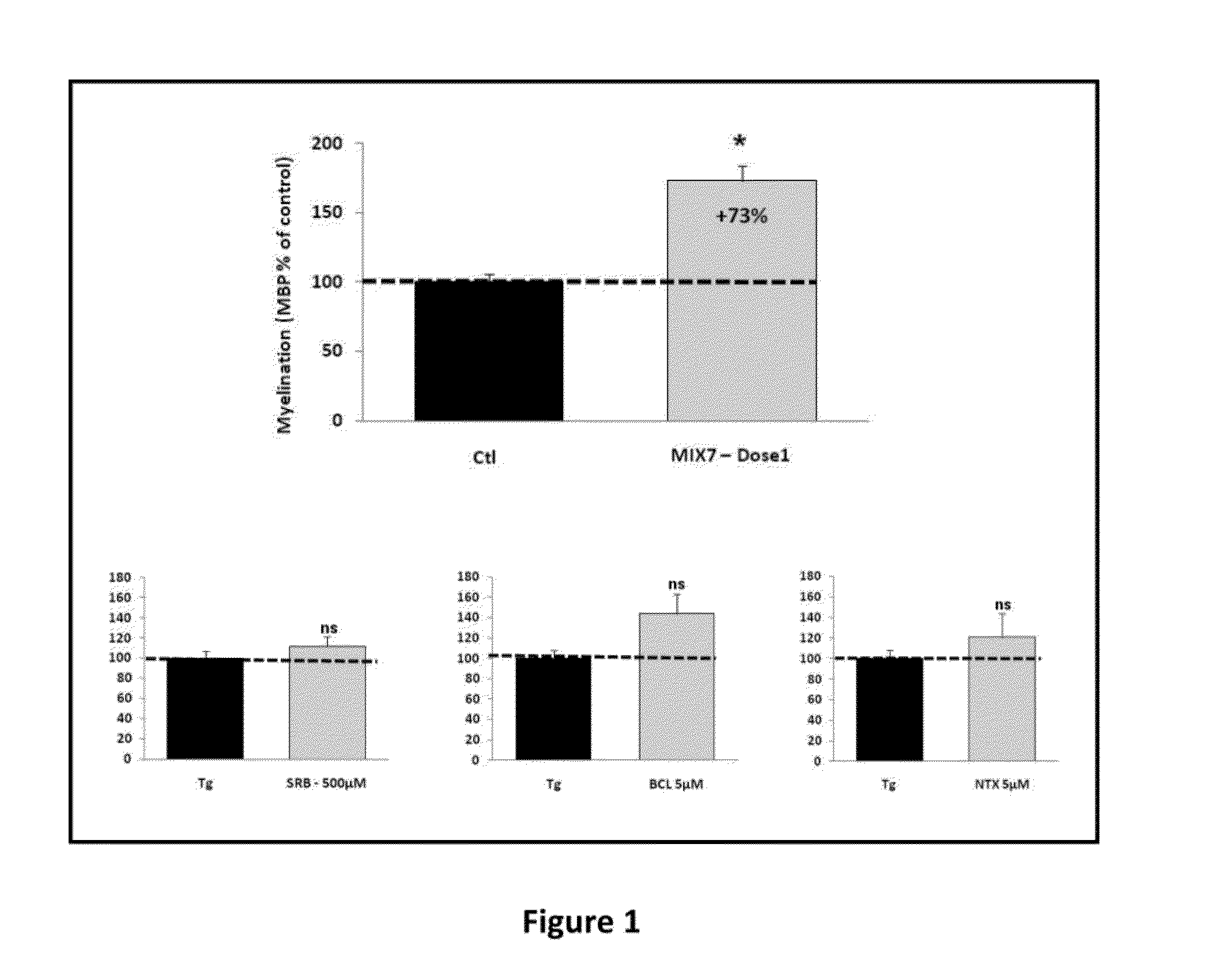
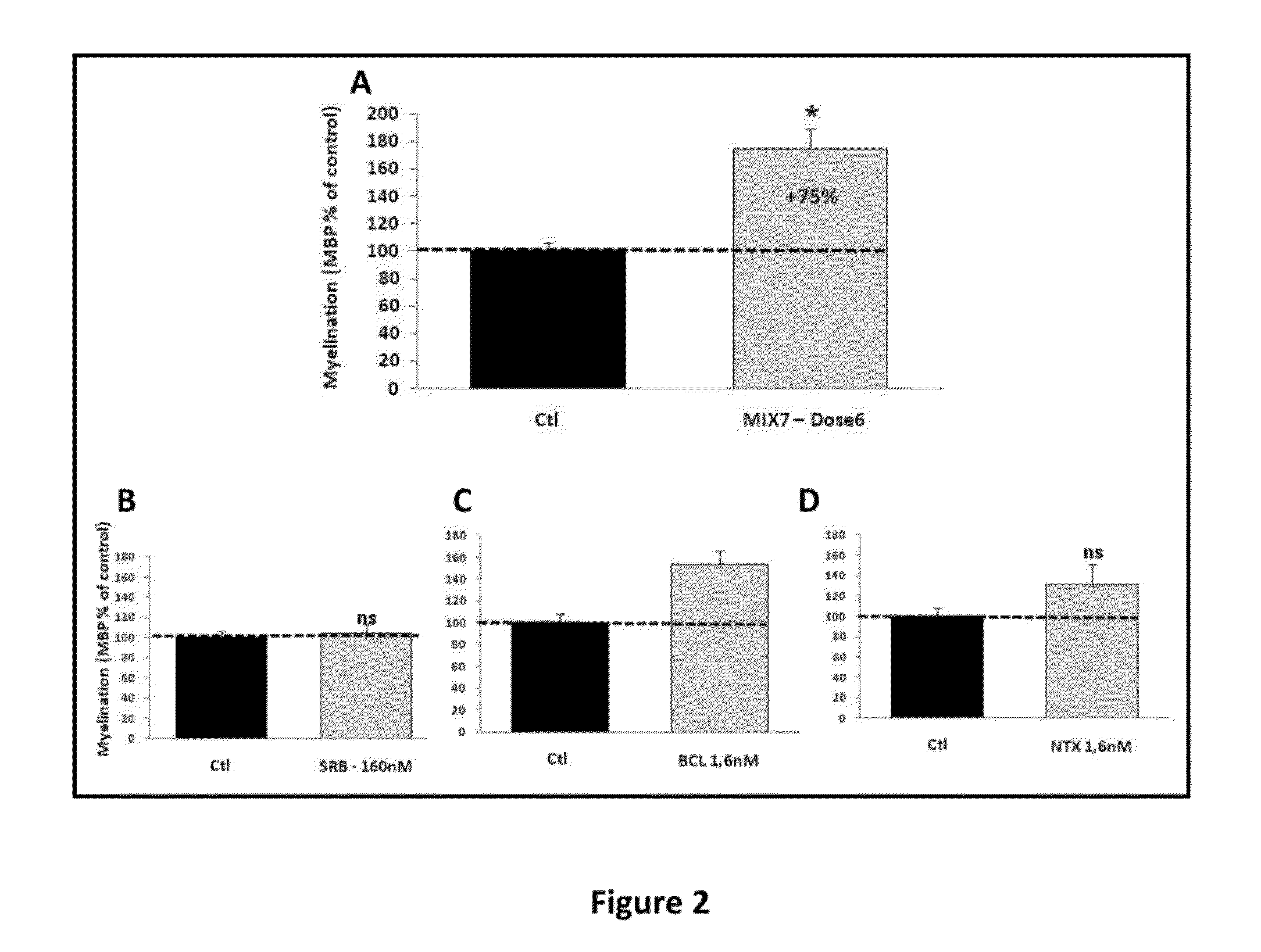
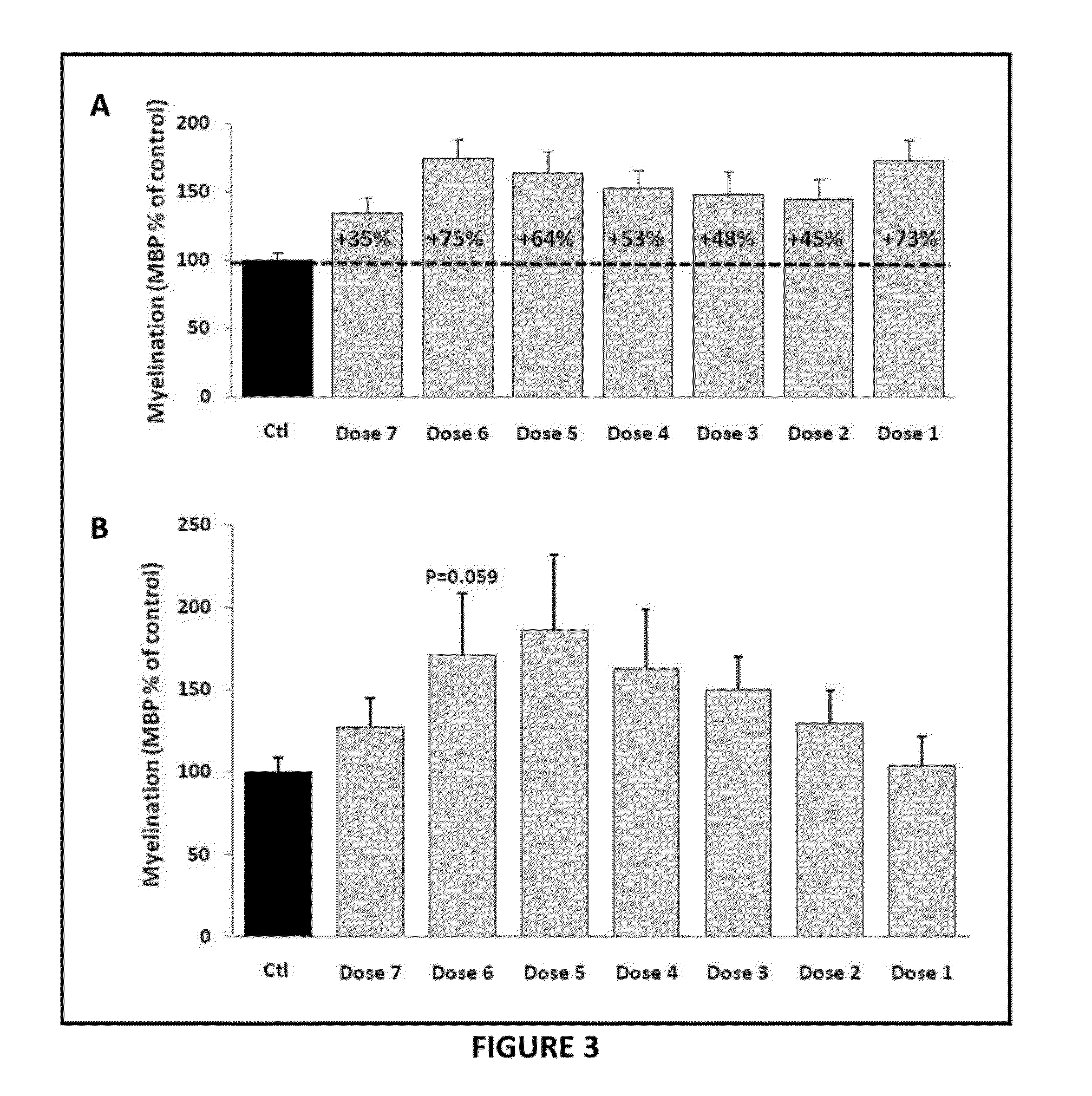
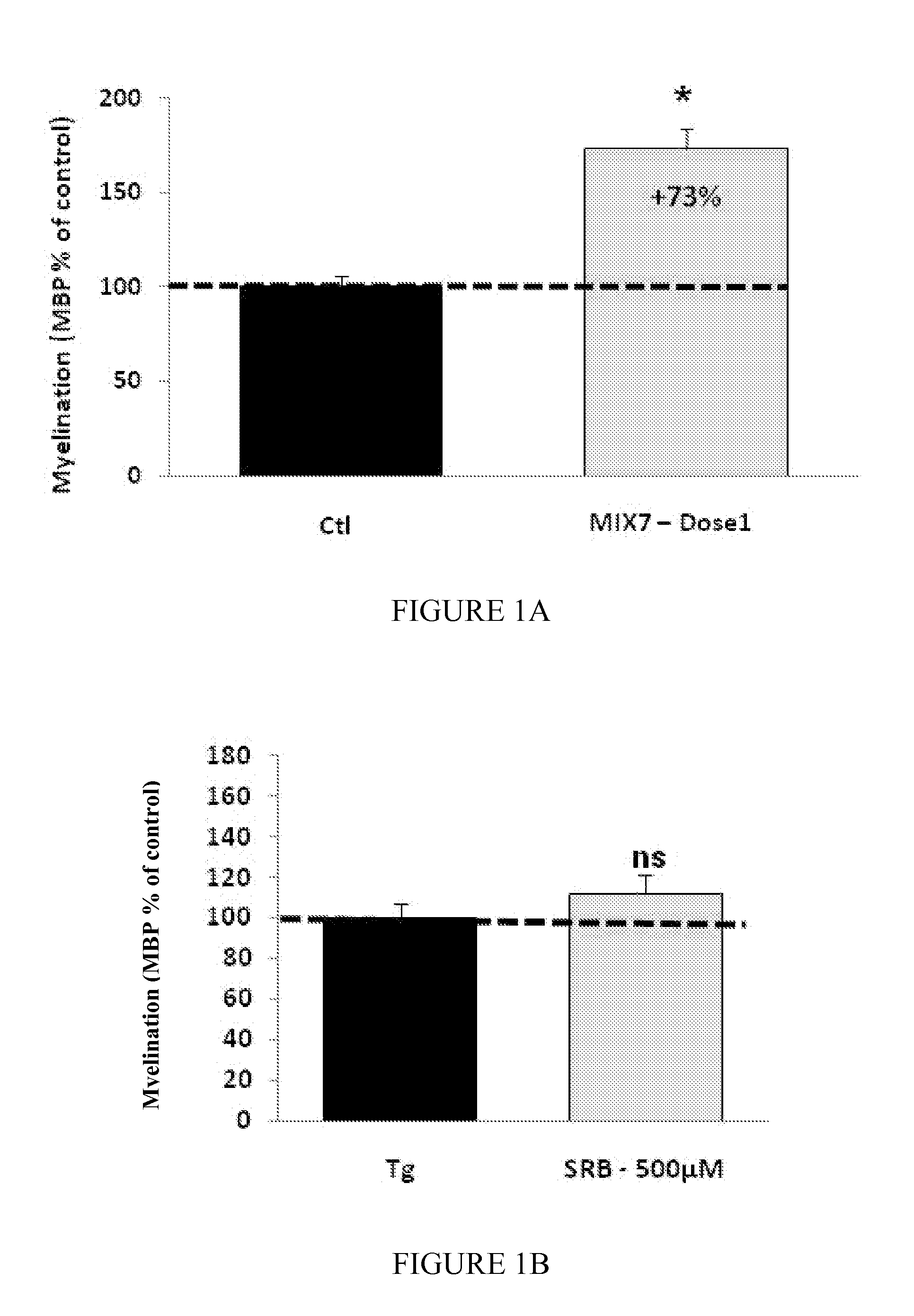
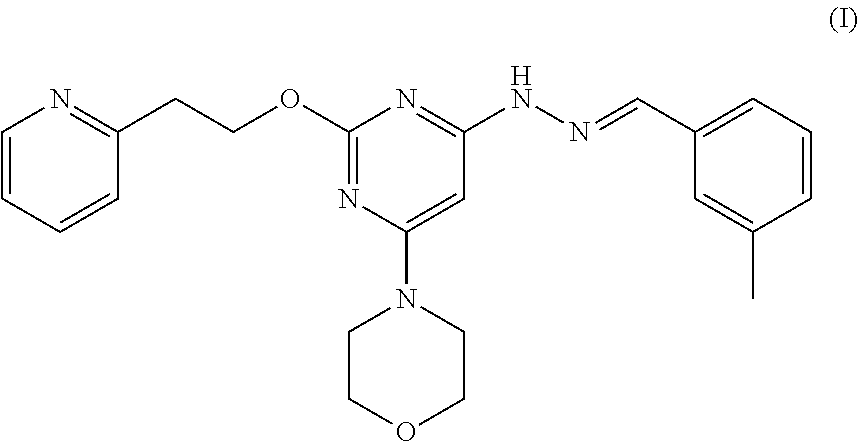
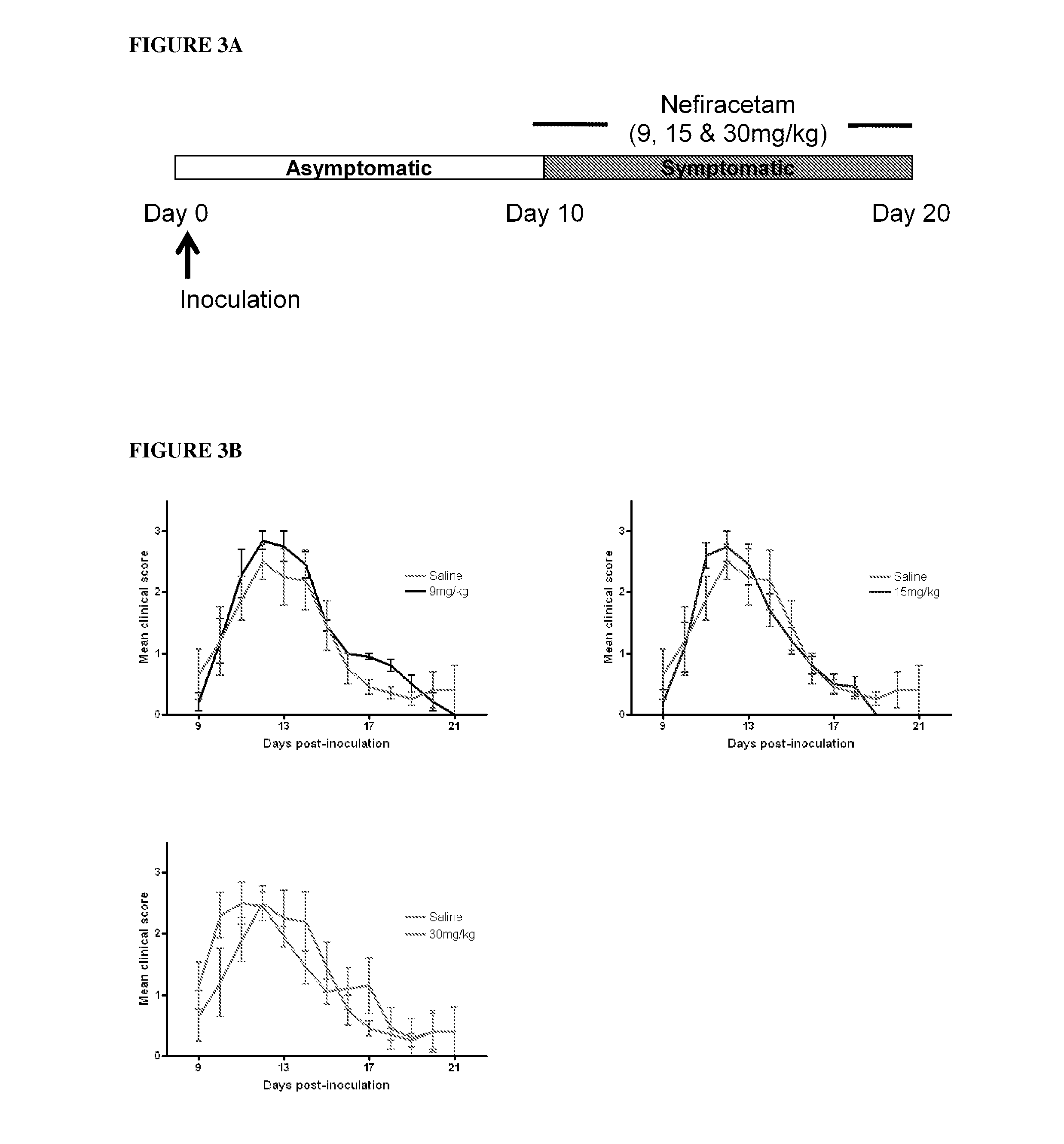
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Marie disease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
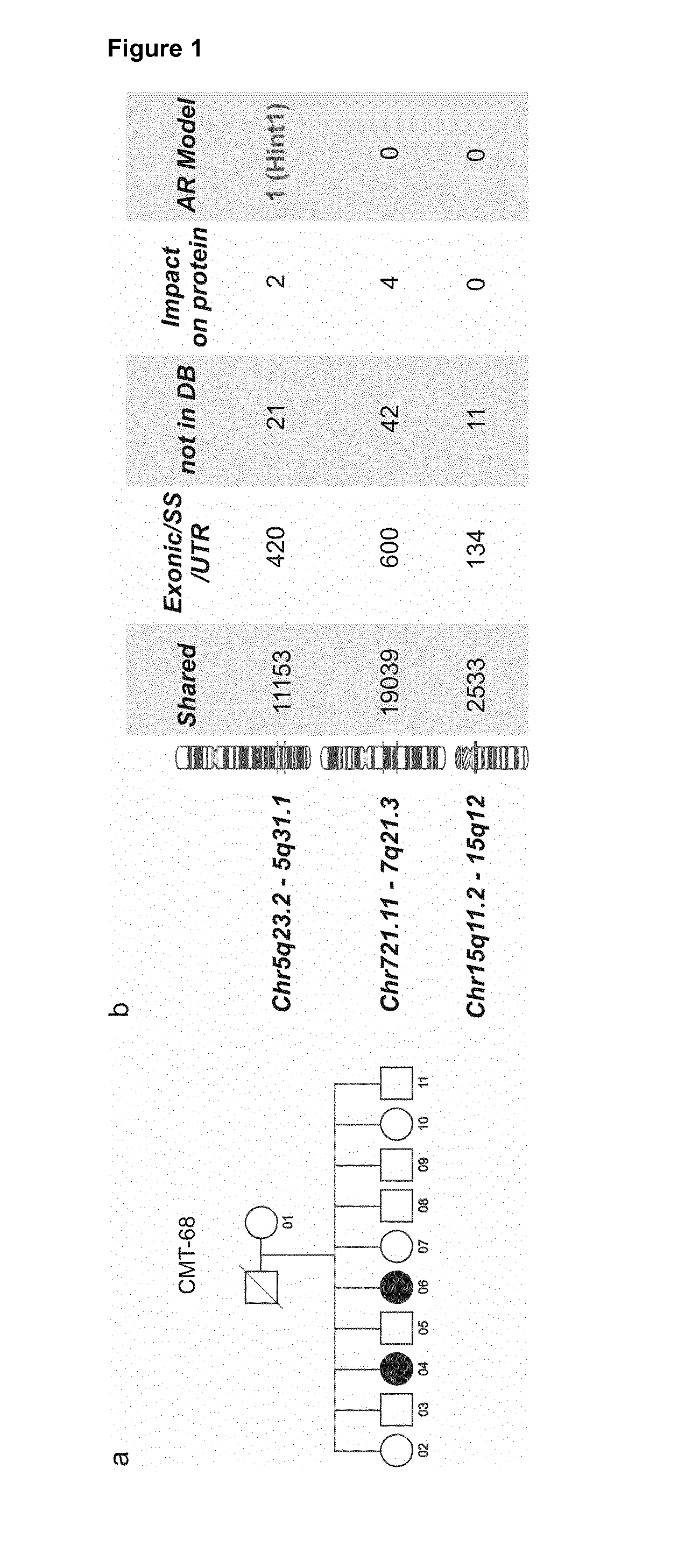
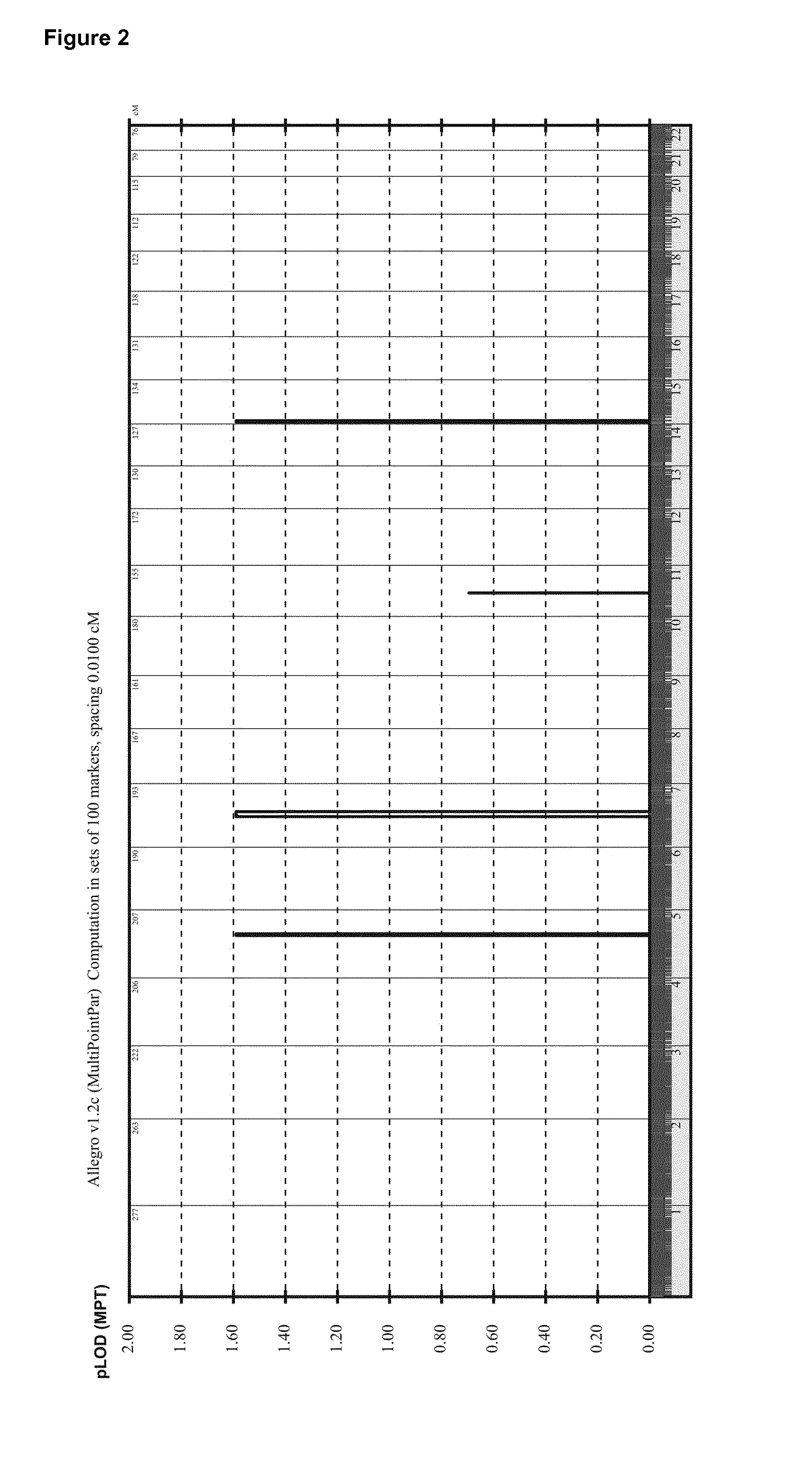
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) is one of the hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies, a group of varied inherited disorders of the peripheral nervous system characterized by progressive loss of muscle tissue and touch sensation across various parts of the body.
