Processing method for improving high temperature creep properties of magnesium alloys by rolling and hammering
A processing method and high temperature creep technology, applied in metal processing equipment, metal rolling, temperature control and other directions, to achieve the effect of low equipment requirements, low cost and simple process method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The magnesium alloy is prepared by water-cooled semi-continuous casting method, and the pure magnesium ingot (Mg 99.9%), pure aluminum ingot (Al 99.9%), pure zinc ingot (Zn 99.9%), Al-Mn master alloy and Mg-Y master alloy are smelted , the as-cast structure of the magnesium alloy is obtained by casting, and the mass percentage composition of the magnesium alloy is: Al: 8.5%, Zn: 0.90%, Mn: 0.3%, Y: 0.5%, and the rest is magnesium and impurity elements that cannot be removed.
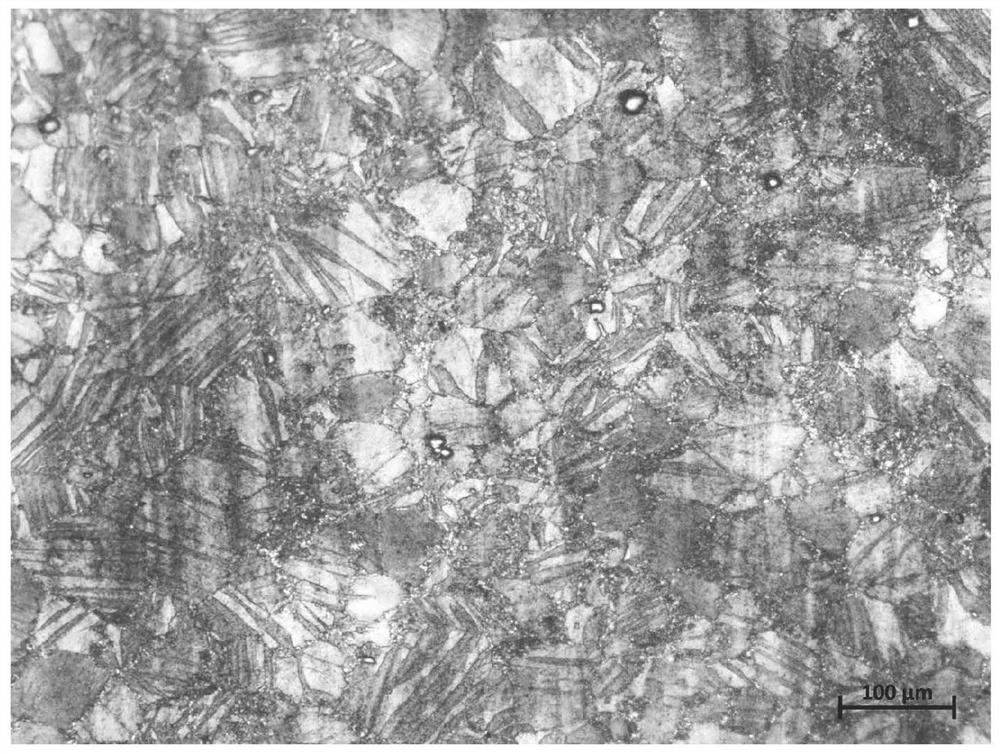
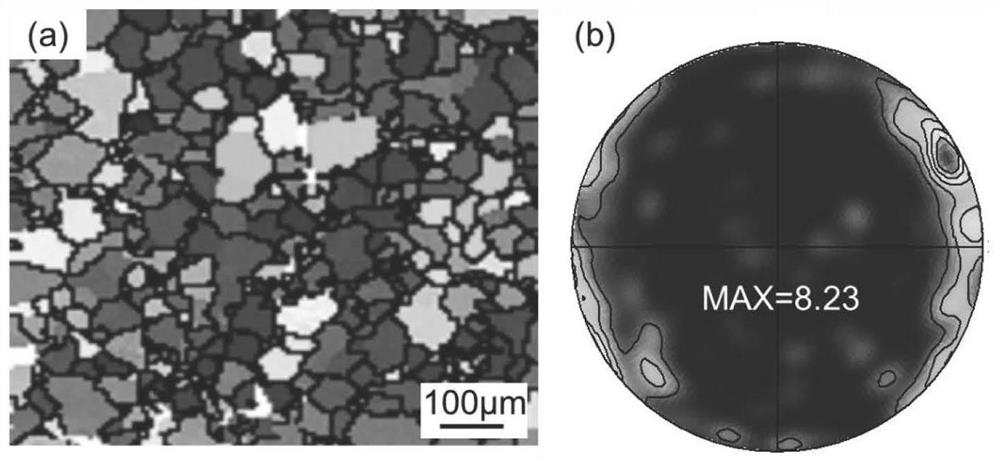
[0034] The as-cast structure is subjected to solution treatment at 380°C×12h; then the solid solution structure is cut and rolled. The thickness before rolling is 80mm, the rolling temperature is 300°C, and the rolling speed is 0.2m / s. The number of passes is 8, the total deformation is 80%, and the temperature of the magnesium alloy after rolling is 305°C. The EBSD microstructure of the rolled magnesium alloy is as follows: figure 1 As shown, it can be seen that it has an obvious preferred orien...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The magnesium alloy is prepared by water-cooled semi-continuous casting method, and the pure magnesium ingot (Mg 99.9%), pure aluminum ingot (Al 99.9%), pure zinc ingot (Zn 99.9%), Al-Mn master alloy and Mg-Y master alloy are smelted , the as-cast structure of the magnesium alloy is obtained by pouring, and the mass percentage composition of the magnesium alloy is: Al: 9.5%, Zn: 0.45%, Mn: 0.4%, Y: 0.8%, and the rest is magnesium and impurity elements that cannot be removed.
