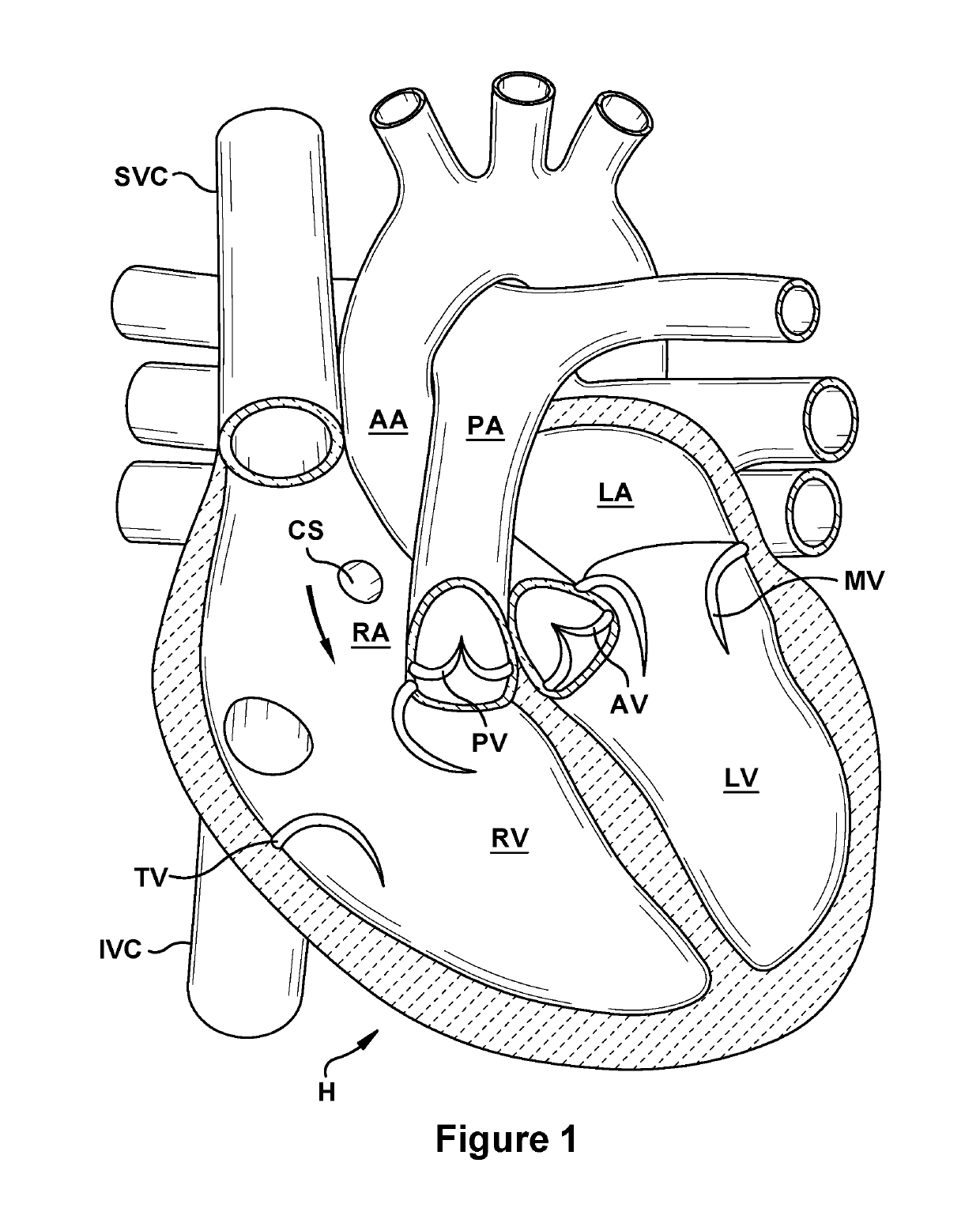
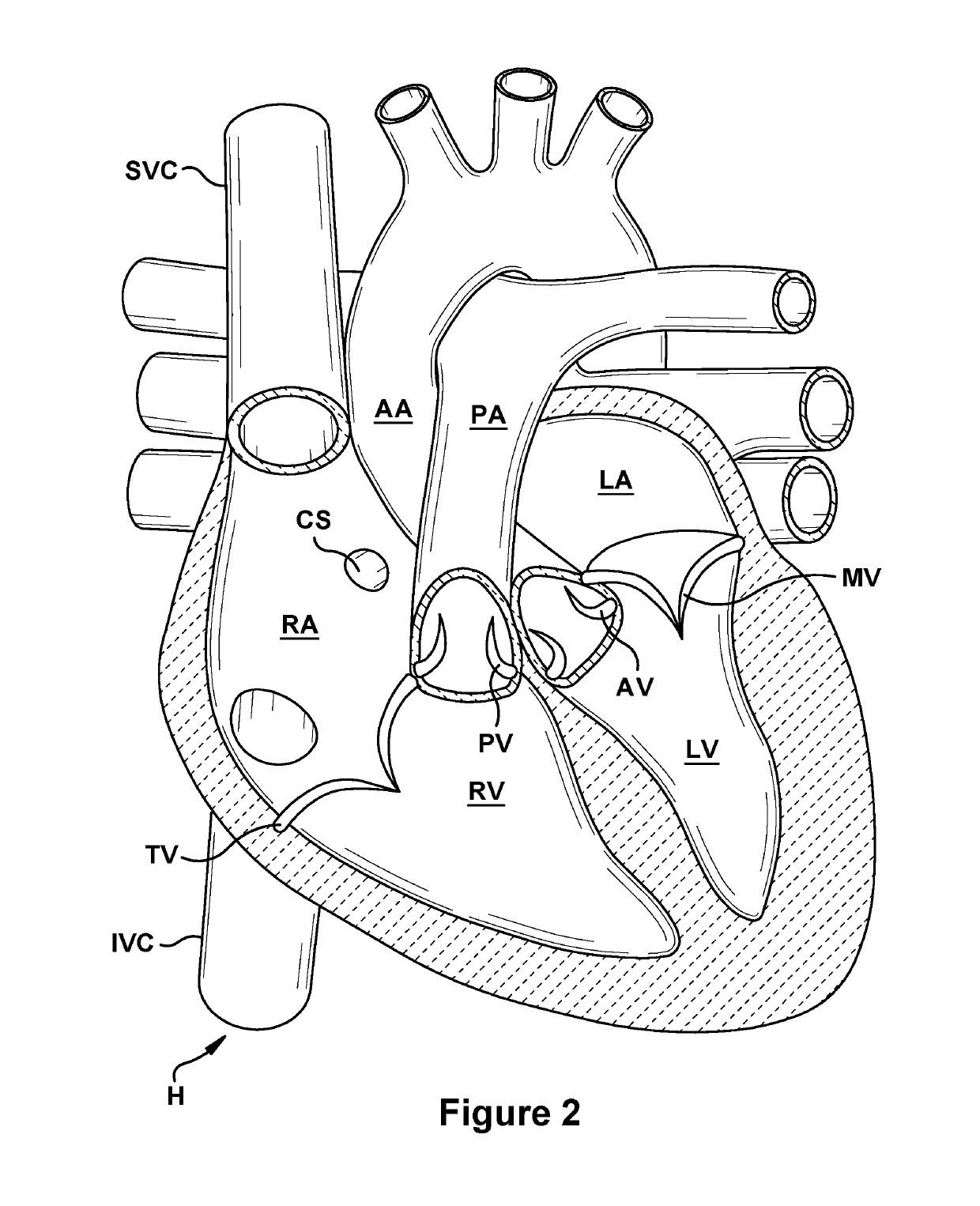
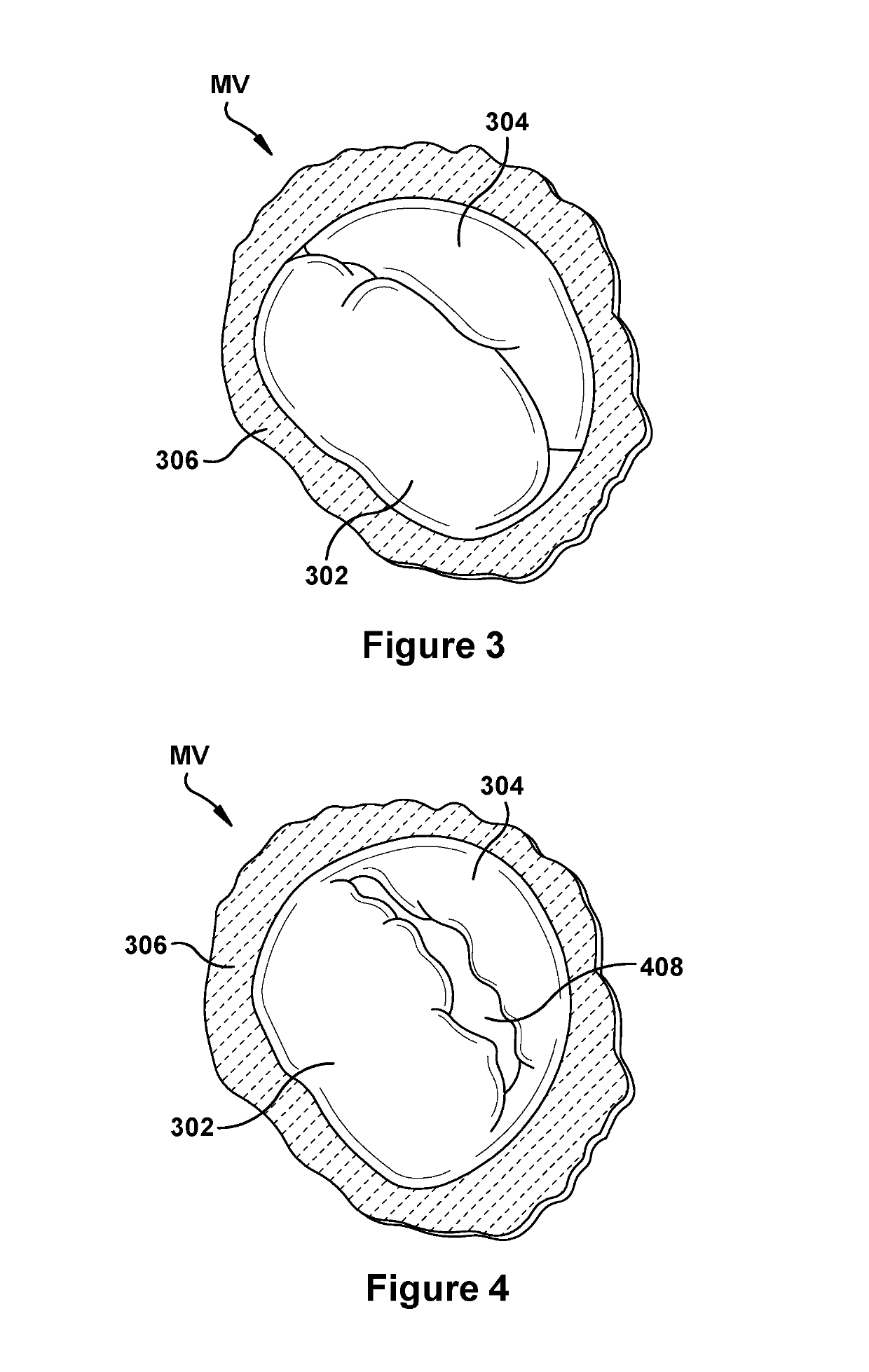
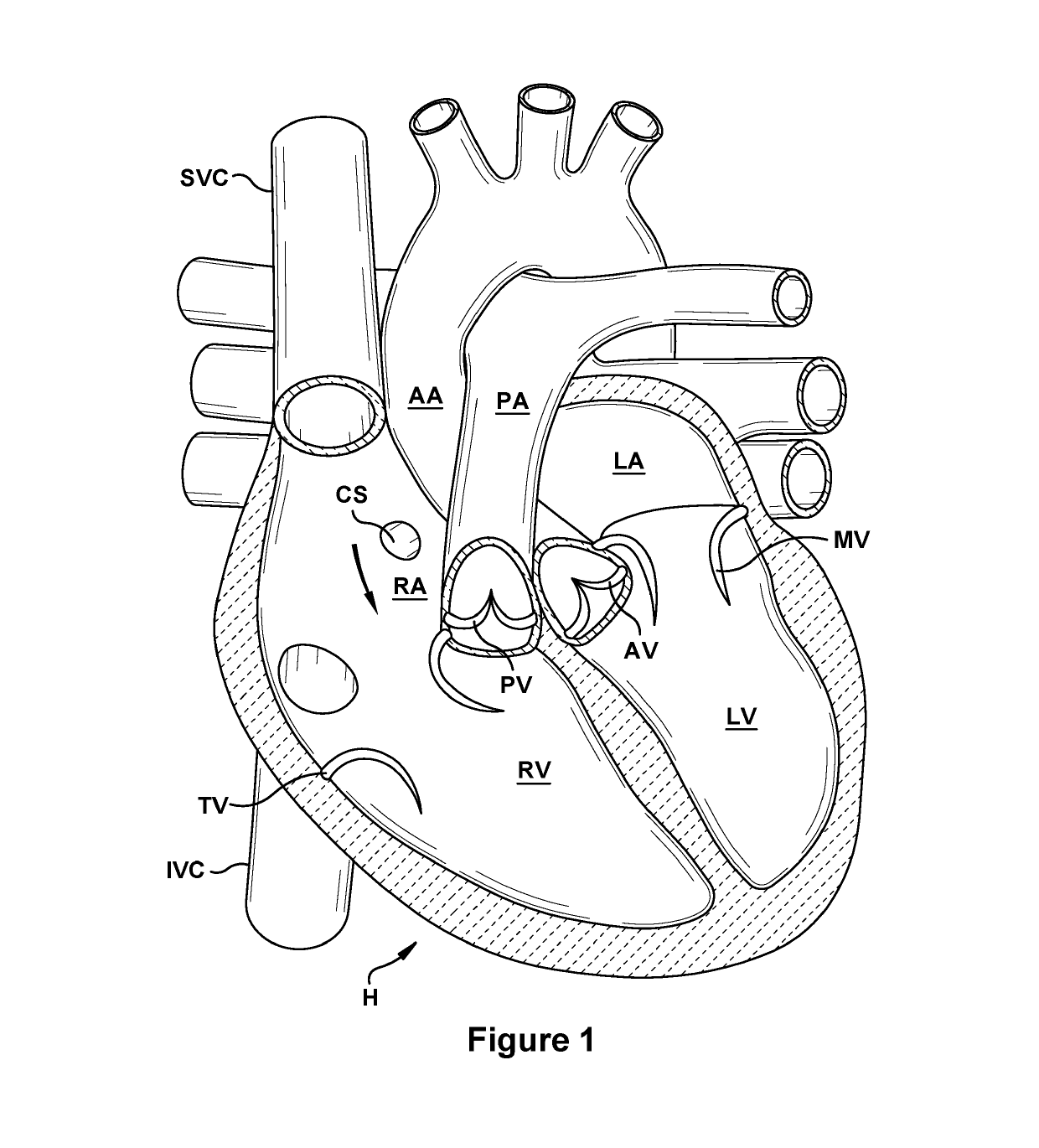
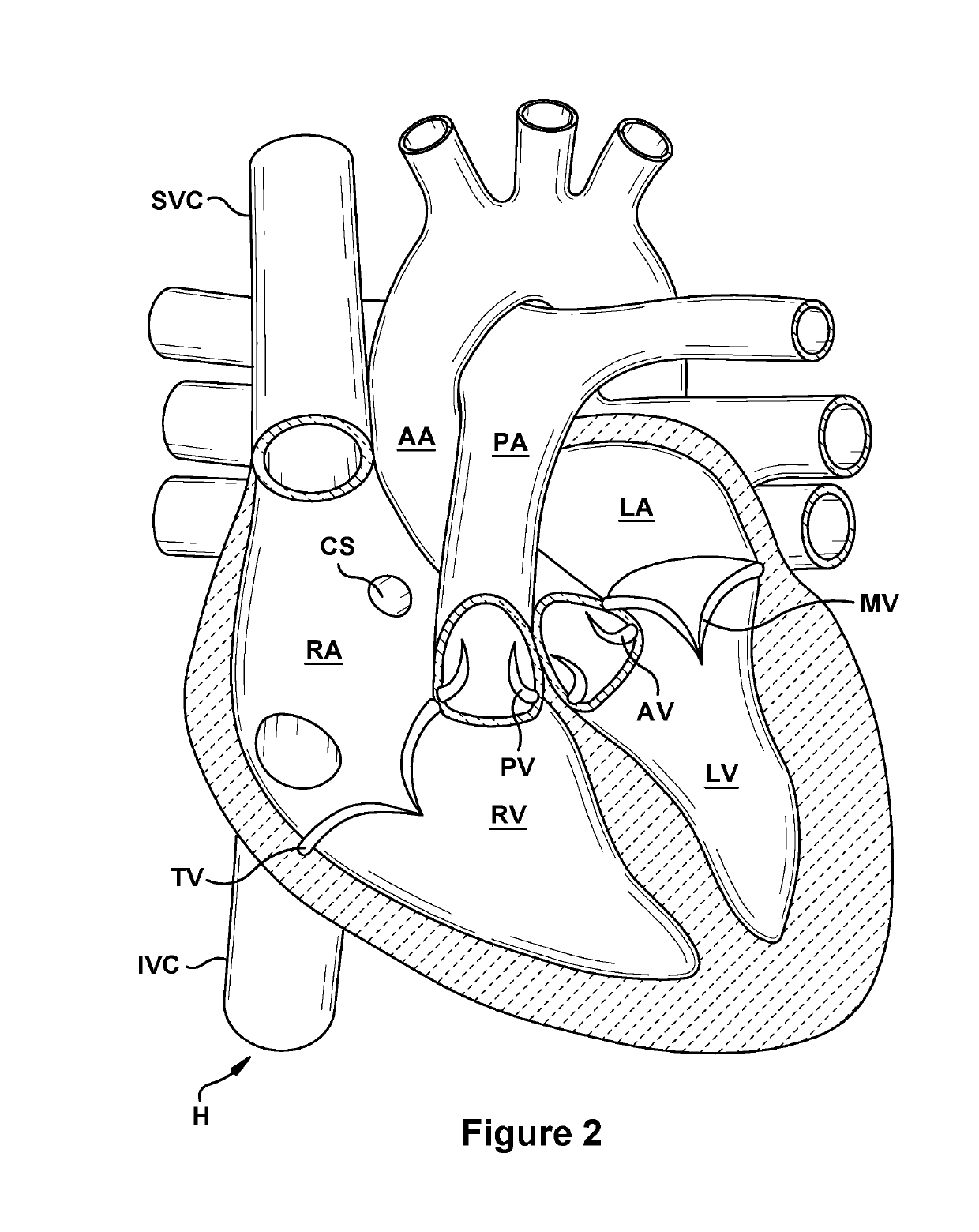
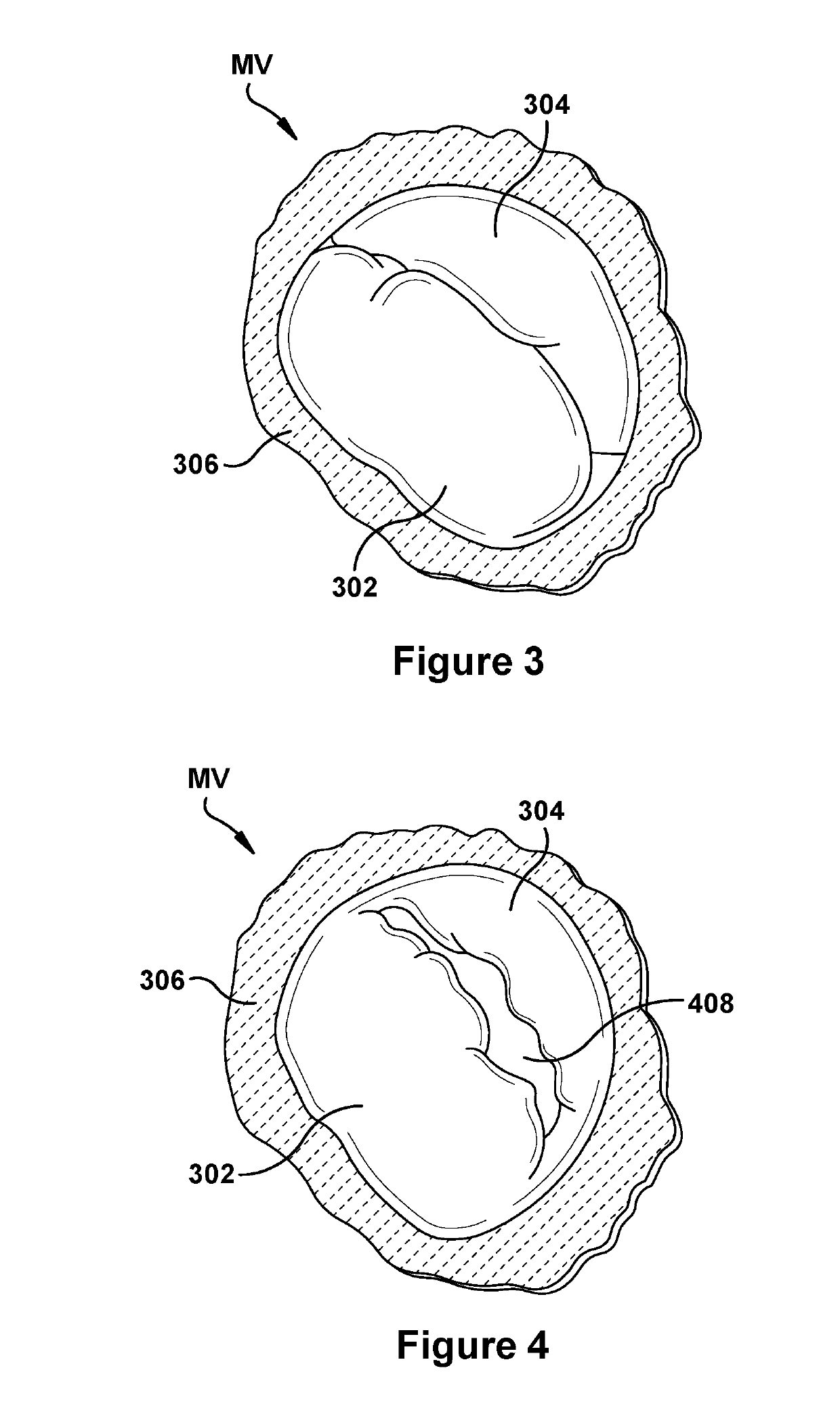
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Heart procedures" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
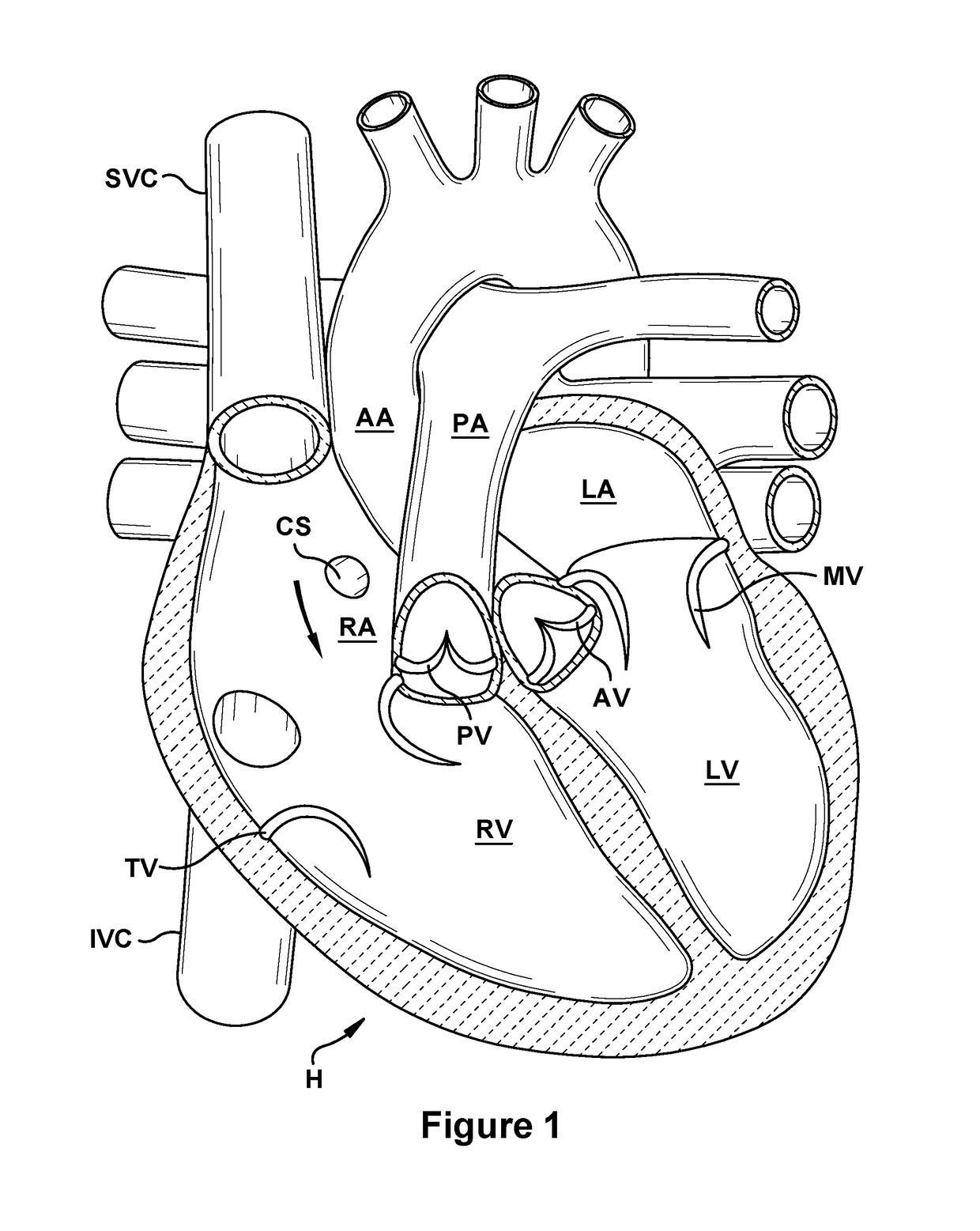
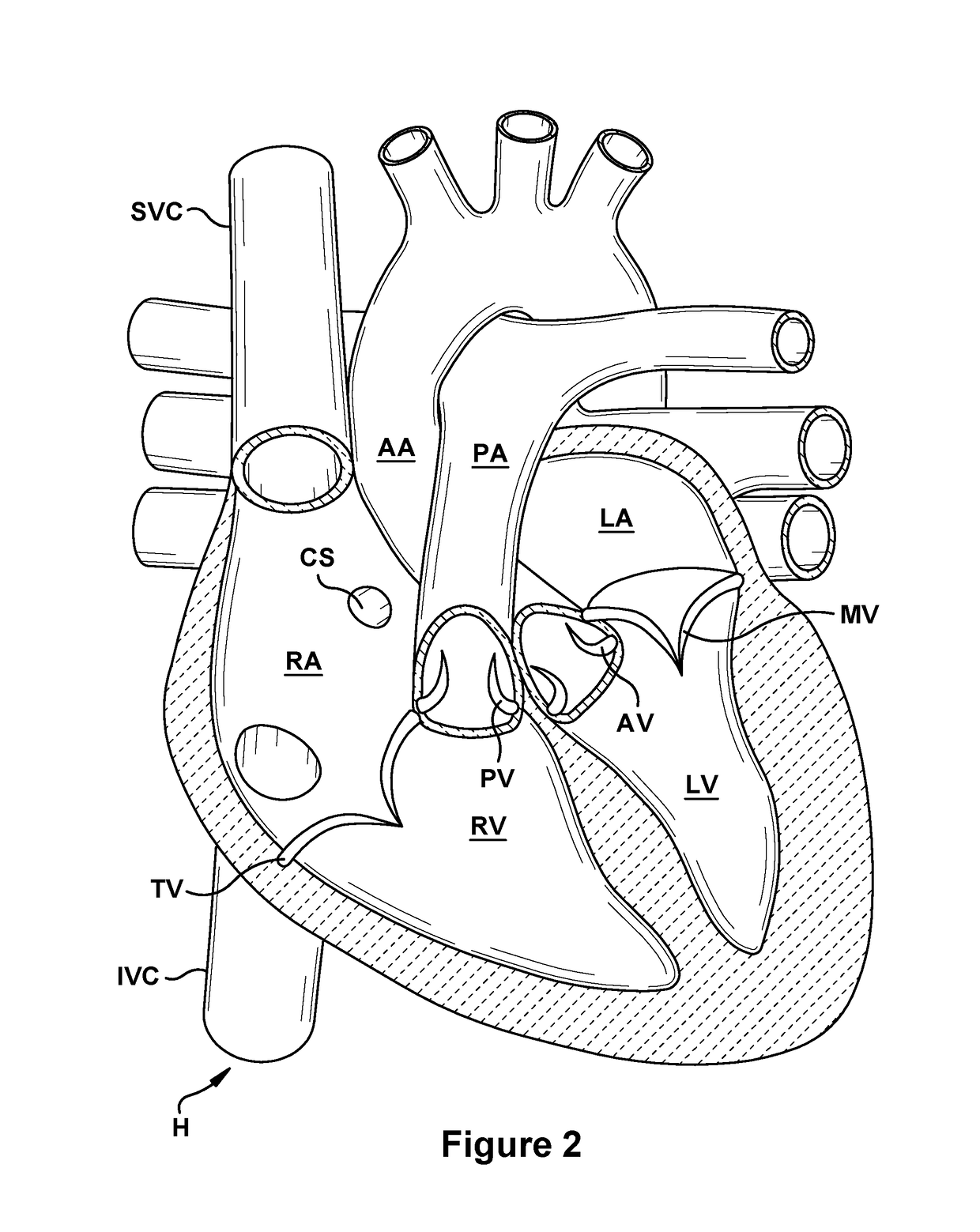
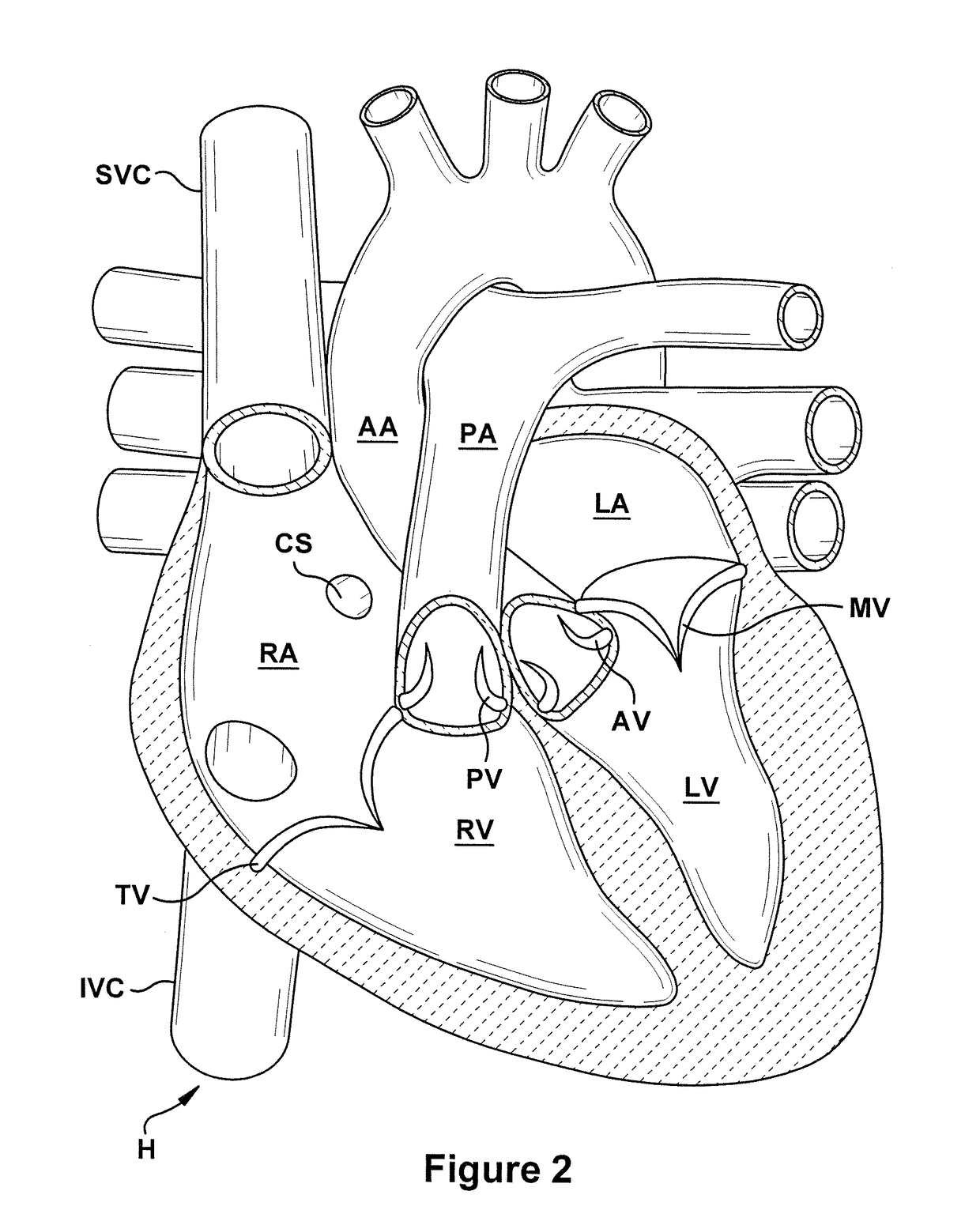
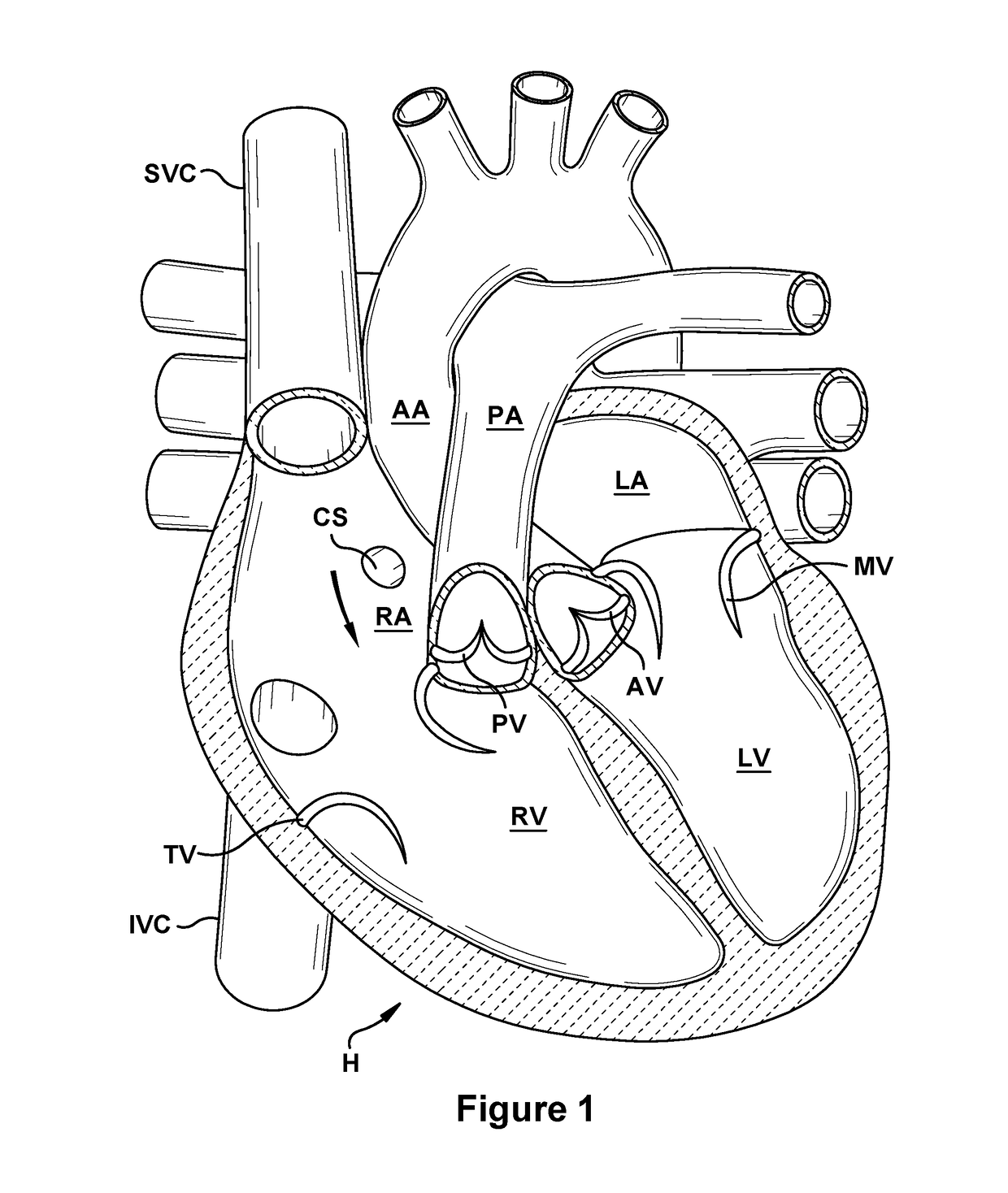
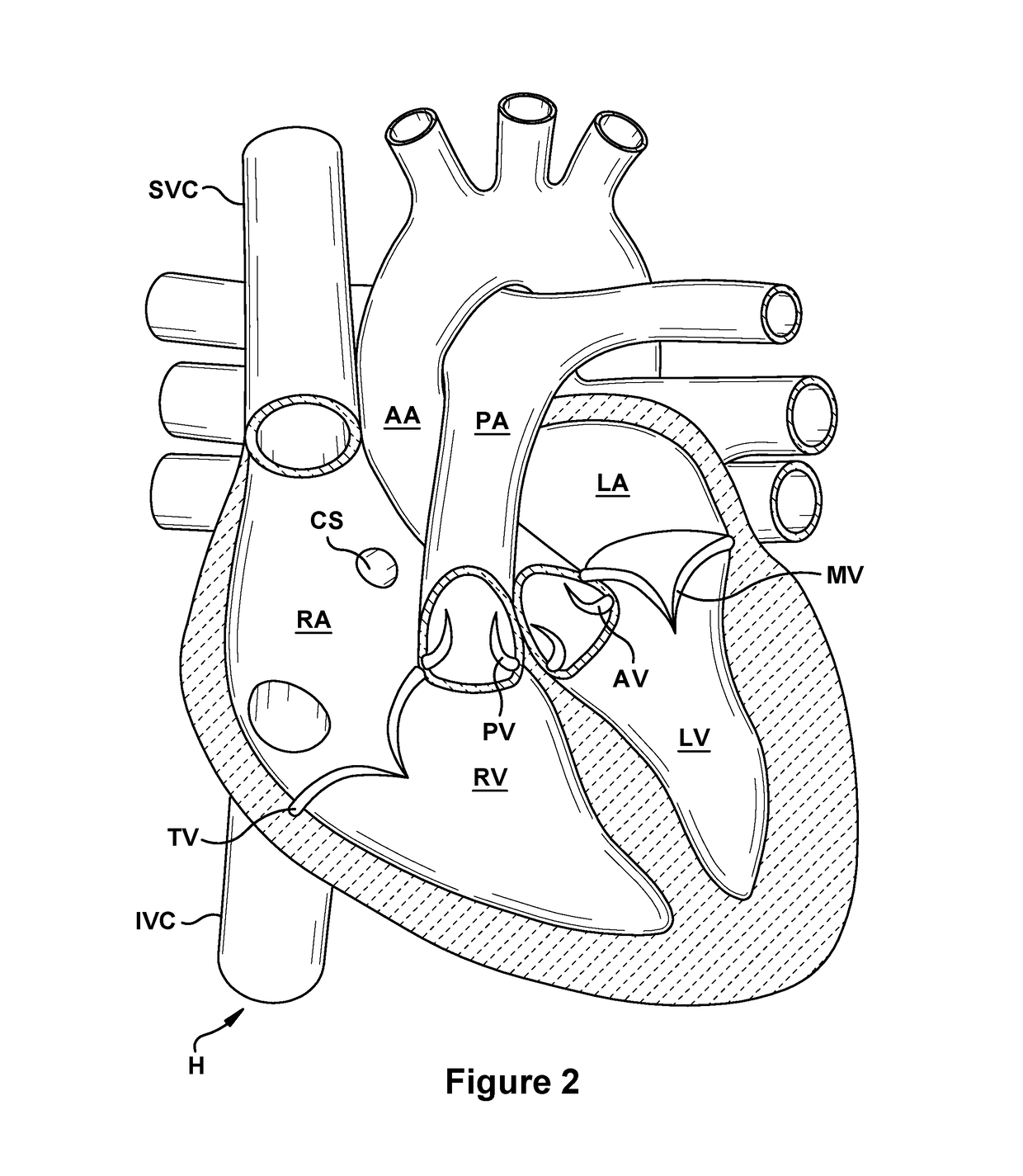
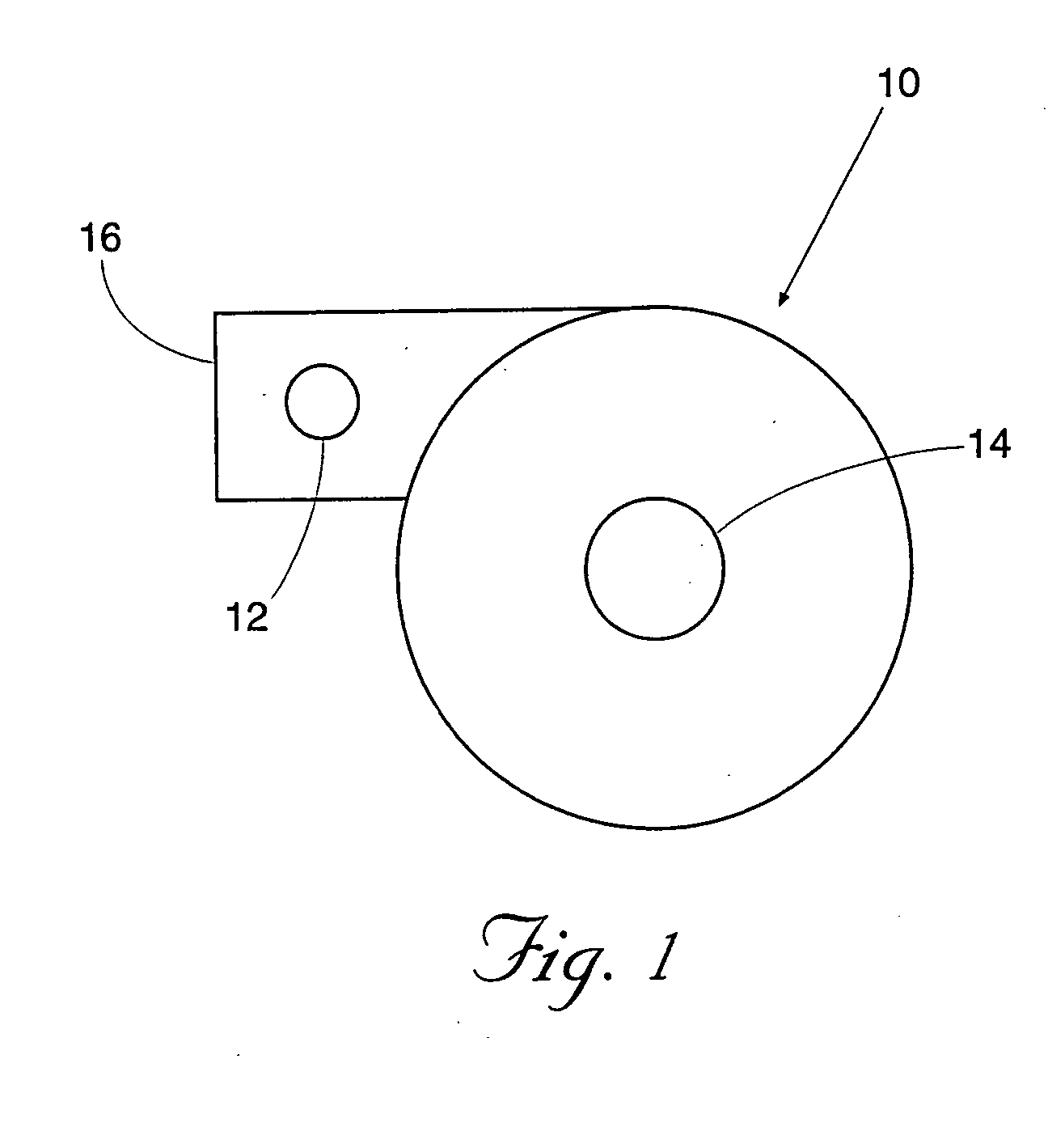
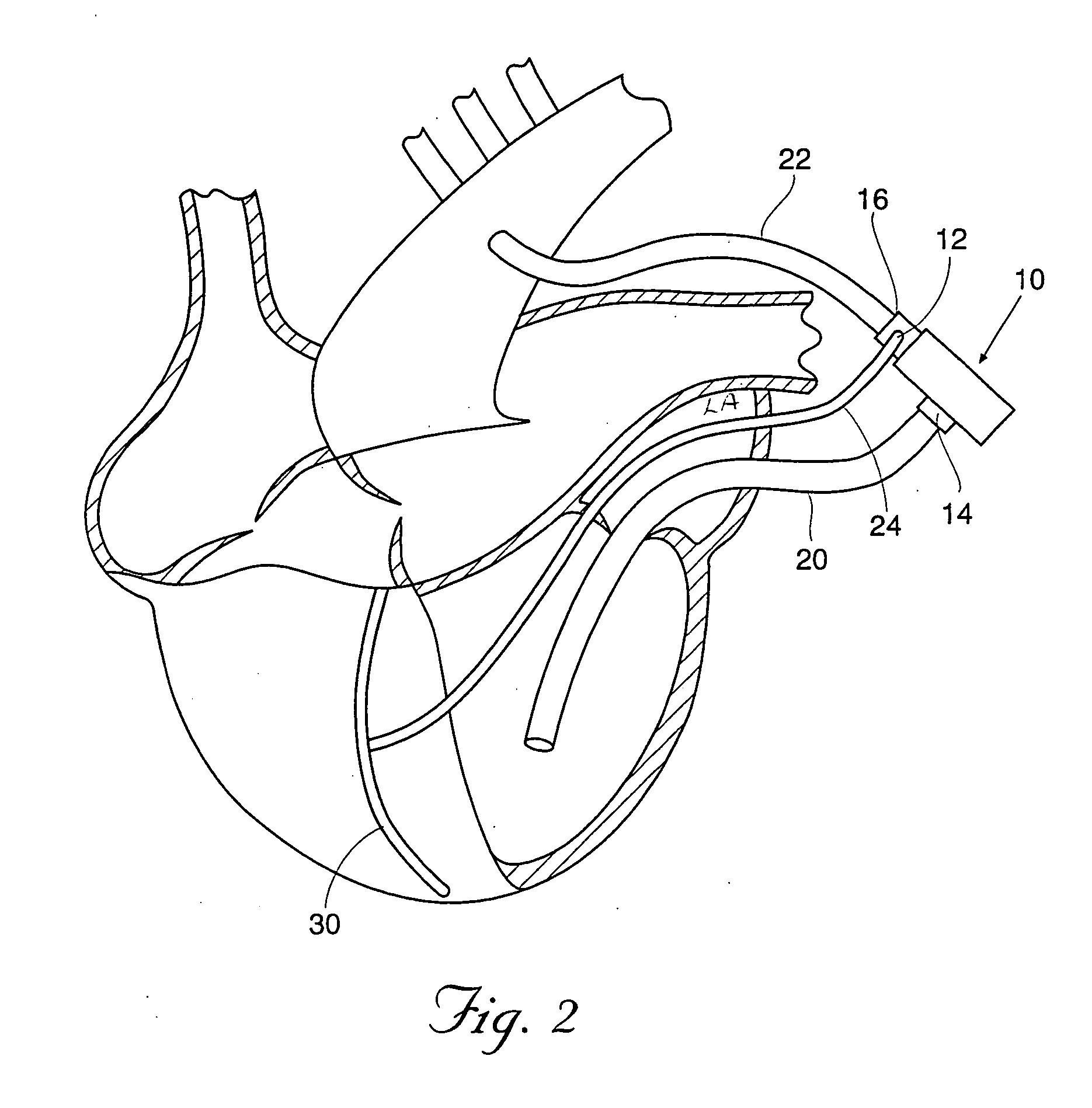
Performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia
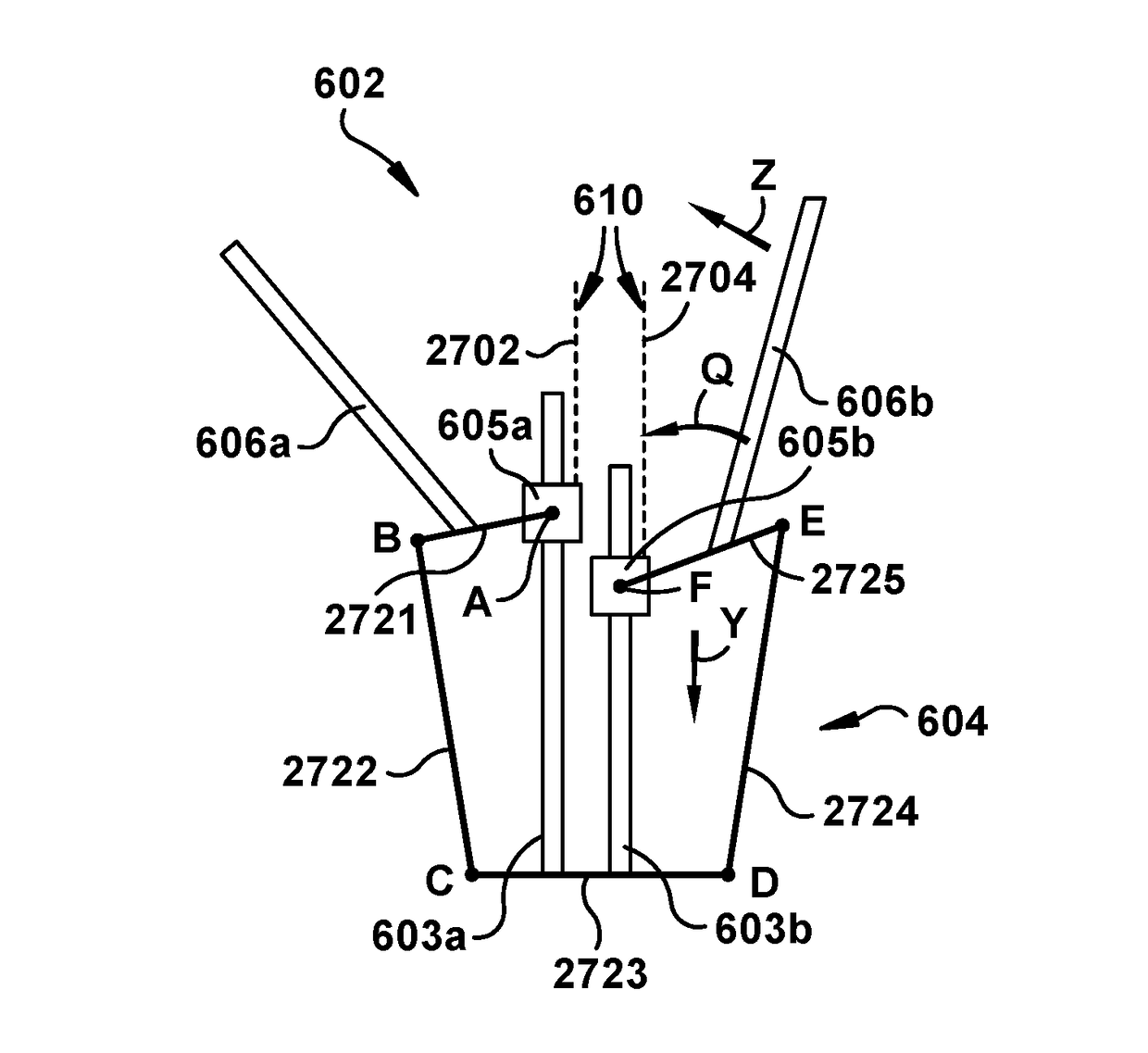
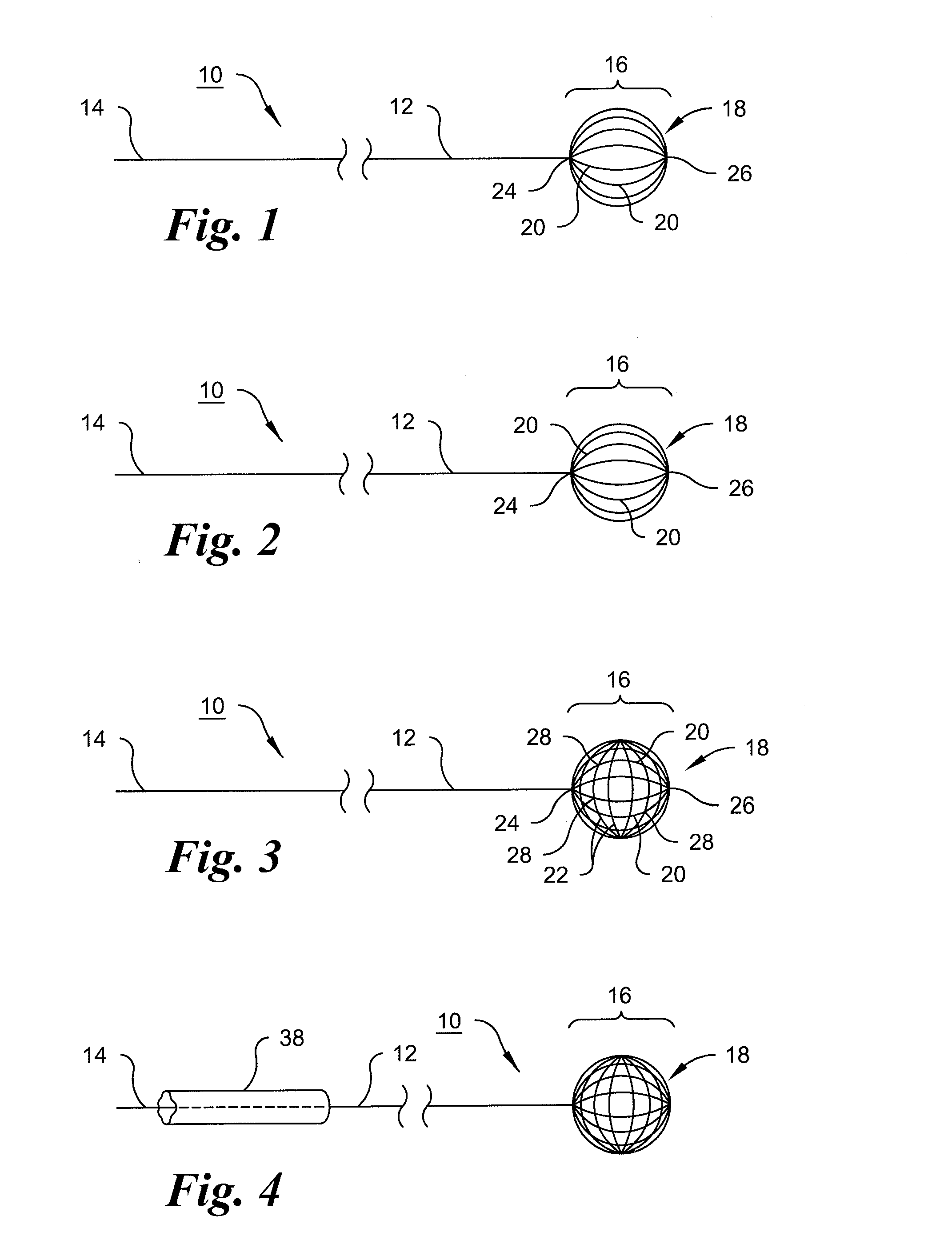
InactiveUS6468265B1Improve abilitiesEasy to controlSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsForcepsMotion tracking system
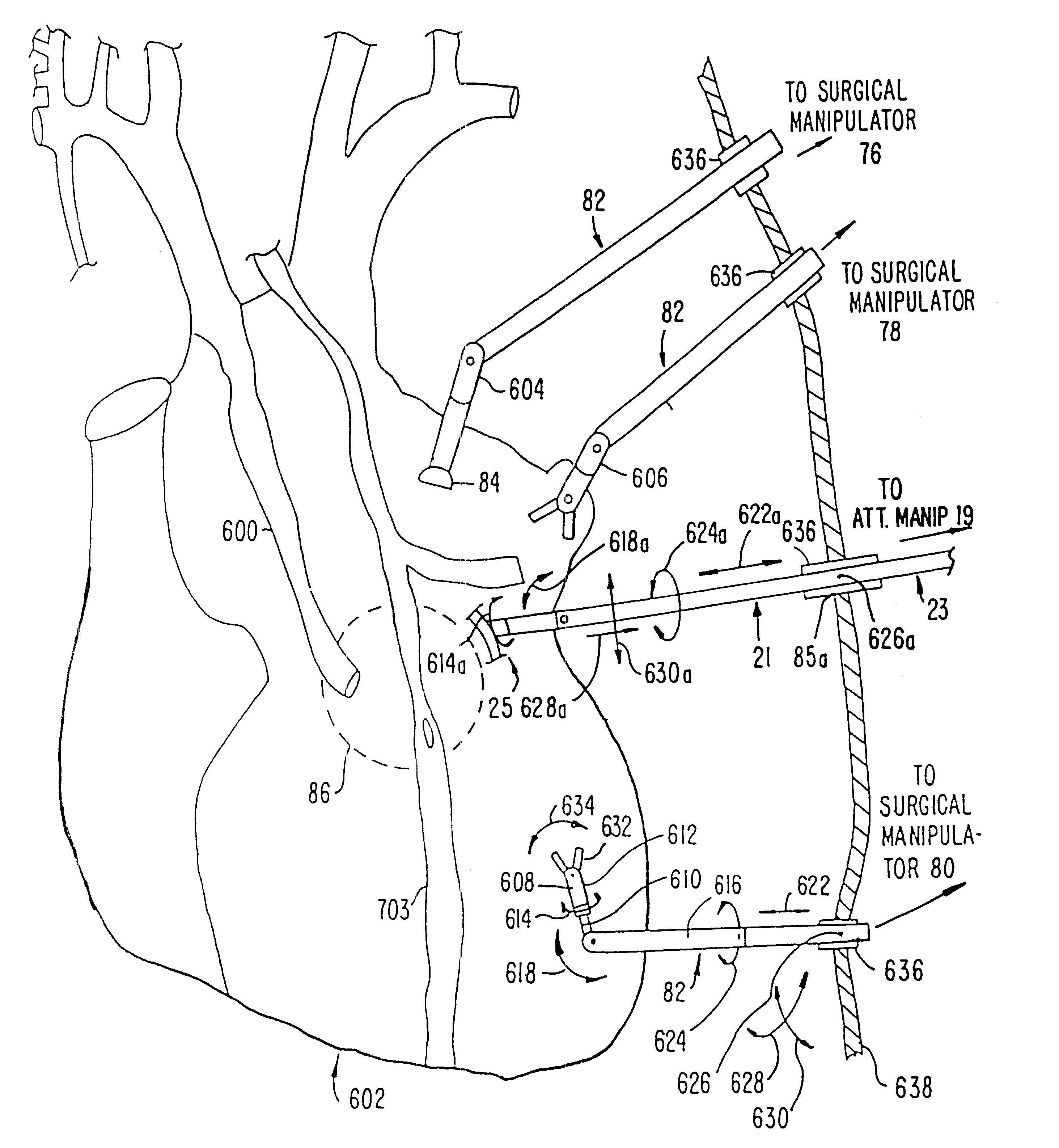
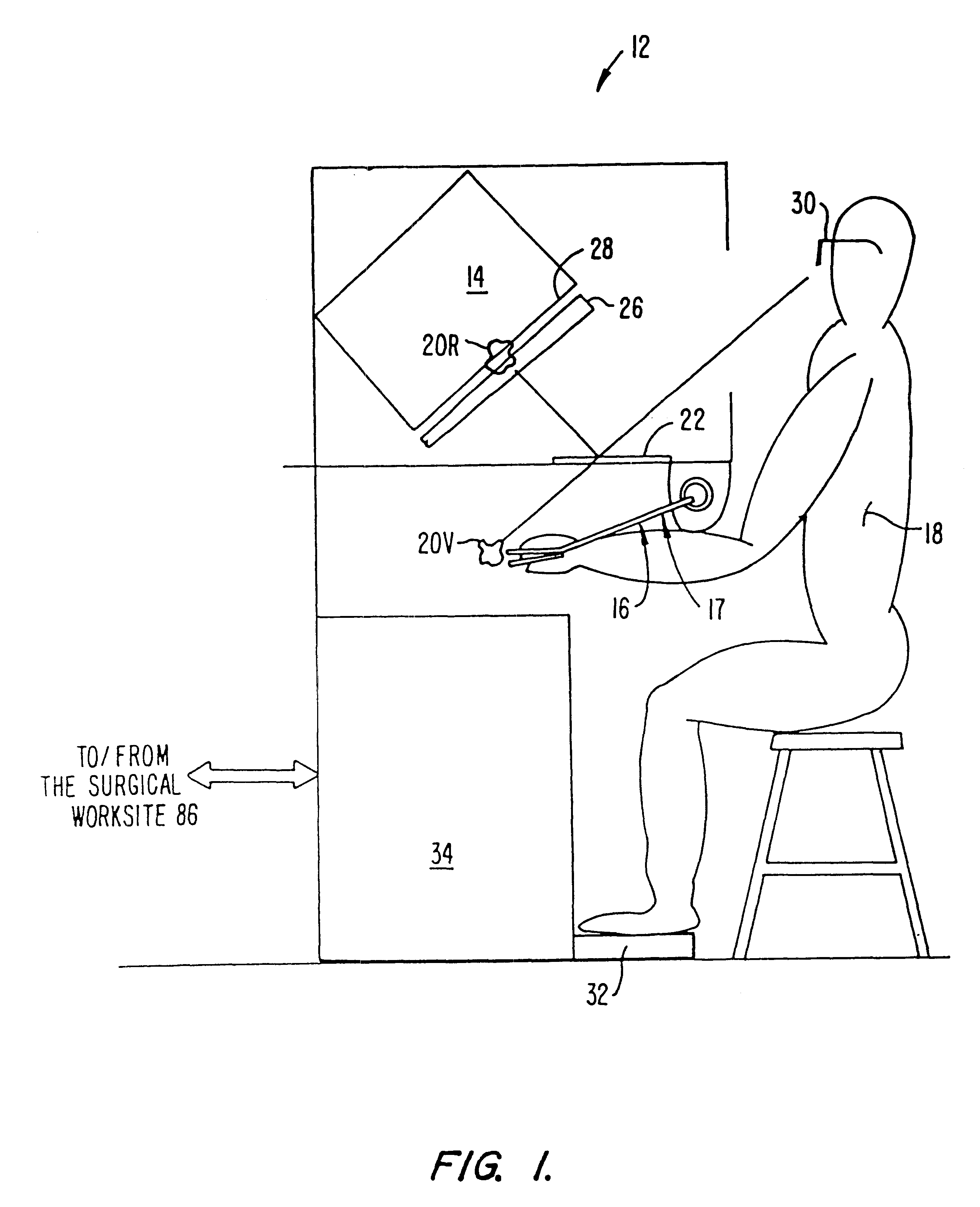
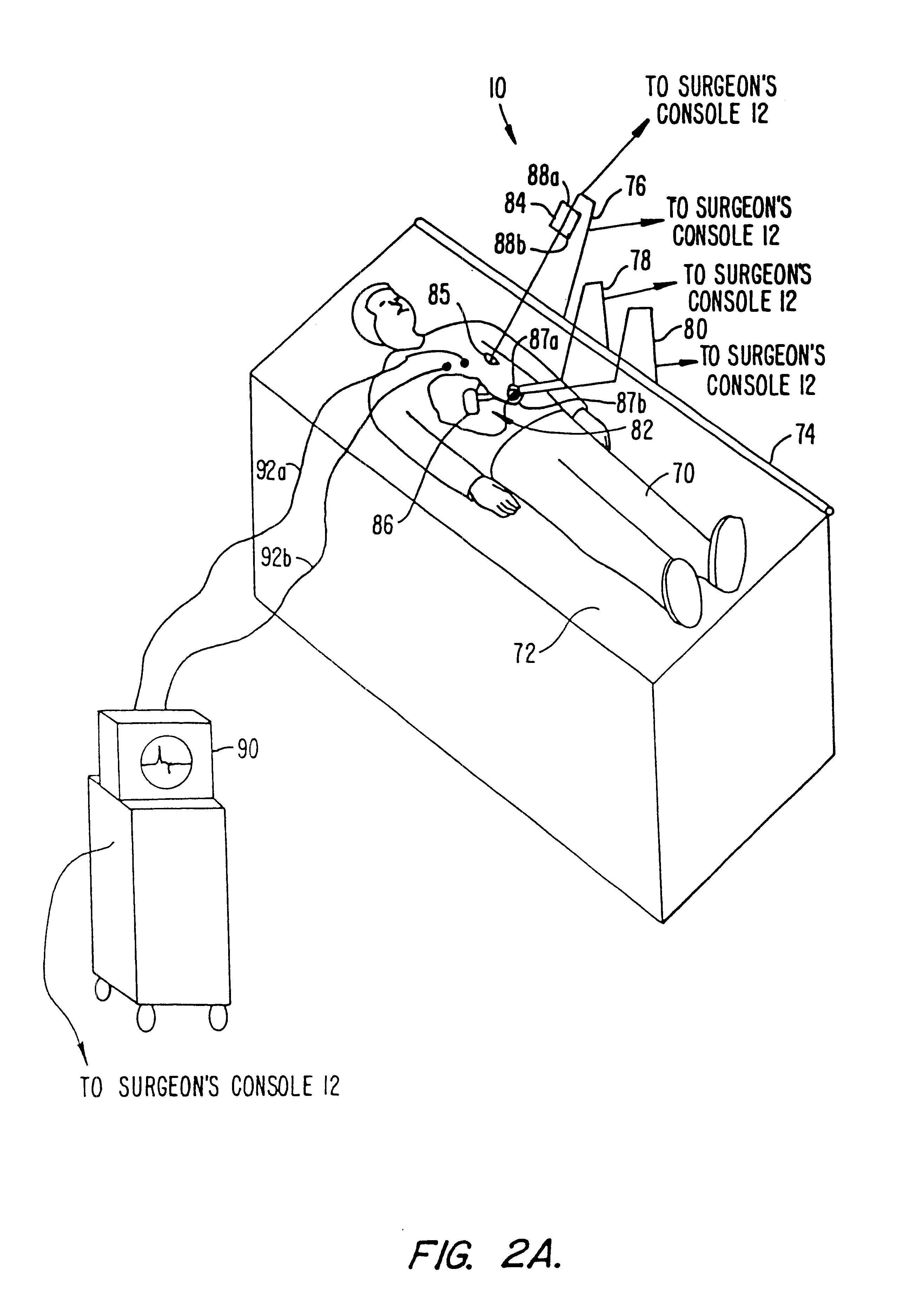
A surgical system or assembly for performing cardiac surgery includes a surgical instrument; a servo-mechanical system engaged to the surgical instrument for operating the surgical instrument; and an attachment assembly for removing at least one degree of movement from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. The surgical system or assembly also includes a motion tracking system for gathering movement information on a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. A control computer is engaged to the attachment assembly and to the motion tracking system and to the servo-mechanical system for controlling movement of the attachment assembly and for feeding gathered information to the servo-mechanical system for moving the surgical instrument in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite such that a relative position of the moving surgical instrument with respect to the resultant surgical cardiac worksite is generally constant. A video