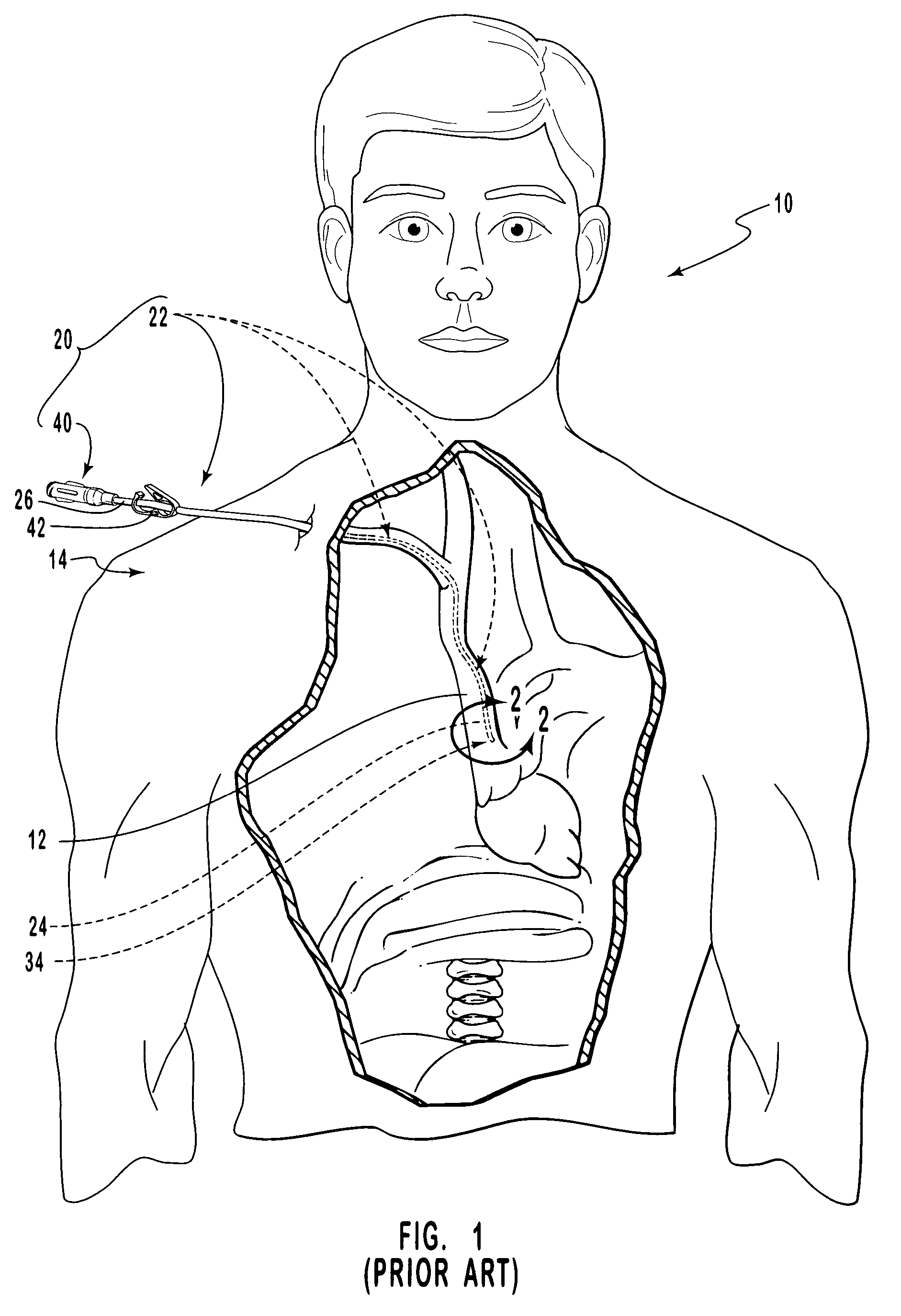
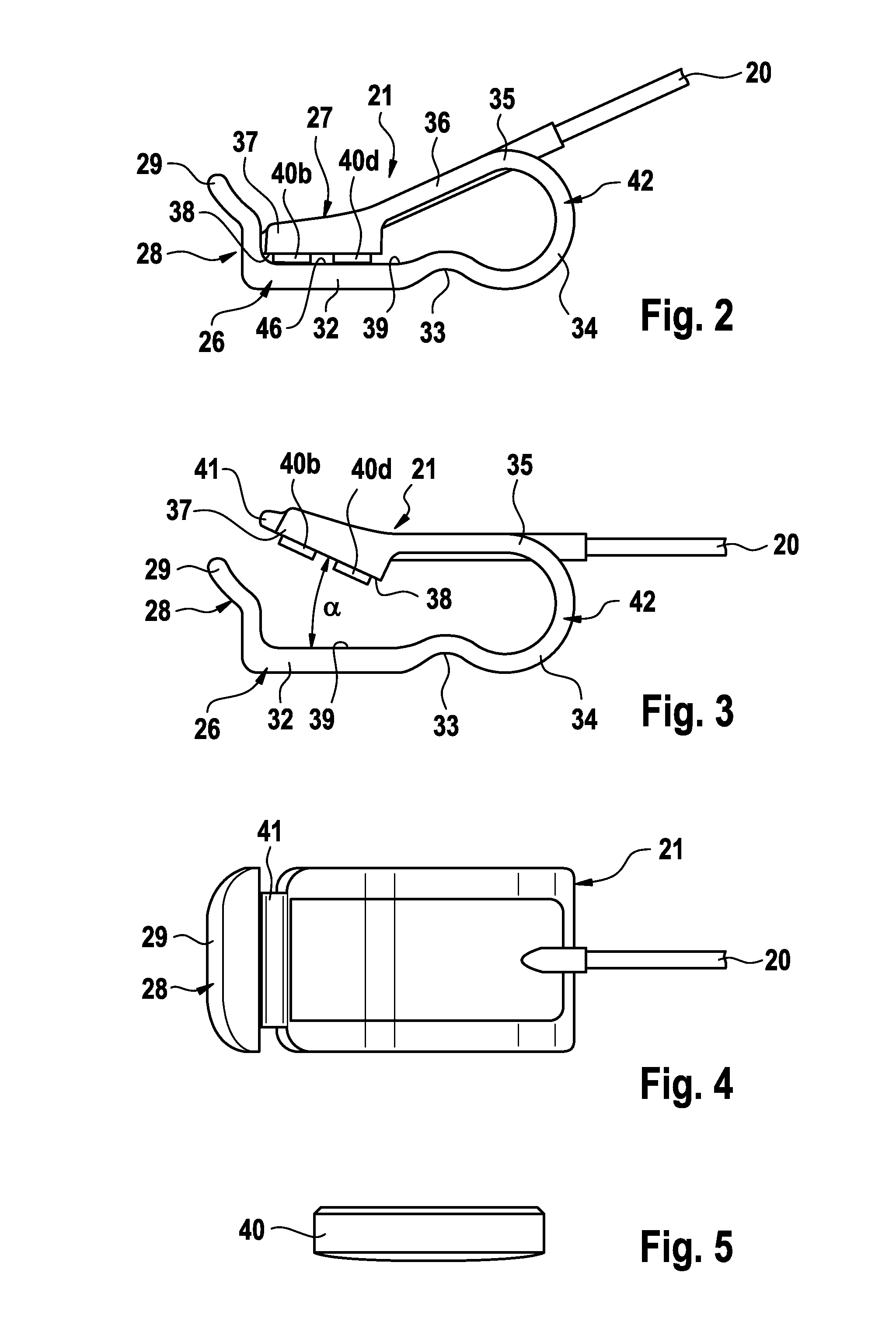
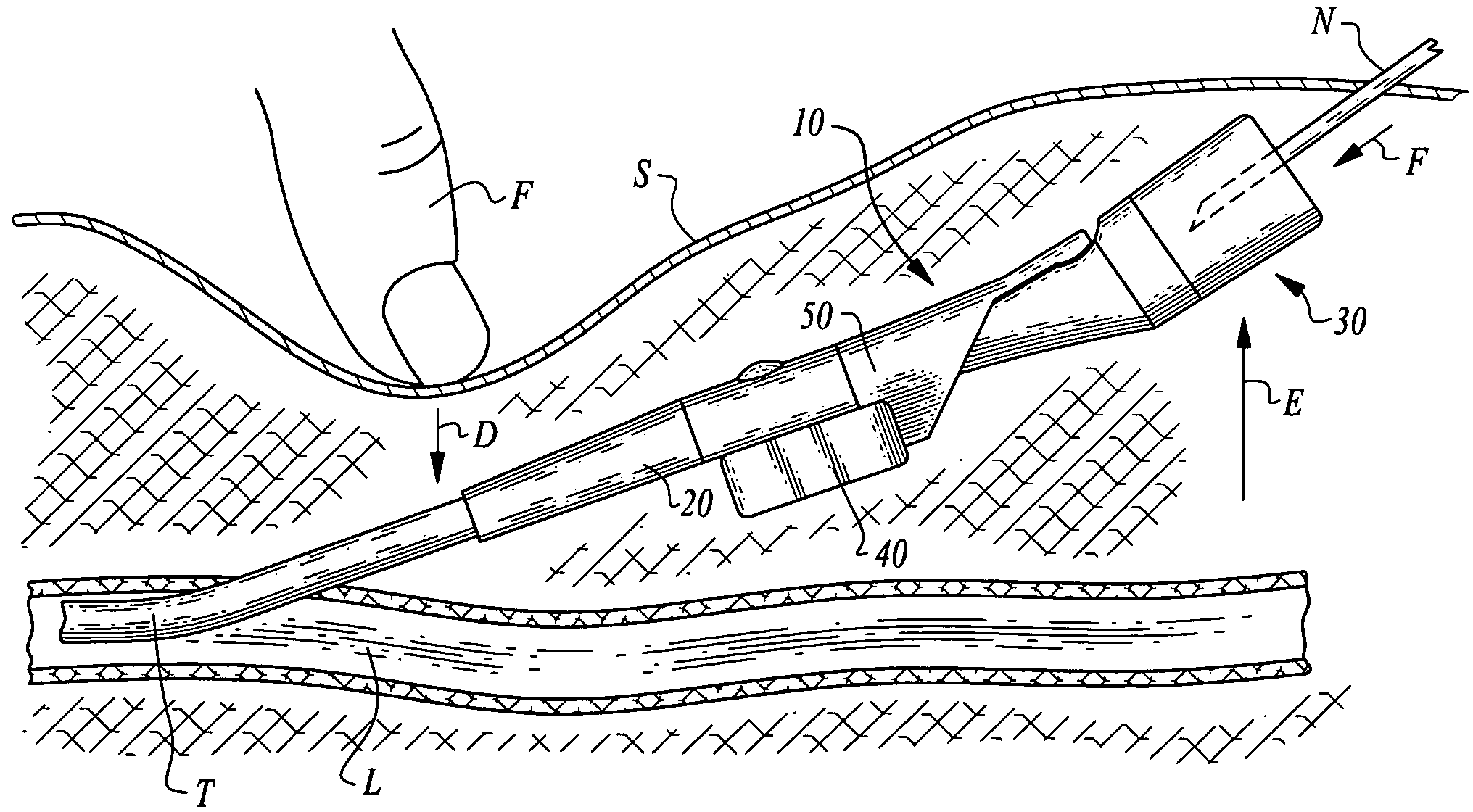
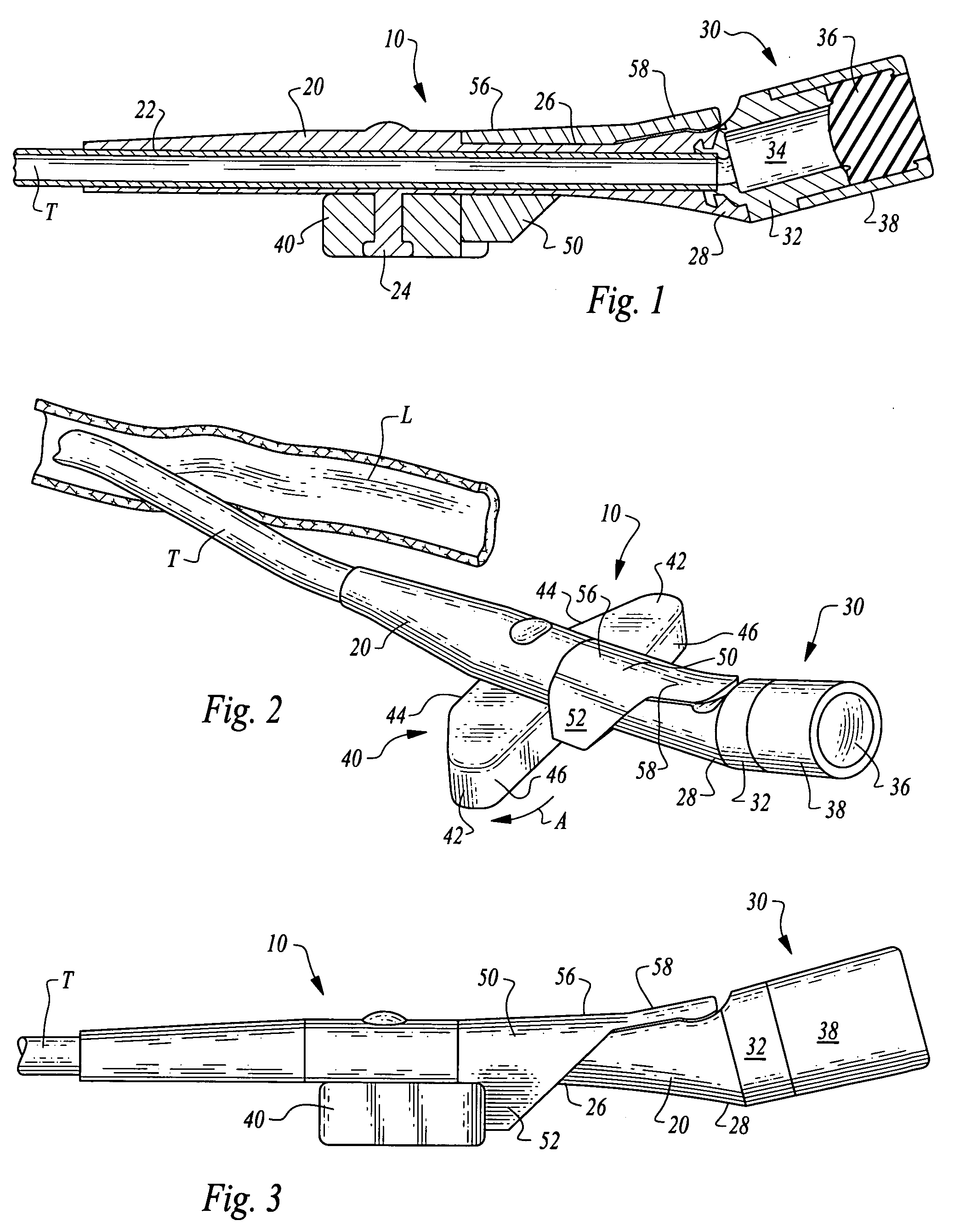
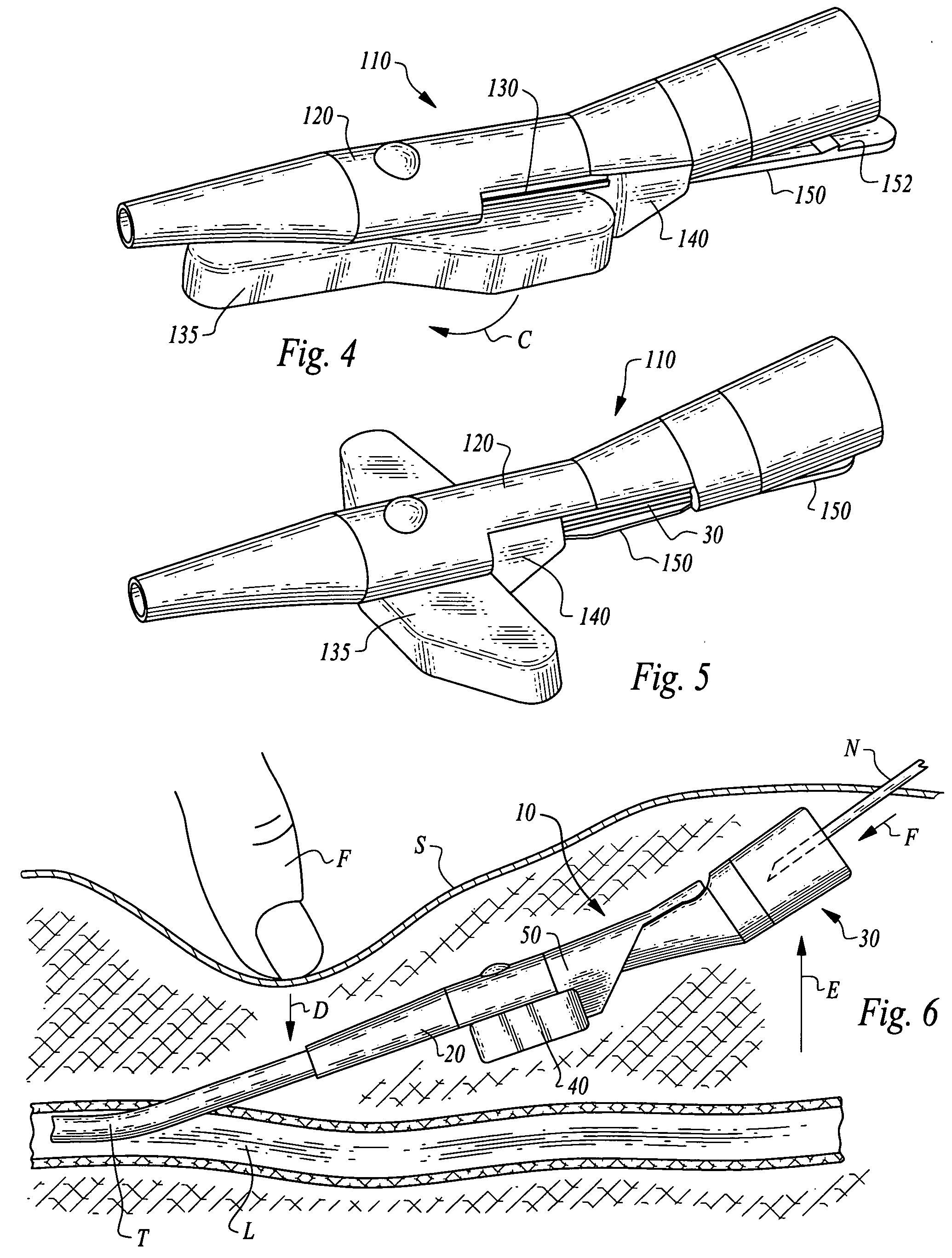
Vascular access ports (VAPs) are medical implant devices occasionally recommended for patients that are undergoing long-term medical treatment or that require frequent blood tests for monitoring of chronic conditions. Routinely used in human medicine, a VAP is implanted under the skin during a brief,...
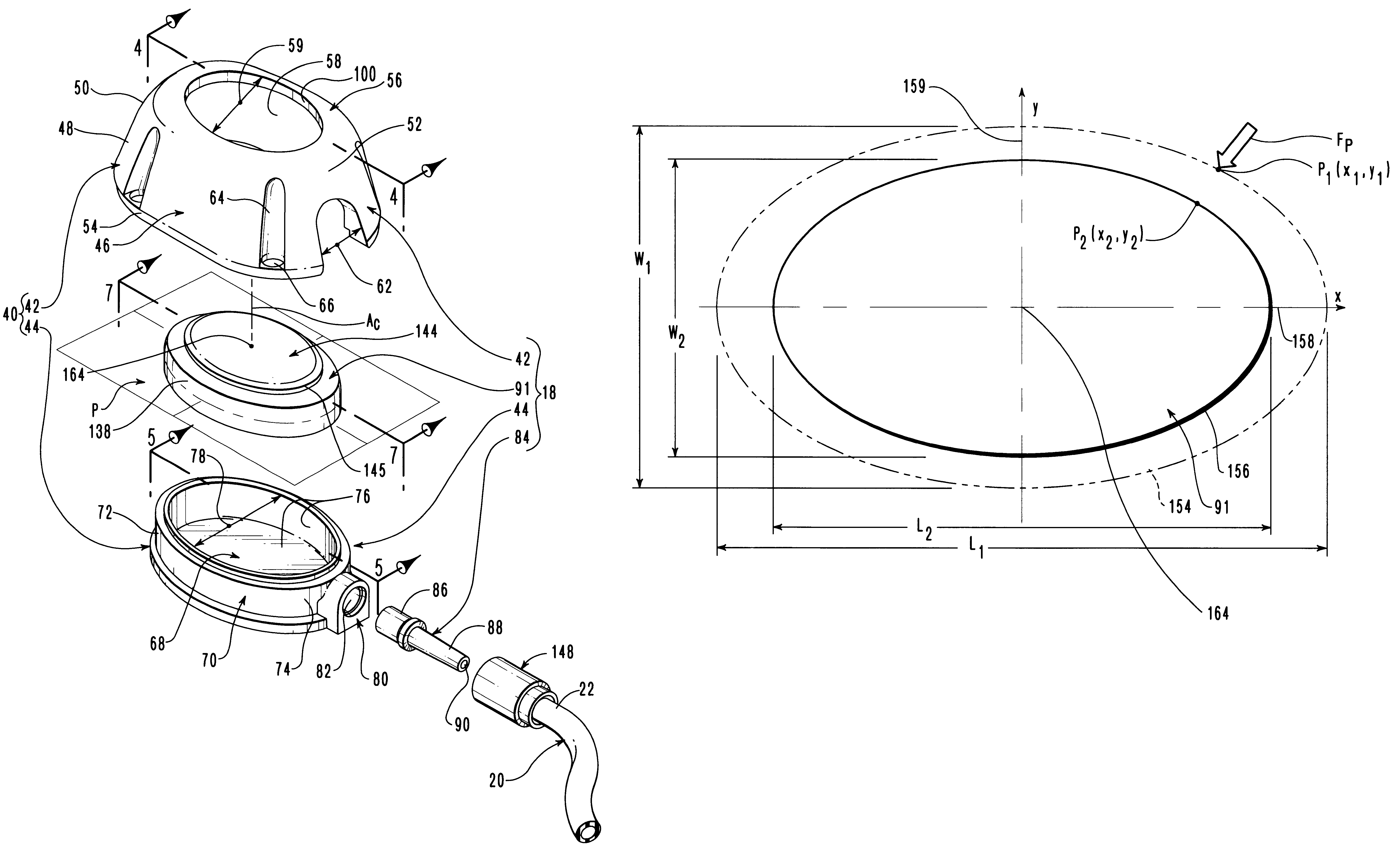
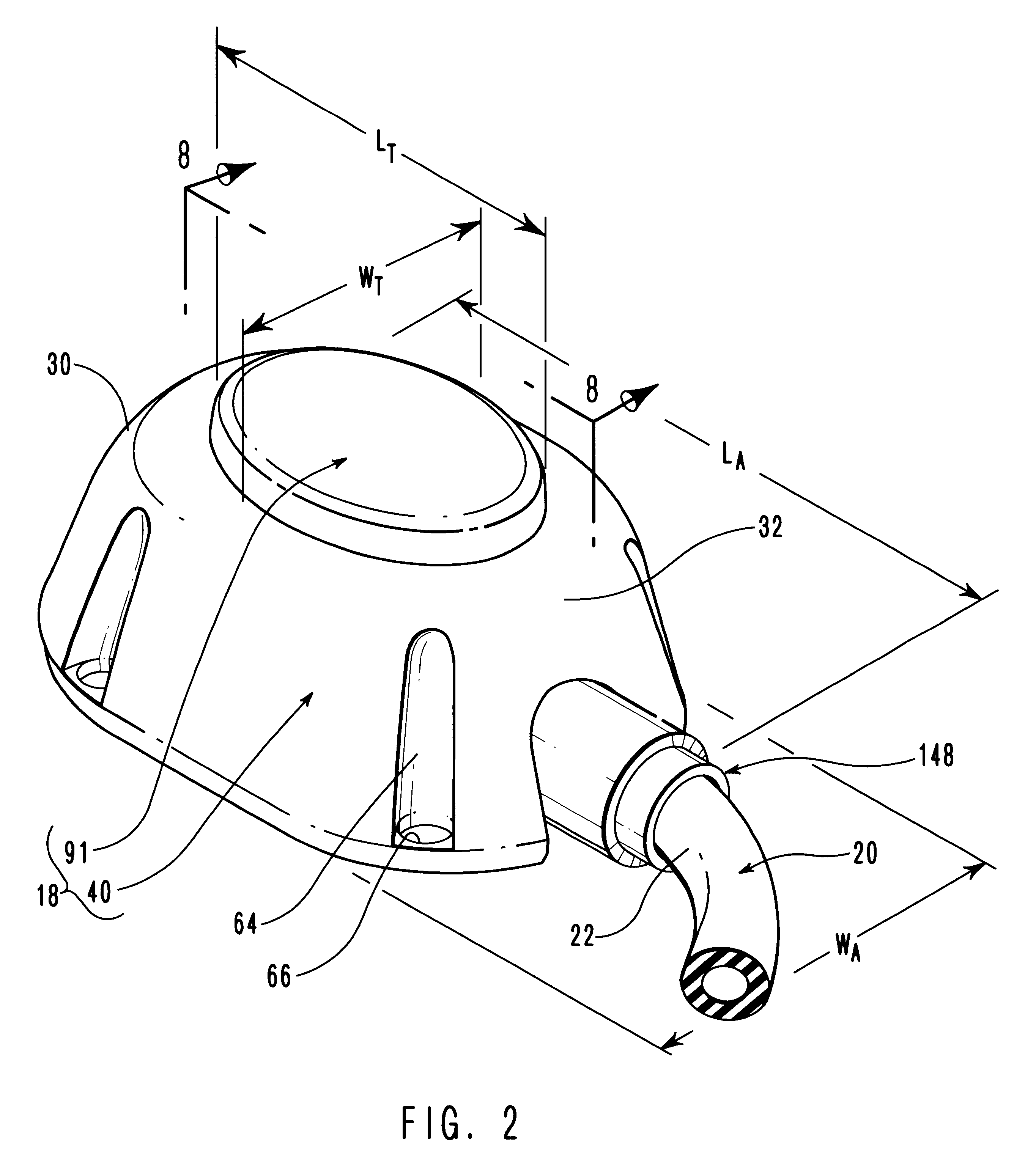
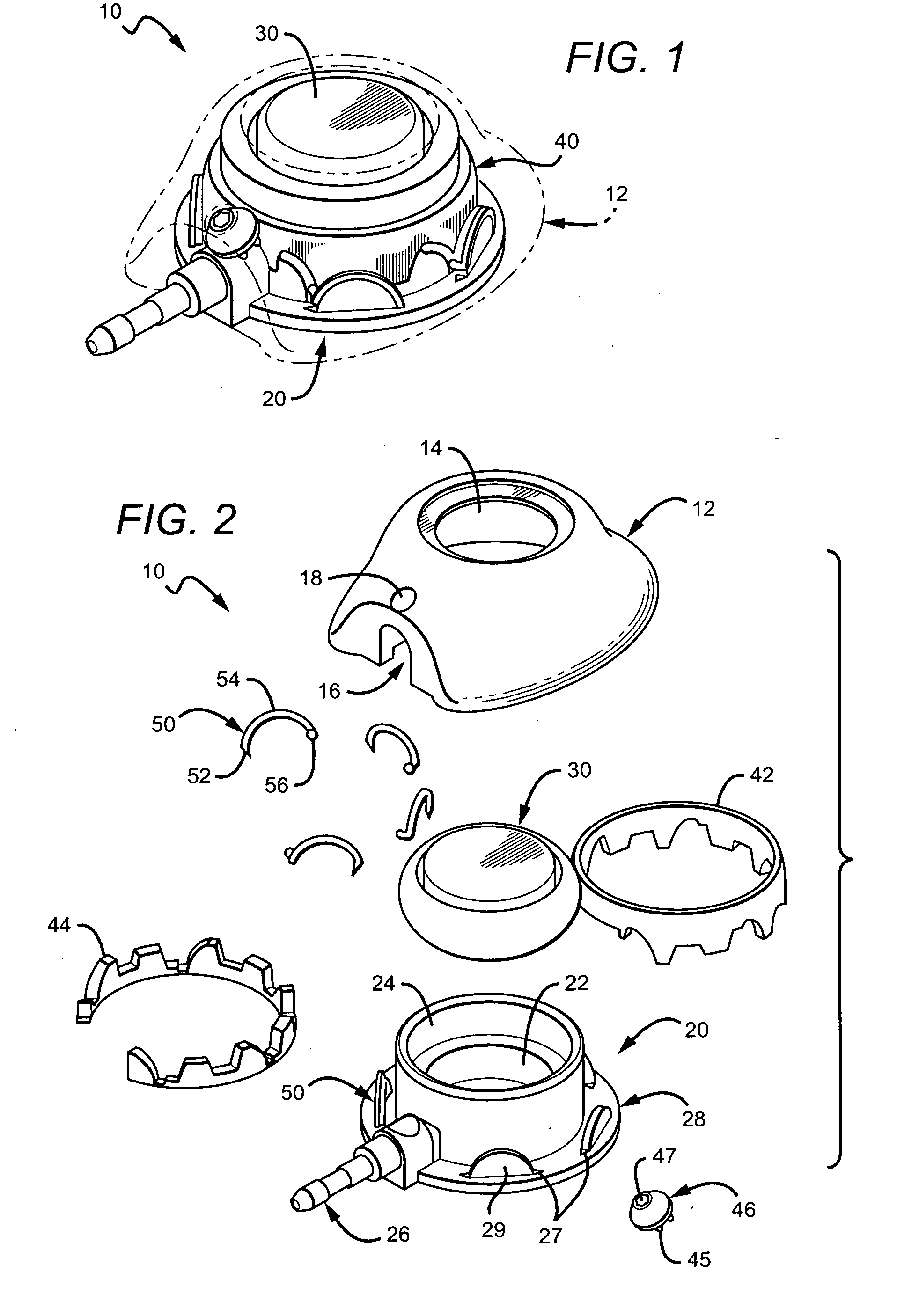
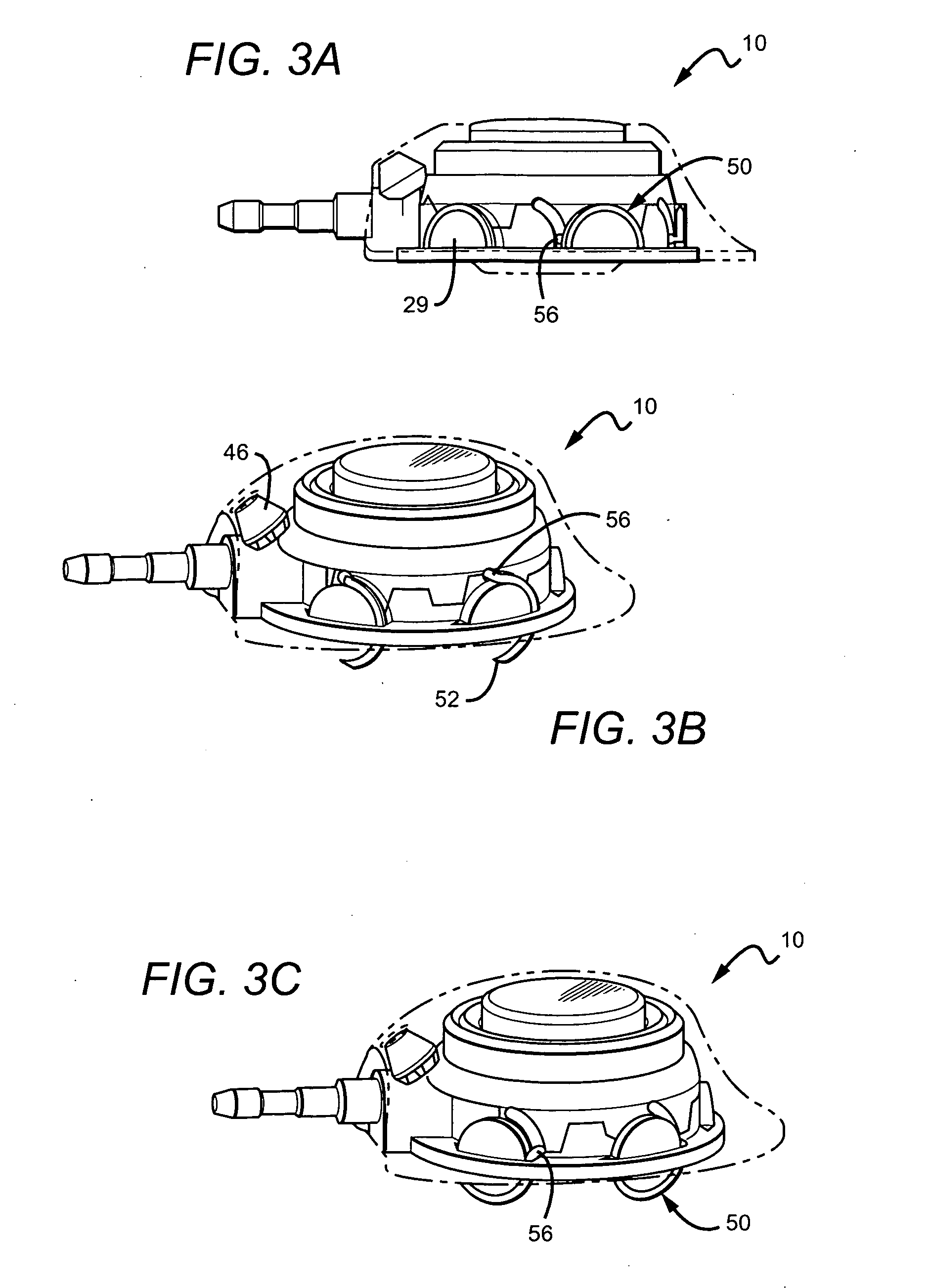
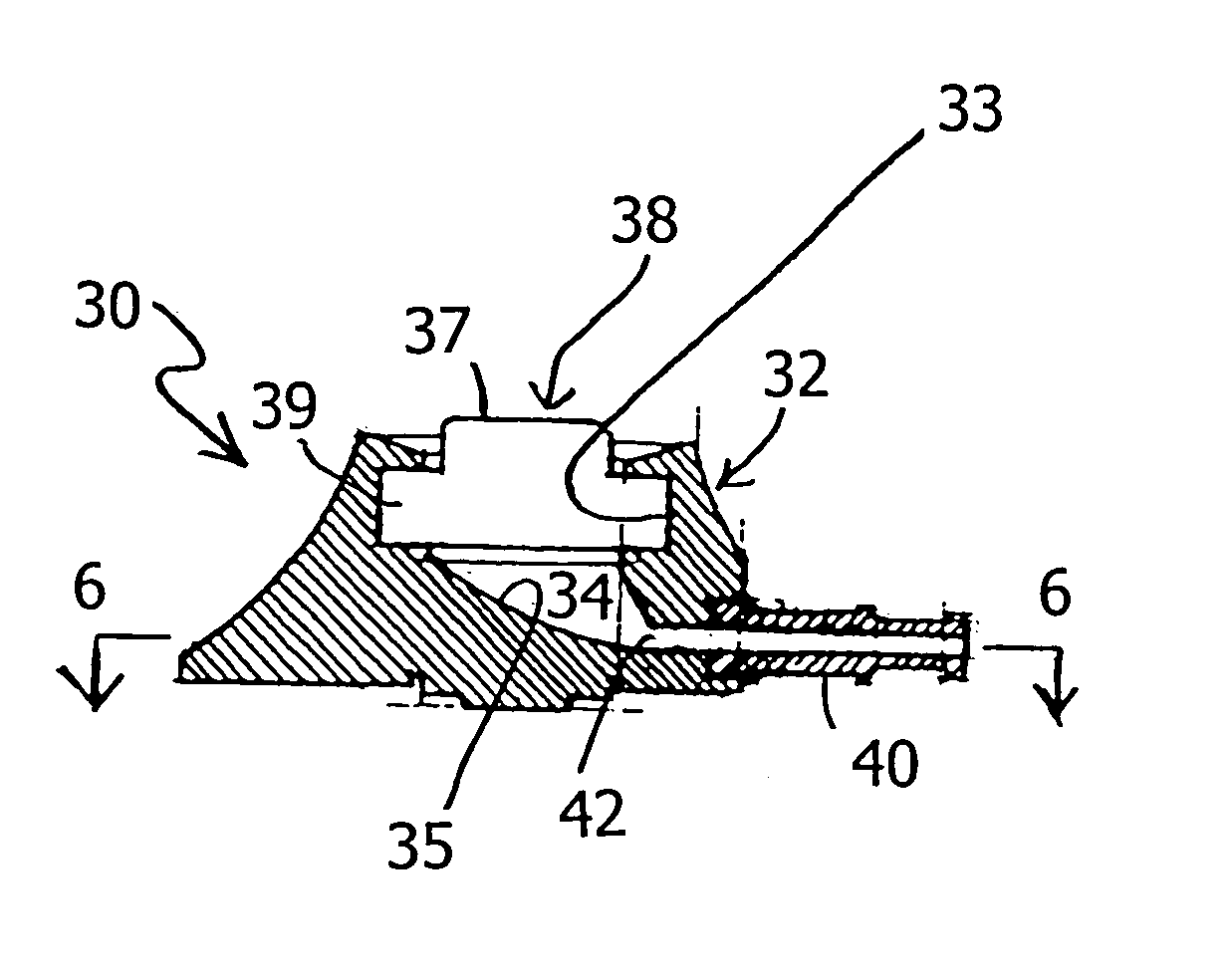
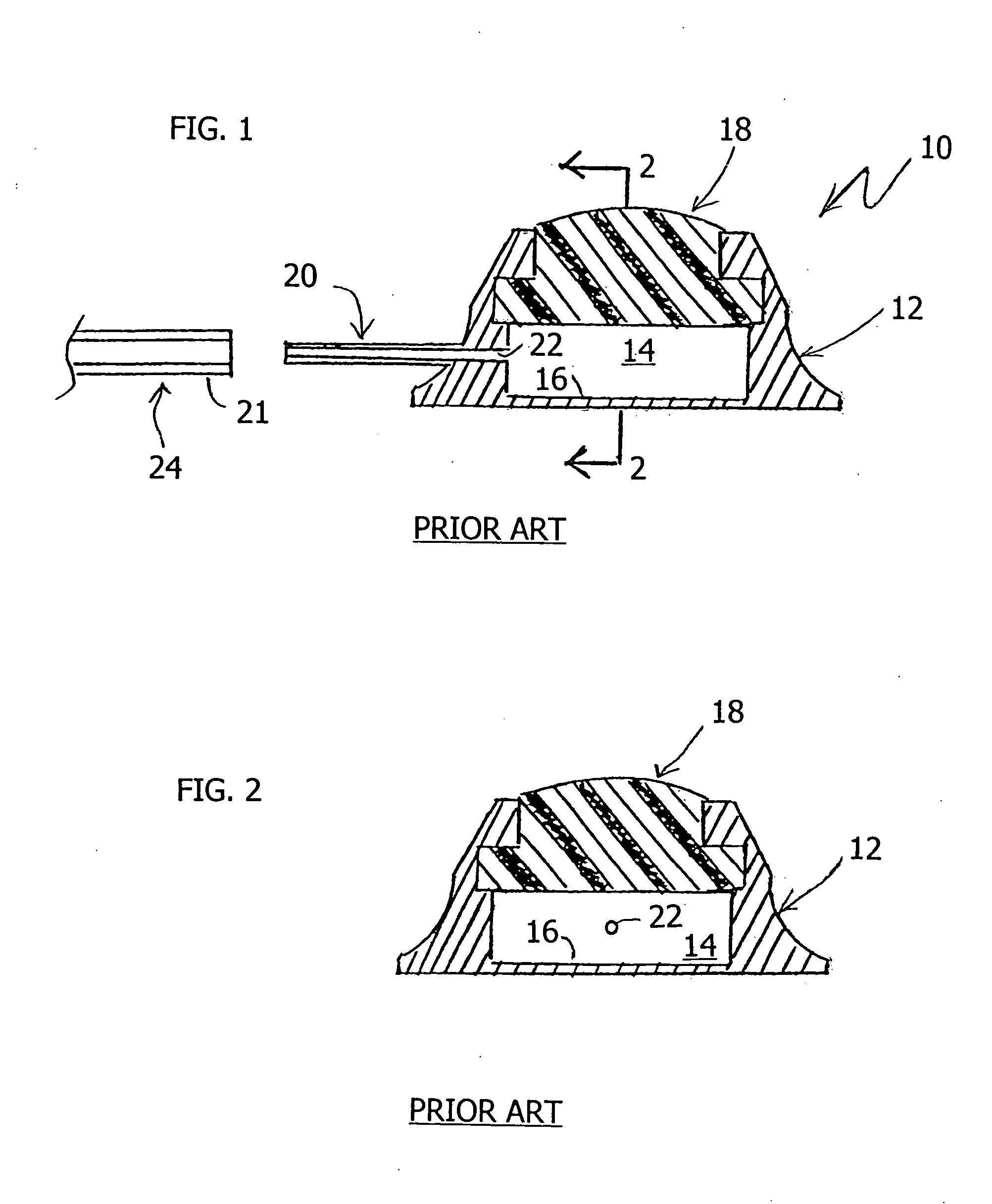
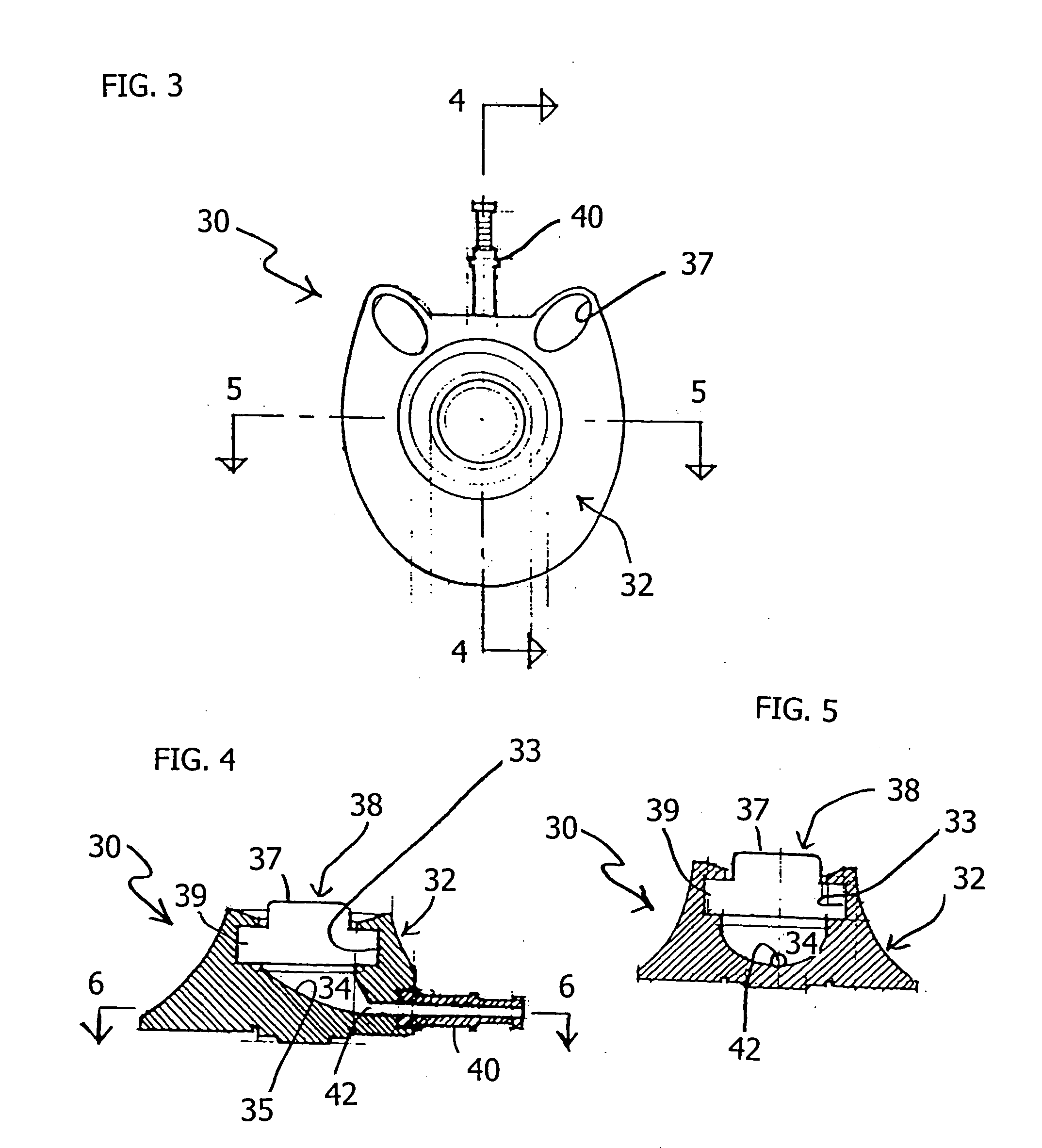
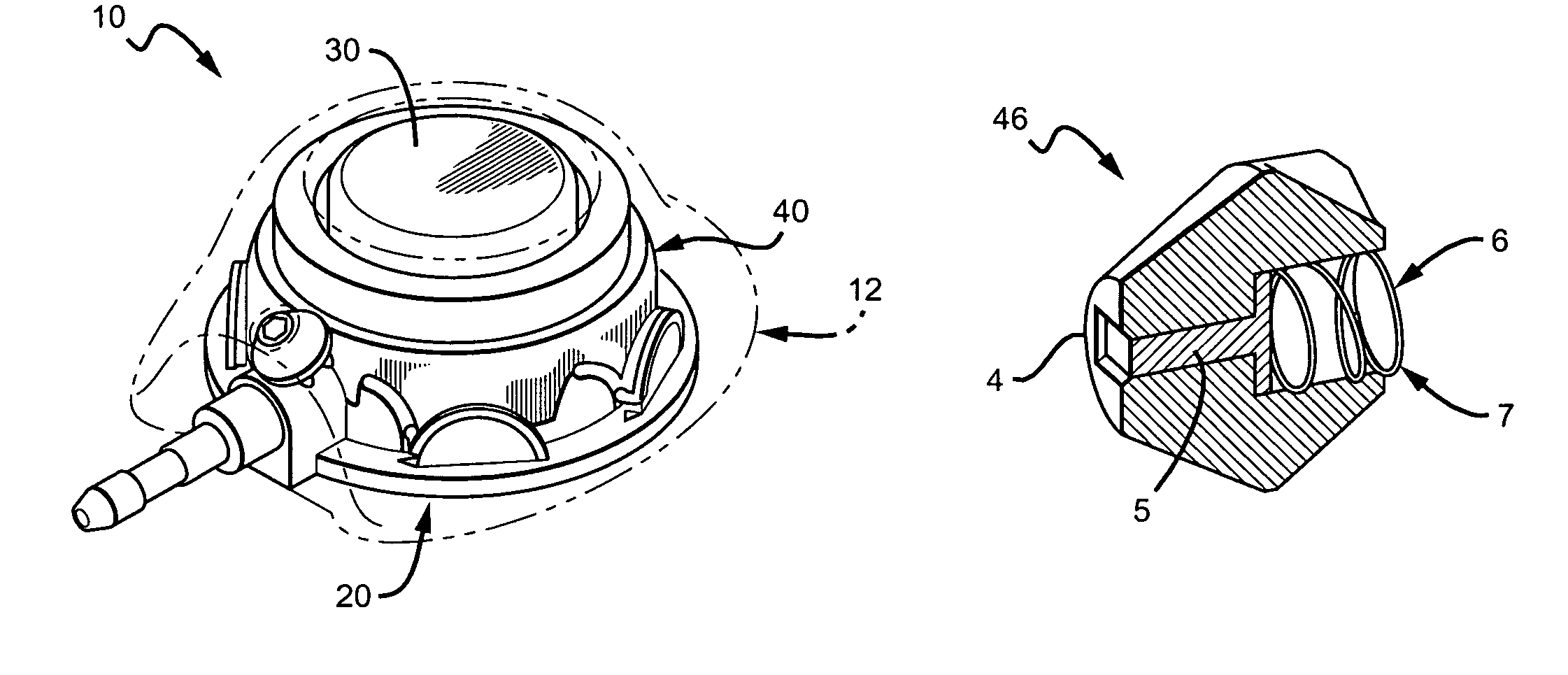
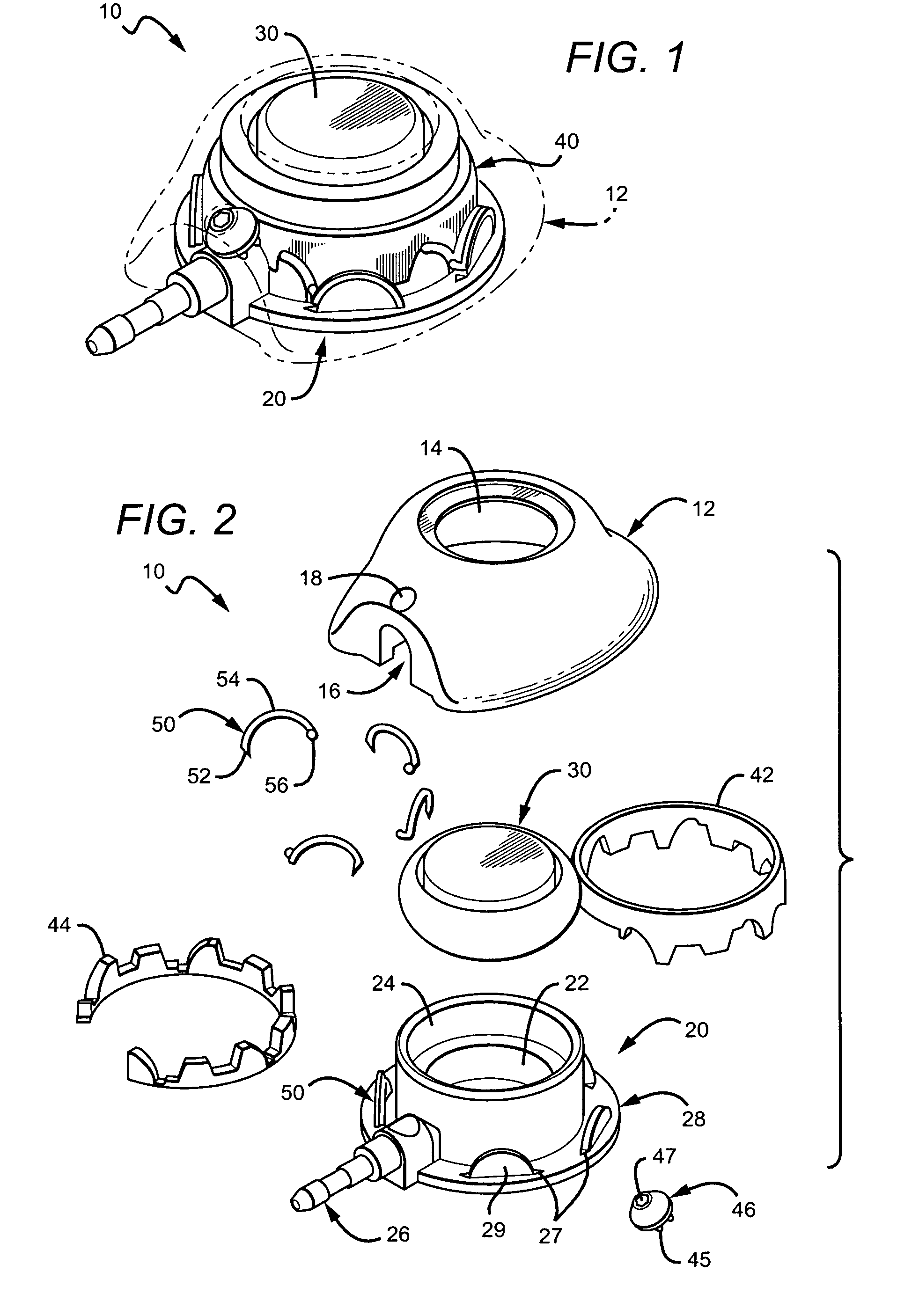
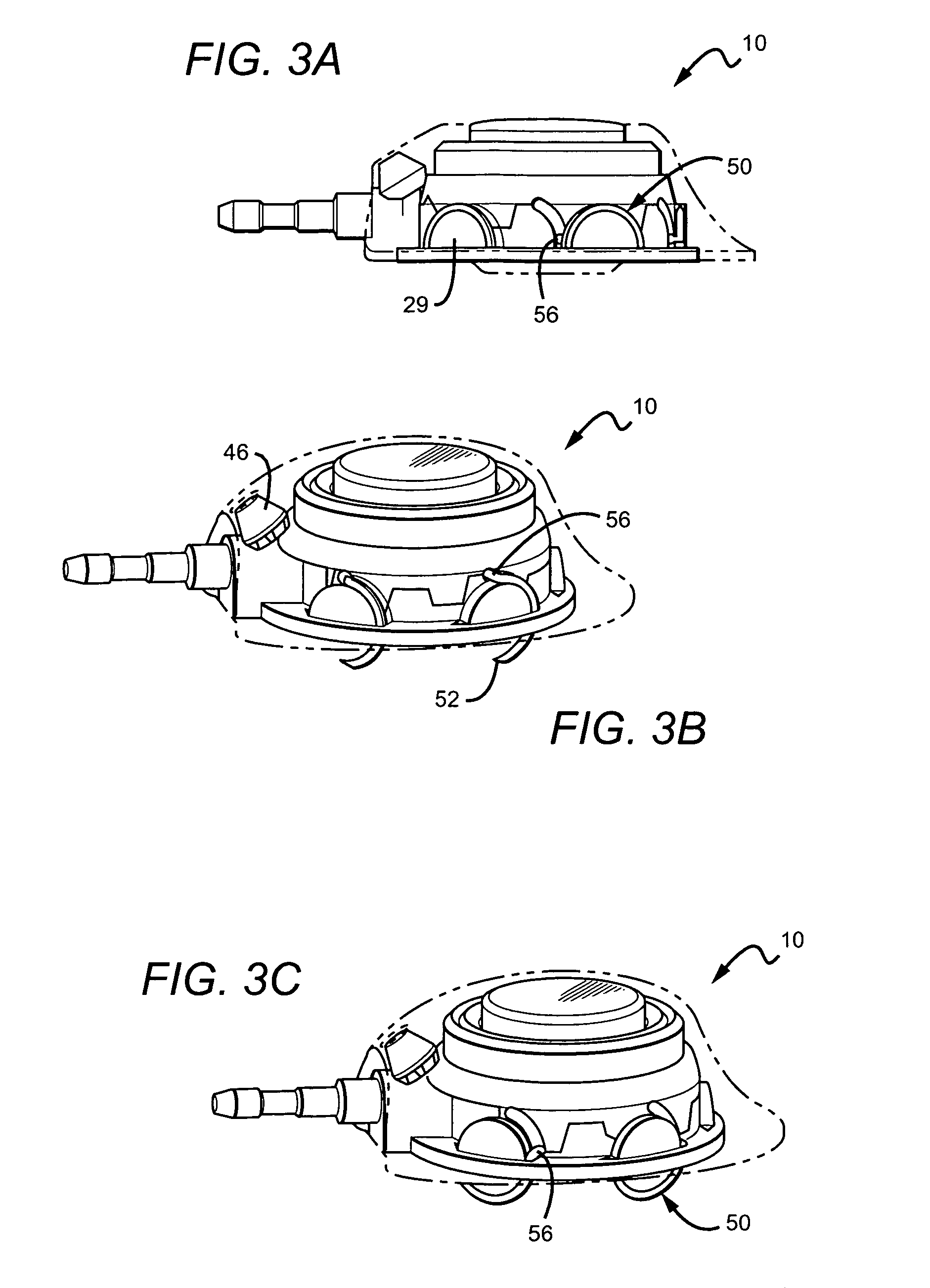
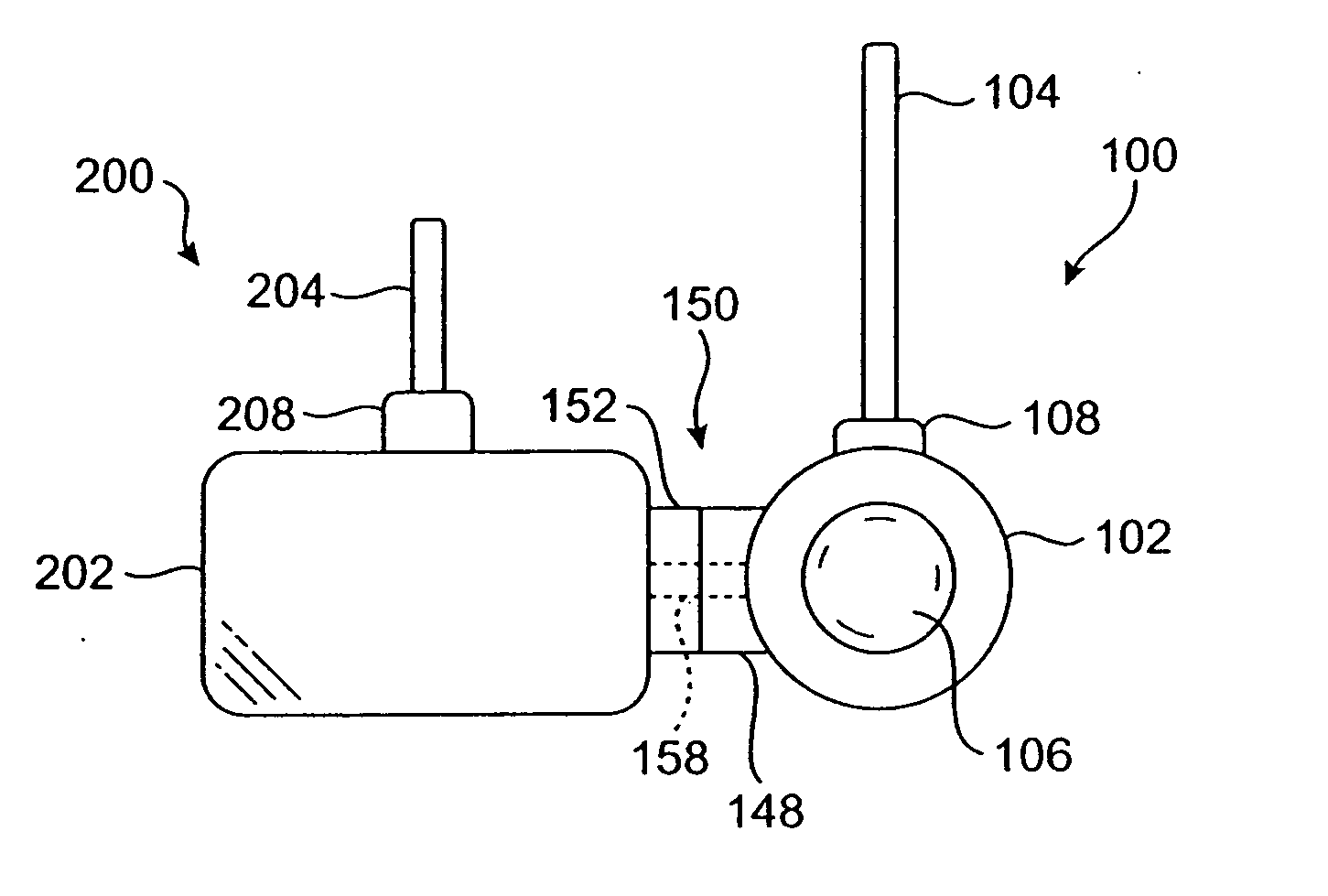
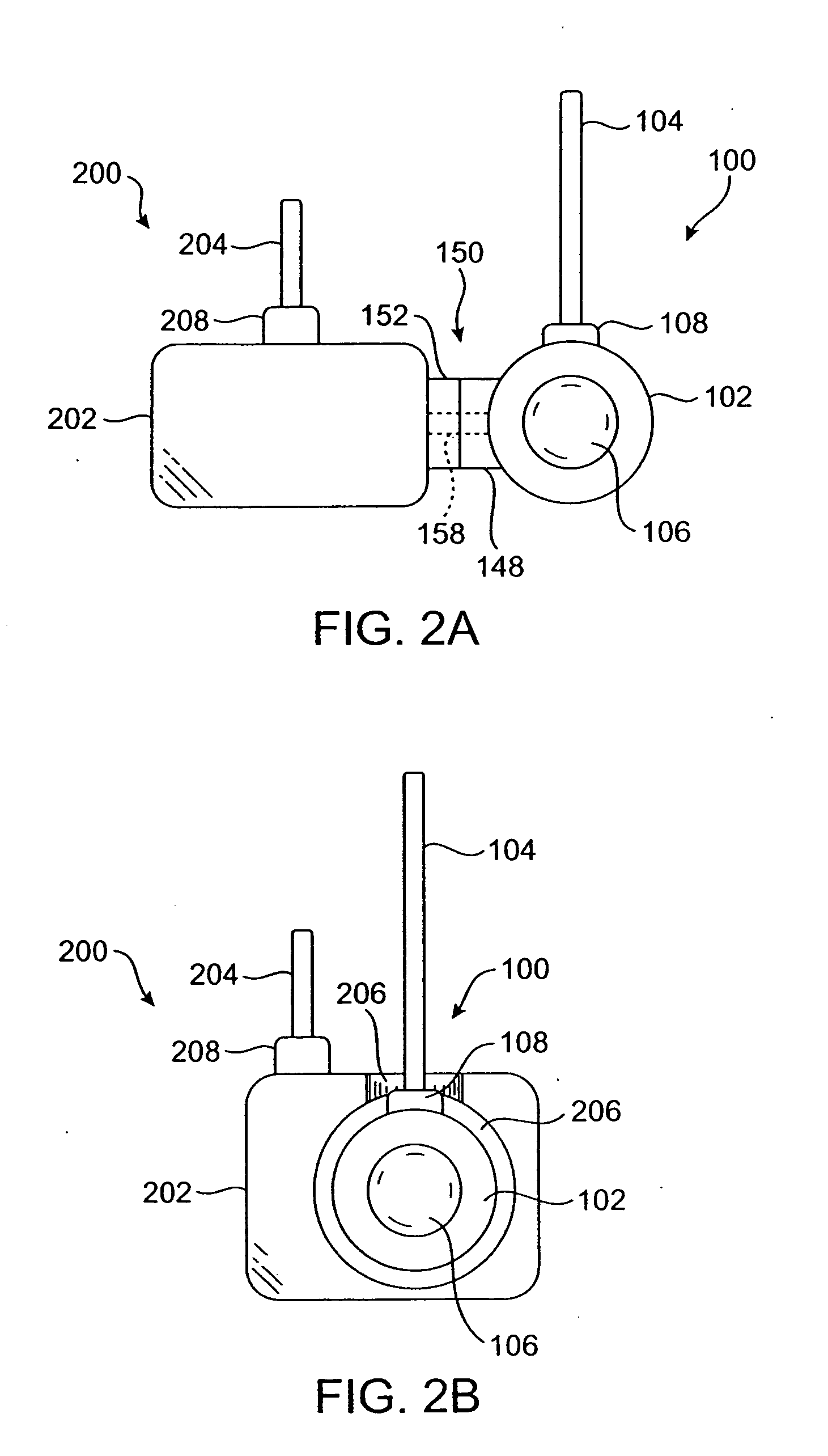
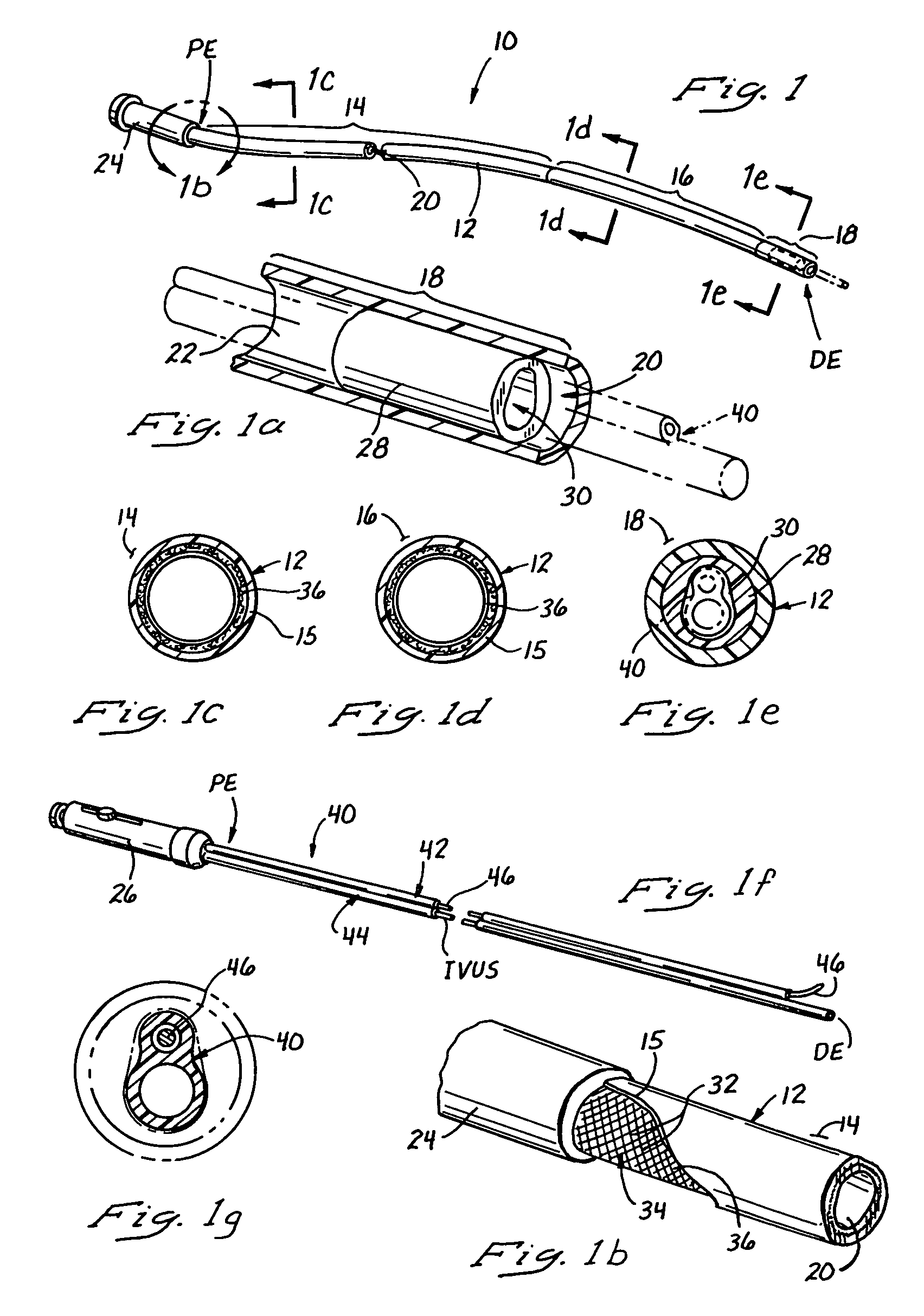
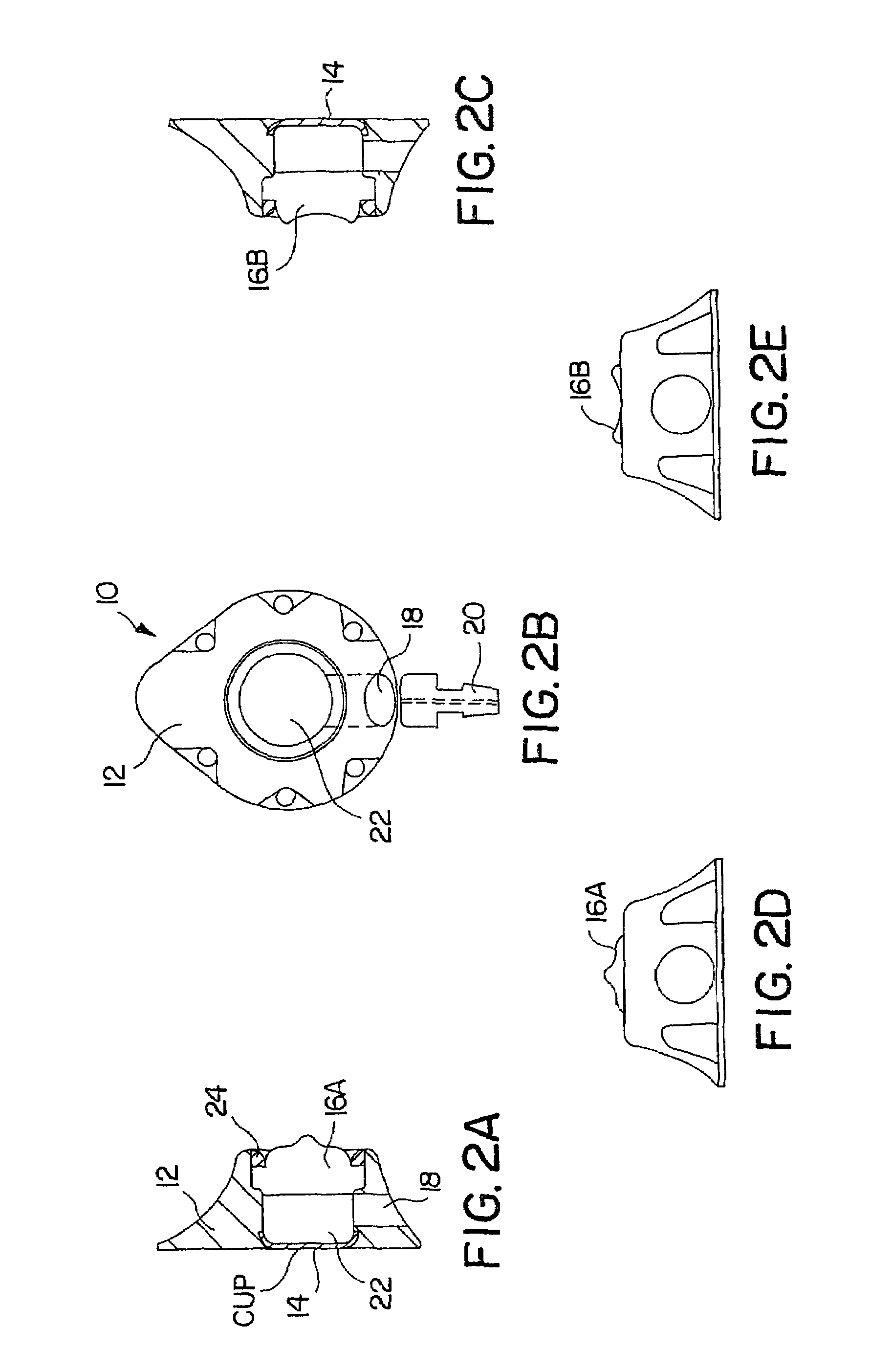
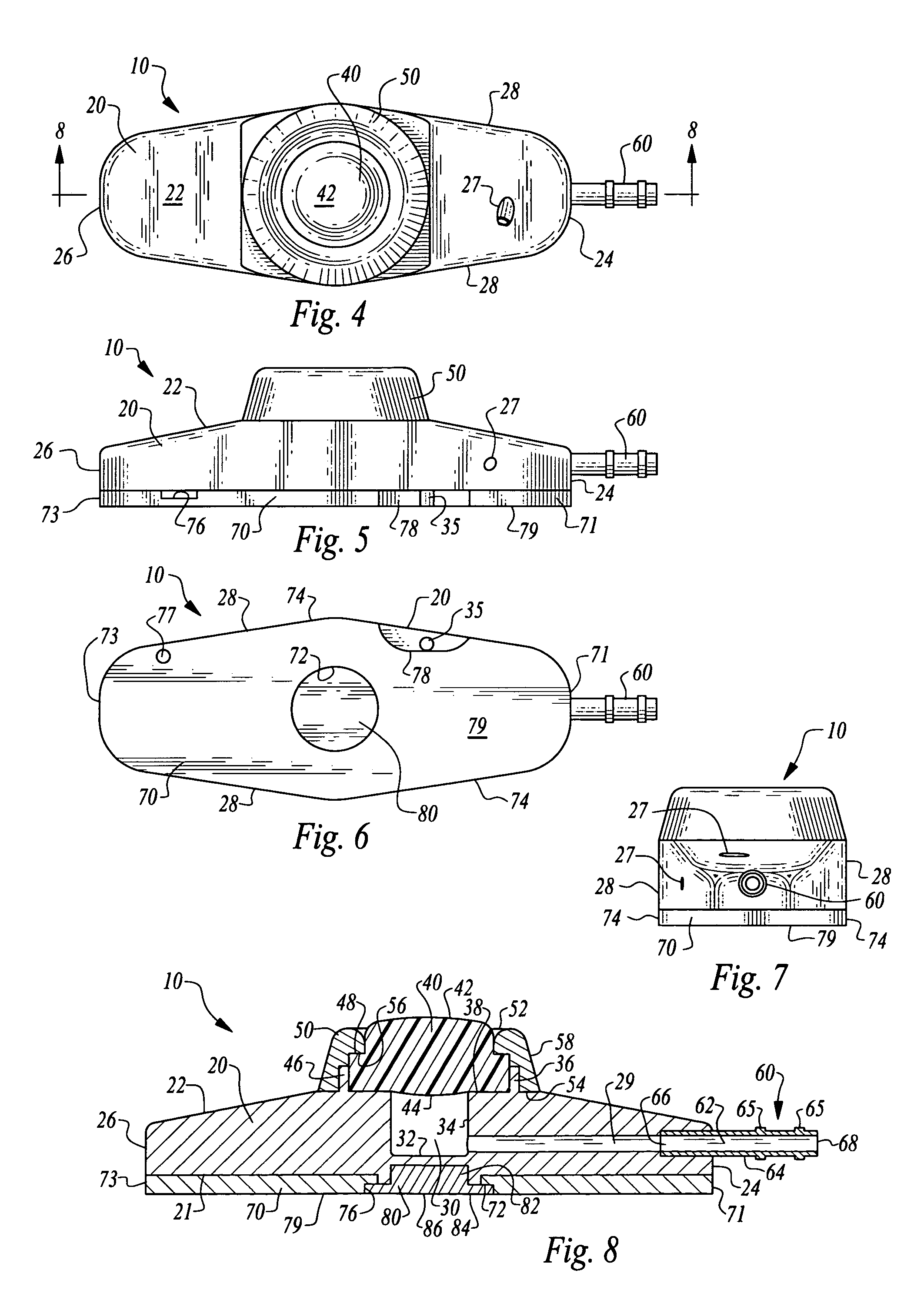
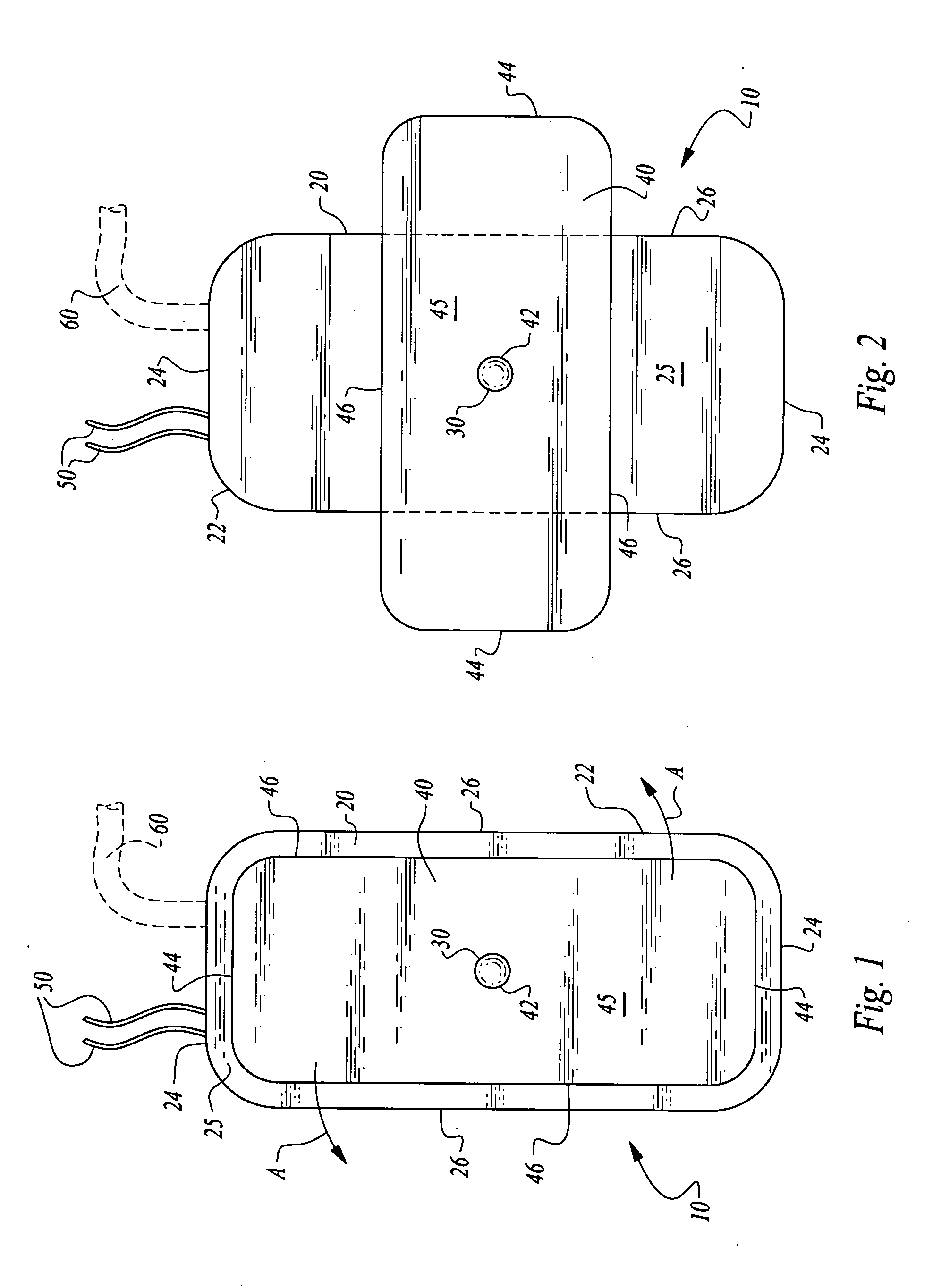
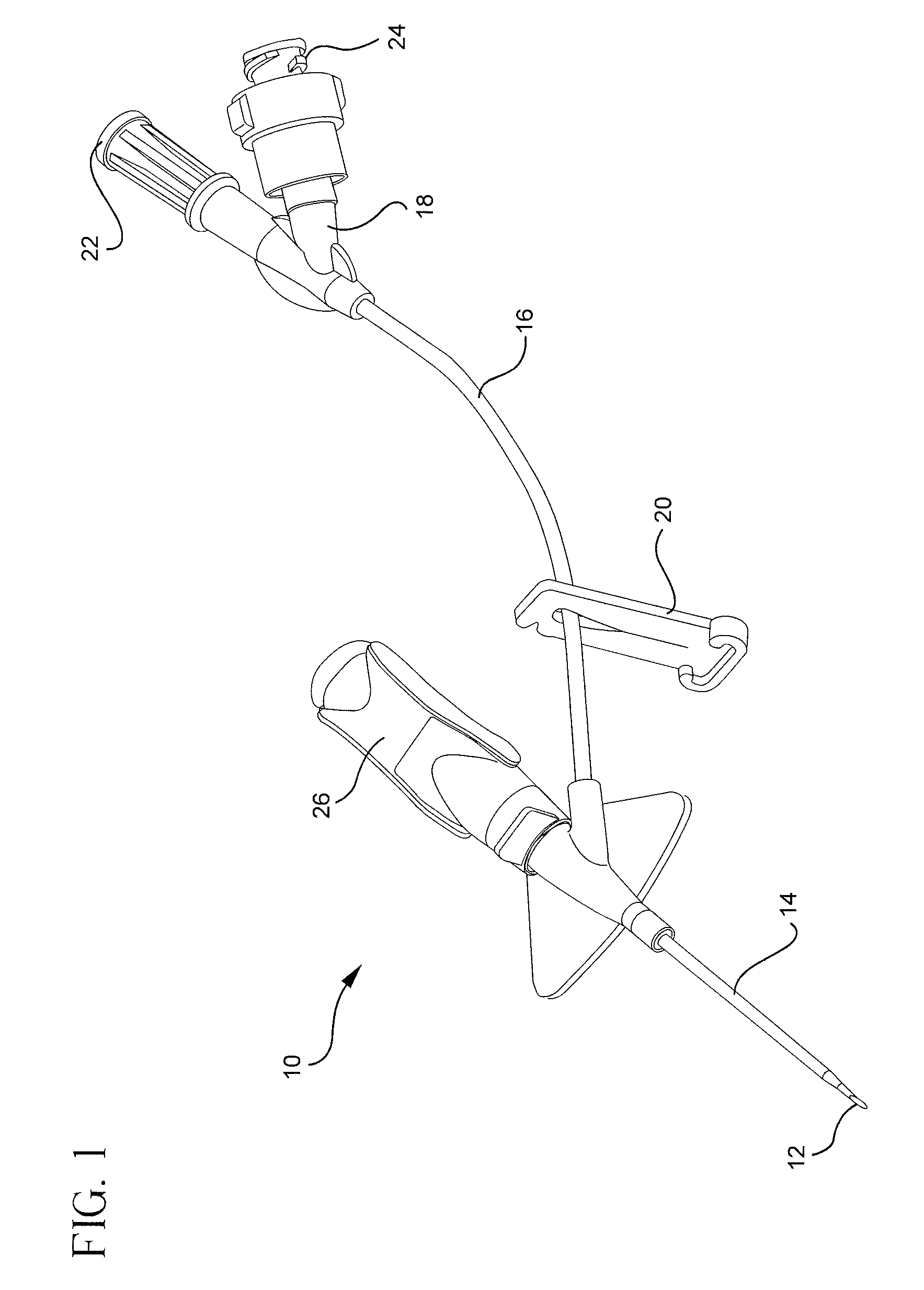
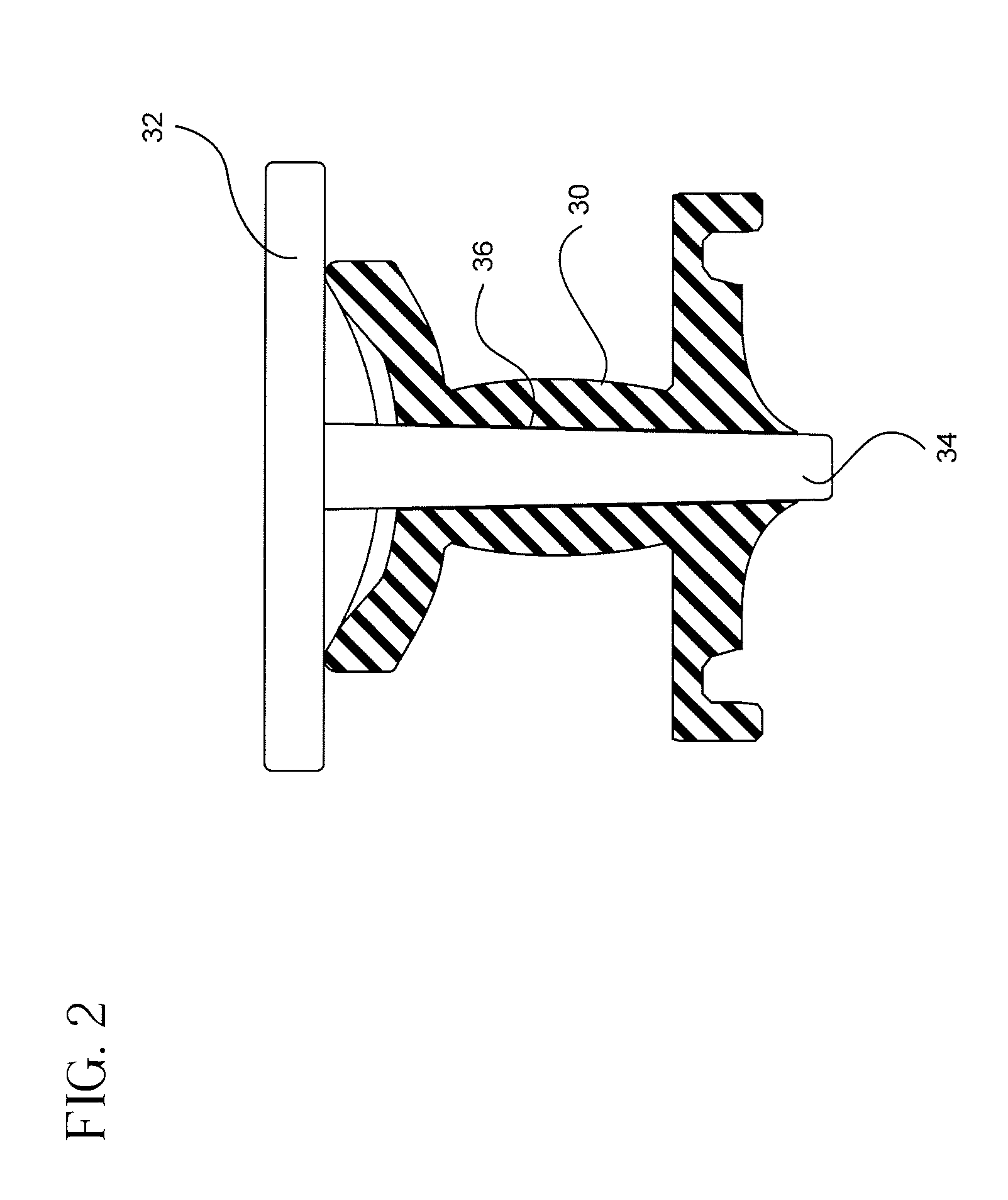
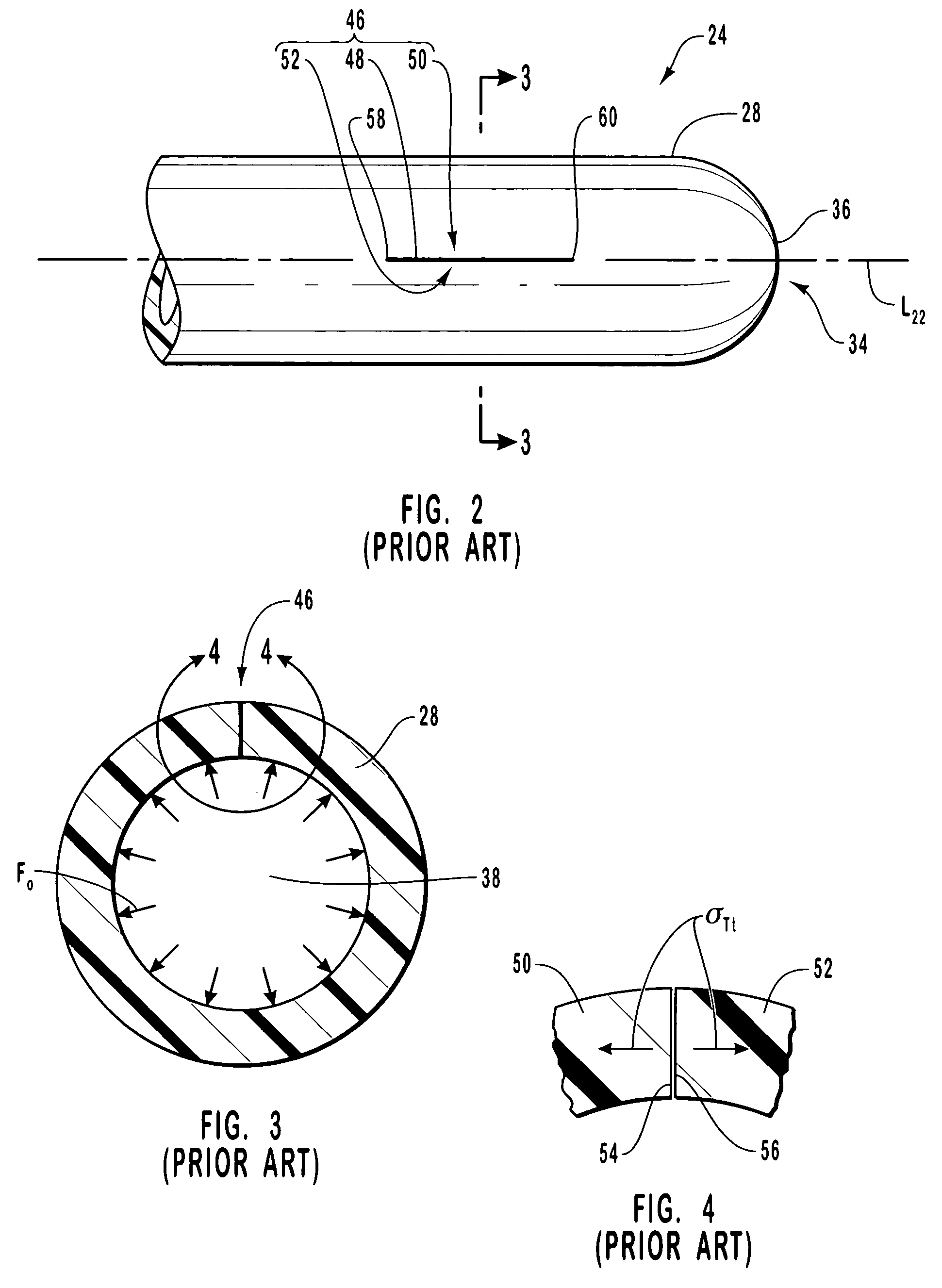
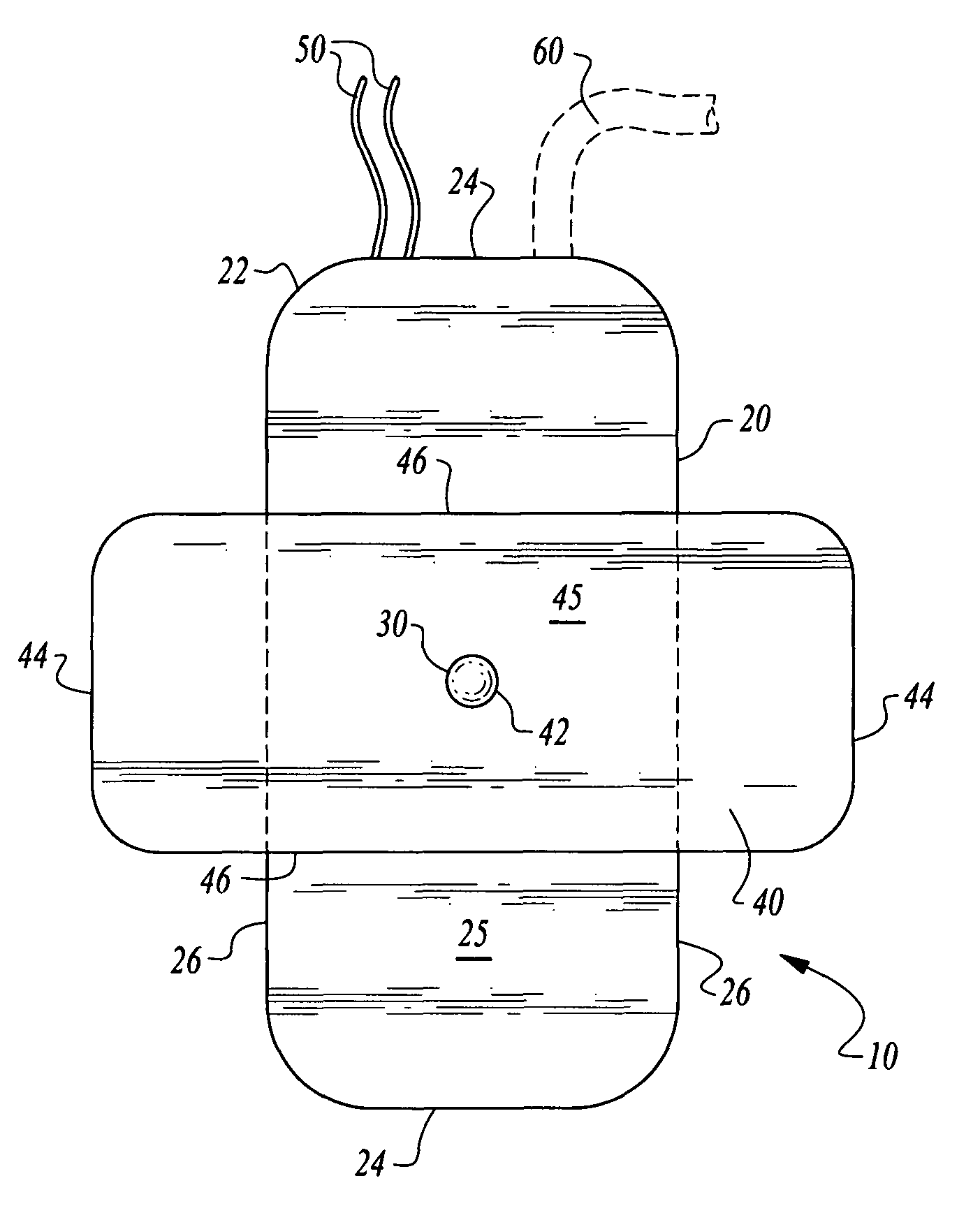
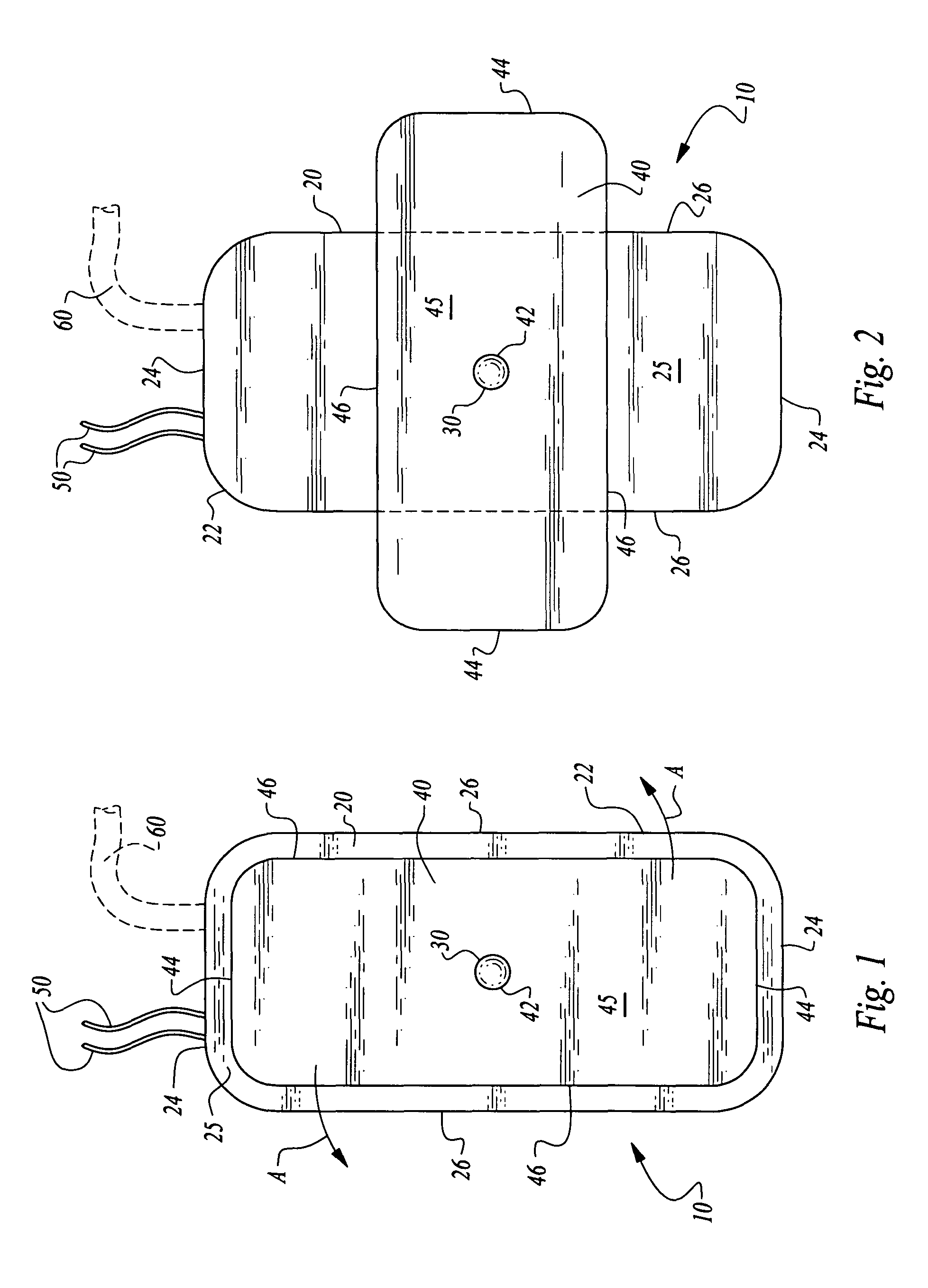
Vascular access port with elongated septum
InactiveUS6213973B1Large target areaPreventing buckling of the septumSurgeryMedical devicesNeedle penetrationHydrostatic pressure
