Solar thermal tube plate heat exchanger
a heat exchanger and solar thermal technology, applied in solar heat collector safety, speed sensing governors, light and heating equipment, etc., can solve the problems of loss of efficiency in flat-plate collectors, detracting from their overall thermal efficiency, tube-plate surface needs wind protection, etc., to achieve rapid and proper length on site, easy to conform to the cap or cap, and inexpensive and thermally conductive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
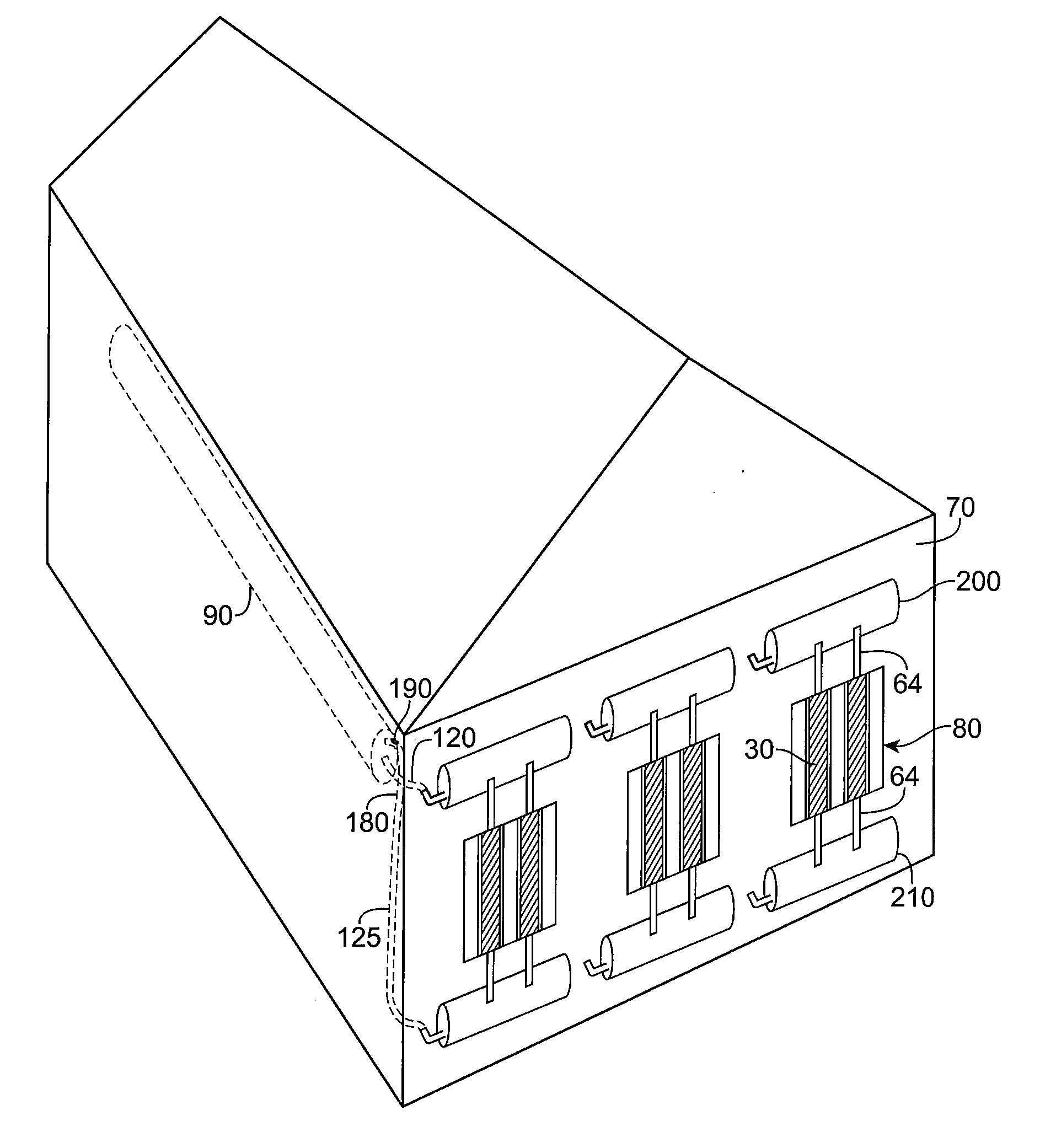