monitor is coupled to the control computer; and an input system is coupled to the servo-mechanical system and to the control computer for providing a movement of the surgical instrument. The video monitor displays movement of the surgical instrument while the resultant surgical cardiac worksite appears substantially stationary, and while a relative position of the surgical instrument moving in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite, as a result from the movement information gathered by the motion tracking system, remains generally constant. A method of performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia comprising removing at least one degree of movement freedom from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce at least a partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite while allowing a residual heart section, generally separate from the at least partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite, to move as a residual moving heart part. Cardiac surgery is performed on the at least partially stationary cardiac worksite with a surgical instrument such as needle drivers, forceps, blades and scissors.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Device to permit offpump beating heart coronary bypass surgery
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
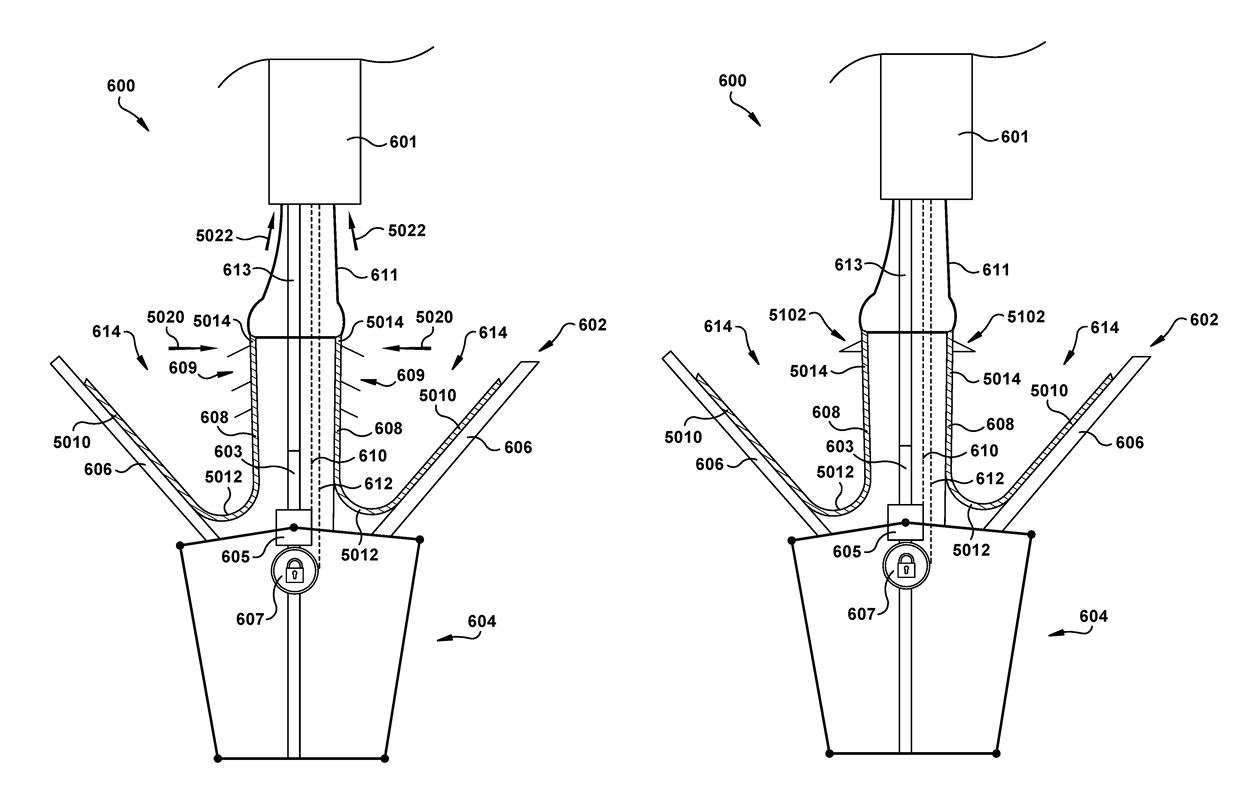
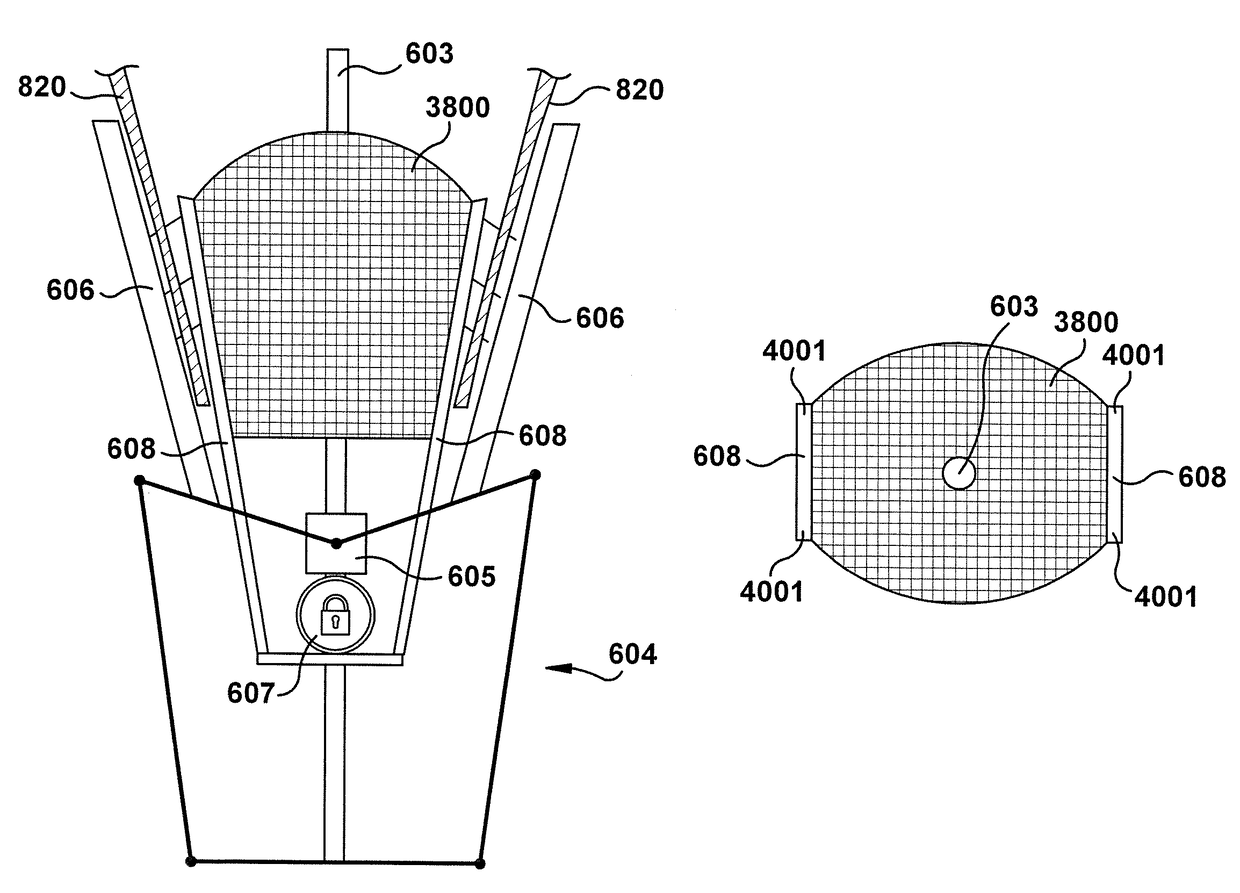
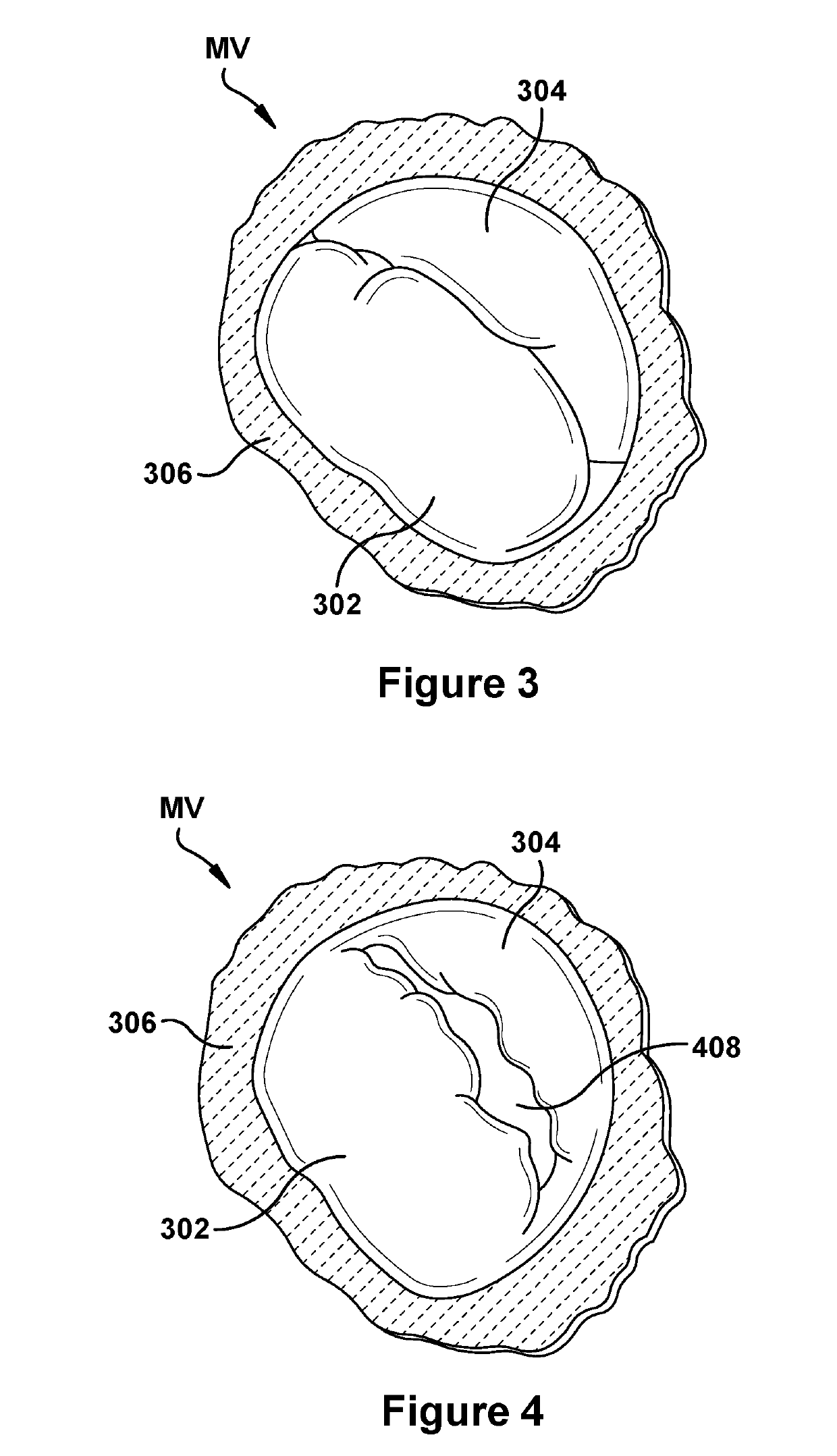
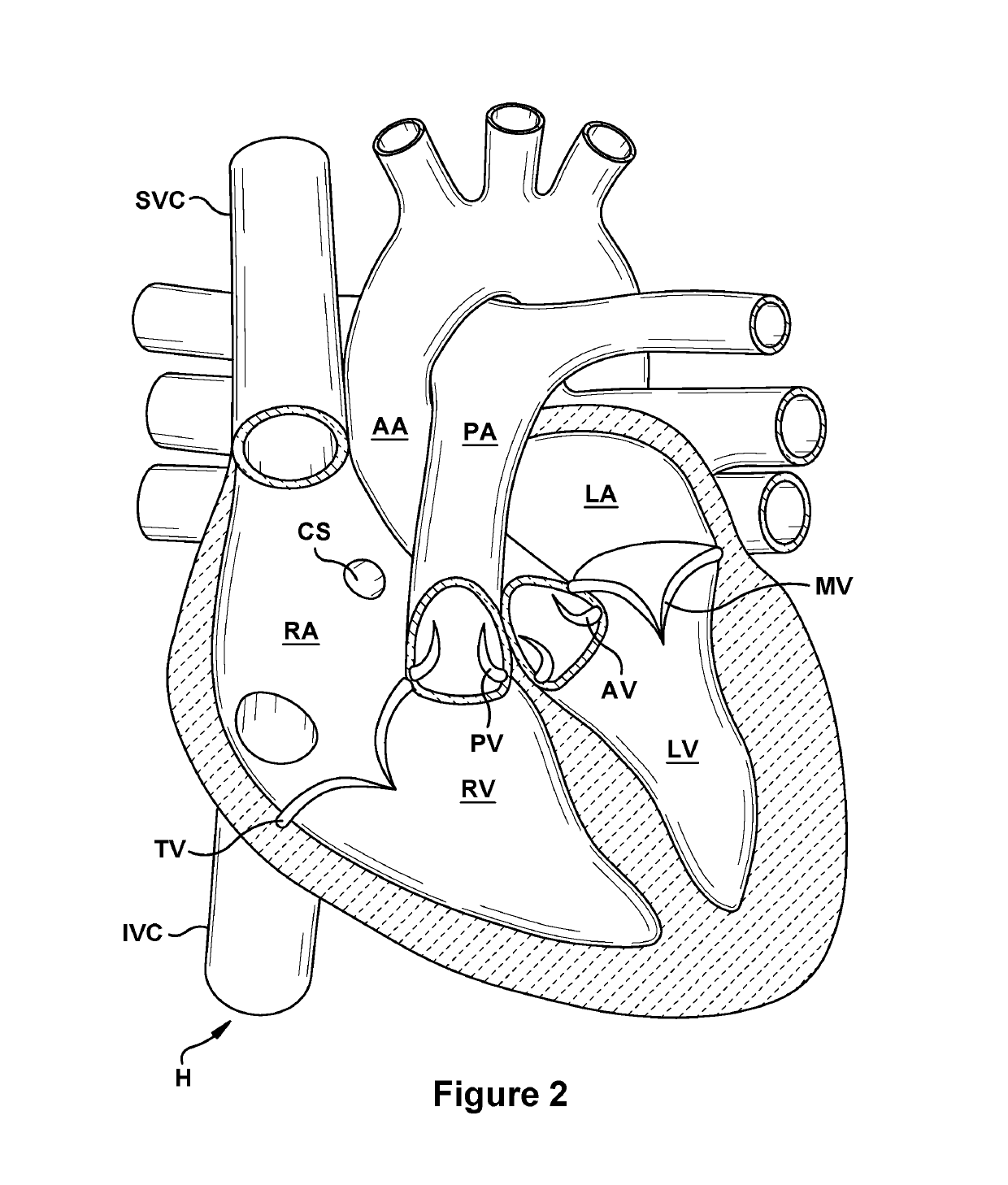
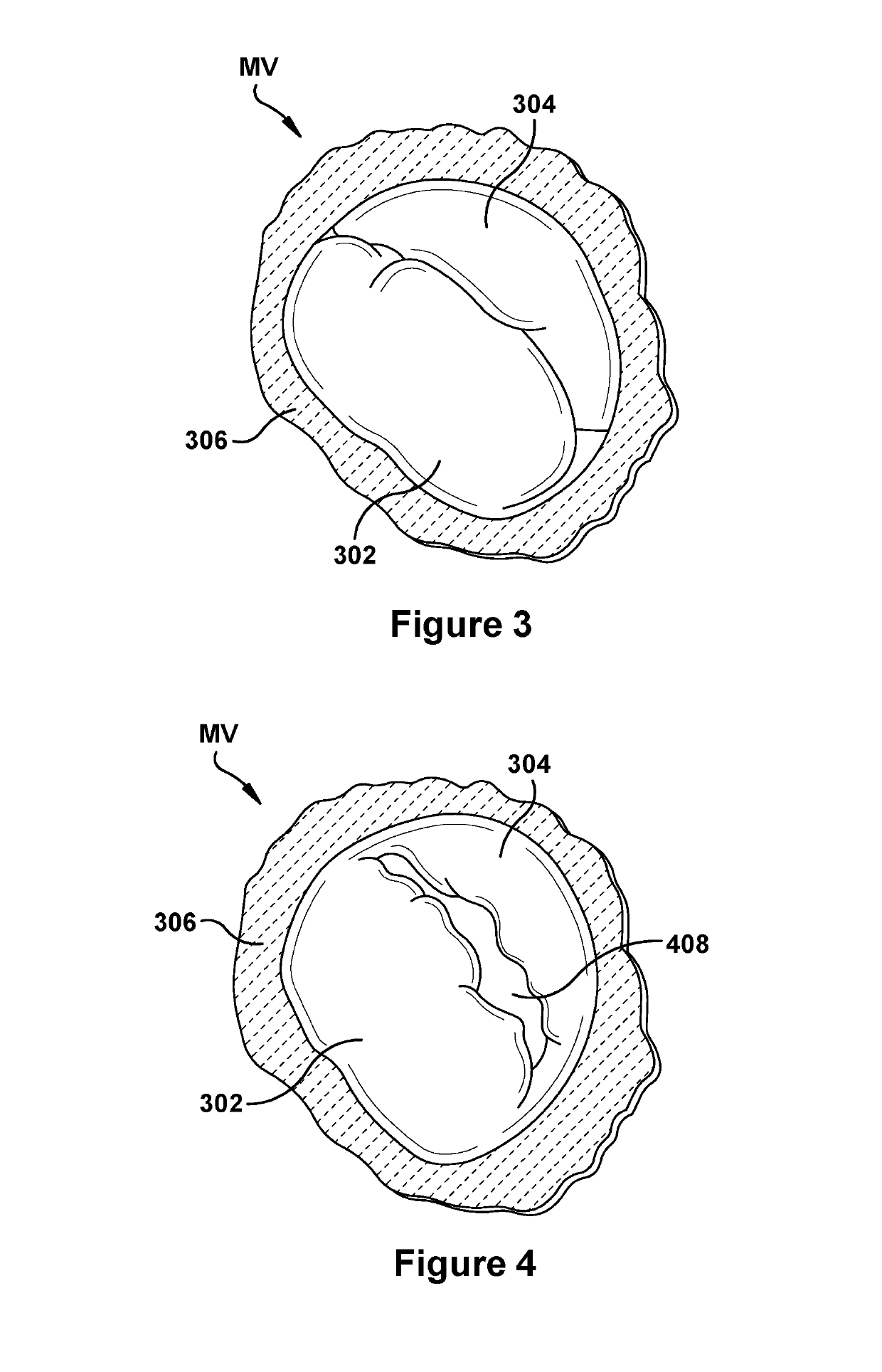
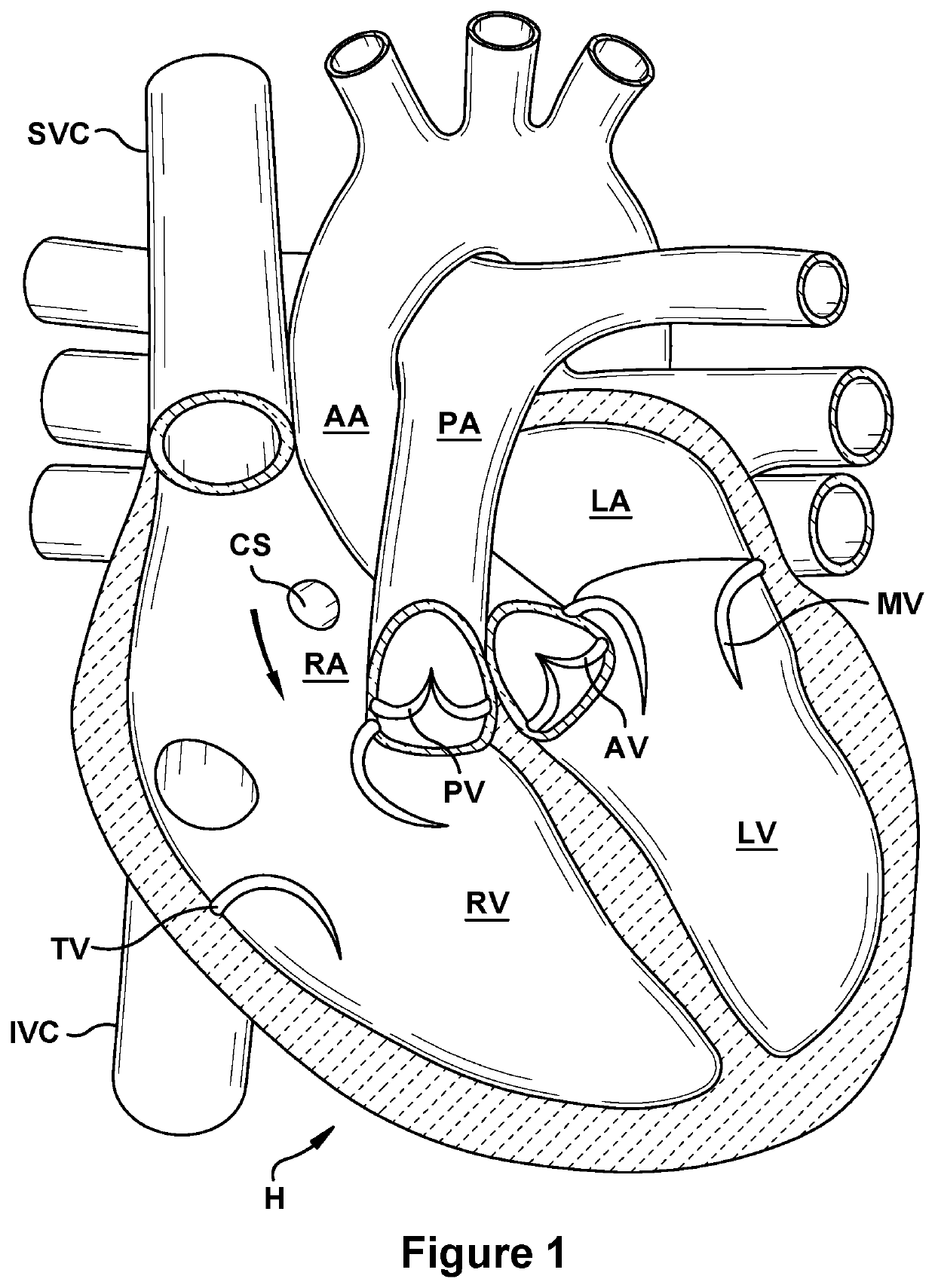
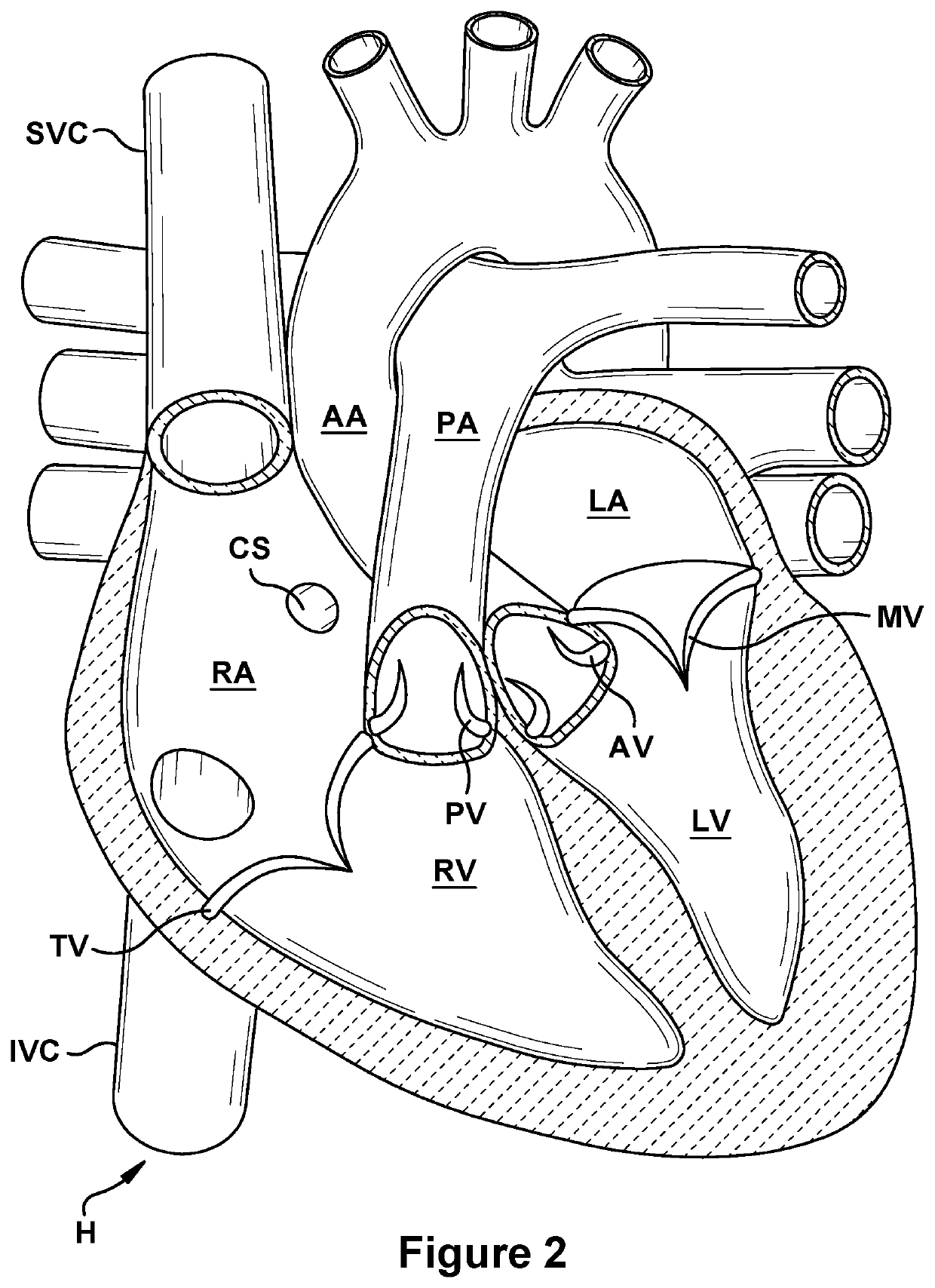
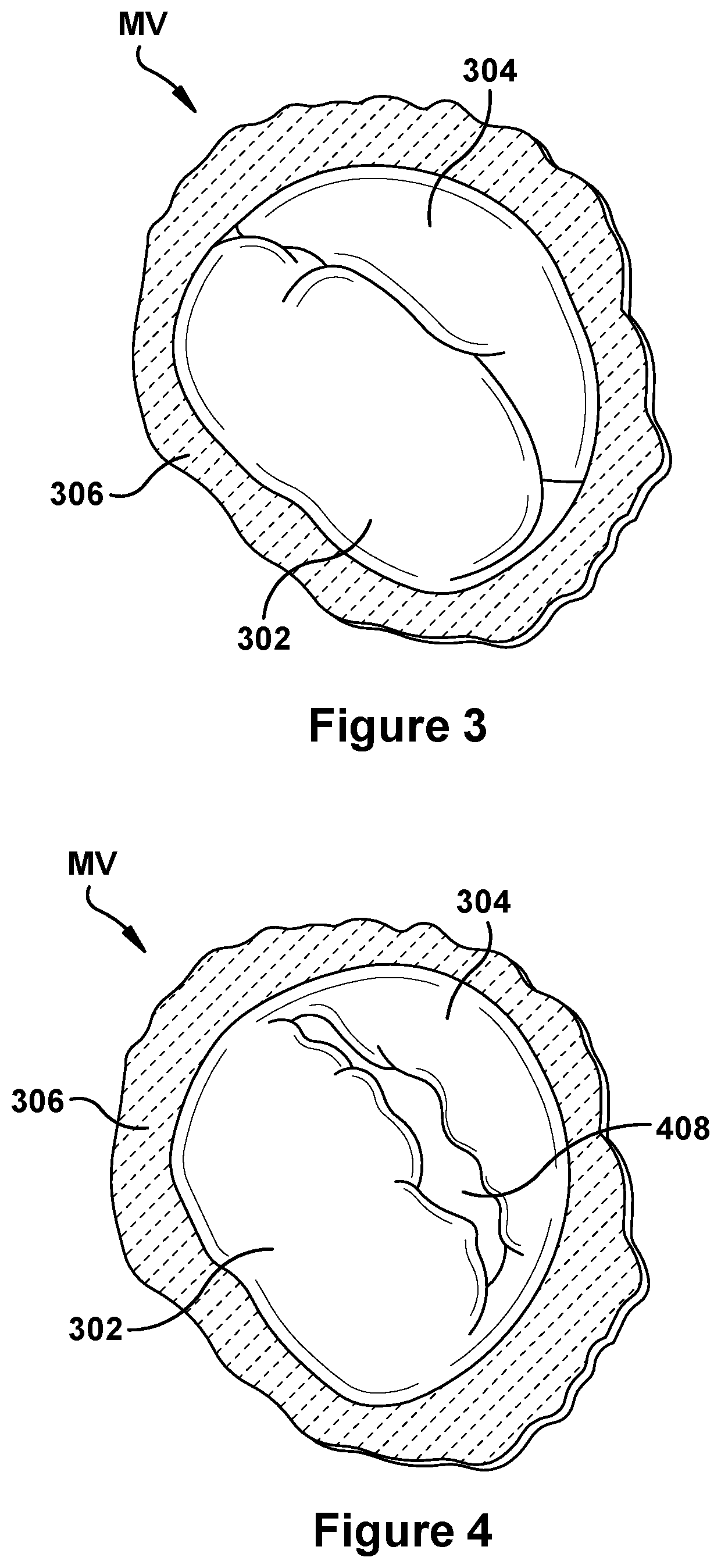
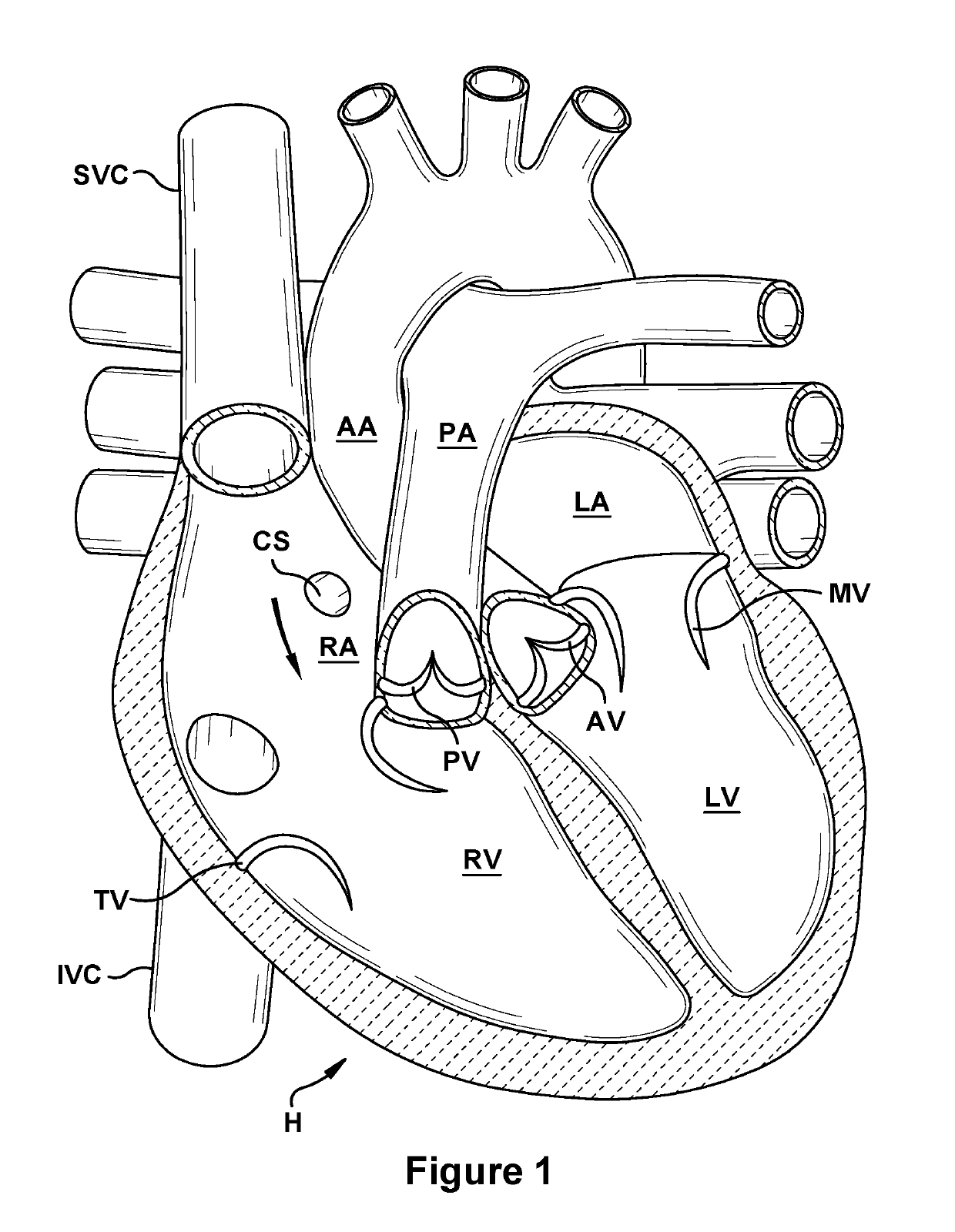
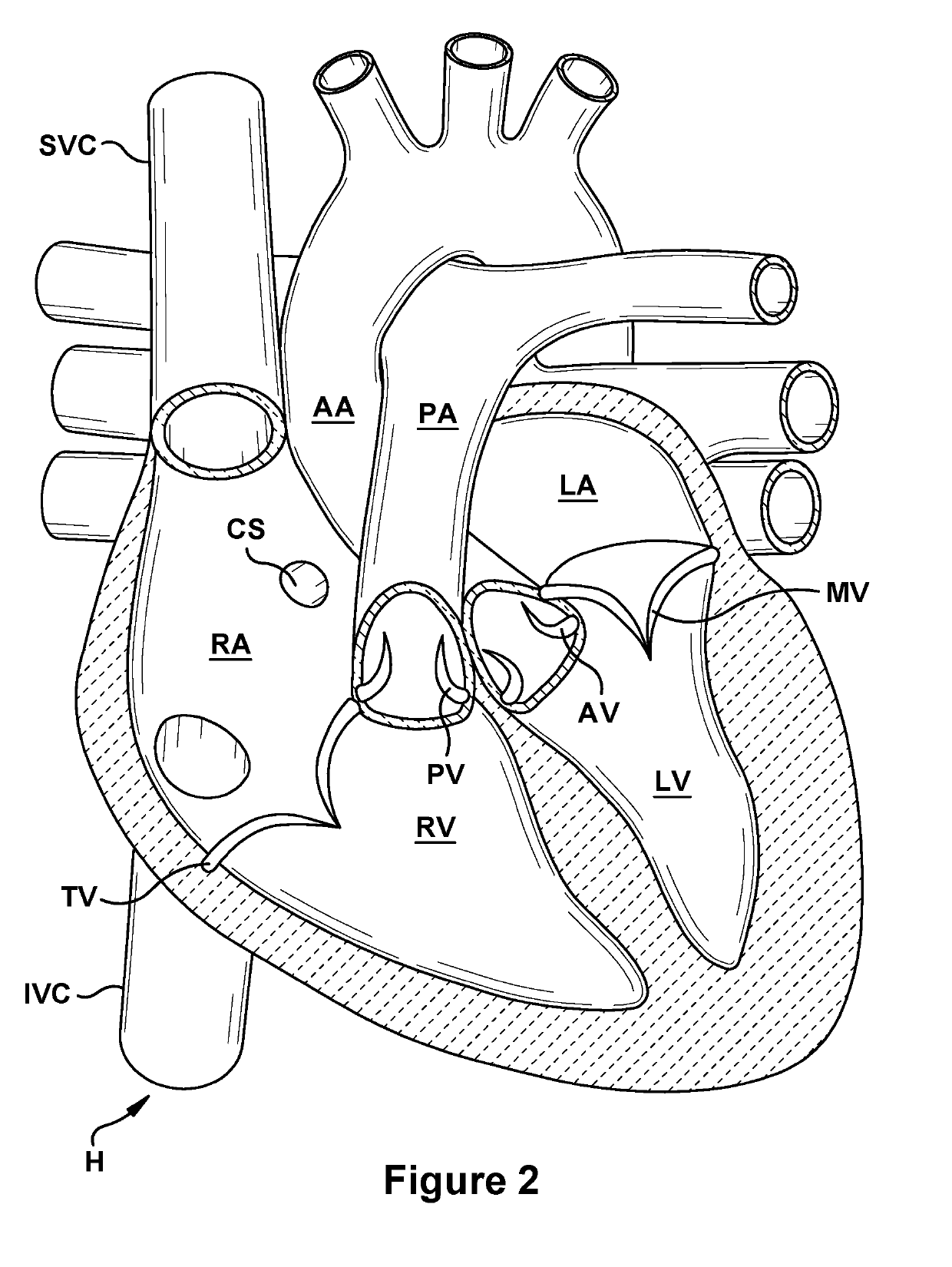
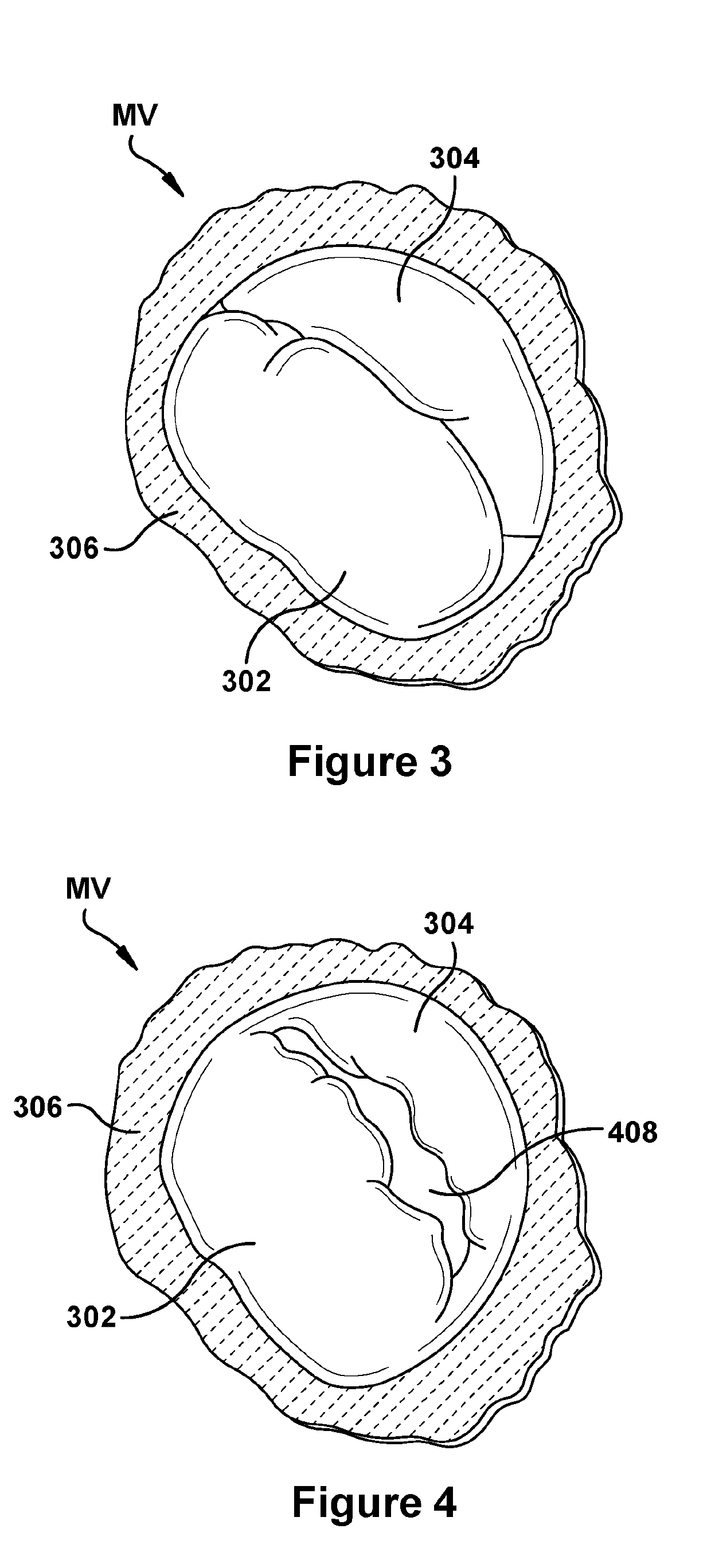
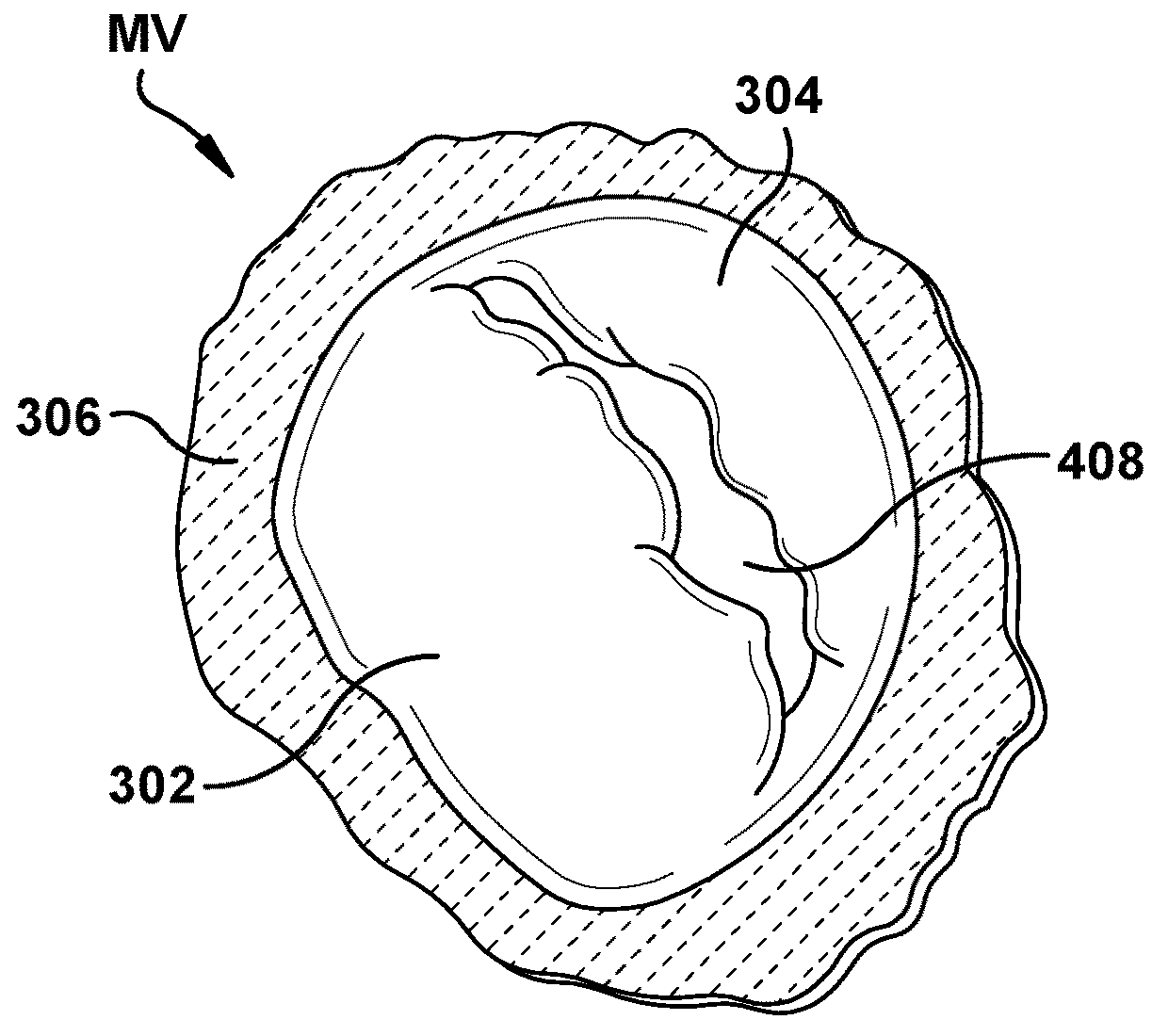
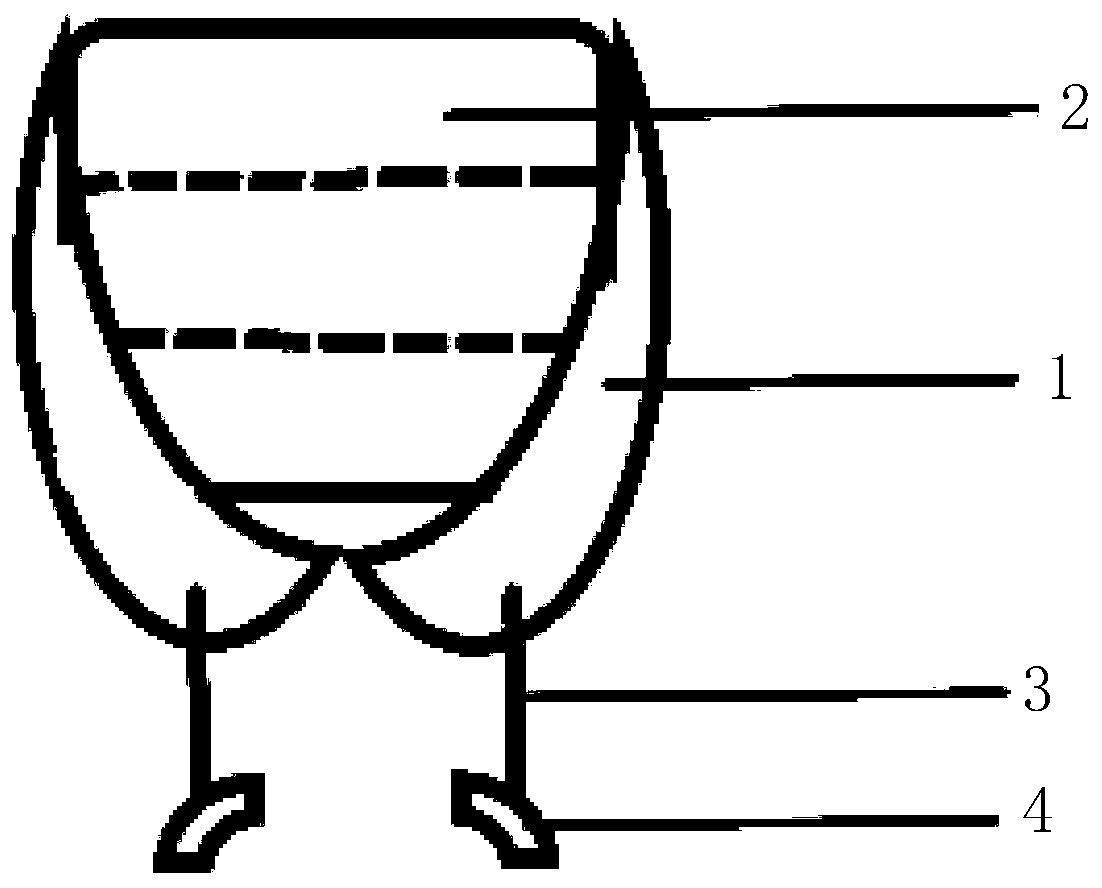
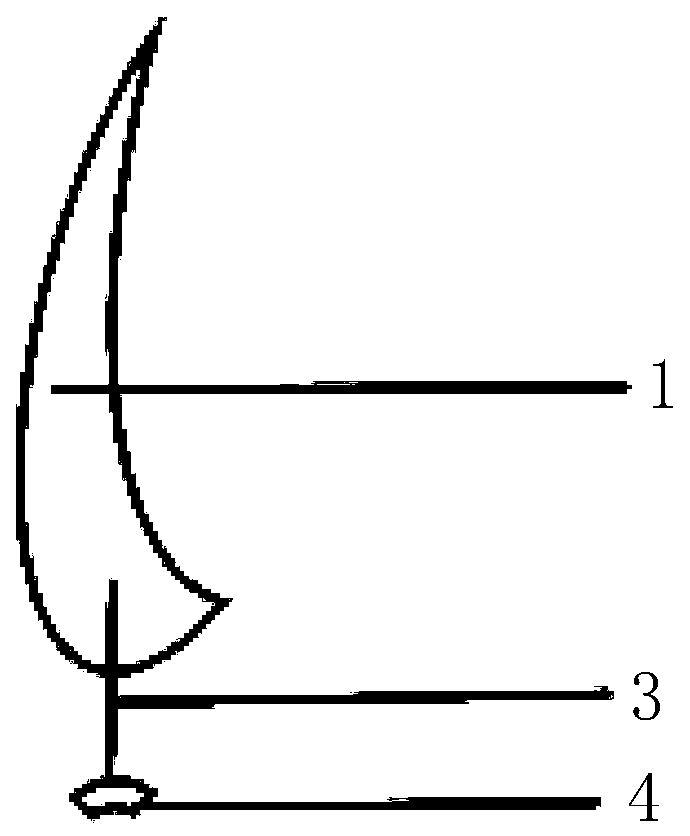
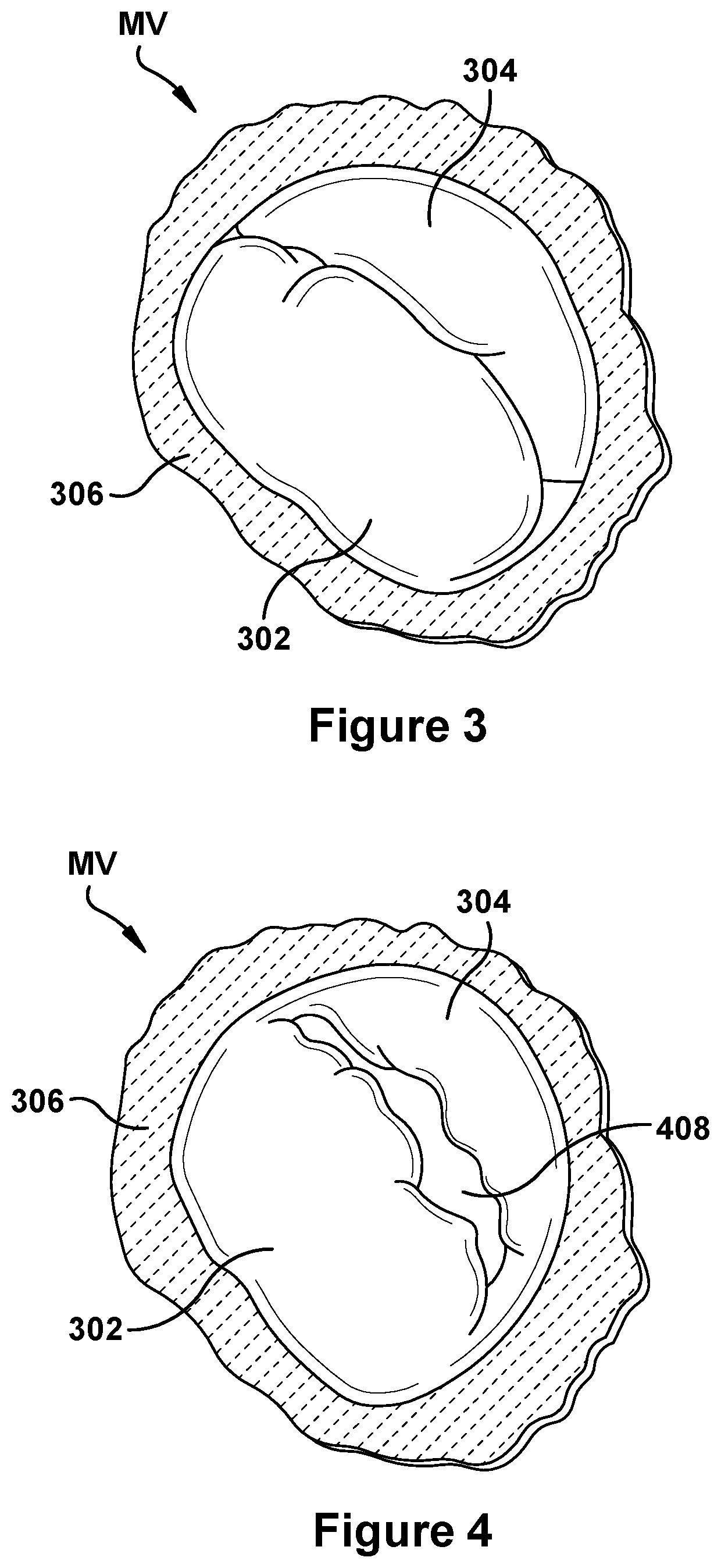
Native valve repair devices and procedures
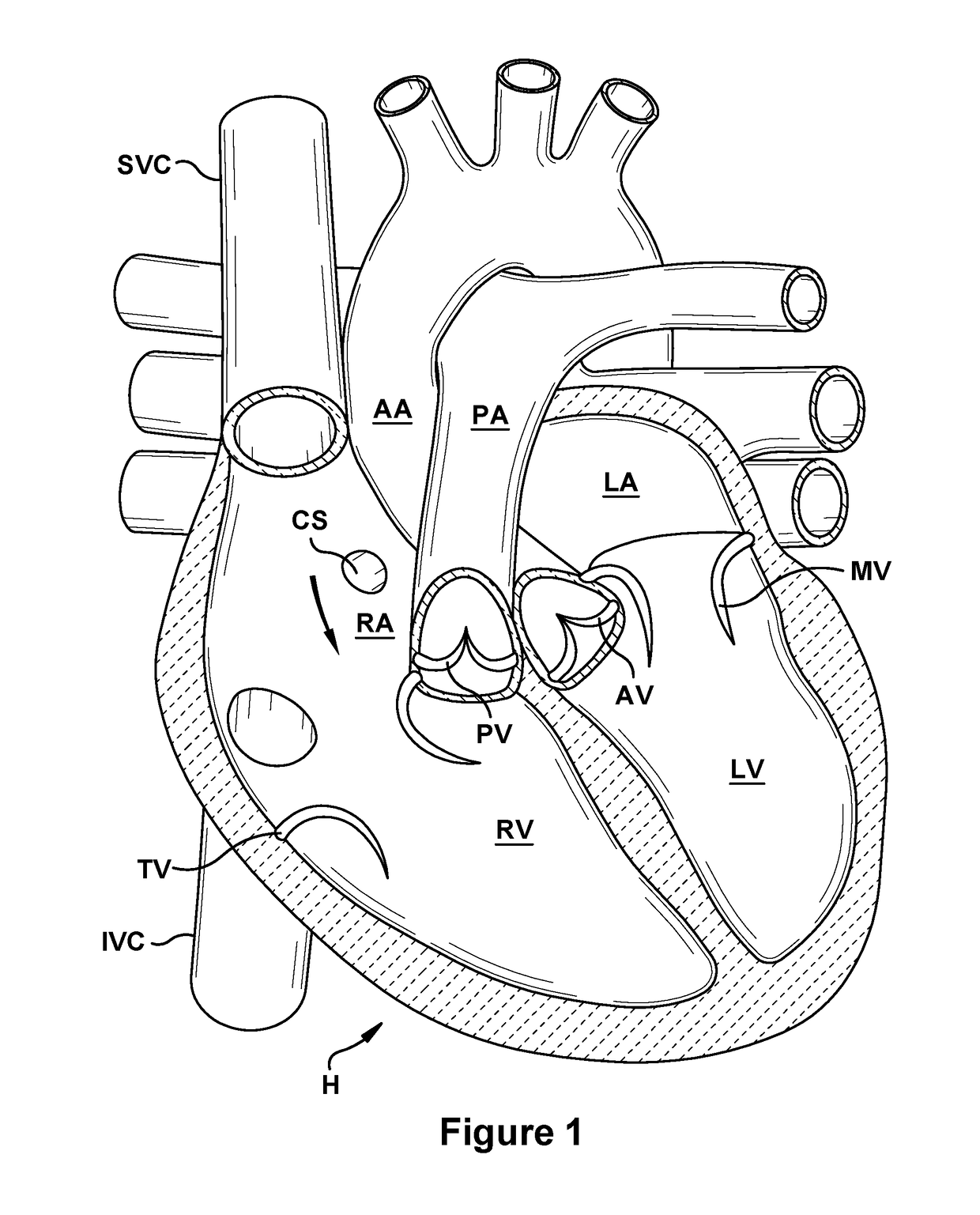