An elongated access port has a needle-impenetrable housing enclosing a fluid reservoir. The housing includes a base having a floor with an upstanding encircling sidewall and a cap having a top wall with a depending encircling skirt. The skirt of the cap receives the sidewall of the base. An access aperture extends through the top wall of the cap to communicate with the fluid reservoir. The access aperture is encircled by a continuous rim having an elongated shape in the plane of the access aperture. The rim of the access aperture may be elliptical, oval, polygonal, or parabolic-ended. An elastomeric, needle-penetrable, generally planar septum is disposed in the access aperture with the periphery of the septum in sealing engagement with the rim of the access aperture. Prior to installation, the septum has a periphery with a cross section in the plane of the septum that is geometrically proportional to and larger than the shape of the access aperture. Installation causes the periphery of the septum to be displaced inwardly by the rim of the access aperture in a direction parallel to the plane of the septum. In view of the relative shapes of the rim of the access aperture and the periphery of the septum, this produces substantially uniform hydrostatic pressure in regions of the installed septum that are subjected in use of the access port to needle penetrations. Opposite faces of the periphery of the septum are urged toward each other between the cap of the housing and the top of the sidewall of the base of the housing.
Owner:CR BARD INC
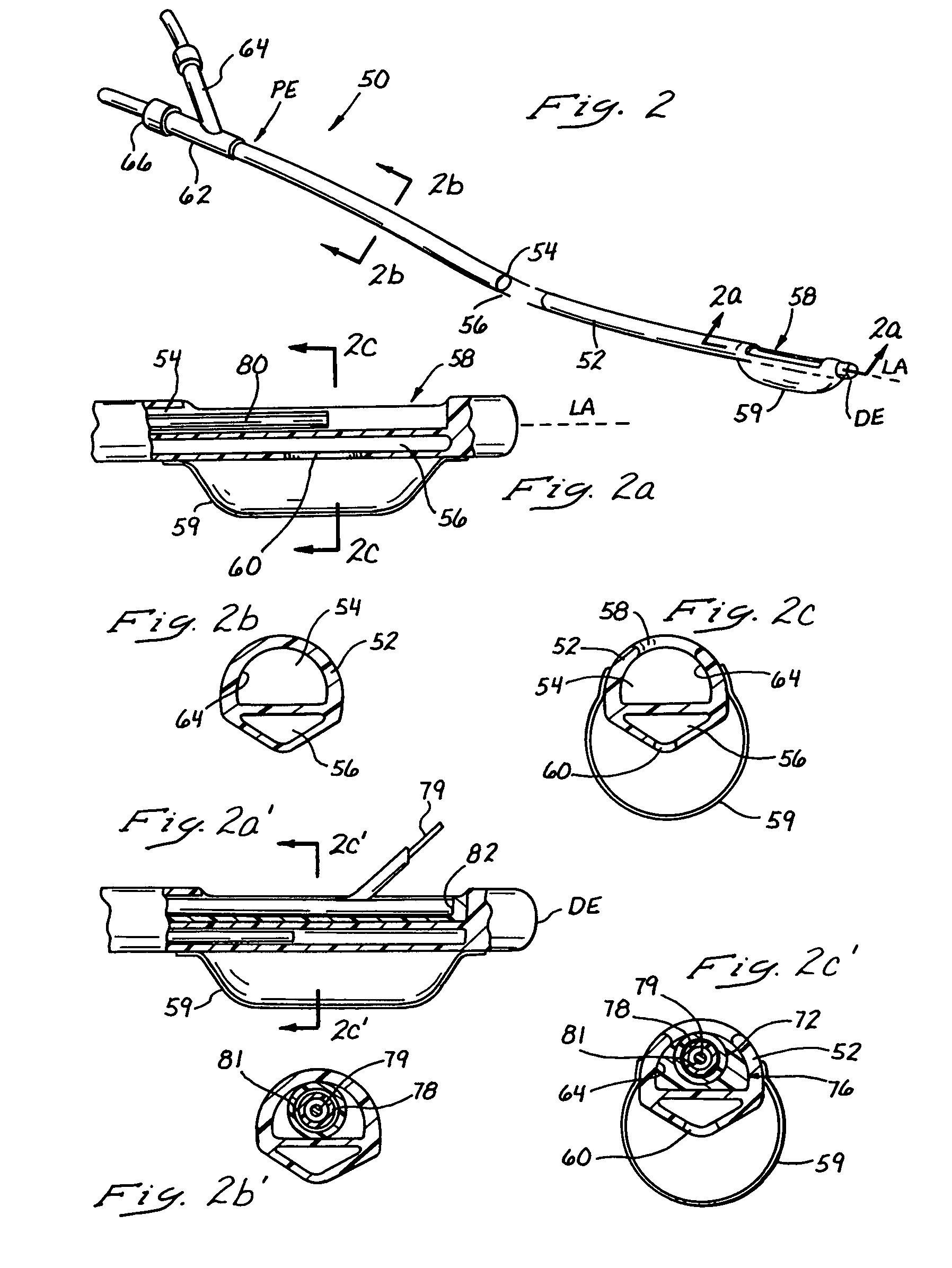
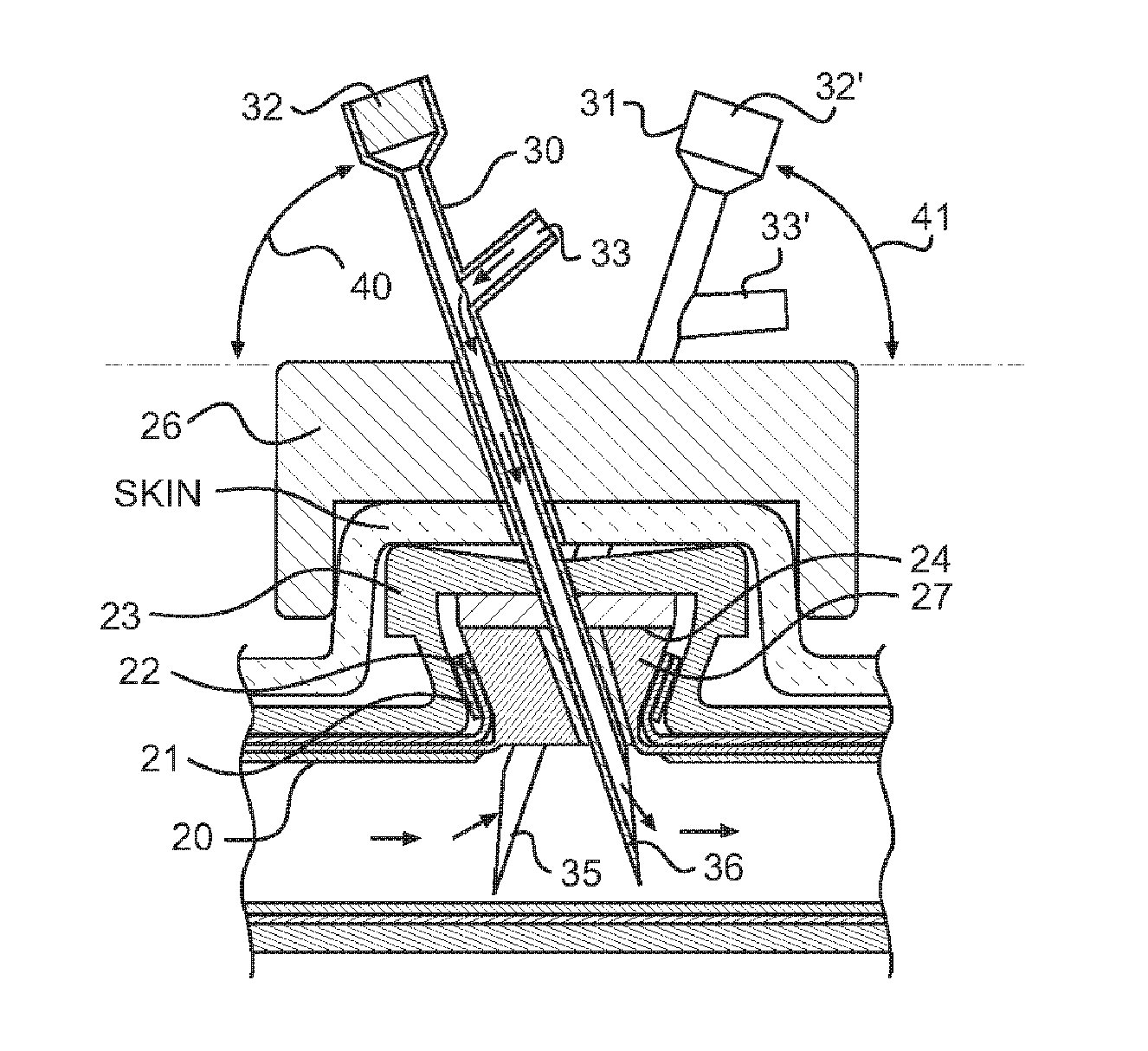
Safety needle with positive flush
ActiveUS20050049553A1Easy to disassembleAvoid negative pressureMedical devicesInfusion needlesLocking mechanismNeedle puncture
