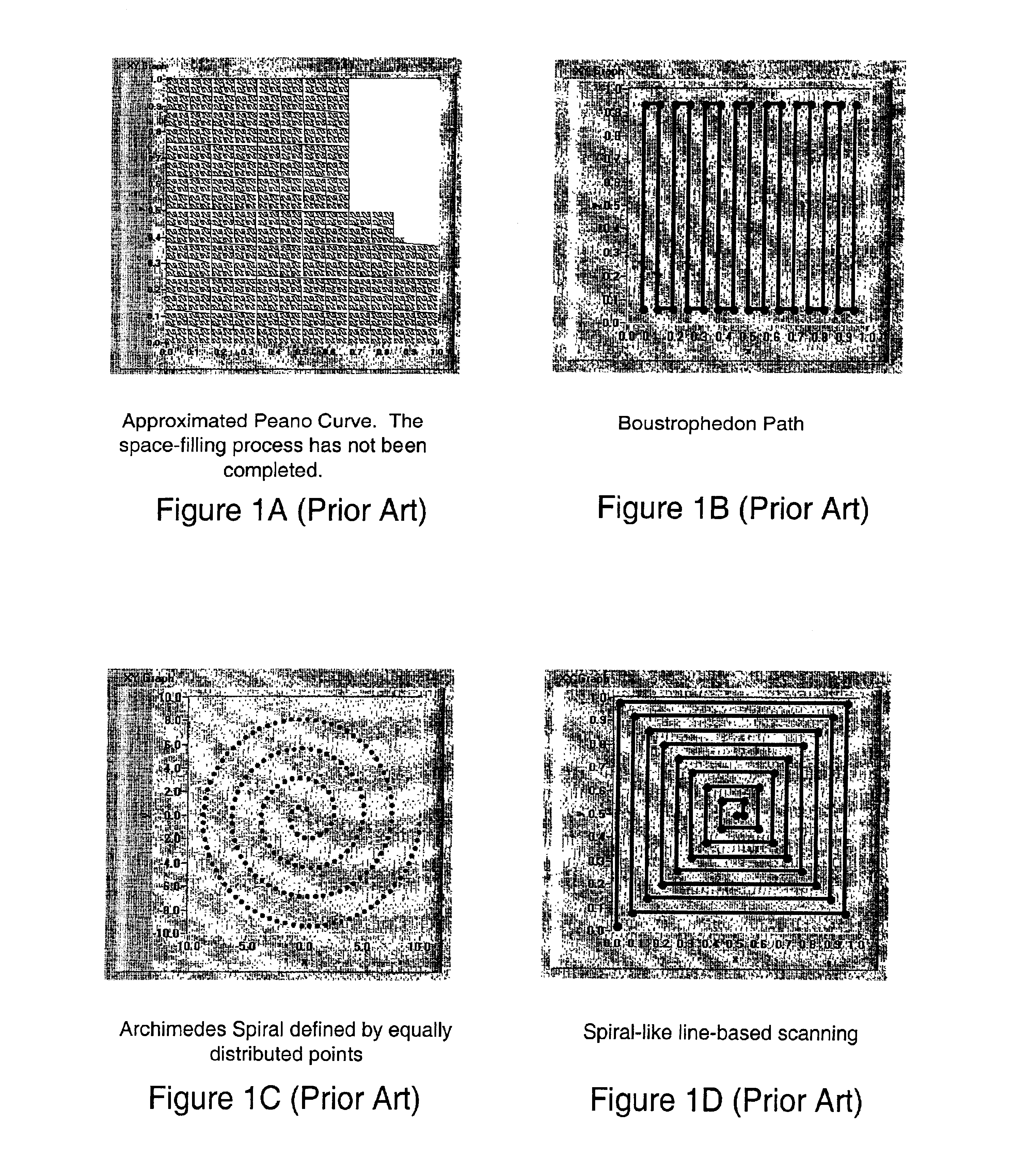
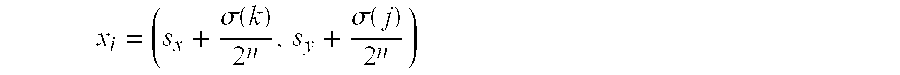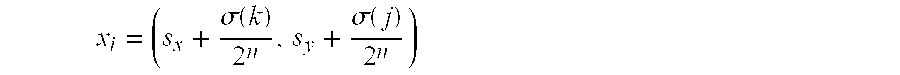Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Low-discrepancy sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
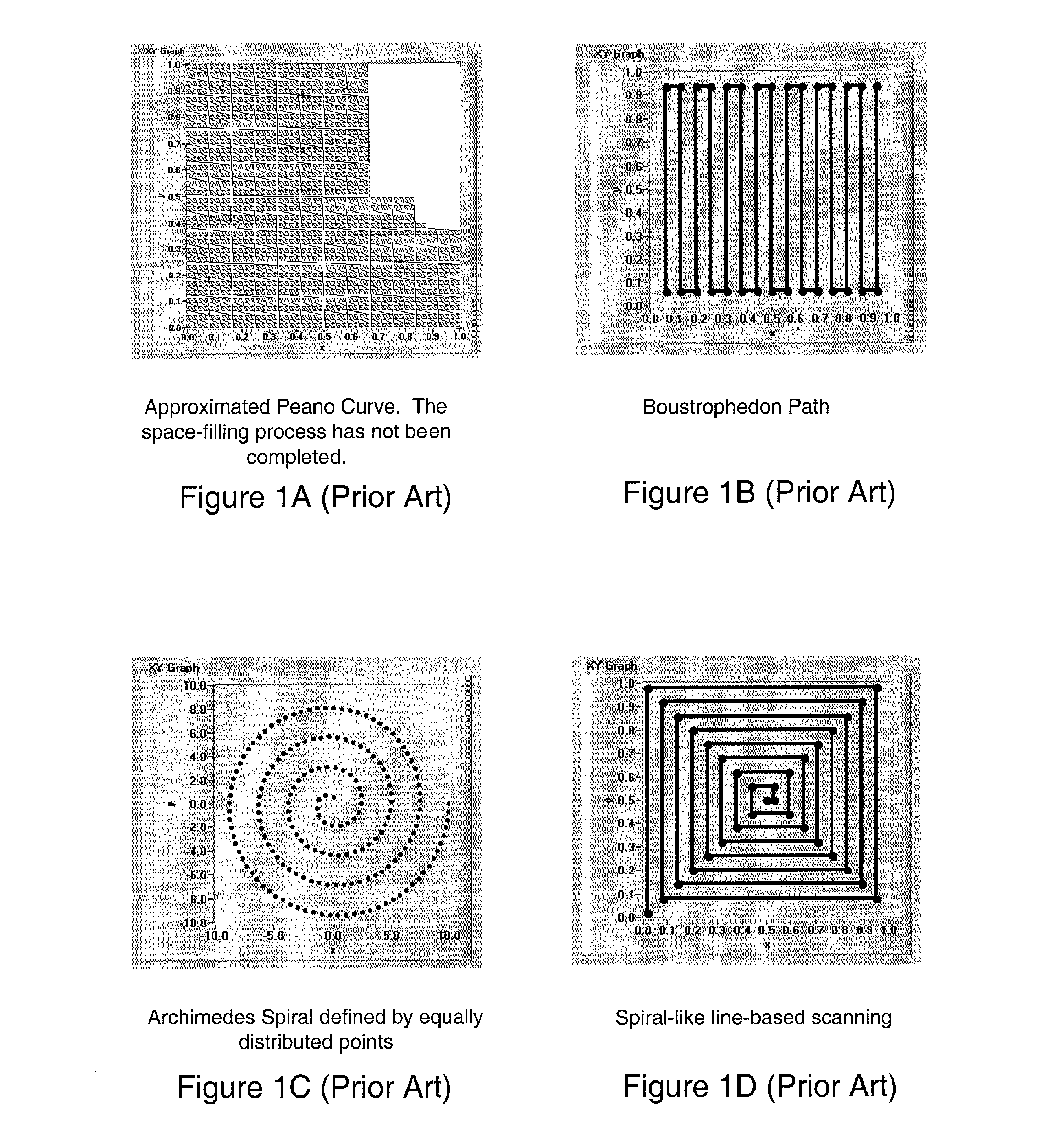
In mathematics, a low-discrepancy sequence is a sequence with the property that for all values of N, its subsequence x₁, ..., xN has a low discrepancy. Roughly speaking, the discrepancy of a sequence is low if the proportion of points in the sequence falling into an arbitrary set B is close to proportional to the measure of B, as would happen on average (but not for particular samples) in the case of an equidistributed sequence. Specific definitions of discrepancy differ regarding the choice of B (hyperspheres, hypercubes, etc.) and how the discrepancy for every B is computed (usually normalized) and combined (usually by taking the worst value).
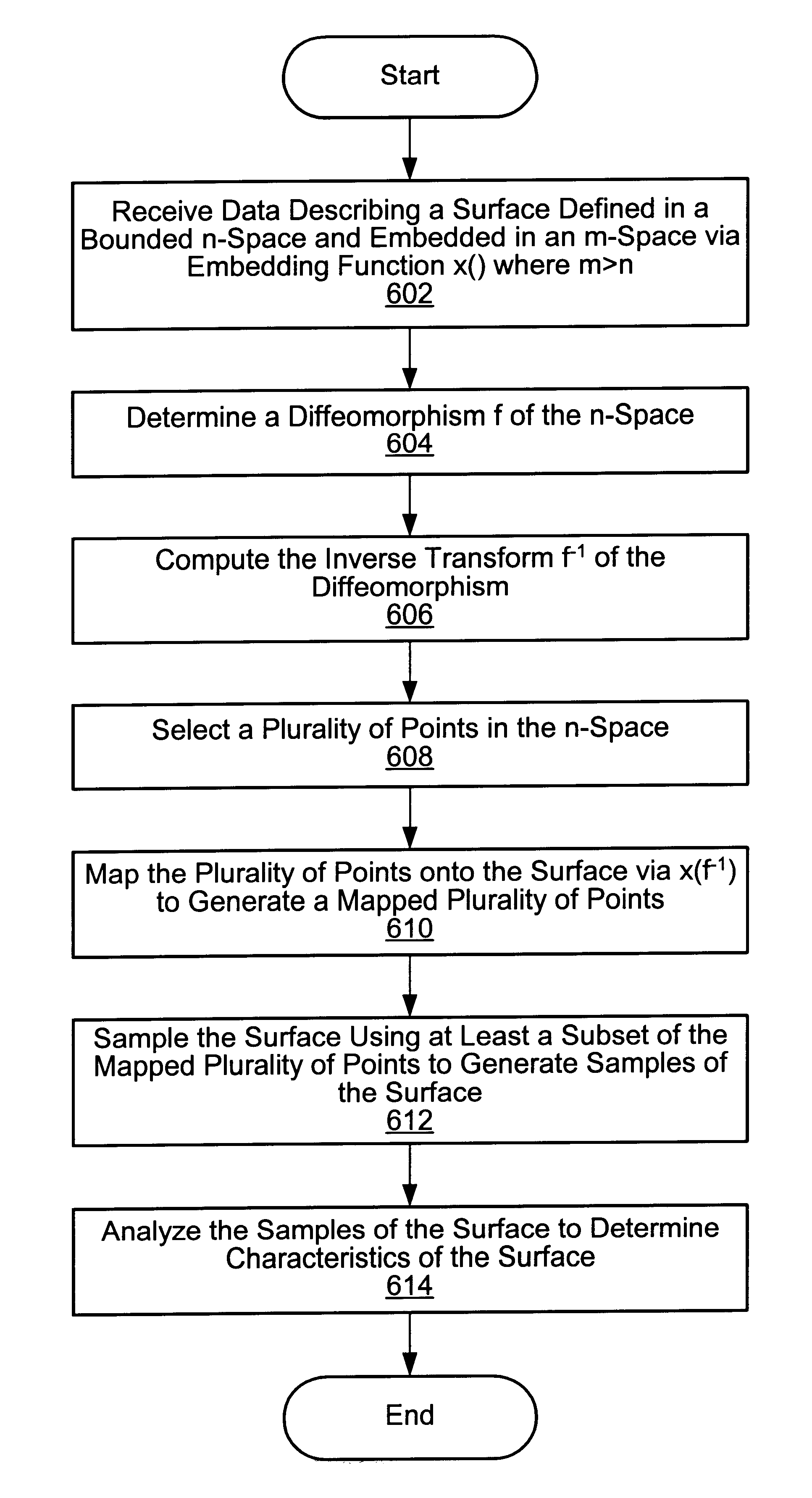
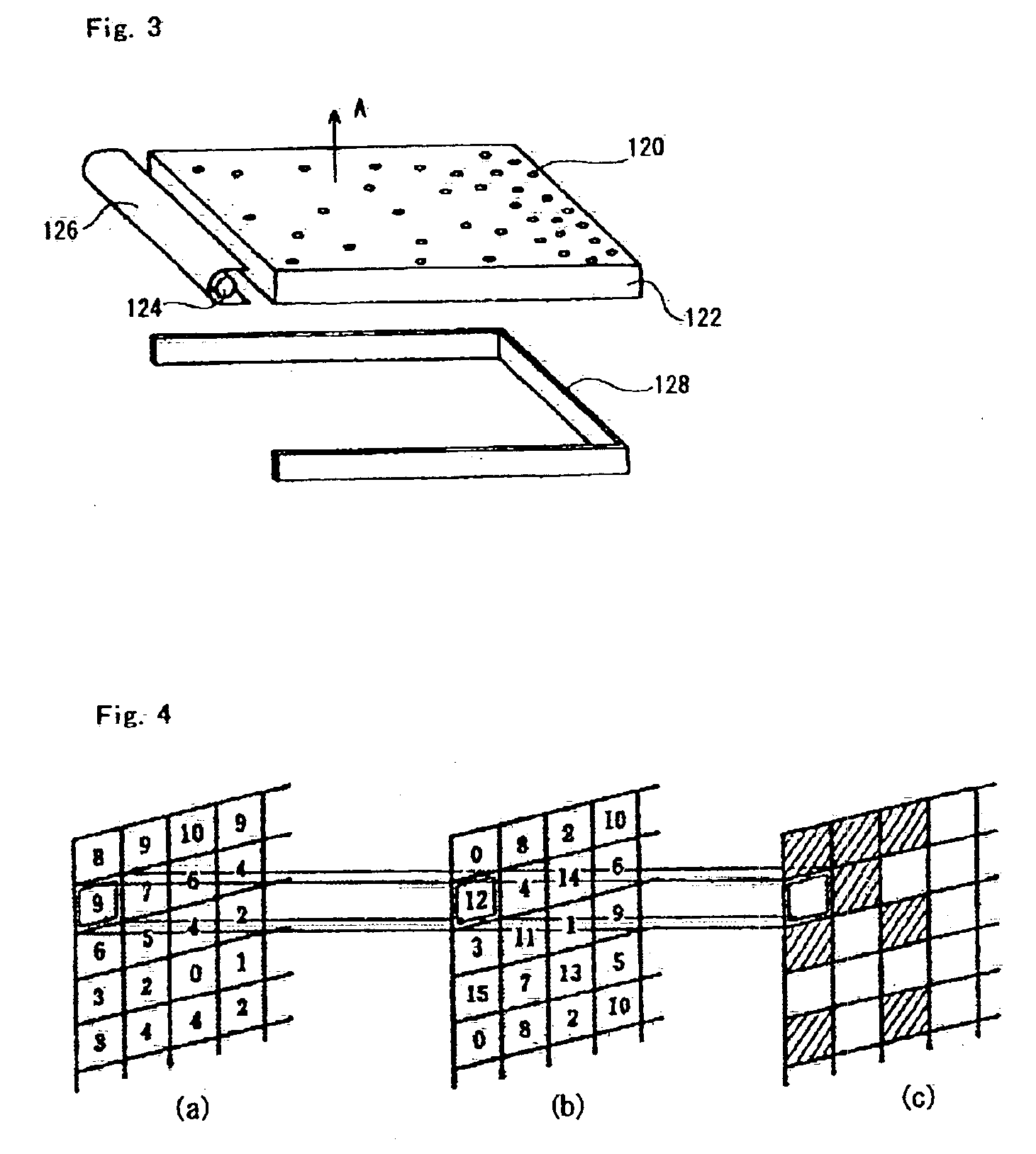
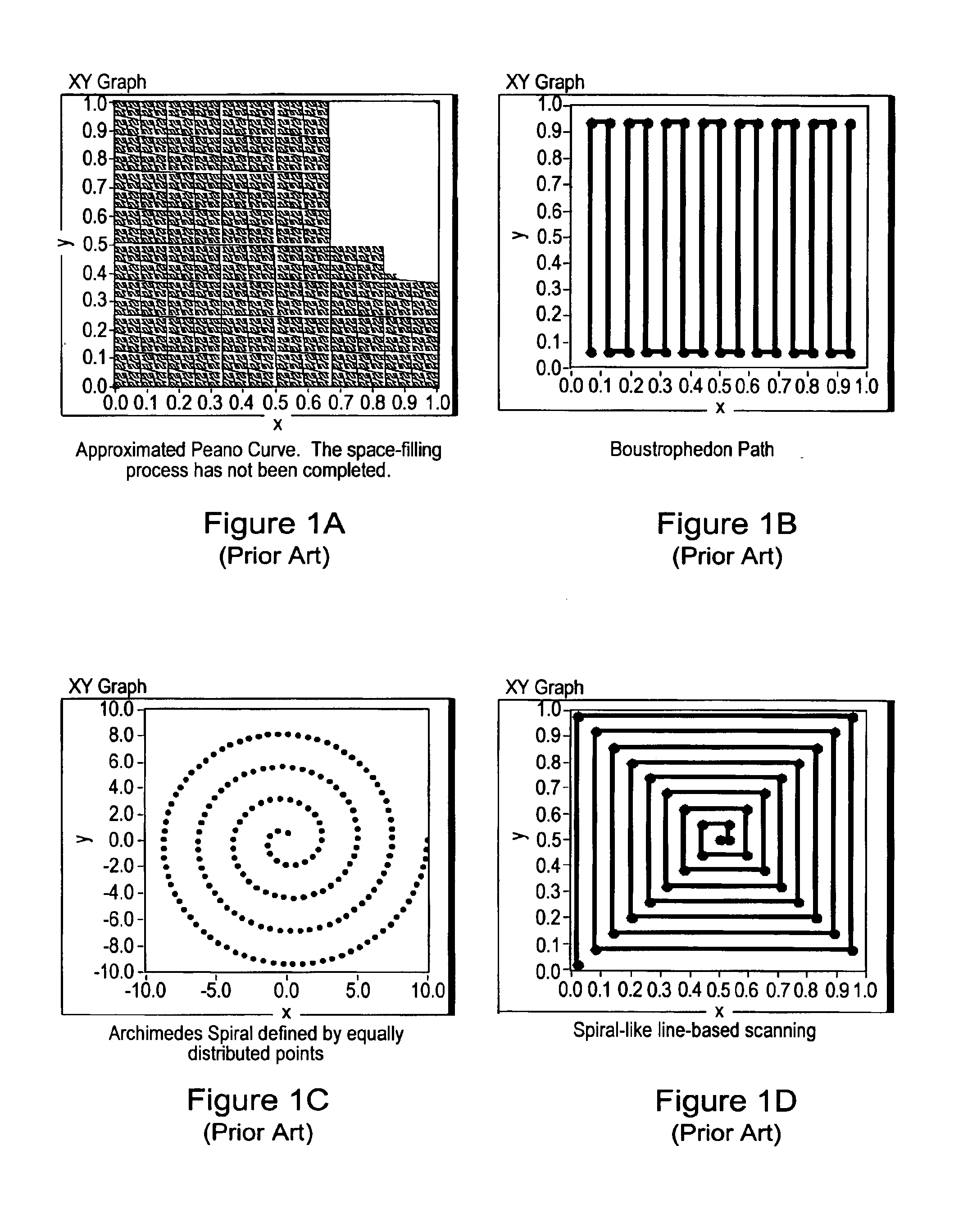
System and method for analyzing a surface by mapping sample points onto the surface and sampling the surface at the mapped points
A system and method for analyzing a surface. The system includes a computer including a CPU and a memory medium operable to store programs executable by the CPU to perform the method. The method may include: 1) receiving data describing an n-dimensional surface defined in a bounded n-dimensional space, where the surface is embedded in an m-dimensional real space via embedding function x( ), and where m>n; 2) determining a diffeomorphism f of the n-dimensional space; 3) computing the inverse transform f-1 of the diffeomorphism f; 4) selecting points, e.g., a Low Discrepancy Sequence, in the n-dimensional space; 5) mapping the points onto the surface using x(f-1), thereby generating mapped points on the surface; 6) sampling the surface using at least a subset of the mapped points to generate samples of the surface; and 7) analyzing the samples of the surface to determine characteristics of the surface.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
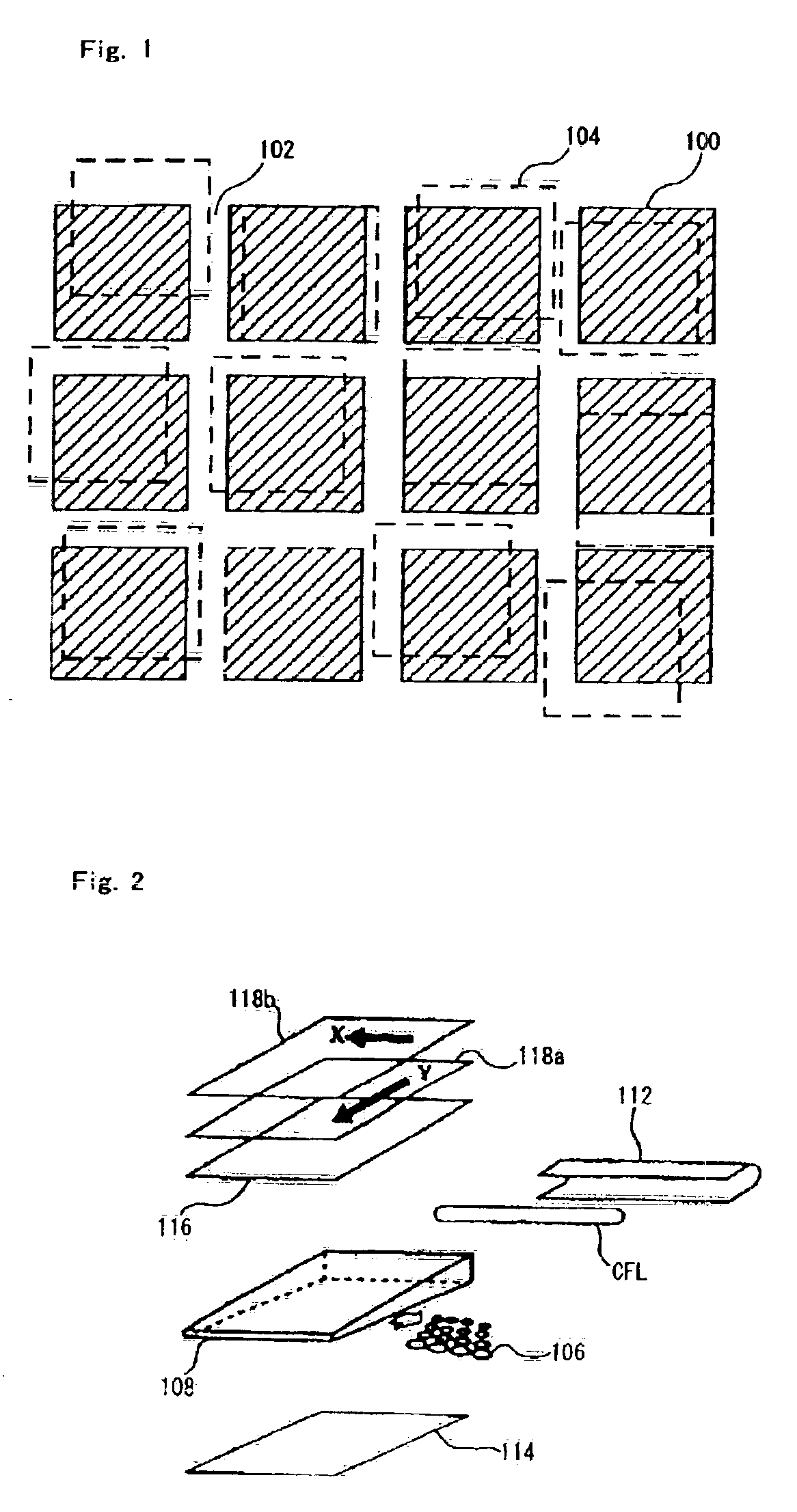
Discrete pattern, apparatus, method, and program storage device for generating and implementing the discrete pattern
InactiveUS6865325B2Increase randomnessRemove overlapMechanical apparatusStatic indicating devicesFill factorSoftware engineering
A discrete pattern, formed by dots discretely arranged in two dimensions, is provided wherein the dots are generated in a low discrepancy sequence. The dots are preferably generated in a discrete pattern wherein the square of discrepancy D satisfies the formula,D≦0.13N−1.15 (1)Further, the method provides for generation of, and the appartus provides implementation of, a discrete pattern even when the filling factor rapidly changes by automatically generating or deleting dots.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
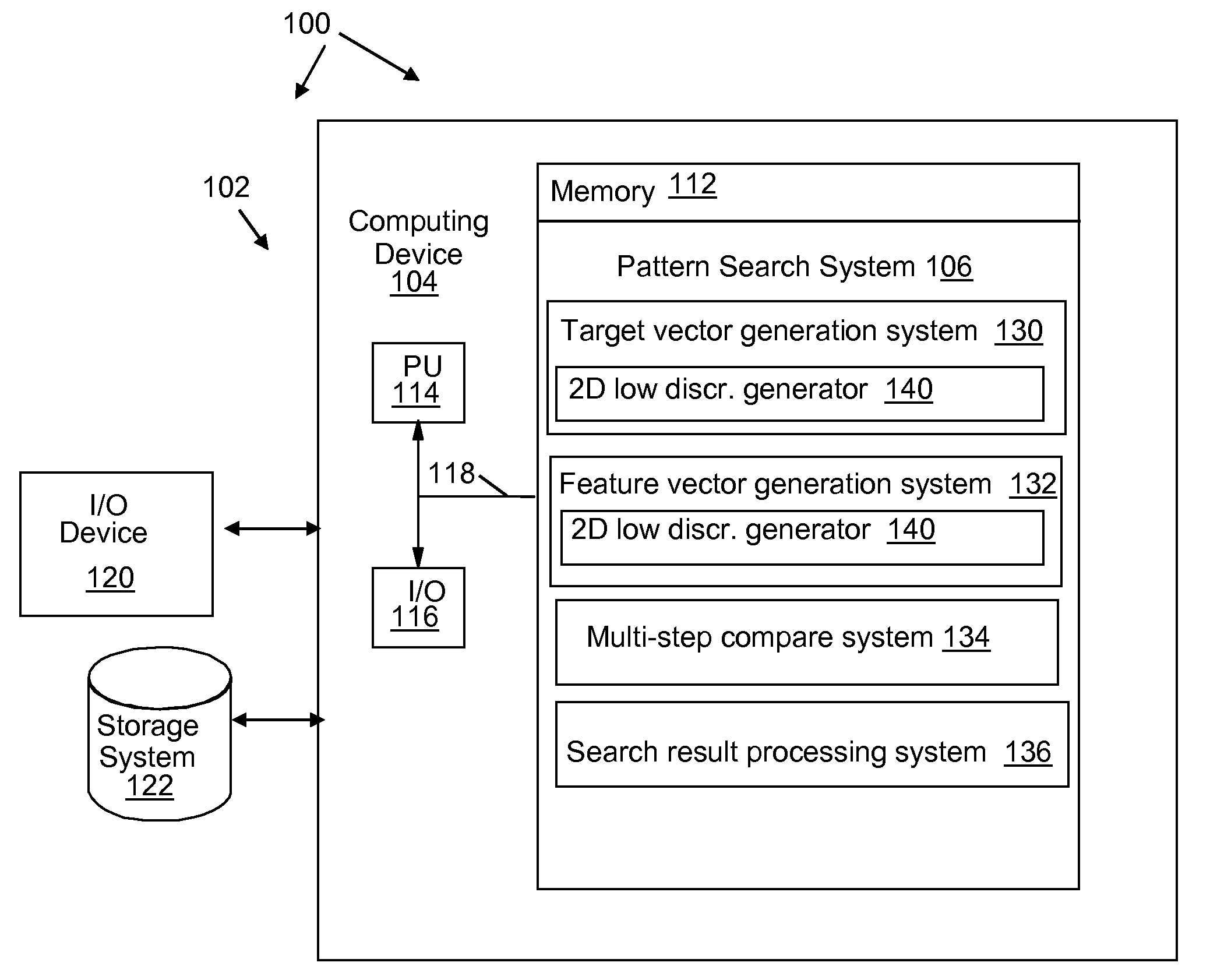
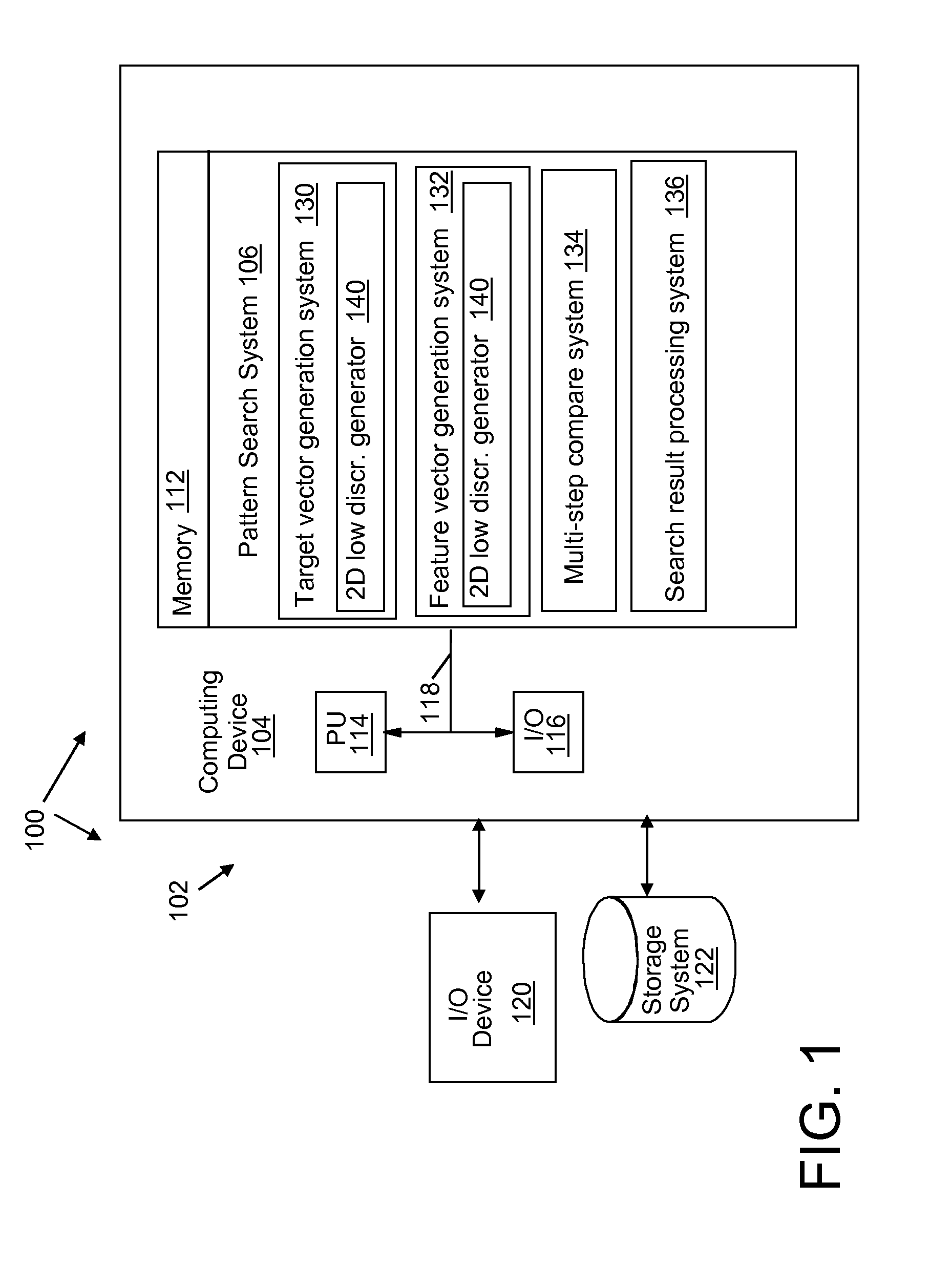
Feature extraction that supports progressively refined search and classification of patterns in a semiconductor layout
InactiveUS20080320421A1Reduce computational overheadLow sequenceDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designFeature vectorFeature extraction
A system, method and program product for searching and classifying patterns in a VLSI design layout. A method is provided that includes generating a target vector using a two dimensional (2D) low discrepancy sequence; identifying layout regions in a design layout; generating a feature vector for a layout region; comparing a subset of sequence values in the target vector with sequence values in the feature vector as an initial filter, wherein the system for comparing determines that the layout region does not contain a match if a comparison of the subset of sequence values in the target vector with sequence values in the feature vector falls below a threshold; and outputting search results.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for generating pixel values for pixels in an image using strictly deterministic methodologies for generating sample points