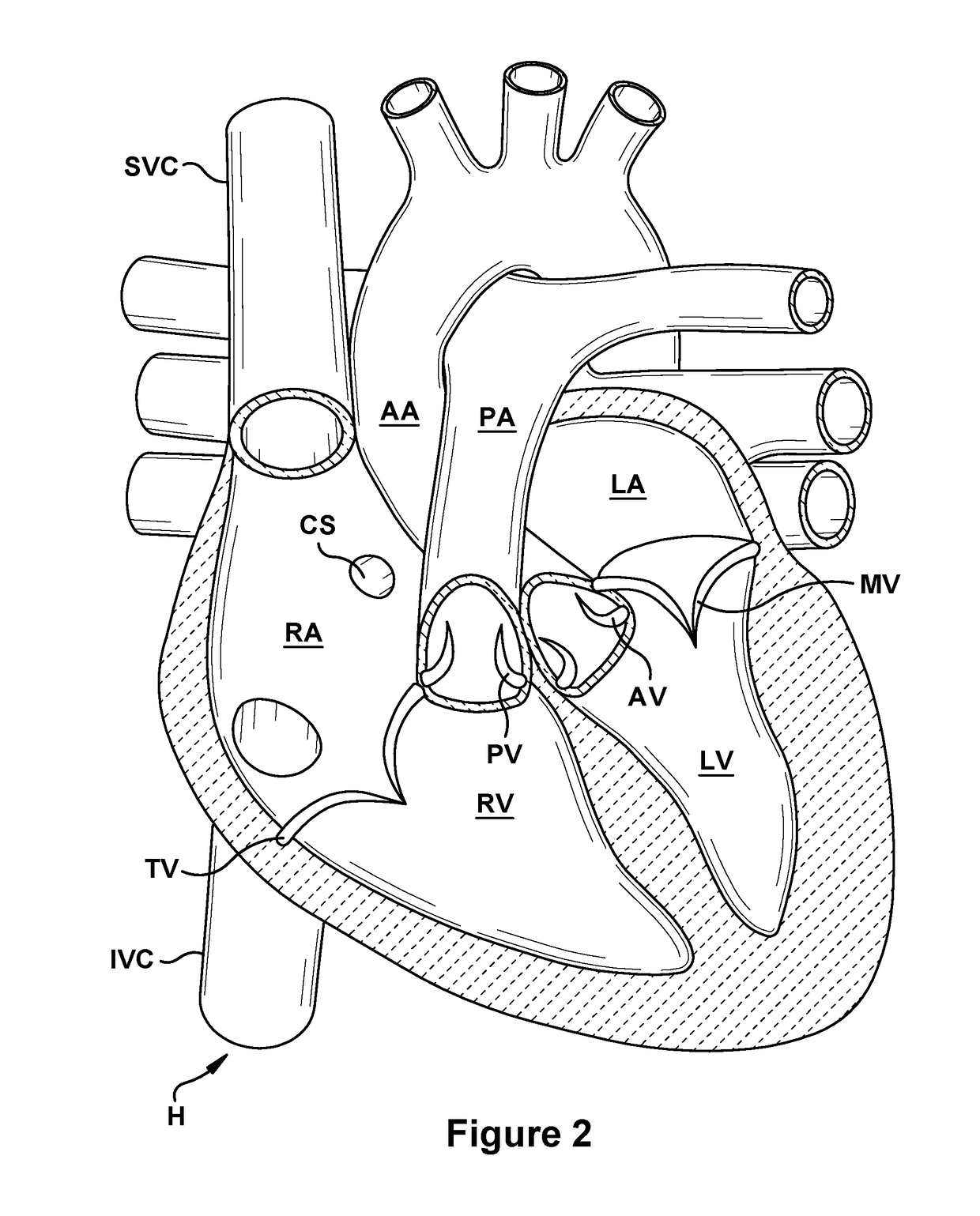
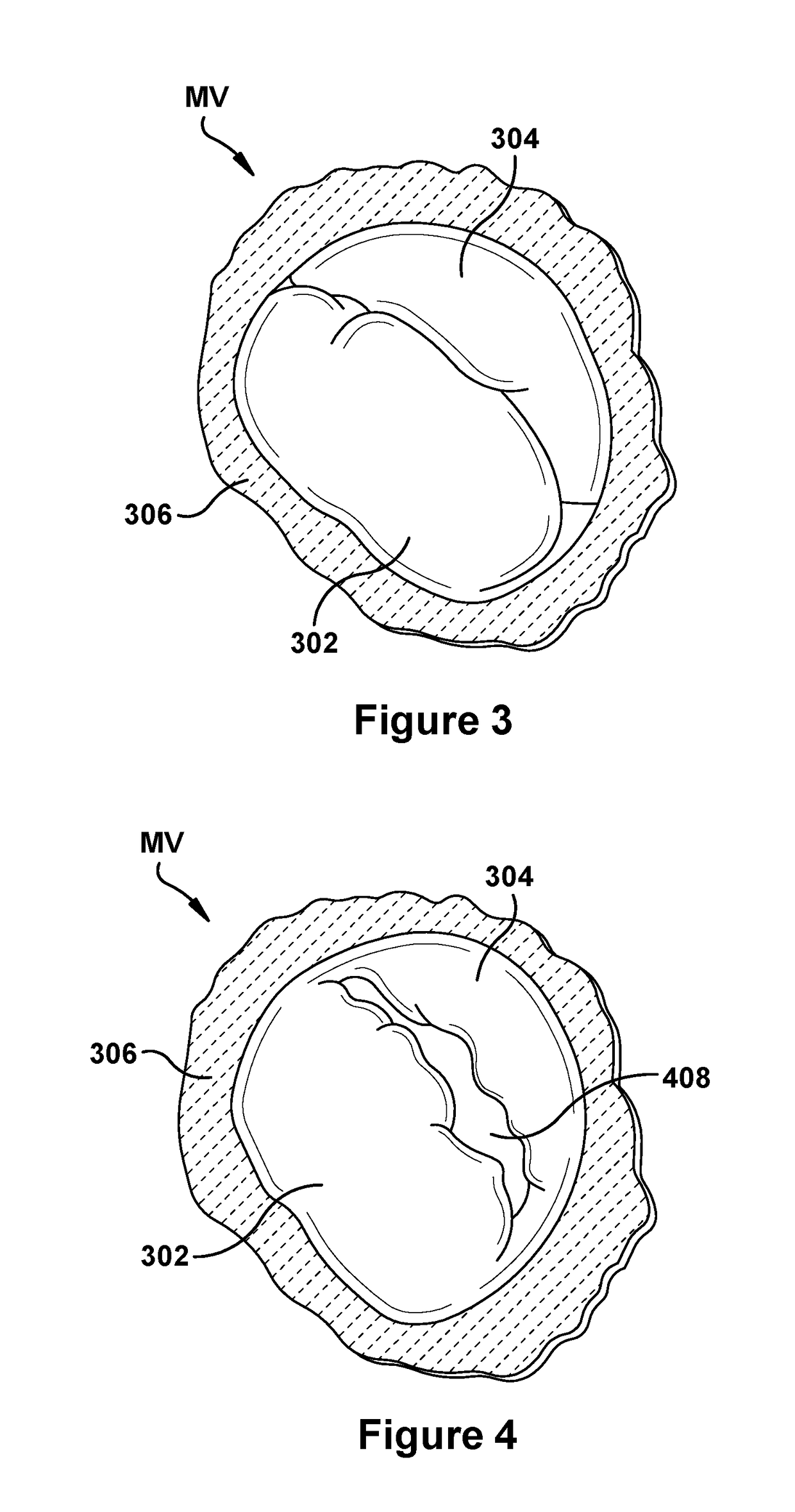
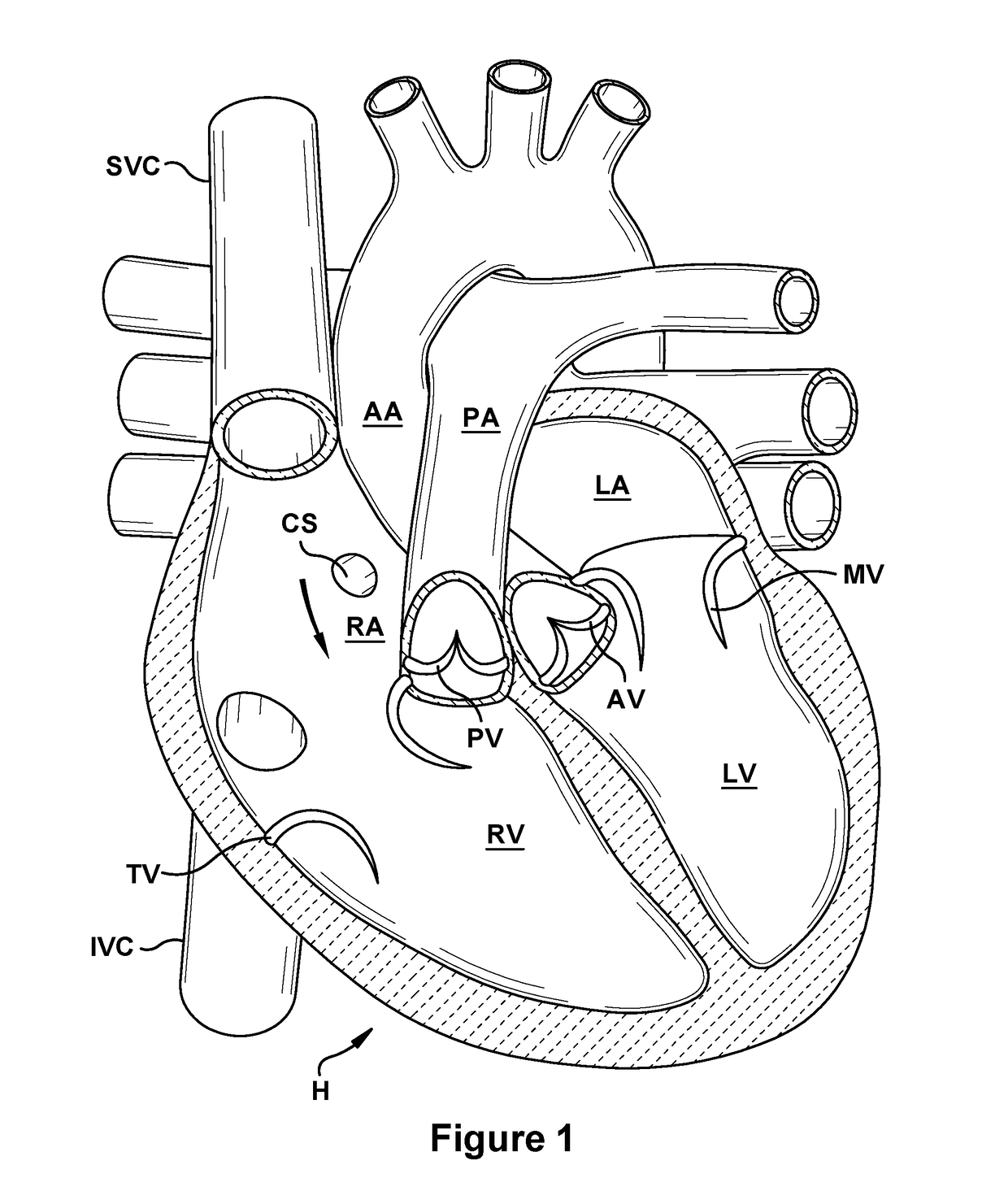
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repair the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a surgical delivery instrument and a valve repair device. The surgical delivery instrument has at least one lumen. The valve repair device is configured to be delivered through the lumen of the surgical delivery instrument and to be attached to a native valve of a patient. The valve repair device includes a pair of paddles and a pair of gripping members. The paddles are movable between an open position and a closed position, and the paddles are configured to flex upon being attached to the native valve of a patient. The paddles and the gripping members are configured to attach to the native valve of the patient.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repairing the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a surgical delivery instrument, a valve repair device, and a gripper control mechanism. The surgical delivery instrument has at least one lumen. The valve repair device is configured to be delivered through the lumen of the surgical delivery instrument and to be attached to a native valve of a patient. The valve repair device has a pair of paddles, and first and second gripping members. The paddles are movable between an open position and a closed position. The paddles and the first and second gripping members are configured to attach to the native valve of the patient. The gripper control mechanisms each include a suture and a wire having a loop at a distal end. The suture extends from the surgical delivery instrument and through the loop of the wire. The suture is removably attached to the gripping member. The loop of the wire is configured to engage the gripping member to move the gripping member between one or more positions.