Degradable biomedical magnesium alloy drug eluting intravascular stent and preparation method thereof
A biomedical and vascular stent technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as inapplicable degradation of magnesium alloy vascular stents, reduction of coating protection effect, and magnesium ion proliferation, so as to reduce the risk of stent degradation and shedding, inhibit the growth of smooth muscle cells, The effect of reducing the damage of the protective layer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0149] This embodiment provides a series of degradable biomedical magnesium alloy materials, and its elemental component content is as shown in Table 1:
[0150]
[0151] The processing method includes: according to the composition ratio of each group of elements described in Table 1, each alloy element is smelted into a magnesium alloy ingot by vacuum semi-continuous casting, wherein the purity of each component raw material is 99.99%. The magnesium alloy ingot is subjected to solution treatment, the solution temperature is 450 degrees Celsius, the solution time is 8 hours, and then the magnesium alloy ingot is extruded into a rod with a diameter of 10 mm by hot extrusion, and the hot extrusion temperature is 340 degrees Celsius. Then cut off 20% of the material at both ends of the rod, and only take the middle section of the rod as the preparation material for the vascular stent, so as to avoid the influence of uneven mixing.
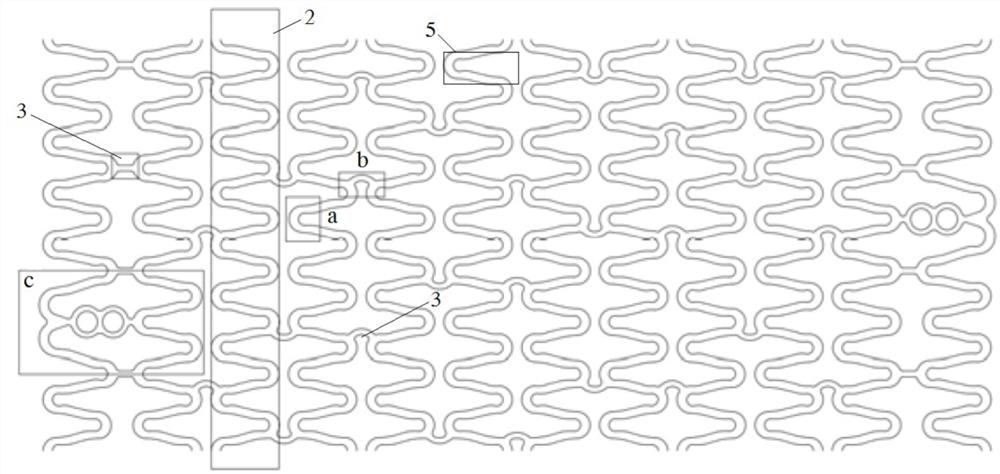
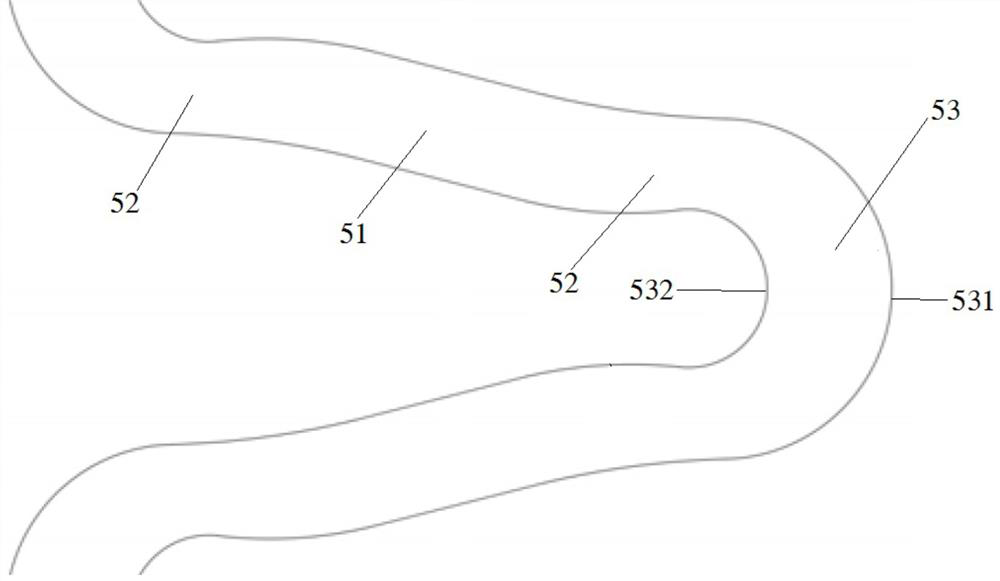
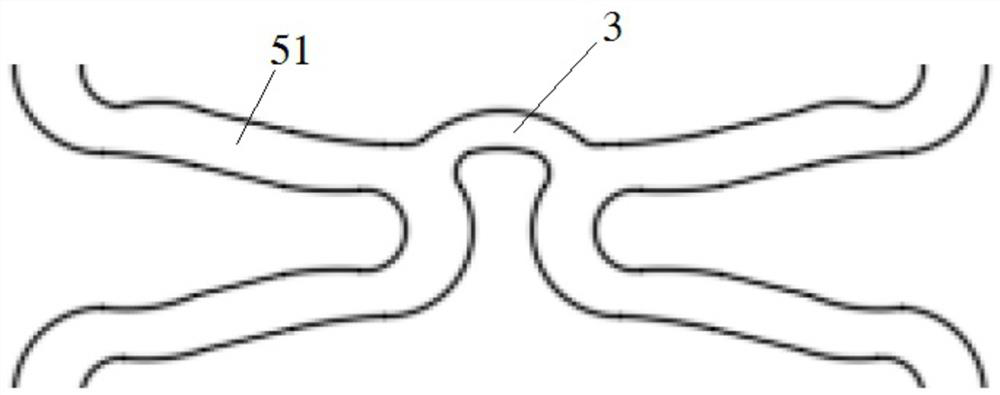
[0152] Scaffold structure embodiment 1
[01...
Embodiment 2
[0175] This embodiment provides a degradable biomedical magnesium alloy drug-eluting vascular stent, which only consists of a stent base 1 to form a bare stent (without surface treatment and without any coating).