InactiveUS7071938B2Reduce errorsPromote generationCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphicsDeterministic method
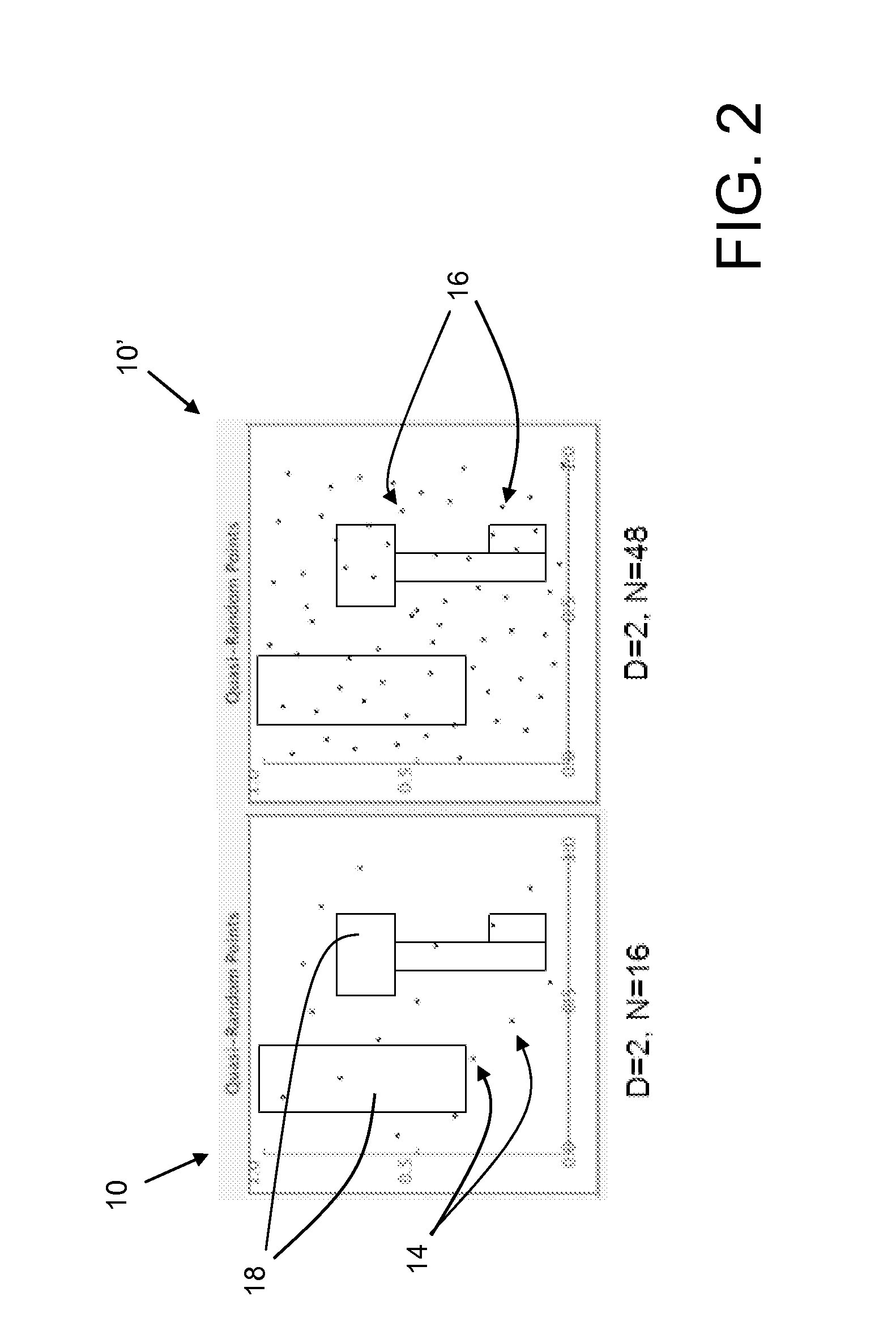
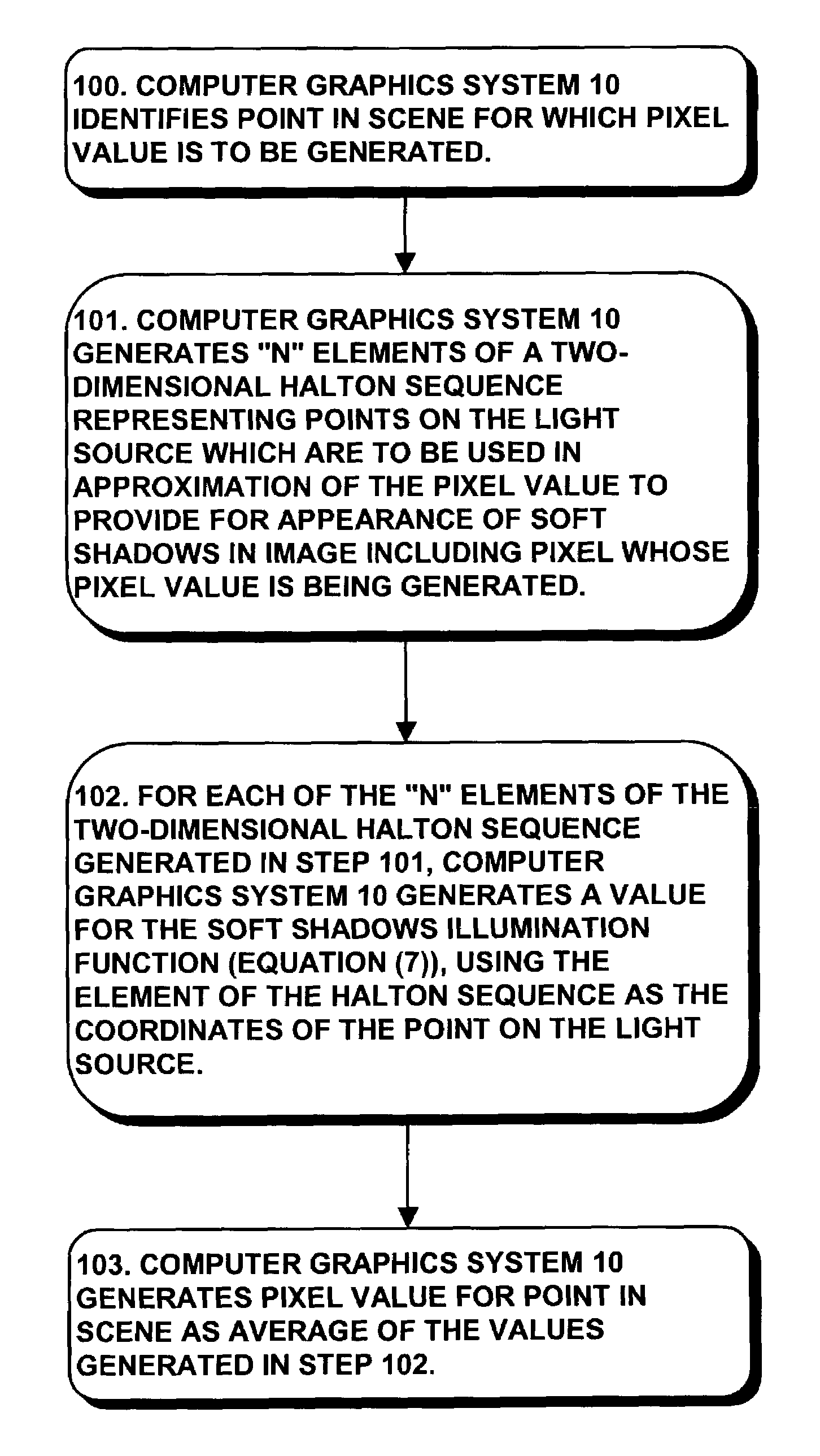
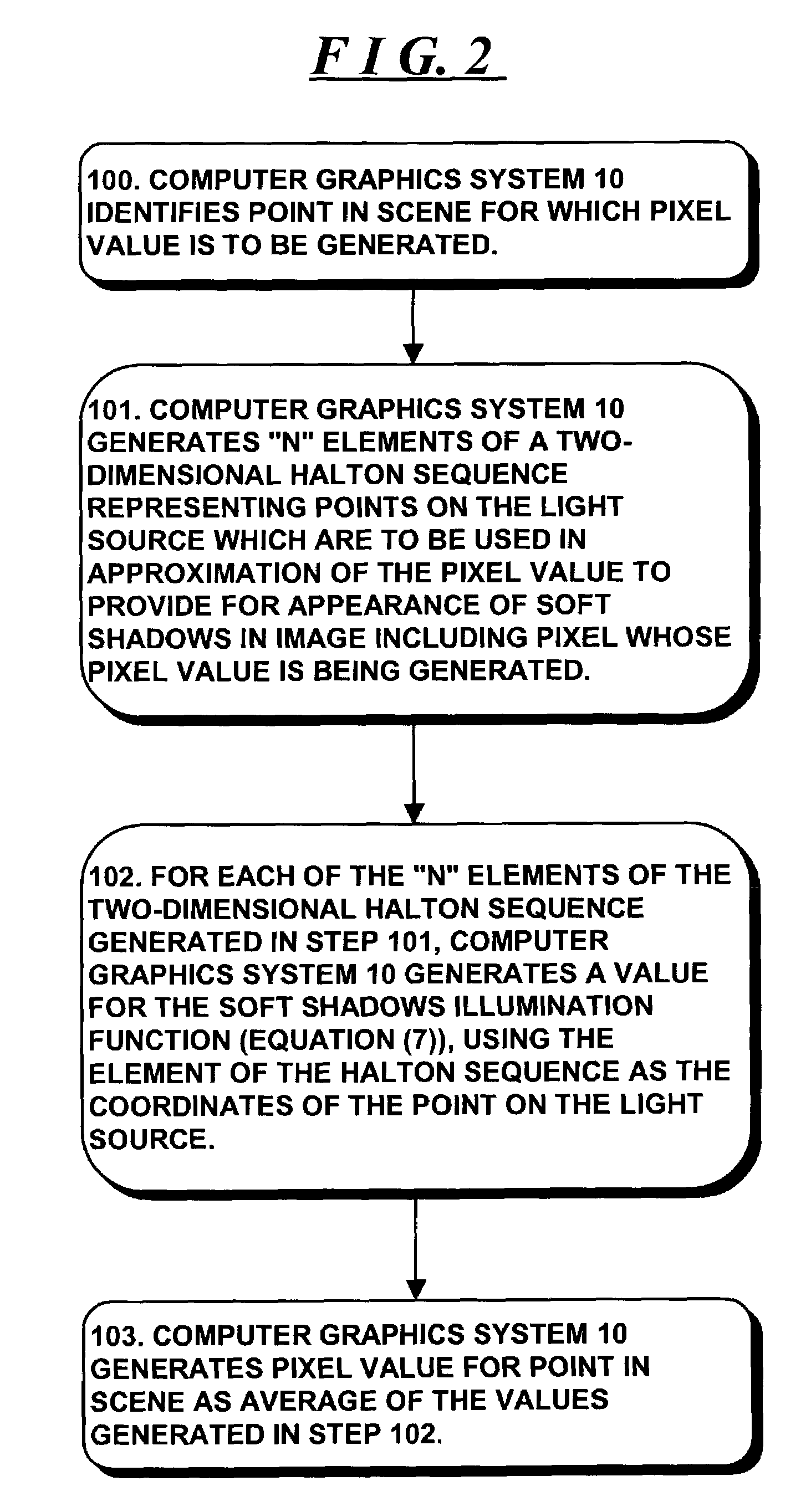
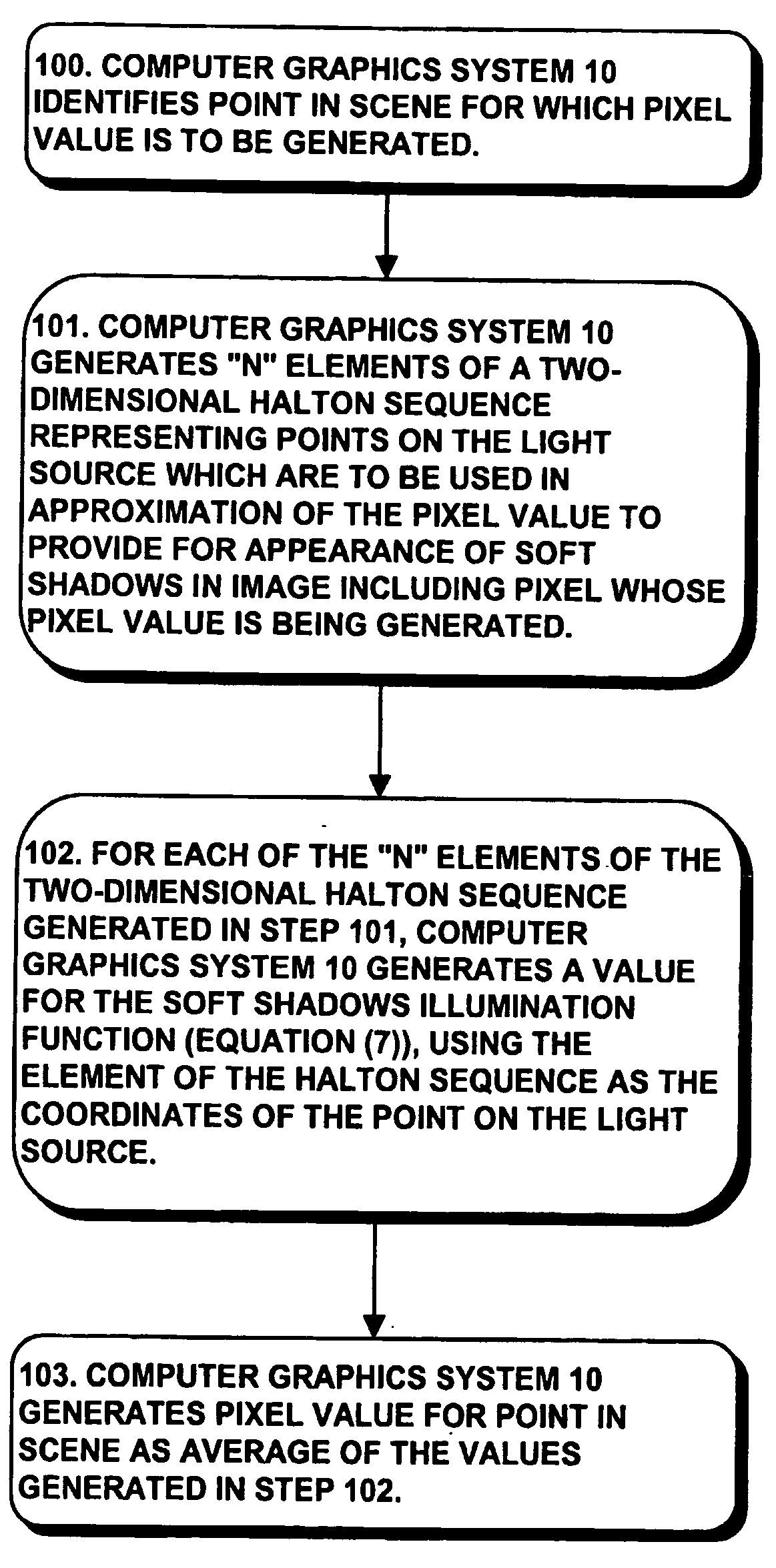
A computer graphics system generates pixel values for pixels in an image of objects in a scene, using strictly-deterministic low-discrepancy sequences, as sample points for evaluating integrals which are used to simulate a number of computer graphic techniques, including soft shadows generated for scenes illuminated by a light source having a finite extent, such as a disk, simulation of depth of field; motion blur; and jittering. The computer graphics system uses the low-discrepancy sequence to generate sample points. The low discrepancy sequences ensure that the sample points are evenly distributed over a respective region or time interval, thereby reducing error in the image which can result from clumping of such sample points which can occur in the Monte Carlo technique. The invention facilitates the generation of images of improved quality when using the same number of sample points at the same computational cost as in the Monte Carlo technique.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
Computer graphic system and computer-implemented method for generating an image using sample points determined on a sub-pixel grid offset using elements of a low-discrepancy sequence
InactiveUS20050264565A1Random number generatorsGeometric image transformationLow-discrepancy sequenceMesh grid
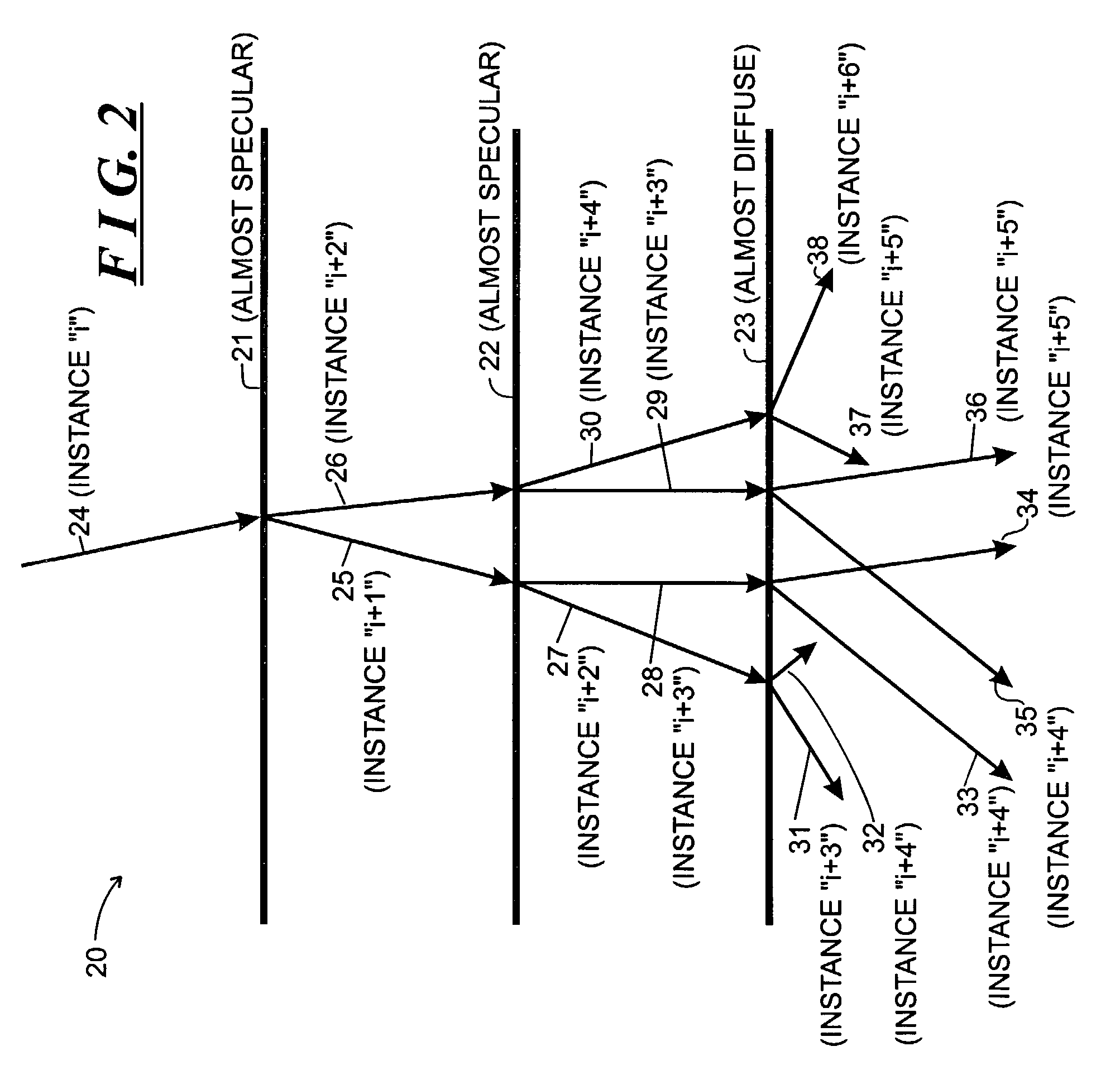
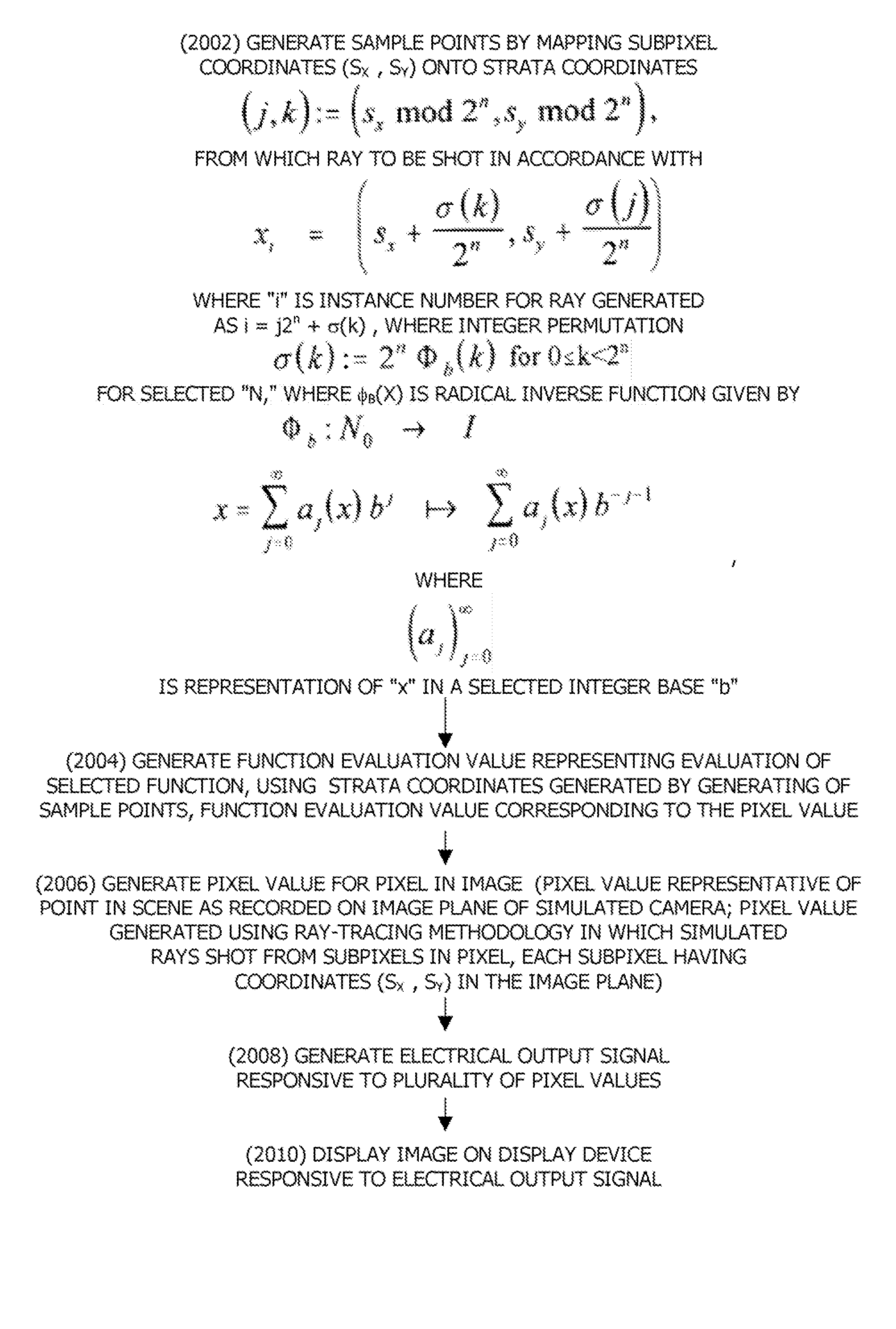
A computer graphics system generates a pixel value for a pixel in an image, the pixel being representative of a point in a scene as recorded on an image plane of a simulated camera, the computer graphics system being configured to generate the pixel value for an image using a selected ray-tracing methodology in which simulated rays are shot from respective ones of a plurality of subpixels in the pixel, each subpixel having coordinates (sx,sy) in the image plane The computer graphics system comprises a sample point generator and a function evaluator. The sample point generator is configured to map subpixel coordinates (sx,sy) onto strata coordinates (j,k):=(sx mod 2n,sy mod 2n), from which a ray is to be shot, in accordance with xi=(sx+σ(k)2n,sy+σ(j)2n)where “i” is an instance number for the ray generated as i=j2n+σ(k), where integer permutation σ(k):=2nΦb(k) for 0≦k<2n for selected “n,” where Φb(x) is a radical inverse function given by Φb:N0→Ix=∑j=0∞aj(x)bj↦∑j=0∞aj(x)b-j-1,where (aj)j=0∞is the representation of “x” in a selected integer base “b”. The function evaluator is configured to evaluate a selected function using the strata coordinates generated by the sample point generator, the value generated by the function evaluator corresponding to the pixel value.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
Computer graphics system and computer-implemented method for simulating participating media using sample points determined using elements of a low-discrepancy sequence
InactiveUS20050275652A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsComplex mathematical operationsGraphicsImage plane
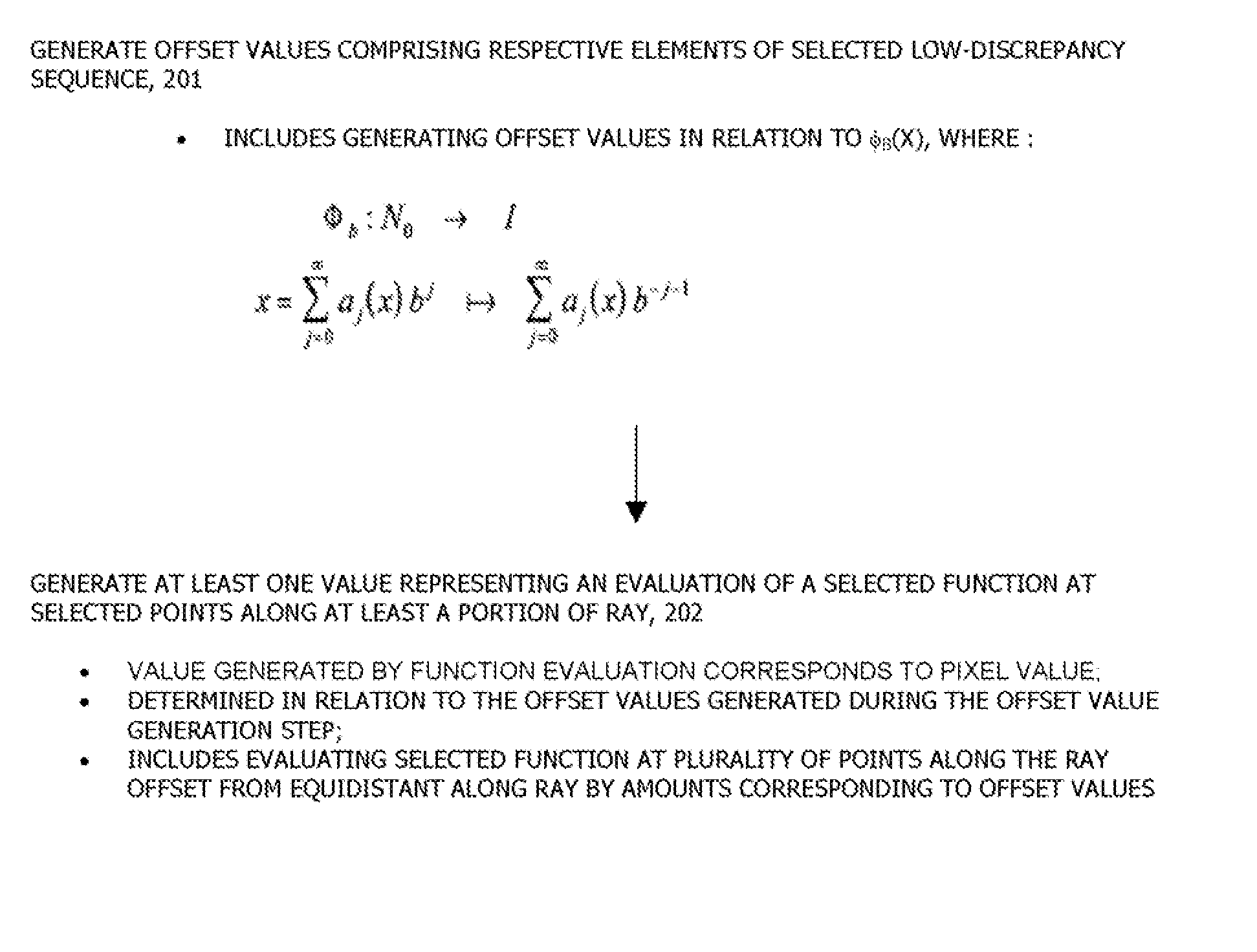
A computer graphics system generates a pixel value for a pixel in an image, the pixel being representative of a point in a scene as recorded on an image plane of a simulated camera. The computer graphics system comprising an offset value generator and a function evaluator. The offset value generator is configured to generate a plurality of offset values, the offset values comprising respective elements of a selected low-discrepancy sequence. The function evaluator is configured to generate at least one value representing an evaluation of a selected function at selected points along at least a portion of the ray, the selected points being determined in relation to the offset values generated by the offset value generator, the value generated by the function evaluator corresponding to the pixel value.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
