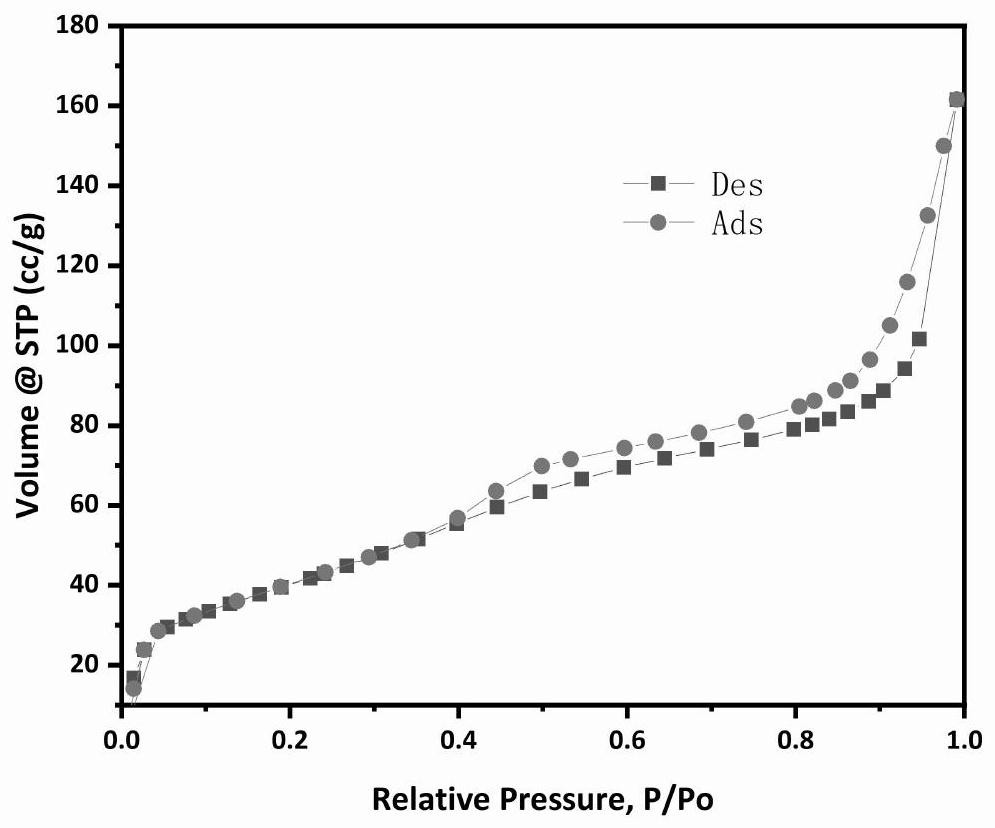
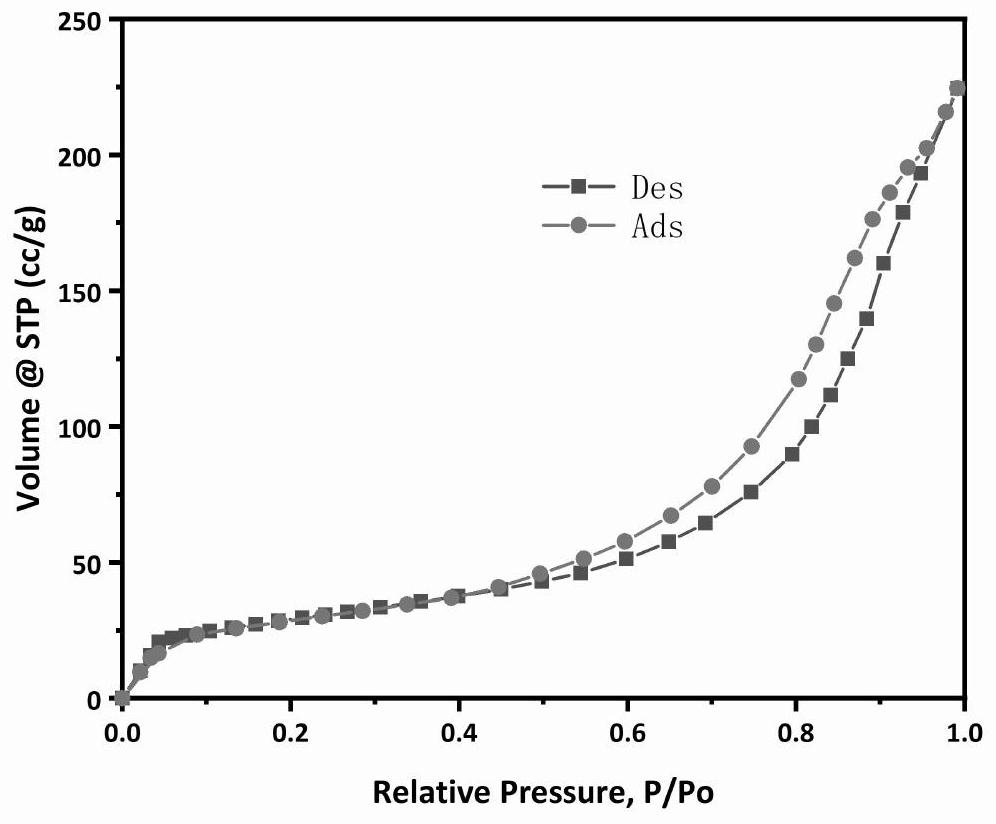
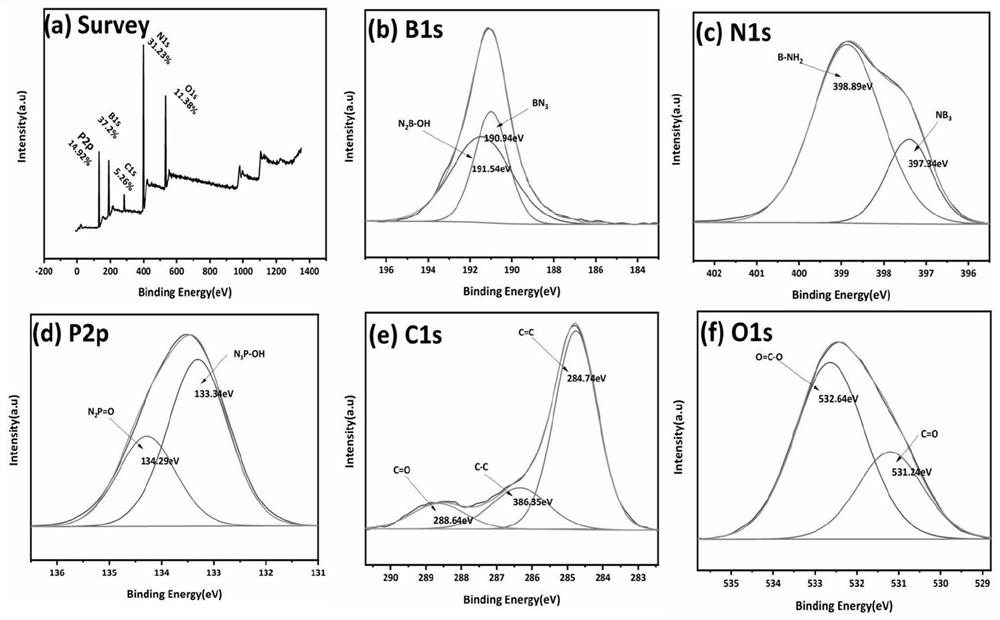
Catalyst for dehydrogenating alkanes to olefins and its preparation and dehydrogenation method
A catalyst and a technology for producing olefins, which are used in catalyst activation/preparation, chemical instruments and methods, catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory long-term stability, unsatisfactory catalytic selectivity, easy carbon deposition, etc., to meet the needs of production technology , good conversion rate, the effect of improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Take a certain amount of boric acid (boron source, 0.4g), thiourea (sulfur source and nitrogen source), hydroxyethylidene diphosphonic acid (phosphorus source), in the raw material, the molar ratio of B:N:S:P is 1 :90:48:1.2), add 40mL of distilled water, stir to dissolve, and then recrystallize the beaker containing the precursor solution in an oil bath at 80°C and stirring at 300rpm until there is no obvious moisture, and then the obtained white The recrystallized product was transferred to a vacuum oven at 50°C for further drying for 12 hours. Grind the dried recrystallized product into powder, put it into a corundum ark, place it in a tube furnace, feed 60mL / min of ammonia gas to provide a roasting atmosphere, and raise the temperature from room temperature to 800°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min Roast for 3 hours, then cool down to room temperature naturally under the protection of ammonia gas (the flow rate of ammonia gas is 20mL / min) to obtain the catalyst, record:...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Compared with Example 1, the only difference is that the composition of the sulfur source was changed, and ammonium thiosulfate and ammonium sulfate were used for research respectively. Wherein, when ammonium thiosulfate was used as the sulfur source, urea was used as a supplementary nitrogen source, and urea was used as a supplementary nitrogen source. The ratio of control B:N remains unchanged, and other parameters and operations are the same as in Example 1.
[0088] Adopt the catalyst performance testing method among the embodiment 1, record the performance of catalyst as shown in table 1:
[0089] Table 1:
[0090]
[0091]
Embodiment 3
[0093] Compared with Example 1, the only difference is that the molar ratio of the sulfur source is changed, respectively, the molar ratios of B:S are 1:16, 1:20, 1:24, 1:28, and urea is used to supplement nitrogen Source, to keep B:N unchanged, in addition, the molar ratio of B:S is 1:60 in the case, no additional urea is added as a nitrogen source; other parameters and operations are the same as in Example 1.
[0094] Adopt the catalyst performance test method in embodiment 1, record the performance of catalyst as shown in table 2:
[0095] Table 2
[0096]
[0097] a: No additional urea was added.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com