Method of therapeutic administration of dhe to enable rapid relief of migraine while minimizing side effect profile
a technology of dhe and migraine, applied in the field of migraine treatment, can solve the problems of gastrointestinal cramping and distress, increased risk of rebound headache and habituation, and no longer fully supporting the vasodilator/vasoconstrictor mechanism of vascular headache, etc., and achieve the effect of rapid treatment of the diseas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Pharmacokinetic Profile of DHE Required to Achieve Pain Relief
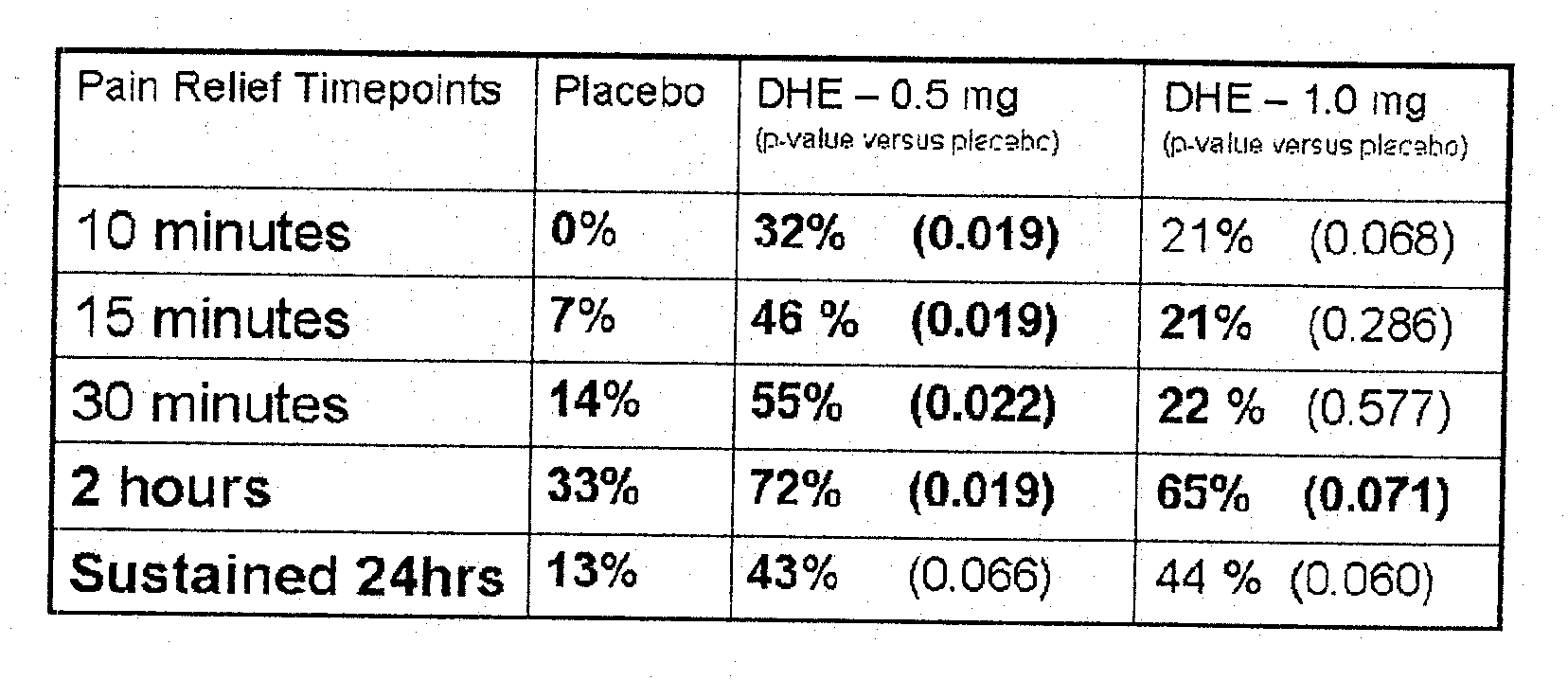
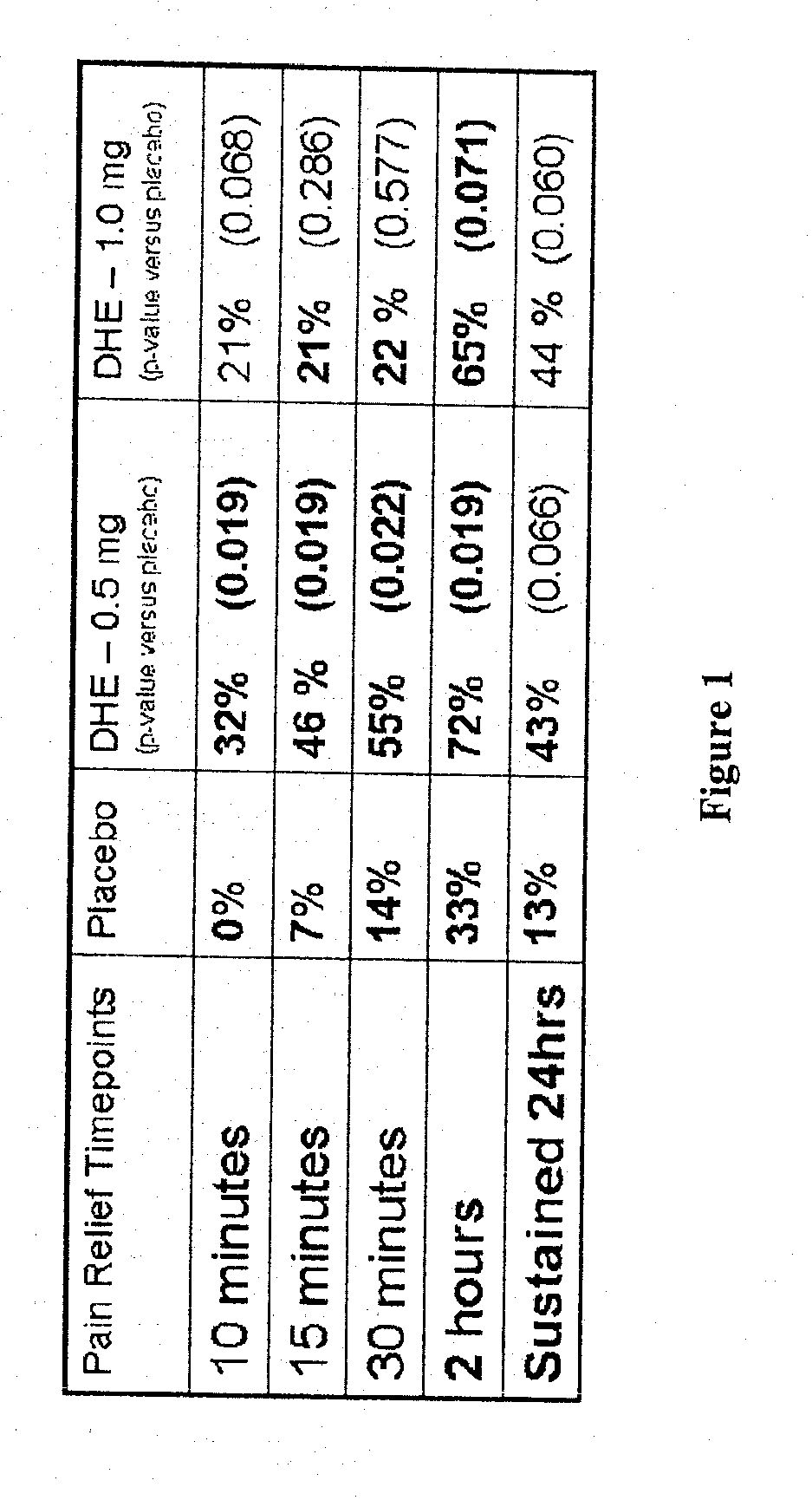
[0116]FIG. 1 shows the rapid pain relief (within 10 minutes) achieved by administering DHE by a method that achieves the two lower peak plasma concentration profiles shown in FIG. 2.
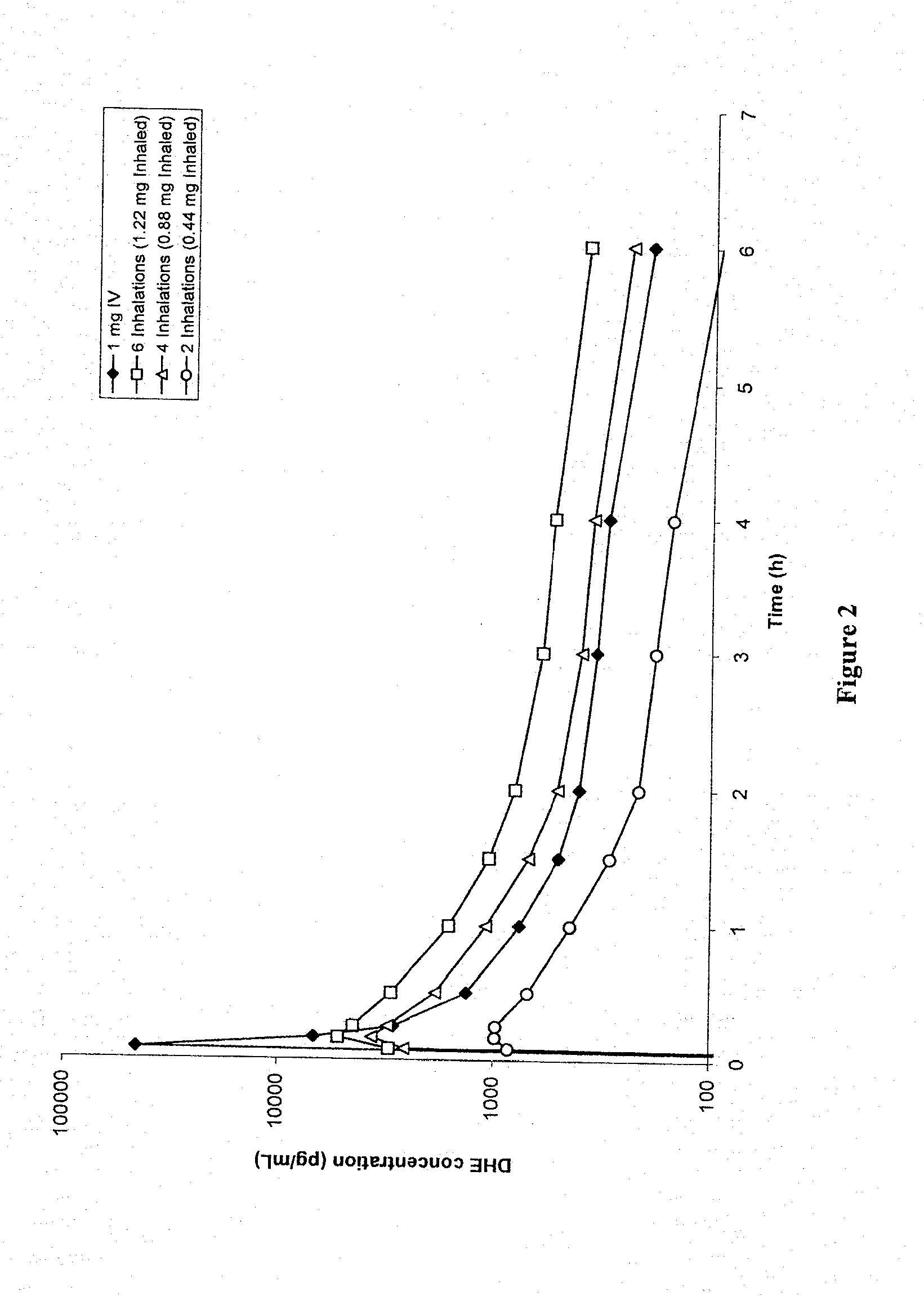
[0117]FIG. 2 shows DHE plasma profiles for 1 mg IV-administered DHE, compared to 6 inhalations (1.22 mg inhaled / fine particle dose), 4 inhalations (0.88 mg inhaled / fine particle dose) and 2 inhalations (0.44 mg inhaled / fine particle dose) of DHE respectively. A large plasma spike was observed following IV DHE administration, but not with inhaled delivery of DHE. This plasma spike difference (of at least “10” fold) was hypothesized to be associated with the reduced side effect profile, despite smaller differences in AUC between 1 mg IV and 0.88 mg inhaled DHE.