Therapeutic approaches for treating cmt and related disorders
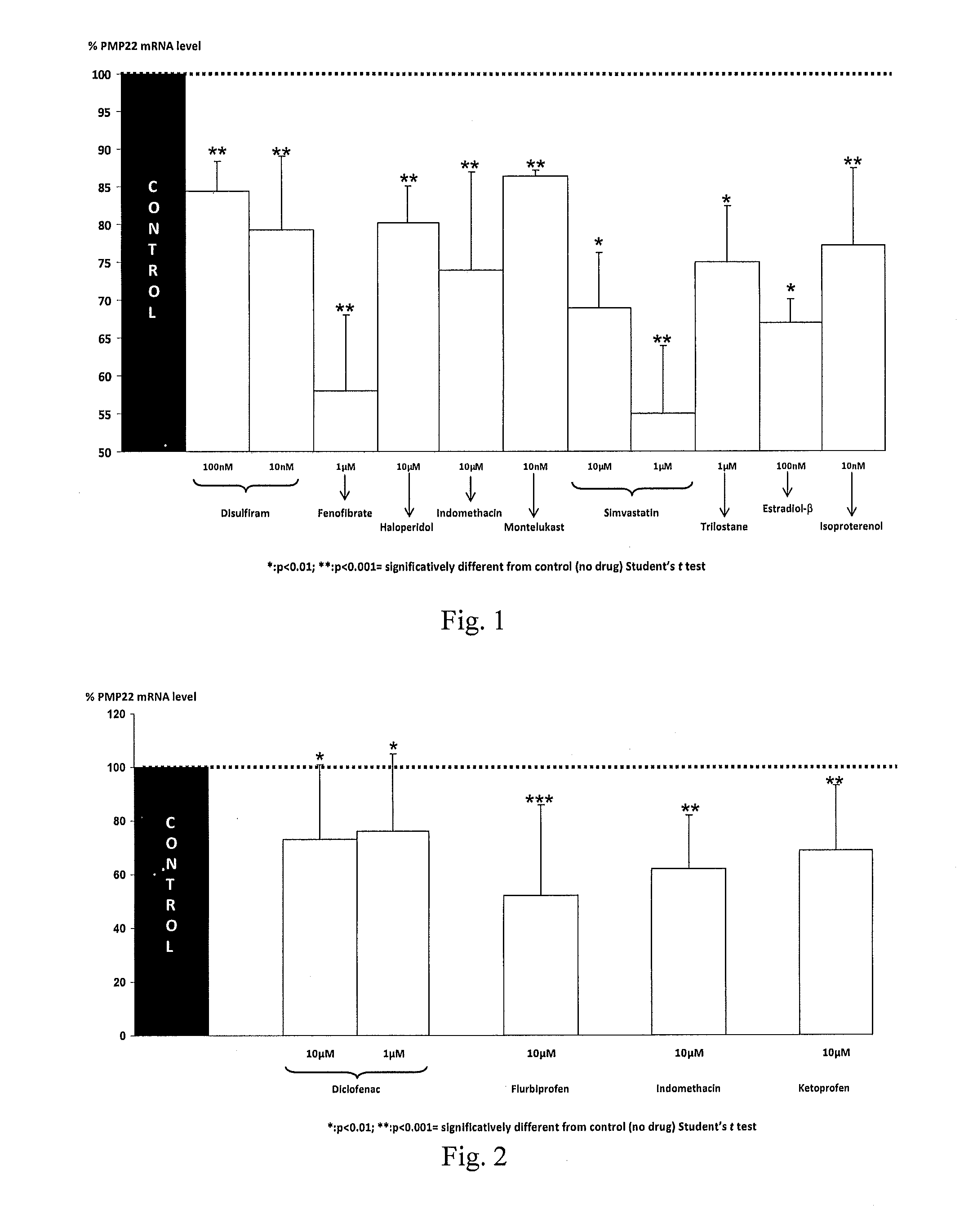
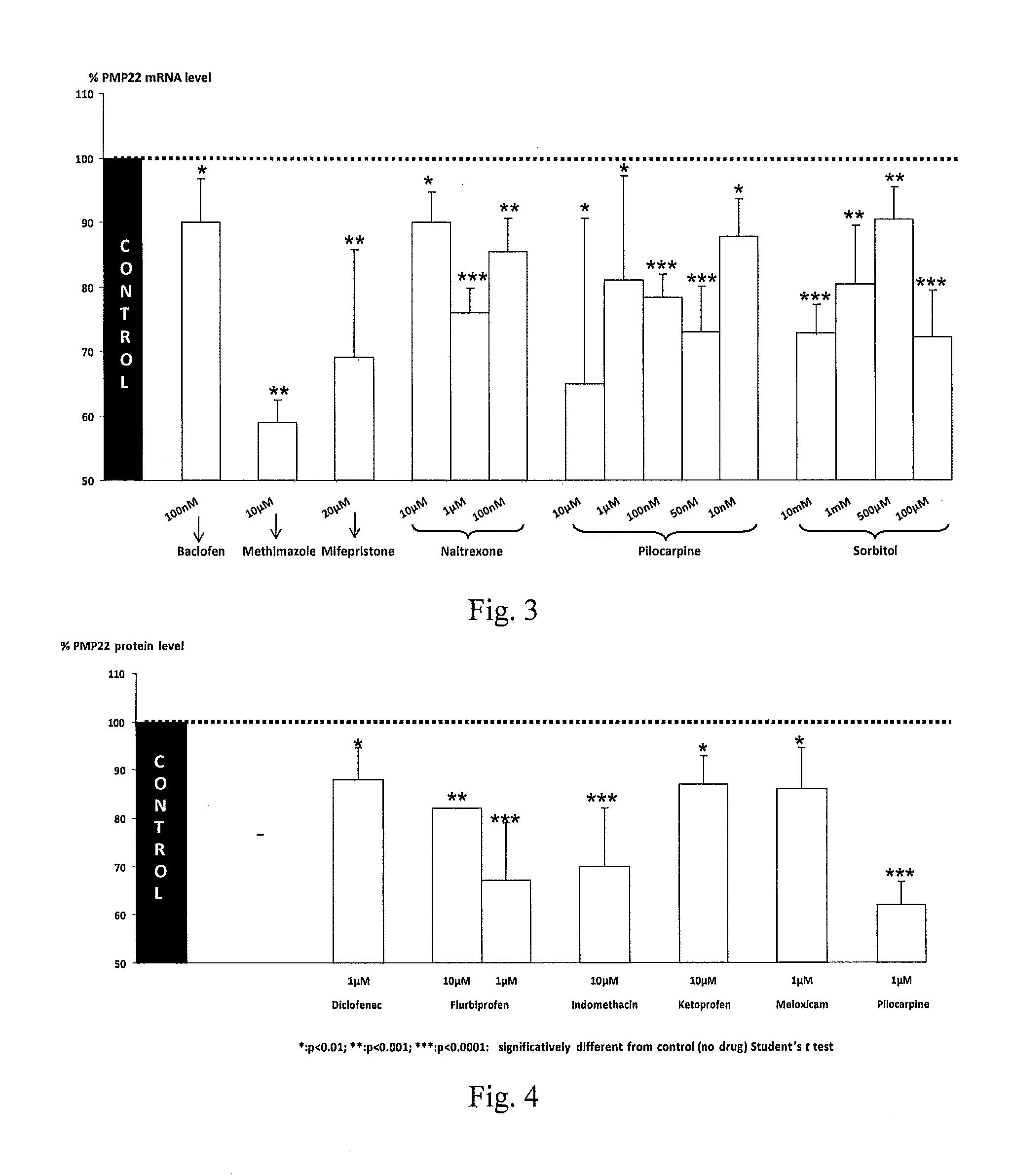
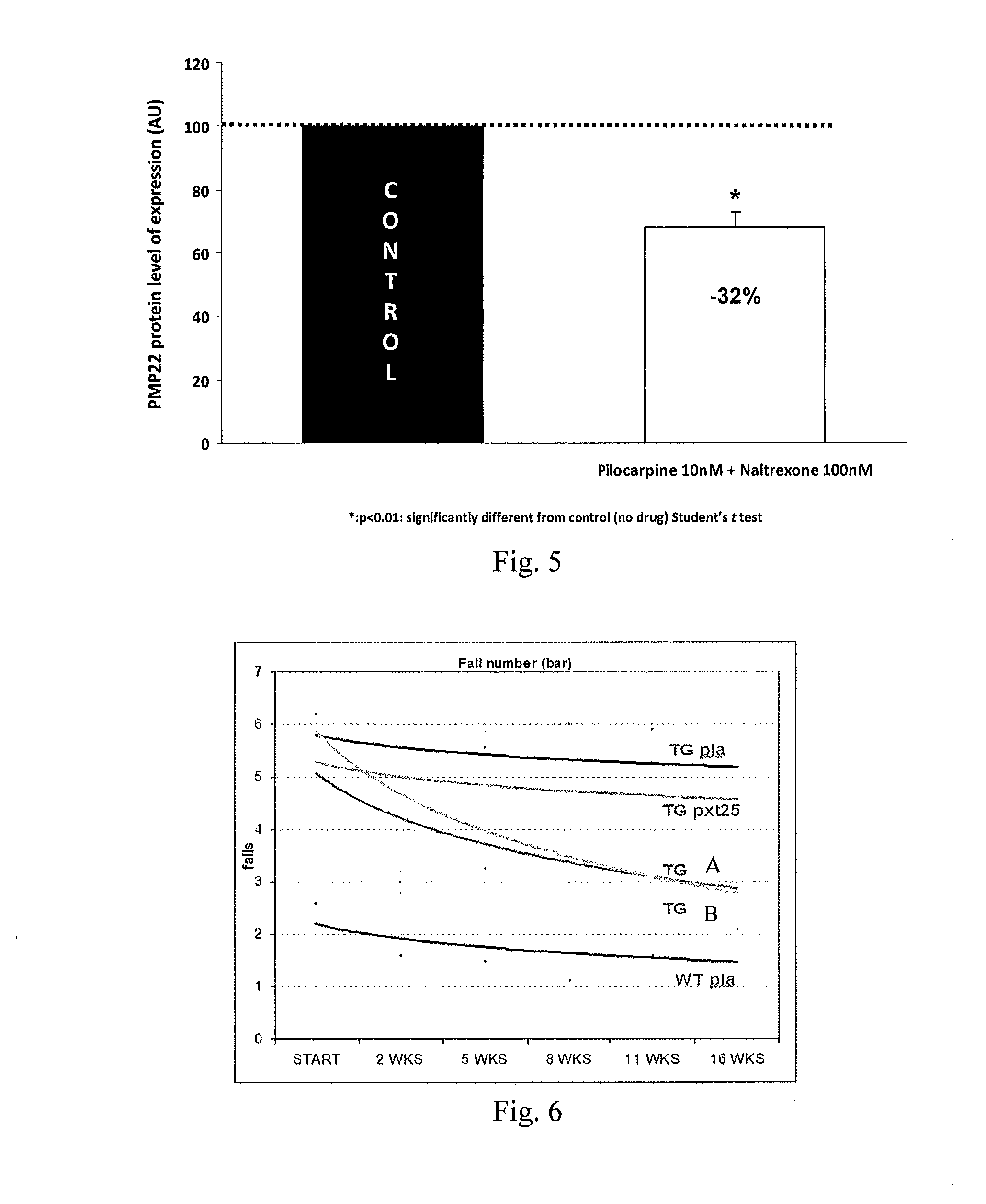
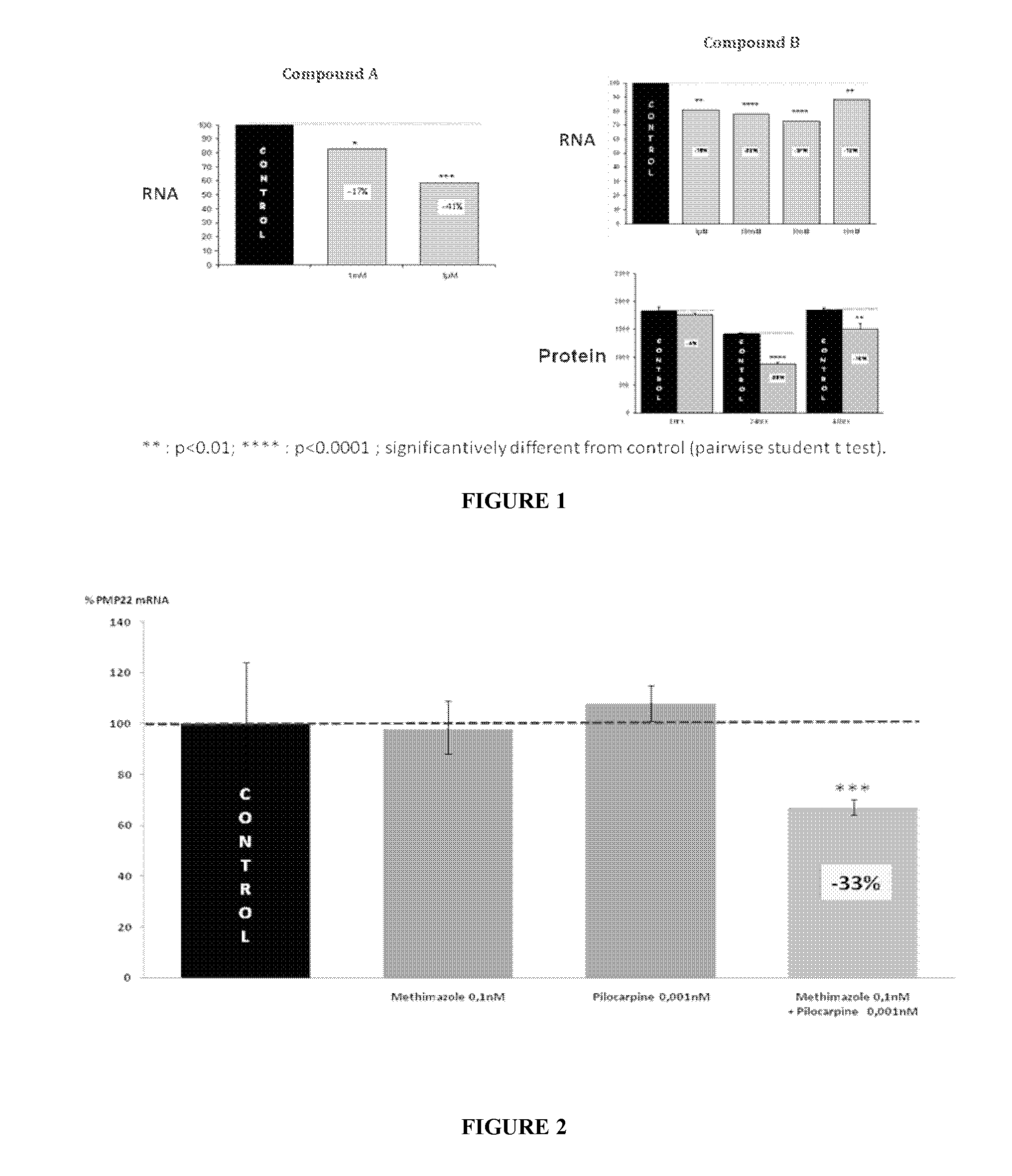
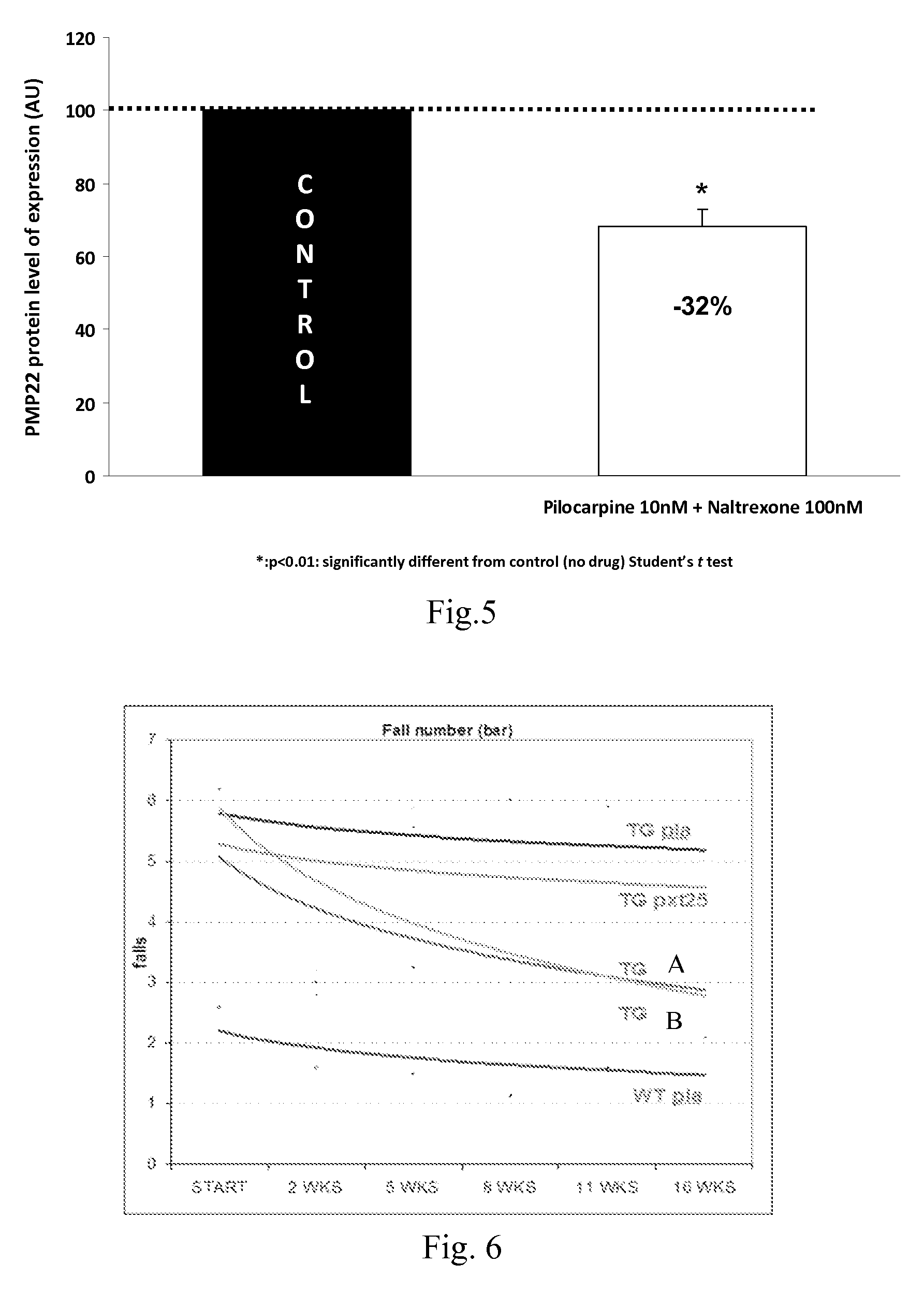
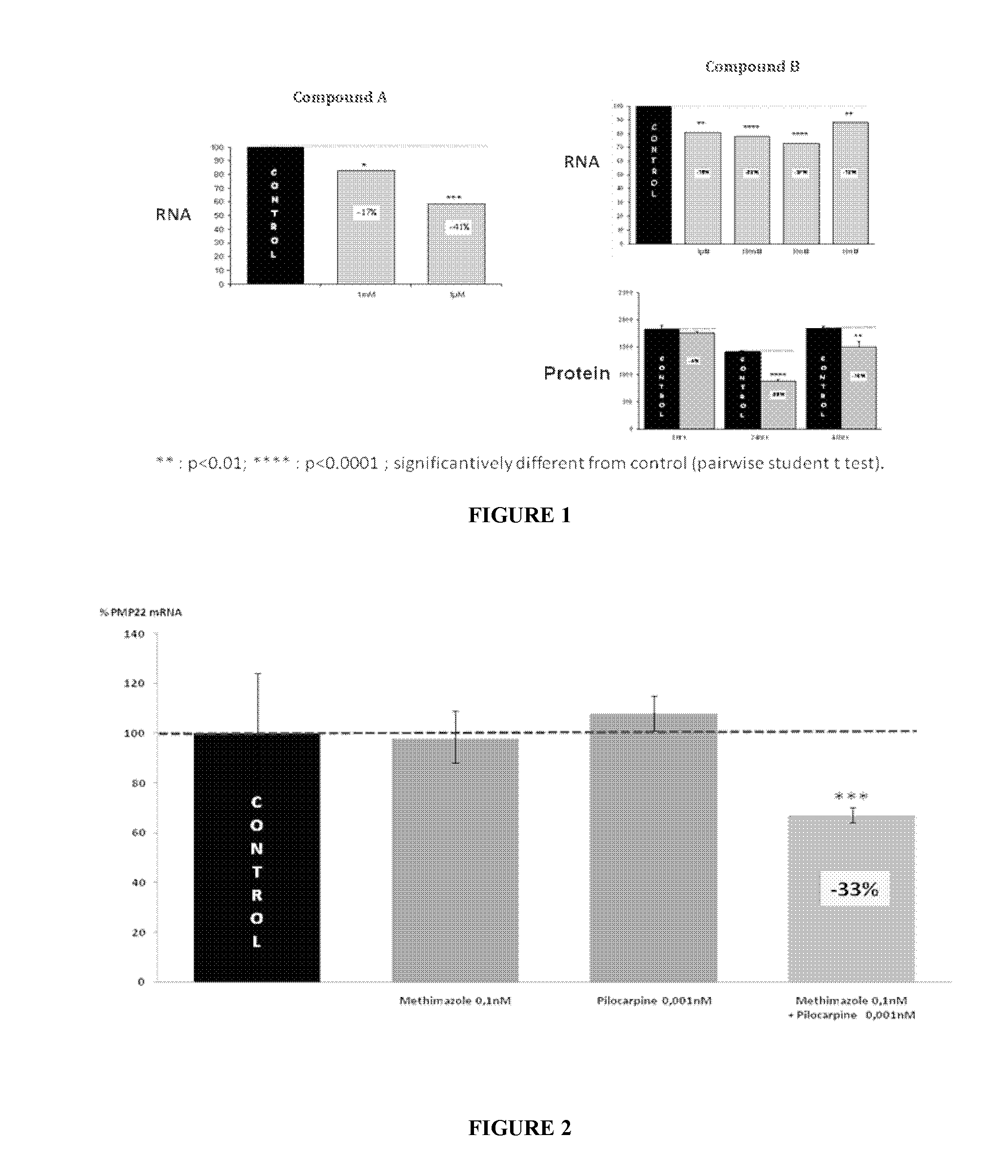
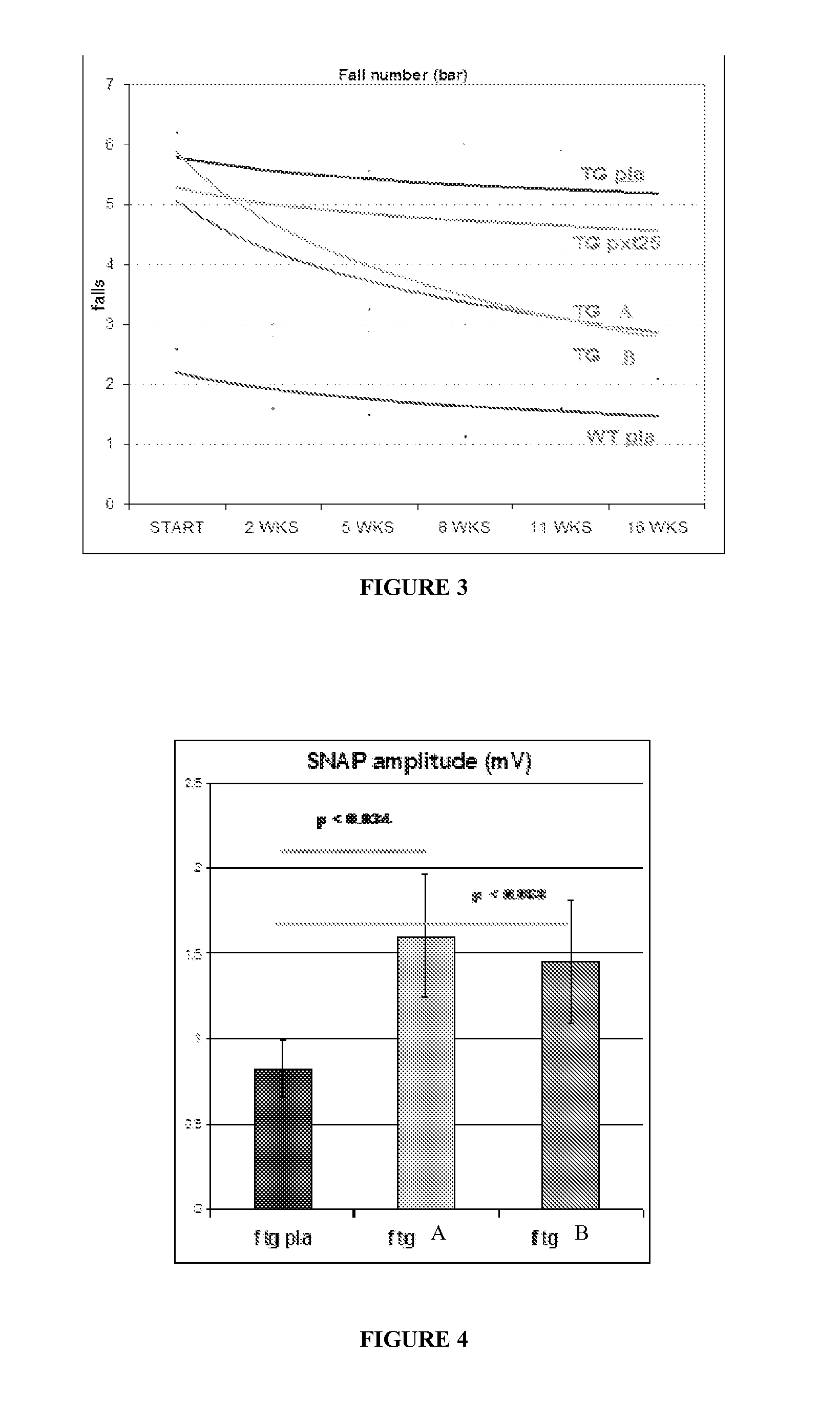
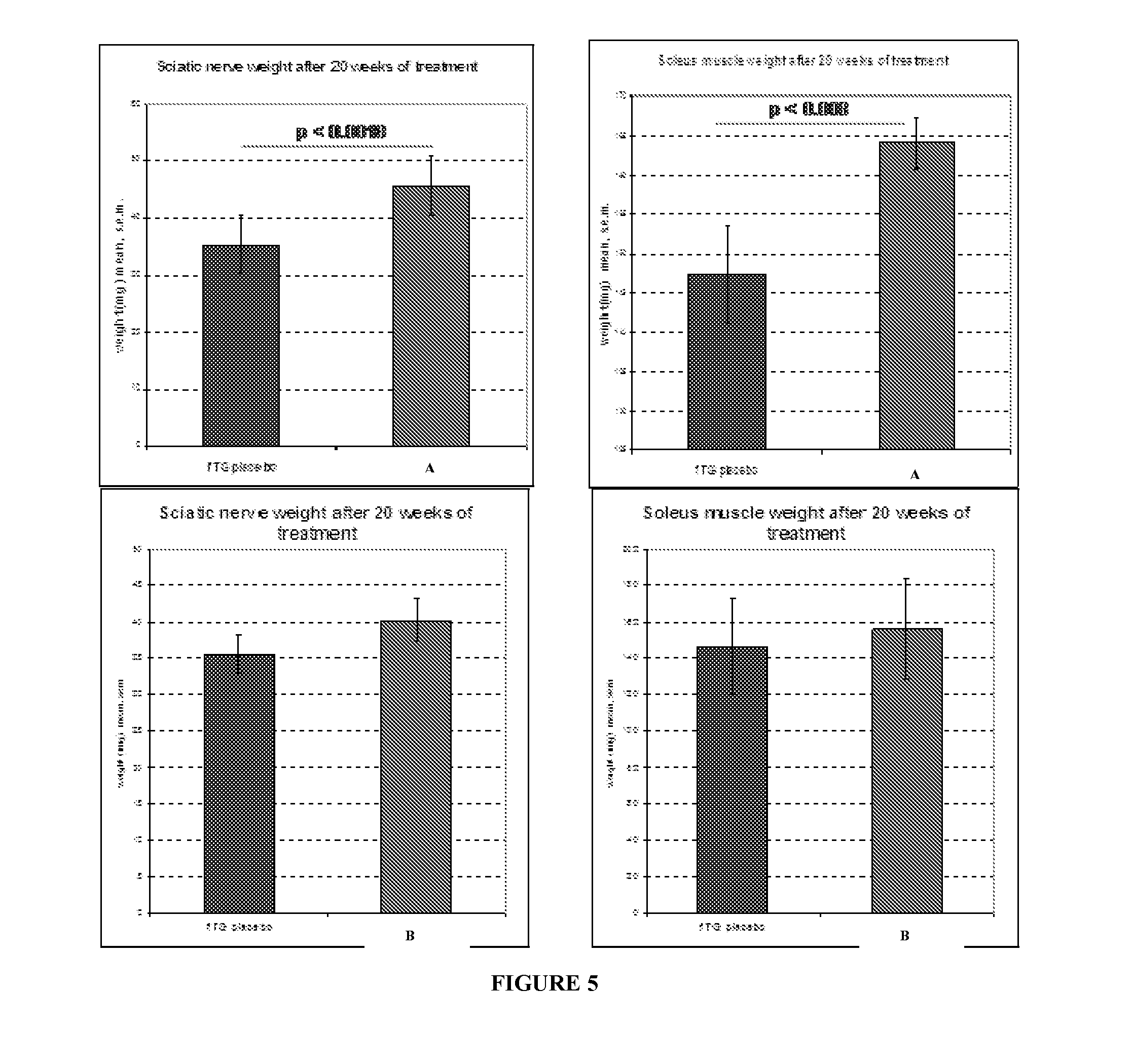
Compositions and methods for the treatment of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related disorders. Also provided are combination therapies for treating this disease by decreasing PMP22 expression in a subject.
Owner:PHARNEXT
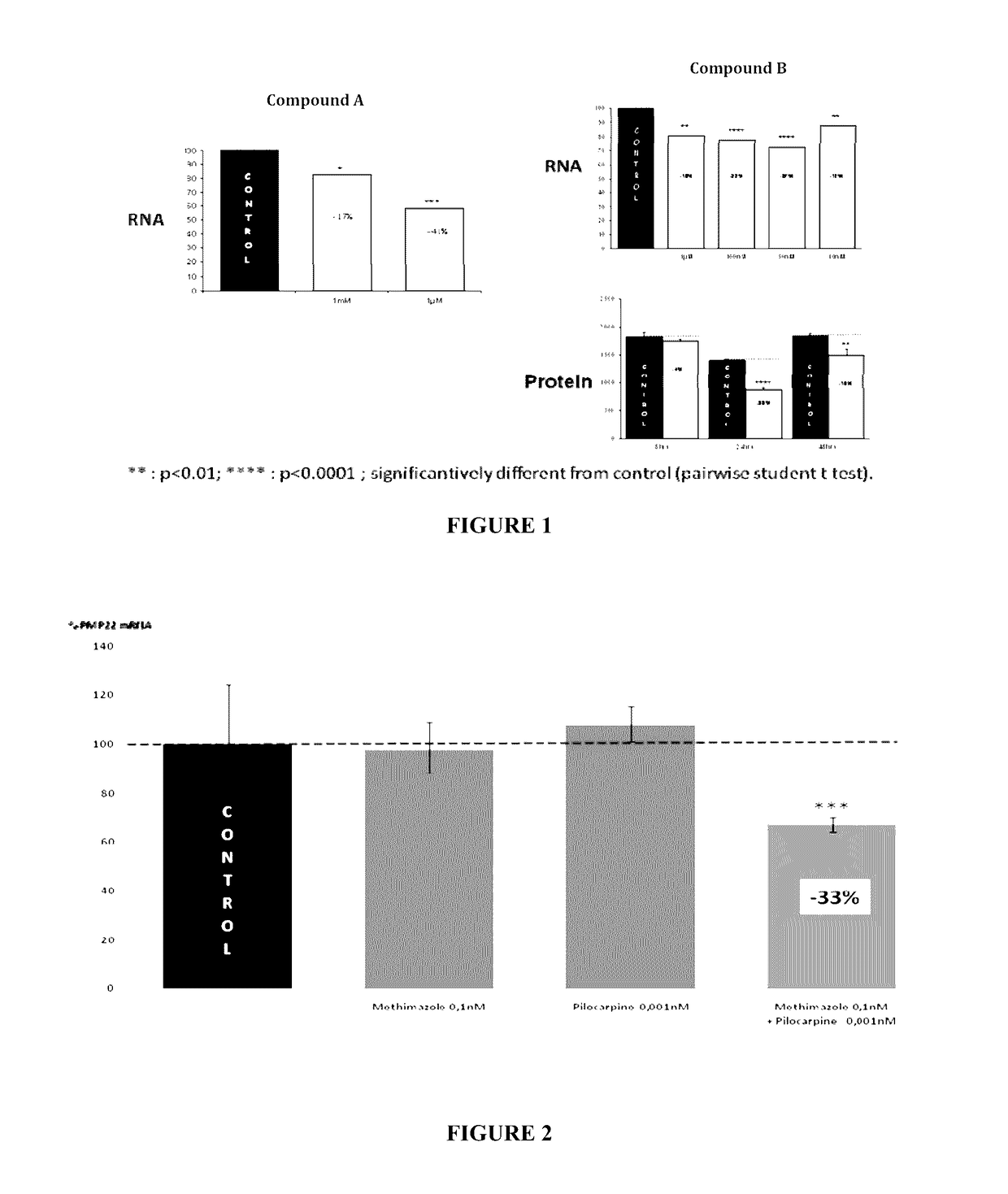
Combination of pilocarpin and methimazol for treating Charcot-Marietooth disease and related disorders
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related peripheral neuropathies. More particularly, the invention relates to combined therapies for treating said disease by affecting simultaneously muscarinic receptor signaling and thyroid hormone pathway in a subject.
Owner:PHARNEXT
Therapeutic approaches for treating CMT and related disorders
ActiveUS8992891B2Ameliorating and slowing progressionReduce expressionCosmetic preparationsBiocidePsychiatryRelated disorder
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related disorders. More particularly, the invention relates to combined therapies for treating said disease by affecting PMP22 expression in a subject.
Owner:PHARNEXT
Combination of pilocarpin and methimazol for treating charcot-marietooth disease and related disorders
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related peripheral neuropathies. More particularly, the invention relates to combined therapies for treating said disease by affecting simultaneously muscarinic receptor signaling and thyroid hormone pathway in a subject.
Owner:PHARNEXT
Compositions for treating CMT and related disorders
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related disorders.
Owner:PHARNEXT
Compositions for treating cmt and related disorders
ActiveUS20140178463A1Severe incapacitySignificant positive effectBiocideDispersion deliveryPsychiatryRelated disorder
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related disorders.
Owner:PHARNEXT
Compositions for treating CMT and related disorders
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related disorders.