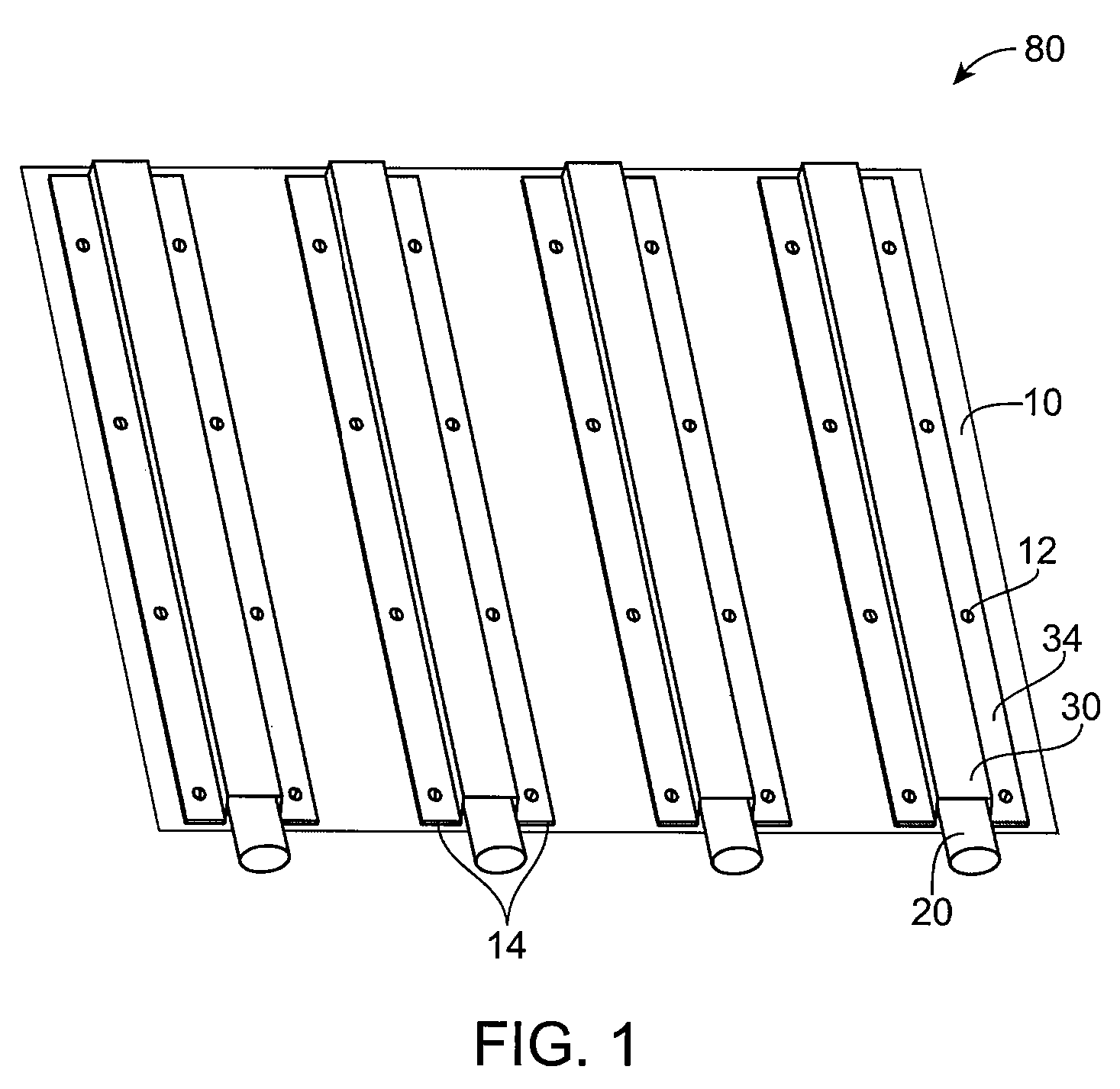
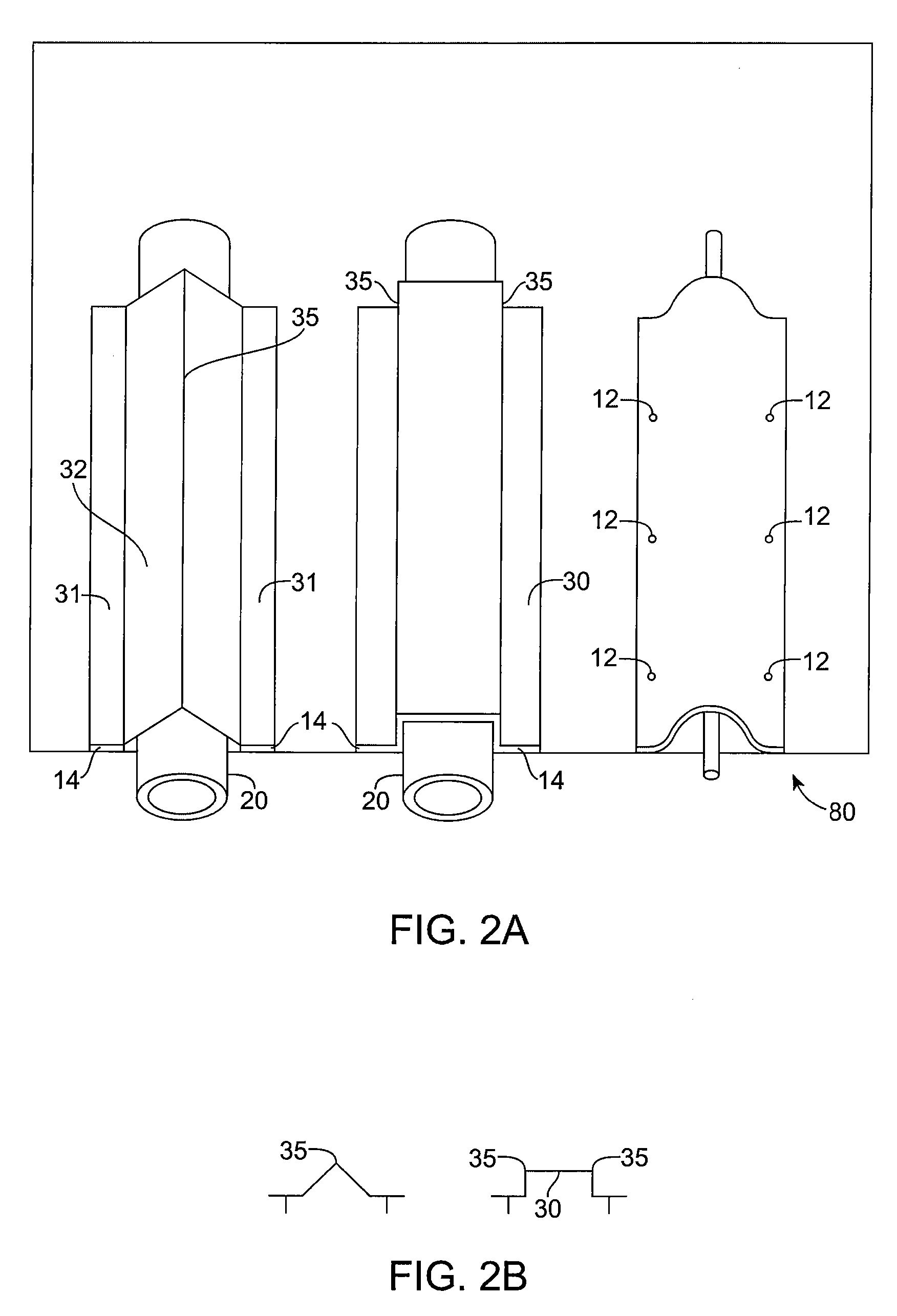
[0074] One embodiment of the apparatus uses flexible thin wall plastic or rubber tubes or hoses (which more generally are types of “tubular fluid conduit or conduits”) pressed against the metal roof or walls of a building to gain heat from the sun in the day or dispose of heat to the atmosphere at night. A heat exchange fluid, such as water flows through the tubes by convection, or is pumped, to pick up solar heat during the day or to give out heat at night. Metal caps flatten, squash or otherwise securely fasten the tubes against the metal of the building. For an existing metal roof or metal sidewall, the caps can be held against the flattened tubes by adhesive such as silicone sealant. For a new metal roof or metal sidewall, the metal of the building can be formed in a series of raised sections with undercuts along the sides so that a cap may mechanically snap in place.
[0075] The skins of most metal buildings are poor heat conductors. Most metal buildings are actually made of ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com