A safety needle device and positive flush mechanism for use with a vascular access port. In one embodiment, the combination needle assembly includes a needle, a body and a base, the body being collapsible to expunge fluid therefrom as the needle is withdrawn from a vascular access port. In another embodiment, the combination needle assembly includes a needle, a housing and a reservoir, the housing squeezing the reservoir to expunge fluid therefrom as the needle is withdrawn from the port. In another embodiment, the needle assembly includes a compression plate and balloon extension, the compression plate forcing fluid out of the balloon extension as the needle is withdrawn from the port. In all embodiments, the needle assembly is configured to provide a positive flush to overcome negative pressures in the vascular access port, while also providing a locking mechanism to prevent accidental needle sticks.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Safety needle with positive flush
ActiveUS7097637B2Easy to disassembleAvoid negative pressureMedical devicesInfusion needlesLocking mechanismEngineering
A safety needle device and positive flush mechanism for use with a vascular access port. In one embodiment, the combination needle assembly includes a needle, a body and a base, the body being collapsible to expunge fluid therefrom as the needle is withdrawn from a vascular access port. In another embodiment, the combination needle assembly includes a needle, a housing and a reservoir, the housing squeezing the reservoir to expunge fluid therefrom as the needle is withdrawn from the port. In another embodiment, the needle assembly includes a compression plate and balloon