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repairing the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a paddle and a gripping member. The paddle is movable between an open position and a closed position. The gripping member has a weakened portion and a barbed portion. The barbed portion is configured to secure the gripping member to valve tissue of the native valve of the patient. A gripper control mechanism is configured to move the gripping member between an open position and a closed position. The gripper control mechanism comprises a suture removably attached to the gripping member at a first connection point and a pushing member configured to engage the gripping member at a second connection point. The weakened portion is between the first and second connection points. The pushing member is configured to push on the gripping member and the suture is configured to pull on the gripping member to flex the weakened portion and pivot the barbed portion.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repairing the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a pair of paddles and a pair of gripping members. The paddles are moveable between an open position and a closed position. The gripping members can have different configurations for effective attachment and release from the native valve of the patient.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repair the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a base assembly having a plurality of pivoting links, a pair of paddles attached to the base assembly, a pair of gripping members attached to the base assembly, and at least one coaptation or spacer element disposed between the pair of gripping members. Movement of the pivoting links of the base assembly causes the paddles to move between an open position and a closed position. The paddles and the gripping members are configured to attach to valve leaflets of the patient. The coaptation or spacer element is configured to fill at least a portion of a gap between the valve leaflets of the patient.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repairing the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a pair of paddles and a pair of gripping members. The paddles are movable between an open position and a closed position. Each of the gripping members has a barbed portion for securing the gripping members to the native valve of a patient. Each gripping member is slidably attached to a corresponding paddle. Each gripping member can be moved in a first direction along the paddle before the barbed portion of the gripping member pierces the native valve of the patient. Each gripping member can be moved in a direction substantially opposite the first direction after the barbed portion pierces the native valve of the patient such that the gripping members create a tensioning force on the native valve of the patient.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repair the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a surgical delivery instrument, a valve repair device, and a paddle control mechanism. The surgical delivery instrument has at least one lumen. The valve repair device is configured to be delivered through the lumen of the surgical delivery instrument and to attach to a native valve of a patient. The valve repair device includes a first paddle, a second paddle, and a pair of gripping members. The first and second paddles are movable between an open position and a closed position. The paddles and the gripping members are configured to attach to the native valve of the patient. The paddle control mechanism is configured to move the first and second paddles independently of each other.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repair the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a pair of paddles and a pair of gripping members. The paddles are movable between an open position and a closed position. The paddles and the gripping members are configured to attach to the native valve of the patient. The paddles are biased to the closed position, latched to the gripping members in the closed position, maintained in the closed position by a threaded connection, or otherwise maintained in the closed position.