Owner:PHARNEXT
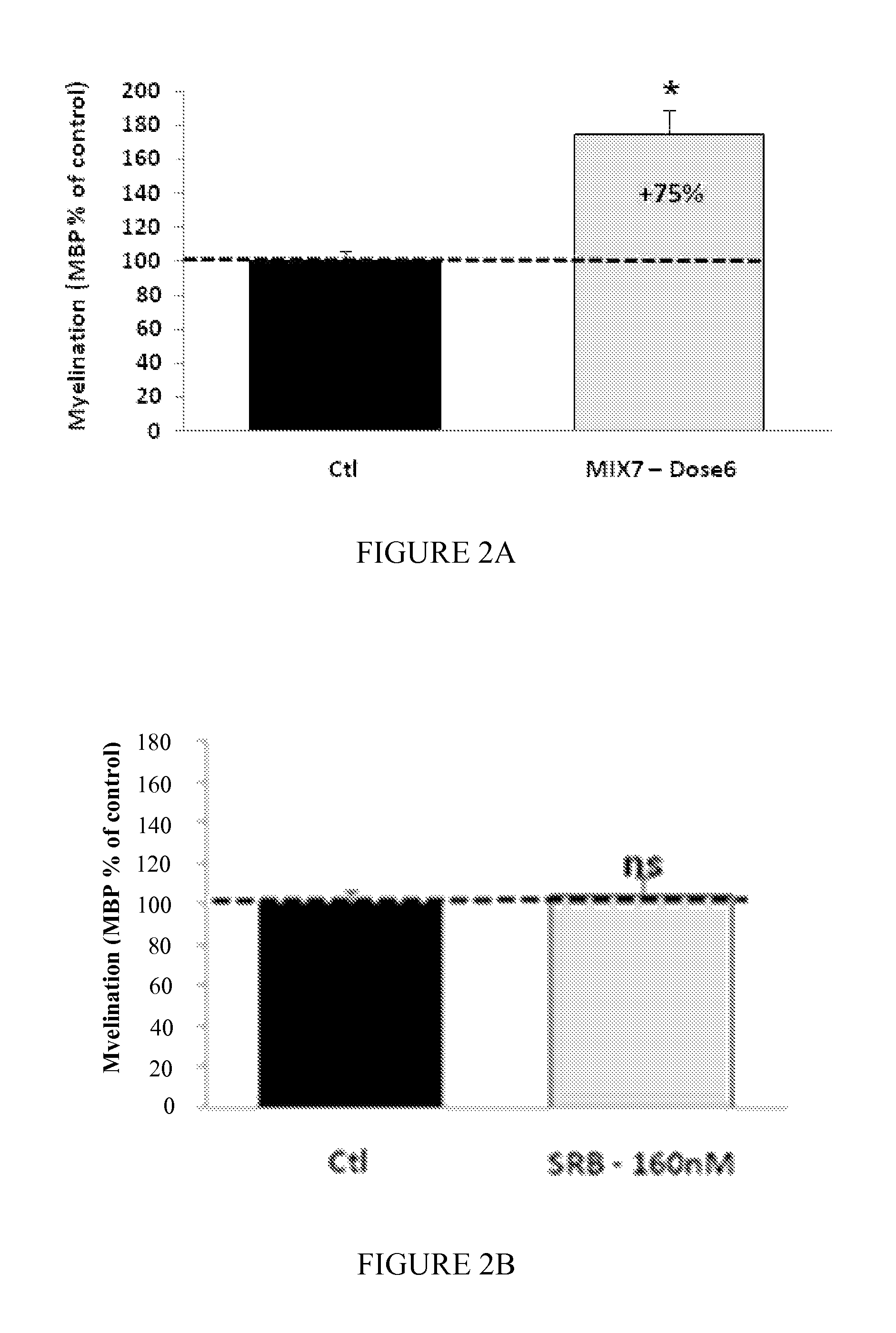
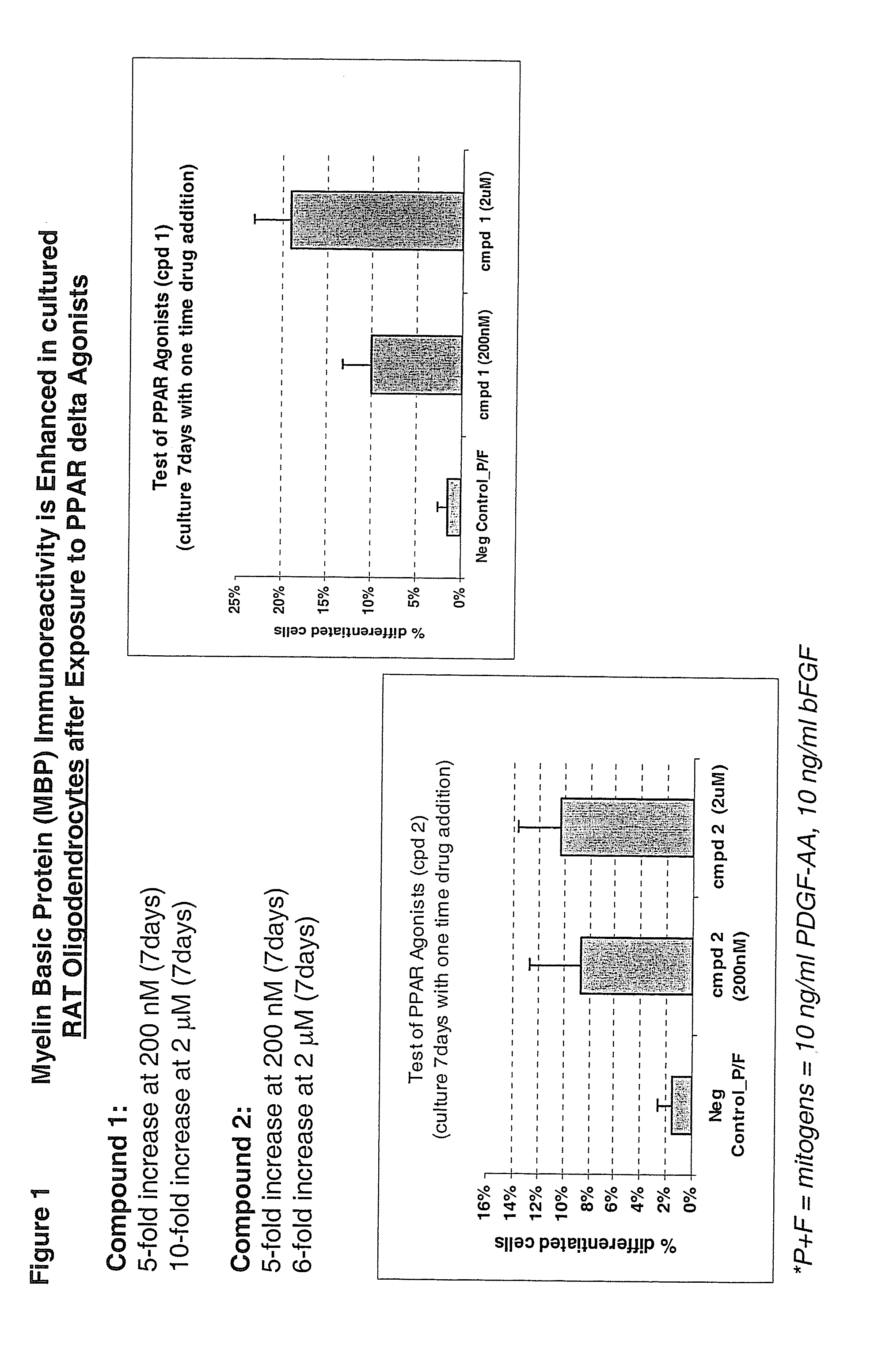
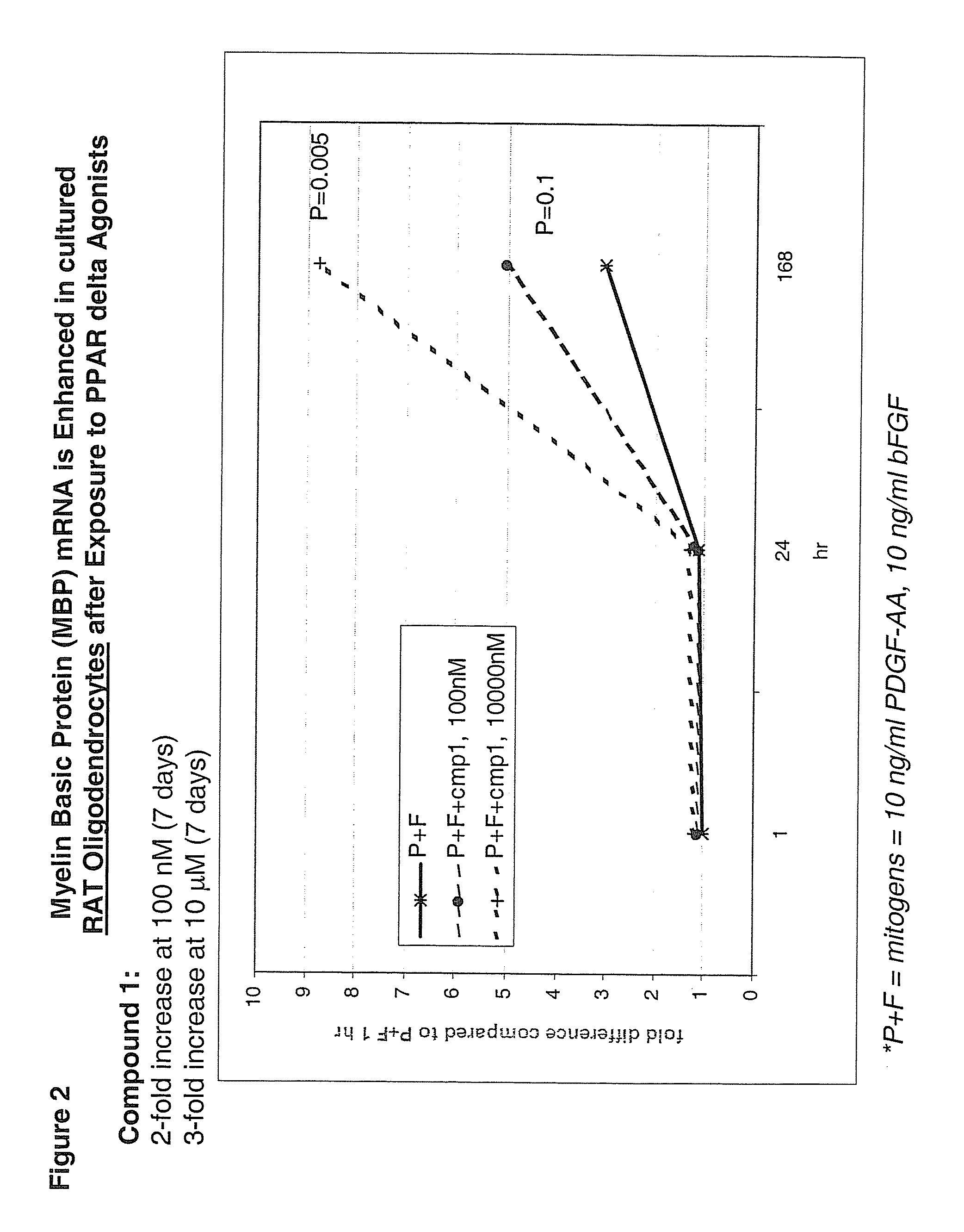
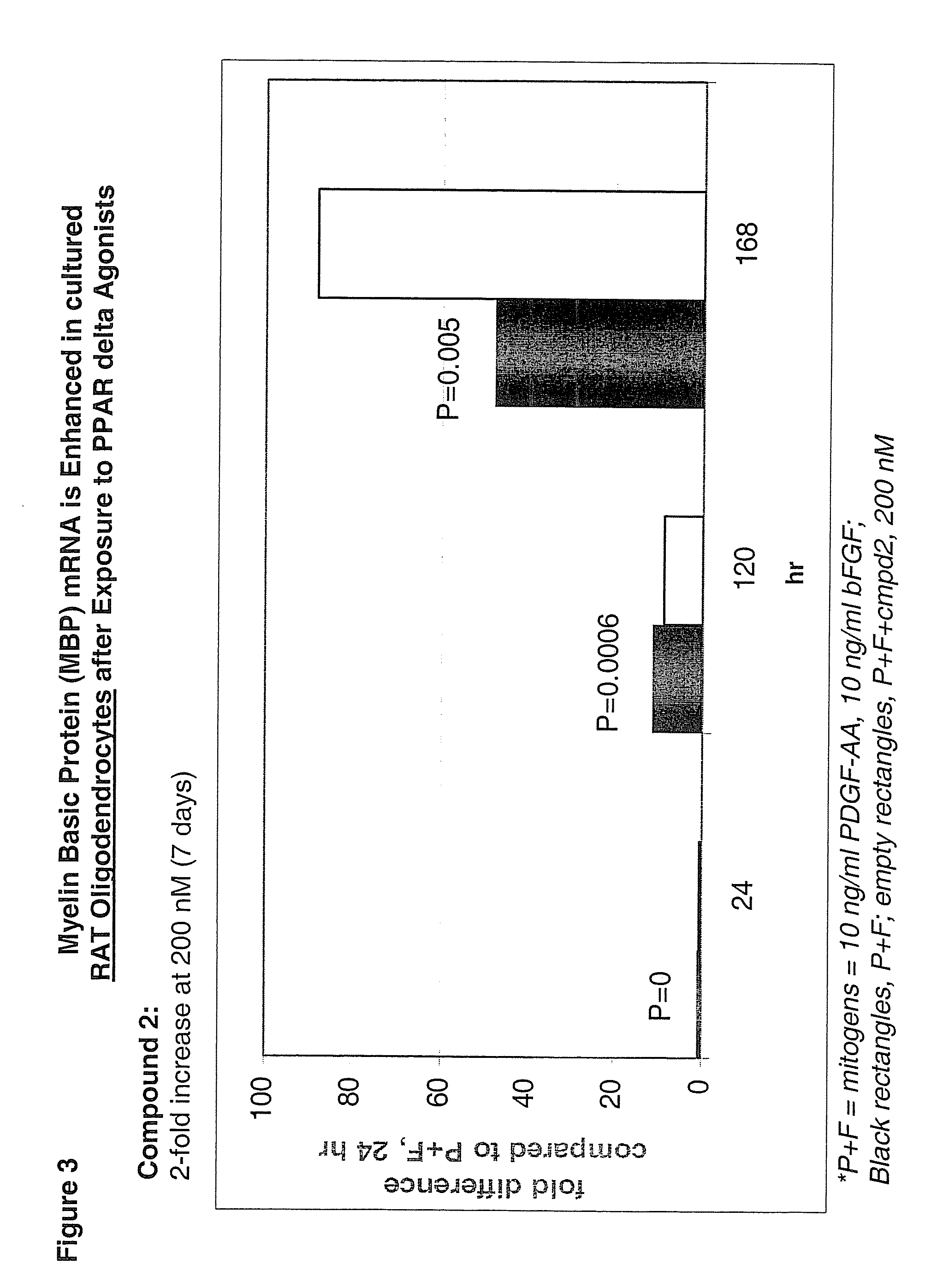
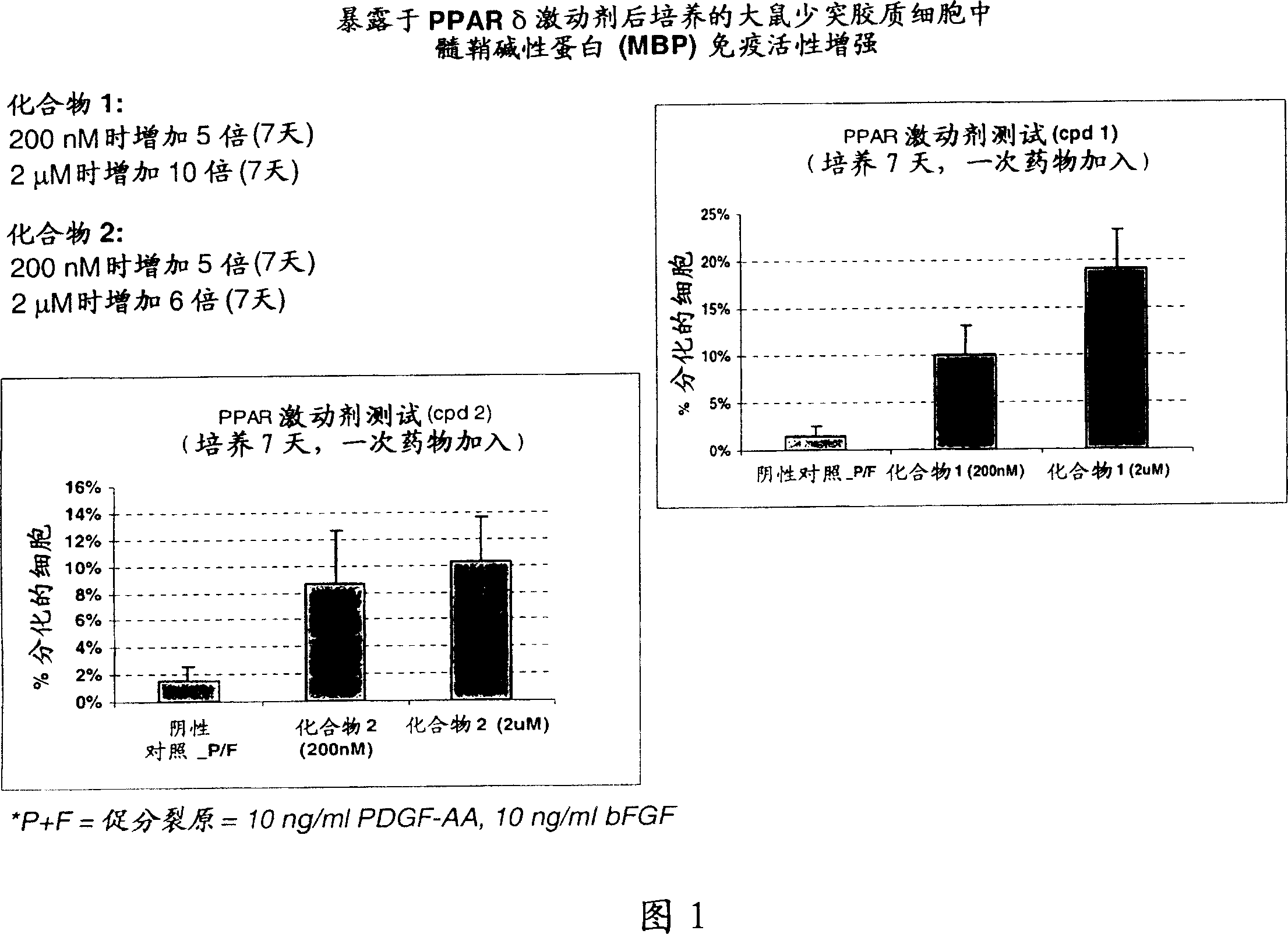
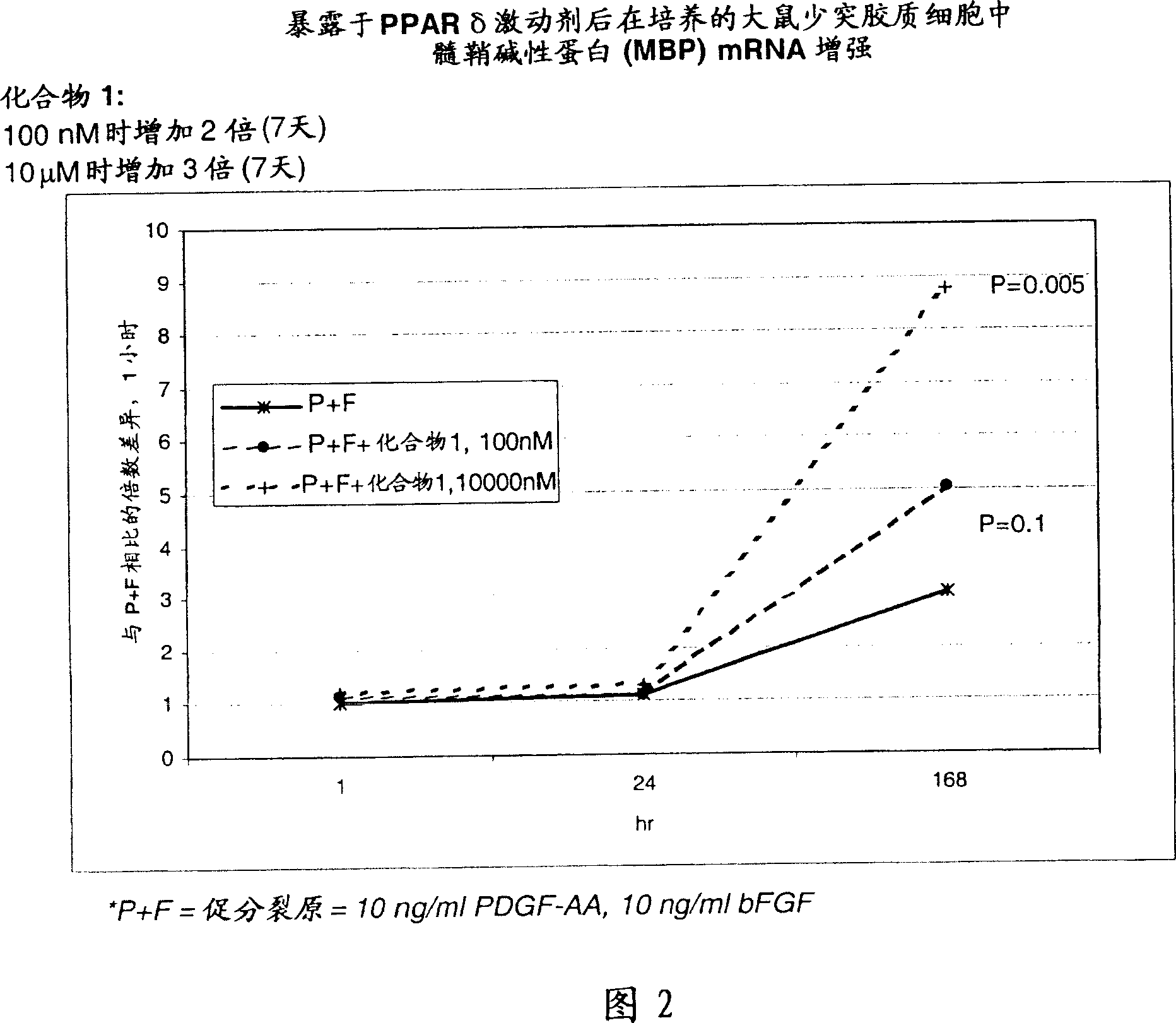
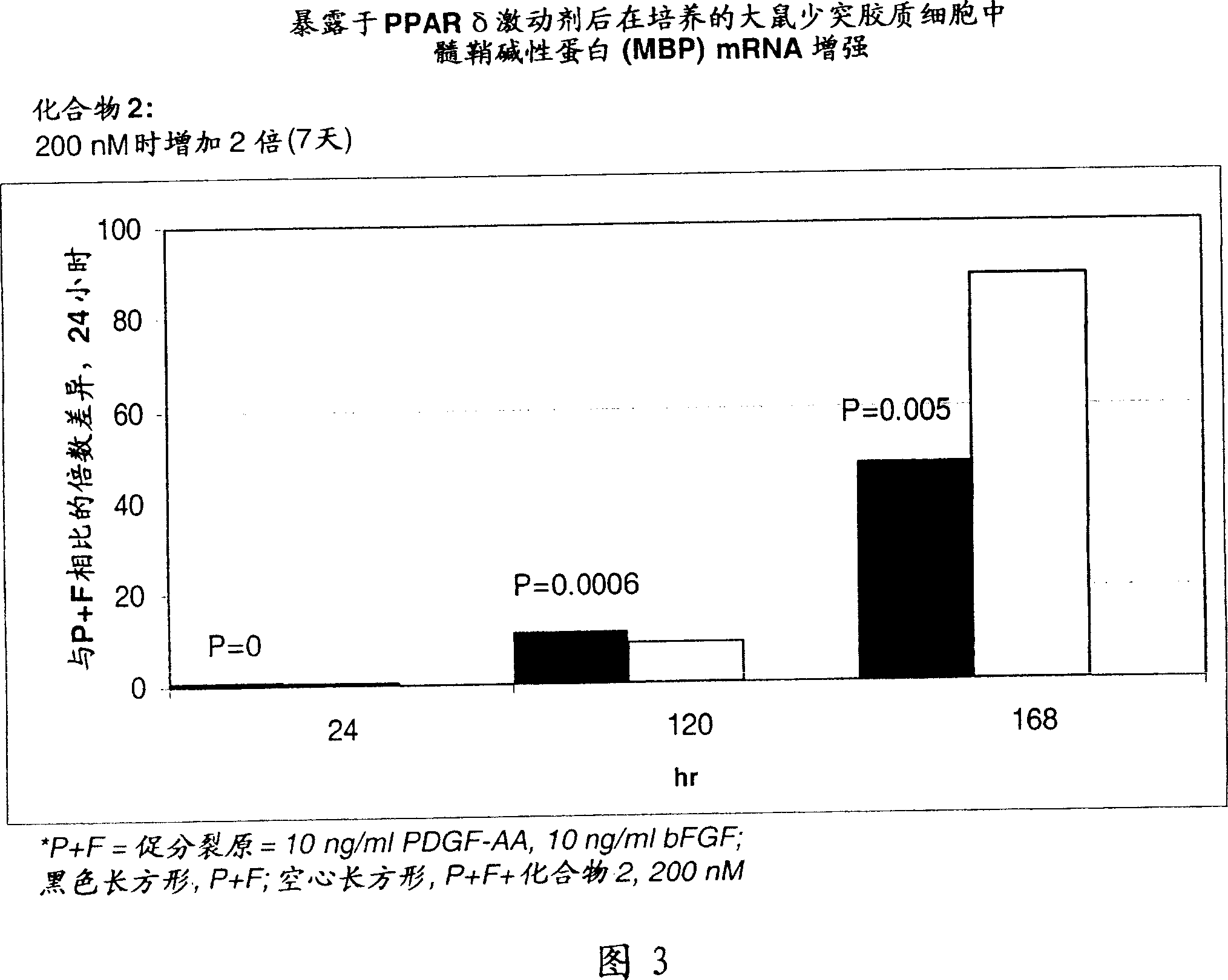
Use of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor delta agonists for the treatment of ms and other demyelinating diseases
InactiveUS20070149580A1Effective treatmentBiocideNervous disorderX-linked adrenoleukodystrophyPeroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
A method for treating demyelinating diseases in a patient in need thereof by treatment with an effective amount of a PPAR delta agonist is disclosed. Demyelinating diseases that may be effectively treated by this method include but are not limited to multiple sclerosis, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, adrenoleukodystrophy, Guillian-Barre syndrome and disorders in which myelin forming glial cells are damaged including spinal cord injuries, neuropathies and nerve injury.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA INC
Apilimod compositions and methods for using same
InactiveUS20180015098A1Reducing PI(3,5)P levelOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPsychiatryMarie disease
The present invention relates to methods for treating Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease (CMT) with apilimod and related compositions and methods.