extension, the compression plate forcing fluid out of the balloon extension as the needle is withdrawn from the port. In all embodiments, the needle assembly is configured to provide a positive flush to overcome negative pressures in the vascular access port, while also providing a locking mechanism to prevent accidental needle sticks.
Owner:CR BARD INC
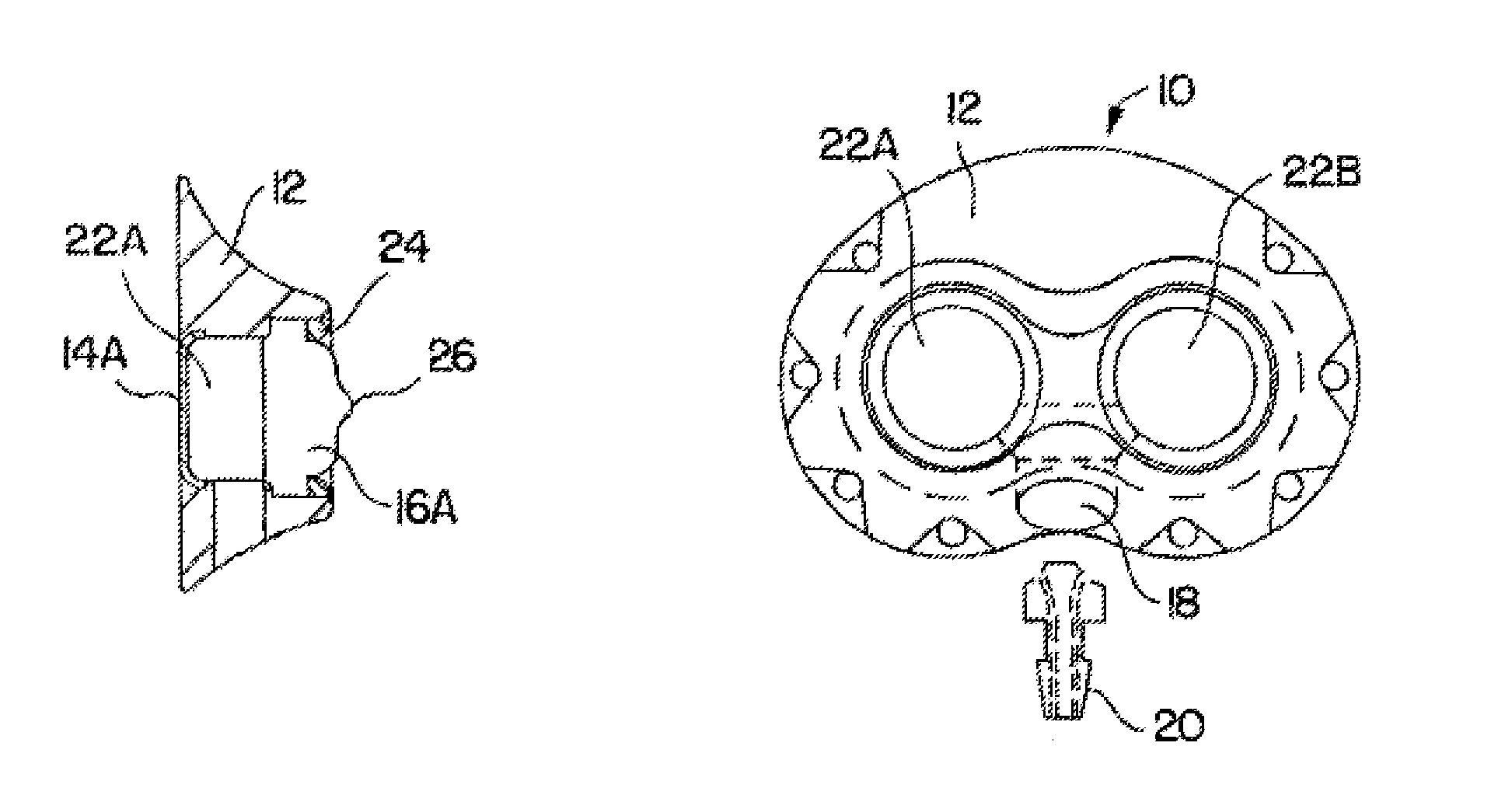
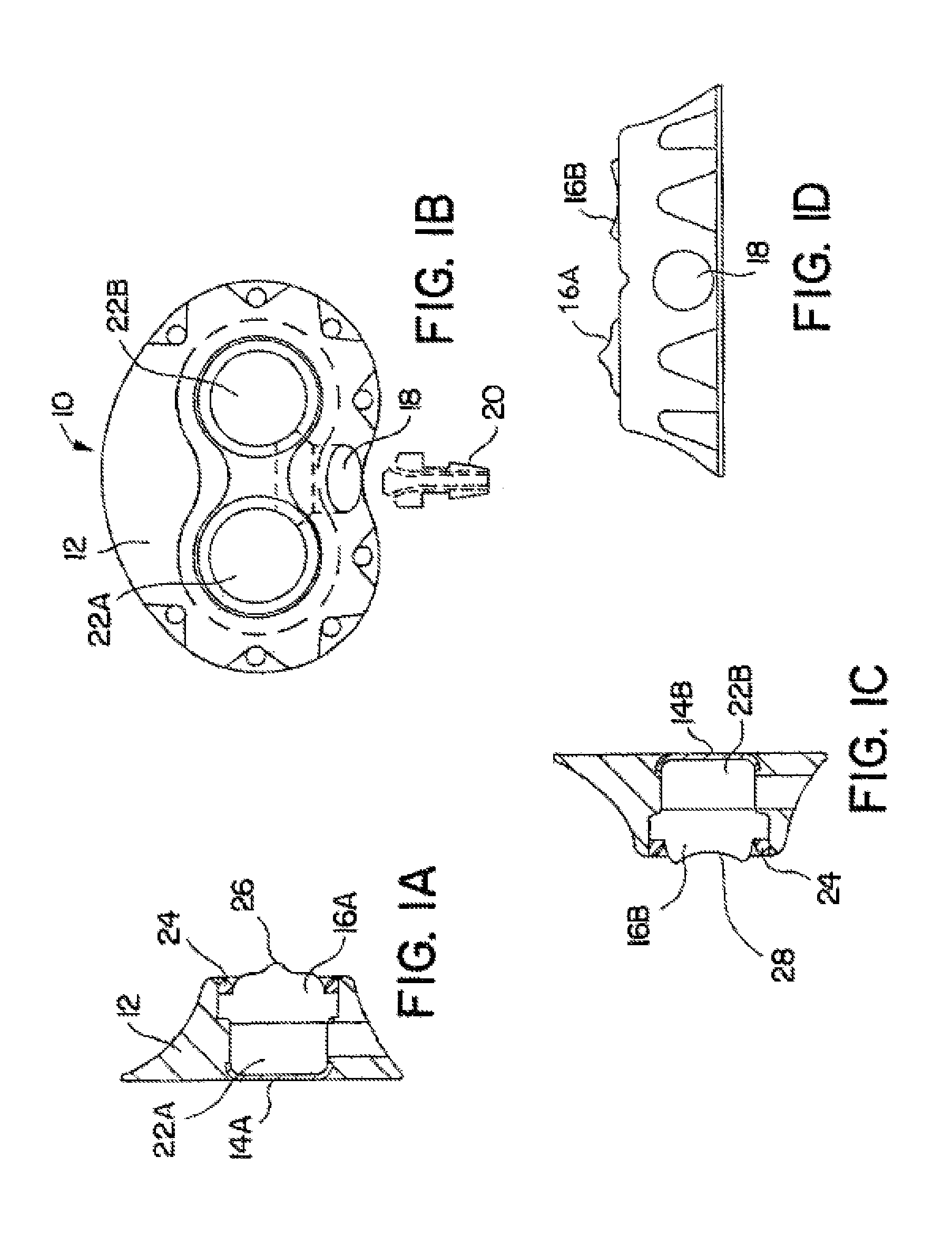
Vascular access port with integral attachment mechanism
An implantable port with an integral attachment mechanism. The implantable port includes one or more suture needles enclosed within a port body, the suture needle(s) coupled to a movable member such that movement of the movable member results in movement of the suture needle(s) out of the port body and into the tissue of a body into which it is implanted. The movable member can be a cam or tensioning member that rotates about a central port axis. The movable member can be coupled to a gear to permit movement of the movable member following implantation of the port within a subcutaneous pocket.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Biodegradable and/or bioabsorbable member for vascular sealing
An implantable, bioresorbable and / or biodegradable sealing member, such as a staple, clip, snap or rivet, is used for clamping vessels, vessel side-branches, aneurysms, or any other tube like body-parts or for sealing vascular access sites and wound site management. The implantable, bioresorbable and / or biodegradable member comprises a combination of materials which dissolve or degrade in the human body without any harmful effects on the person that wears the member.