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repairing the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a surgical delivery instrument, a valve repair device, and a gripper control mechanism. The surgical delivery instrument has at least one lumen. The valve repair device is configured to be delivered through the lumen of the surgical delivery instrument and to be attached to a native valve of a patient. The valve repair device includes a pair of paddles, and at least four gripping members. The paddles are movable between an open position and a closed position, and the paddles and the at least four gripping members are configured to attach to the native valve of a patient. The gripper control mechanism is configured to independently move each of the at least four gripping members.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
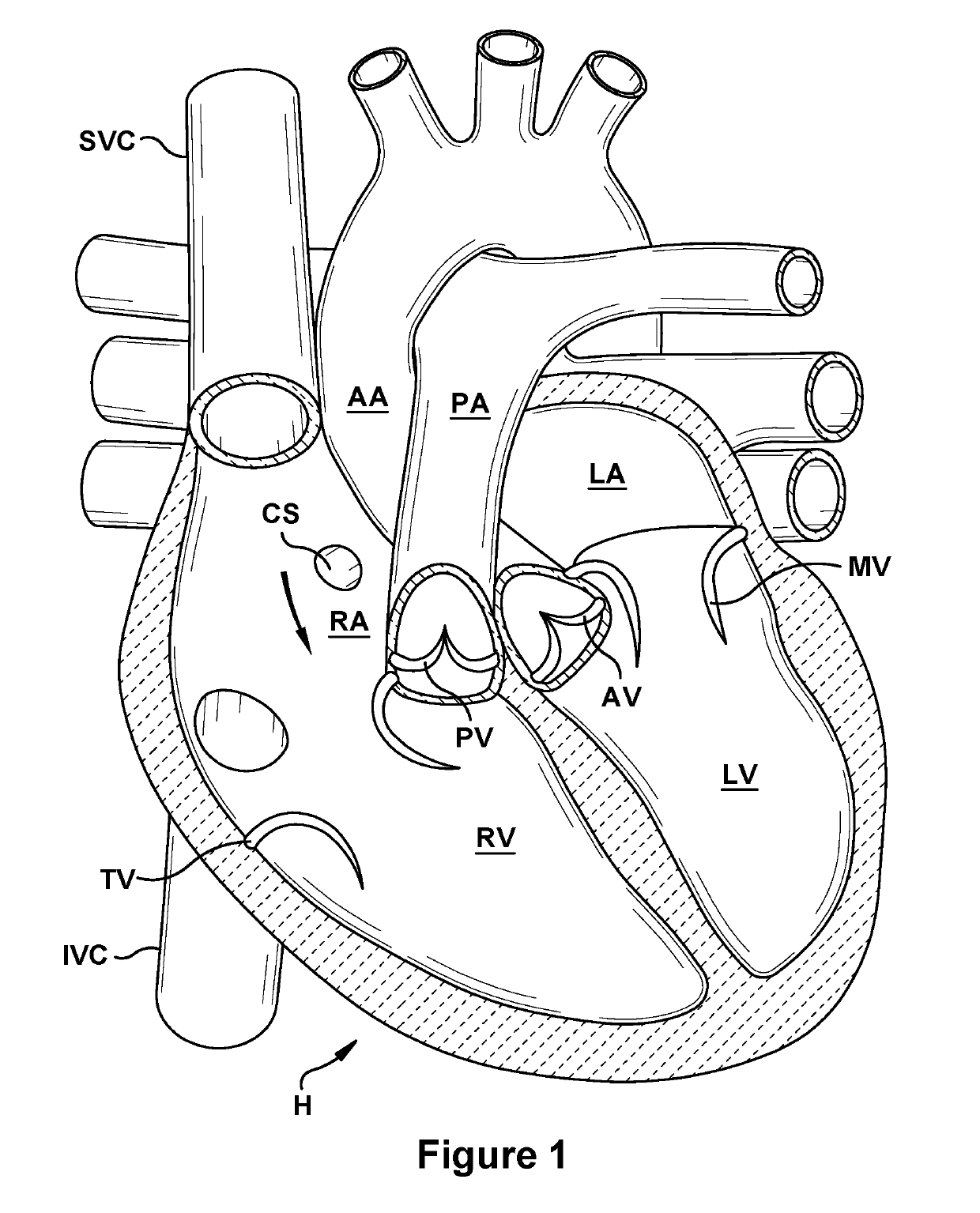
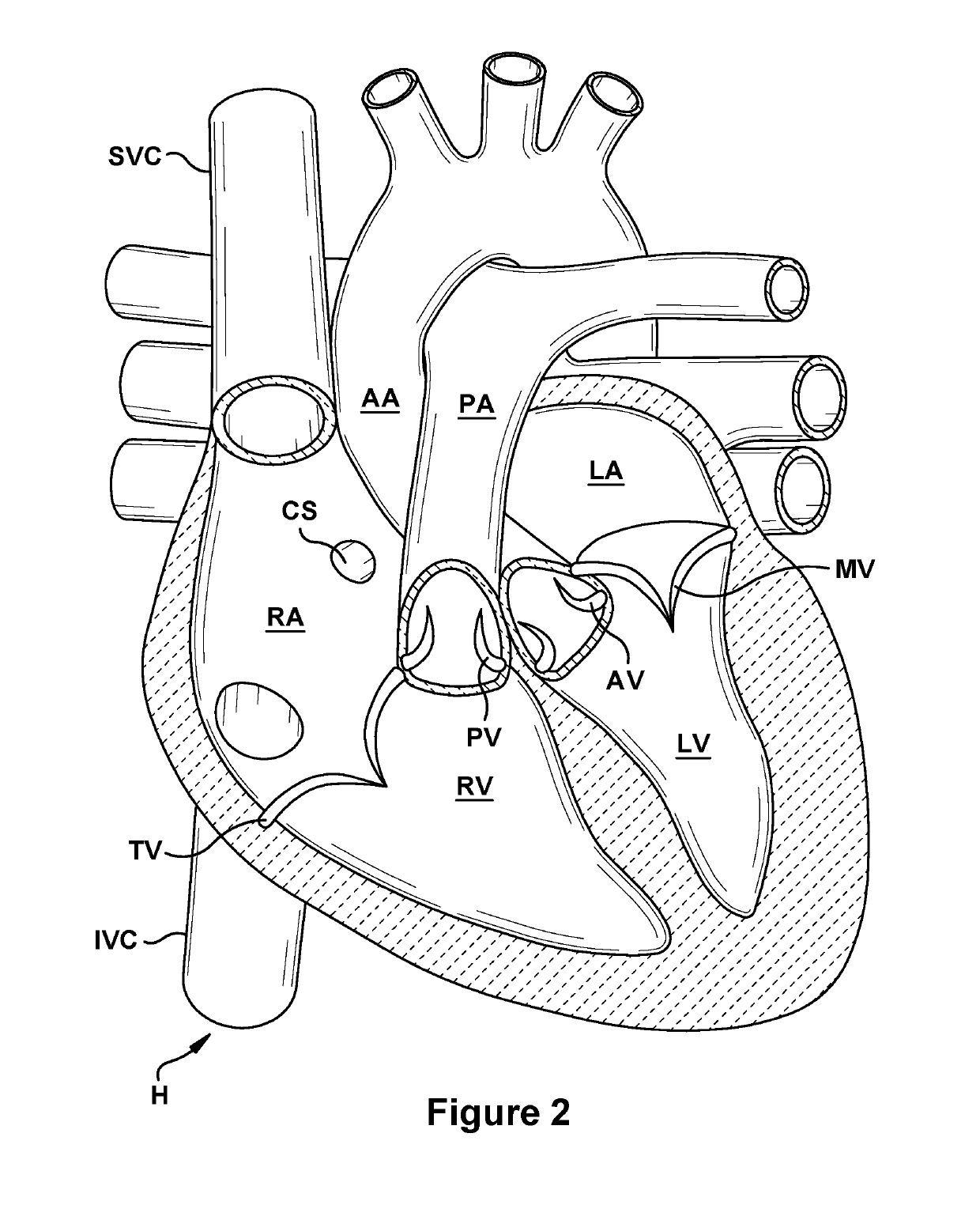
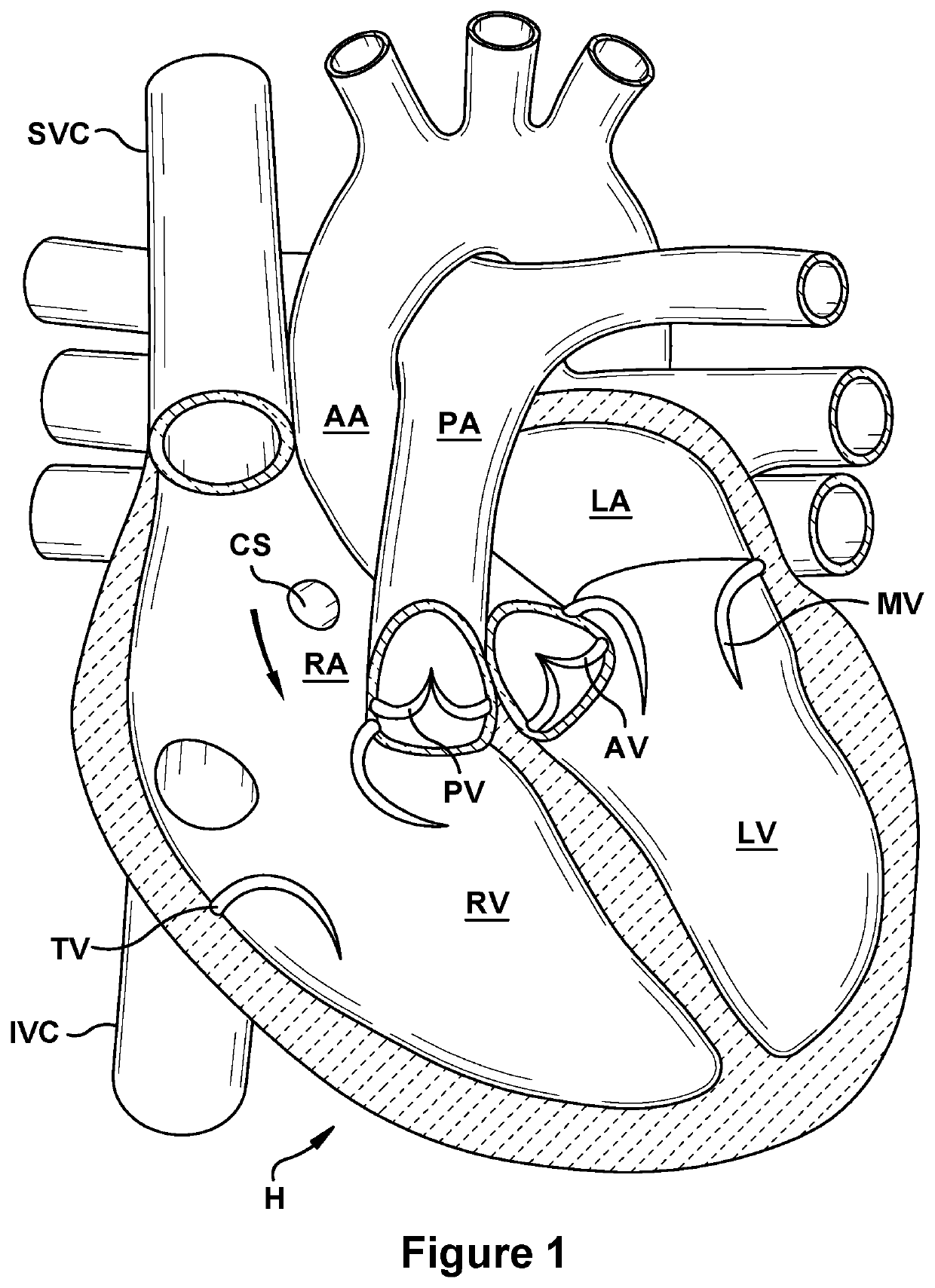
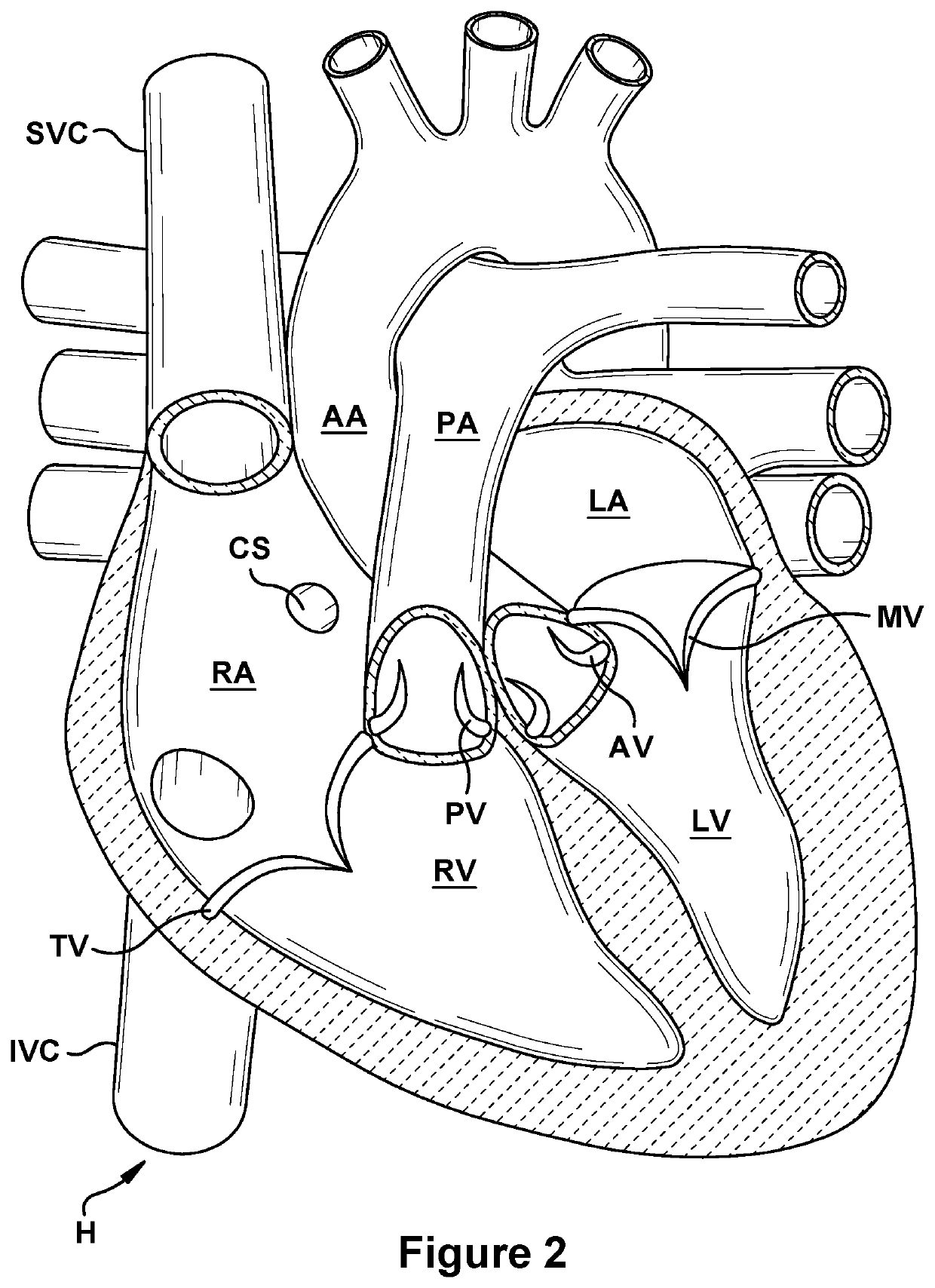
Anatomic device delivery and positioning system and method of use
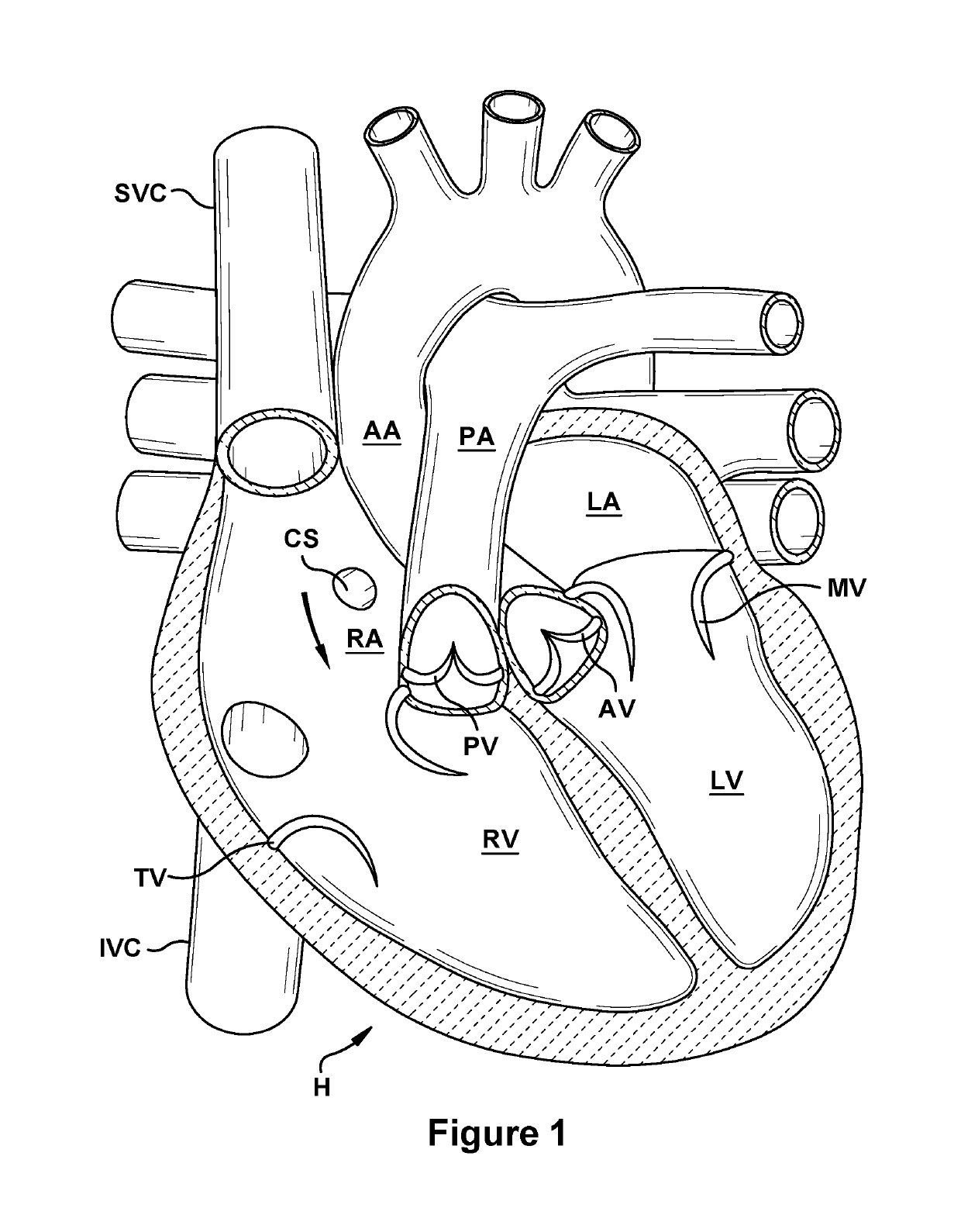
An anatomic device delivery and positioning system has a stabilizing guide wire for placement of a catheter or other medical device or material into a vessel or cavity of a tissue or organ within a body of a living subject into which the guide wire is insertable. The guide wire includes an elongated member having a proximal end and a distal end, the proximal end to extend out of the body and the distal end to extend into the body, the distal end having an expandable portion that expands from a compressed condition when inside of a delivery tube or catheter to an expanded condition when outside of the delivery tube or catheter. A method is also disclosed of performing a percutaneous procedure within a vessel or cavity of a tissue or organ of a subject using the guide wire, particularly but not exclusively involving a heart procedure.