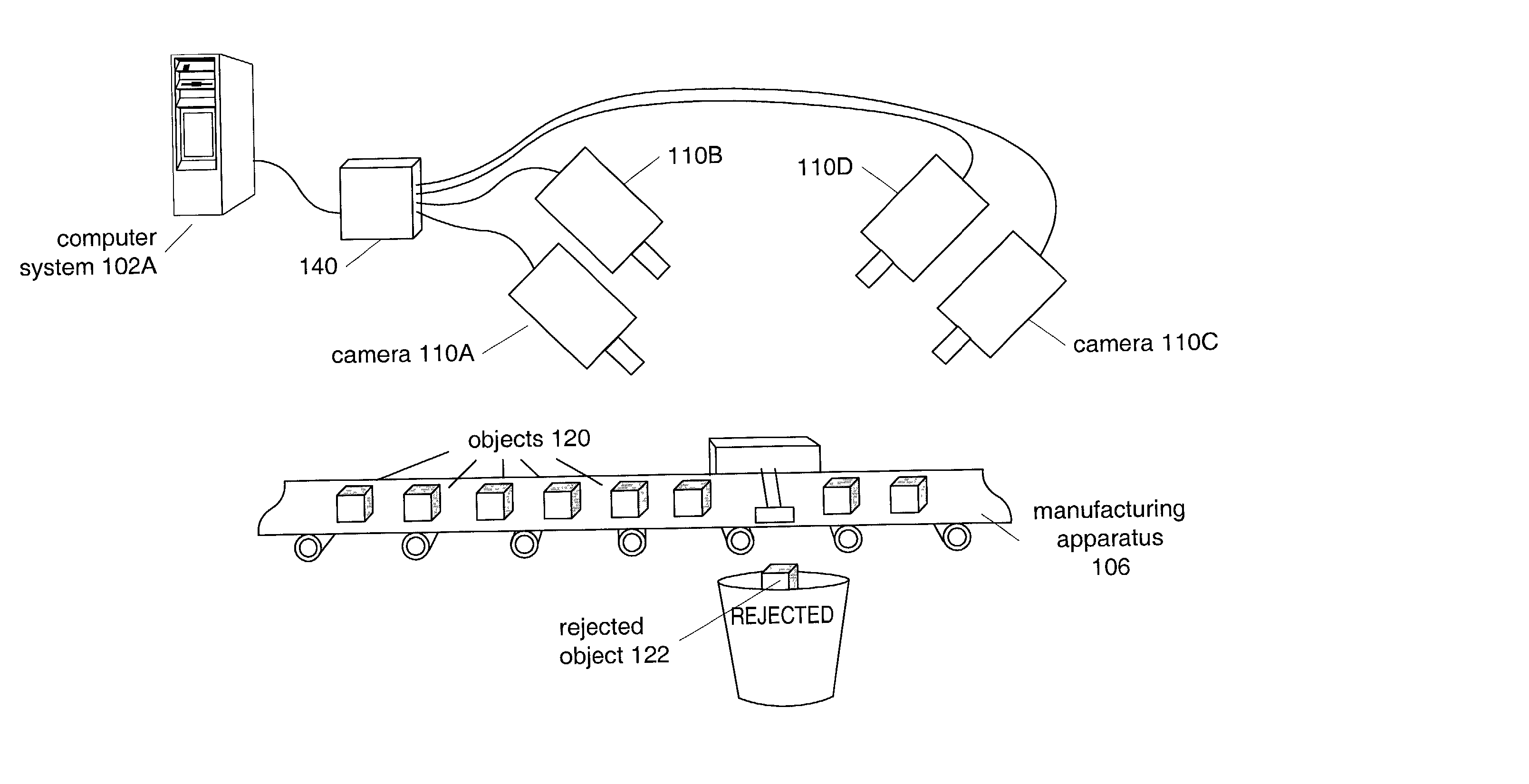
System and method for scanning a region using a low discrepancy sequence
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Generating images using multiple photon maps
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
Generating an image using sample points determined on a sub-pixel grid offset using elements of a low-discrepancy sequence
A computer graphics system generates a pixel value for a pixel in an image, the pixel being representative of a point in a scene as recorded on an image plane of a simulated camera, the computer graphics system being configured to generate the pixel value for an image using a selected ray-tracing methodology in which simulated rays are shot from respective ones of a plurality of subpixels in the pixel, each subpixel having coordinates (sx,sy) in the image plane The computer graphics system comprises a sample point generator and a function evaluator. The sample point generator is configured to map subpixel coordinates (sx,sy) onto strata coordinates (j,k):=(sx mod 2n,sy mod 2n), from which a ray is to be shot, in accordance with x i = ( s x + sigma ( k ) 2 n , s y + sigma ( j ) 2 n ) where "i" is an instance number for the ray generated as i=j2n+sigma(k), where integer permutation sigma(k):=2nPhib(k) for 0<=K<2n for selected "n," where Phib(x) is a radical inverse function given by Phi b : N 0 -> I x = ∑ j = 0 ∞ a j ( x ) b j ↦ ∑ j = 0 ∞ a j ( x ) b - j - 1 , where ( a j ) j = 0 ∞ is the representation of "x" in a selected integer base "b". The function evaluator is configured to evaluate a selected function using the strata coordinates generated by the sample point generator, the value generated by the function evaluator corresponding to the pixel value.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
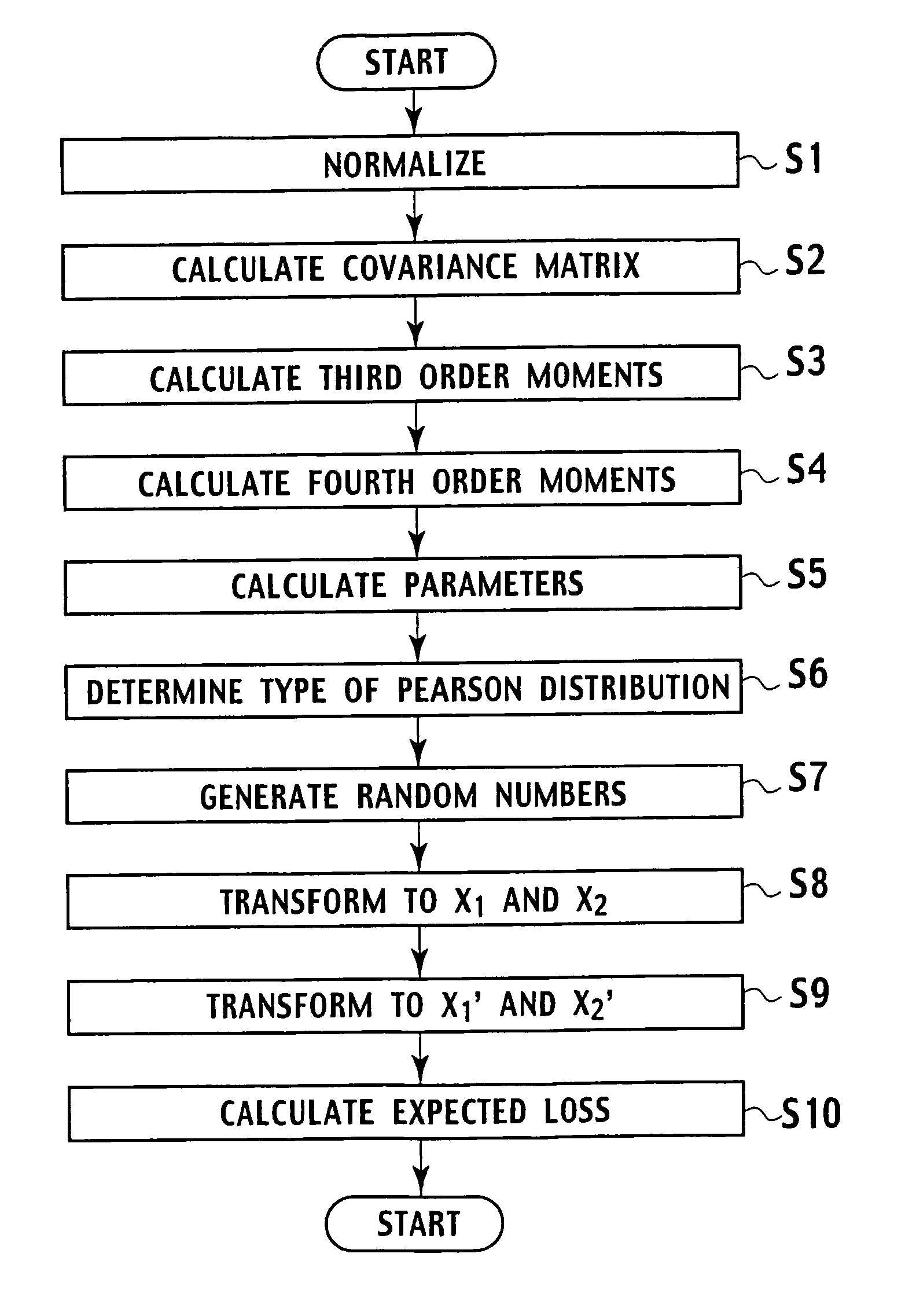
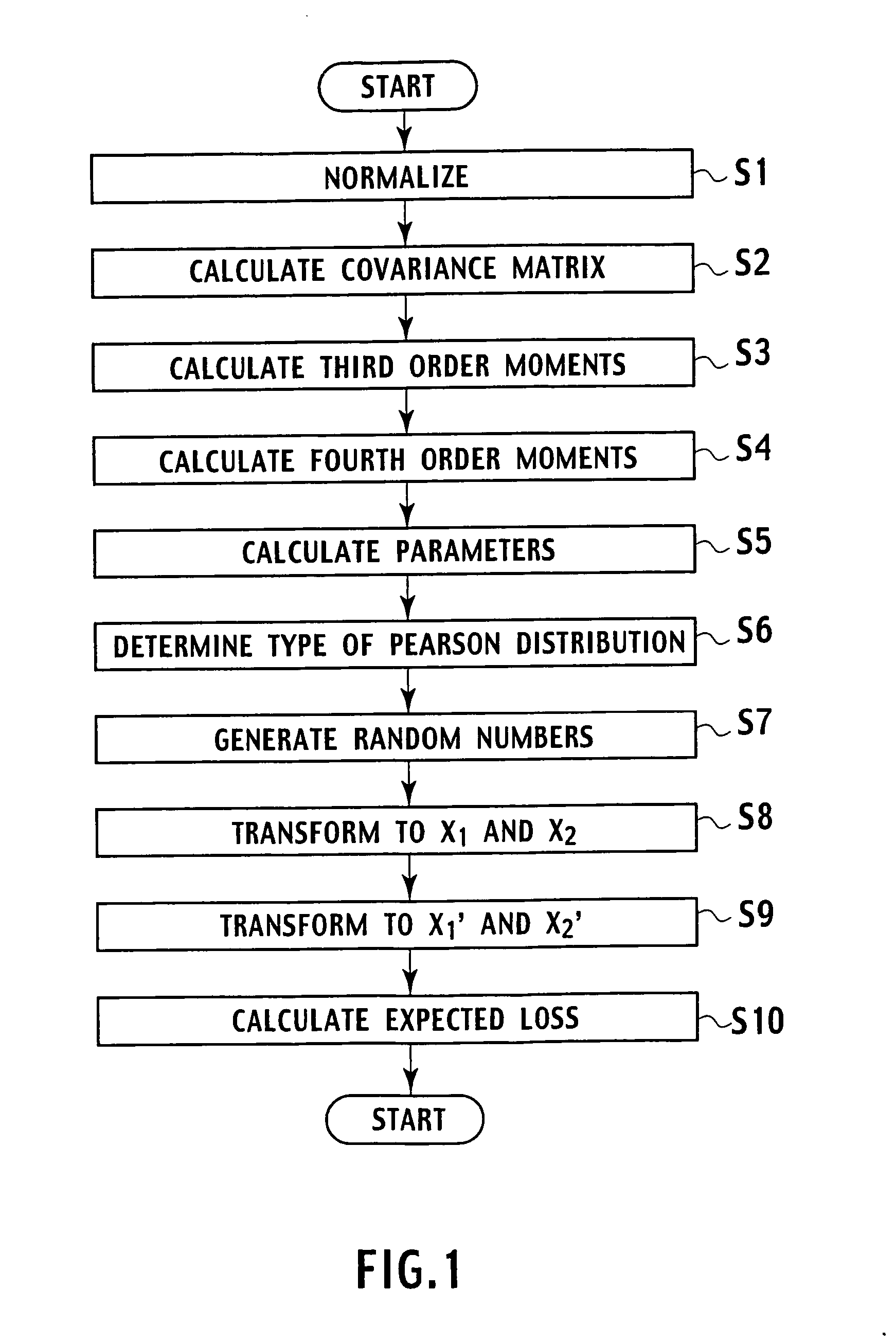
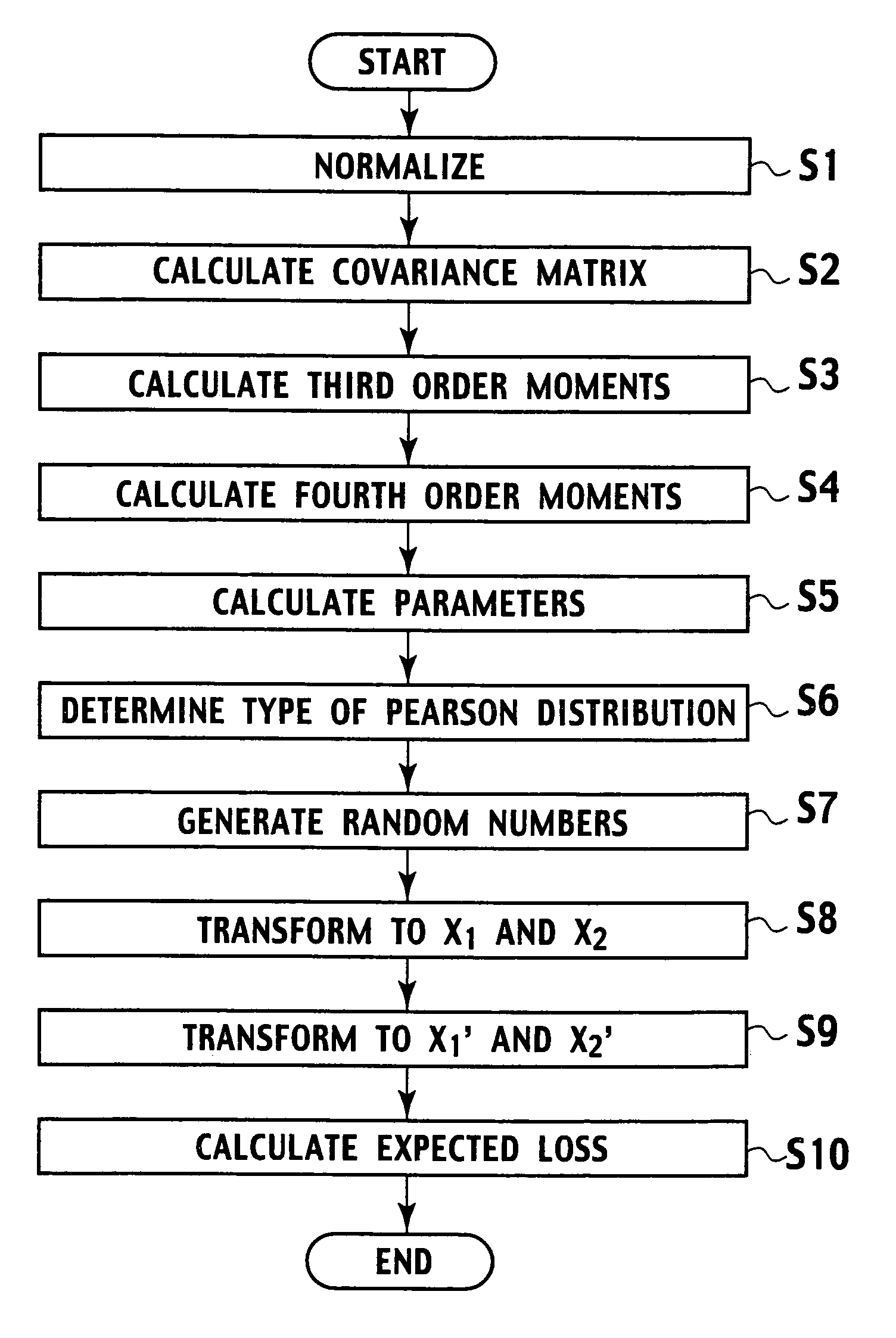
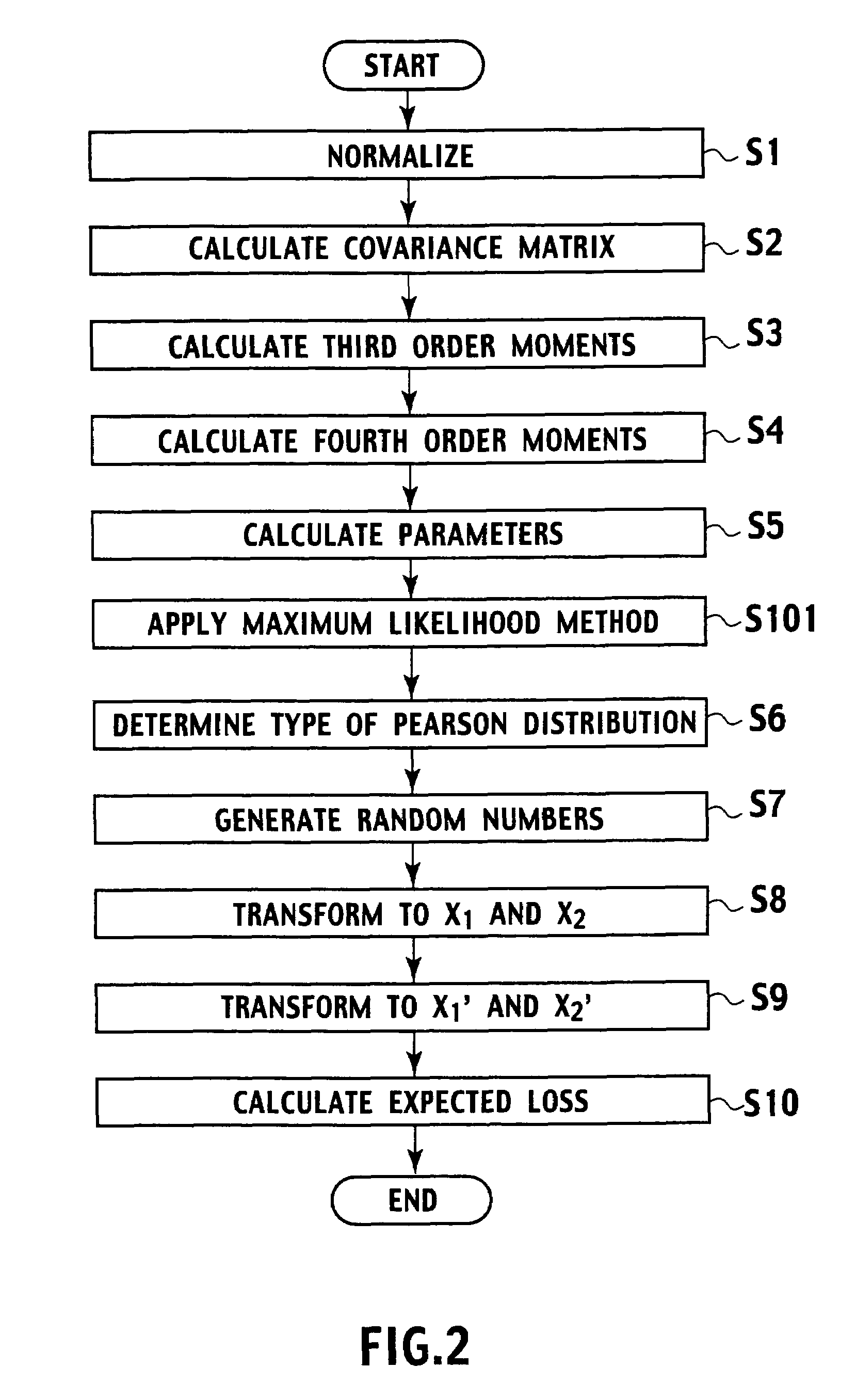
Random number generation method based on multivariate non-normal distribution, parameter estimation method thereof, and application to simulation of financial field and semiconductor ion implantation
Random number generating method for generating random numbers in accordance with multivariate non-normal distributions based on the Yuan and Bentler method I on computer. The method includes application steps for applying n-dimensional multivariate non-normal distributions to n-dimensional experience distribution by using computer and steps for generating random numbers including pseudo-random numbers, quasi-random numbers, low discrepancy sequences, and physical random numbers by methods including additive generator method, M-sequence, generalized feedback shift-register method, and Mersenne Twister, and excluding congruential method, by using computer. The application steps use predetermined relationship equations for the third and fourth order moments to perform application associated with the third and fourth order moments of the empirical distributions. Moreover, by using random numbers generation method, parameters are estimated by maximum likelihood method. Furthermore, the random number generation method and the parameters estimation method are applied to simulation of financial field, semiconductor ion implantation, and the like.
Owner:NAGAHARA YUICHI
System and method for rendering images using a strictly-deterministic methodology for generating a coarse sequence of sample points
InactiveUS6911976B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationDeterministic methodAlgorithm
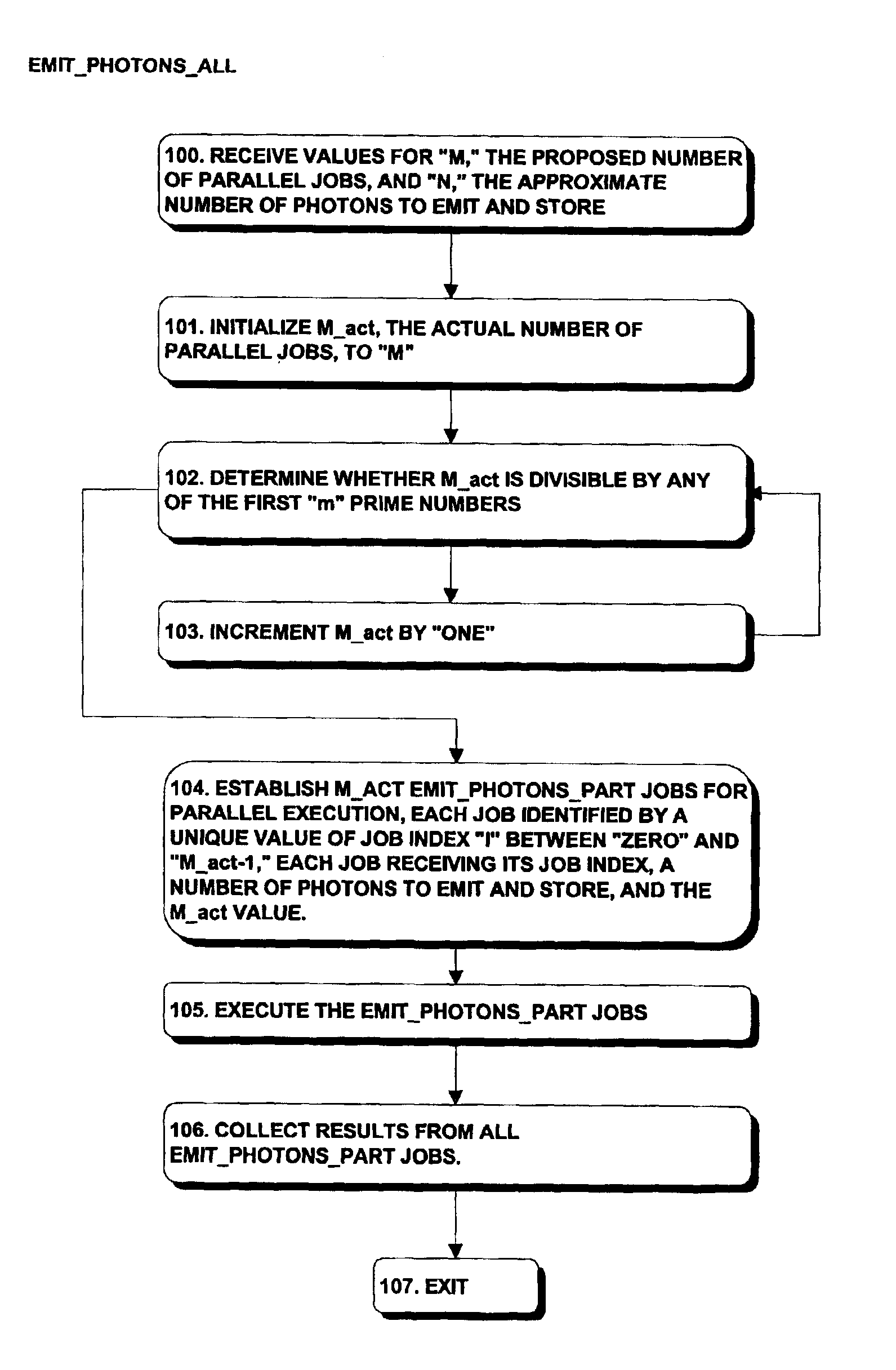
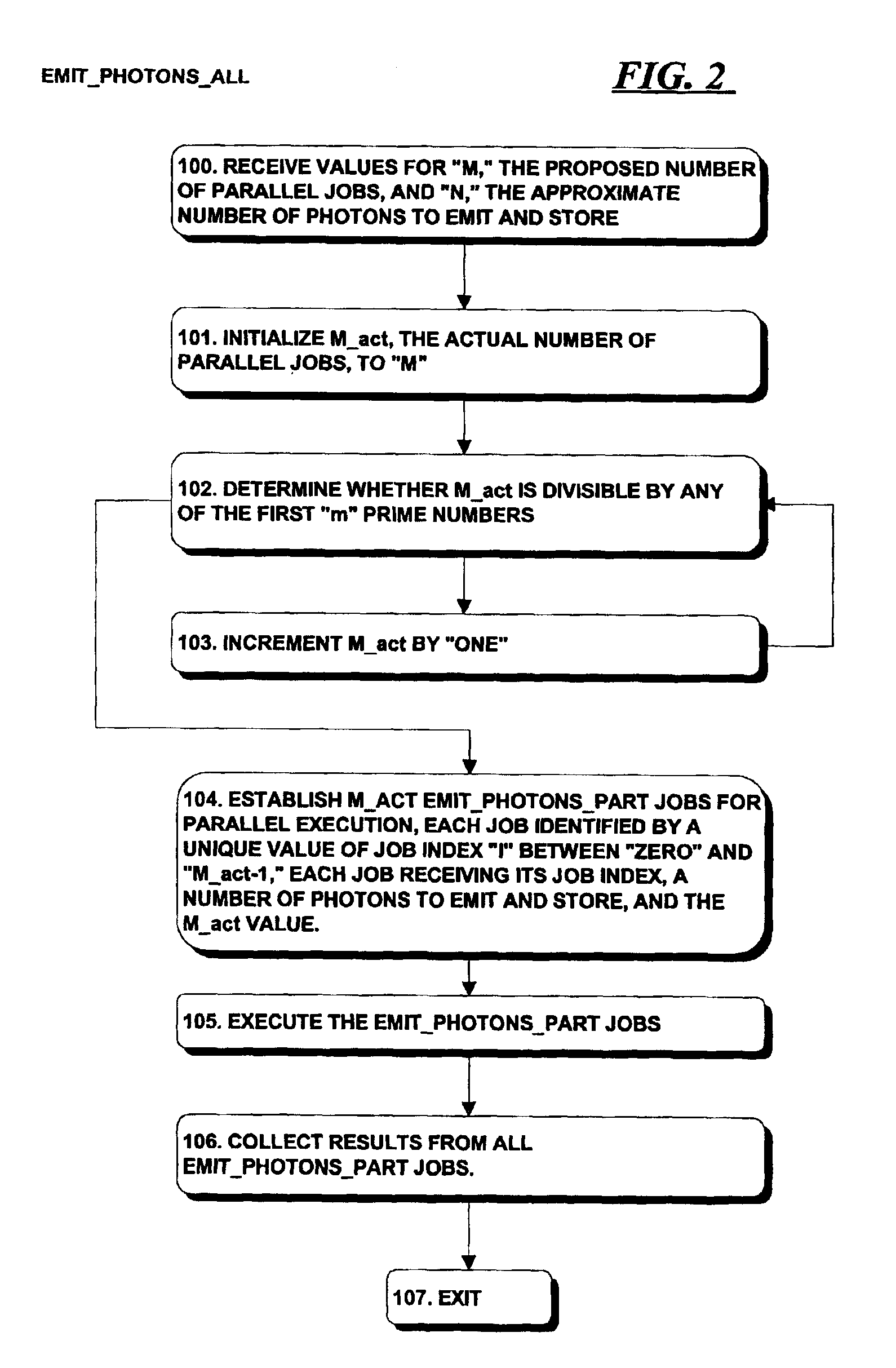