Owner:BIOTRONIK VI PATENT
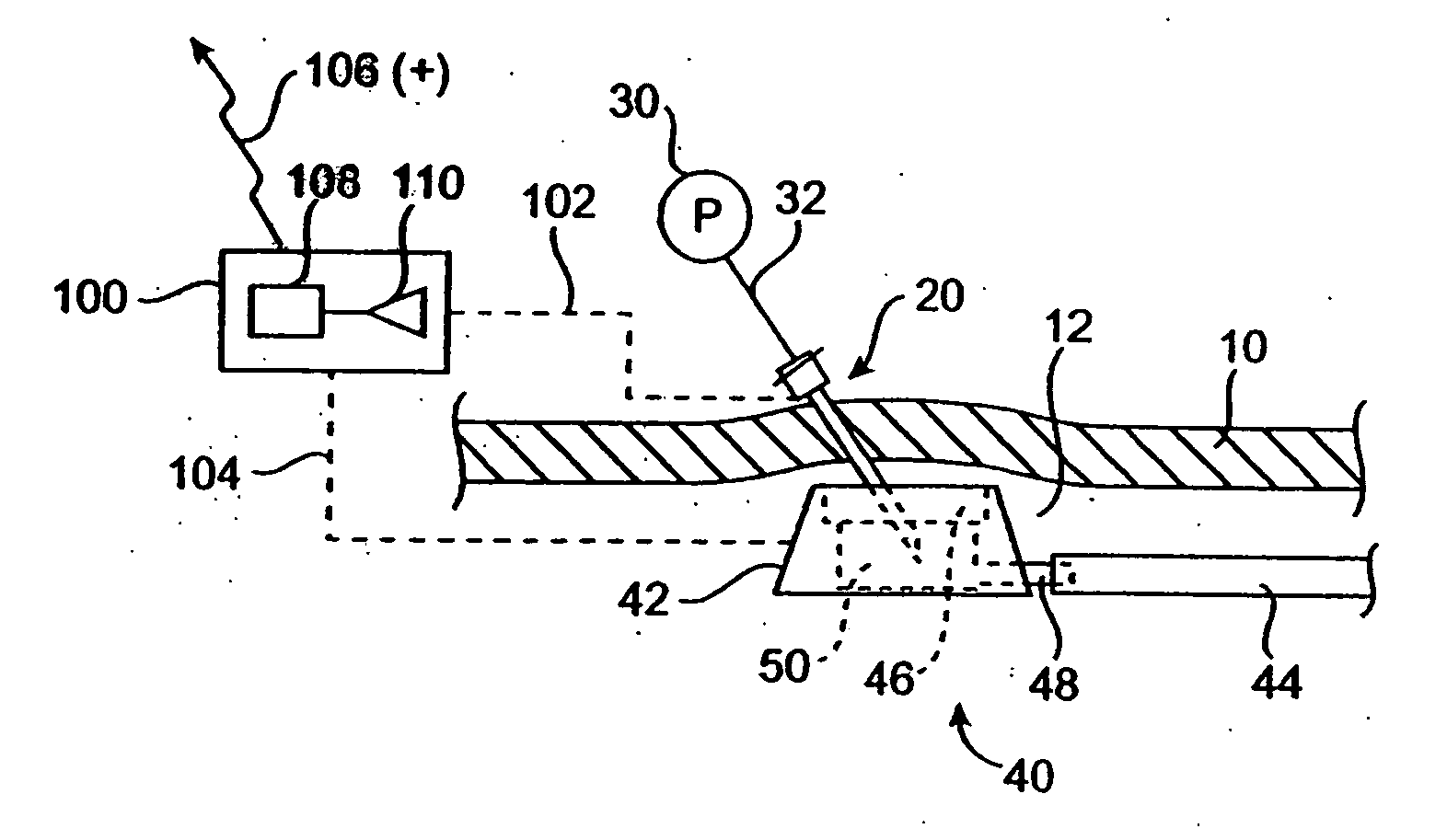
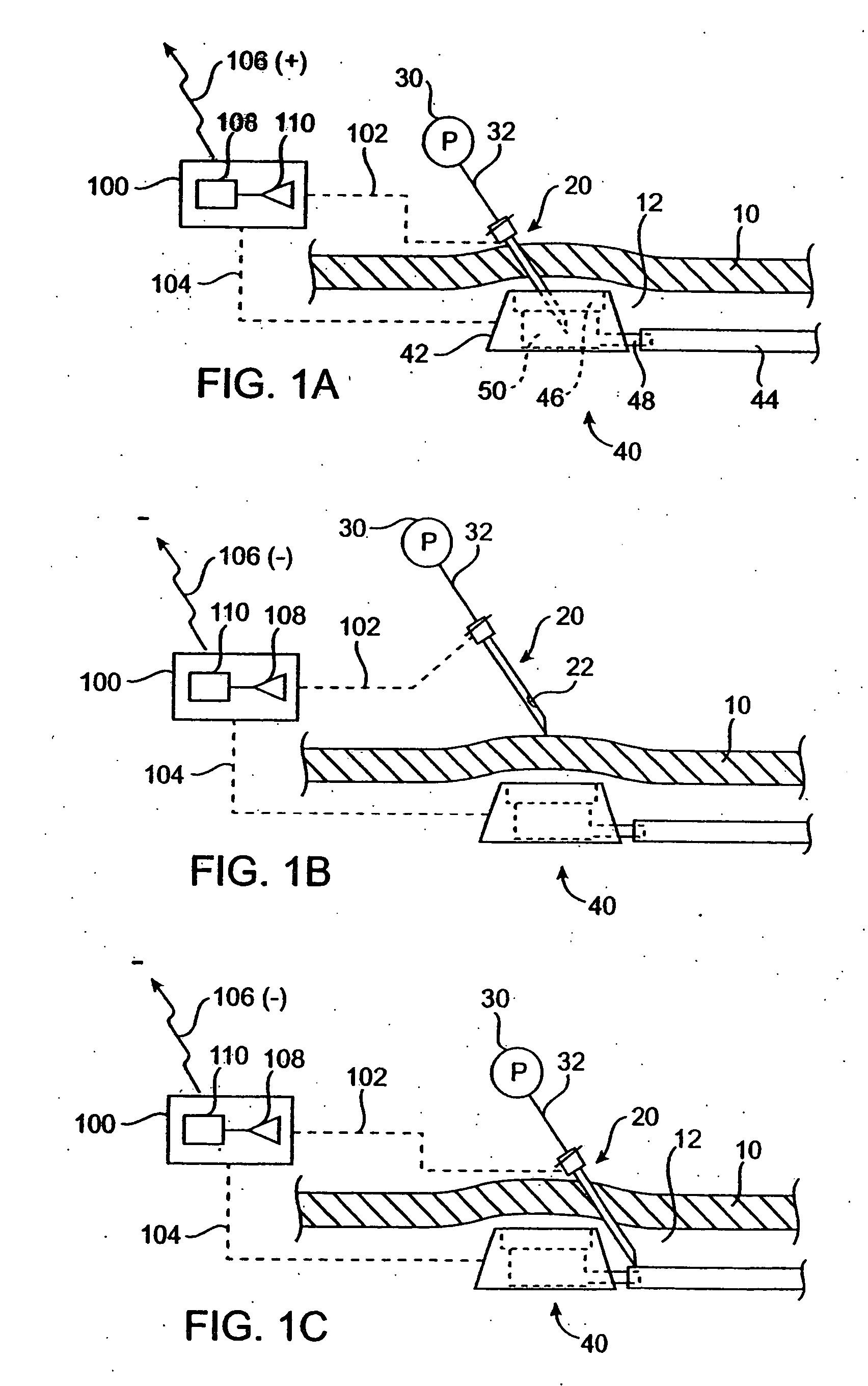
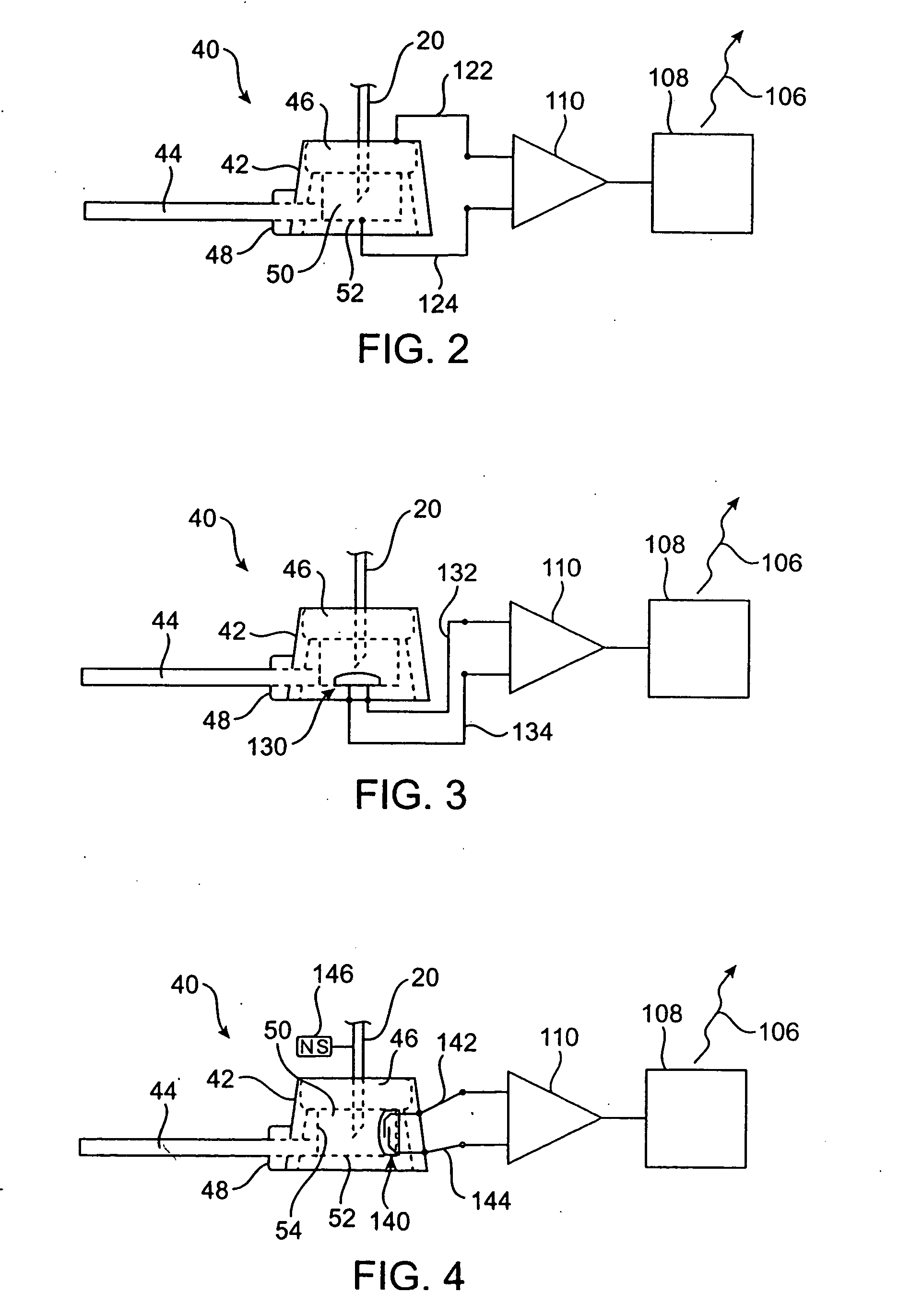
Vascular access port with needle detector
InactiveUS20050256451A1Wave based measurement systemsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismInductorMagnetic switch
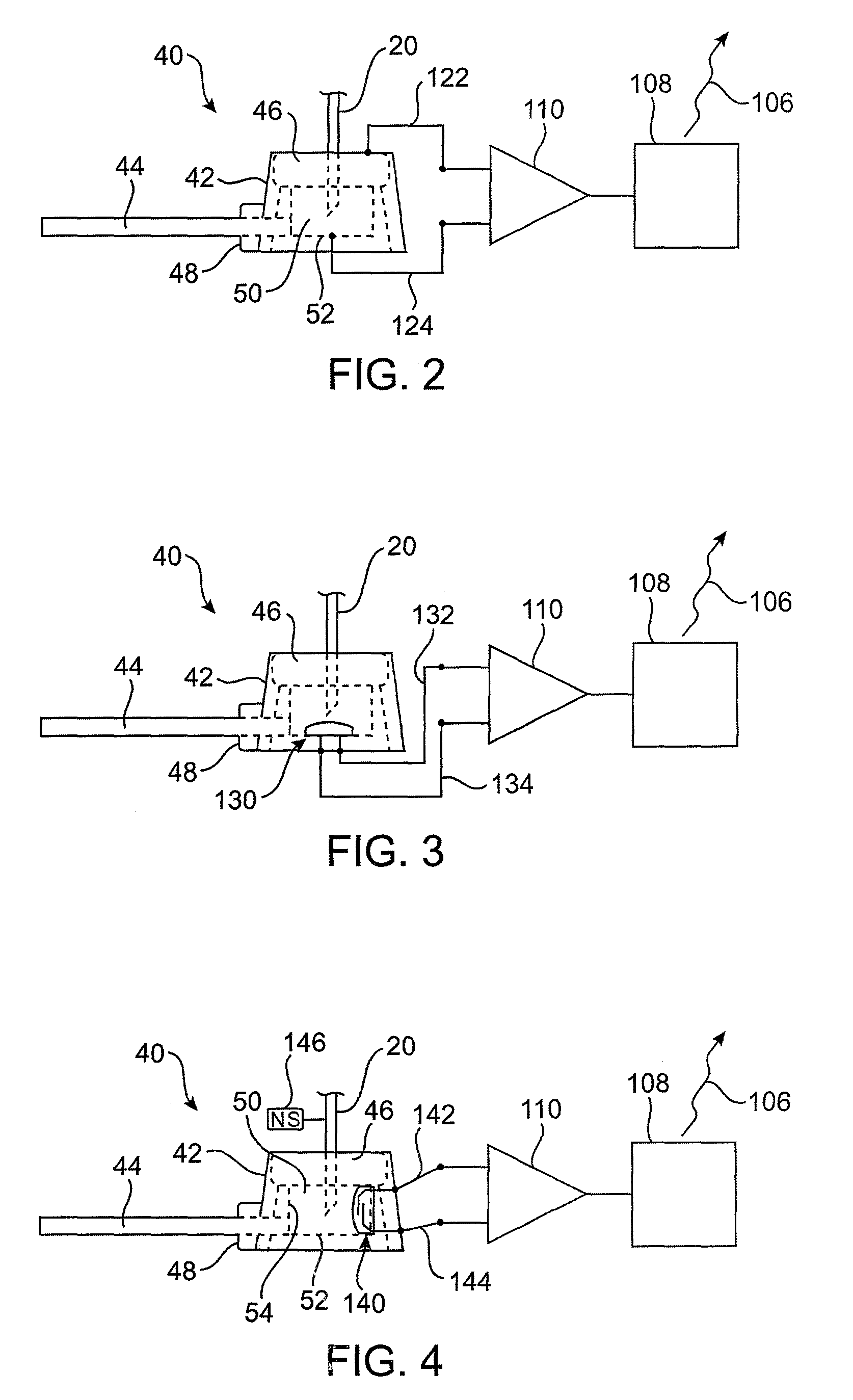
A vascular access port system including means for detecting and indicating the presence or absence of a needle. The detecting and indicating means may be carried in whole or in part by one of or both of the needle and / or the vascular access port. The detecting and indicating means may utilize a conductive needle, a mechanical switch, a magnetic switch, a Hall effect sensor, an electric field, a magnetic field, or an inductor, for example, for detection purposes. The vascular access port system permits the practitioner to confirm that the needle has been correctly inserted into the VAP, and notifies the patient and / or practitioner if the needle has been accidentally withdrawn.
Owner:TRANSOMA MEDICAL
Vascular access port with physiological sensor
InactiveUS7070591B2Easy to optimizeImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyMedical devicesCollection systemCommunication link
A combined vascular access port and physiologic parameter monitoring device. The vascular access port and the monitoring device may be connected by a cooperative geometry. The vascular access port and the monitoring device may be implanted at the same time and in the same anatomical location (e.g., subcutaneous pocket). The monitoring device may include a telemetry unit that transmits physiological measurement data to a local data collection system (e.g., carried by the patient or located in the patient's home), which may re-transmit the data to a remote data collection system (e.g., located at a physician's office or clinic) via a suitable communication link.
Owner:TRANSOMA MEDICAL
Vascular access port with needle detector
A vascular access port system including circuits for detecting and indicating the presence or absence of a needle. The detecting and indicating circuits may be carried in whole or in part by one of or both of the needle and / or the vascular access port. The detecting and indicating circuits may utilize a conductive needle, a mechanical switch, a magnetic switch, a Hall effect sensor, an electric field, a magnetic field, or an inductor, for example, for detection purposes. The vascular access port system permits the practitioner to confirm that the needle has been correctly inserted into the VAP, and notifies the patient and / or practitioner if the needle has been accidentally withdrawn.
Owner:TRANSOMA MEDICAL
Vascular Access Port with Catheter Connector
An implantable vascular access port assembly that has a septum, a reservoir, and a catheter connector assembly for use in connecting a catheter with the vascular access port. The catheter connector assembly has an O-ring, an O-ring seal, a locking ring, and a catheter connection plug, which components are located in secured adjacent relationship to one another, respectively, in the vascular access port. The catheter connector assembly securely locks the catheter inside of the vascular access port without compromising the lumen cross-sectional area and can withstand high pressures.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
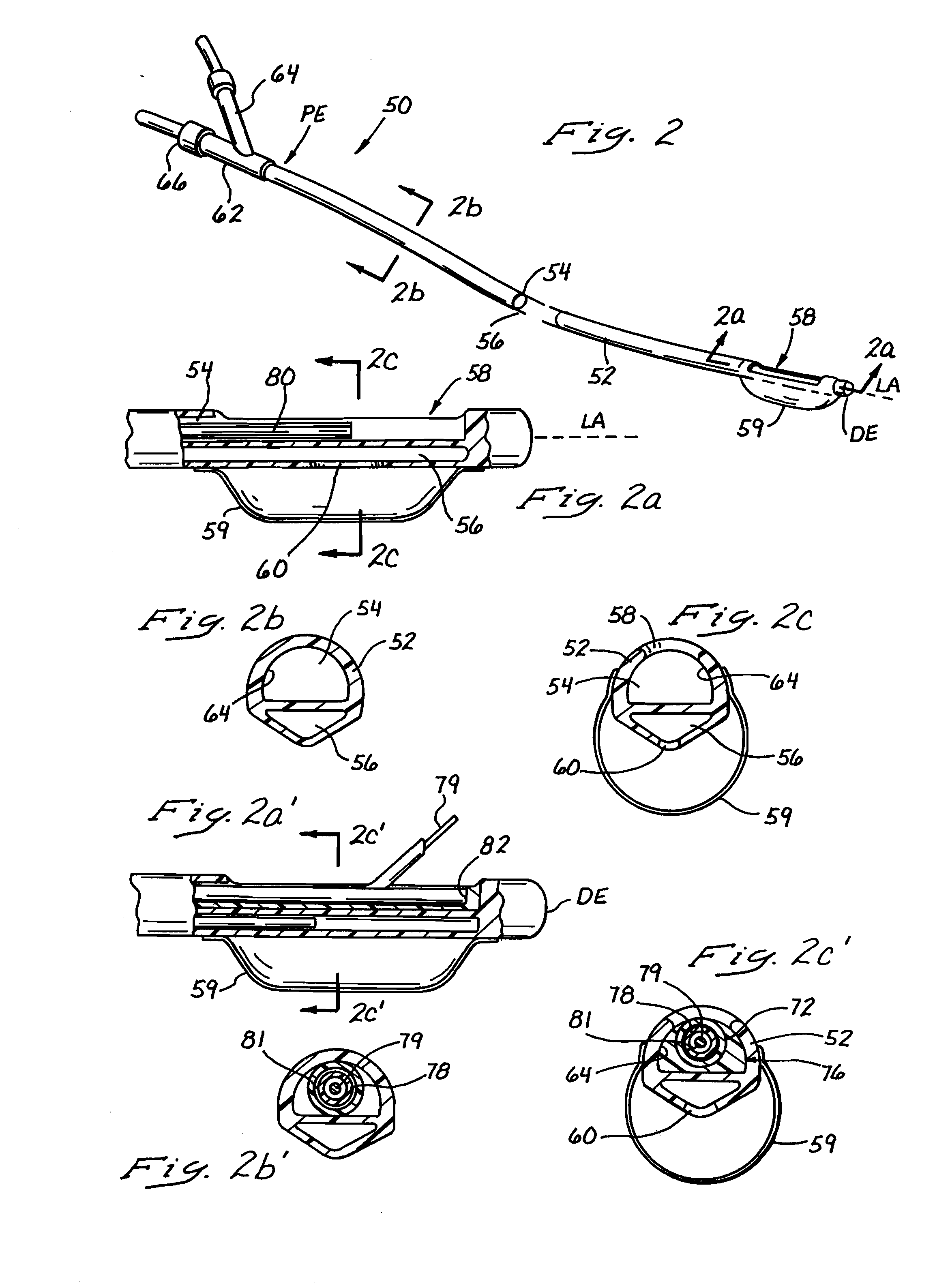
Subcutaneous vascular access port, and method of using same
A surgically implantable access port has a main port body with an internal chamber formed therein, and an outlet tube connected to the main port body. The internal chamber is configured to readily receive a guide wire therein, and to passively direct the tip of a guide wire to an outlet, which is in fluid communication with the outlet tube. The chamber in the main port body is formed in a directionally aimed conical shape. The outlet may be located at the lowest area of the chamber, to help direct a guide wire thereto. A specialized needle is also described, having a curved tip with an opening formed therein. The top inner and the and the bottom outer surfaces of the needle, adjacent the tip opening, are rounded and non-sharp to avoid damaging a guide wire when used therewith. Methods of using the port and needle are also disclosed.
Owner:PARKS ROBERT A
Vascular access port with integral attachment mechanism
An implantable port with an integral attachment mechanism. The implantable port includes one or more suture needles enclosed within a port body, the suture needle(s) coupled to a movable member such that movement of the movable member results in movement of the suture needle(s) out of the port body and into the tissue of a body into which it is implanted. The movable member can be a cam or tensioning member that rotates about a central port axis. The movable member can be coupled to a gear to permit movement of the movable member following implantation of the port within a subcutaneous pocket.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Vascular access port with physiological sensor
InactiveUS20060178617A1Improve accuracyConvenient for physicianElectrocardiographyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTelecommunications linkCollection system
A combined vascular access port and physiologic parameter monitoring device. The vascular access port and the monitoring device may be connected by a cooperative geometry. The vascular access port and the monitoring device may be implanted at the same time and in the same anatomical location (e.g., subcutaneous pocket). The monitoring device may include a telemetry unit that transmits physiological measurement data to a local data collection system (e.g., carried by the patient or located in the patient's home), which may re-transmit the data to a remote data collection system (e.g., located at a physician's office or clinic) via a suitable communication link.
Owner:TRANSOMA MEDICAL
Subcutaneous vascular access port, needle and kit, and methods of using same
A surgically implantable access port has a main port body with an internal chamber formed therein, and an outlet tube connected to the main port body. The internal chamber is configured to readily receive a guide wire therein, and to passively direct the tip of a guide wire to an outlet, which is in fluid communication with the outlet tube. The chamber in the main port body is formed in a directionally aimed conical shape. The outlet may be located at the lowest area of the chamber, to help direct a guide wire thereto. A specialized needle is also described, having a curved tip with an opening formed therein. The top inner surface and the bottom outer surface of the needle, adjacent the tip opening, are rounded and non-sharp to avoid damaging a guide wire or catheter when used therewith. Methods of using the port and needle are also disclosed.
Owner:PARKS ROBERT A
Catheters and related devices for forming passageways between blood vessels or other anatomical structures
InactiveUS7648517B2Precise rotation controlPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasAnatomical structuresDistal portion
The inventions described in this patent application include i) a torqueable introducer sheath which is useable in conjunction with a transvascular passageway forming catheter to effect precise rotational control of the catheter; ii) an anchorable guide catheter which is useable in conjunction with an intravascular imaging catheter and a transvascular passageway-forming catheter to effect precise positioning and aiming of the passageway-forming catheter; iii) a passageway forming catheter having a torqueable proximal portion to facilitate precise rotational positioning of the distal portion of the catheter; iv) a deflectable-tipped passageway forming catheter, v) various markers and other apparatus useable in conjunction with any of the passageway-forming catheters to facilitate precise positioning and aiming of the catheter, and vi) an apparatus which may be formed within a catheter to prevent a member, apparatus of flow of material from being inadvertently advanced through a lumen of the catheter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
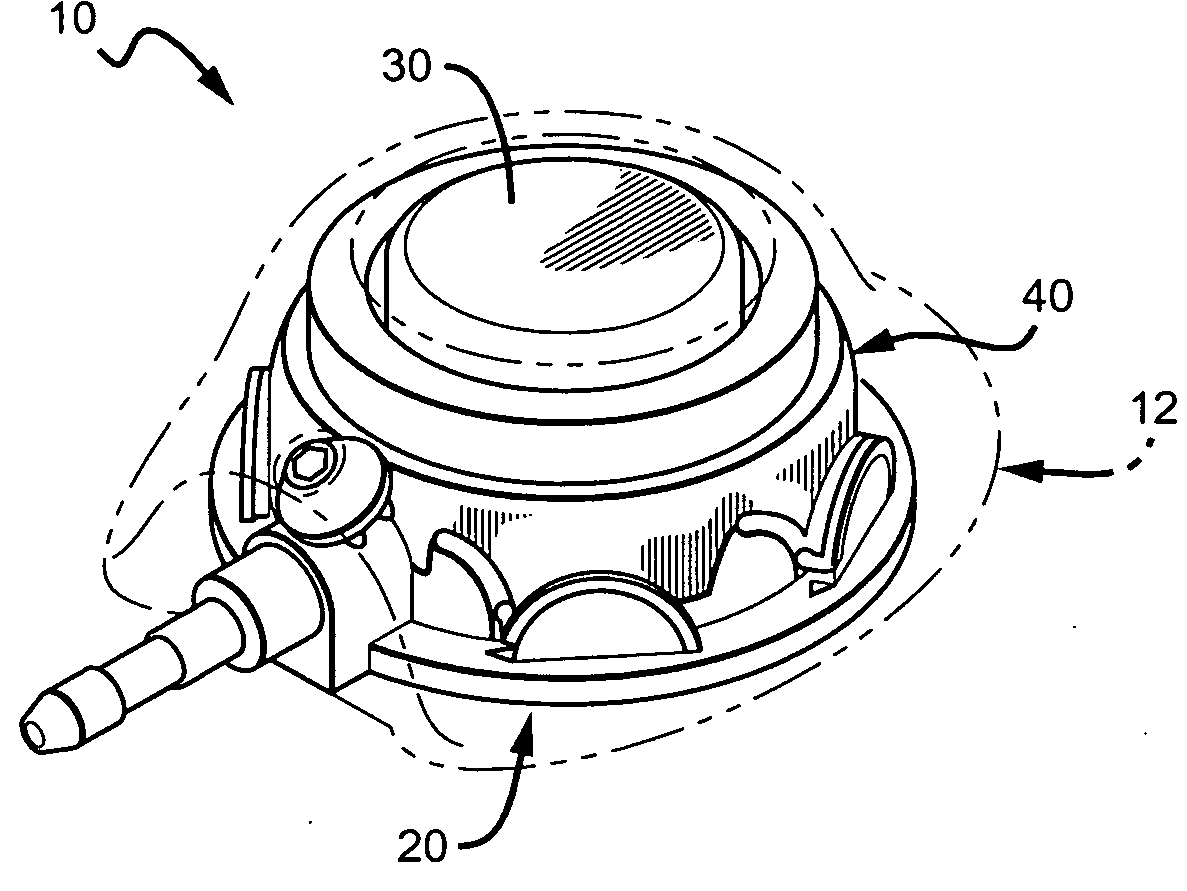
Implantable vascular access device with ceramic needle guard insert
InactiveUS7713251B2Increase the areaReduce coagulationMedical devicesMuscle tissueVascular Access Devices
The present invention provides an improved vascular access port comprising a port base with a metallic dish insert molded (or bonded) into the bottom of the reservoir. In one embodiment, a single reservoir is provided. In another embodiment, plural reservoirs are provided. The metallic bottom of the reservoir provides a hard surface that will resist abrasion and puncture by the access needles used to infuse medication or withdraw blood. Additionally, the single and dual ports can include exit ports that are intended to better anatomically fit into the subcutaneous areas around muscle tissue.
