Optimization method for improving performance of Nb3Sn superconducting strand Rutherford stranded cable
An optimization method and strand technology, applied in the usage of superconducting elements, superconducting devices, superconducting/high-conducting conductors, etc., can solve problems such as subcomponent rupture and performance degradation of Sn wire twisted cables, etc., to improve reliability performance, control critical performance reduction, and ensure the effect of yield strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
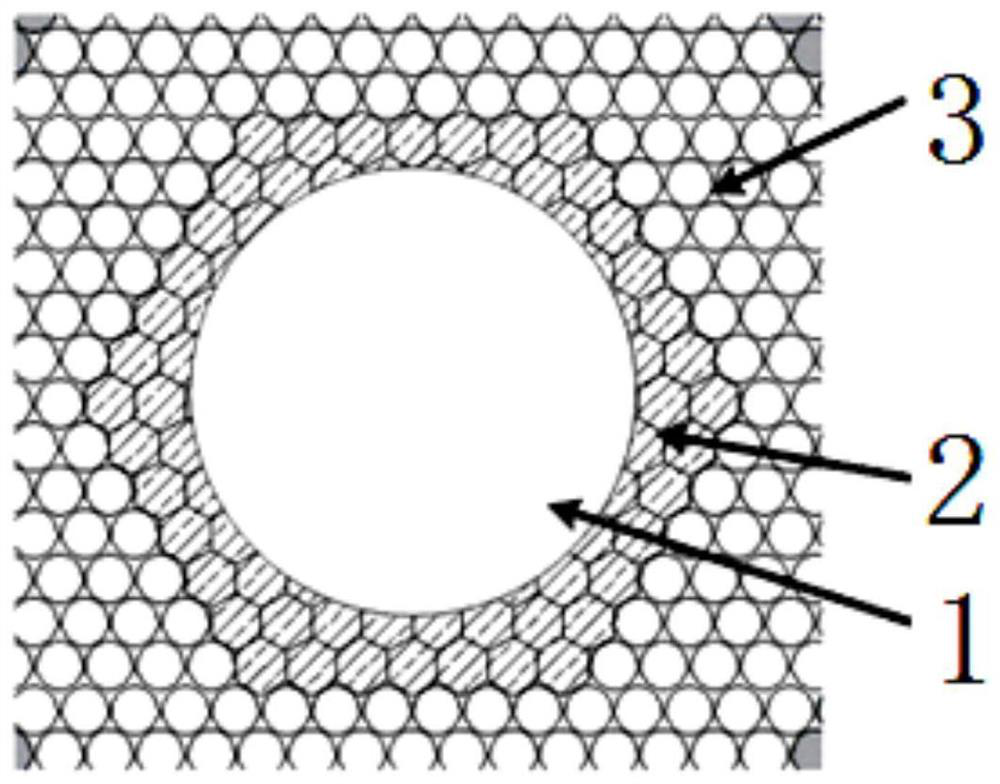
[0017] An improved Nb 3 Optimization method for the performance of Rutherford stranded cables with superconducting strands of Sn, Nb 3 Cross section of Sn superconducting strands, see figure 1 , from the inside to the outside are composed of tin alloy 1, Nb core wire region 2 and Cu substrate region 3 respectively. The optimization method specifically includes the following steps:
[0018] Step 1: Nb with a diameter of 1.00mm 3 The Sn strands are rewound on the steel wire wheel, placed in a vacuum heat treatment furnace, and kept at a constant temperature of 250 ° C for 30 minutes;
[0019] Step 2: stop heating, the Nb obtained by heat treatment in step 1 3 Cut a sample with a length of 10 mm on the Sn strand, grind and polish the cross section of the strand, and use a Vickers hardness tester to test the hardness of different positions of the outer Cu substrate;
[0020] Step 3: Nb obtained by heat treatment in Step 1 3 A sample with a length of 300mm was cut from the Sn...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Step 1: Nb with a diameter of 0.82mm 3 The Sn strands are rewound on the steel wire wheel, placed in a vacuum heat treatment furnace, and kept at a constant temperature of 200 ° C for 120 minutes;