[0176] The stent matrix 1 adopts the structure A with higher radial support force and smaller maximum equivalent strain in the stent structure Example 1, and its material is a magnesium alloy material with better mechanical properties and corrosion resistance in Example 1. BDM-6# material.
[0177] The preparation of the degradable biomedical magnesium alloy drug-eluting vascular stent includes:
[0178] (a) The BDM-6# magnesium alloy rod was prepared by the method in Example 1 of the magnesium alloy material, and then the magnesium alloy pipe was prepared through the pipe drawing process. The outer diameter of the magnesium alloy pipe is 3.0mm, the wall thickness is 0.22mm, and the length is 1m;
[0179] (b) The magnesium alloy tube is prepared into a cut stent b...
Embodiment 3
[0184] This embodiment provides a degradable biomedical magnesium alloy drug-eluting vascular stent, which includes a stent base 1 and a magnesium fluoride protective layer.
[0185] The stent matrix 1 adopts the structure A with higher radial support force and smaller maximum equivalent strain in the stent structure Example 1, and its material is BDM with better mechanical properties and corrosion resistance in the magnesium alloy material Example 1. -6# material.
[0186] The magnesium fluoride protective layer is composed of dense magnesium fluoride, uniformly covers the surface of the stent, and has a thickness of 1000nm.
[0187] The preparation of the degradable biomedical magnesium alloy drug-eluting vascular stent includes:
[0188] (a) The BDM-6# magnesium alloy rod was prepared by the method in Example 1 of the magnesium alloy material, and then the magnesium alloy pipe was prepared through the pipe drawing process. The outer diameter of the magnesium alloy pipe is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com