Owner:KIPPERMAN ROBERT
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repair the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a surgical delivery instrument, a valve repair device, and a gripper control mechanism. The surgical delivery instrument has at least one lumen. The valve repair device is configured to be delivered through the lumen of the surgical delivery instrument and to attach to a native valve of a patient. The valve repair device includes a pair of paddles, and a pair of gripping members. The paddles are movable between an open position and a closed position. The paddles and the gripping members are configured to attach to a native valve of the patient. The gripper control mechanism is configured to independently move the first and second gripping members.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
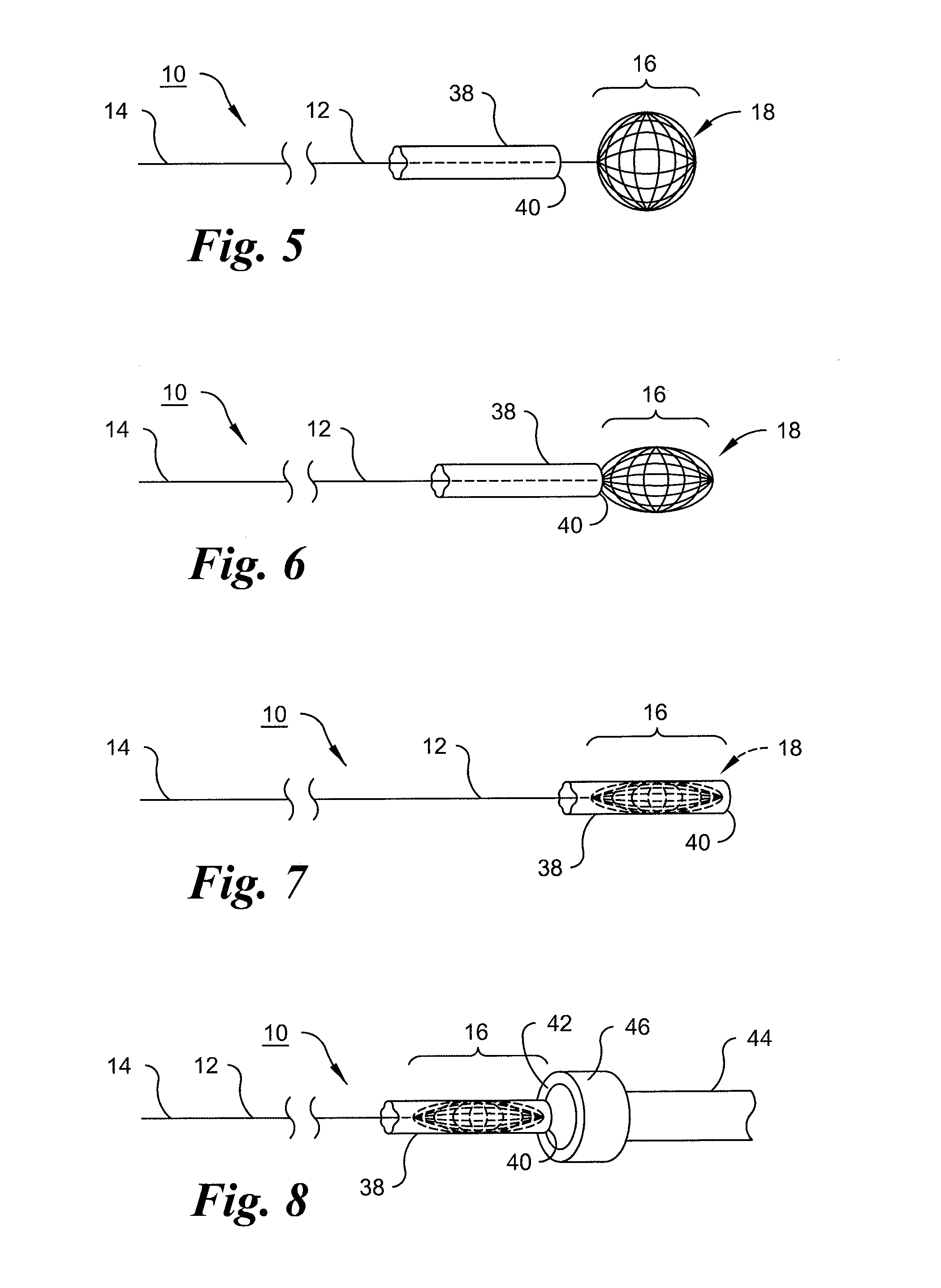
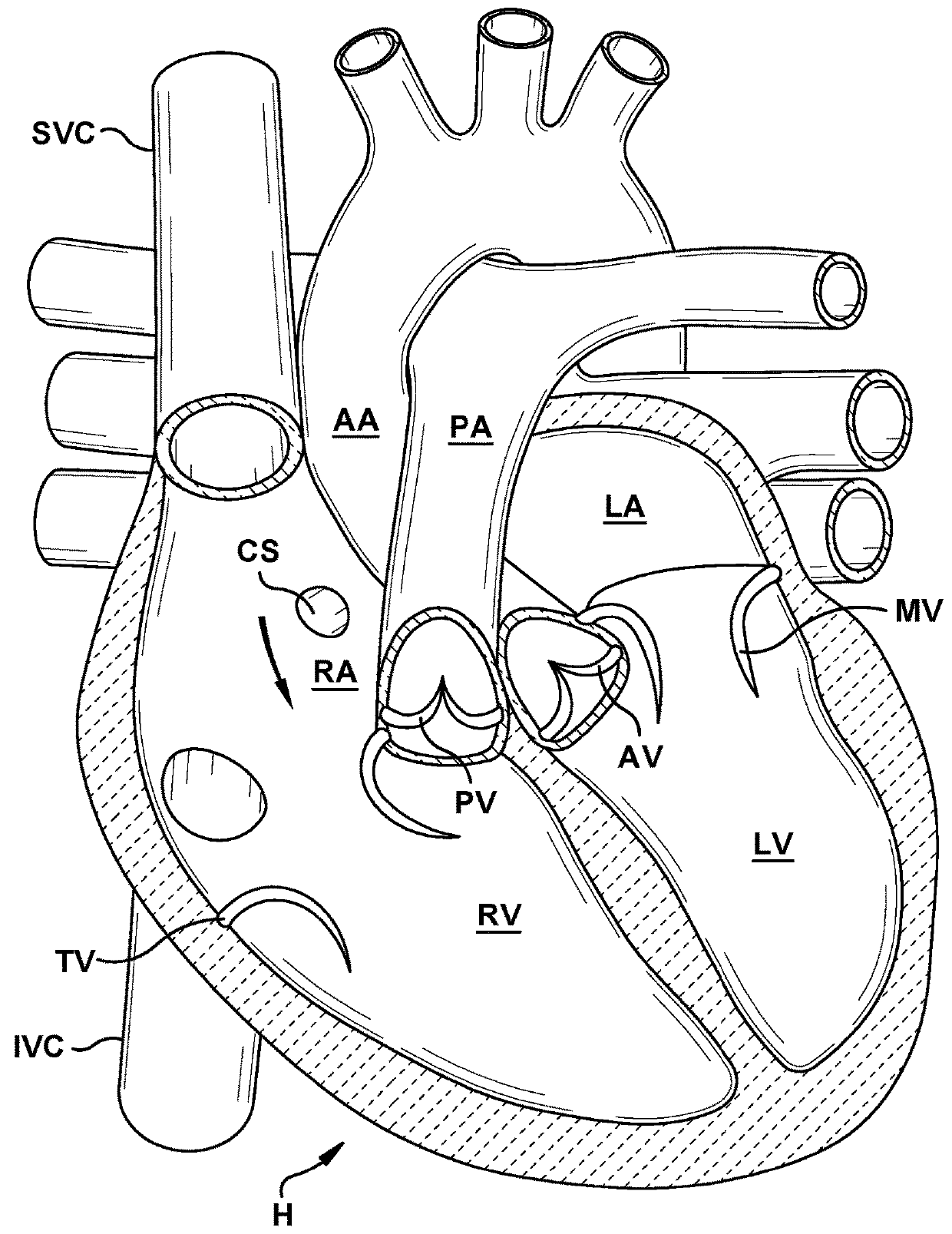
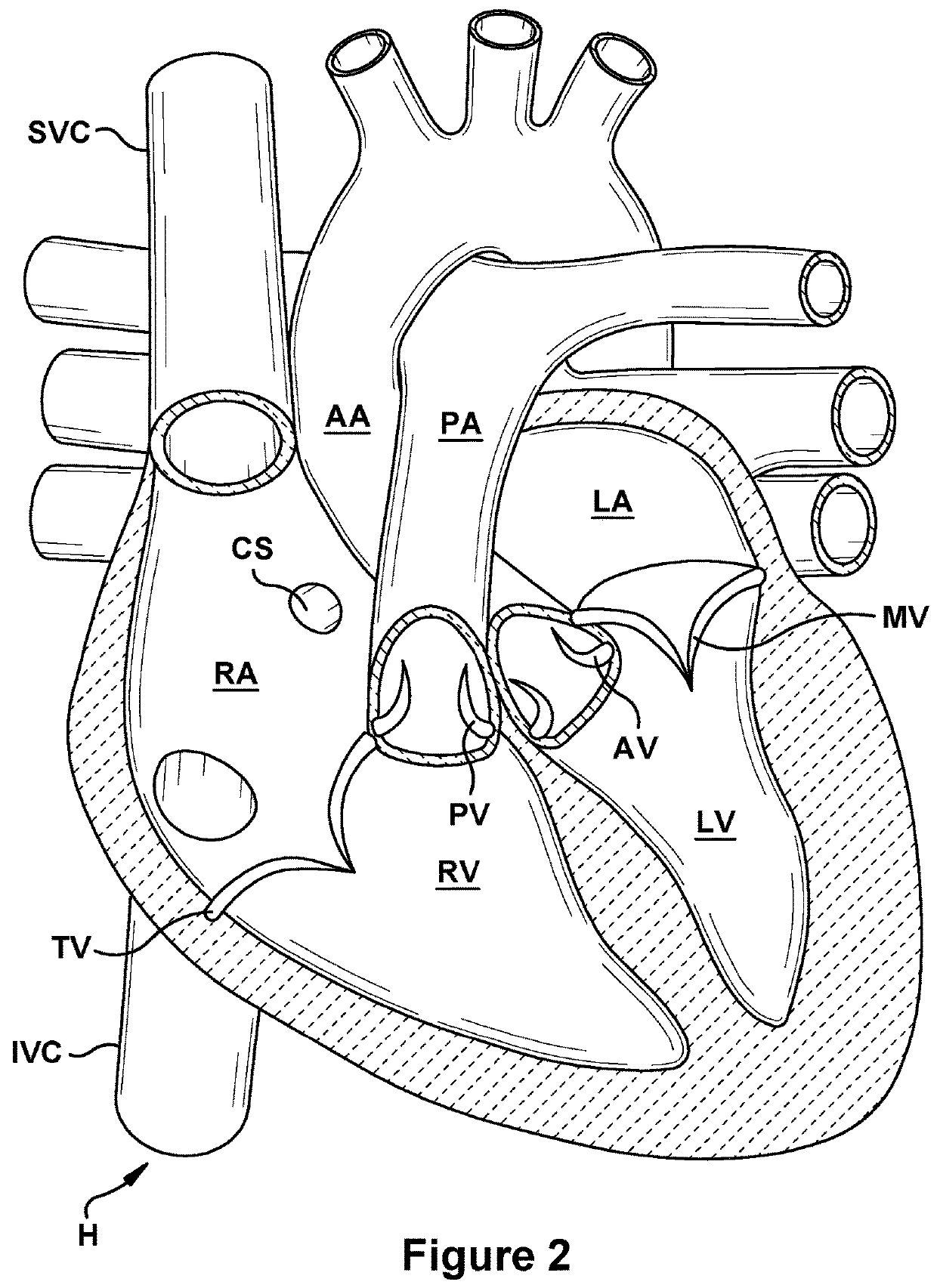
Multichannel catheter with obturator
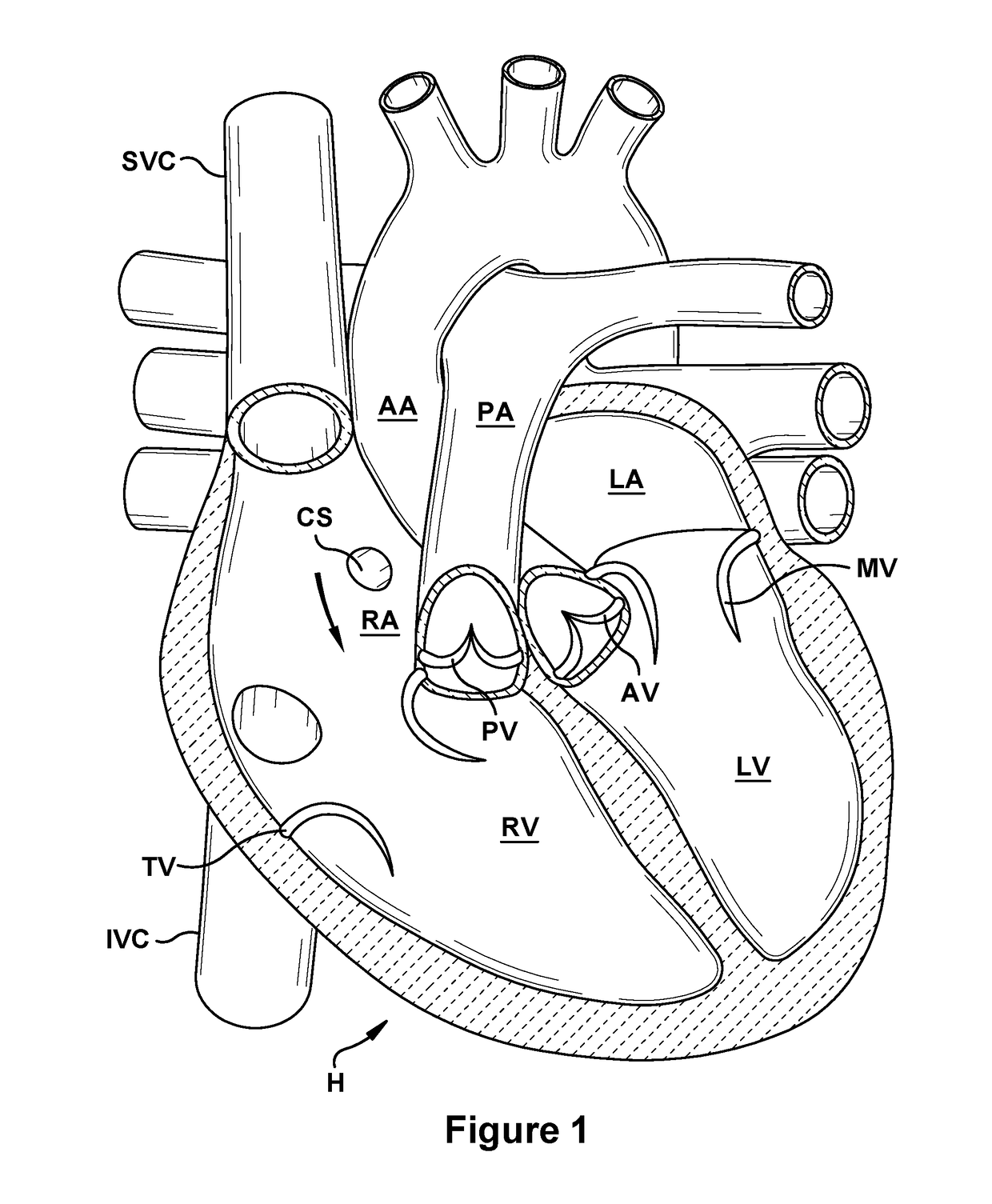
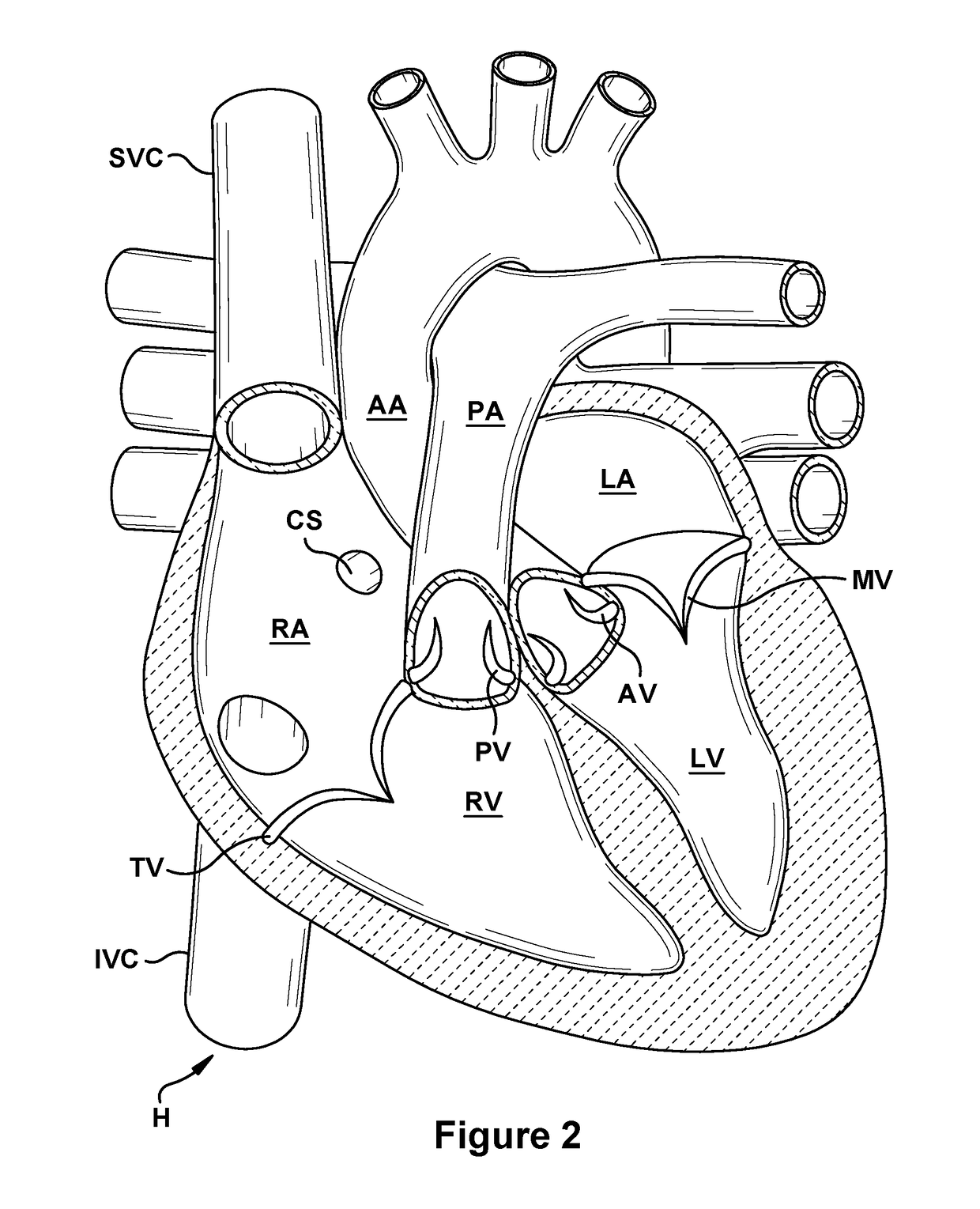
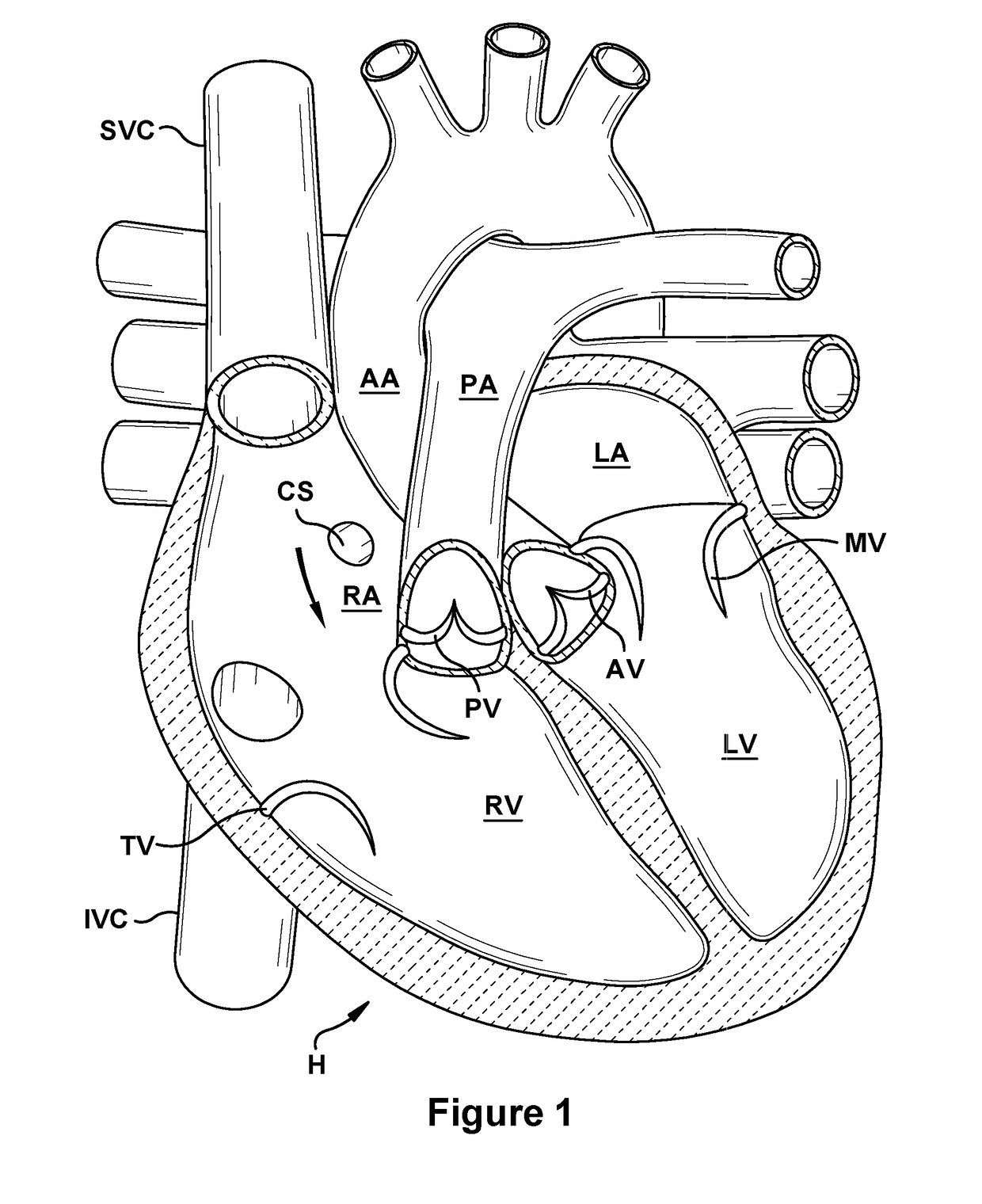
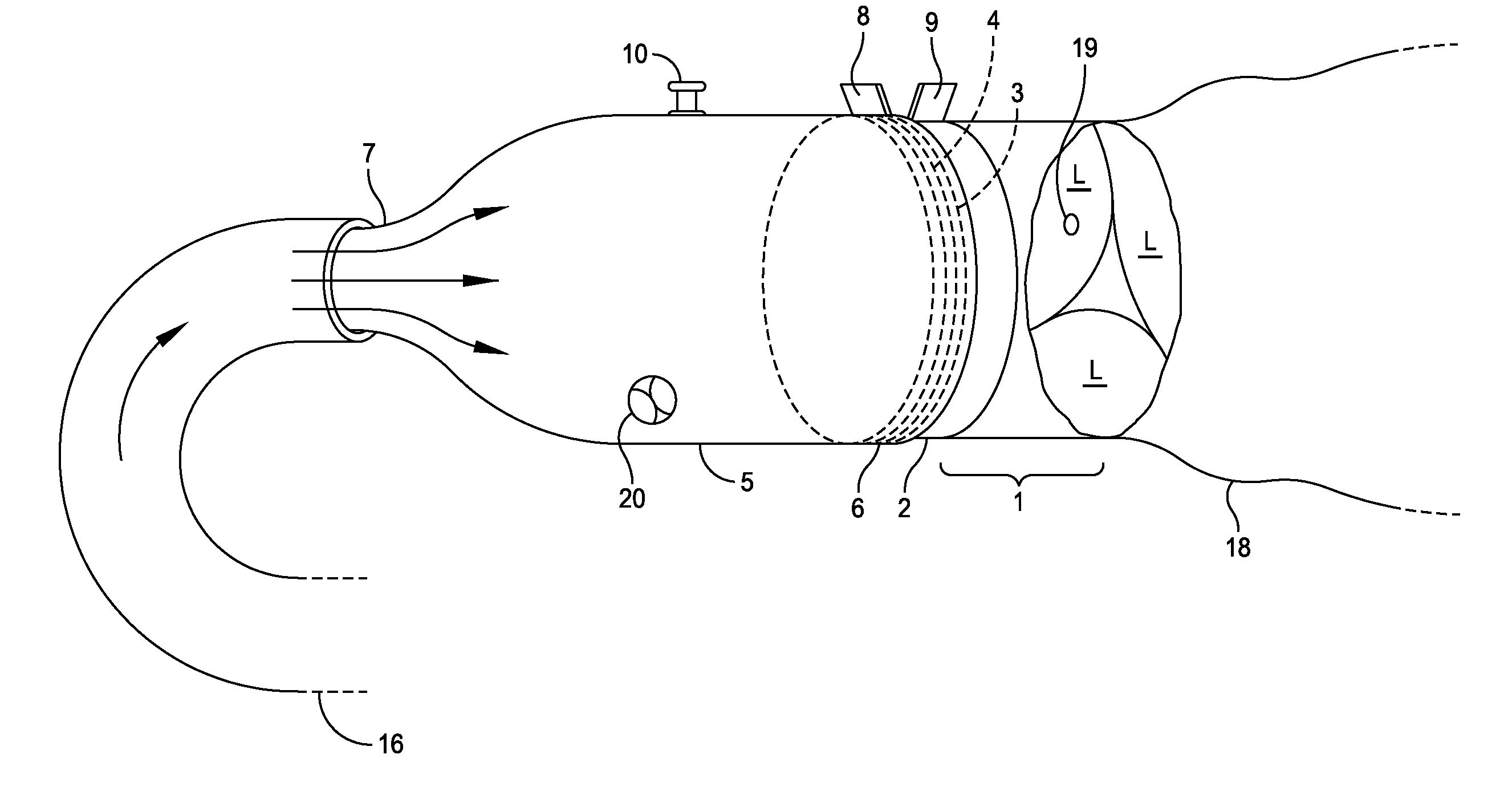
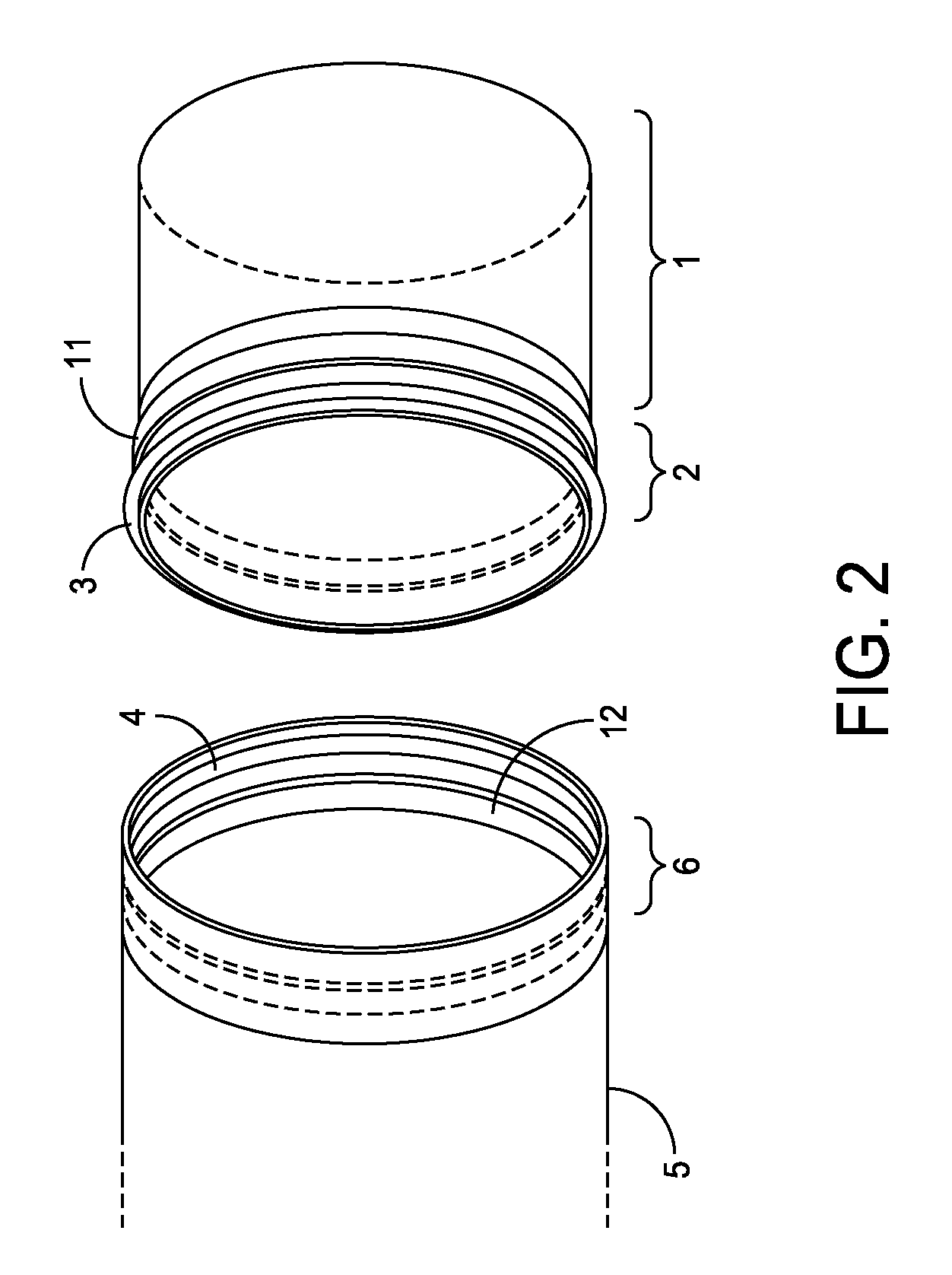
This invention is a multichannel catheter for extracorporeal circulation of blood to a patient undergoing cardiovascular treatments or surgery. The catheter has three independent channels, an obturator and an expandable balloon at one end of the catheter. The first channel is the largest and is of a size that allows for delivery of blood through outlet parts in the wall of the first channel to a patient in an amount sufficient to maintain the patient's metabolism and perfusion throughout the treatment or surgery. The obturator is longitudinally insertable into the first channel. A second channel, smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and is suitable for delivering a biologically active fluid (e.g., for cardioplegia) to the heart and / or venting the left heart. A third channel, also smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and suitable for delivering a fluid to the balloon for its expansion when positioned in the ascending aorta to occlude the flow of blood to the heart. The catheter provides an improved means of preparing for or performing cardiovascular surgery on a patient using a cardiopulmonary machine for extracorporeal circulation of blood. The catheter is particularly useful for cardiac surgery.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Native valve repair devices and procedures
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Native valve repair devices and procedures
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repairing the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a pair of paddles and a pair of gripping members. The paddles are moveable between an open position and a closed position. The gripping members can have different configurations for effective attachment and release from the native valve of the patient.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Multichannel catheter
InactiveUS6821265B1Efficient deliveryMinimize damageSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisExtracorporeal circulationAscending aorta
This invention is a single, multichannel catheter useful for extracorporeal circulation of blood to a patient undergoing cardiovascular treatments or surgery. The catheter has three independent channels and an expandable balloon at one end of the catheter. The first channel (34) is the largest and is of a size that allows for delivery of blood to a patient in an amount sufficient to maintain the patient's metabolism and perfusion throughout the treatment or surgery. A second channel (36), smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and is suitable for delivering a biologically active fluid (e.g., for cardioplegia) to the heart and / or venting the left heart. A third channel (38), also smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and suitable for delivering a fluid to the balloon for its expansion when positioned in the ascending aorta to occlude the flow of blood to the heart. It is important that the first channel accounts for at least about 70% of the total channel volume. The catheter provides an improved means of performing cardiovascular surgery on a patient using a cardiopulmonary machine for extracorporeal circulation of blood. The catheter is particularly useful for cardiac surgery. The multichannel catheter is best prepared using an extrusion molding technique.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
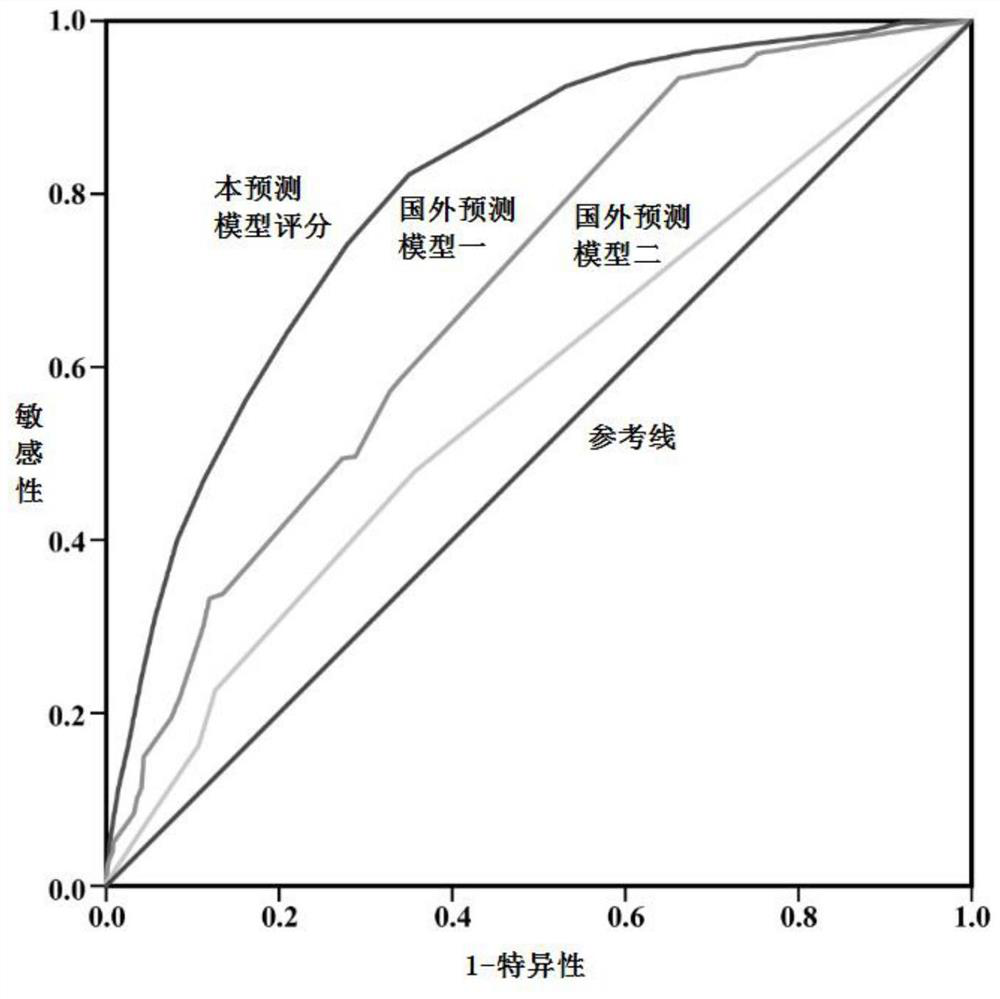
Prediction model for pulmonary infection after cardiac surgery and construction method thereof
PendingCN112017783AReduce morbidityFit closelyMedical simulationMedical data miningPulmonary infectionPerioperative
The invention discloses a prediction model for pulmonary infection after cardiac surgery and a construction method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: screening out evaluation indexes related to pulmonary infection after cardiac surgery from various clinical data of a cardiac surgery patient in a perioperative period; bringing the evaluation indexes into a Logistic regression modelto analyze, calculate and determine regression coefficients of risk factors of pulmonary infection after cardiac surgery; obtaining a risk score through the regression coefficient of each risk factor;and finally, combining the risk score with a pulmonary infection risk prediction function to calculate a pulmonary infection probability value, so that a risk prediction model based on a scoring system can be established. The prediction model disclosed by the invention is good in fitting, shows better risk prediction capability compared with the existing foreign model, can achieve the purpose ofearly screening postoperative pulmonary infection high-risk patients, and plays a role in early prevention, early discovery and early treatment, thereby reducing the incidence rate of postoperative pulmonary infection of the heart.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Multichannel catheter
InactiveUS20050171505A1Efficient deliveryMaximizes rate of blood flowSuture equipmentsOther blood circulation devicesExtracorporeal circulationHeart operations
This invention is a single, multichannel catheter useful for extracorporeal circulation of blood to a patient undergoing cardiovascular treatments or surgery. The catheter has three independent channels and an expandable balloon at one end of the catheter. The first channel (34) is the largest and is of a size that allows for delivery of blood to a patient in an amount sufficient to maintain the patient's metabolism and perfusion throughout the treatment or surgery. A second channel (36), smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and is suitable for delivering a biologically active fluid (e.g., for cardioplegia) to the heart and / or venting the left heart. A third channel (38), also smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and suitable for delivering a fluid to the balloon for its expansion when positioned in the ascending aorta to occlude the flow of blood to the heart. It is important that the first channel accounts for at least about 70% of the total channel volume. The catheter provides an improved means of performing cardiovascular surgery on a patient using a cardiopulmonary machine for extracorporeal circulation of blood. The catheter is particularly useful for cardiac surgery. The multichannel catheter is best prepared using an extrusion molding technique.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
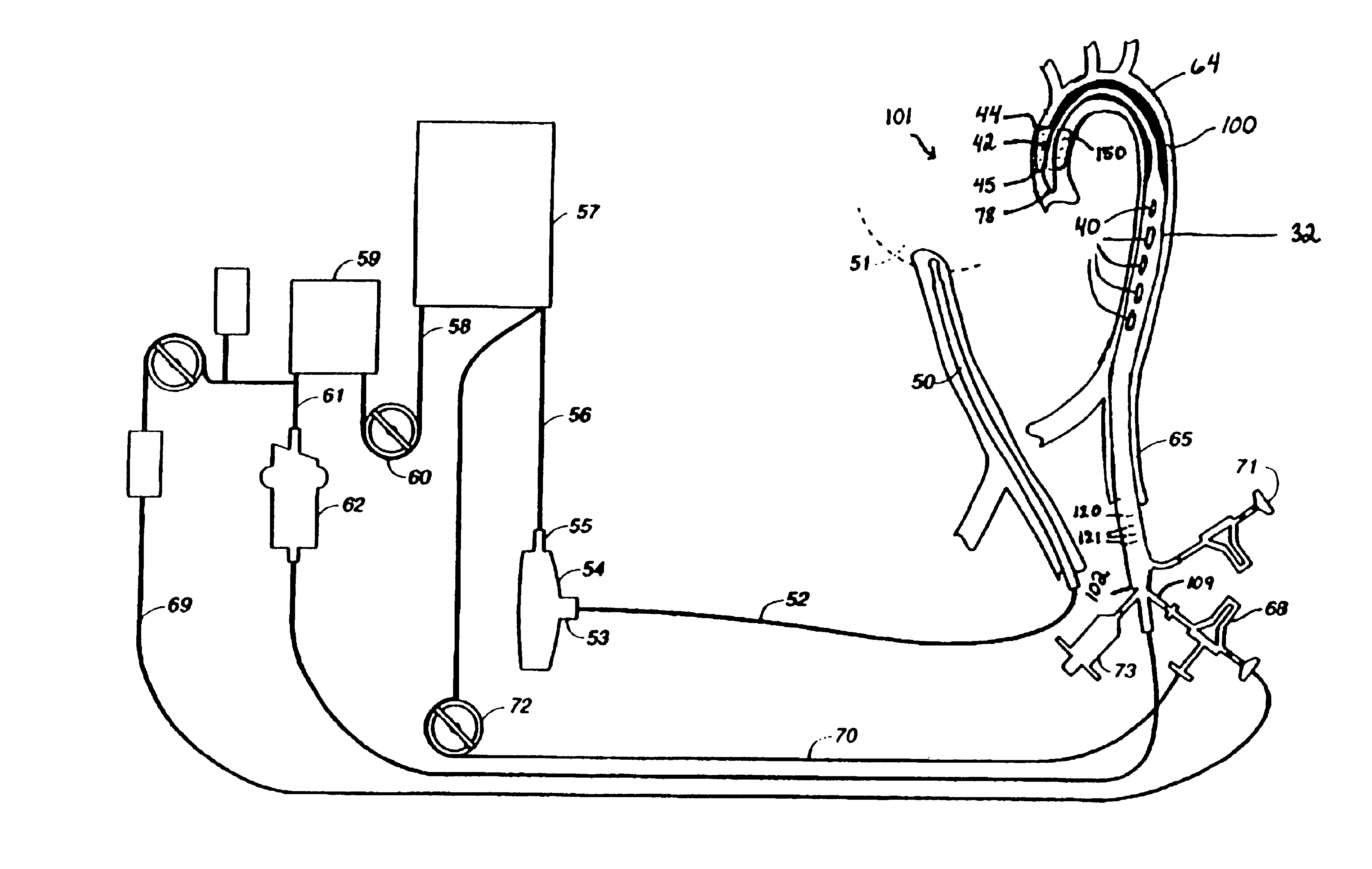
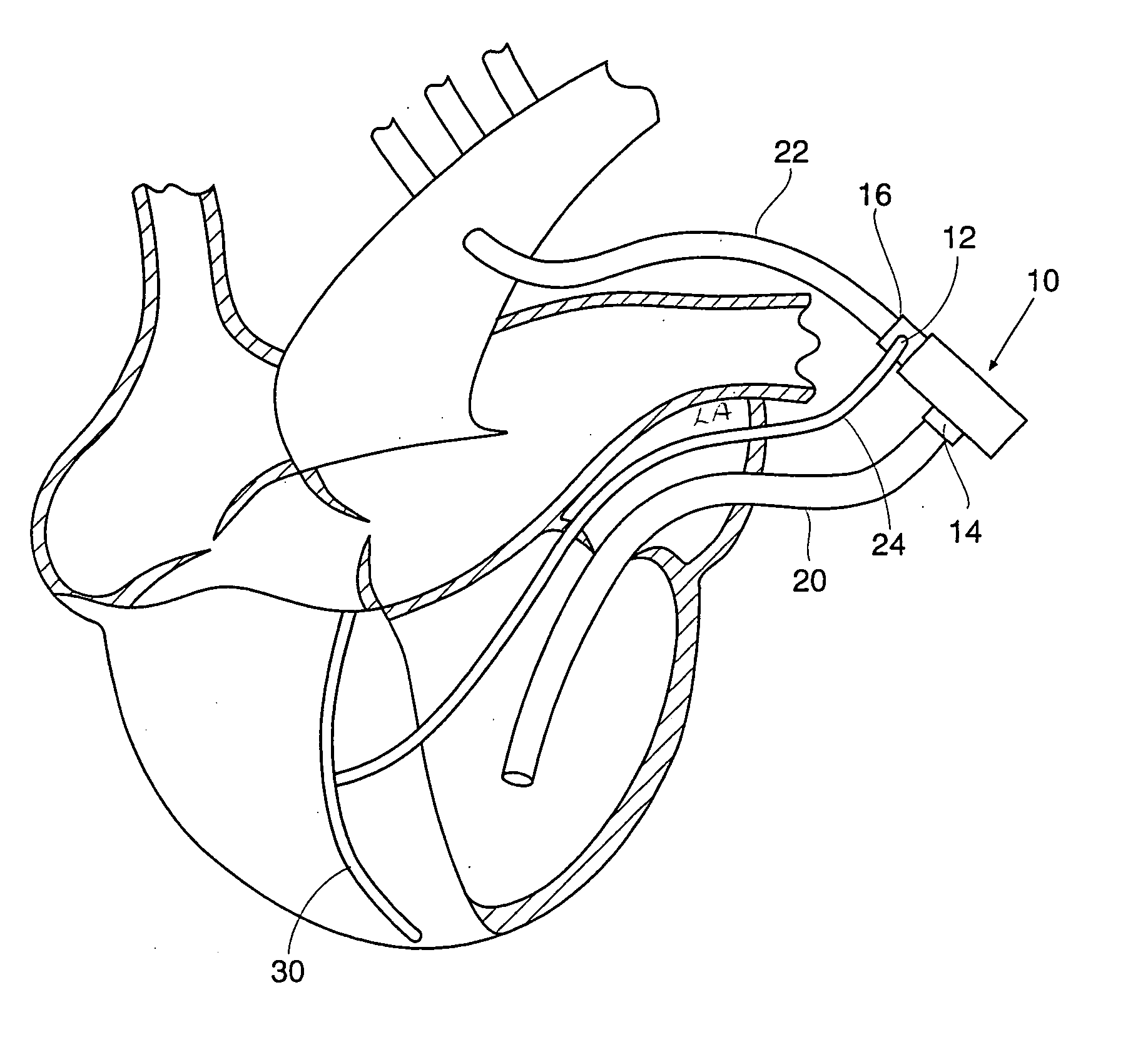
Apparatus and method for simulation of diastole and visualizing the diastolic state of an aortic valve and root during cardiac surgery
A device for evaluating an aortic valve after opening an aorta distal to the aortic valve includes a body defining a chamber. The body has a generally circular proximal open end and a distal end, the proximal open end being configured to be reversibly attachable to one of the aorta and a short open tube distal to the aortic valve in a generally water-tight fashion. At least a portion of the body is transparent to view the aortic valve. Other embodiments of the device and related methods are further disclosed.