Owner:LAM THERAPEUTICS
Methods of detecting Charcot-Marie Tooth disease type 2A
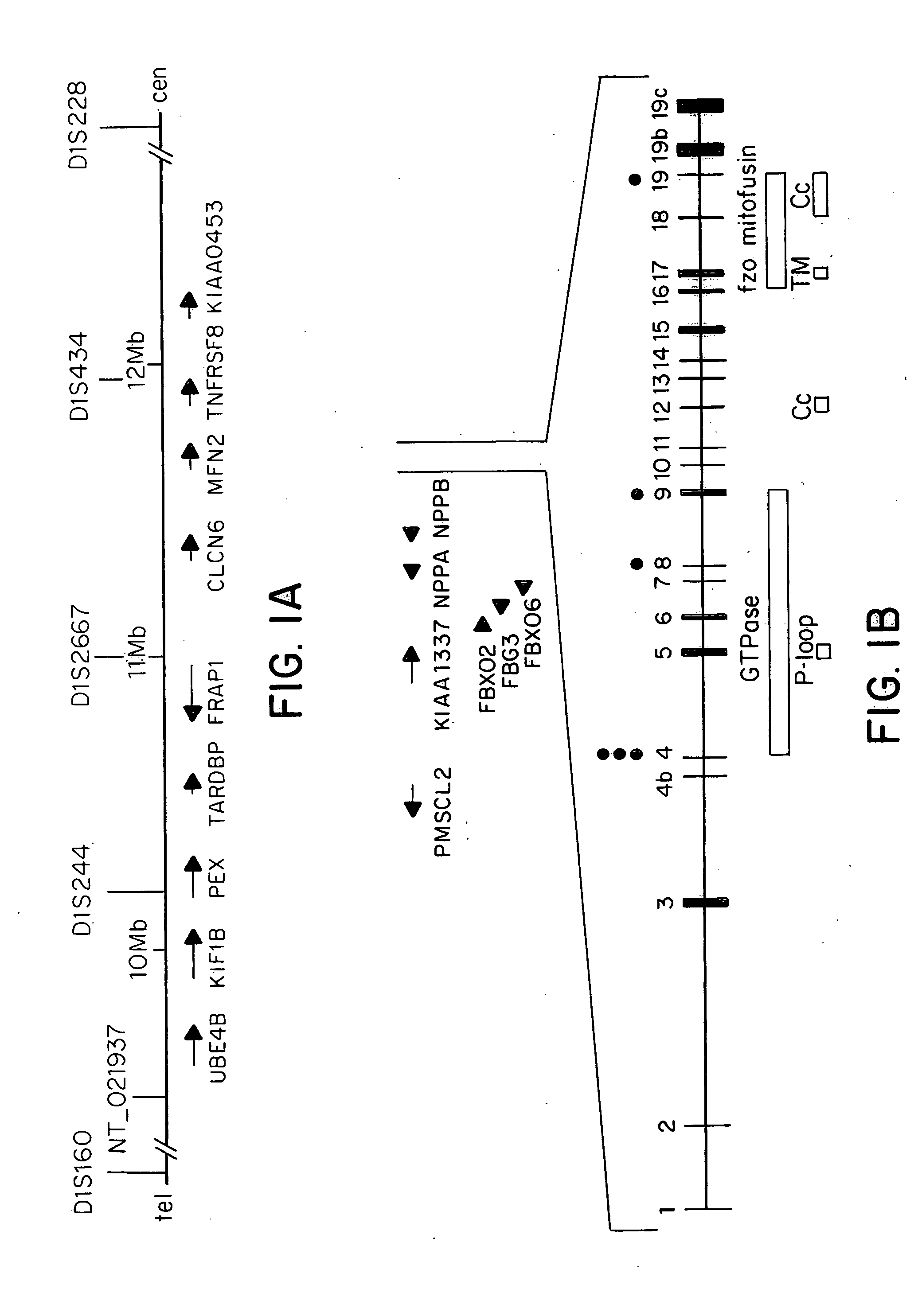
Methods are described for screening a subject for risk of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2A or for diagnosing Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease or a predisposition for developing Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in a subject, by detecting the presence or absence of a mutation in the mitofusin gene in a biological sample collected from the subject. Methods are also described for detecting the presence of a genetic polymorphism associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2A in a sample of patient nucleic acid, by amplifying a mitofusin gene sequence in the patient nucleic acid to produce an amplification product; and identifying the presence of a Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2A associated polymorphism in the amplification product.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
New diagnostic tools for charcot-marie-tooth disease
InactiveUS20130217036A1ResponsivenessHydroxy compound active ingredientsDisease diagnosisMetaboliteTherapeutic effect
The present invention relates in particular to methods of detecting predisposition to or diagnosis and / or prognosis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) and related disorders. More specifically, the invention relates to development, validation and application of new biomarkers, which can be used for detecting the presence or risk of CMT disease and related disorders. In particular, the present invention relates to metabolite, lipid, carbohydrate and proteinaceous biomarkers that can be measured in biological body fluids and easily available extracts of biopsies, which can be used to aid in the detection, prediction of drug treatment and follow up of this treatment of neurodegenerative disorders, including CMT disease. The present invention also relates to methods for identification of CMT disease subtypes, assessing the responsiveness to the treatments and the efficacy of treatments in subjects having CMT or a related disorder.
Owner:PHARNEXT
Screening method for therapeutic agents for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and self-differentiation motor neurons used therefor
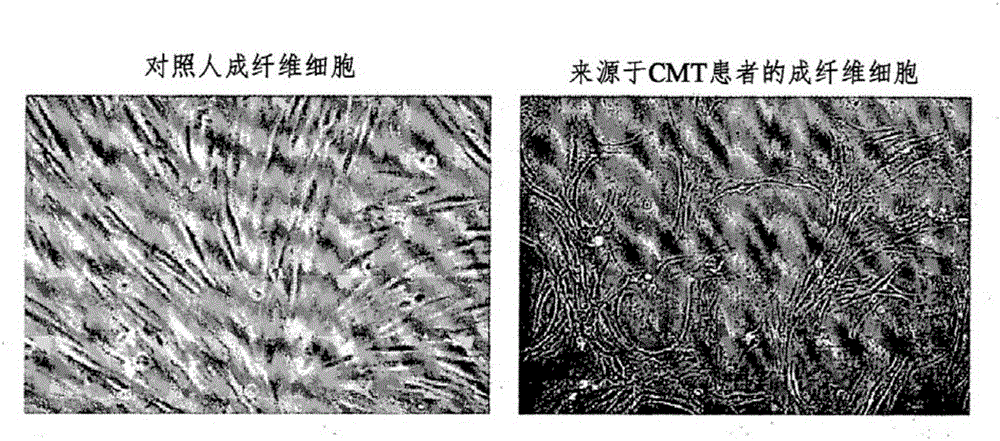
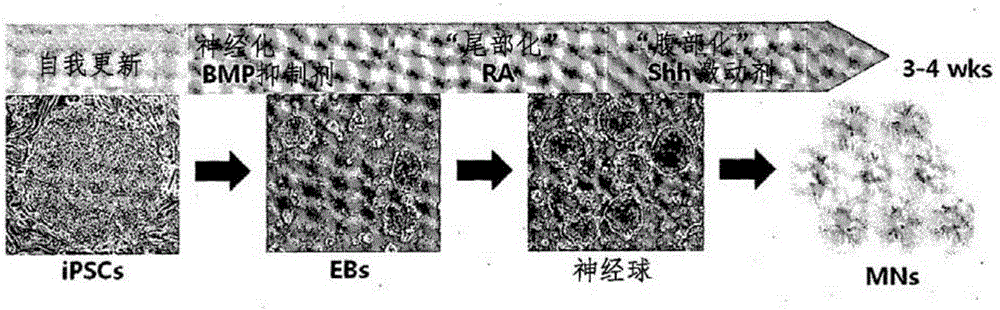
InactiveCN105264068AEffective confirmation of pharmaceutical effectsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFibroblastScreening method
Owner:SAMSUNG LIFE PUBLIC WELFARE FOUND +1
Gel electrophoresis method useful for resolution and characterization of nerve tissue ultra high molecular weight protein aggregates
The instant disclosure describes an electrophoretic procedure capable of resolving and isolating ultra high molecular weight (MW) protein aggregates from nerve tissue. The procedure is based on the use of composite agarose-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (CAPAGE) and resolves proteins and protein aggregates over the range of from approximately 225 kDa to approximately 30,000 kDa. Triton X-100 precipitation is used to obtain a cytoskeleton protein fraction that is subsequently resuspended and subjected to gel electrophoresis. This method demonstrates that a protein aggregate of approximately 30,000 kDa is characteristic of normal murine spinal cord tissue and that the amount of said protein aggregate is increased in spinal cord homogenate obtained from transgenic mice bearing copies of a mutant human gene characteristic of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. This method for separating nerve tissue ultra high MW cytoskeleton protein aggregates can prove useful in a variety of future biophysical and pharmacological studies related to the etiologies of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, diseases based on expansions in tandem DNA repeats, spinal muscular atrophy, Friedreich's ataxia, giant axon neuropathy, juvenile ceroid-lipofuscinosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, diabetic polyneuropathy and Down's syndrome.
Owner:SHAPIRO HOWARD K
Screening method for therapeutic agents for charcot-marie-tooth disease and self-differentiation motor neurons used therefor
InactiveUS20160011177A1Easy to useConfirm effectCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFibroblastScreening method
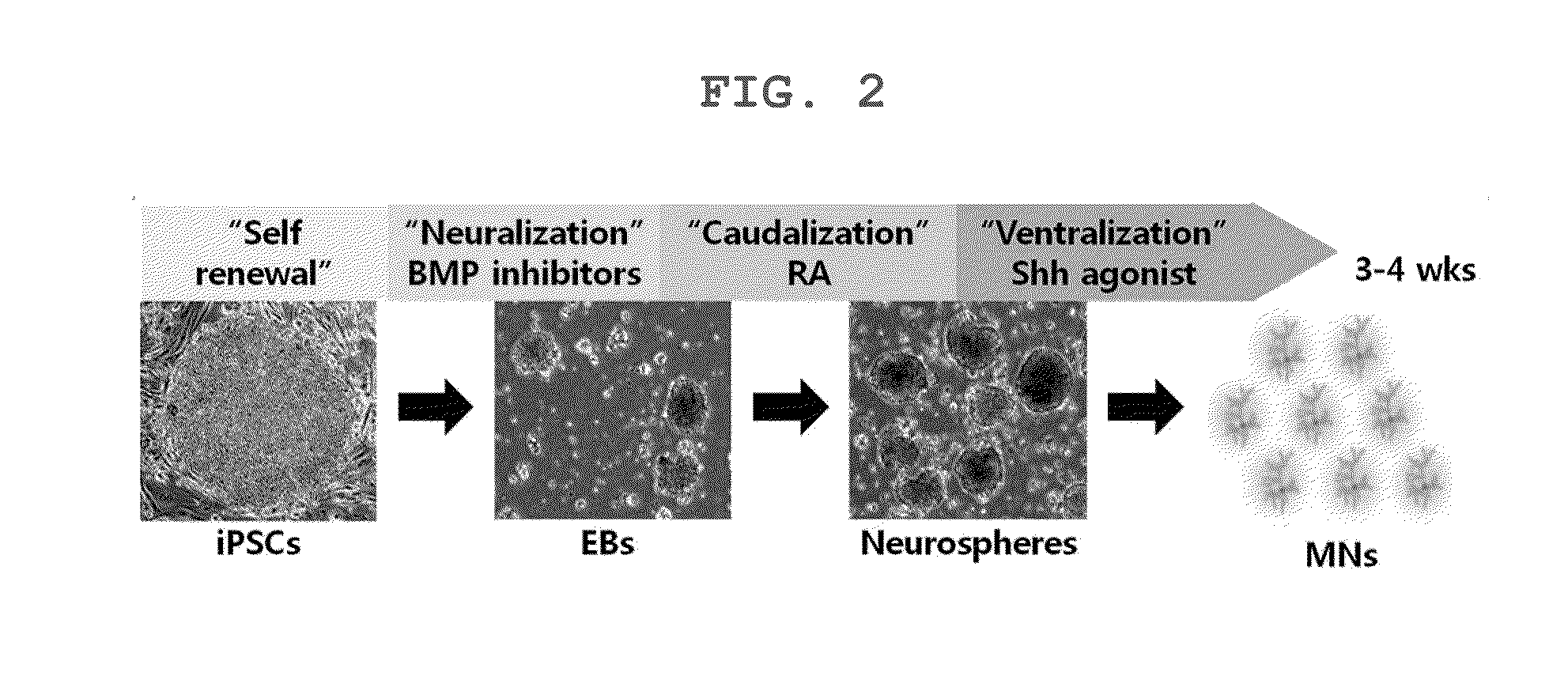
The present invention relates to a method for the screening of a therapeutic agent for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) using induced pluripotent stem cells and motor neurons differentiated therefrom. Particularly, the present inventors prepared induced pluripotent stem cells from the human fibroblasts originated from CMT patient. When the motor neurons differentiated from the said induced pluripotent stem cells are used for the screening of a therapeutic agent for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, the pharmaceutical effect of the therapeutic agent candidates can be easily evaluated during the screening. In addition, by the method to prepare the induced pluripotent stem cells, autologous motor neurons which are usable for the screening of a patient-specific therapeutic agent and the patient-specific treatment can be prepared.
Owner:SAMSUNG LIFE PUBLIC WELFARE FOUND +1
Microfluidic cell culture systems
ActiveUS20160186112A1Reduce restrictionsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell adhesionCell survival
As with many human physiological systems, issues within the central nervous system can arise for individuals leading to a variety of neurological disorders including, but not limited to, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Alzheimer' disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, demyelination, and axonal degeneration. However, culture devices presently provide researchers with limitations in their research. Embodiments of the invention aims to address these various limitations and allow studies, methods and screenings which cannot be performed with prior art culture devices. These include reducing manufacturing complexity, volumes of pharmaceuticals and cells required, allowing use in fields other than neurobiology, improved adhesion within the desired micro-channel regions of the devices, and increasing cell survival in cultures. Accordingly, microfluidic devices comprising a connecting chamber and micro-channel having the same depth which prevents hydrostatic pressure, end walls of the connecting chamber and micro-channel arrays having a high angle relative to the fluid flow direction for supporting culturing and topside of the connecting chamber that has been profiled in order to improve the adhesion of cells is provided.
Owner:9493662 CANADA
Compositions and methods for treating charcot-marie-tooth diseases and related neuronal diseases
InactiveUS20160144003A1Reduce symptom and progression of GlyRS-associatedPeptide/protein ingredientsLigasesRNA synthetasesNeuronal disease
Provided are compositions and methods for the treatment of mutant glycyl-tRNA synthetase (GlyRS)-associated diseases, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) diseases, and related compositions and methods for diagnostic, drug discovery, and research applications. Also provided are mutant glycyl-tRNA synthetases and uses thereof.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Methods of detecting Charcot-Marie Tooth disease type 2A
ActiveUS20050181390A1Diagnosing presenceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMitochondrial fusionBiology
Methods are described for screening a subject for risk of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2A or for diagnosing Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease or a predisposition for developing Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in a subject, by detecting the presence or absence of a mutation in the mitofusin gene in a biological sample collected from the subject. Methods are also described for detecting the presence of a genetic polymorphism associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2A in a sample of patient nucleic acid, by amplifying a mitofusin gene sequence in the patient nucleic acid to produce an amplification product; and identifying the presence of a Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 2A associated polymorphism in the amplification product.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
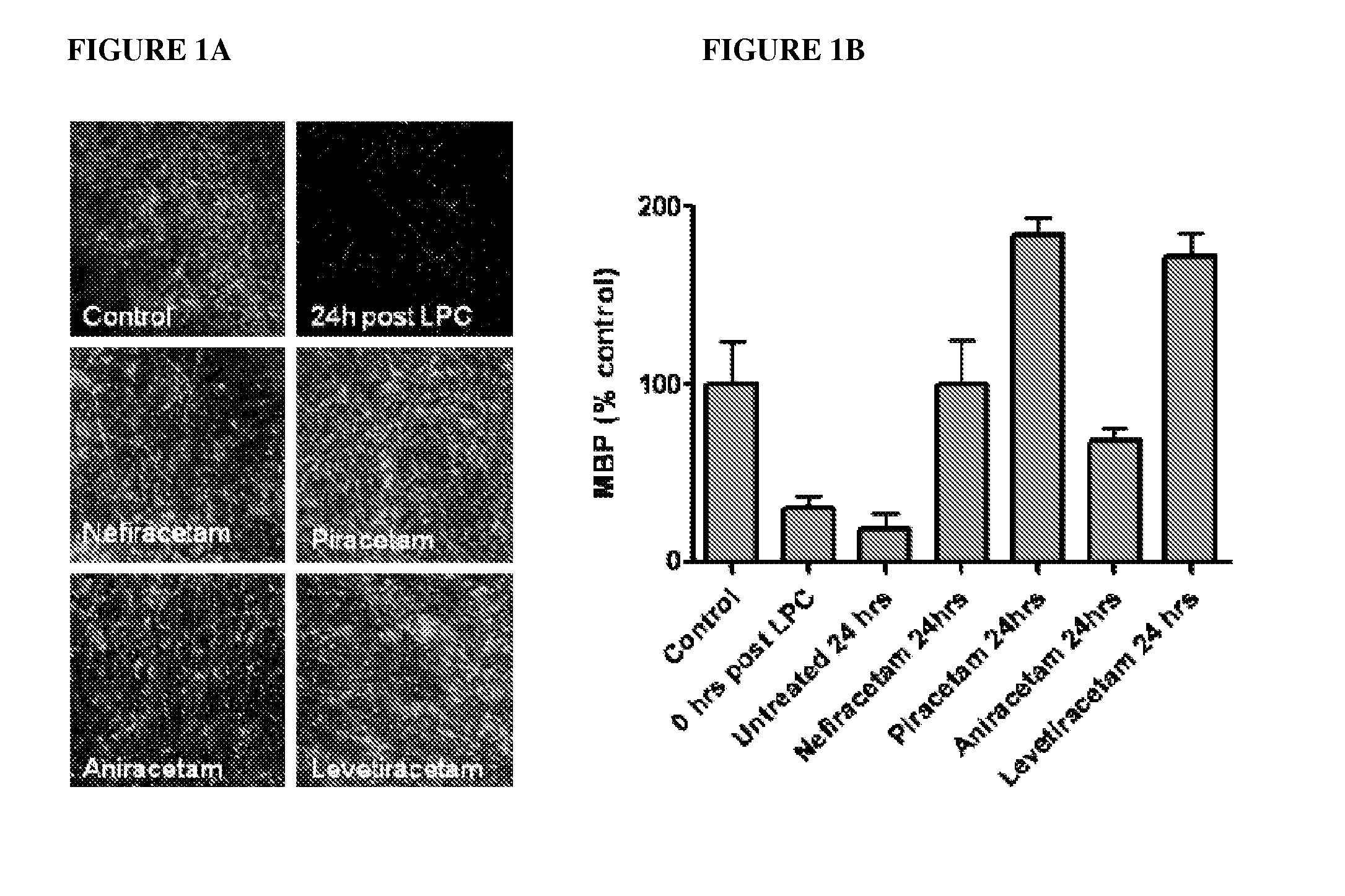
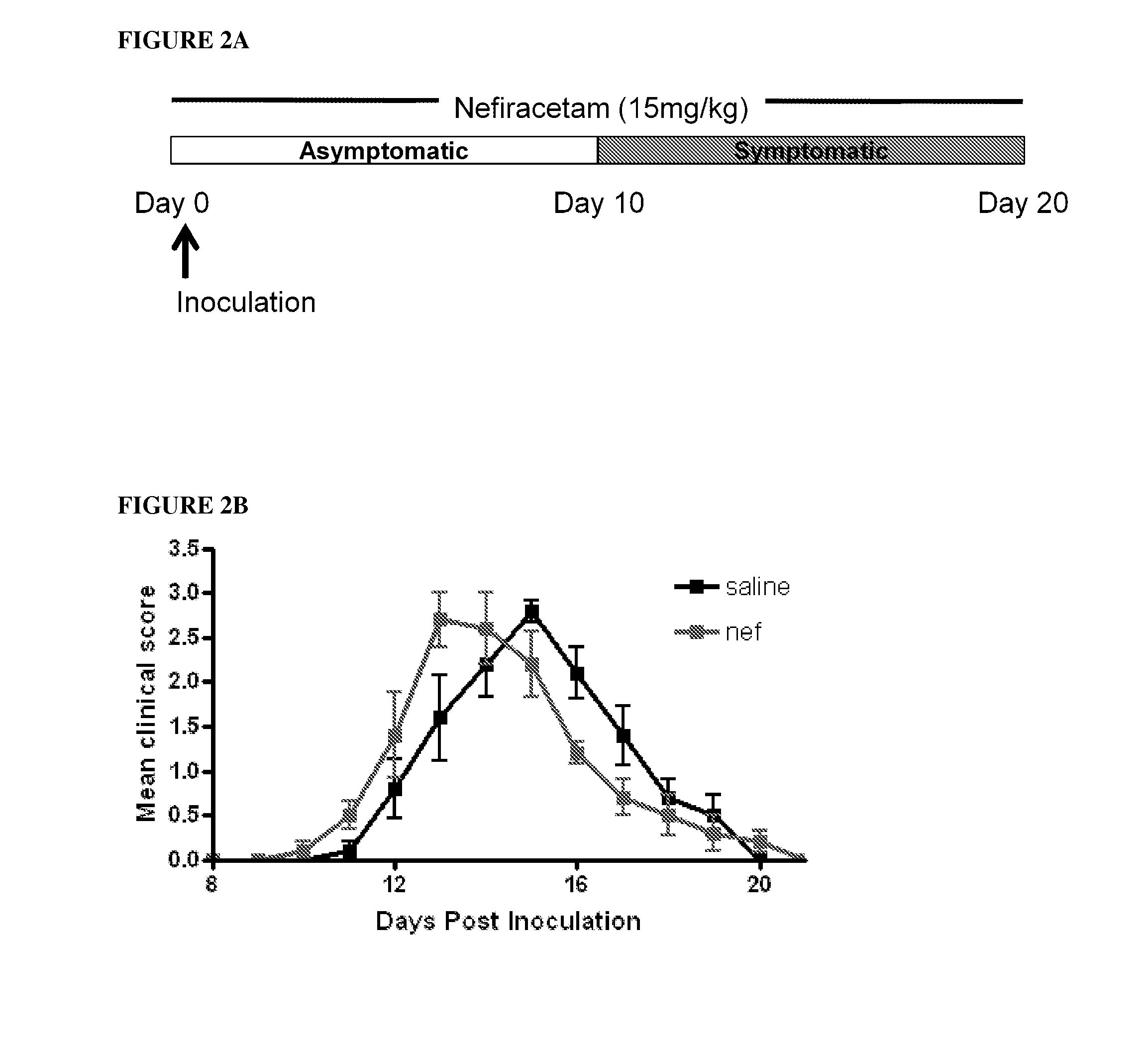
HDAC inhibitors to treat charcot-marie-tooth disease
The disclosure relates to diseases in the peripheral nervous system, particularly hereditary neuropathies, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease. It is shown that this disease is associated with decreased acetylated tubulin levels, which can be overcome by inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs). Using HDAC inhibitors, it is shown herein that the symptoms of the CMT phenotype can be overcome both in vitro and in vivo. Also provided herein are two different mouse models of CMT disease.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Causal therapy of diseases or conditions associated with CNS or pns demyelination
ActiveUS20120269762A1Maintain integrityAccelerates myelin repairBiocideNervous disorderActive agentRemyelination
The invention broadly relates to the use of the Active in the causal treatment of a disease caused by axonal demyelination, in which the Active maintains the integrity of myelination (for example by promoting remyelination, and / or preventing demyelination, of the axonal sheaths). The invention is particularly directed to the causal treatment of CNS demyelination diseases, for example MS, especially primary progressive MS and / or relapse remitting MS, and PNS demyelination diseases, for example Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. The Active of the invention may be suitably administered when a patient is in relapse (i.e. upon relapse), and be continued while the patient is in relapse, with a view to attenuating the severity of the relapse, and / or accelerating disease remission. Alternatively, the Active may be administered continuously with a view to prolonging the remission period, and / or attenuating the severity of the relapse, and / or preventing relapse. The invention also relates to the use of the Active as a treatment for symptoms of demyelination disease, especially MS, selected from vision deficits, motor control deficits, and sensation deficits.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE DUBLIN NAT UNIV OF IRELAND DUBLIN
Detection kit for charcot marie tooth disease related PMP22 gene copy number variation
InactiveCN107529555AHigh precisionConsistent amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePolymerase L
The invention discloses a detection kit for charcot marie tooth disease related PMP22 gene copy number variation. The detection kit comprises a 10*PCR buffer solution, a 4*GC solution, a PCR primer mixed solution, TaqDNA polymerase, a probe primer mixed solution, a DNA diluent, a 10*Taq connecting buffer solution, Taq ligase, 20m MEDTA, dNTP (2.5mM) and MgCl2 (25mM). The kit and the system for detecting PMP22 gene copy number variation on the basis of a CNVplex-high flux connecting probe amplification technology (HLPA) disclosed by the invention are mainly used for detecting the charcot marietooth disease caused by the PMP22 gene deletion or repeated mutation so as to acquire the correct copy number of each target locus of the PMP22 gene. The detection kit has the advantages of quick detection, high accuracy, high repeatability, high resolution ratio, and the like.