A system and method for generating sample points that can generate the sample points in parallel. The sample points can be used in processing in parallel, with the results subsequently collected and used as necessary in subsequent rendering operations. Sample points are generated using a coarse Halton sequence, which makes use of coarse radical inverse values Φbi,M(j) as follows:Φbi,M(j)=Φb(jM+i)where base “b” is preferably a prime number, but not a divisor of “M,” and “i” is an integer. Using this definition, the s-dimensional coarse Halton sequence USCHal,i,M, which may be used to define sample points for use in evaluating integrals, is defined asUsCHal,i,M=(Φb1i,M(j), . . . , Φb<sub2>s< / sub2>i,M(j))where b1, . . . , bs are the first “s” prime numbers that are not divisors of “M.” Each value of “i” defines a subsequence that is a low-discrepancy sequence, and so can be used in connection with processing. Similarly, the union of all subsequences for all values of “i” between “zero” and “M−1” is also a low-discrepancy sequence, so results of processing using the coarse Halton sequences for all such values of “i” can be collected together and used in the same manner as if the results had been generated using a Halton sequence to define the sample points.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
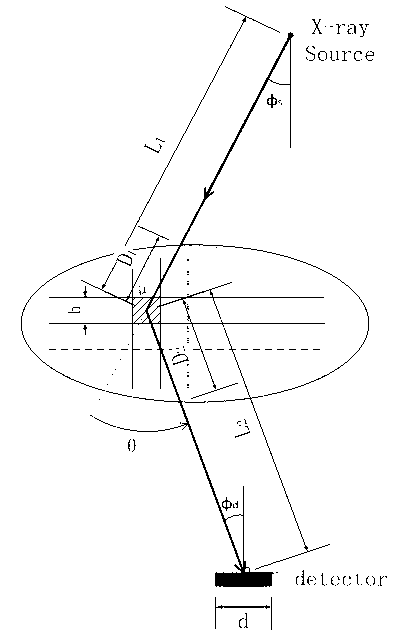
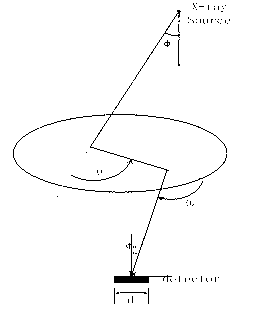
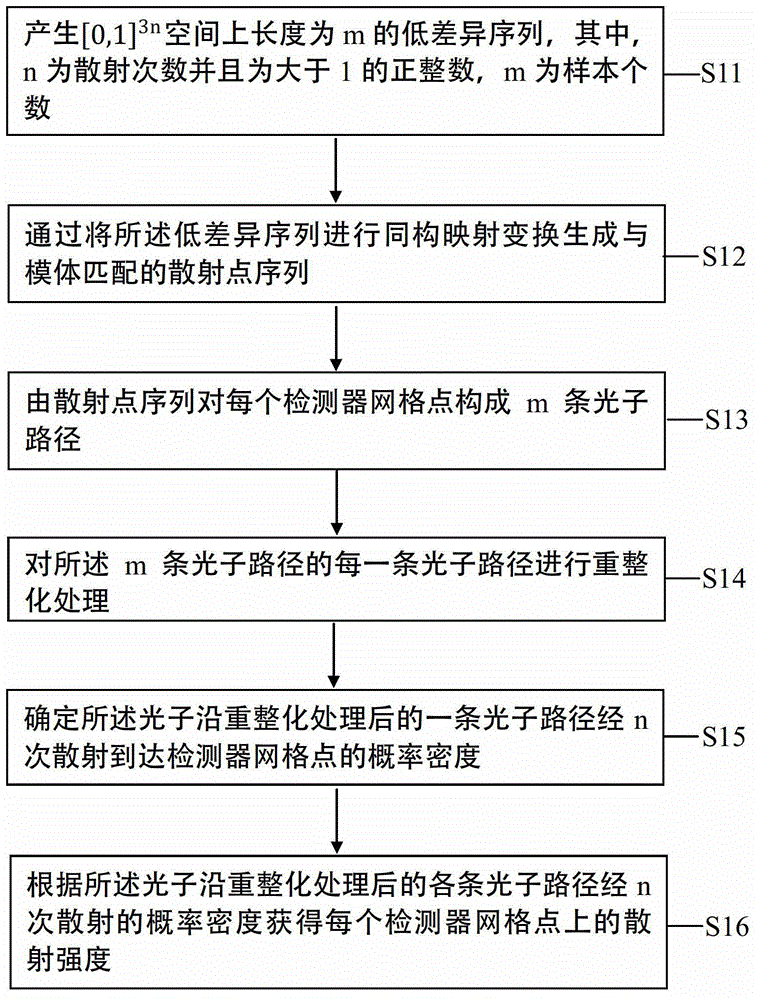
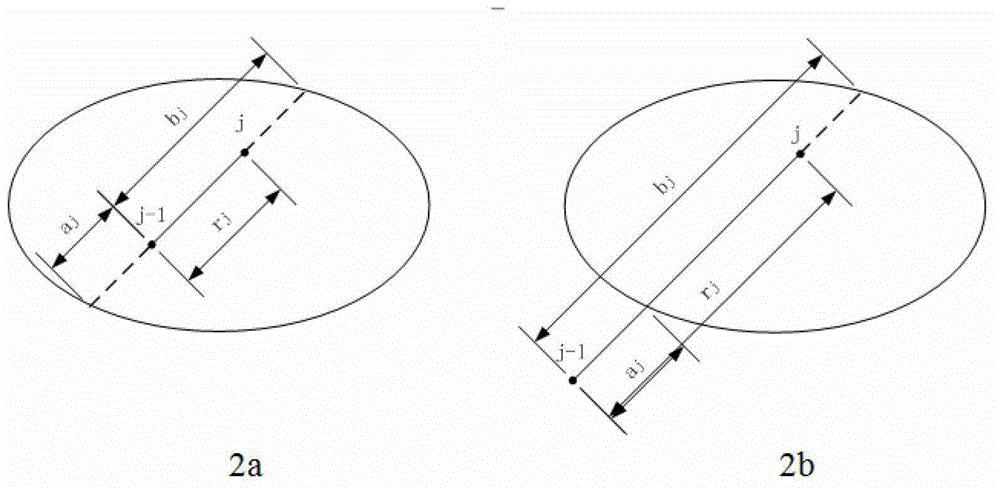
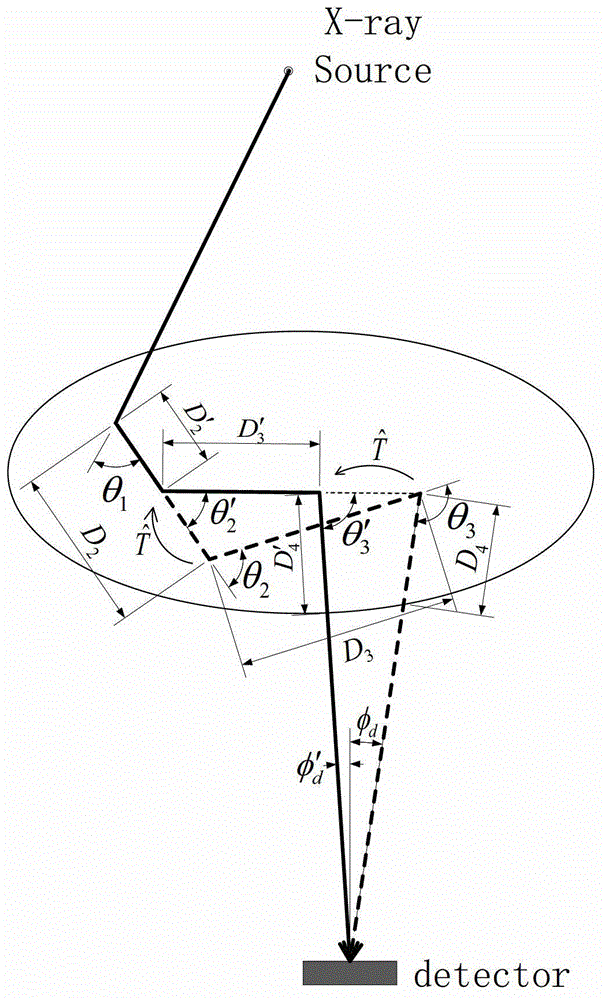
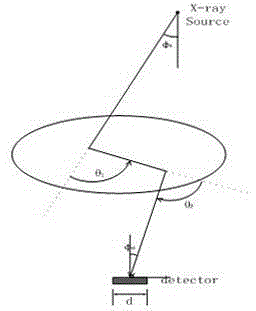
Path integral method for X-ray Monte Carlo simulation
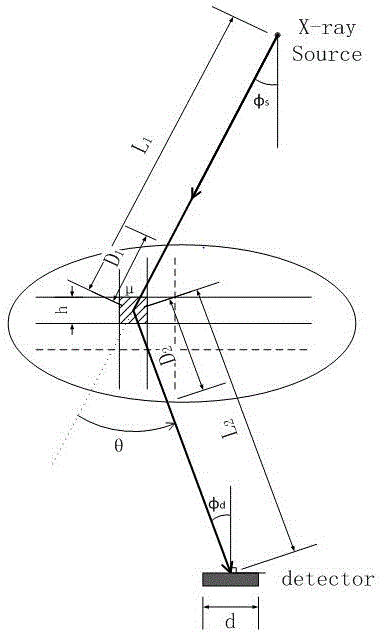
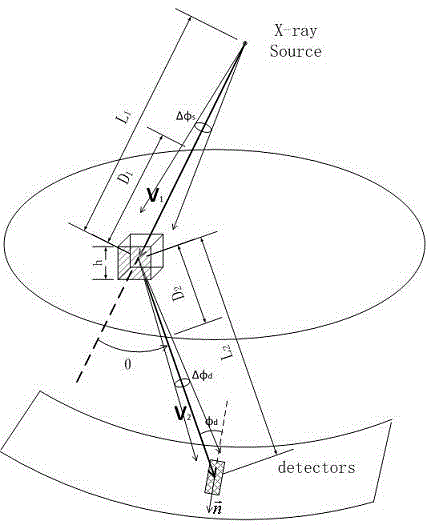
The invention discloses a path integral method for X-ray Monte Carlo simulation. The path integral method for the X-ray Monte Carlo simulation comprises the following steps: step a, a low-difference sequence with the length of m in a [0,1] 3n dimension is generated, wherein the n is the scattering times and the m is the number of samples; step b, scattering point sequences geometrically matched with a motif are generated through an isomorphic mapping of the low-difference sequence; step c, m photon paths are formed by the scattering point sequences on each detector grid point; step d, the probability density of passing through the photon paths to reach the detector grid points is determined; step e, the probability density is weighted and summed to obtain the scattering intensity of each detector grid point. According to the path integral method for the X-ray Monte Carlo simulation, errors caused by discontinuity on a boundary are eliminated, variances of the samples are lowered, calculation is finished with fewer samples under given accuracy, and the calculated amount is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
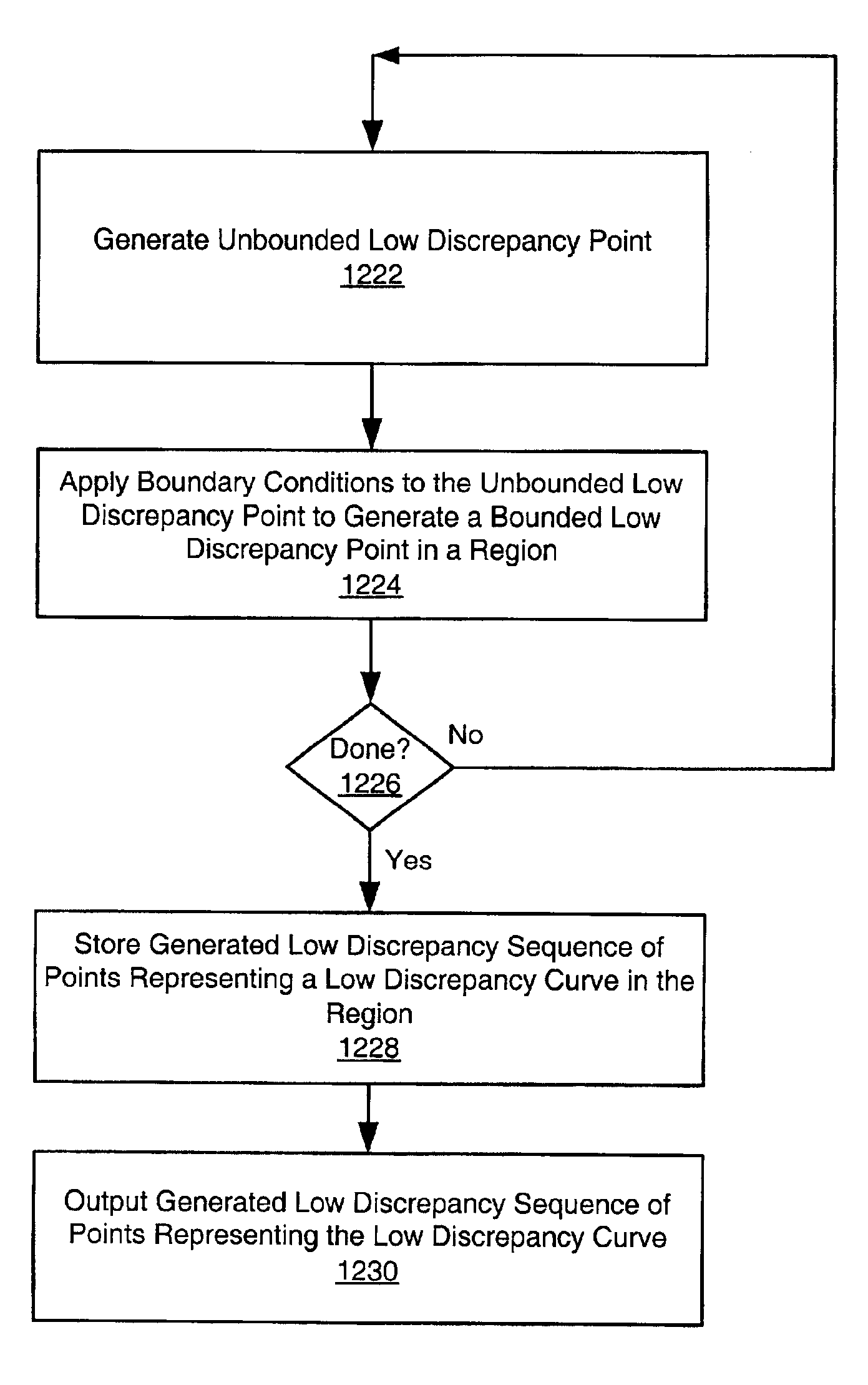
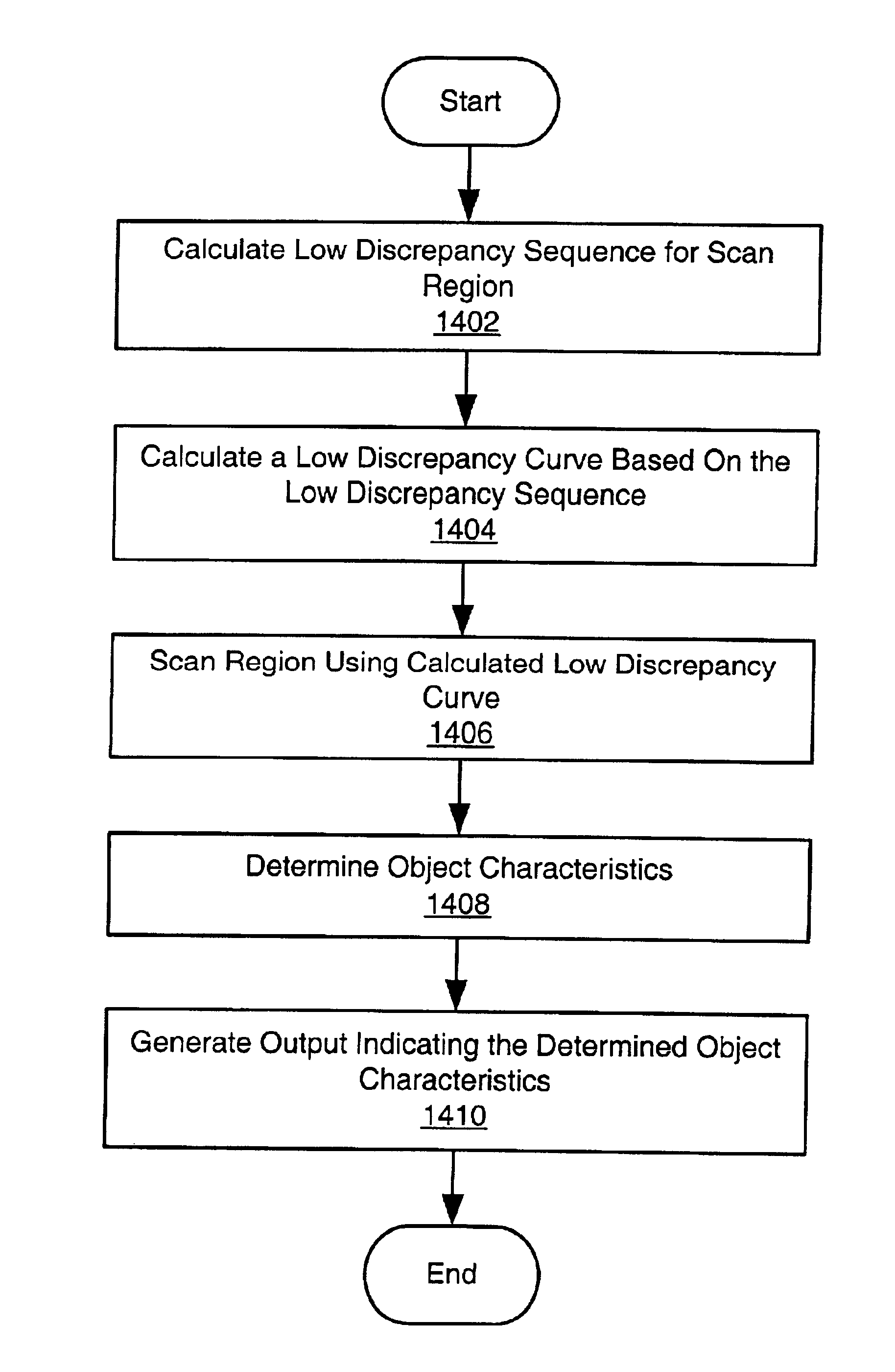
System and method for generating a low discrepancy curve in a region
InactiveUS7034831B2Television system detailsDrawing from basic elementsGreek letter epsilonComputer science
A system and method for generating a curve in a region, e.g., a Low Discrepancy Curve. The method may generate an unbounded Low Discrepancy Point (LDP); apply one or more boundary conditions to the unbounded LDP to generate a bounded LDP located within the region; repeat said generating and said applying one or more boundary conditions one or more times, generating a Low Discrepancy Sequence (LDS) in the region; store the LDS; and generate output comprising the LDS, wherein the LDS defines the curve in the region. The method may scan the region according to the defined curve. In generating the unbounded LDP, the method may select two or more irrational numbers, a step size epsilon (ε), and a starting position; initialize a current position to the starting position; and increment components of the current position based on ε and the irrational numbers to generate the unbounded LDP.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
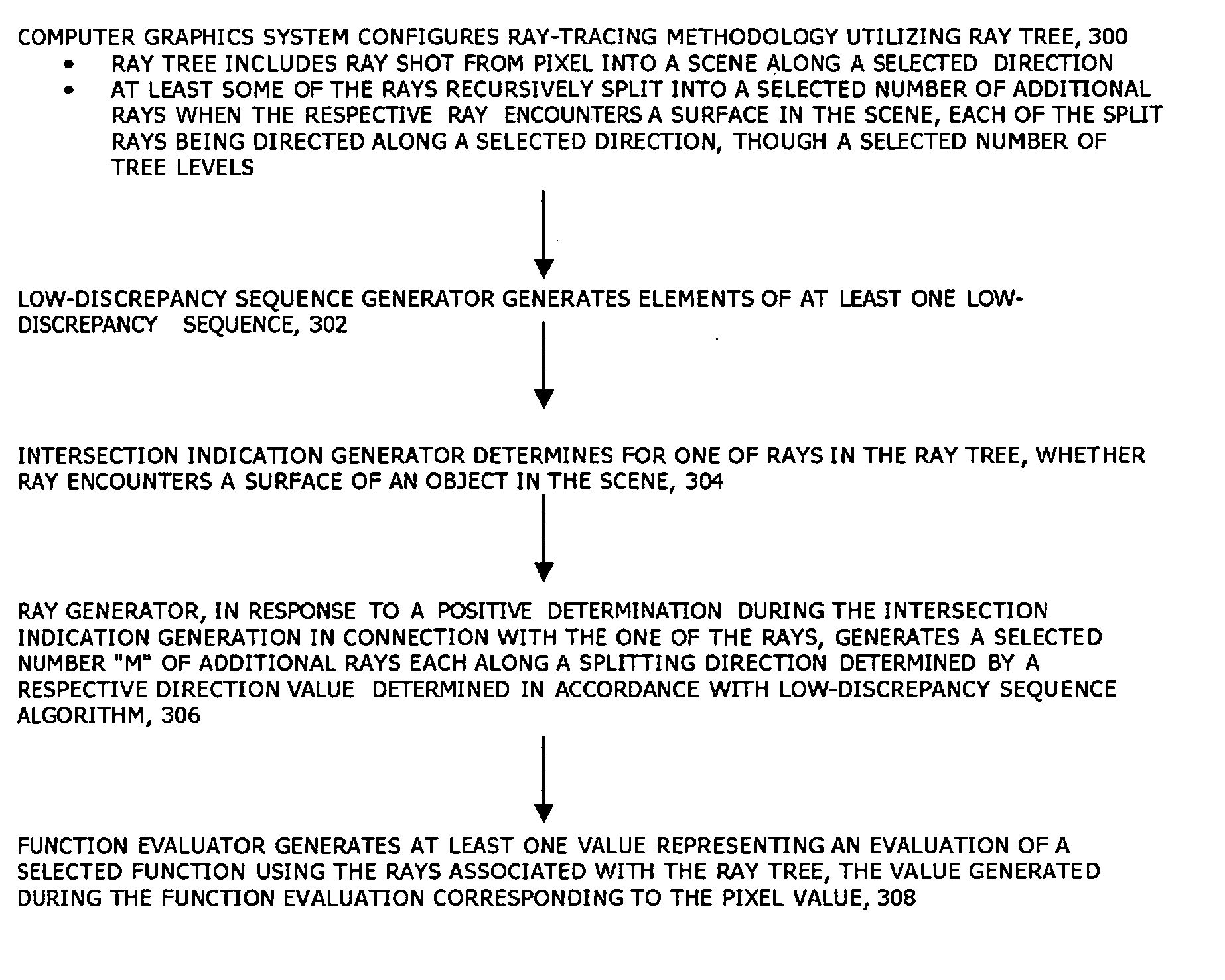
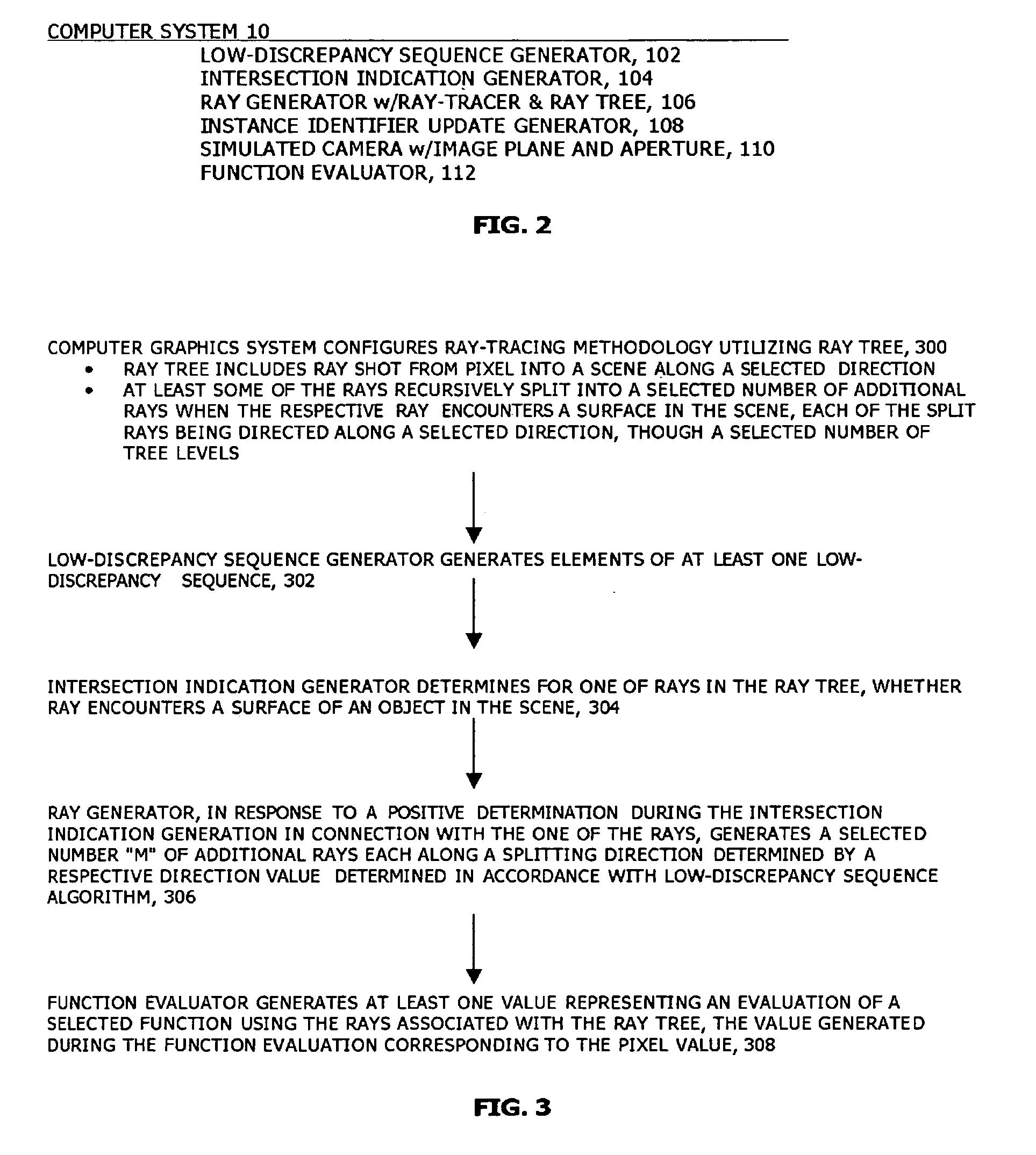
Computer graphic system and computer-implemented method for generating images using a ray tracing methodology that makes use of a ray tree generated using low-discrepancy sequences and ray tracer for use therewith
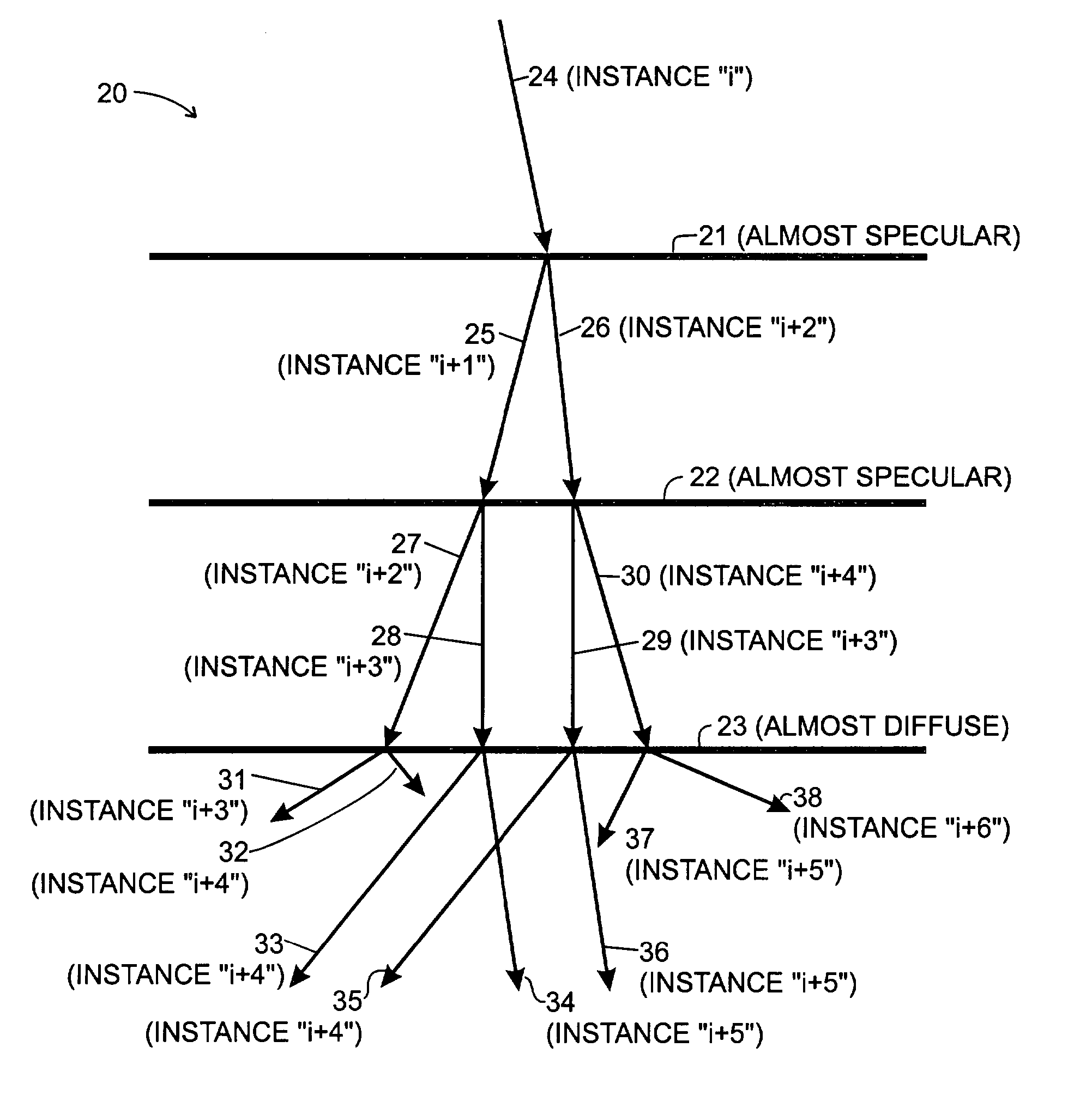