[0118]FIG. 7 shows the plasma profile of the primary metabolite of DHE, 8′-OH Dihydroergotamine, following intravenous and inhalation delivery of DHE. A larger plasma spike in 8′-OH Dihydr...
example 2
Receptor Binding at the Cmax Concentrations
[0120]A differential adverse effect profile was reported in a clinical study comparing 1 mg IV-administered DHE with inhaled DHE (Table 2). A greater incidence of adverse effects were apparent following IV dosing. To investigate pharmacologically-mediated adverse effect differences between (1) intravenous and (2) inhaled Dihydroergotamine Mesylate (DHE), biogenic amine receptor binding (serotonin (5-HT), adrenergic, dopaminergic) of dihydroergotamine mesylate in vitro was determined, based on concentrations corresponding to the Cmax levels reported following inhaled and intravenous (IV) dosing in a clinical study.
[0121]To investigate the unexpected result that the lower spikes of DHE may have resulted in a different receptor binding profile thus achieving efficacy, but avoiding side effects, a clinical investigation of receptor binding at the Cmax concentrations were undertaken.
[0122]Peak Plasma DHE concentrations (Cmax) were determined fro...
example 3
Serotonin, Adrenergic and Dopaminergic Receptor Binding by DHE at Concentrations Equivalent to Peak Plasma Concentrations
[0124]Radioligand receptor binding assays clearly show that DHE exhibits wide ranging pharmacology at multiple receptor sites. (FIGS. 3-5.) For the majority of receptors, DHE achieves significant binding at concentrations equivalent to the IV Cmax whereas inhaled binding at each dose yields a different profile. In most instances, binding is reduced when non-IV methods are used to administer.
[0125]The anti-migraine efficacy of DHE is due to agonist activity at 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors. FIG. 3 shows receptor binding data at various serotonergic receptor subtypes, indicating greater response at several subtypes for intravenous administration at Cmax. The notation “(h)” represents cloned human receptor subtypes. Similar trends were observed for adrenergic and dopaminergic subtypes. Binding at these receptors is demonstrated with 100% binding at 5-HT1B following bot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mean peak plasma concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mean peak plasma concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com