Owner:上海和卓医学检验实验室有限公司 +1
Combination of pilocarpin and methimazol for treating Charcot-Marietooth disease and related disorders
InactiveUS9597297B2Effective treatmentNervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsThyroid hormonesPsychiatry
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the treatment of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related peripheral neuropathies. More particularly, the invention relates to combined therapies for treating said disease by affecting simultaneously muscarinic receptor signalling and thyroid hormone pathway in a subject.
Owner:PHARNEXT
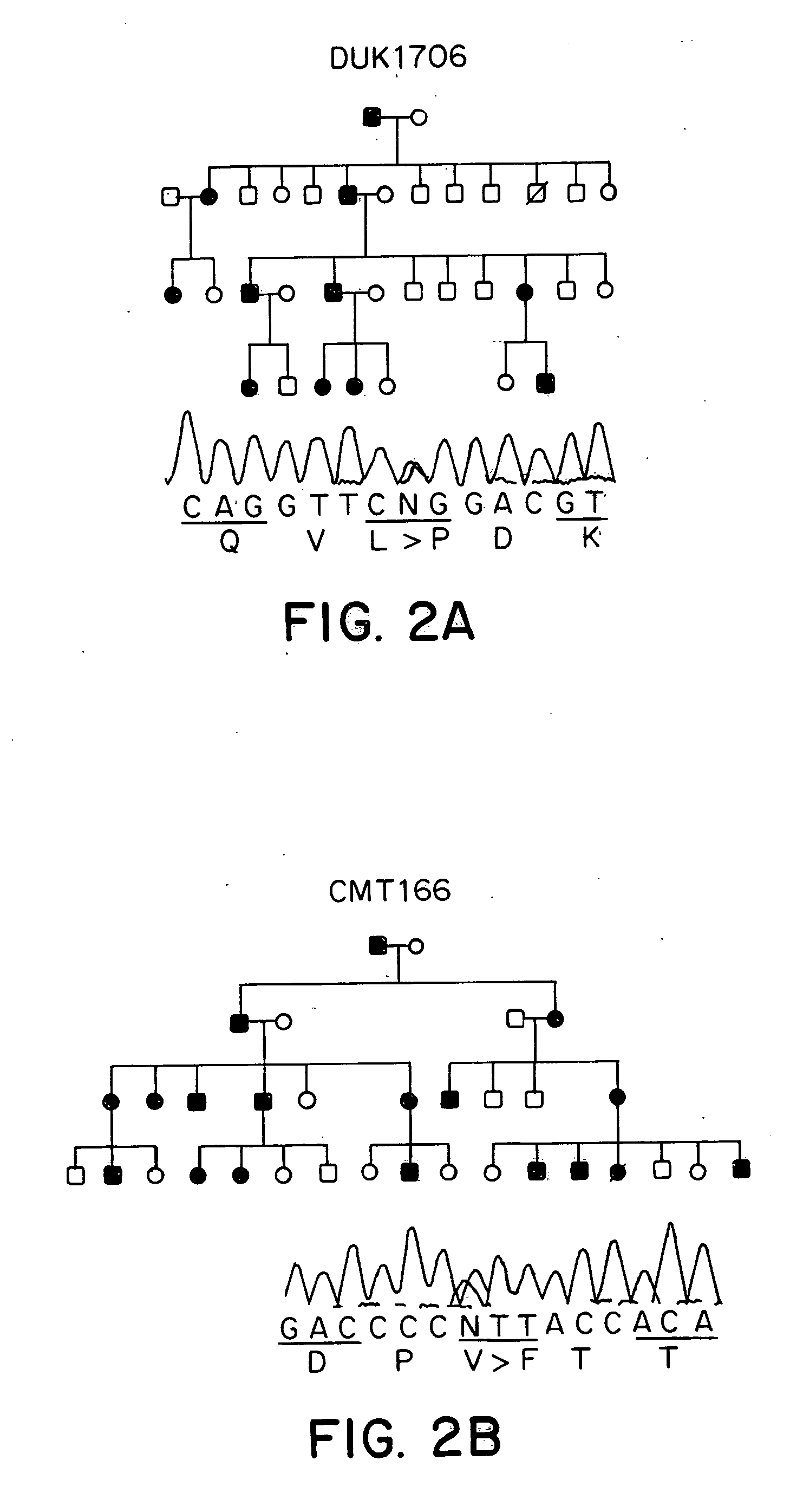
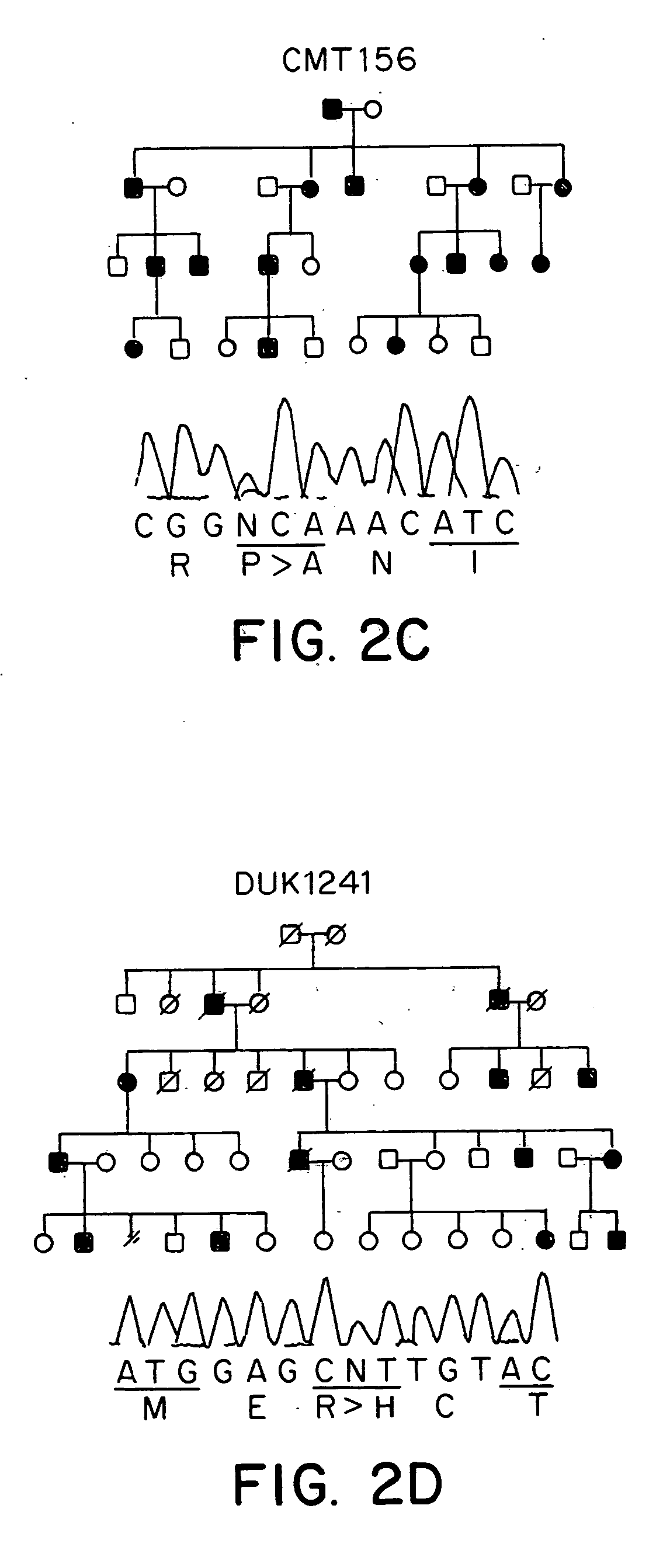
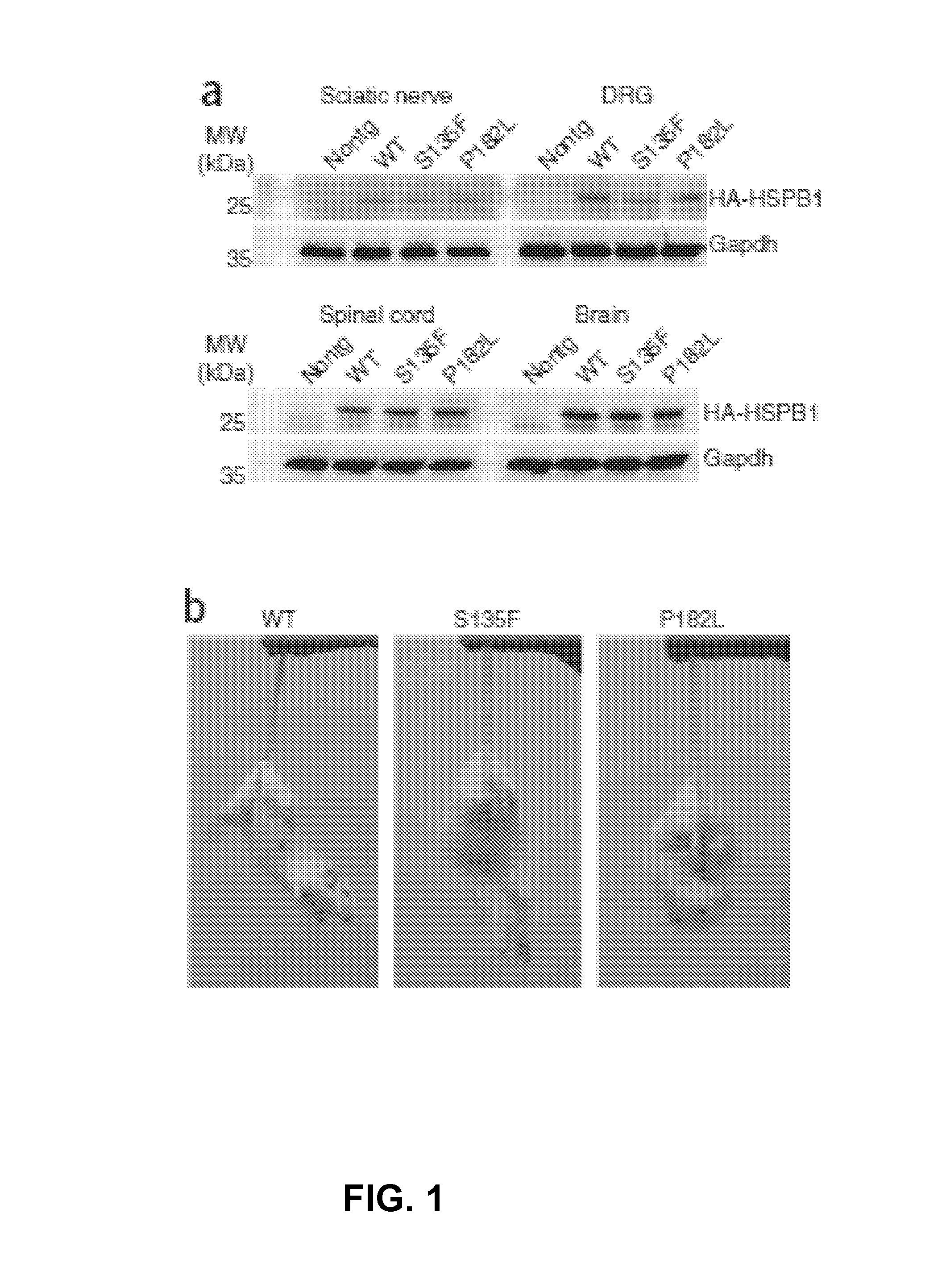
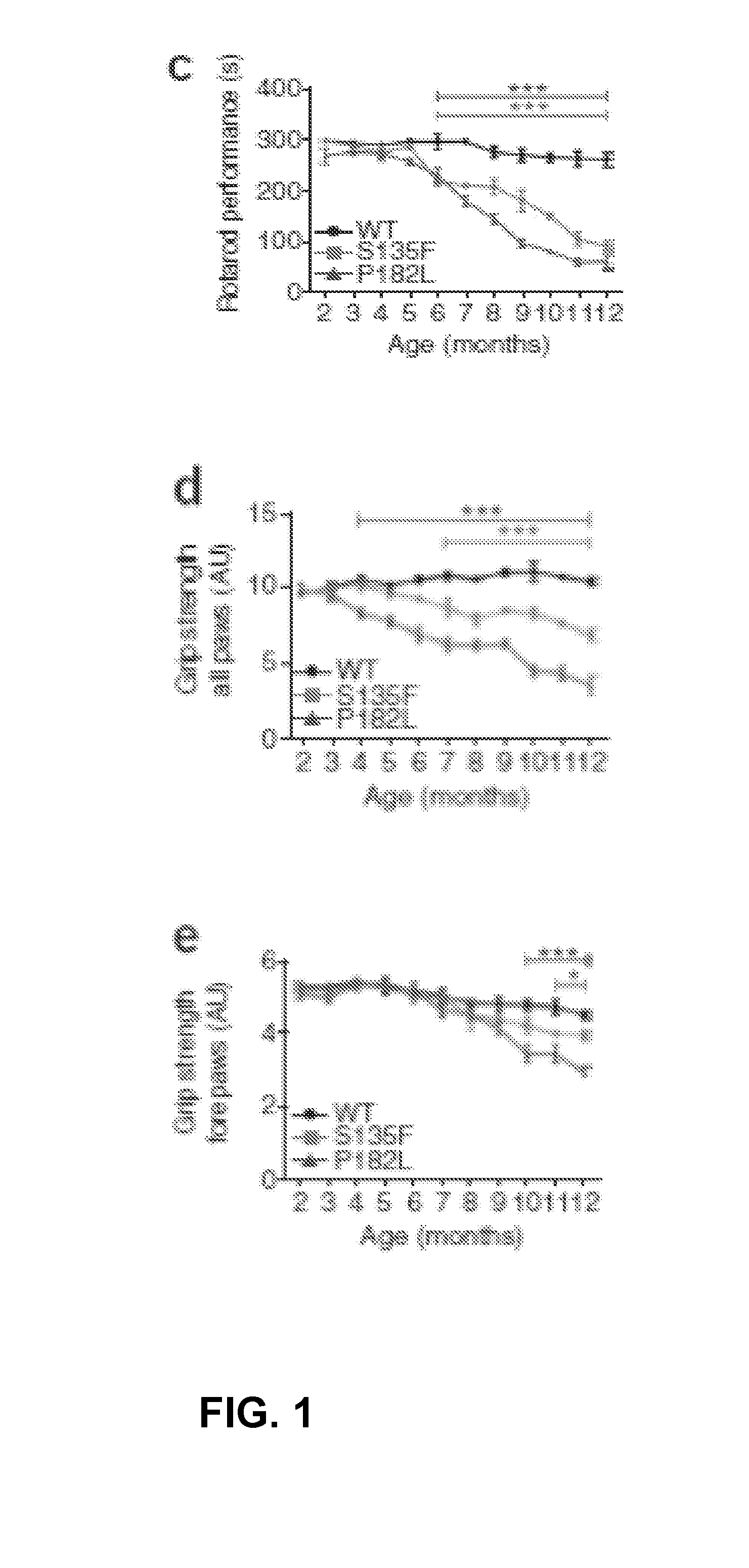
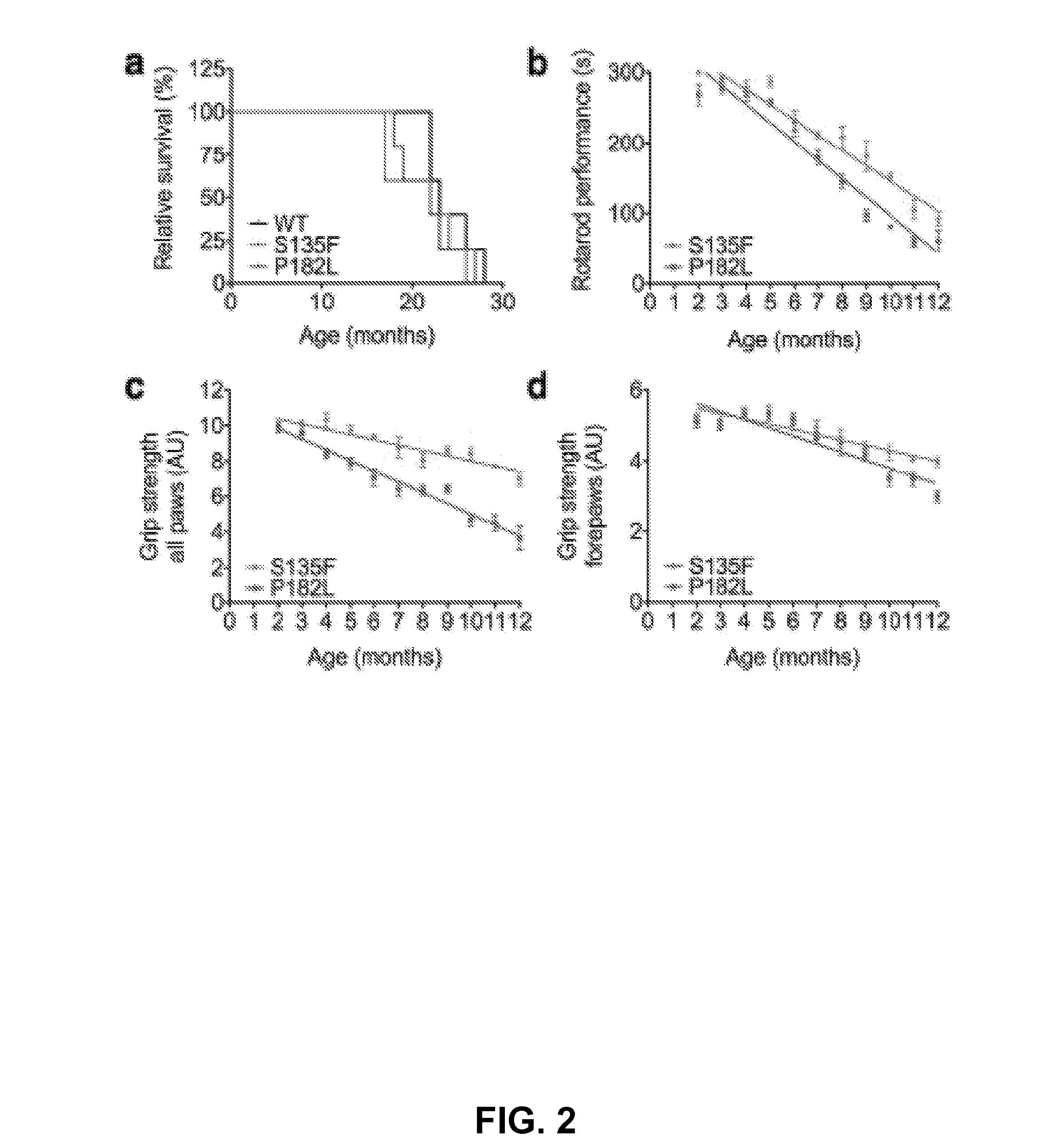
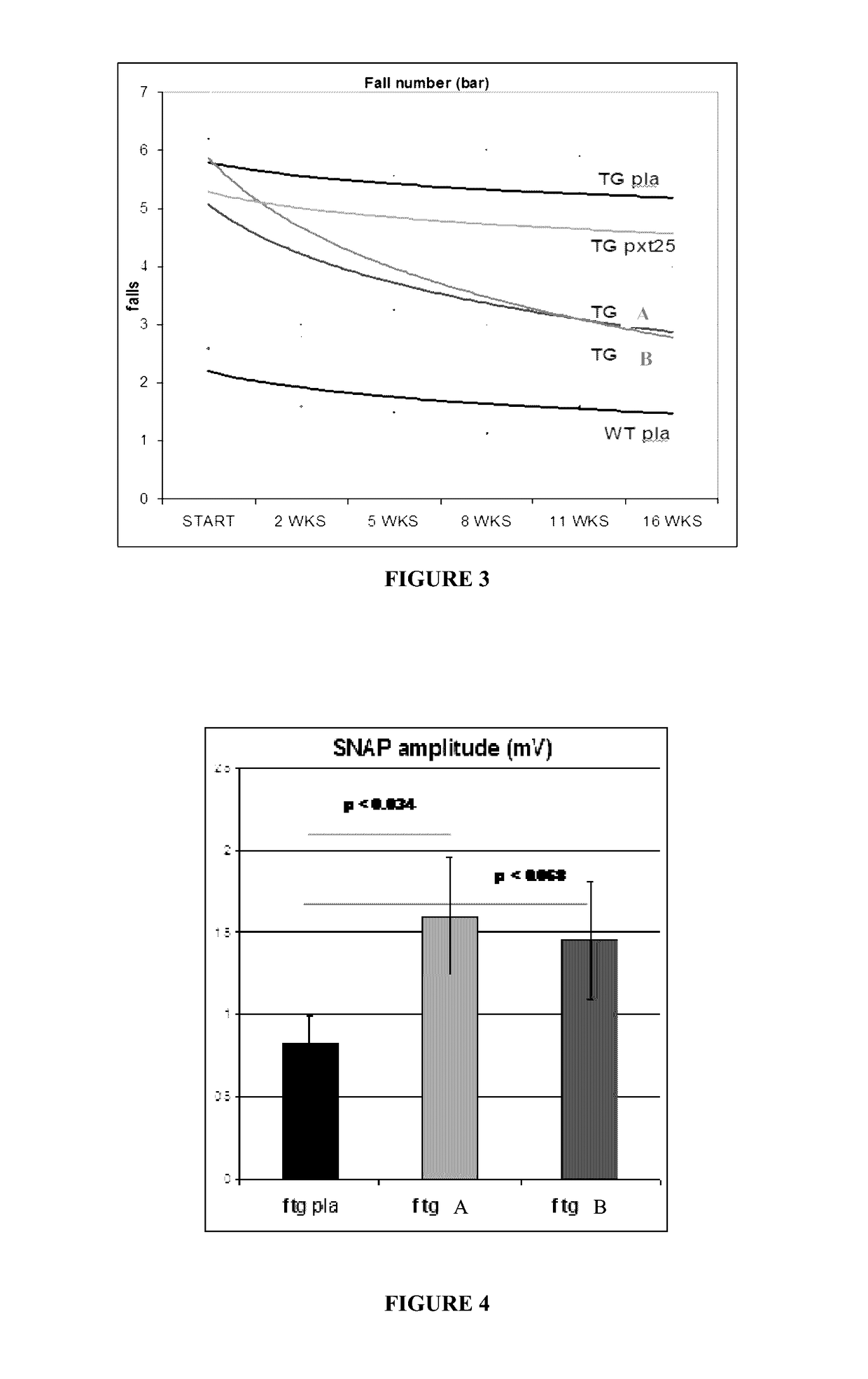
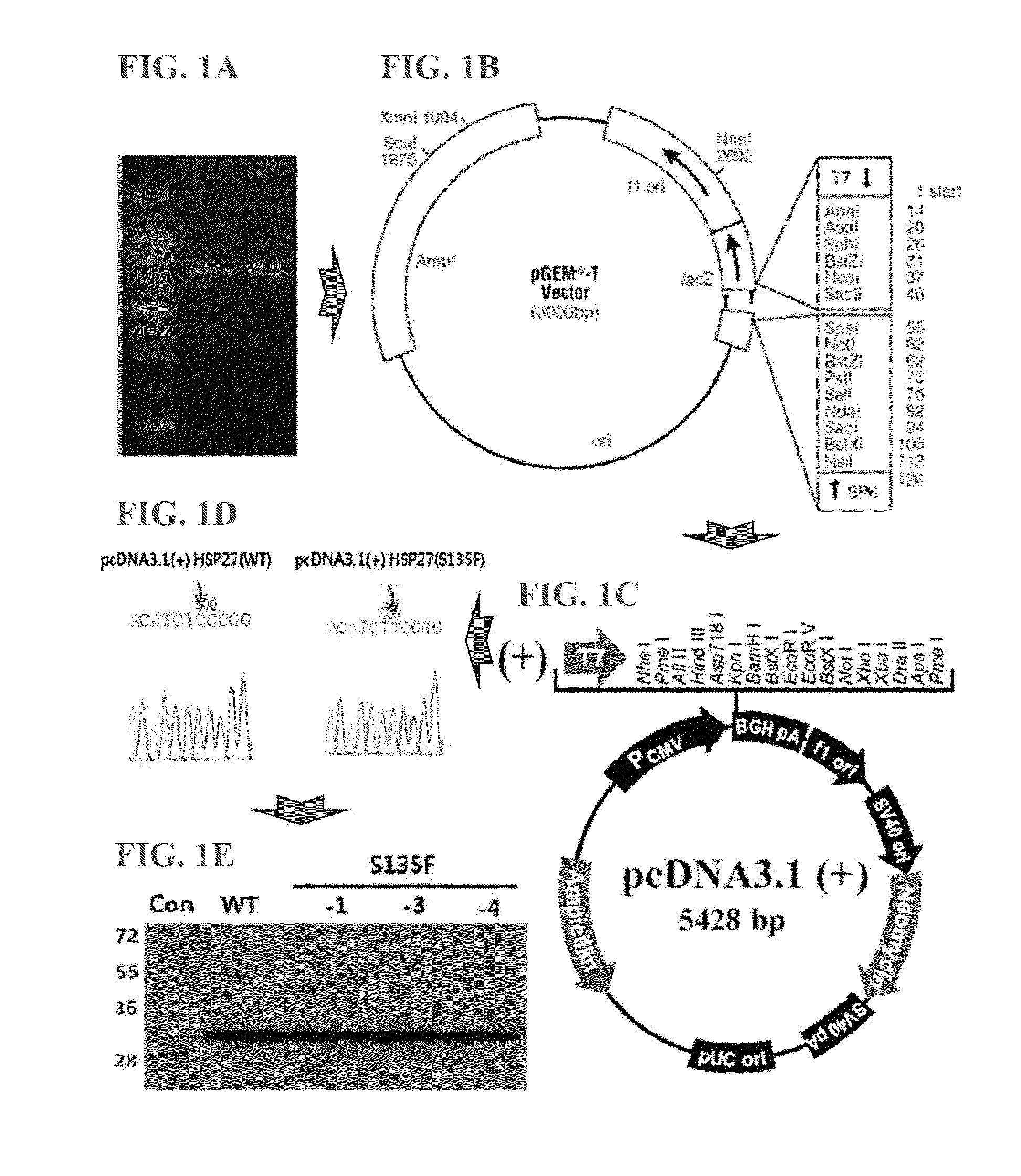
Animal model of charcot-marie-tooth disease as hsp27 mutant (S135F) carrier
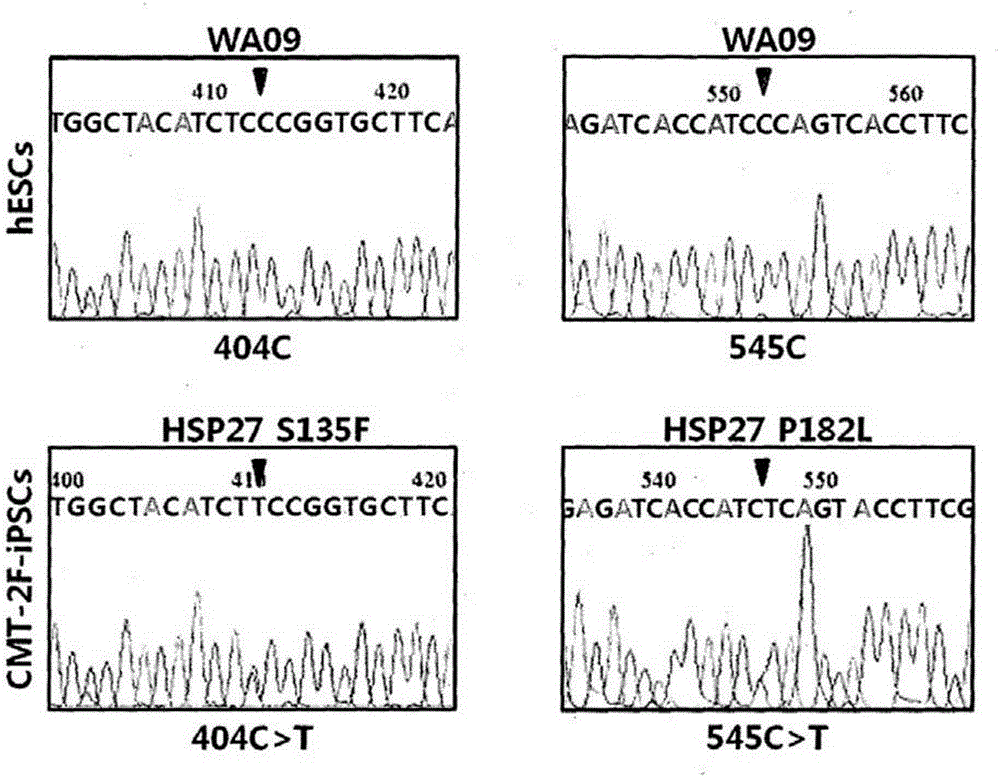
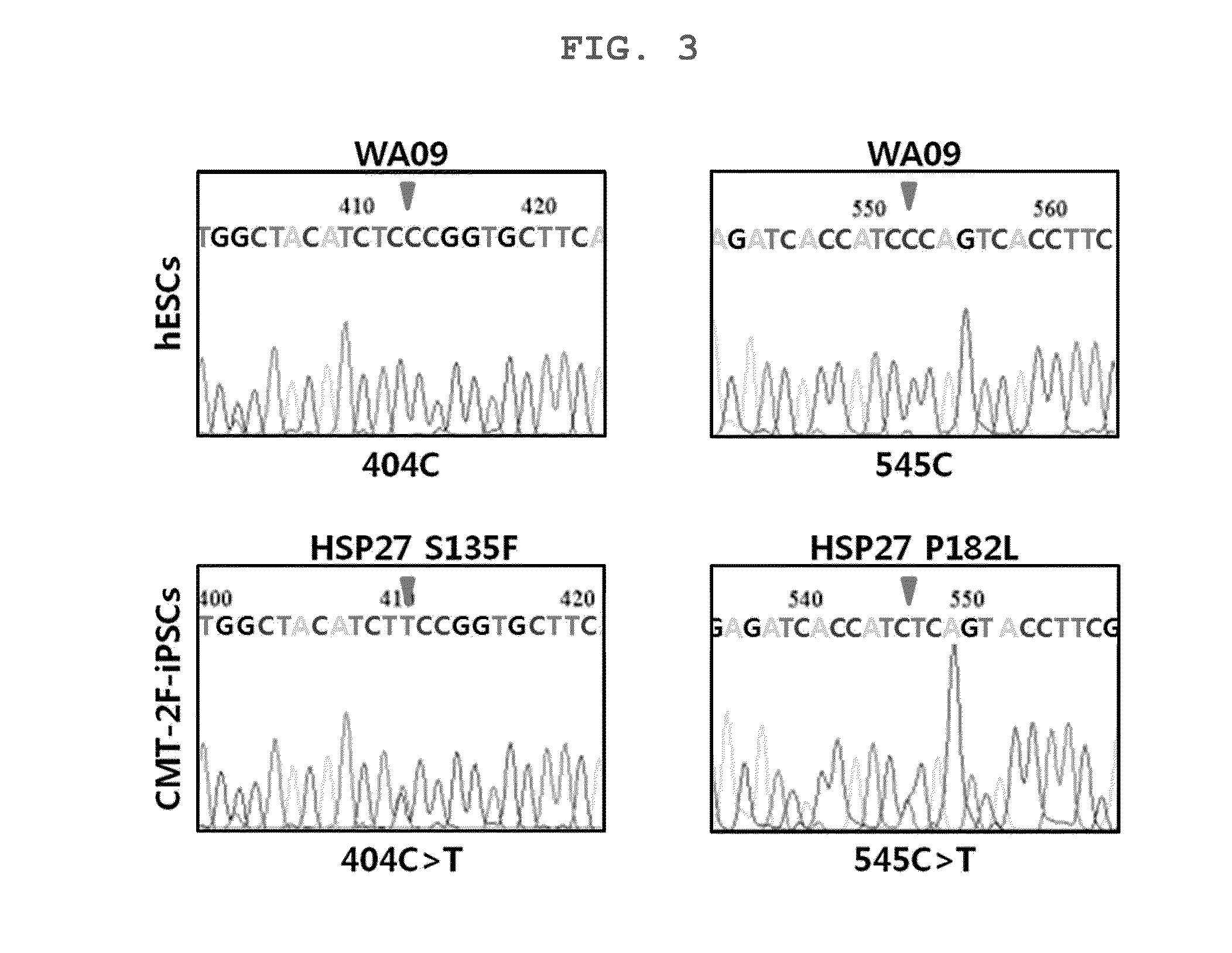
The present invention relates to a HSP27 mutation (S135F) mediated Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) animal model. Particularly, the vector expressing mutant HSP27 protein wherein the 135th serine is substituted with phenylalanine has been injected in the mouse zygote and then the mouse harboring the expression vector was selected. The selected mouse was confirmed to display Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease phenotype, so that the animal model was expected to be efficiently used for the evaluation of the effect of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease treating material candidates.
Owner:SAMSUNG LIFE PUBLIC WELFARE FOUND +1
AMSH gene mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN105821062AImprove early diagnosis rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGene MutantMarie disease