A ray tracer generates a ray tree, the ray tree comprising a primary ray shot along a selected direction and a plurality of other rays, the other rays being generated by recursive splitting. A ray is split when it encounters a predetermined condition, and each of the rays into which it is split is directed directed along a selected direction. The ray tracer comprises a low-discrepancy sequence generator an condition detector and a ray generator. The low-discrepancy sequence generator is configured to generate elements of at least one low-discrepancy sequence. The condition detector is configured to determine, for one of the rays in the ray tree, whether the one of the rays encounters the predetermined condition. The ray generator is configured to, when the condition detector makes a positive determination in connection with the one of the rays, generate a selected number “M” of split rays each along a splitting direction determined by a respective direction value determined in accordance with(yi,j)j=0M-1=(Φbd(i)⊕jM,…,Φbd+Δd-1(i)⊕Φbd+Δd-2(j)),where{Φbd(i),…,Φbd+Δd-1(i)}and{jM,…,Φbd+Δd-2(j)}are low-discrepancy sequences, for selected bases b and dimensions Δd, generated by the low-discrepancy sequence generator, and where ⊕ represents addition modulo “one” and “i” is an instance number in connection with the one of the rays.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
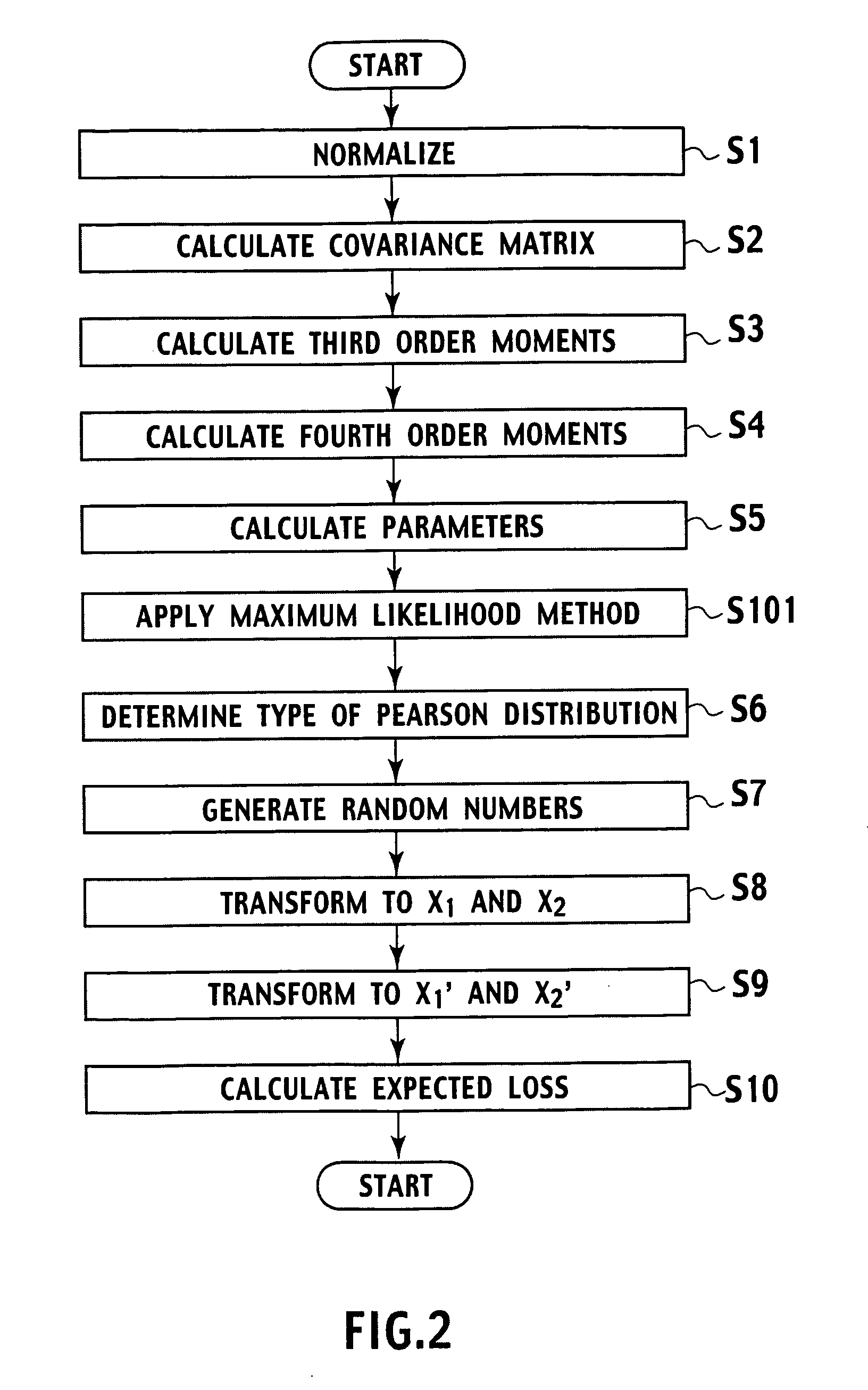
Random number generation method based on multivariate non-normal distribution, parameter estimation method thereof, and application to simulation of financial field and semiconductor ion implantation
Random number generating method for generating random numbers in accordance with multivariate non-normal distributions based on the Yuan and Bentler method I on computer. The method includes application steps for applying n-dimensional multivariate non-normal distributions to n-dimensional experience distribution by using computer and steps for generating random numbers including pseudo-random numbers, quasi-random numbers, low discrepancy sequences, and physical random numbers by methods including additive generator method, M-sequence, generalized feedback shift-register method, and Mersenne Twister, and excluding congruential method, by using computer. The application steps use predetermined relationship equations for the third and fourth order moments to perform application associated with the third and fourth order moments of the empirical distributions. Moreover, by using random numbers generation method, parameters are estimated by maximum likelihood method. Furthermore, the random number generation method and the parameters estimated method are applied to simulation of financial field, semiconductor ion implantation, and the like.
Owner:NAGAHARA YUICHI
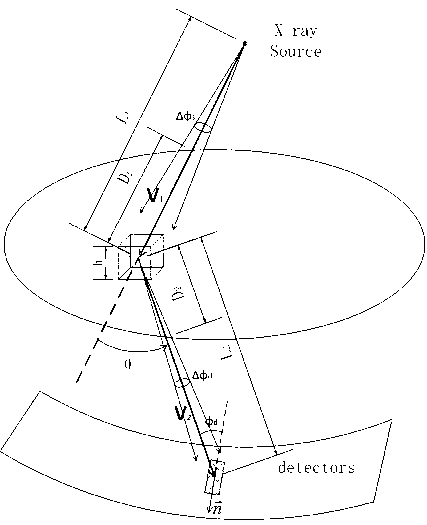
Method for renormalization of X-ray multiple scattering simulation
ActiveCN104027121AEliminate errorsSmall amount of calculationRadiation diagnosticsSoft x rayRenormalization
The invention provides a method for renormalization of X-ray multiple scattering simulation. The method comprises a first step of generating a low-difference sequence with the length of m in [0,1]<3n> space, enabling n to be scattering times and be a positive integer larger than 1, and enabling m to be the sample number; a second step of generating a scattering point sequence matched with the geometrical shape of a die body by performing isomorphic mapping transformation on the low-difference sequence; a third step of forming m photon paths for each detector grid point through the scattering point sequence; a fourth step of performing renormalization processing on each photon path among the m photon paths; a fifth step of determining the probability density of photons reaching the detector grid points through n-time scattering along each photon path after renormalization processing; and a sixth step of obtaining scattering intensity of each detector grid point according to the probability density of the photons through n-time scattering along each photon path after renormalization processing. The method can improve multiple scattering simulation efficiency and eliminate errors caused by die body edge incontinuity.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Computer Graphics Systems, Methods and Computer Program Products Using Sample Points Determined Using Low-Discrepancy Sequences
