Polishing agent for synthetic quartz glass substrates, method for producing same, and method for polishing synthetic quartz glass substrate
A technology for glass substrates and synthetic quartz, which is applied to polishing compositions containing abrasives, grinding/polishing equipment, chemical instruments and methods, and can solve problems such as easy sedimentation of particles, scratches on quartz glass substrates, and poor dispersion stability , to achieve the effect of improving productivity and yield, and suppressing defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
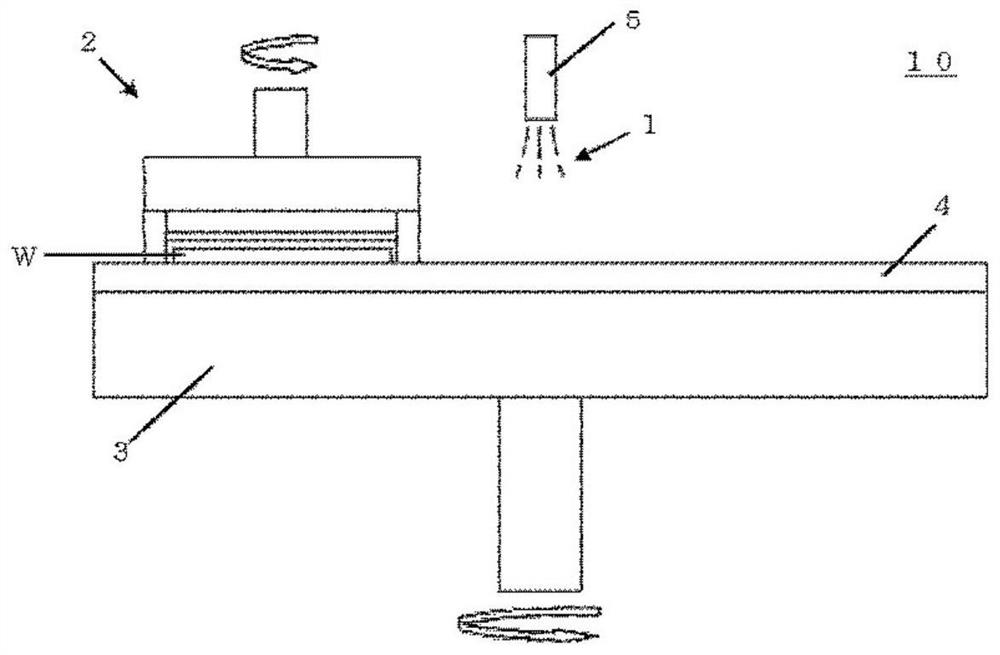
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
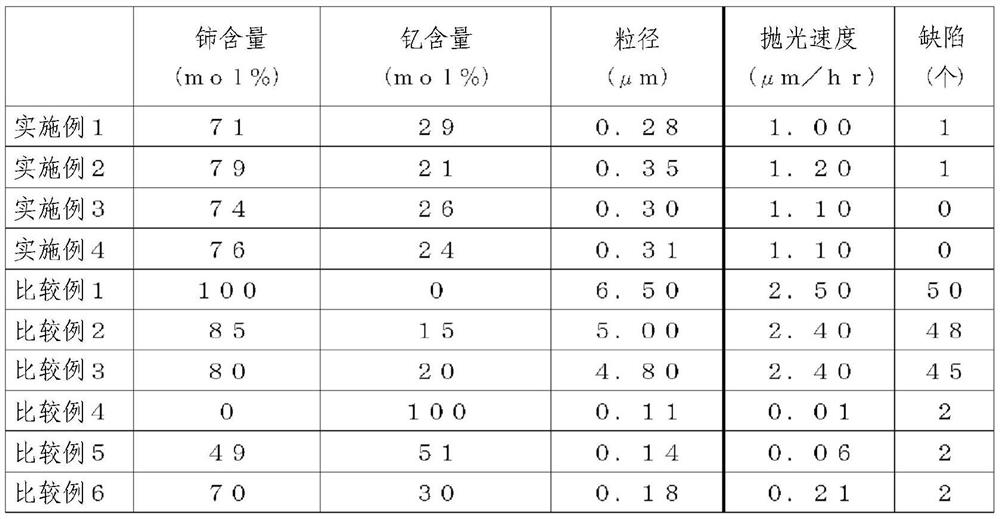
[0049] As a preparation method of polishing particles, first, a cerium solution is prepared by mixing cerium nitrate as a precursor as a rare earth salt with ultrapure water. Similarly, a yttrium solution was prepared by mixing yttrium nitrate as a rare earth salt with ultrapure water, and mixed with the cerium solution so that the cerium content was in the range of 71 mol% to 79 mol% to prepare a cerium-yttrium mixed solution.
[0050] Next, an alkaline solution is prepared. As the alkali compound of the alkaline solution, urea or a urea-based compound can be used, which is mixed with ultrapure water and adjusted to an appropriate concentration for use. Here, as the urea compound, dimethylacetylurea, benzenesulfonylurea, trimethylurea, tetraethylurea, tetramethylurea, triphenylurea, tetraphenylurea, etc. can also be used.
[0051] The ion concentration in the cerium-yttrium mixed solution whose cerium content is adjusted to be 71 mol% or more and 79 mol% or less can be set t...
Embodiment 1
[0068] 2.84 g of 1 mol / l cerium nitrate solution and 1.16 g of 1 mol / l yttrium nitrate solution were diluted with pure water so that the ion concentration of cerium became 71 mol % and the ion concentration of yttrium became 29 mol %, thereby preparing 400 g of cerium yttrium mixture.
[0069] Next, 48 g of a 5 mol / l urea solution was diluted with 600 g of pure water to prepare a urea solution, and mixed with the cerium-yttrium mixed solution to prepare 1000 g of a reaction solution.
[0070] The prepared reaction solution was charged into a separable flask, and the reaction solution was heated and stirred at 90° C. for 2 hours to precipitate particles in the reaction solution.
[0071] The precipitated particles were collected by a centrifuge and dried to obtain polishing particles. The composition ratio of the obtained polishing particles based on ICP-AES elemental analysis was 71 mol% of cerium and 29 mol% of yttrium.
[0072] In addition, the average primary particle dia...
Embodiment 2
[0077] 3.12 g of 1 mol / l cerium nitrate solution and 0.88 g of 1 mol / l yttrium nitrate solution were diluted with pure water to prepare 400 g of cerium yttrium mixture.
[0078] Then, a polishing agent was prepared in the same procedure as in Example 1, and the synthetic quartz glass substrate W was polished. The composition ratio of the obtained polishing particles based on ICP-AES elemental analysis was 79 mol% of cerium and 21 mol% of yttrium.
[0079] In addition, the average primary particle diameter converted by the transmission electron microscope was 350 nm. The polishing rate was 1.2 μm / hr, and the number of defects was 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com