The invention discloses an AMSH gene mutant and an application thereof, and concretely relates to isolated nucleic acid for coding the AMSH mutant, isolated nucleic acid, a method for screening a biological sample predisposed to charcot-marie-tooth disease, a system for screening the biological sample predisposed to charcot-marie-tooth disease, and a kit used for screening the biological sample predisposed to charcot-marie-tooth disease. Compared with SEQ ID NO:1, the isolated nucleic acid for coding the AMSH mutant comprises c.364A>G mutation. By detecting whether the new mutant exists in the biological sample or not, whether the biological sample is predisposed to charcot-marie-tooth disease or not can be effectively detected.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Methods and compositions for development of drug screening procedures and diagnostic tools
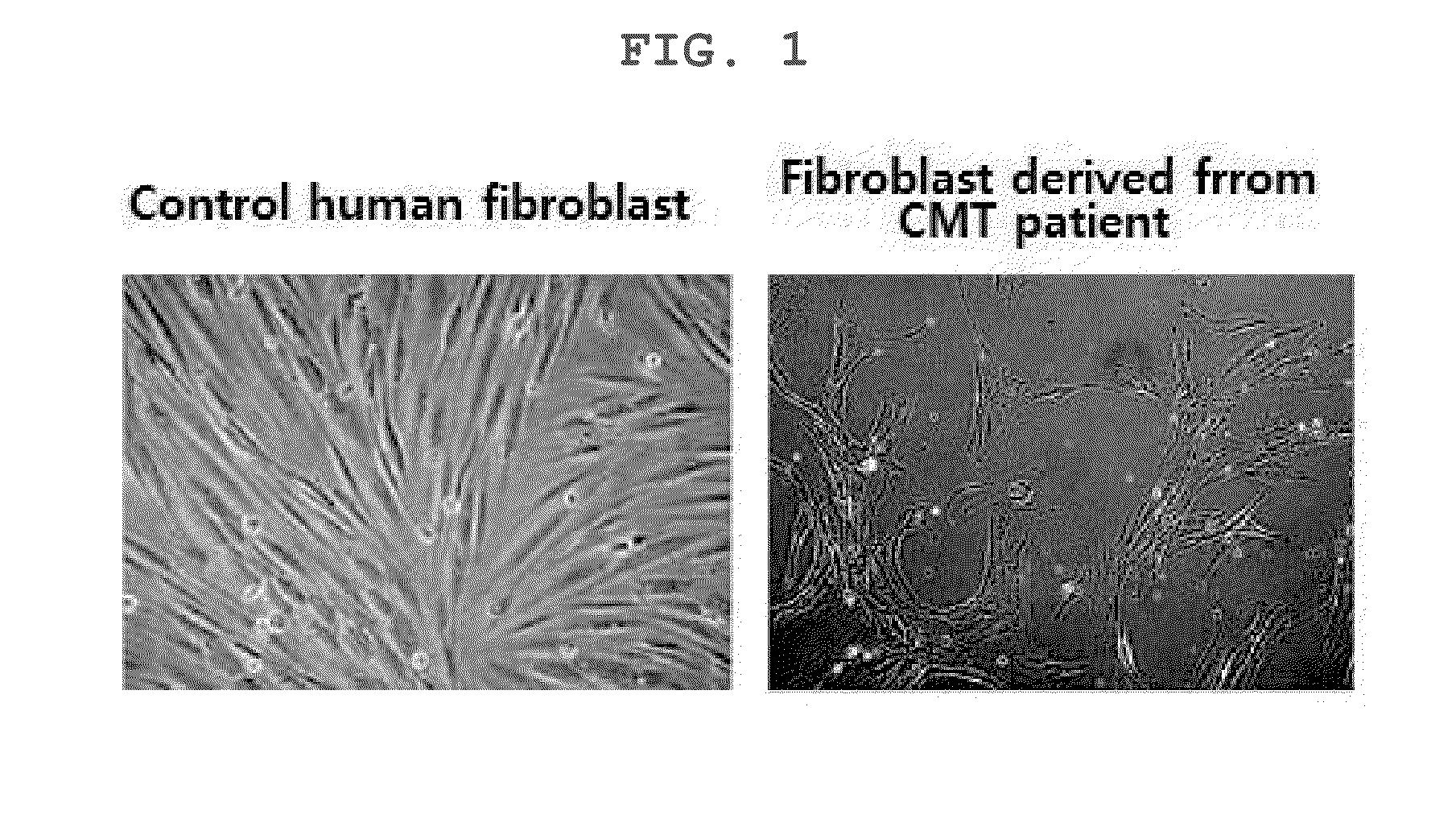
This invention defines novel research methodology for use in (a) monitoring the ongoing status of the physiological expression of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and (b) screening candidate therapeutic drug agents for possible effectiveness. The presence of this neurodegenerative disease can be characterized in part by the expression in cultured fibroblasts obtained from the patient of one or more proteins which are not the product of a defective disease-inducing gene, but which are stress proteins, one or more other proteins modified by conditions of oxidative stress or other disease-related proteins. This candidate drug screening technology offers advantages in terms of (a) providing new research opportunities, (b) cost effectiveness, (c) ability to be used readily on a large scale, (d) ability to generate meaningful data in a comparatively short period of time, and (e) providing an opportunity to obtain information based on direct interaction of a candidate drug and a living tissue disease model.
Owner:SHAPIRO HOWARD K
Methods of treating charcot-marie-tooth disease
PendingUS20220175803A1Nervous disorderTetracycline active ingredientsAntibacterial activityDentistry
A method of treating Charcot Marie Tooth Disease in a human in need thereof. The method comprises systemically administering to the human a non-antibacterial tetracycline compound or antibacterial tetracycline compound, in an amount that is effective to treat Charcot Marie Tooth Disease but has substantially no antibacterial activity.