Owner:PRIMO MEDICAL GRP INC
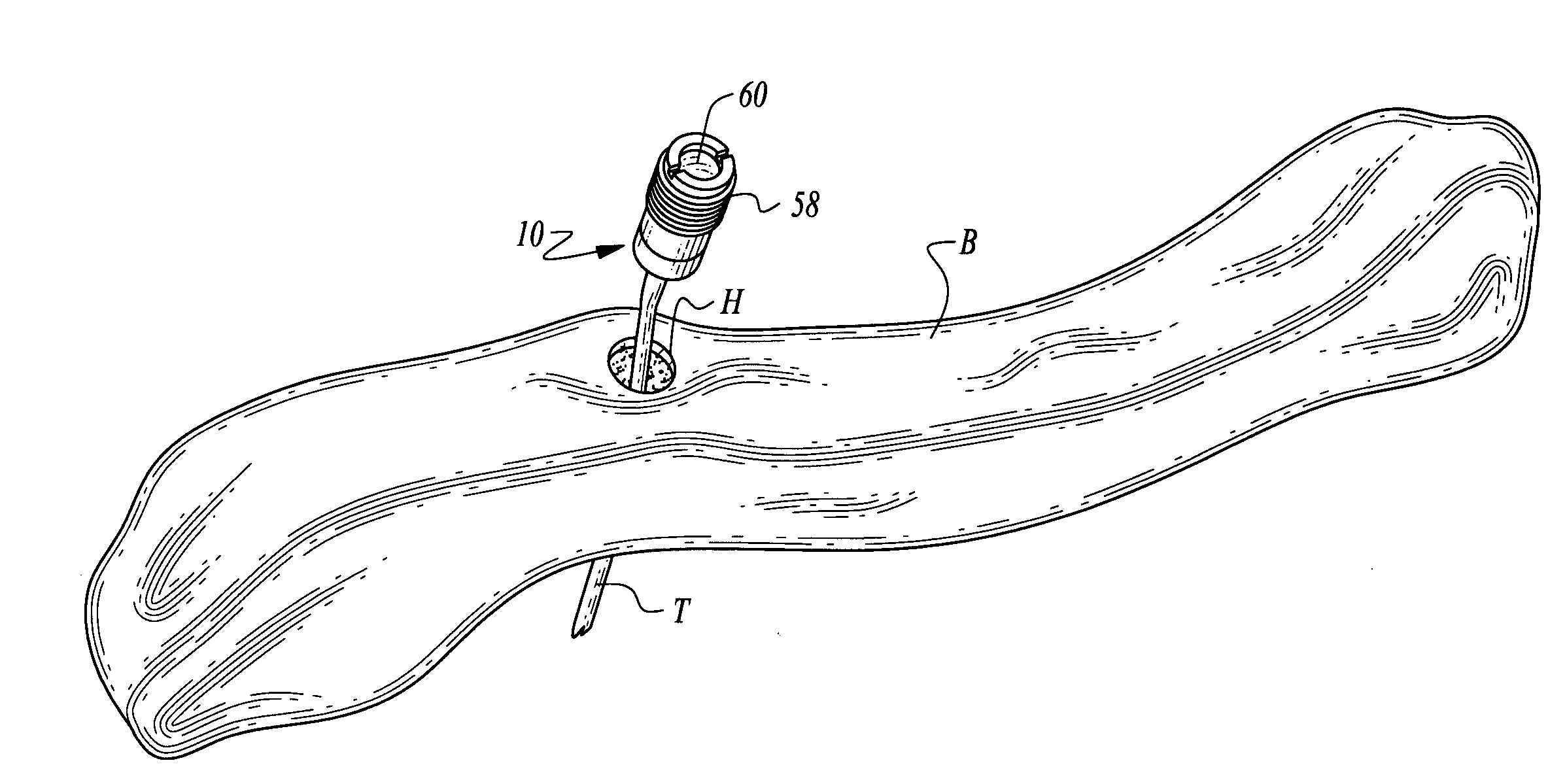
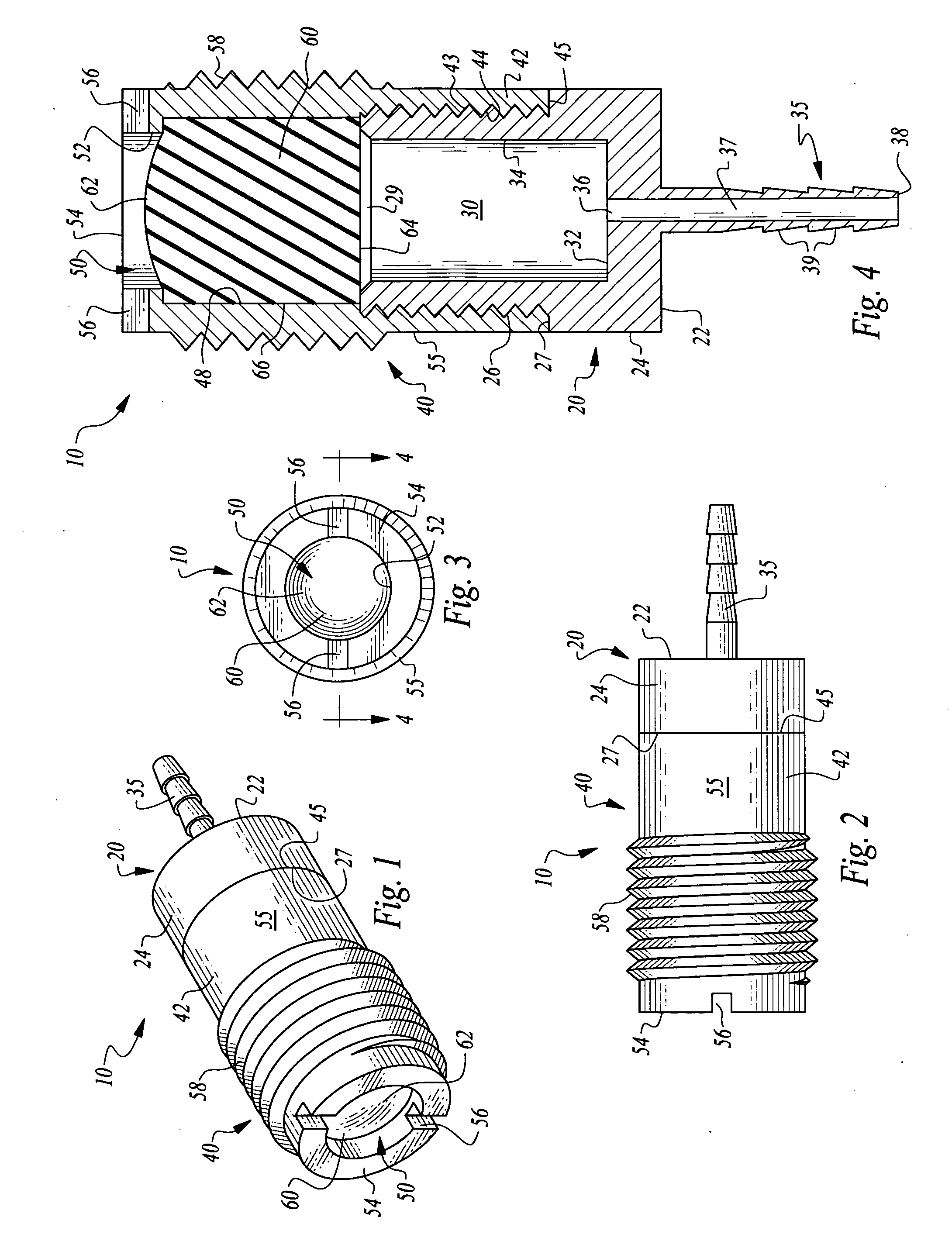
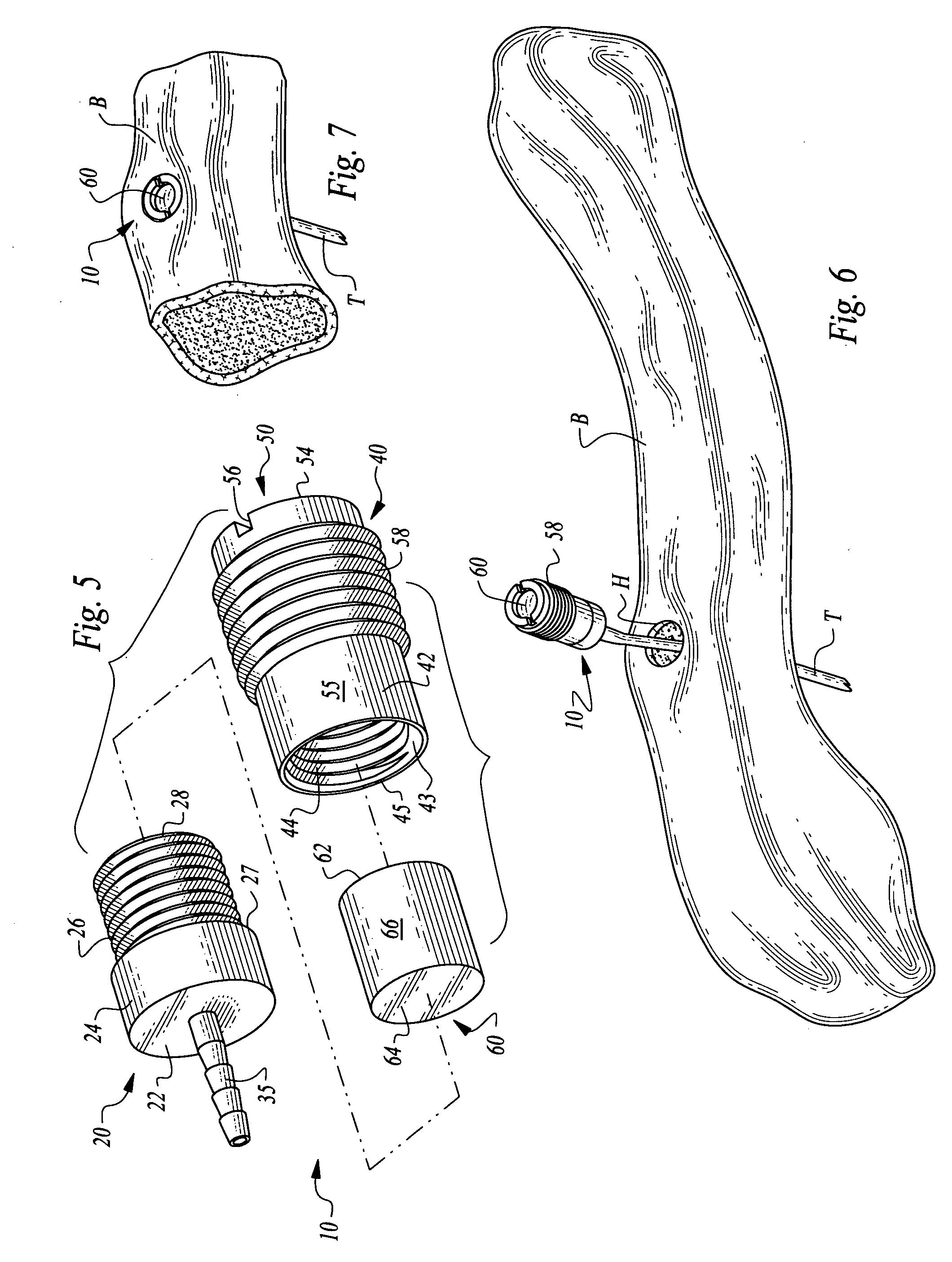
Bone supported vascular access port
InactiveUS20070179456A1Easy to disassembleSecurely holdSurgical needlesMedical devicesVisibilitySubcutaneous implantation
A vascular access port is disclosed for subcutaneous implantation. The port is particularly adapted to be affixed to a bone to securely hold the port in position, to assist medical personnel in finding the port and to decrease a visibility of the port. The port has a chamber therein which is accessed by a needle through a septum adjacent the chamber. The chamber is placed into fluid communication with the vascular structure of the patient, such as through catheter tubing. The chamber is surrounded by a body with an outer surface which is preferably fitted with threads to facilitate secure but removable attachment of the port within a hole in the bone where the port is to be implanted.
Owner:GLENN BRADLEY J
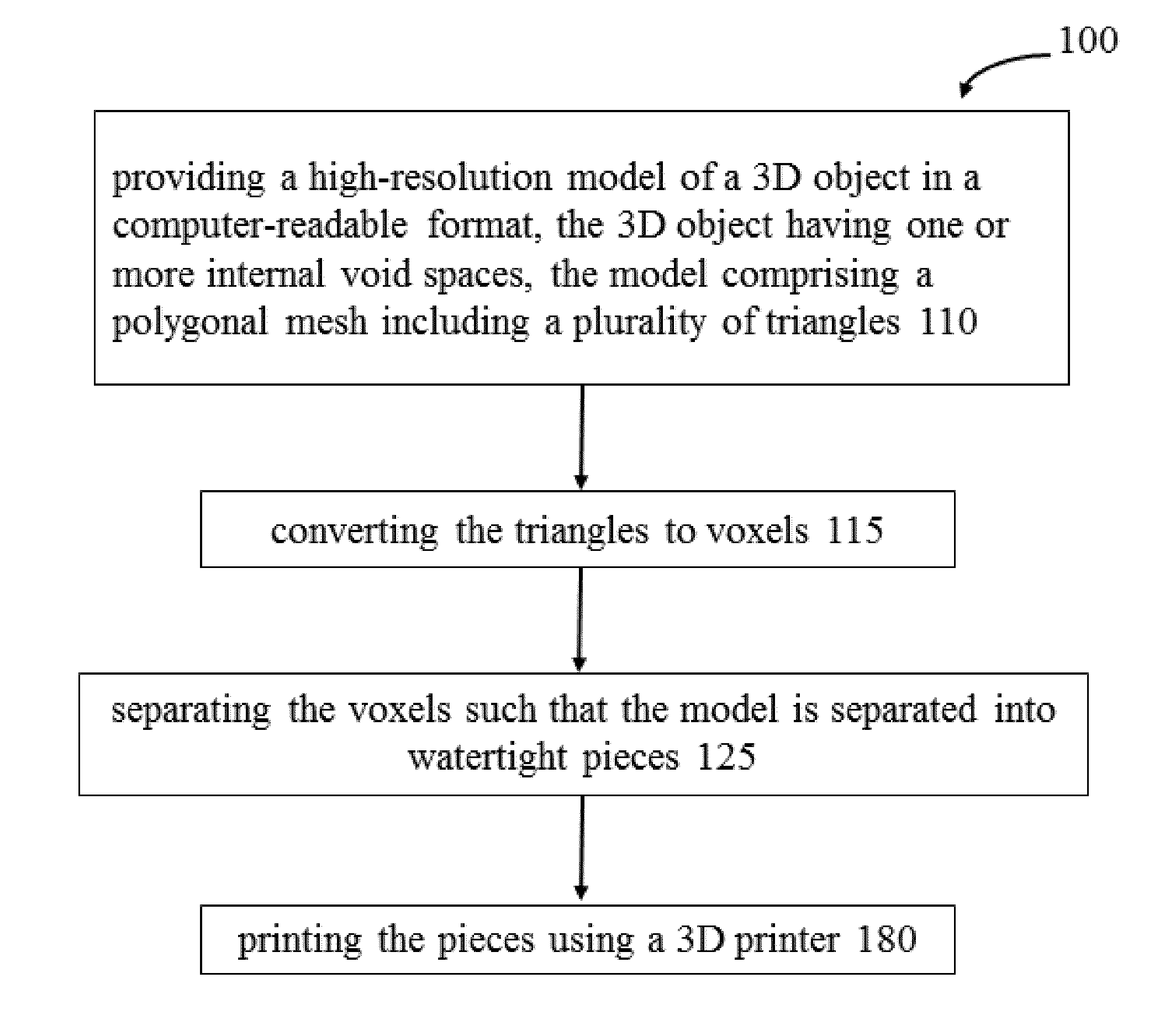
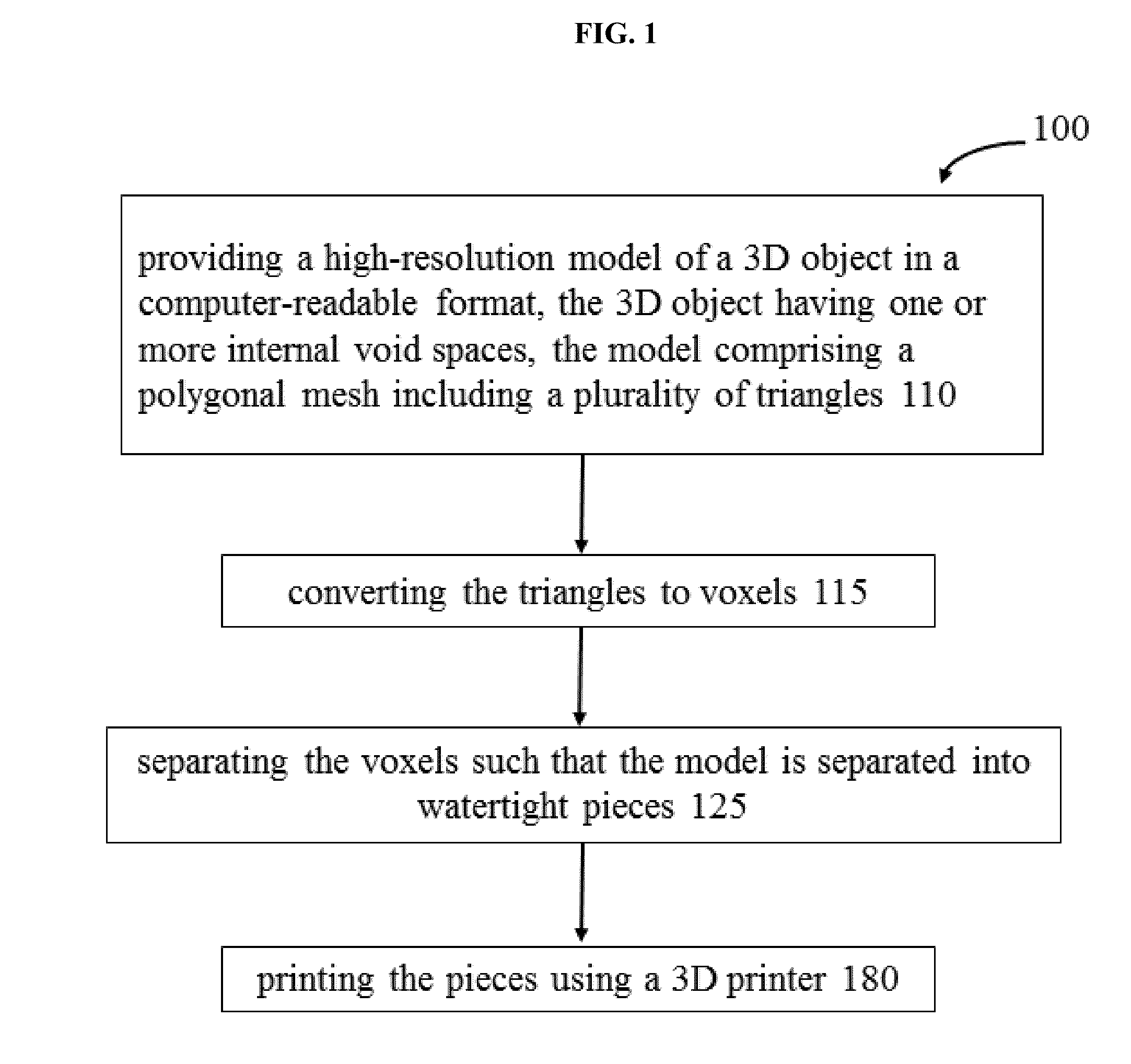
Method and system for rapid prototyping of complex structures
InactiveUS20140031967A1Facilitate user-directed placementHigh densityAdditive manufacturing apparatusManufacturing data aquisition/processingBone structureVoxel
A method is provided for rapid prototyping of complex structures, such as complex bone structures and internal neural and cardiovascular pathways. The method involves loading the triangles from a polygonal mesh computer model of a 3D object having one or more internal void spaces, converting the triangles to voxels, separating the voxels of the model into watertight pieces, and printing the pieces using a 3D printer such as a ZPrinter™. The method allows realistic internal void space representation through removal of excess powder from printing which would otherwise be trapped in the whole object and also allows the application of a resin to internal surfaces which may provide realistic internal object density useful for medical and other applications. Pegs and holes may also be added to and subtracted from the pieces to allow for assembly of the printed object. A system and computer program product is also provided.
Owner:6598057 MANITOBA
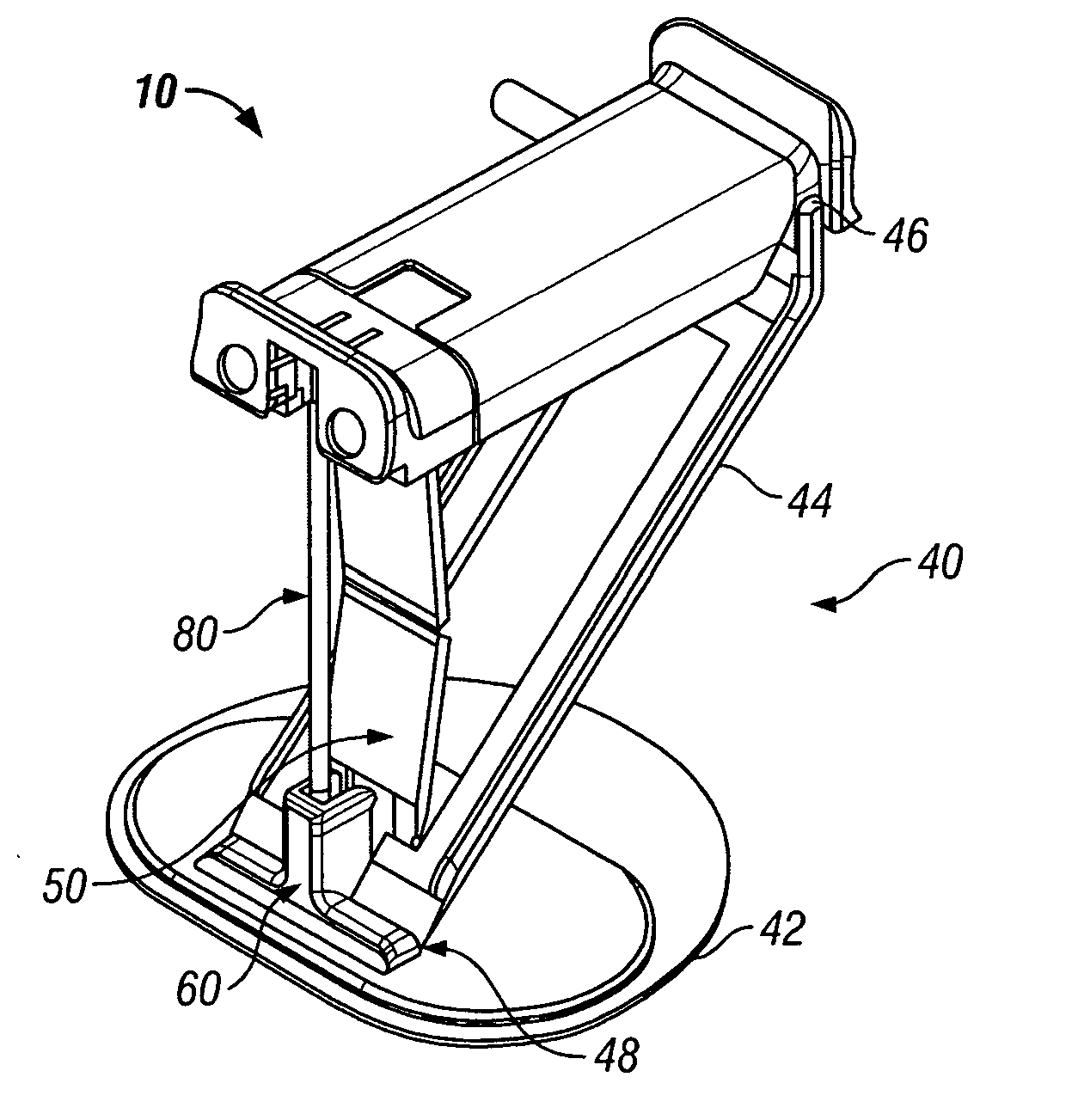
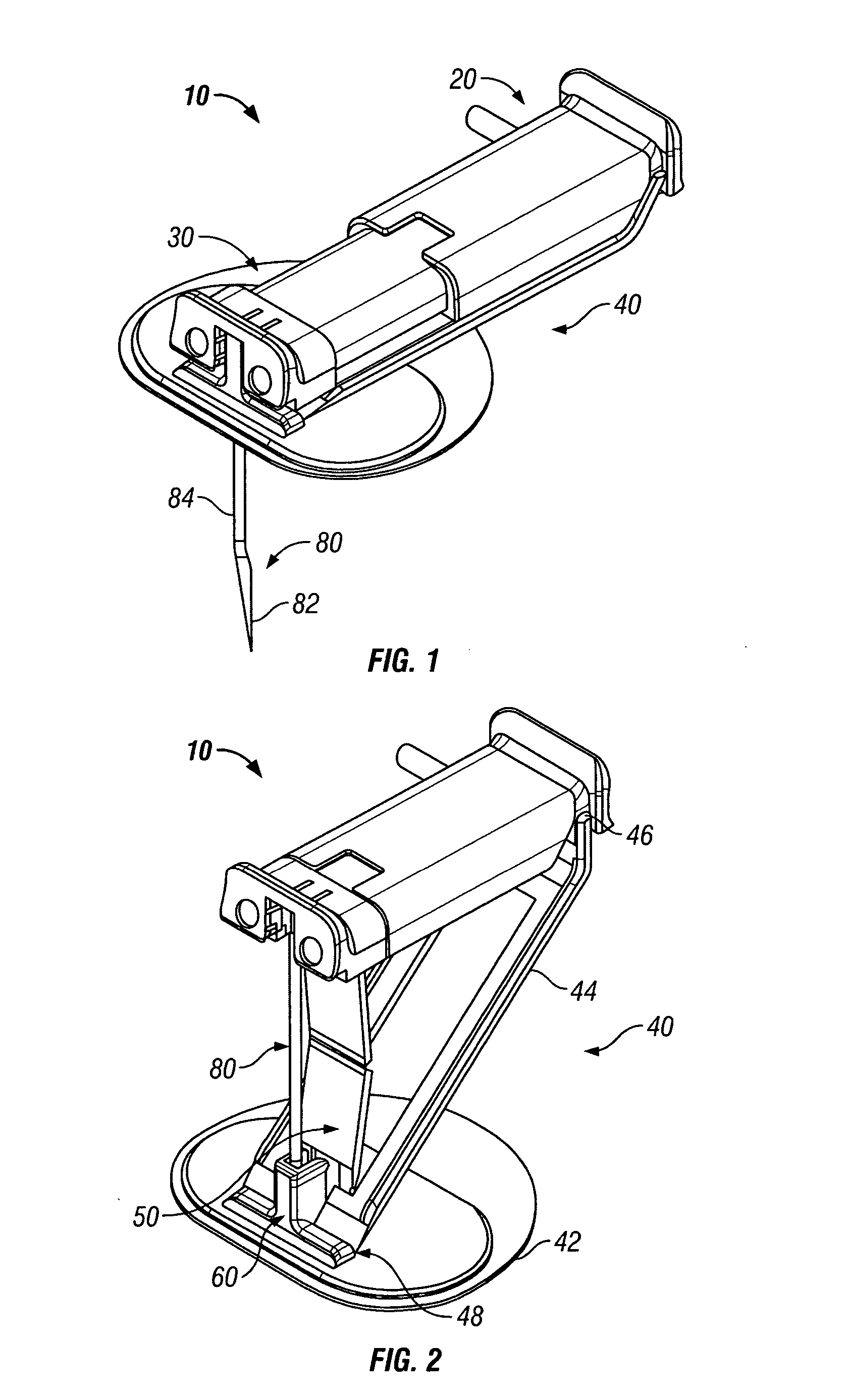
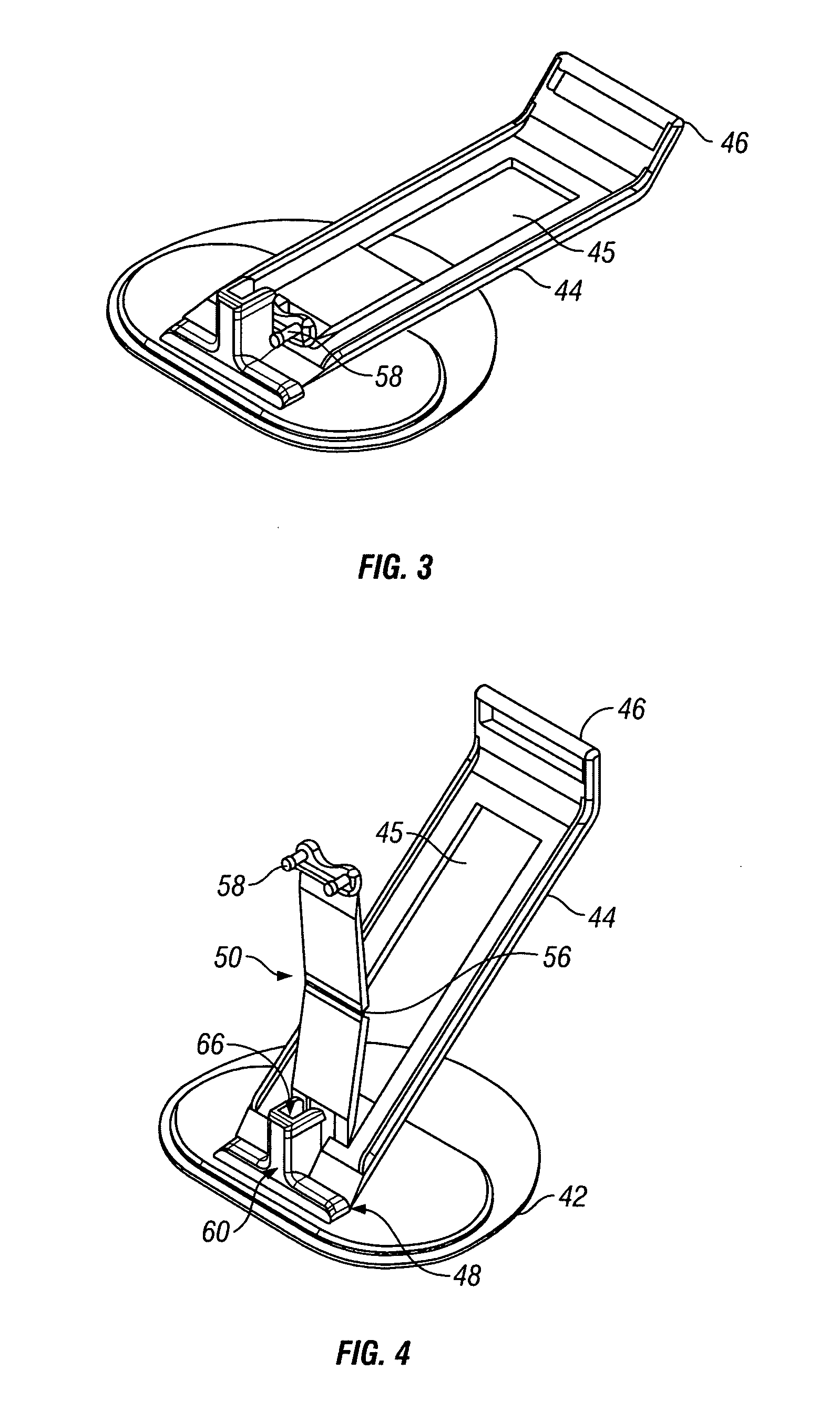
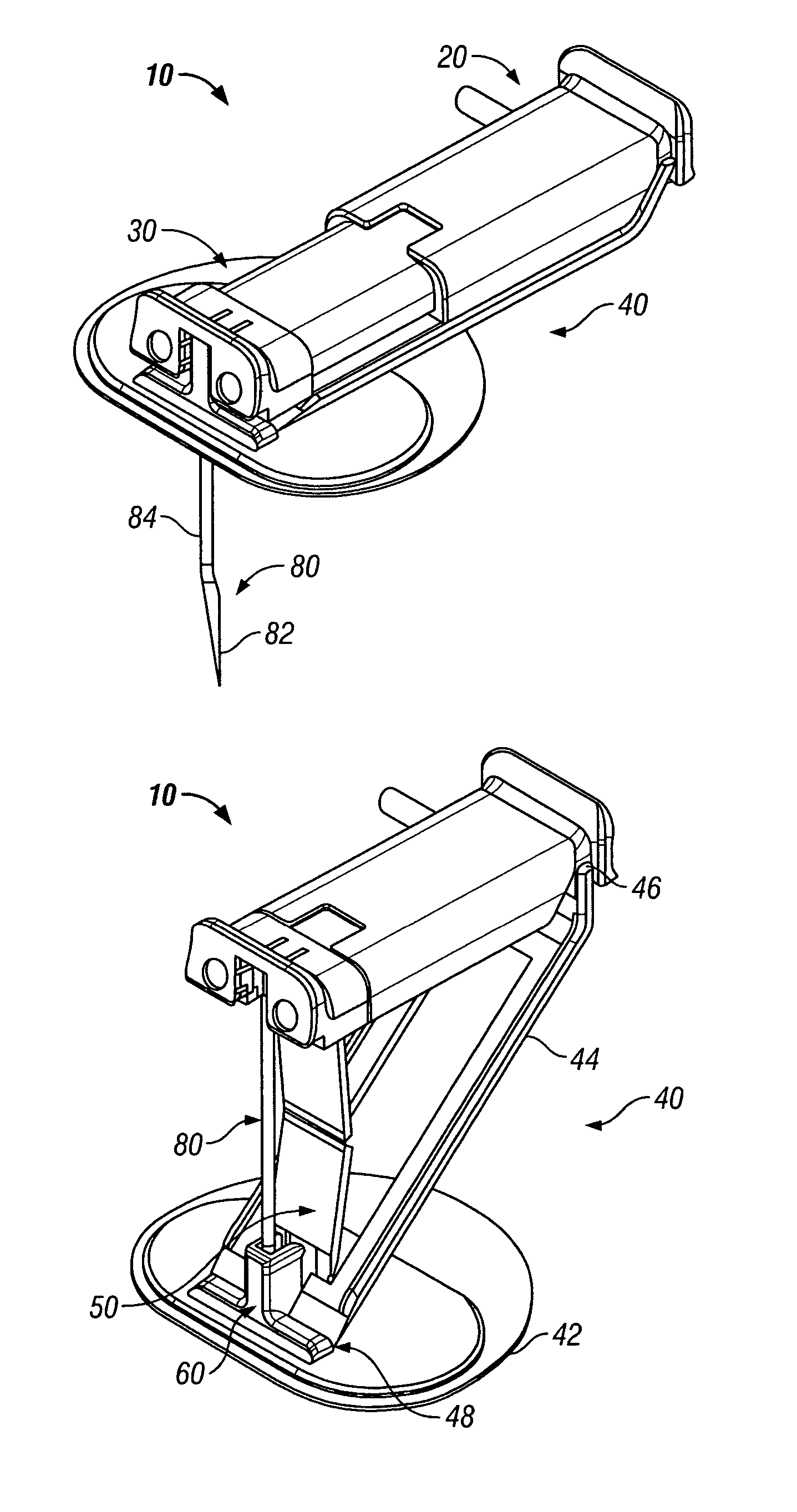
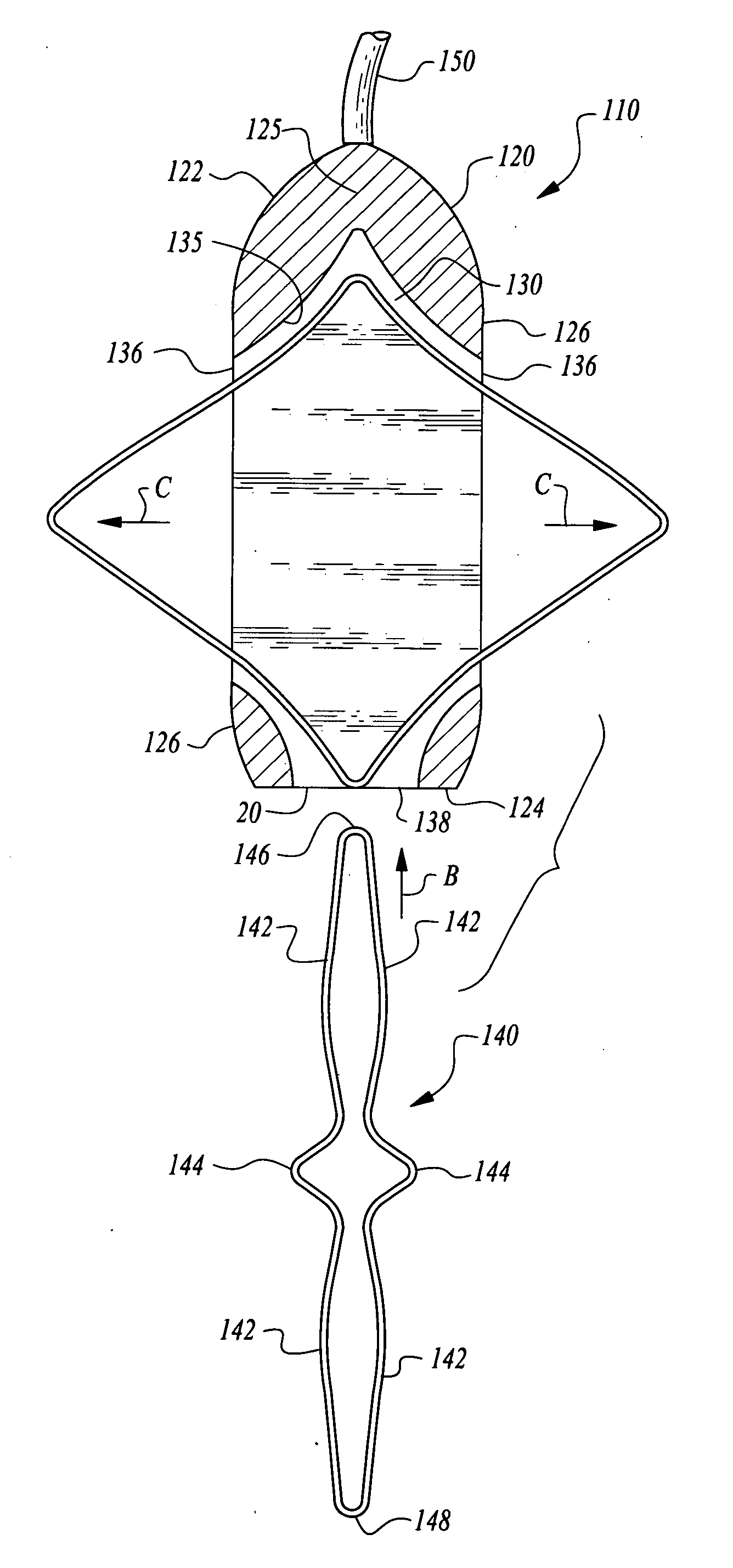
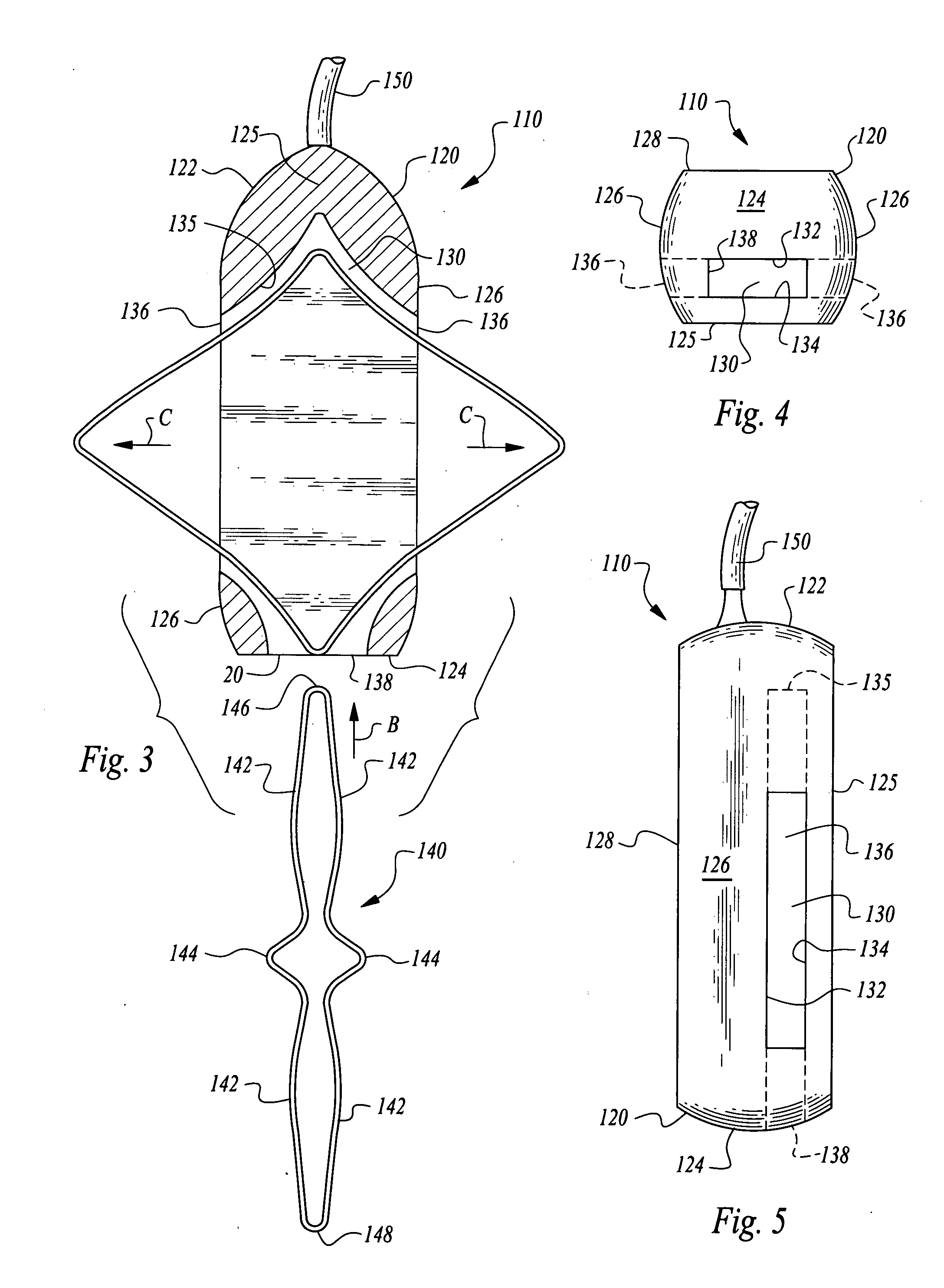
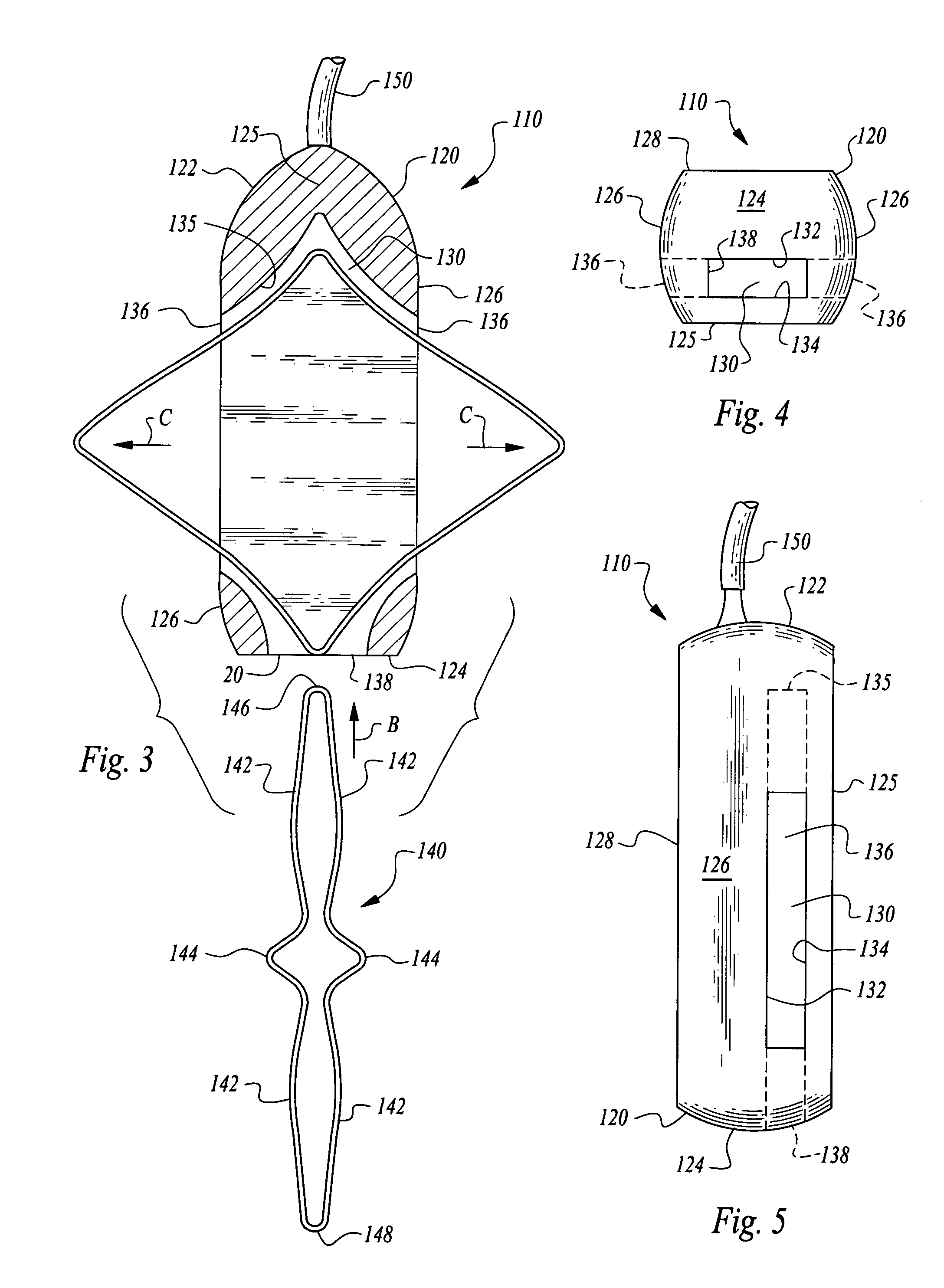
Stabilized implantable vascular access port
The subcutaneously implantable vascular access port has two parts including a body and a wing. The body supports a chamber covered by a septum, with a septum held in place over the chamber by a collar. The chamber is coupleable to a vascular structure, such as through tubing extending from the body, for delivery of medical preparations. The body is preferably elongate in form. The wing is configured to be adjustable in width. In one embodiment the wing rotates relative to the body and has an elongate form similar to that of the body. When the wing is rotated it extends laterally from the body and enhances a stability of the body. In another embodiment, the wing is provided as a deformable wing which can expand laterally out of side openings of a cavern in the body into which the deformable wing is inserted.
Owner:STEALTH THERAPEUTICS
Enhanced stability implantable medical device
InactiveUS20090093765A1Improve stabilitySmall sectionElectrotherapyMedical devicesSubcutaneous implantationInfusion pump
An implantable medical device is provided which has a housing of an elongate form to minimize a size of an incision required for implantation. A stabilizing element is associated with the elongated form housing for the medical device. The stabilizing element transitions from a low profile initial form to a higher width final form to provide the medical device with a stabilized footprint after implantation. The stabilizing element is in the form of a rotating wing in one embodiment. In another embodiment, the stabilizing element is in the form of an expanding loop that can bend to extend out of side openings of a cavity within the housing, to provide such stabilization at the implantation site. The medical device can be in the form of a pacemaker, infusion pump, vascular access port or other subcutaneously implanted medical device.
Owner:STEALTH THERAPEUTICS
Method and device for easy access to subintimally implanted vascular access ports
InactiveUS20100010339A1Easy to useIncrease awarenessMedical devicesIntravenous devicesInjection siteFluorescent polymer
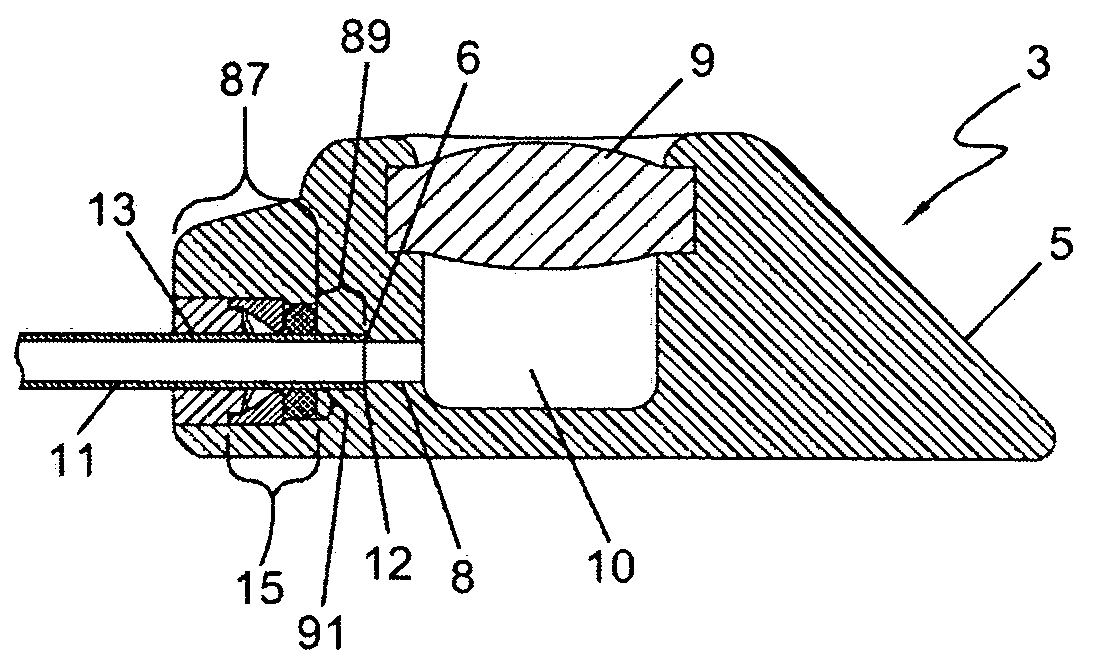
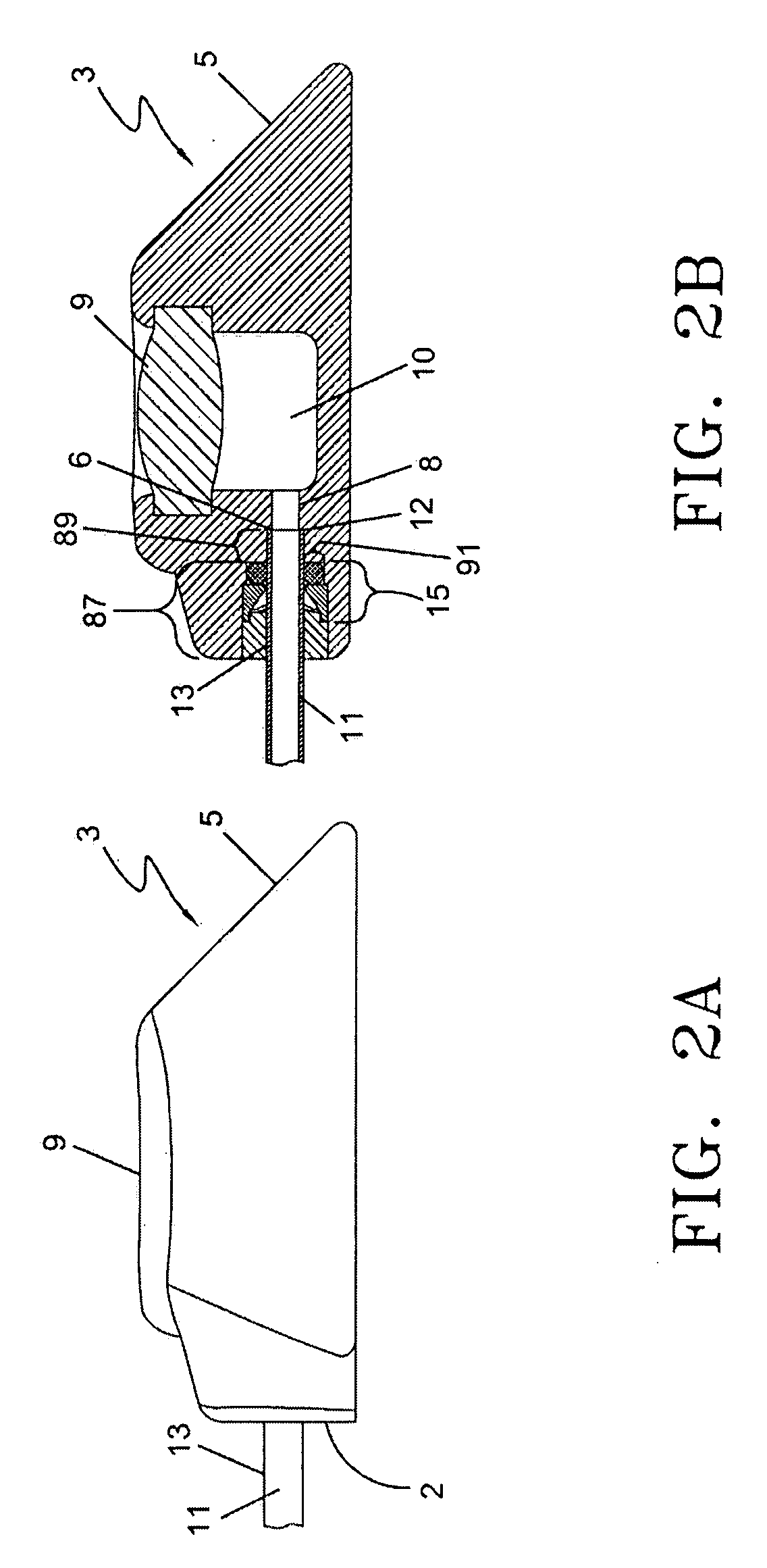
The present invention relates to a novel vascular access port for administering chemotherapeutics and the like that are subintimally implanted and attached to the fascia. By inclusion of one or more UV fluorescing polymers in the port a healthcare worker can shine a UV light in the area of the port and use the fluorescing polymer to find the injection site.
Owner:SMITH CHRISTOPHER K +1
Vascular access device septum venting
ActiveUS20080200904A1Efficient vascular accessMedical devicesCatheterVascular Access DevicesGas passing