Owner:CORFIGO INC
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repairing the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a surgical delivery instrument, a valve repair device, and a gripper control mechanism. The surgical delivery instrument has at least one lumen. The valve repair device is configured to be delivered through the lumen of the surgical delivery instrument and to be attached to a native valve of a patient. The valve repair device has a pair of paddles, and first and second gripping members. The paddles are movable between an open position and a closed position. The paddles and the first and second gripping members are configured to attach to the native valve of the patient. The gripper control mechanisms each include a suture and a wire having a loop at a distal end. The suture extends from the surgical delivery instrument and through the loop of the wire. The suture is removably attached to the gripping member. The loop of the wire is configured to engage the gripping member to move the gripping member between one or more positions.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Supplemental port for catheter perfusion of surgical site and methods of use
InactiveUS20050119599A1Reduce post-surgical damageEliminate needBlood pumpsMedical devicesSurgical siteBlood pump
A blood pump having a supplemental outflow port and / or a supplemental inflow port. A supplemental outflow port can be used to supply blood to regions of the body during heart bypass operations, such as to perfuse heart tissue downstream from an anastomosis site during CABG procedures so as to reduce the damage to the heart tissue. A supplemental inflow port can be used to infuse blood and / or various other fluids or compositions into the patient's blood stream, such as may be helpful or advantageous during emergency situations in cardiac surgery.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repair the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a base assembly, a pair of paddles, and a pair of gripping members. The base assembly includes a shaft and a coupler attached to the shaft such that the coupler can be moved along the shaft. The paddles are movable between an open position, a closed position and a bailout position. The paddles and the gripping members are configured to attach to the native valve of the patient. Movement of the coupler along the shaft causes the paddles to move between the open position, the closed position, and the bailout position. When the paddles are in the bailout position, a bailout angle between each paddle of the pair of paddles and the shaft is greater than or equal to 120 degrees.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and method for connecting a blood pump without trapping air bubbles
An apparatus and a method for connecting medical tubing or any other type of fluidic circuit conduits (e.g., cannulae) to a ventricular assist device (“VAD”) or any other pumping device used for blood pumping during cardiac circulatory support for vascular surgery. The apparatus and the method prevent air bubbles from entering a cardiac circulatory support system when connecting cannulae to a VAD that may later enter the blood stream of a patient during cardiac surgery, and also provide for purging any air bubbles that may have entered the cardiac circulatory support system during a cannulae-VAD connection.
Owner:VITALMEX INT DE C V
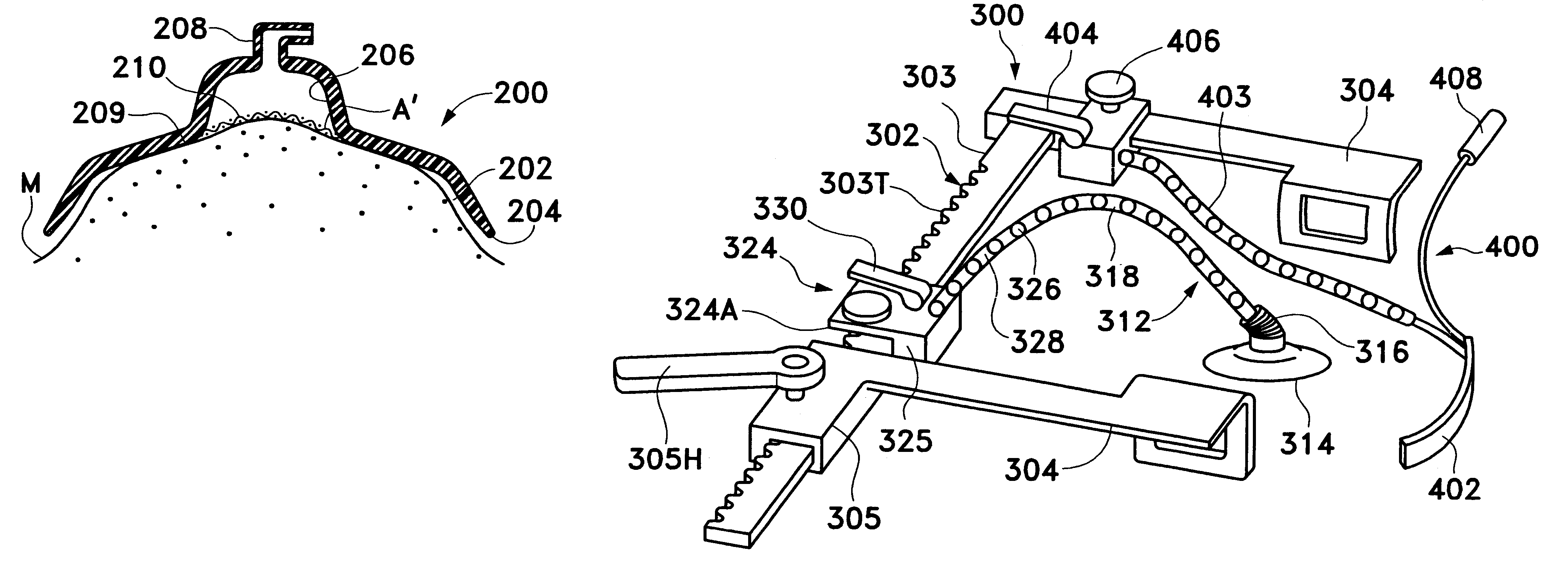
Lung fixer for thoracoscopic cardiac surgery of newborn baby
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical appliances and discloses a lung fixer for a thoracoscopic cardiac surgery of a newborn baby. The lung fixer is of a symmetrical structure and comprises 2 sleeves, a thin-walled structure, connecting pipes and snapping buckles, wherein the sleeves are of hollow structures, the thin-walled structure is arranged between middle-upper parts of thetwo sleeves, lower parts of the two sleeves are connected with each other, and the two sleeves are omega-shaped; the sleeves sleeve forceps head ends of a pair of separating forceps and can cover theforceps head ends of the separating forceps; and first ends of the connecting pipes are connected with lower ends of the sleeves, second ends of the connecting pipes are connected with the snapping buckles, and the snapping buckles are in snapped connection with handle ends of the separating forceps so as to prevent the lung fixer from falling off during the surgery. The lung fixer is used in a manner of being matched with a thoracoscope and can serve as a lung baffle, blind areas pressing lung tissue are reduced, the omission of breaks of lungs is prevented, the risk of operative complications is lowered, and an appliance purchasing expense and an appliance disinfection and depletion expense are reduced; and the lung fixer disclosed by the invention can also serve as a disposable product, so that the possibility of cross infection is lowered.
Owner:BEIJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Composition and methods to improve neural outcome
InactiveUS20020013277A1Increase concentrationReduce severityNervous disorderDipeptide ingredientsMammalHeart operations
The tripeptide glycine-proline-glutamine (GPE) may be administered before, or usually after, injury to reduce damage to the central nervous system. GPE appears useful for neuronal rescue particularly but not exclusively within the hippocampus. Advantages of GPE include: (a) that it crosses the blood-brain barrier, so is effective by injected peripheral administration, (b) it is unlikely to challenge the immune system, (c) it is cheap, and (d) its therapeutic ratio is high. GPE may also be infused into the CSF. It may be administered prior to parturition or elective brain or cardiac surgery. Transdermal routes may be useful for chronic neural disorders. The CNS of mammals (including foetal mammals) after trauma including hypoxic / ischaemic experimental insults showed reduced damage under GPE protection as measured by histological assessment of cell damage or death and regional shrinkage.
Owner:NEUREN PHARMA LTD
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repairing the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a surgical delivery instrument, a valve repair device, and a gripper control mechanism. The surgical delivery instrument has at least one lumen. The valve repair device is configured to be delivered through the lumen of the surgical delivery instrument and to be attached to a native valve of a patient. The valve repair device includes a pair of paddles, and at least four gripping members. The paddles are movable between an open position and a closed position, and the paddles and the at least four gripping members are configured to attach to the native valve of a patient. The gripper control mechanism is configured to independently move each of the at least four gripping members.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Acute kidney injury
The present invention relates to a method of predicting the severity of acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Native valve repair devices and procedures
A system for implanting a repair device onto a native valve of a natural heart to repair the native valve of a patient during a non-open-heart procedure. The system includes a base assembly having a plurality of pivoting links, a pair of paddles attached to the base assembly, a pair of gripping members attached to the base assembly, and at least one coaptation or spacer element disposed between the pair of gripping members. Movement of the pivoting links of the base assembly causes the paddles to move between an open position and a closed position. The paddles and the gripping members are configured to attach to valve leaflets of the patient. The coaptation or spacer element is configured to fill at least a portion of a gap between the valve leaflets of the patient.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com