A computer graphics system generates, and displays or stores for later use, human-perceptible images, such as for animated motion pictures or other applications, by generating pixel values for respective pixels in an image, each pixel being representative of a point in a scene as recorded on an image plane of a simulated camera. The computer graphics system comprises an offset value generator and a function evaluator. The offset value generator is configured to generate a plurality of offset values, the offset values comprising respective elements of a selected low-discrepancy sequence. The function evaluator is configured to generate at least one value representing an evaluation of a selected function at selected points along at least a portion of the ray, the selected points being determined in relation to the offset values generated by the offset value generator, the value generated by the function evaluator corresponding to the pixel value.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
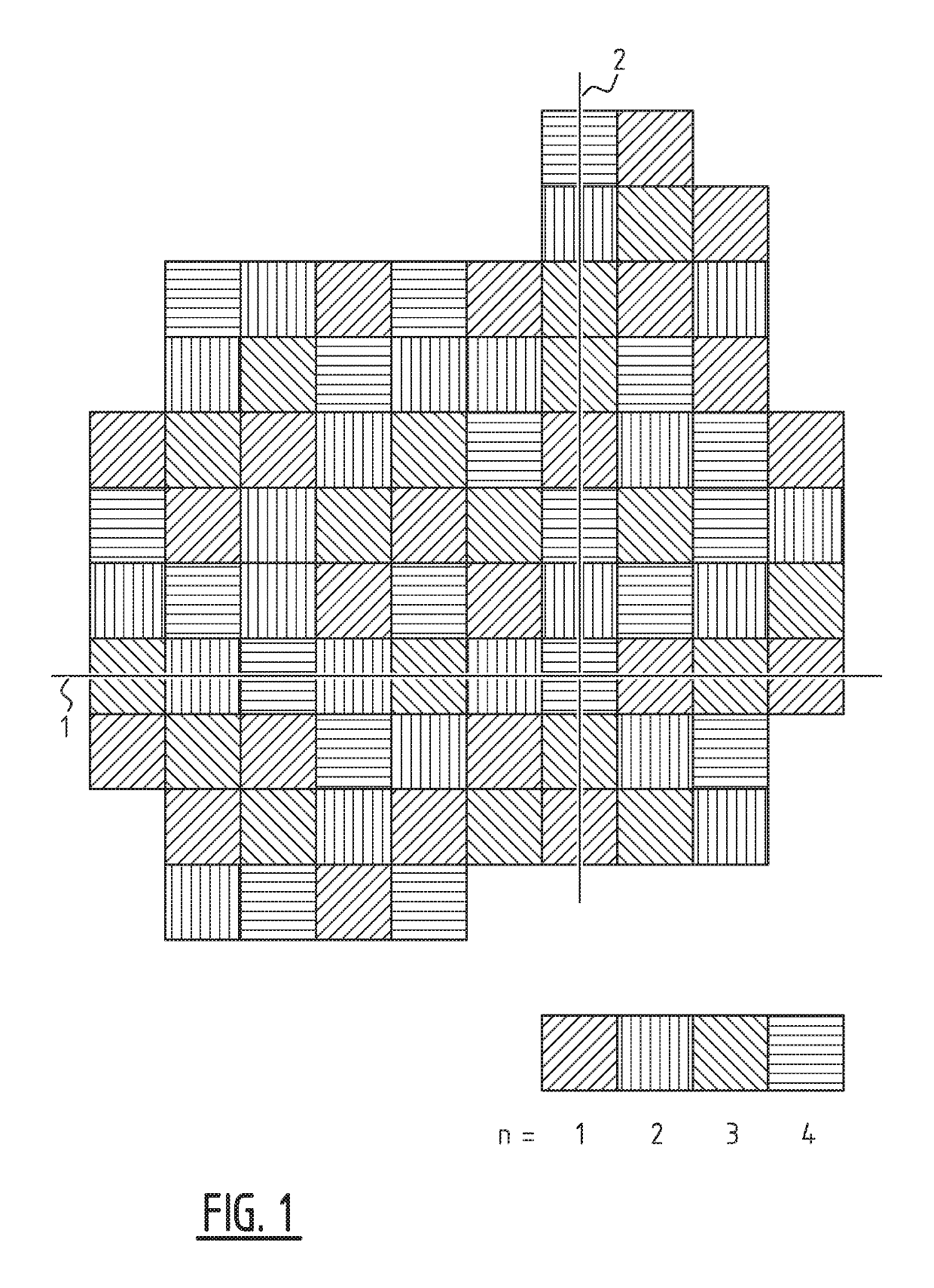
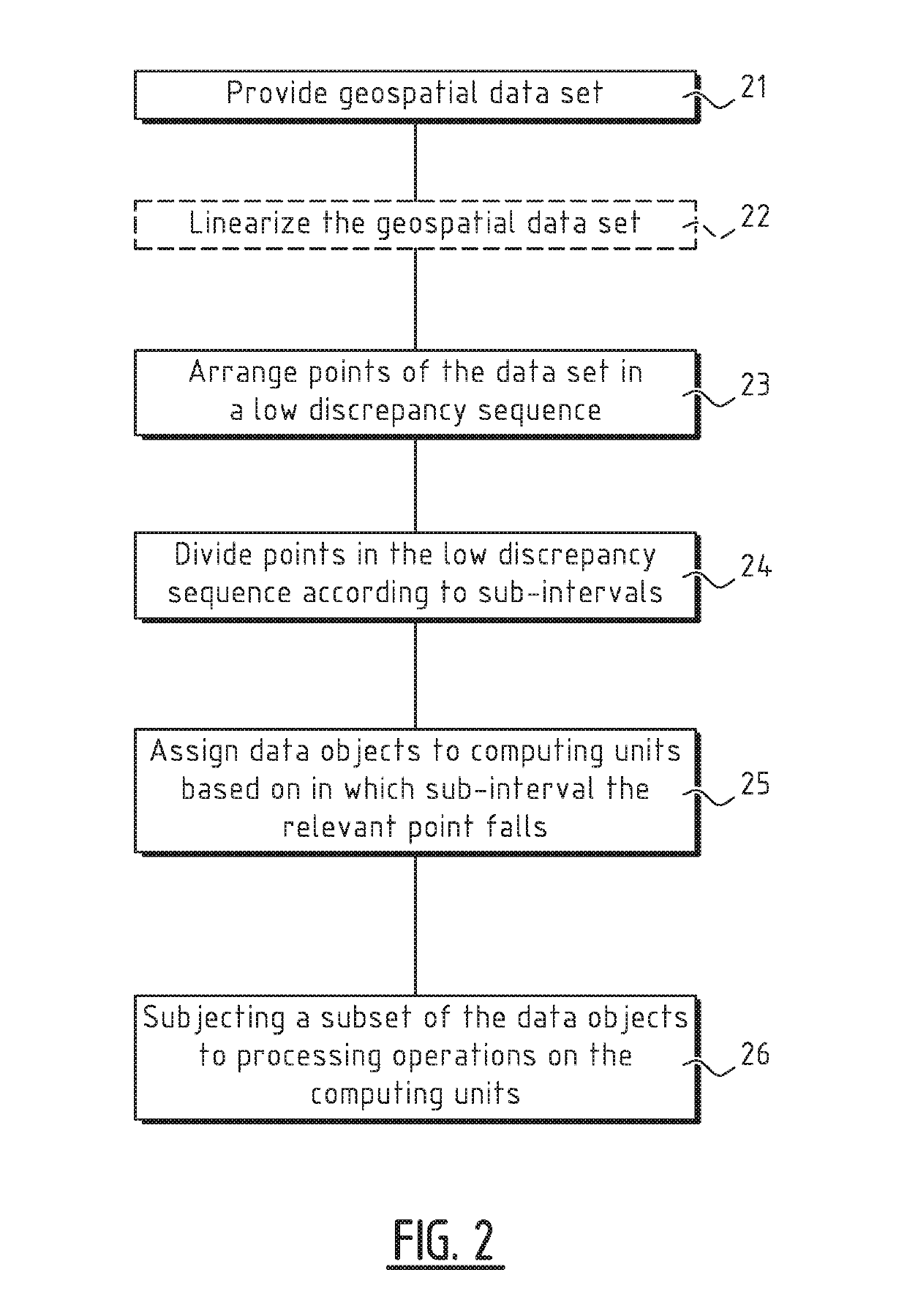
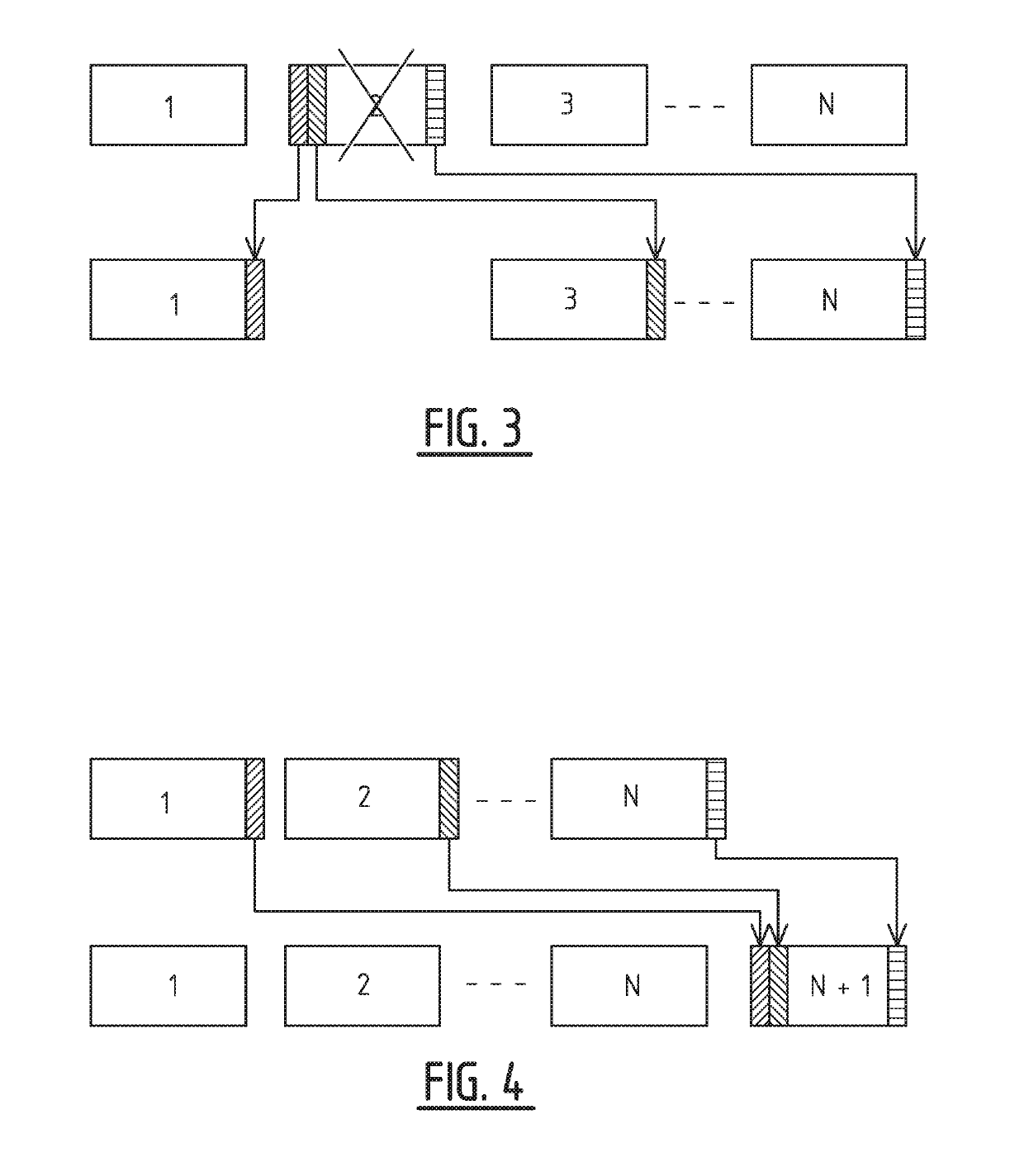
Method of processing a geospatial dataset
ActiveUS20190285770A1Processor architectures/configurationSeismic signal processingData setGeospatial big data
Data objects of a geospatial data set are arranged in a low-discrepancy sequence spanning over a pre-defined interval, and assigned to N computing units based on in which sub-interval within the pre-defined interval the point, to which the data object belongs, falls. A subset of the data objects that have been distributed over the N computing units is subjected to processing operations by computer readable instructions loaded on each of the N computing units.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
System and method for rendering images using a strictly-deterministic methodology including recursive rotations for generating sample points
InactiveUS7046244B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsDeterministic method
A computer graphics system generates a pixel value for a pixel in an image, the pixel being representative of a point in a scene. The computer graphics system generates the pixel value by an evaluation of an integral of a selected function. The computer graphics system comprises a sample point generator and a function evaluator. The a sample point generator is configured to generate respective sets of sample points each associated with one of a series of rays in a ray trace configured to have a plurality of trace levels. The ray at at least one level can be split into a plurality of rays, with each ray being associated with a ray instance identifier. The sample point generator is configured to generate the sample points as predetermined strictly-deterministic low-discrepancy sequence to which a selected rotation operator is applied recursively for the respective levels. The function evaluator is configured to generate a plurality of function values each representing an evaluation of the selected function at one of the sample points generated by the sample point generator and use the function values in generating the pixel value. In one embodiment, the selected rotation operator is the Cranley-Patterson rotation operator.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
Computer graphics system and computer-implemented method for generating images using multiple photon maps
A computer graphics system generates a pixel value for a pixel in an image, the pixel value being representative of a point in a scene as recorded on an image plane of a simulated camera, the computer graphics system comprising a photon map generator, a sample point generator and a function evaluator. The photon map generator is configured to a plurality of photon maps, each photon map being associated with a respective point in time during a time interval. The sample point generator is configured to generate a set of sample points in accordance with a selected low-discrepancy sequence, each sample point representing a respective point in time during the time interval. The function evaluator is configured to generate at least one value representing an evaluation of a selected function using selected ones of the photon maps associated with respective ones of the points in time associated with the sample points generated by the sample point generator, the value generated by the function evaluator corresponding to the pixel value.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