A vascular access device may include a septum and a gas permeable vent in communication with at least a portion of the septum. The vent may be capable of venting gas from an extravascular system to which the vascular access device is capable of attaching. A method of venting a medical device may include providing a vascular access device having a septum and forming part of an extravascular system, providing a gas permeable vent in communication with at least a portion of the septum, and venting gas from the extravascular system through the gas permeable vent of the device.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Cardiovascular access catheter with slit valve
ActiveUS7491192B2Minimize injuryIncreased durabilityCatheterIntravenous devicesPressure differenceBiomedical engineering
Two-way, three-position and one-way, two-position slit valves in cardiovascular access catheters with closed distal ends have slit geometries configured to overcome adhesion between opposed abutting slit faces, when pressure differentials are applied between the interior and the exterior of the catheter. Portions of the slit are oriented at a non-zero angle relative to the longitudinal axis of the catheter causing shear forces to be generated in abutting slit faces. Shear forces arise from tangential, radial, or longitudinal stresses generated in the catheter body. Slit geometries are planar or curved or include multiple end-to-end connected slit subsections. If a slit partially circumscribes a portion of the adjacent outer wall of the catheter body, restraint to outward and inward movement on that portion is reduced. Slit valves are configured to open inwardly to aspirate fluids, to open outwardly to infuse fluids, or both.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Implantable vascular access system
ActiveUS20120245536A1Easy to moveAvoiding operator errorMedical devicesIntravenous devicesAntithromboticReoperative surgery
The invention relates to implantable vascular access ports that can release agents such as antibiotics, anti-thrombogenics and anti-proliferatives. The invention also relates to ports having locking mechanisms that prevent accidental disengagement, and structures that facilitate surgical implantation and provide for long-term stability and use of the port.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Enhanced stability implantable medical device
InactiveUS8209015B2Improve stabilityAdverse impact functionalityElectrotherapyMedical devicesSubcutaneous implantationImplantation Site
An implantable medical device is provided which has a housing of an elongate form to minimize a size of an incision required for implantation. A stabilizing element is associated with the elongated form housing for the medical device. The stabilizing element transitions from a low profile initial form to a higher width final form to provide the medical device with a stabilized footprint after implantation. The stabilizing element is in the form of a rotating wing in one embodiment. In another embodiment, the stabilizing element is in the form of an expanding loop that can bend to extend out of side openings of a cavity within the housing, to provide such stabilization at the implantation site. The medical device can be in the form of a pacemaker, infusion pump, vascular access port or other subcutaneously implanted medical device.
Owner:STEALTH THERAPEUTICS
Terminal clamp for a moisture sensor for monitoring a vascular access
ActiveUS20130072870A1Produced cost-effectivelyReliable electrical contactDialysis systemsMedical devicesMoisture sensorBiomedical engineering
A terminal clamp for a moisture sensor to be placed on a patient's skin in order to monitor a vascular access to a patient includes first, lower and second, upper legs for clamped fixing of terminal tab of moisture sensor, rear end pieces of the legs being connected. The terminal clamp includes terminal contacts for contacting electrical contact points of terminal tab, and a guide piece having a slot-shaped cutout for receiving terminal tab. Slot-shaped cutout of guide piece is bounded laterally by two stop elements so that terminal tab is held in terminal clamp in a predetermined position, in which terminal contacts of terminal clamp contact the electrical contact points of terminal tab. Upper leg comprises a latching device, which is fixed in slot-shaped cutout in a snap-in manner when terminal clamp is closed to lock upper leg in position on lower leg.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Stabilized elongate implantable vascular access device
InactiveUS20080249509A1Easy to findEasy injectionMedical devicesCatheterVascular Access DevicesSurgery
A vascular access port is described that is elongate in form. A distal end is coupled to a tube which leads into a body lumen. A proximal end has a head thereon with a septum which can be repeatedly penetrated by a needle and reseal, for repeated administration of medications or other compositions through the port and into the body of the patient. A wing is attached to the body that has two positions including a streamlined first position for implantation and a wider second position for stabilization of the port after implantation. A stay is preferably also provided to abut the wing when in the second position to keep the wing in the second position when fully deployed.
