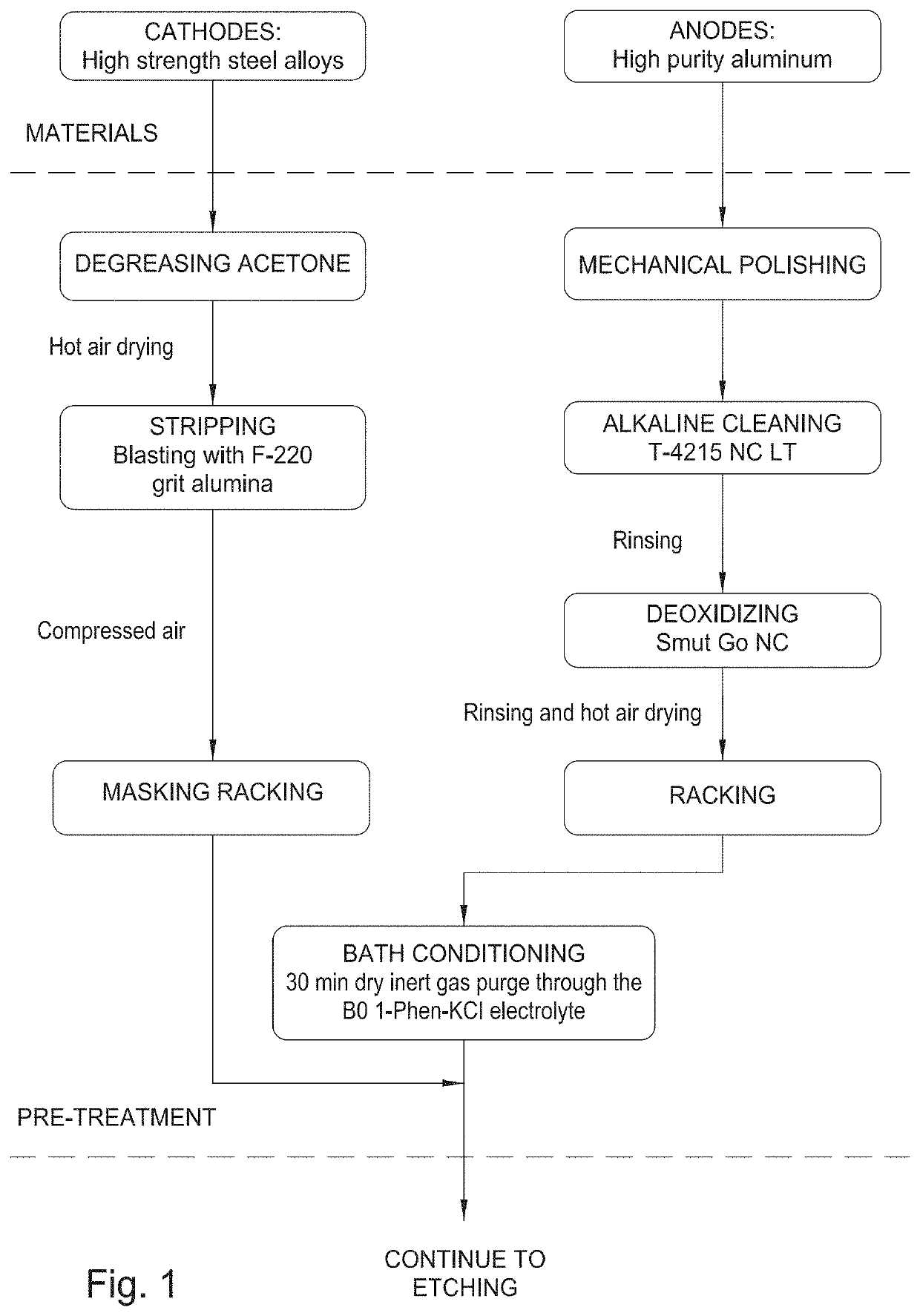
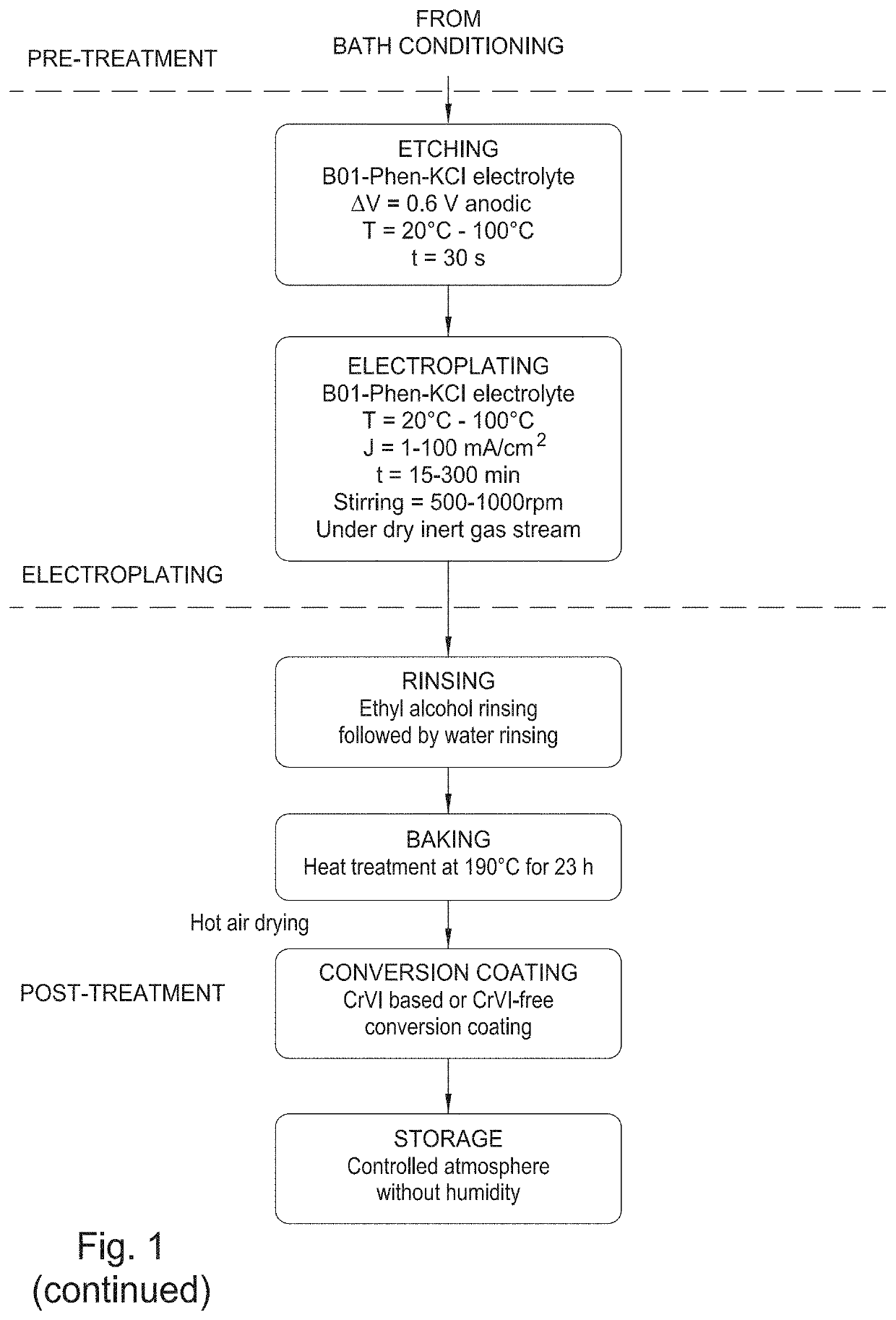
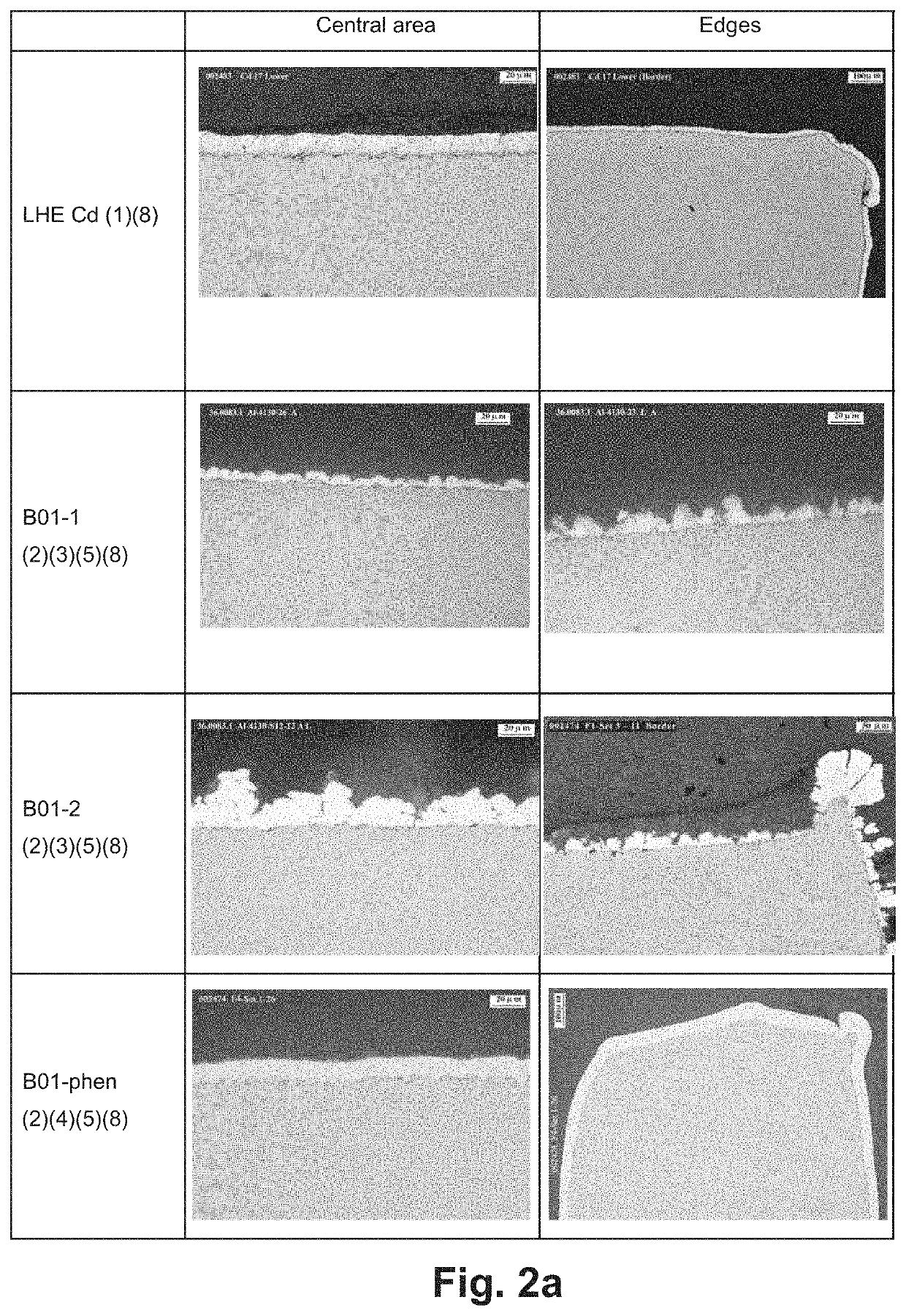
Environmentally friendly aluminum coatings as sacrificial coatings for high strength steel alloys
a technology of aluminum coating and high strength steel alloy, which is applied in the direction of chromatisation, electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to coat internal and deeply recessed surfaces, handling hazardous and non-environmental plating solutions, and not being able to meet the requirements of environmental protection. , to achieve the effect of facilitating handling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
1. Ionic Liquid Electrolytes
[0137]The ionic liquid electrolytes used in these examples were synthesized as follows:
[0138]B01: Either the as-received Basionics™ Al01 ionic liquid electrolyte from BASF or the house-made AlCl3-EMIC 60:40 electrolyte (see below) were independently used as baseline electrolytes to be modified with the different additives.
[0139]AlCl3-EMIC 60:40 electrolyte was prepared by mixing the corresponding amounts of aluminum trichloride and 1-ethyl-3-methyl-imidazolium chloride, as follows: The 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride [EMIC] (Fluka Ref. 30764, purity min 93%), was dried at 70° C. under vacuum for several hours. Then, it was placed into a glass vessel. The aluminum trichloride [AlCl3] (Across Organics Ref. 19578, anhydrous, 99%, granules) was weighted (as received) inside a glovebox filled with argon inside a glass dispenser; then, it was transferred to an addition funnel, taken out of the glovebox, and placed on top of the glass vessel already contain...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com