Synthetic quartz glass substrate polishing agent, production method therefor, and synthetic quartz glass substrate polishing method
A glass substrate, synthetic quartz technology, applied in polishing compositions containing abrasives, machine tools suitable for grinding workpiece planes, grinding devices, etc., can solve the problem of easy sedimentation of particles, scratches on quartz glass substrates, poor dispersion stability, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of sufficient grinding speed, suppression of defects, and improvement of productivity and yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
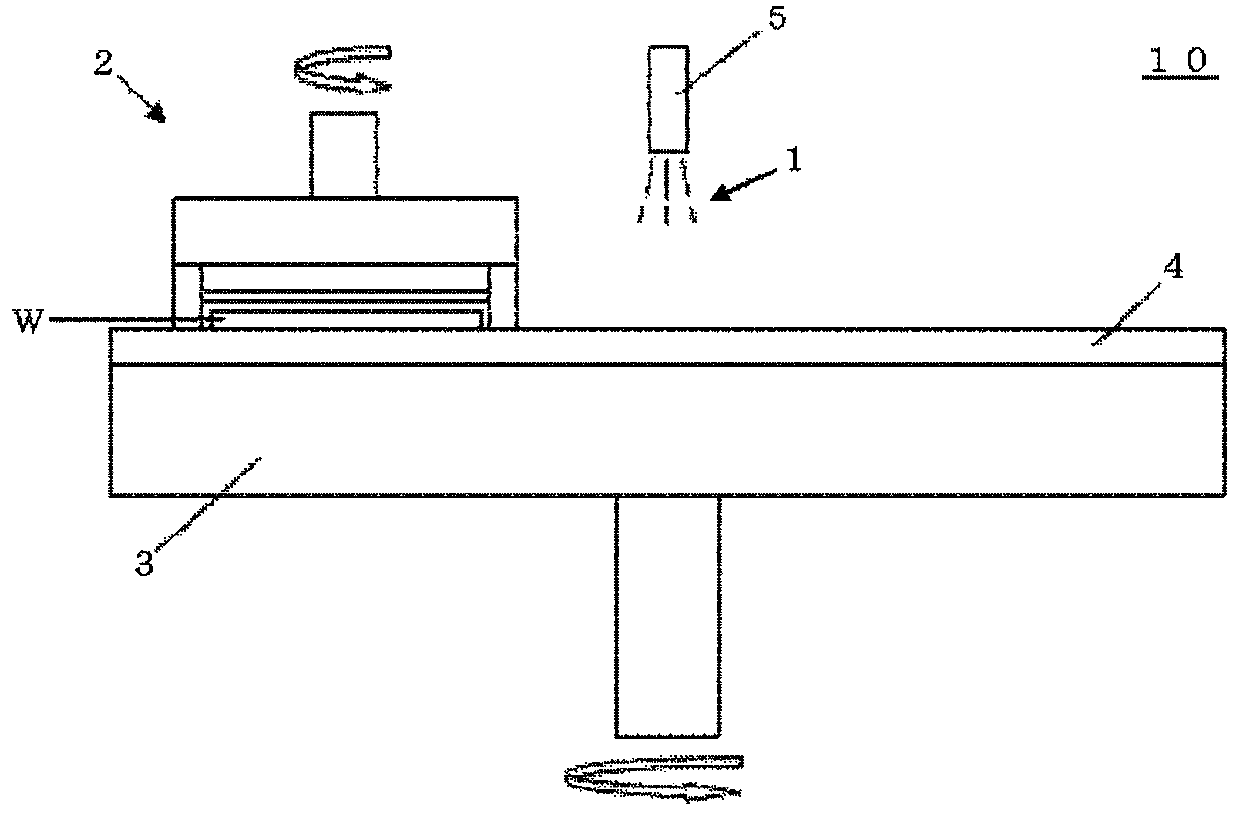
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] (Synthesis of Composite Oxide Supported Silica Particles)
[0079] Solution A was prepared by diluting 100 g of a colloidal silica dispersion containing silica particles having an average particle diameter of 80 nm and having a silica particle concentration of 20% with 2000 g of ultrapure water. After transferring this solution A to a reaction container, it stirred. Next, 500 g of ammonia water (solution B) was dripped in the reaction container, and it stirred.
[0080] Next, 280 g of diammonium cerium nitrate and 55 g of lanthanum nitrate hexahydrate were dissolved in pure water so that the molar ratio of cerium and lanthanum was 80 / 20, to obtain a composite oxide precursor solution (solution C).
[0081] Next, the composite oxide precursor solution was added dropwise to the reaction container, stirred, and heated to 80° C. under a nitrogen atmosphere. Heat treatment was performed for 8 hours to obtain a mixed solution containing silica particles having composite oxi...
Embodiment 2
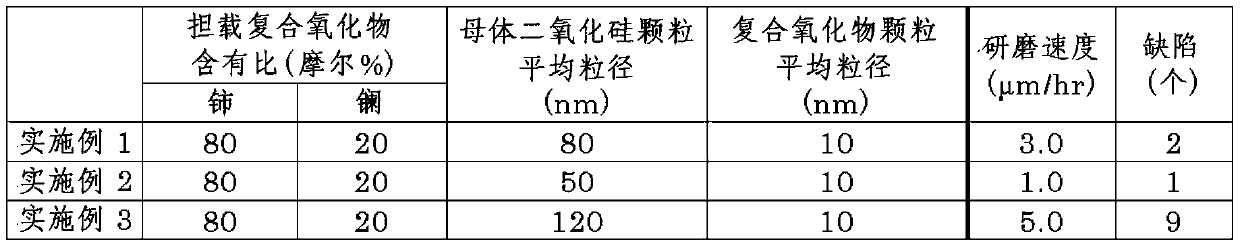
[0091] An abrasive was prepared by the same procedure as in Example 1 except that a colloidal silica dispersion liquid containing silica having an average particle diameter of 50 nm was used. The average particle diameter measured with an electron microscope was 70 nm. In addition, the average particle diameter of the composite oxide particles supported on the silica particles was 10 nm. With this abrasive, the synthetic quartz glass substrate was polished in the same manner as in Example 1. As a result, the polishing rate was 1.0 μm / hr and the number of defects was one.
Embodiment 3
[0093] An abrasive was prepared by the same procedure as in Example 1 except that a colloidal silica dispersion liquid containing silica having an average particle diameter of 120 nm was used. The average particle diameter measured with an electron microscope was 140 nm. In addition, the average particle diameter of the composite oxide particles supported on the silica particles was 10 nm. With this abrasive, the synthetic quartz glass substrate was polished in the same manner as in Example 1. As a result, the polishing rate was 5.0 μm / hr and the number of defects was 9.
[0094] Table 1 shows the results of Examples 1 to 3 above. In addition, the numbers in the table are the average values of five synthetic quartz glass substrates polished in each of Examples 1 to 3.
[0095] [Table 1]
[0096]
[0097] As shown in Table 1, by polishing the synthetic quartz glass substrate using the abrasive of Example 1, that is, silica matrix particles of a predetermined size, the o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com