System and method for scanning a region using a low discrepancy sequence
InactiveUS20020146152A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMovement controlComputer science
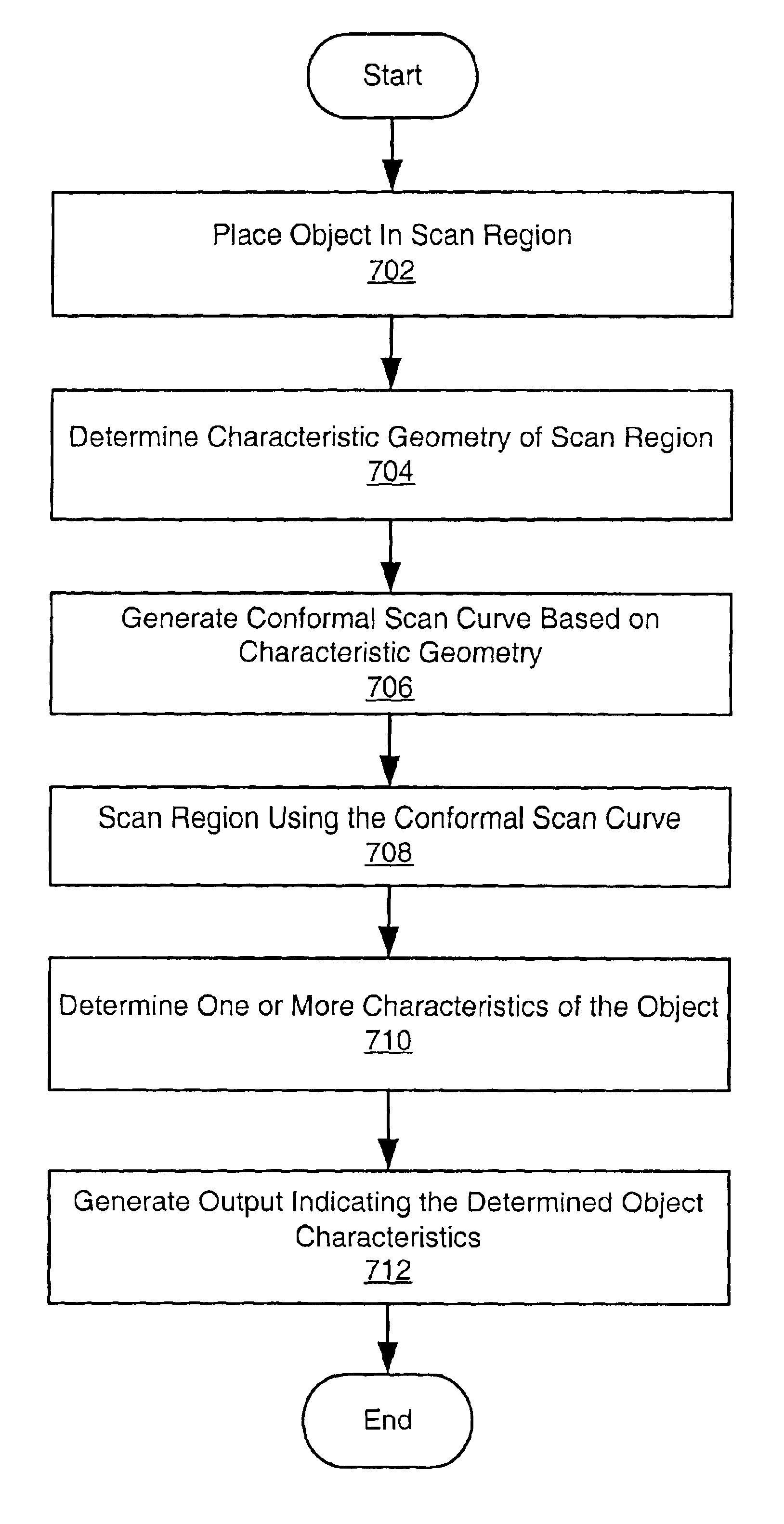
A system and method for scanning for an object within a region using a Low Discrepancy Sequence scanning scheme. The system may comprise a computer which includes a CPU and a memory medium which is operable to store one or more programs executable by the CPU to perform the method. The method may: 1) calculate a Low Discrepancy Sequence of points in the region; 2) generate a motion control trajectory from the Low Discrepancy Sequence of points (e.g., by generating a Traveling Salesman Path (TSP) from the Low Discrepancy Sequence of points and then re-sampling the TSP to produce a sequence of motion control points comprising the motion control trajectory); 3) scan the region along the motion control trajectory to determine one or more characteristics of the object in response to the scan. The method may also generate output indicating the one or more characteristics of the object.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
System and method for scanning a region using a low discrepancy curve
InactiveUS6917710B2Confirm correctnessCharacter and pattern recognitionCurve fittingComputer science
A scanning system and method for scanning for an object within a region, or for locating a point within a region. Embodiments of the invention include a method for scanning for an object within a region using a Low Discrepancy Curve (LDC) scanning scheme. The method may: 1) generate a Low Discrepancy Sequence (LDS) of points in the region; 2) calculate an LDC in the region based on the LDS of points; and 3) scan the region along the LDC to determine one or more characteristics of the object in response to the scan. In calculating the LDC in the region based on the LDS of points, the method may connect sequential pairs of the LDS with contiguous orthogonal line segments (each parallel to a respective axis of the region), then sample the segments, generating points which may be used to generate the LDC, such as by a curve fit.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
System and computer-implemented method for evaluating integrals using a quasi-monte carlo methodology in which sample points represent dependent samples generated using a low-discrepancy sequence
A computer graphics system generates a pixel value for a pixel in an image, the pixel value being representative of a point in a scene as recorded on an image plane of a simulated camera, the computer graphics system comprising a sample point generator and a function evaluator. The sample point generator is configured to generate a set of sample points, at least one sample point being generated using at least one dependent sample, the at least one dependent sample comprising at least one element of a low-discrepancy sequence offset by at least one element of another low-discrepancy sequence. The function evaluator is configured to generate at least one value representing an evaluation of a selected function at one of the sample points generated by the sample point generator, the value generated by the function evaluator corresponding to the pixel value.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
Image generation using low-discrepancy sequences