Owner:CMTX BIOTECH INC
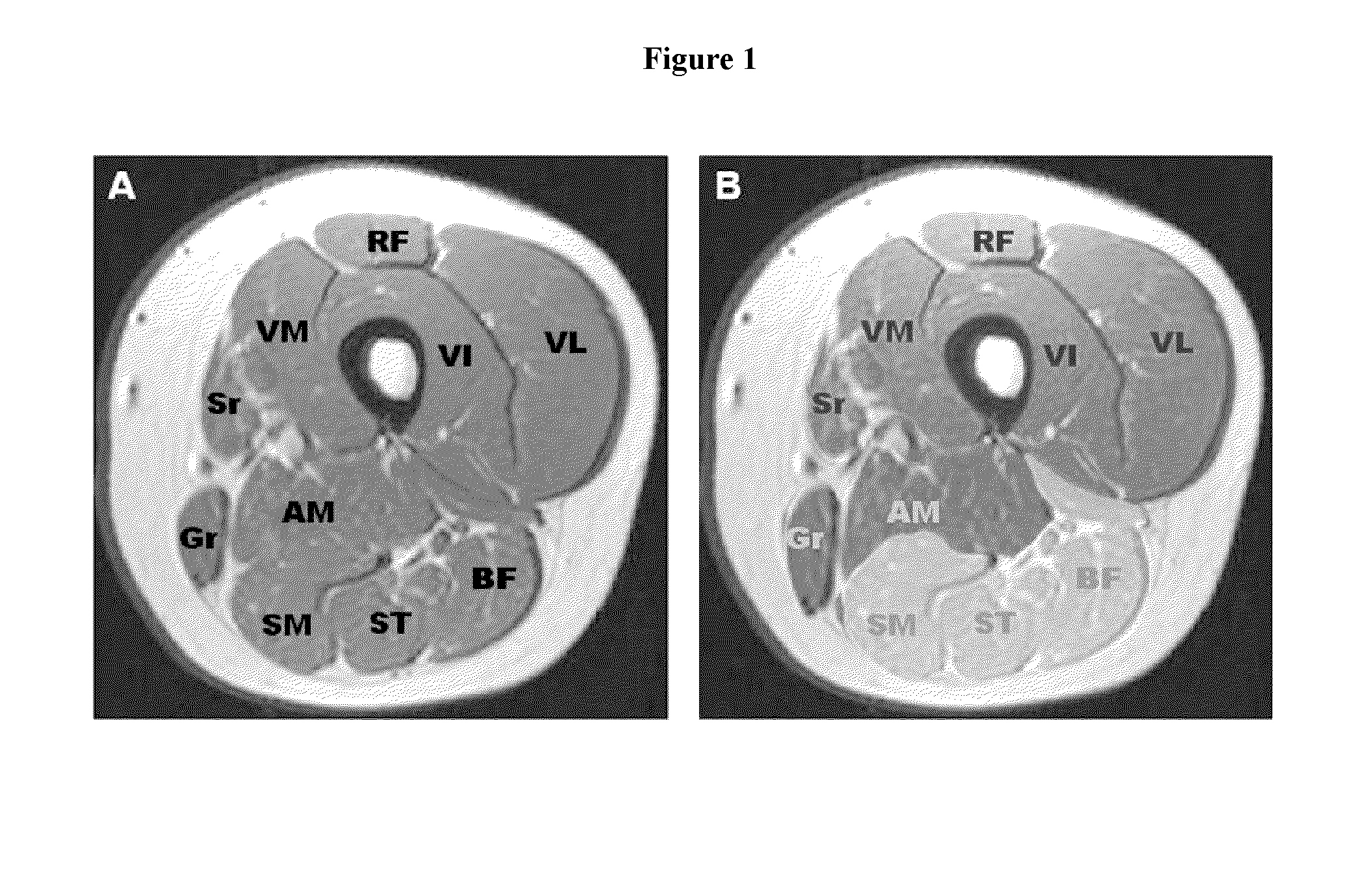
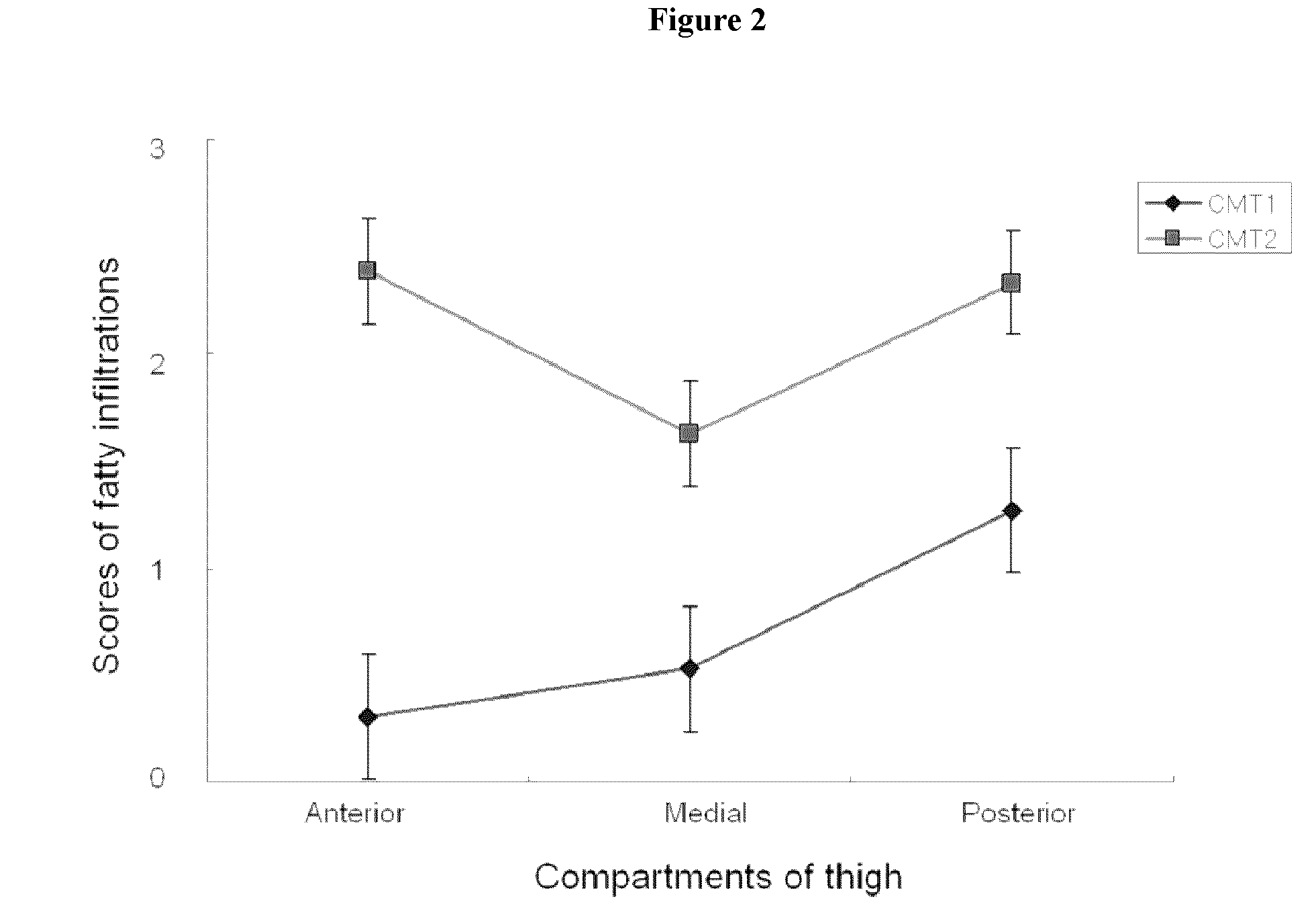
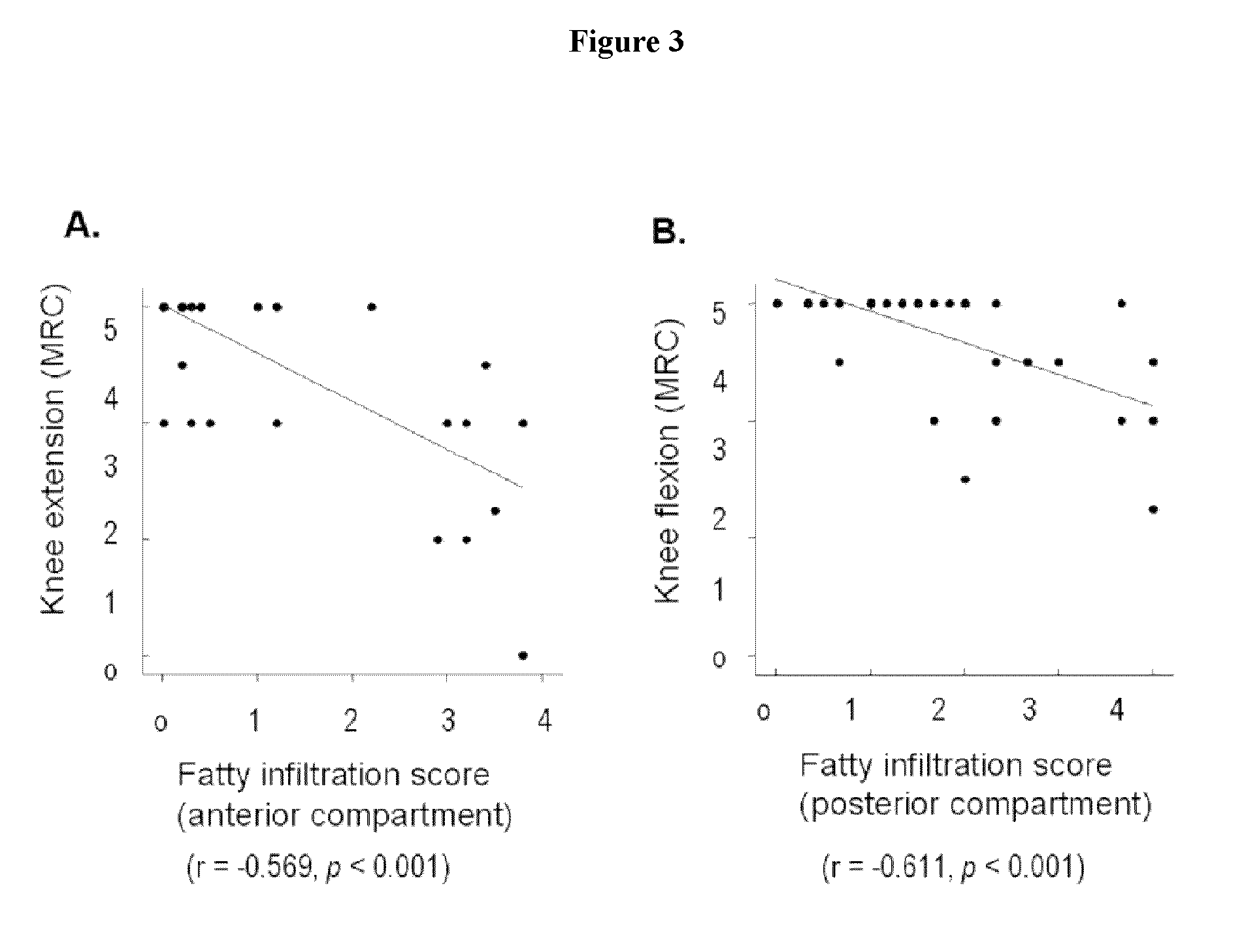
Method for diagnosing cmt1a and cmt2a by MRI
Disclosed is a method for diagnosing Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease. More specifically, disclosed is a method for diagnosing a subtype of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1, (i.e., CMT1A) and a subtype of the disease type 2 (i.e., CMT2A) by evaluating fatty infiltration behaviors in respective compartments of proximal lower extremity muscles via comparison and analysis of MRI on the proximal lower extremities. Further disclosed is a method for diagnosing CMT1A and CMT2A, by analyzing fatty infiltration levels between respective compartments by MRI examination on distal lower extremity muscles.
Owner:EWHA UNIV IND COLLABORATION FOUND +1
Diagnostic tests for the detection of inherited peripheral neuropathies
The disclosure relates to the field of human genetics, particularly the field of peripheral neuropathy, particularly inherited peripheral neuropathy. Specifically, the disclosure relates to methods and materials to detect hereditary peripheral neuropathy, more particularly autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Use of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor delta agonists for the treatment of ms and other demyelinating diseases
InactiveCN1950077ANervous disorderAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsX-linked adrenoleukodystrophyPPAR-delta Agonists
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA INC
Treatment of disorders of the peripheral nervous system
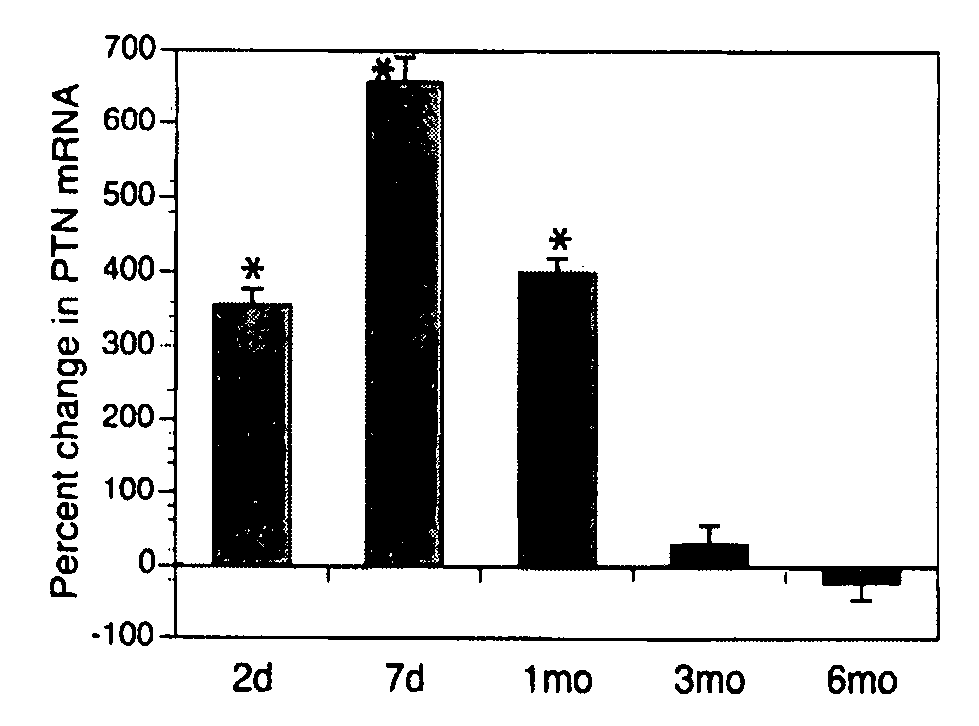
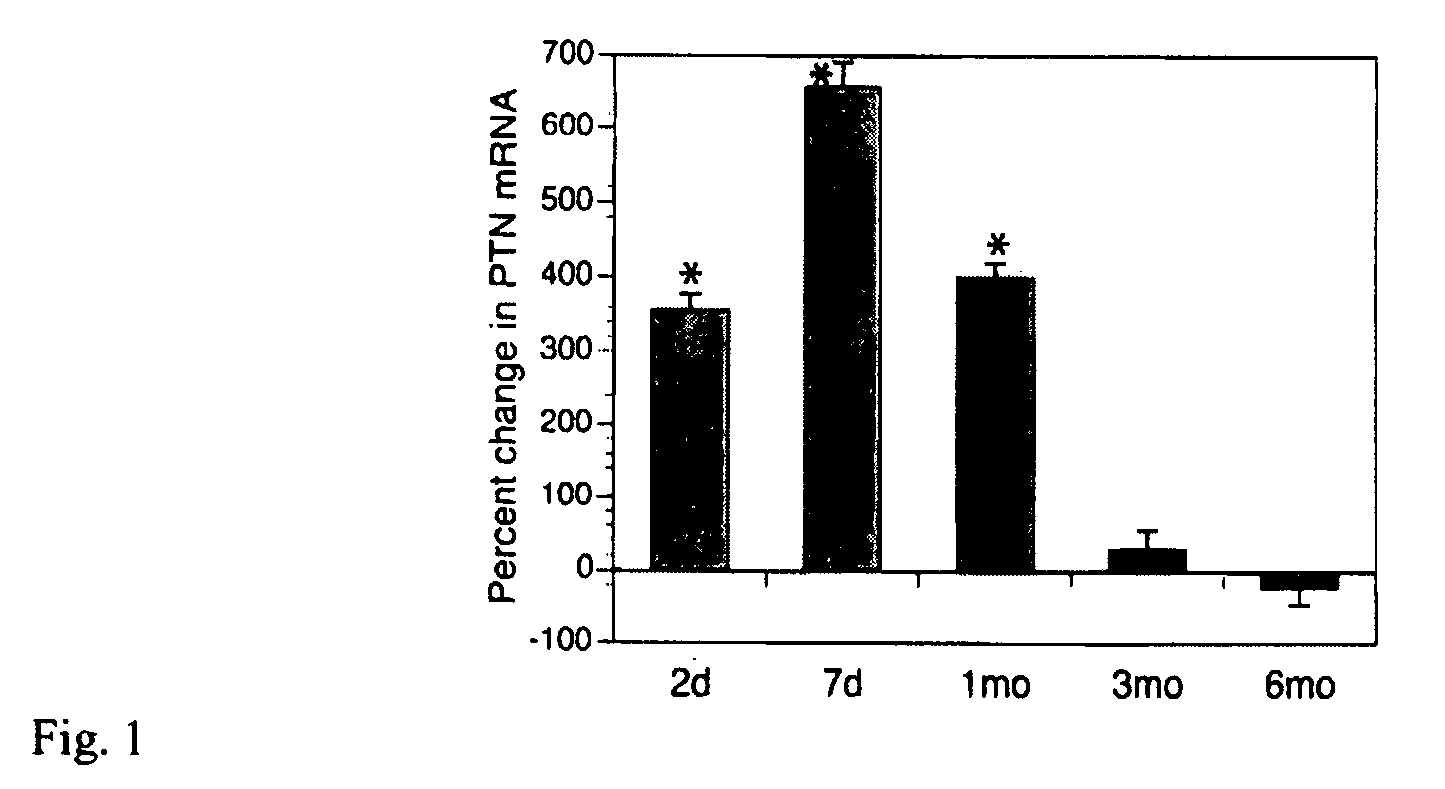
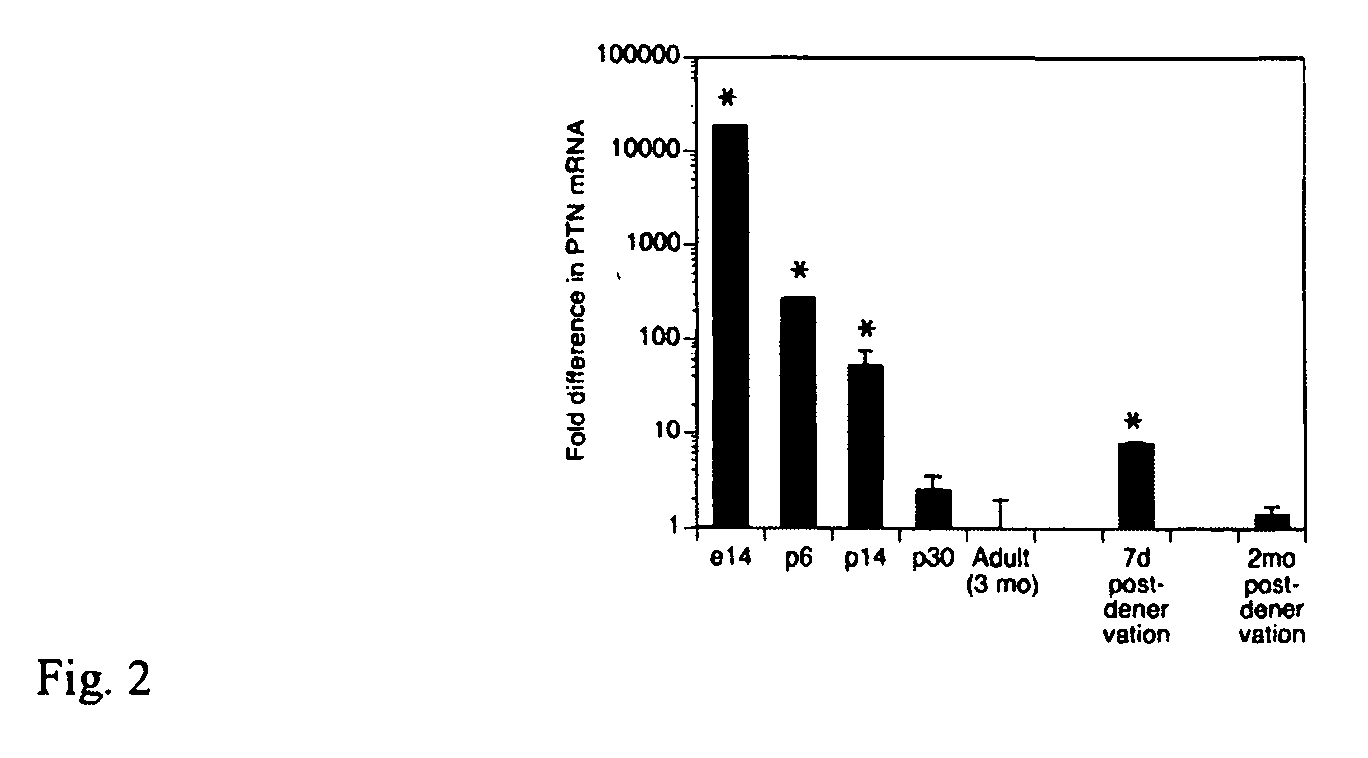
Pleiotrophin is used to treat various conditions, disorders, and diseases which involve damage to the peripheral nervous system. Such conditions include traumatic nerve damage, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinobulbar muscular atrophy, spinal muscular atrophy, diabetic neuropathy, and uremic neuropathy. Pleiotrophin can be provided as a protein or as a gene therapy to a patient in need thereof.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Diagnostic tools for charcot-marie-tooth disease
InactiveUS9494605B2ResponsivenessHydroxy compound active ingredientsDisease diagnosisMetaboliteCvd risk
The present invention relates in particular to methods of detecting predisposition to or diagnosis and / or prognosis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) and related disorders. More specifically, the invention relates to development, validation and application of new biomarkers, which can be used for detecting the presence or risk of CMT disease and related disorders. In particular, the present invention relates to metabolite, lipid, carbohydrate and proteinaceous biomarkers that can be measured in biological body fluids and easily available extracts of biopsies, which can be used to aid in the detection, prediction of drug treatment and follow up of this treatment of neurodegenerative disorders, including CMT disease. The present invention also relates to methods for identification of CMT disease subtypes, assessing the responsiveness to the treatments and the efficacy of treatments in subjects having CMT or a related disorder.
Owner:PHARNEXT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com