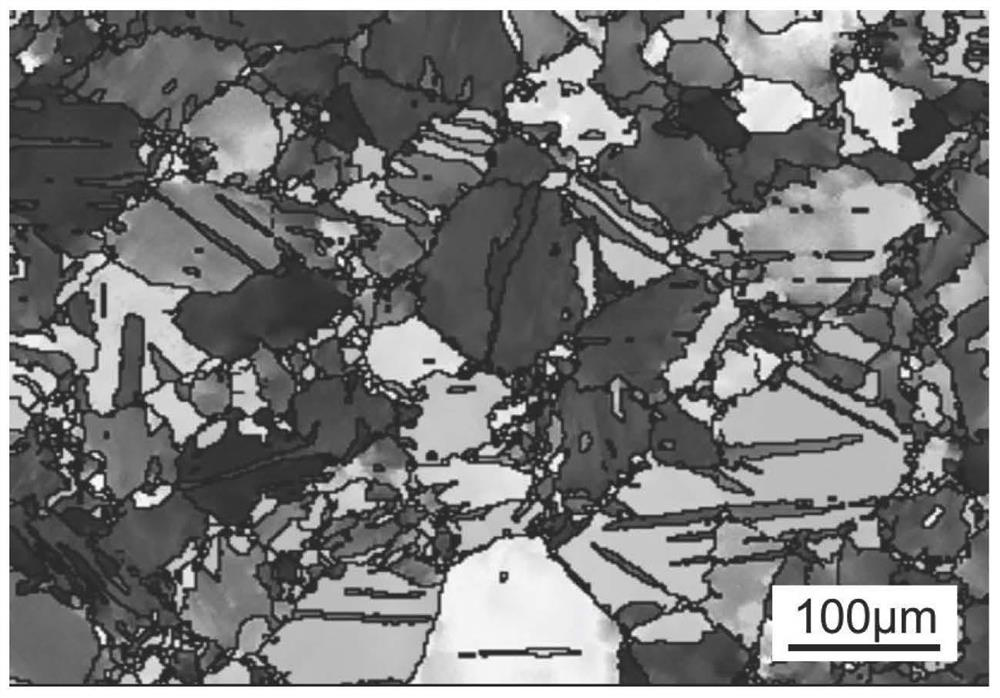
[0040] The as-cast structure is solution treated at 400°C×8h; then the solid solution structure is cut and rolled. The thickness before rolling is 80mm, the rolling temperature is 350°C, and the rolling speed is 0.4m / s. The number of passes is 5, the total deformation is 70%, and the temperature of the magnesium alloy after rolling is 250°C. The EBSD microstructure of the rolled magnesium alloy is as follows: Figure 6 As shown, it can be seen that it has an obvious preferred orientation, and the...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The magnesium alloy is prepared by water-cooled semi-continuous casting method, and the pure magnesium ingot (Mg 99.9%), pure aluminum ingot (Al 99.9%), pure zinc ingot (Zn 99.9%), Al-Mn master alloy and Mg-Y master alloy are smelted , the as-cast structure of the magnesium alloy is obtained by pouring, and the mass percentage composition of the magnesium alloy is: Al: 0.91%, Zn: 0.61%, Mn: 0.15%, Y: 0.3%, and the rest is magnesium and impurity elements that cannot be removed.
[0044] The as-cast structure is solution treated at 420°C×4h; then the solid solution structure is cut and rolled. The thickness before rolling is 80mm, the rolling temperature is 400°C, and the rolling speed is 0.6m / s. The number of passes is 3, the total deformation is 50%, and the temperature of the magnesium alloy after rolling is 340°C. The EBSD microstructure of the rolled magnesium alloy is as follows: Figure 8 As shown, the rolled microstructure has obvious preferred orientation, and t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| texture strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| texture strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com