A computer graphics system generates a pixel value for a pixel in an image and displays a human-perceptible image on an LCD CRT or other display device based on an electrical output generated in response to the pixel value, the pixel being representative of a point in a scene as recorded on an image plane of a simulated camera, the computer graphics system being configured to generate the pixel value for an image using a selected ray-tracing methodology in which simulated rays are shot from respective ones of a plurality of subpixels in the pixel each subpixel having coordinates in the image plane. The computer graphics system comprises a sample point generator and a function evaluator.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
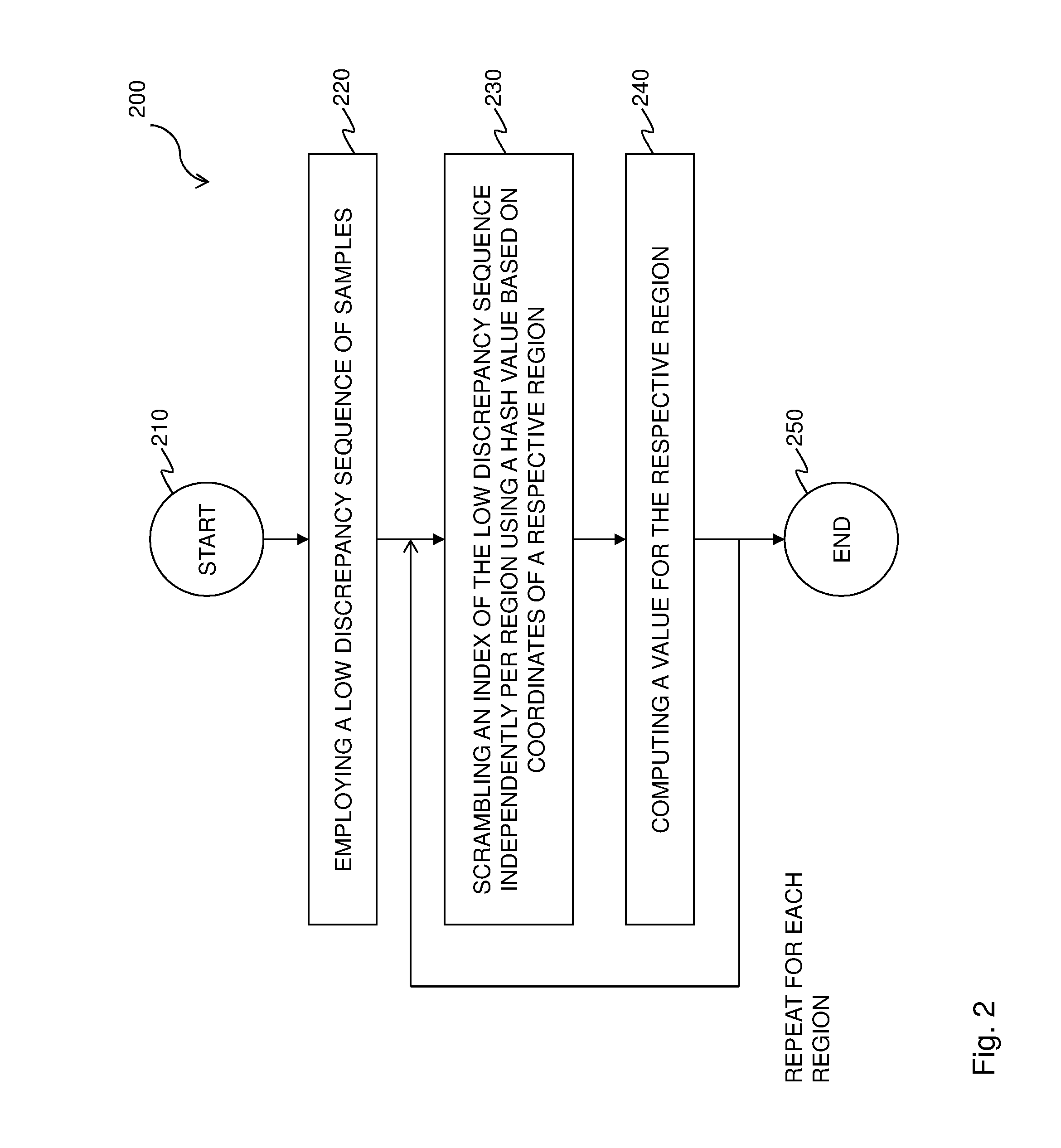
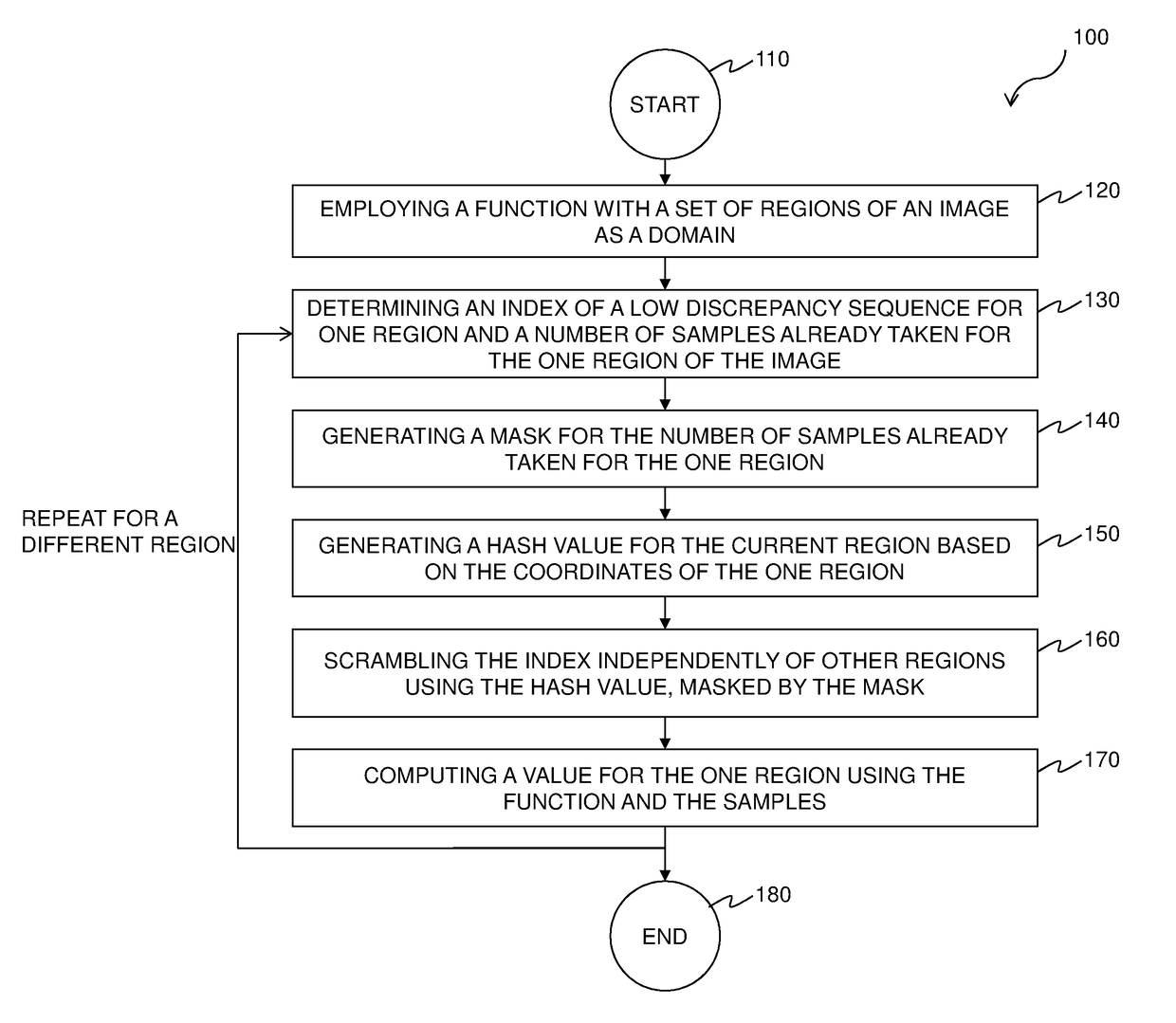
Decorrelation of low discrepancy sequences for progressive rendering
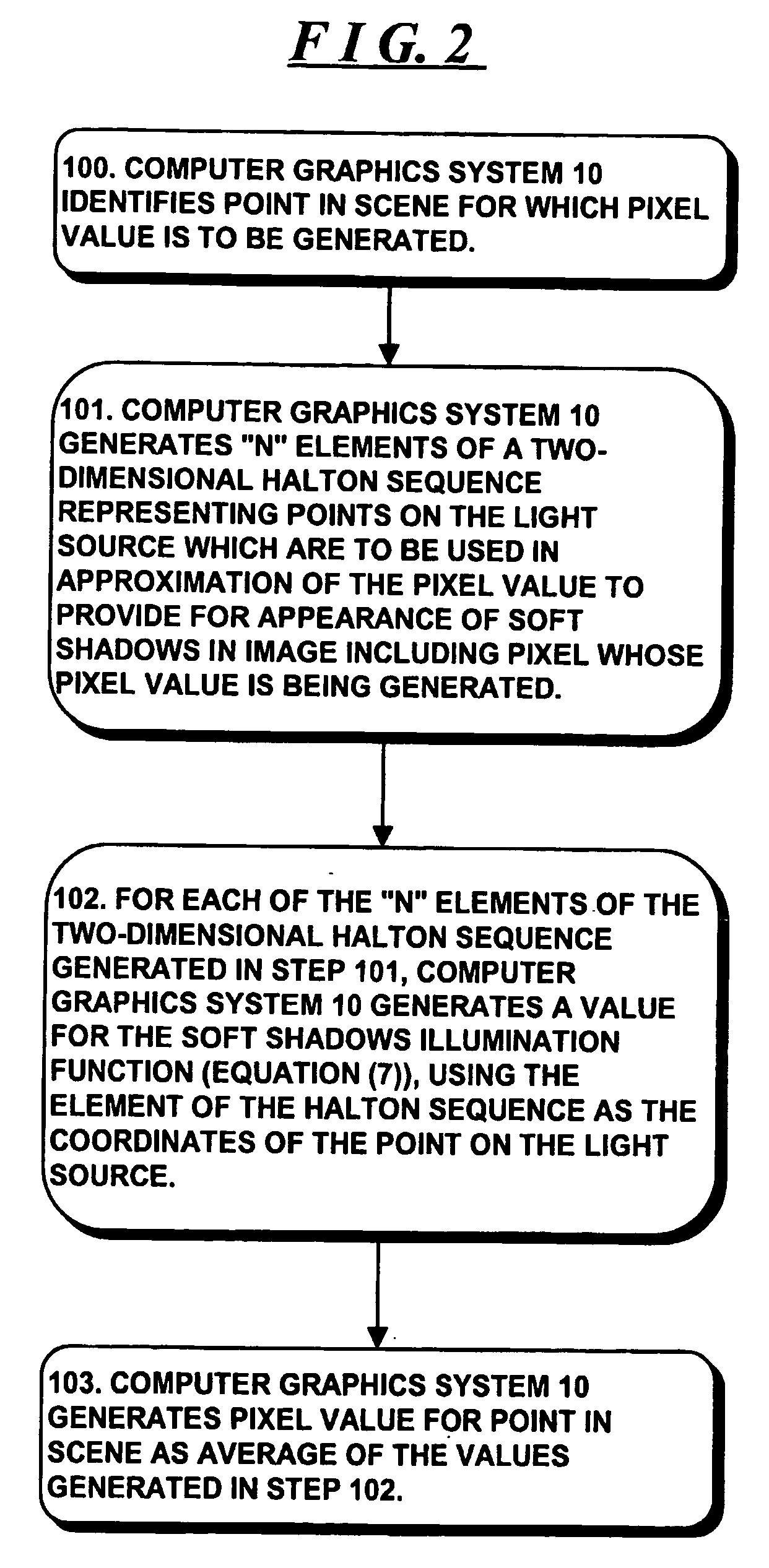
ActiveUS20170032566A1Degrade visual realismAddress limitations3D-image renderingSample sequenceDecorrelation
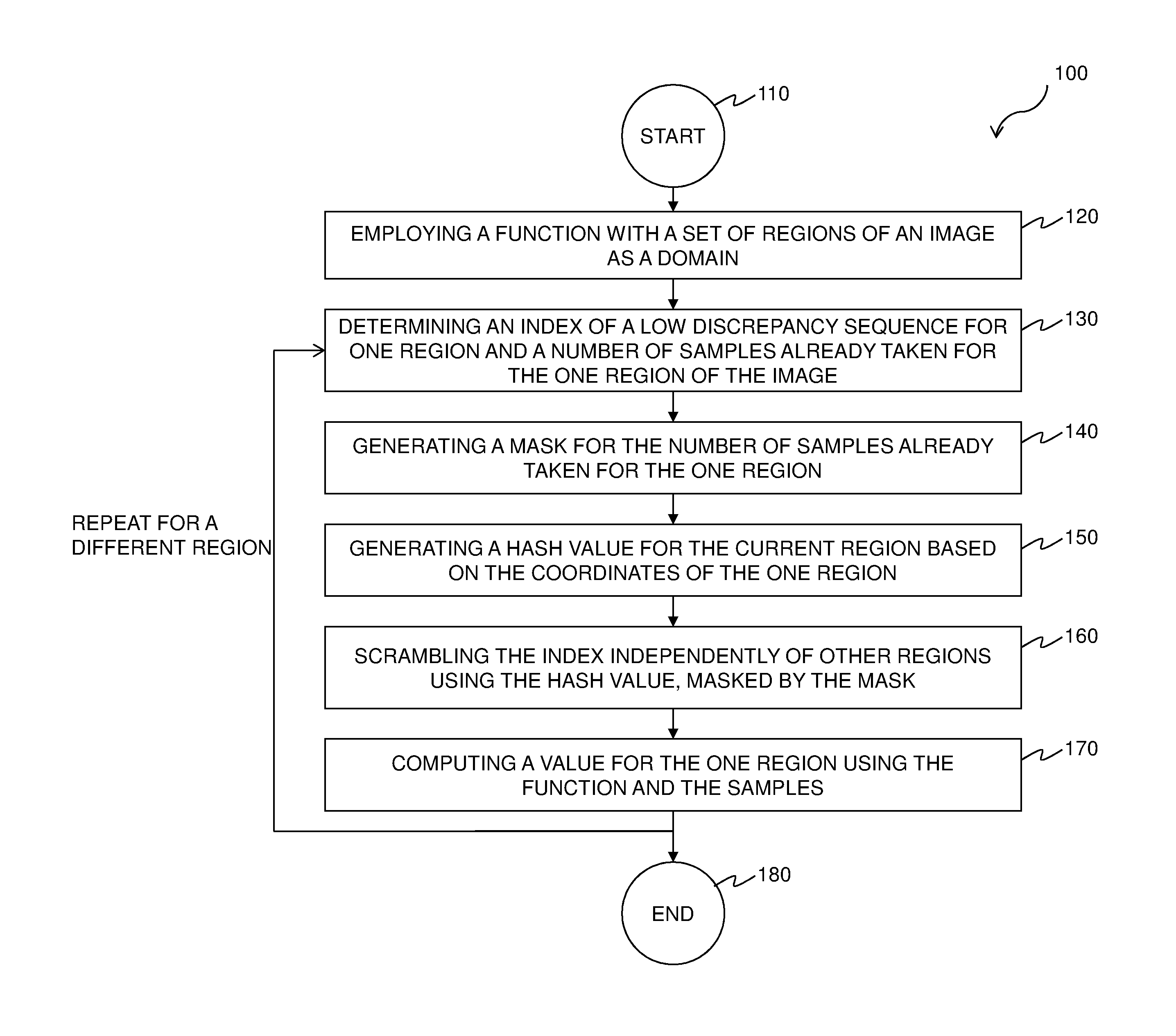
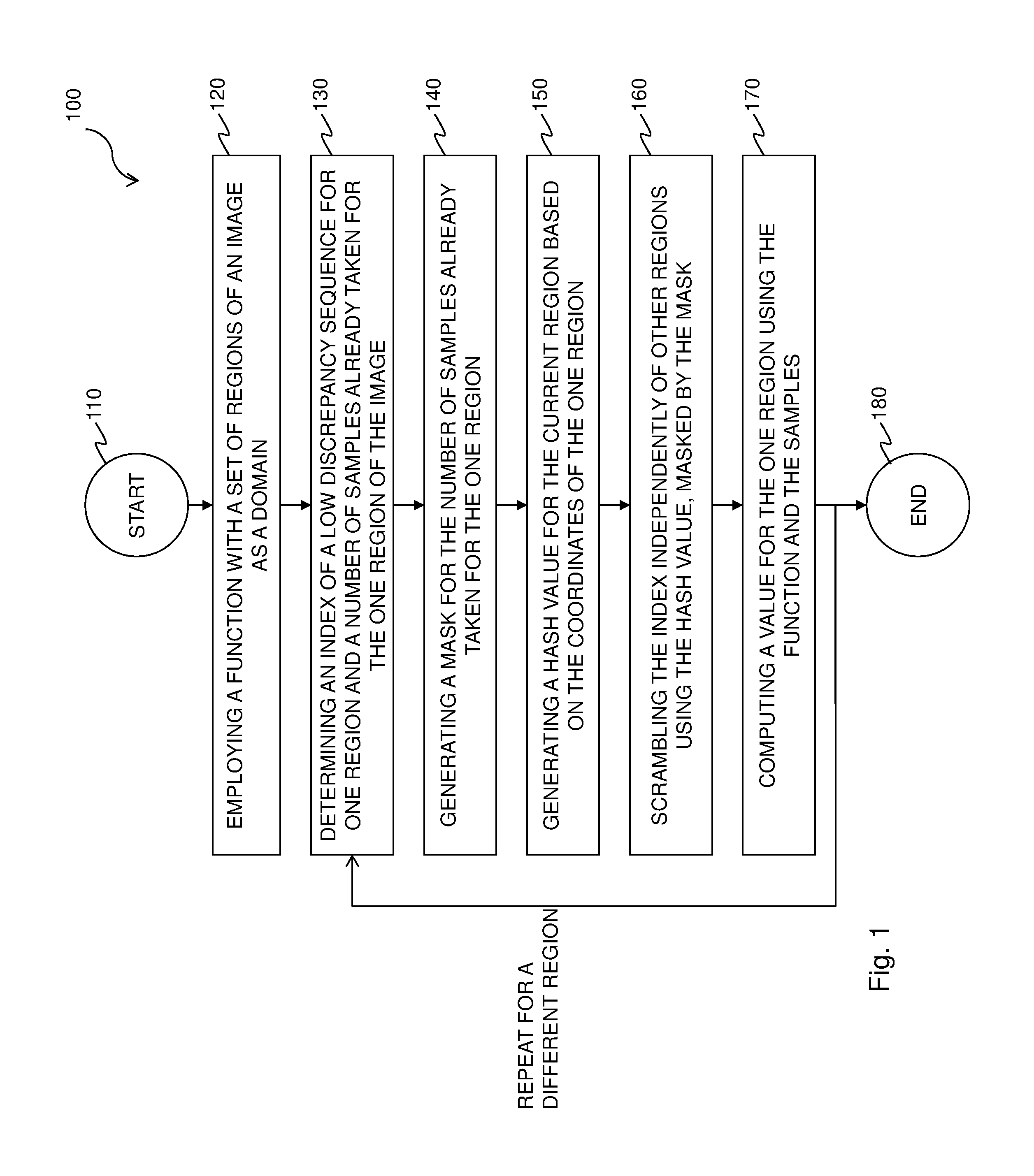
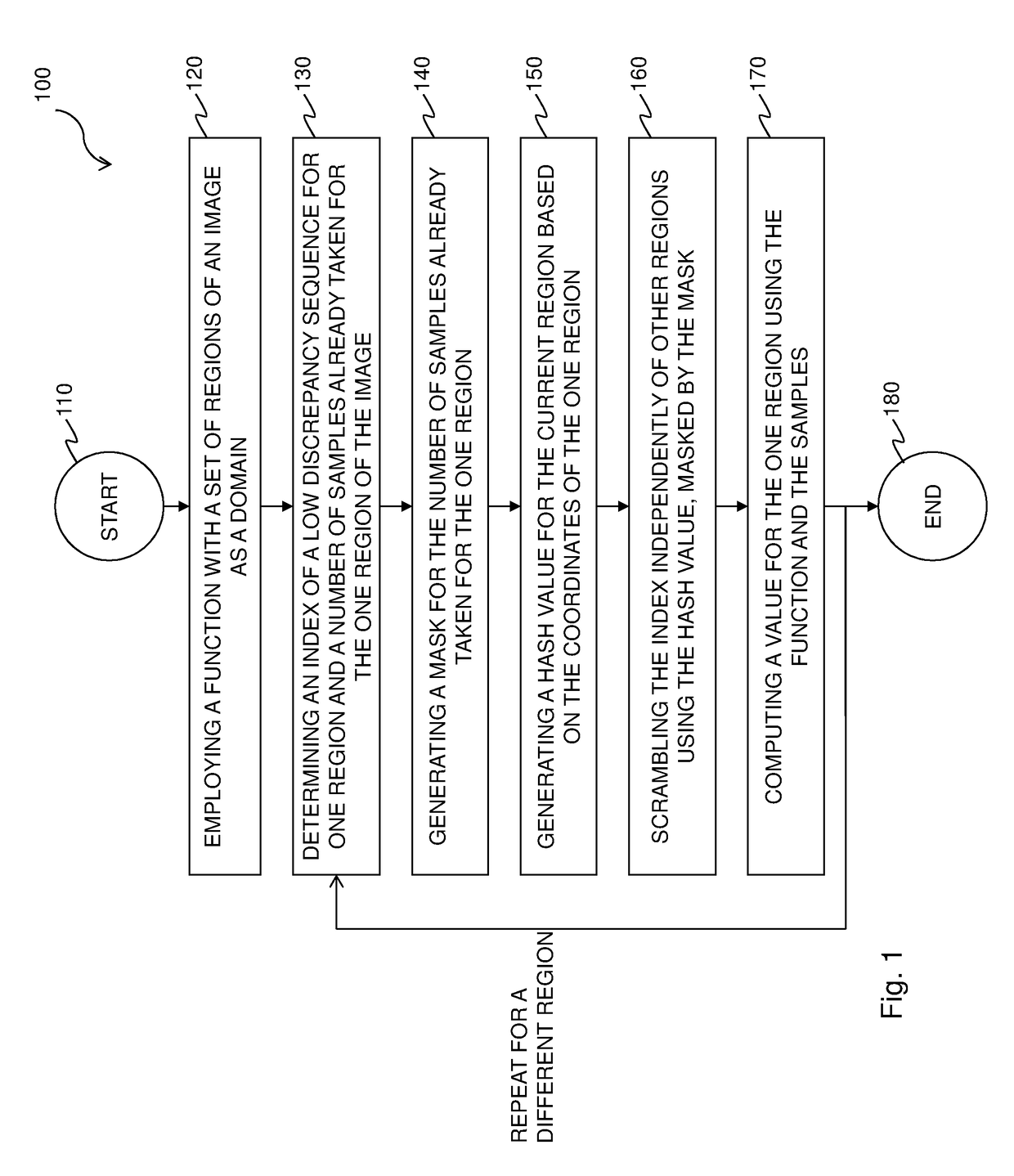
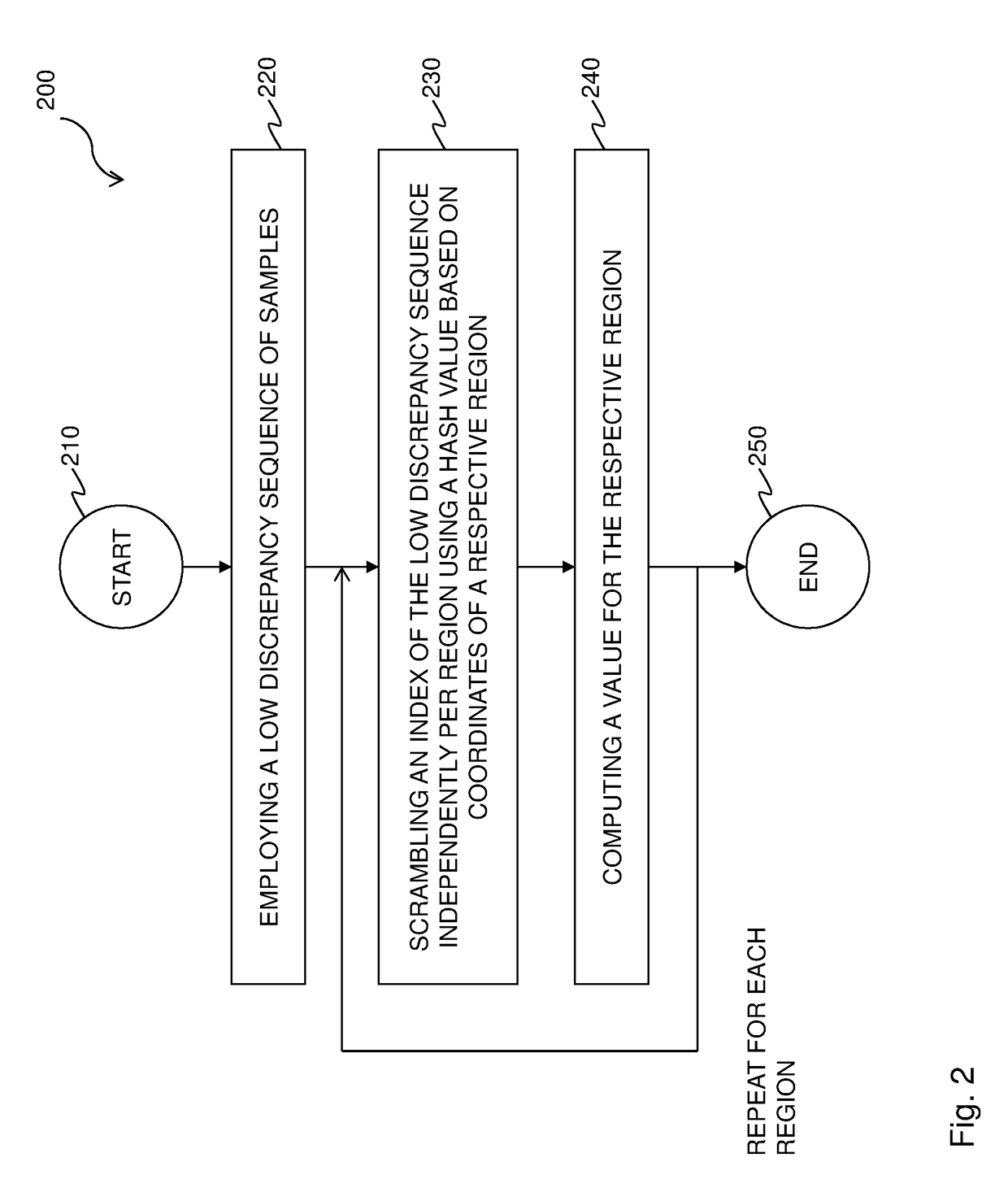
A method and renderer for a progressive computation of a light transport simulation are provided. The method includes the steps of employing a low discrepancy sequence of samples; and scrambling an index of the low discrepancy sequence independently per region using a hash value based on coordinates of a respective region, wherein for each set of a power-of-two number of the samples, the scrambling is a permutation.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
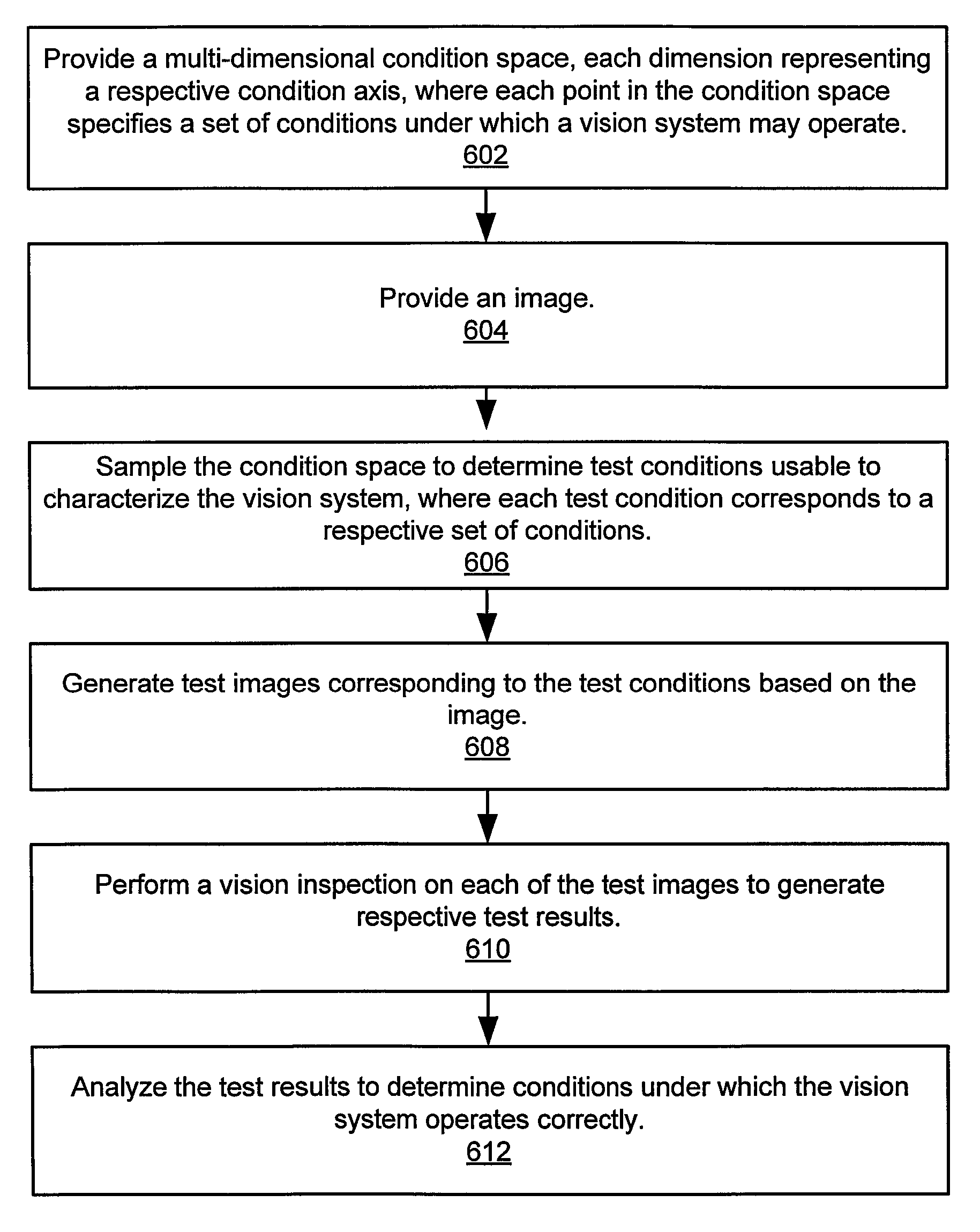
Characterizing vision systems
ActiveUS8068660B2Improve reliability and performanceMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingVision inspection
System and method for characterizing vision systems. A multi-dimensional condition space is provided, each dimension representing a respective condition axis, where each point in the condition space specifies a set of conditions under which a vision system may operate. An image is provided. The condition space is sampled according to a pseudo-random sequence, e.g., a low-discrepancy sequence, to determine a plurality of test conditions usable to characterize the vision system, where each test condition corresponds to a respective set of conditions. A plurality of test images corresponding to the plurality of test conditions are generated based on the image, e.g., by applying image processing functions to the image that simulate the test conditions. A vision inspection is performed on each of the plurality of test images to generate respective test results, and the test results are analyzed to determine conditions under which the vision system operates correctly.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
System and method for generating pixel values for pixels in an image using strictly deterministic methodologies for generating sample points
InactiveUS20070018978A1Reduce errorsPromote generation3D-image renderingDeterministic methodGraphics
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
Decorrelation of low discrepancy sequences for progressive rendering
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Path Integral Method for X-ray Monte Carlo Simulation
The invention discloses a path integral method for X-ray Monte Carlo simulation. The path integral method for the X-ray Monte Carlo simulation comprises the following steps: step a, a low-difference sequence with the length of m in a [0,1] 3n dimension is generated, wherein the n is the scattering times and the m is the number of samples; step b, scattering point sequences geometrically matched with a motif are generated through an isomorphic mapping of the low-difference sequence; step c, m photon paths are formed by the scattering point sequences on each detector grid point; step d, the probability density of passing through the photon paths to reach the detector grid points is determined; step e, the probability density is weighted and summed to obtain the scattering intensity of each detector grid point. According to the path integral method for the X-ray Monte Carlo simulation, errors caused by discontinuity on a boundary are eliminated, variances of the samples are lowered, calculation is finished with fewer samples under given accuracy, and the calculated amount is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com