[0025] Step 2: stop heating and heat treat the resulting Nb in step 1 3 Cut a sample with a length of 10mm on the Sn strand, grind and polish the cross section of the strand, and use a Vickers hardness tester to test the hardness of 5 points on the outer Cu substrate;
[0026] Step 3: Heat-treat the resulting Nb in Step 1 3 A sample with a length of 300mm was cut from the Sn strand, and the Nb after heat treatment was tested 3 Sn strand yield strength;
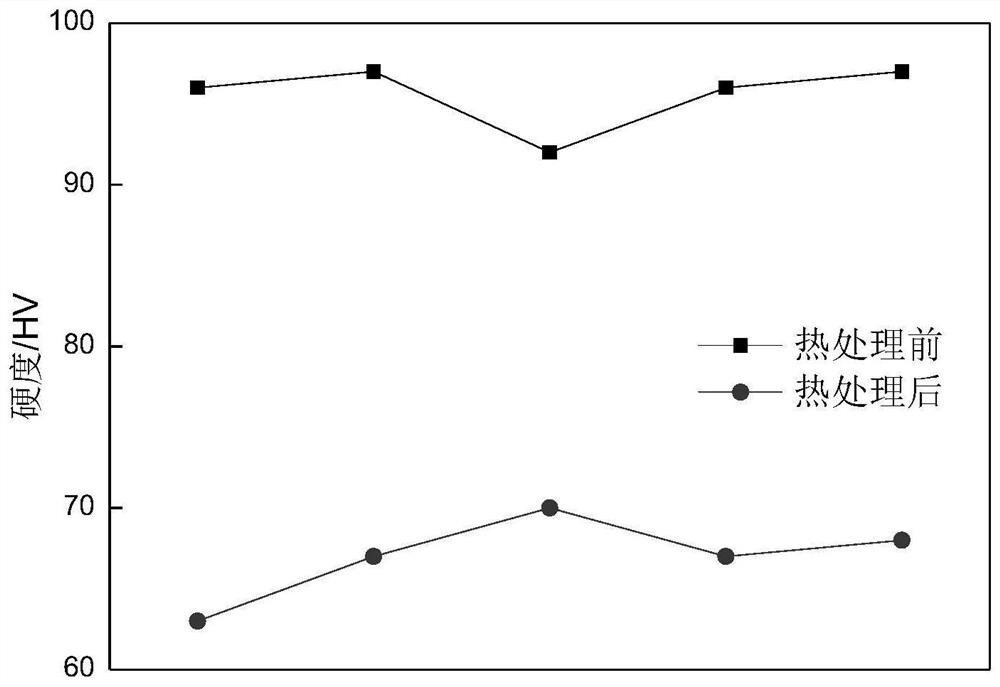
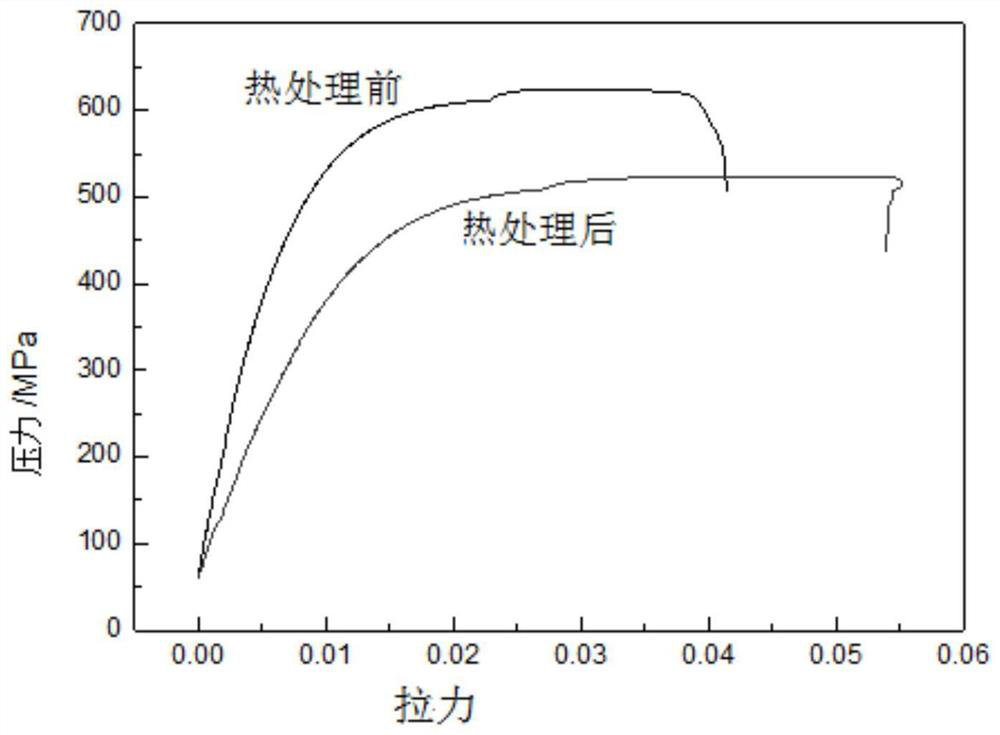
[0027] Step 4: Comparing the hardness of the Cu base material of the outer layer after the heat treatment in step 2 with that before the heat treatment, the hardness of the Cu base material decreased by 22% to 30% after the heat treatment; 3 The tensile mechanical properties of Sn strands were compared with those before ...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Step 1: Nb with a diameter of 1.00mm 3 The Sn strands are rewound on the steel wire wheel, placed in a vacuum heat treatment furnace, and kept at a constant temperature of 180°C for 60 minutes;
[0031] Step 2: stop heating and heat treat the resulting Nb in step 1 3 Cut a sample with a length of 10mm on the Sn strand, grind and polish the cross section of the strand, and use a Vickers hardness tester to test the hardness of 5 points on the outer Cu substrate;
[0032] Step 3: Heat-treat the resulting Nb in Step 1 3 A sample with a length of 300mm was cut from the Sn strand, and the Nb after heat treatment was tested 3 Sn strand yield strength;
[0033] Step 4: Comparing the hardness of the Cu base material of the outer layer after the heat treatment in step 2 with that before the heat treatment, the hardness of the Cu base material after the heat treatment is reduced by 20% to 30%; 3 The tensile mechanical properties of Sn strands were compared with those before he...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com