Method for harmlessly treating and recycling magnesium fluoride waste acid in zinc smelting process
A technology of harmless treatment and magnesium fluoride polluted acid, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve problems such as poor solution filtration performance, poor separation effect of zinc and magnesium, occupational health hazards, etc., to improve economic benefits and social efficiency, reducing safety and environmental risks, and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Get 20,000 grams of (1) zinc sulfite slag produced by a company in Yunnan and dry it for use. %, silver 0.0037wt%, iron 1.9wt%, fluorine 0.021wt%, chlorine 0.19wt%; (2) get 20 liters of dirty acid, this dirty acid contains acid 3.9 grams / liter, fluorine 0.81 grams / liter, chlorine 0.36 grams (3) get 50 liters of electrolytic waste liquid, this electrolytic waste liquid contains 42 grams / liter of zinc, 40 grams / liter of magnesium oxide, 143 grams / liter of sulfuric acid, 0.03 grams / liter of fluorine, 0.34 grams / liter of chlorine; ( 4) Take 2000 grams of zinc calcine, which contains 58.4 wt% zinc and 1.8 wt% magnesium oxide. (5) Take 500 grams of copper slag, which contains 5.5wt% zinc, 32.6wt% copper and 0.022wt% chlorine.
[0078] 1) Slurrying of zinc sulfite slag: take 10 liters of industrial water, 20 liters of electrolytic waste liquid, add 10,000 grams of zinc sulfite slag for slurrying, the slurrying time is 10 minutes, stir and slurry evenly before use;
[0079]2)...
Embodiment 2
[0094] Get 20,000 grams of (1) zinc sulfite slag produced by a company in Yunnan and dry it for use. %, silver 0.0051wt%, iron 3.2wt%, fluorine 0.034wt%, chlorine 0.22wt%; (2) get 20 liters of dirty acid, this dirty acid contains acid 7.4 grams / liter, fluorine 4.8 grams / liter, chlorine 2.1 grams (3) get 50 liters of electrolytic waste liquid, this electrolytic waste liquid contains zinc 44 grams per liter, magnesium oxide 46 grams per liter, sulfuric acid 157 grams per liter, fluorine 0.028 grams per liter, chlorine 0.34 grams per liter; ( 4) Take 2000 grams of zinc calcine, which contains 56.3 wt% of zinc and 1.9 wt% of magnesium oxide. (5) Take 500 grams of copper slag, which contains 7.8wt% zinc, 35.3wt% copper and 0.024wt% chlorine.
[0095] 1) Slurrying of zinc sulfite slag: take 5 liters of industrial water, 30 liters of electrolytic waste liquid, add 11,000 grams of zinc sulfite slag for slurrying, the slurrying time is 10 minutes, stir and slurry evenly before use;
...
Embodiment 3
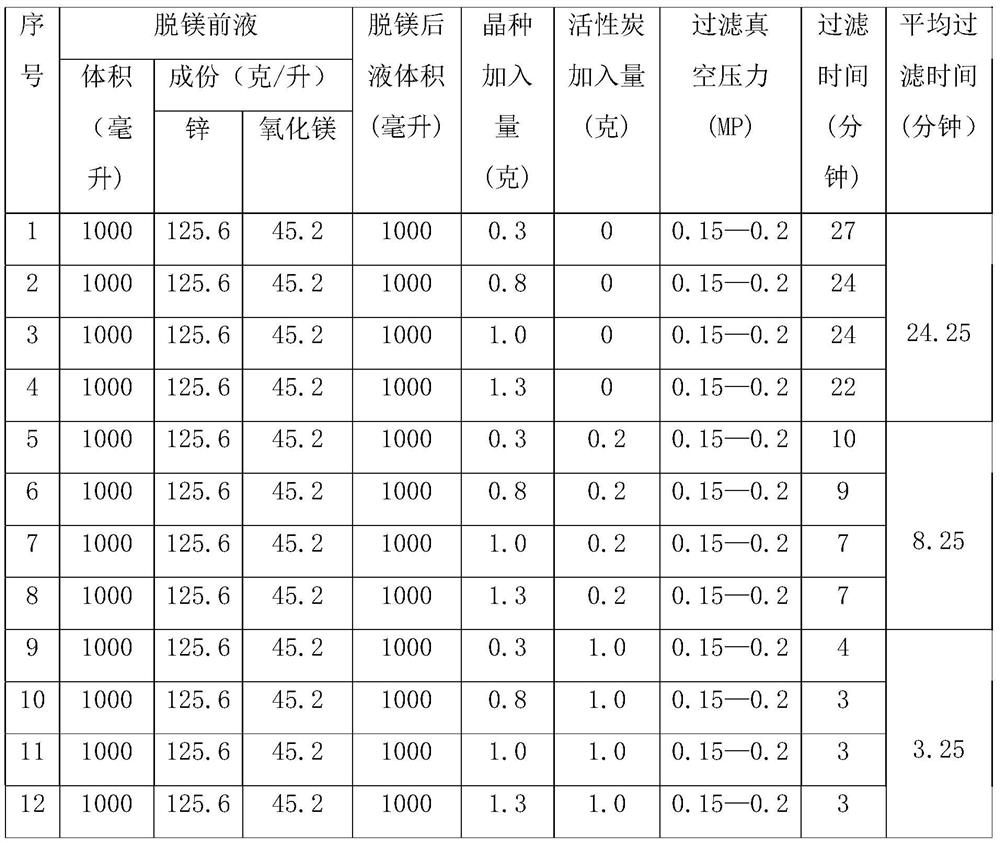
[0111] The difference between this example and the above-mentioned examples 1 and 2 is that, according to the amount of seed crystals added, whether or not activated carbon is added, and the amount of activated carbon added, a comparative table of the influence of these factors on the filtration rate is obtained, as shown in Table 1.
[0112] Table 1 Comparison table of the effect of activated carbon addition on the filtration speed of the liquid after demagnesization
[0113]
[0114] As can be seen from Table 1, although the filtration rate is improved to a certain extent after adding seed crystals, the effect is not ideal. After adding an appropriate amount of activated carbon as a modifier, the filtration effect is very good, and the filtration speed increases with the appropriate increase of the amount of activated carbon added.
[0115] In a word, it can be seen from the examples that by adding an appropriate amount of activated carbon, the problem that high zinc-cont...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com