Owner:STEALTH THERAPEUTICS
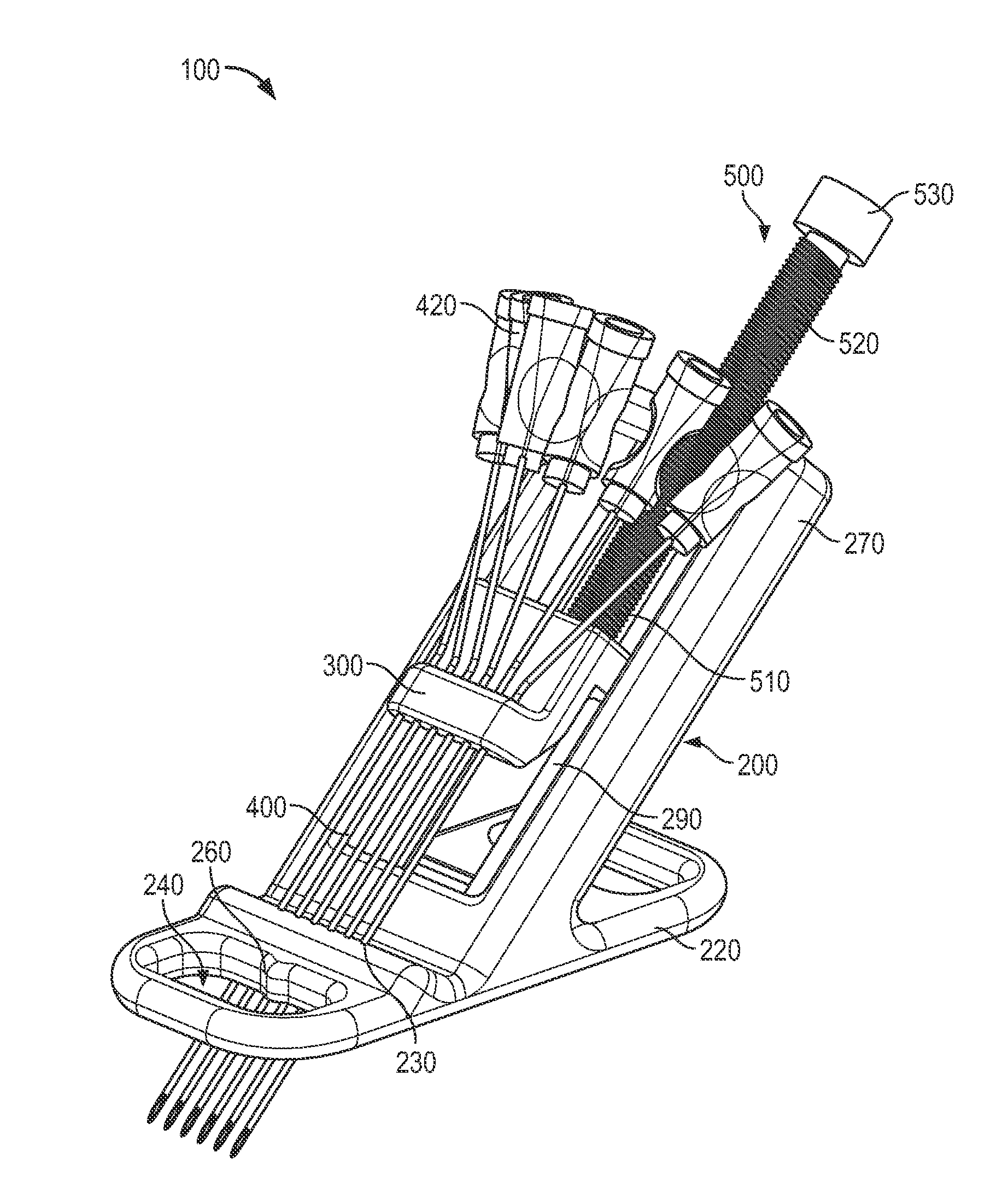
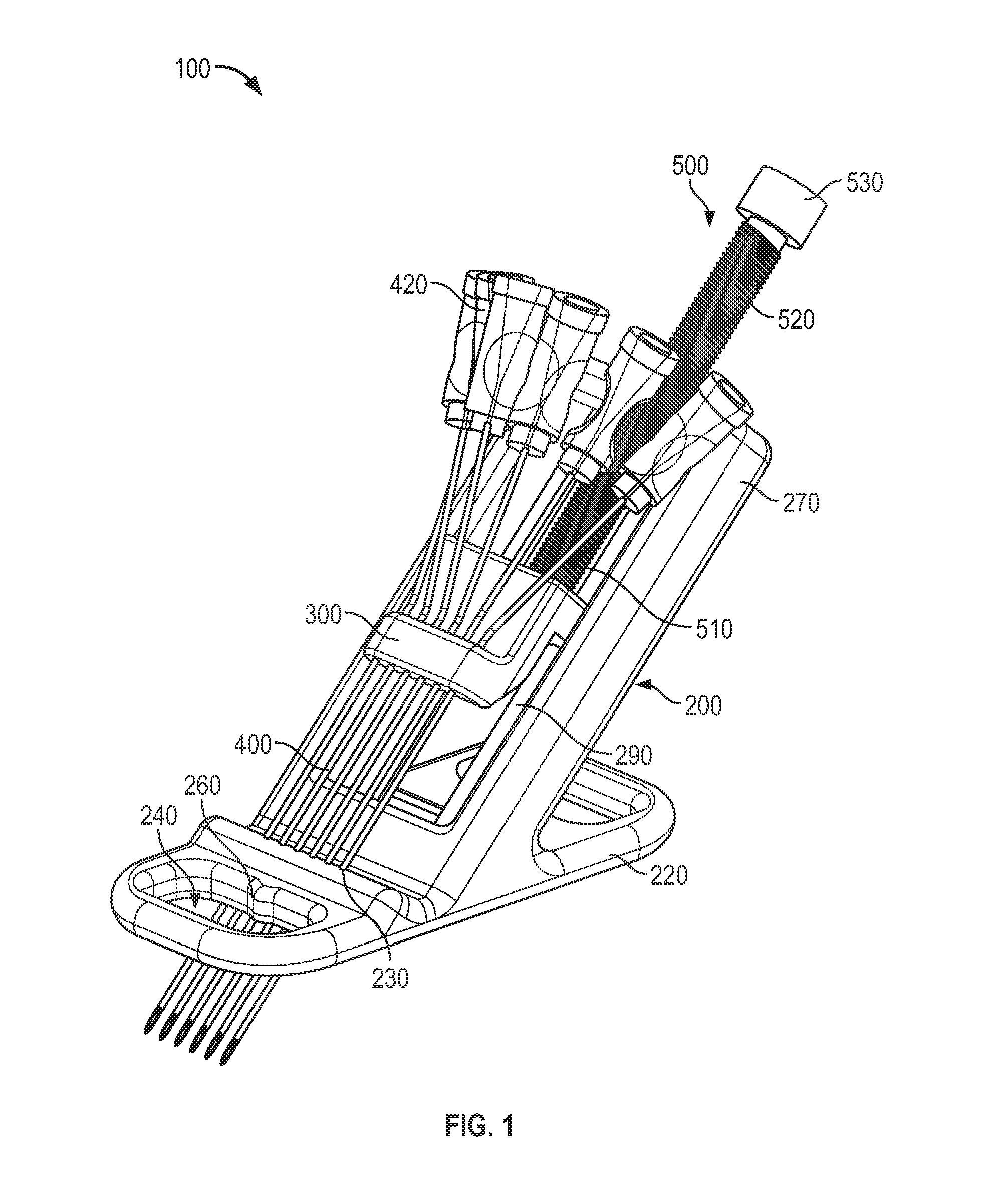
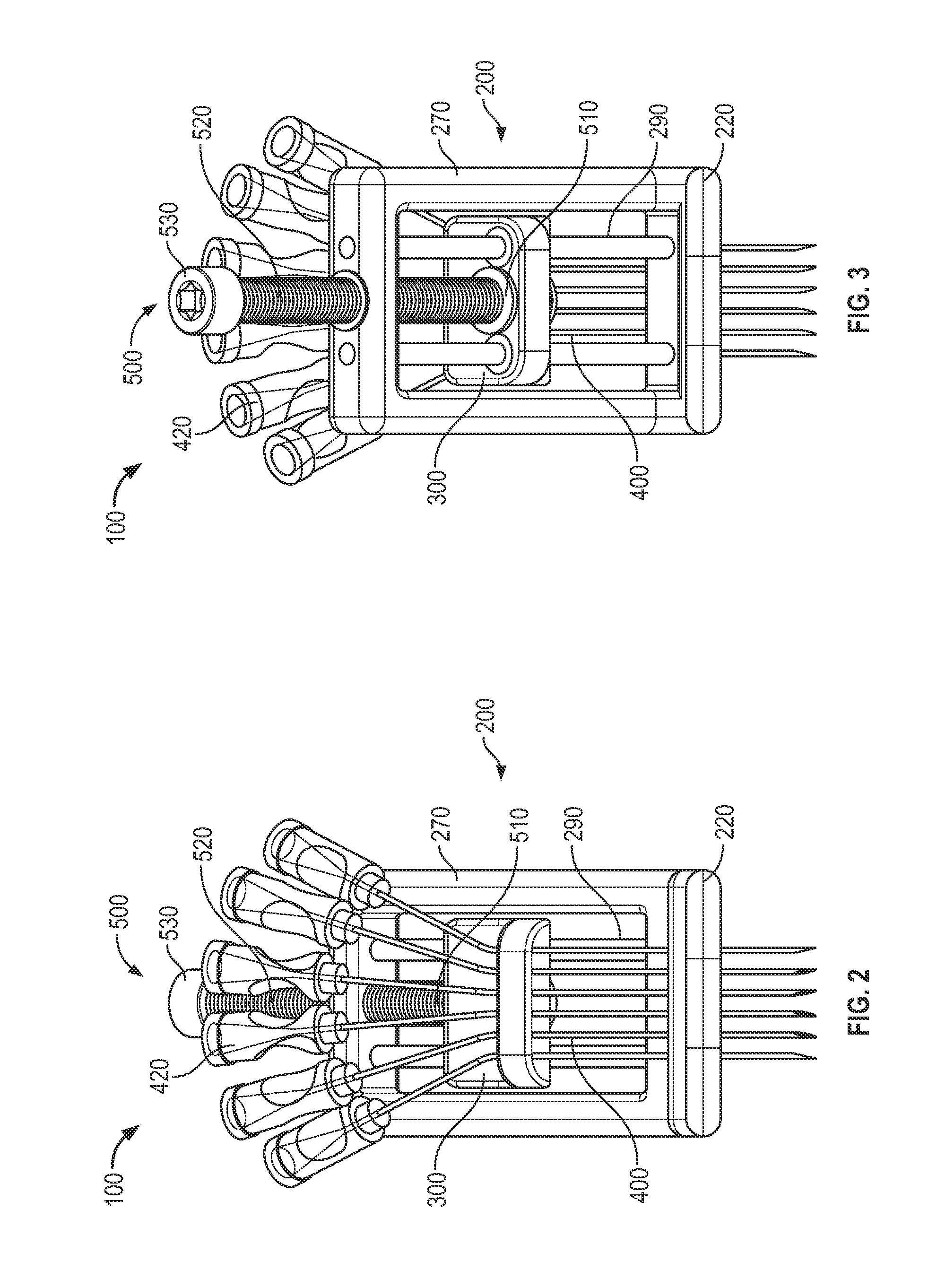
Vascular access systems and methods of use
ActiveUS20140249504A1Optimized lateral spanningEnhance proper vascular accessGuide needlesMedical devicesEngineeringSurgery
A vascular access system and method of use for said system. The vascular access system generally comprises a body member; a shuttle member movably coupled to the body member; and a plurality of access needles fixedly coupled to the shuttle member and extending from the body member to penetrate a patient's skin.
Owner:PRYTIME MEDICAL DEVICES INC
Catheters and Related Devices for Forming Passageways Between Blood Vessels or Other Anatomical Structures
InactiveUS20100094259A1Precise rotation controlPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasAnatomical structuresDistal portion
The inventions described in this patent application include i) a torqueable introducer sheath which is useable in conjunction with a transvascular passageway forming catheter to effect precise rotational control of the catheter; ii) an anchorable guide catheter which is useable in conjunction with an intravascular imaging catheter and a transvascular passageway-forming catheter to effect precise positioning and aiming of the passageway-forming catheter; iii) a passageway forming catheter having a torqueable proximal portion to facilitate precise rotational positioning of the distal portion of the catheter; iv) a deflectable-tipped passageway forming catheter, v) various markers and other apparatus useable in conjunction with any of the passageway-forming catheters to facilitate precise positioning and aiming of the catheter, and vi) an apparatus which may be formed within a catheter to prevent a member, apparatus of flow of material from being inadvertently advanced through a lumen of the catheter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
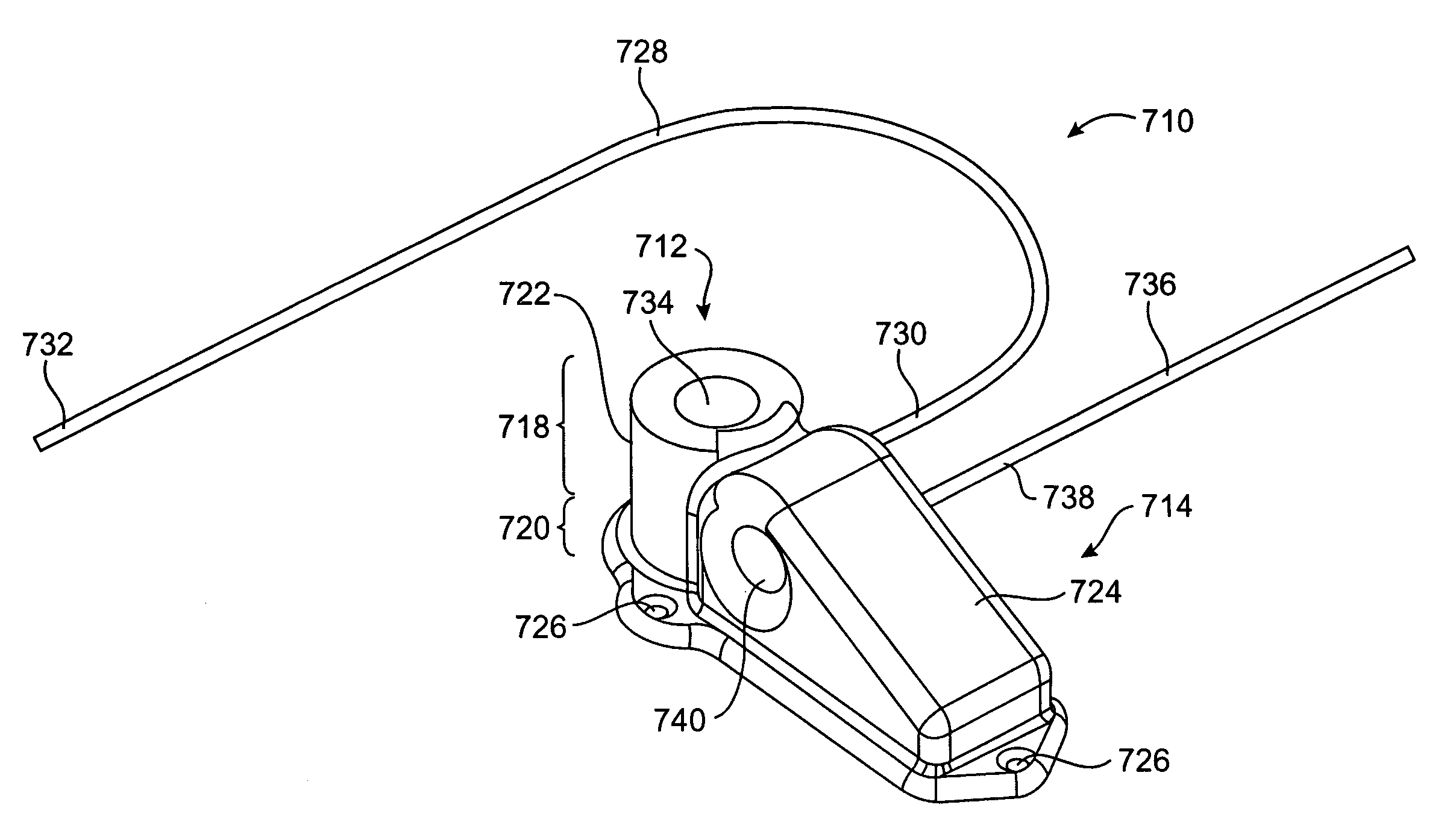
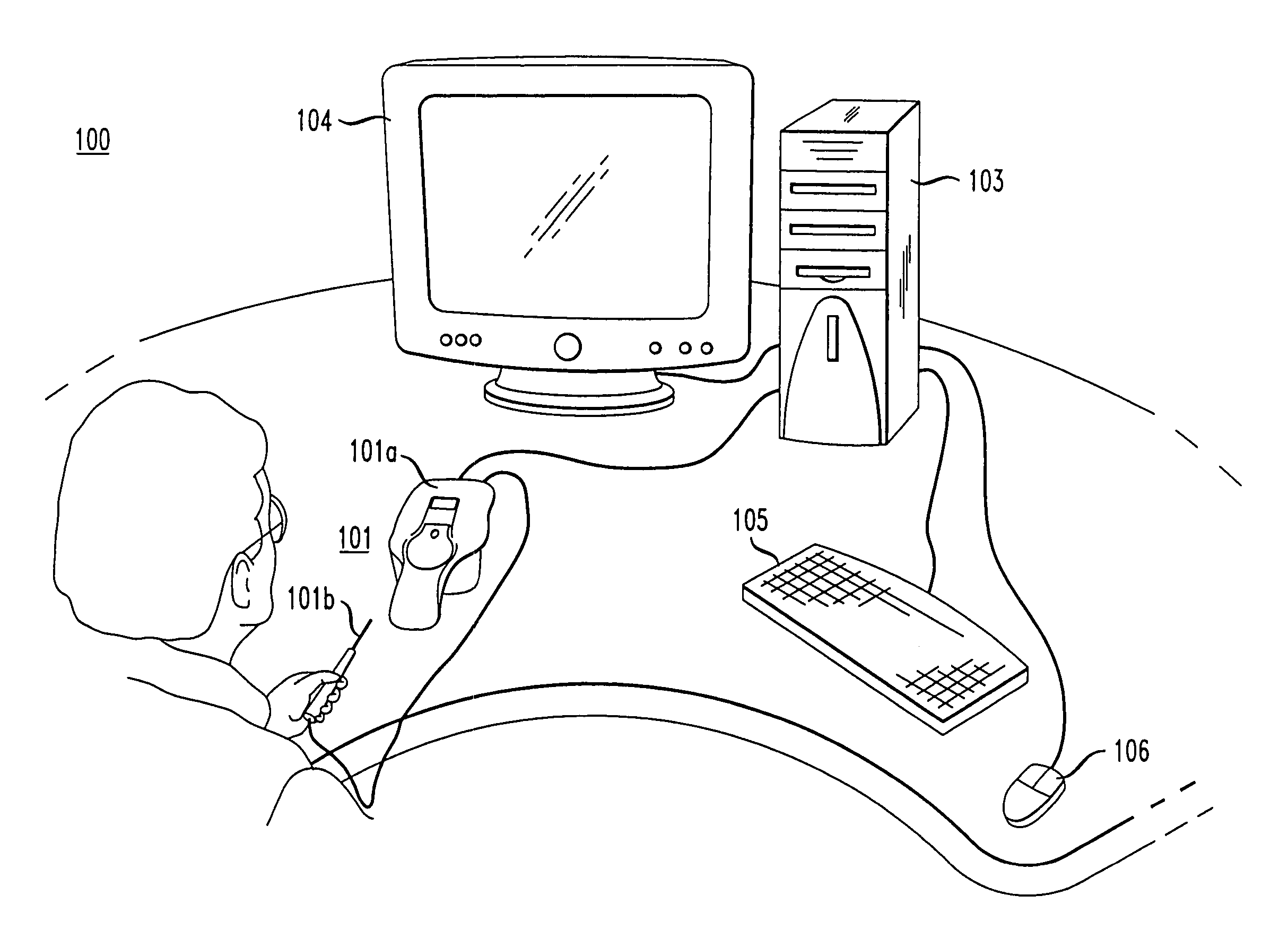
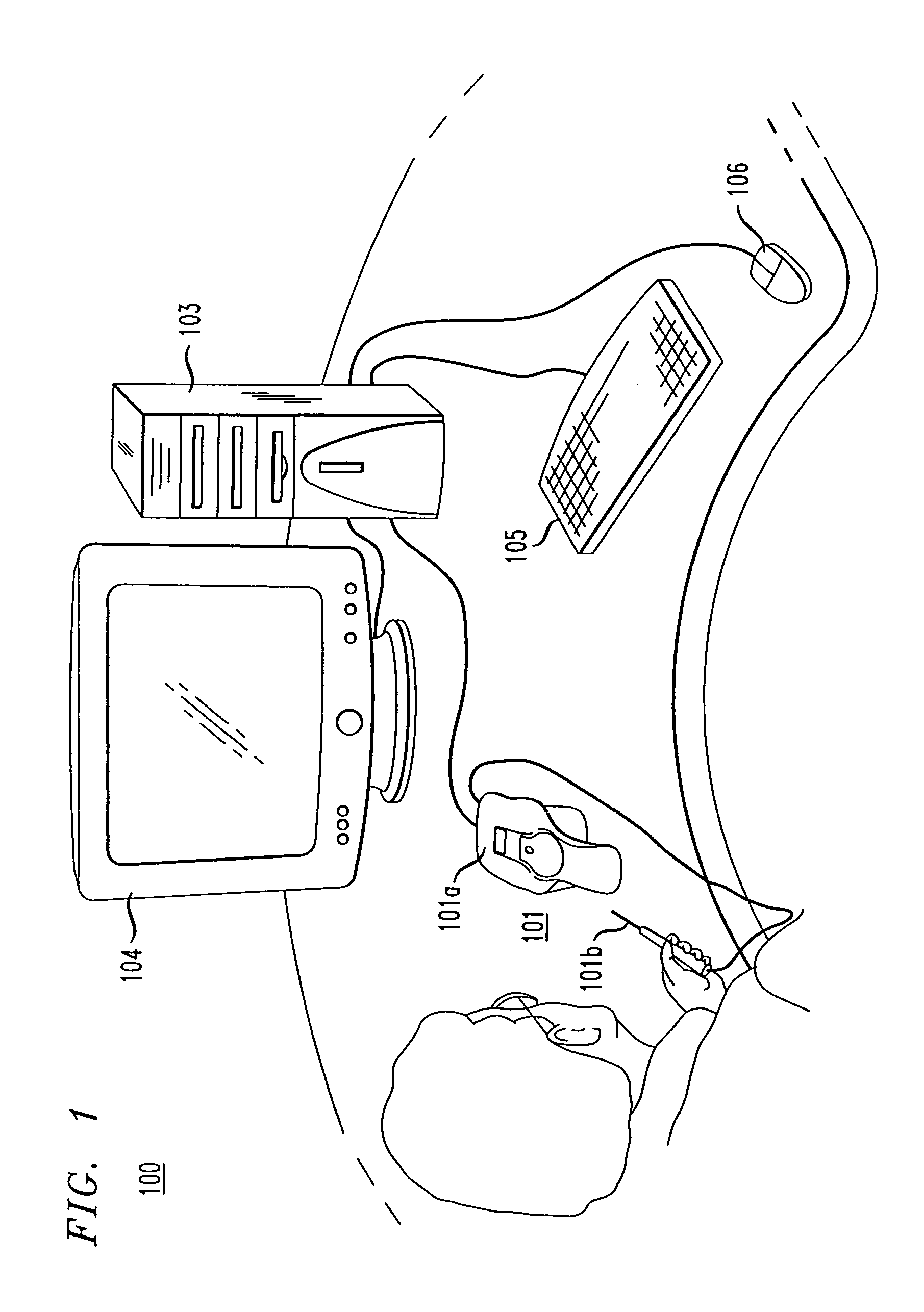
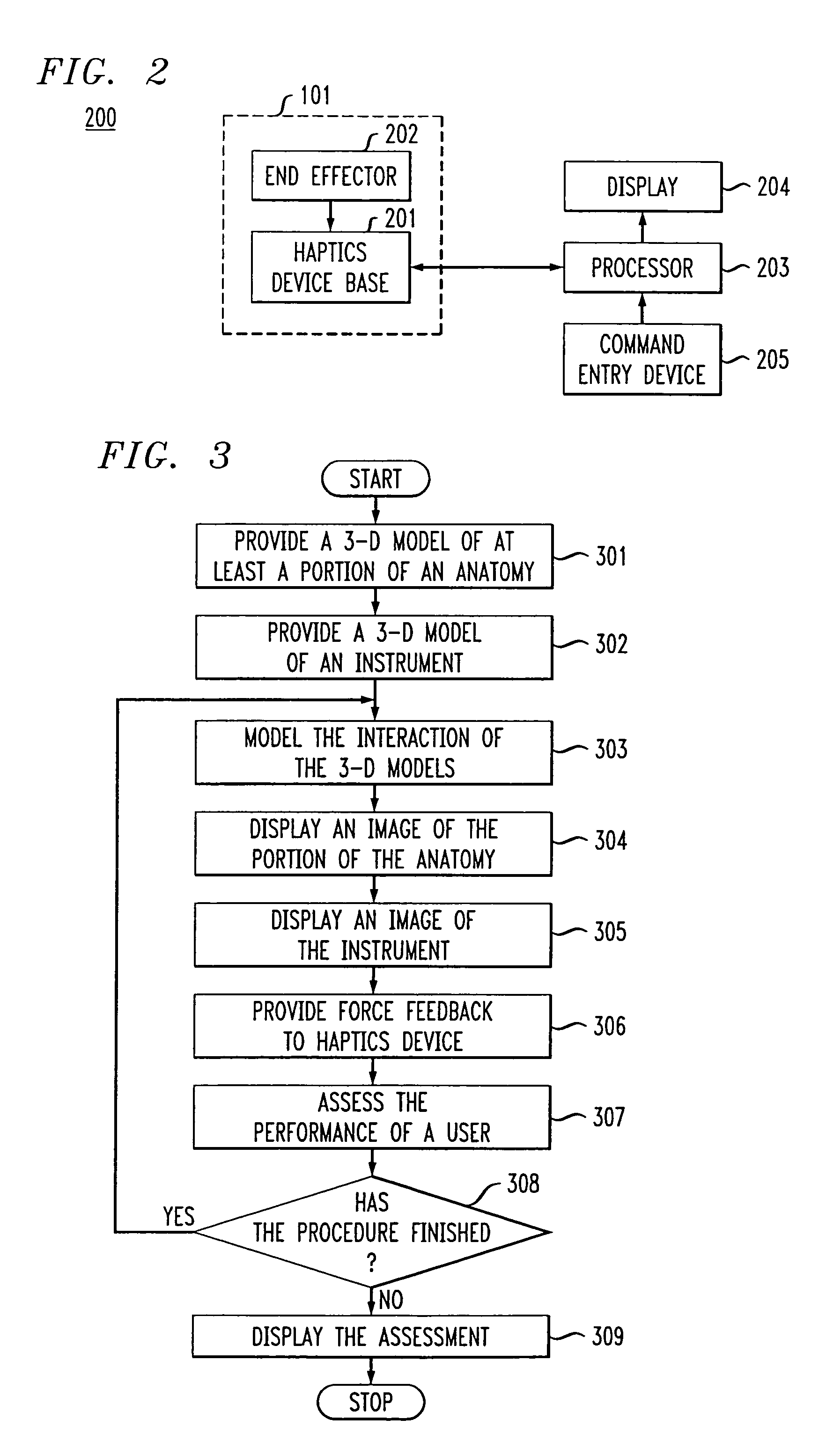
Vascular-access simulation system with three-dimensional modeling
The illustrative embodiment is a simulation system for practicing vascular-access procedures without using human subjects. The simulator comprises a data-processing system and a haptics device. The haptics device provides the physical interface at which an end effector, which is representative of a medical instrument (e.g., a needle, catheter, etc.), is manipulated with respect to a haptics-device base to simulate instrument insertion. The data-processing system, by exchanging signals with the haptics device, provides a three-dimensional simulation that includes the resistive forces that a medical practitioner would experience if the simulated procedure were an actual procedure that was being performed on a real anatomy (e.g., human arm, etc.). The simulator displays the ongoing simulation and assesses the performance of its user.
Owner:LAERDAL MEDICAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com