An antibacterial composite scaffold cs/sf/cms-cip that promotes seawater soaking wound healing and its preparation method
A wound healing and composite stent technology, applied in the field of biomedical engineering materials, can solve problems such as inflammatory response, organ damage, drug burst release, etc., to avoid side effects, resist wound infection, and promote wound healing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0042] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing an antibacterial composite scaffold CS / SF / CMs-CIP that promotes seawater soaked wound healing, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0043] (1) taking by weighing 2g chitosan and being dissolved in 100mL mass fraction is 1% in the acetic acid aqueous solution, continuous stirring makes it dissolve completely, obtains chitosan solution;
[0044] (2) Pour 4.5-5.5 g of sodium bicarbonate, an appropriate amount of sodium lauryl sulfate, and an appropriate amount of shredded cocoons into 1L of deionized water, and degumming in a boiling water bath for 50-70 minutes; weigh 1.8-2.5 g of the washed and dried cocoons. g is dissolved in 0.5L calcium chloride / ethanol aqueous solution to prepare silk fibroin solution; the calcium chloride / ethanol aqueous solution is configured by water, absolute ethanol, and anhydrous calcium chloride with a molar ratio of 8:2:1; After dialyzing the silk fibroin solution, ce...
Embodiment 1~7
[0055] The experimental method that embodiment 1~7 adopts:
[0056] (1) water absorption
[0057] Weigh the weight of the stent with a balance, record it as Mo, place the stent in PBS (10mmol / L, pH=7.4) solution, quickly absorb the surface moisture with filter paper after 30min, weigh and record the sample mass as Mw. Each sample was tested three times in parallel, and the average value was calculated. The water absorption rate X of the sample was calculated according to the following formula:
[0058]
[0059] Among them, M o is the weight of the dry support (g); M w is the weight (g) of the stent after absorbing water; X is the water absorption rate (%) of the stent.
[0060] (2) Porosity
[0061] Measure the porosity of the sample with the medium saturation method, weigh the weight of the support with a balance, and record it as W 1 , soak the bracket in absolute ethanol until the sample is saturated, attach filter paper on both sides to absorb a certain pressure fo...
Embodiment 1
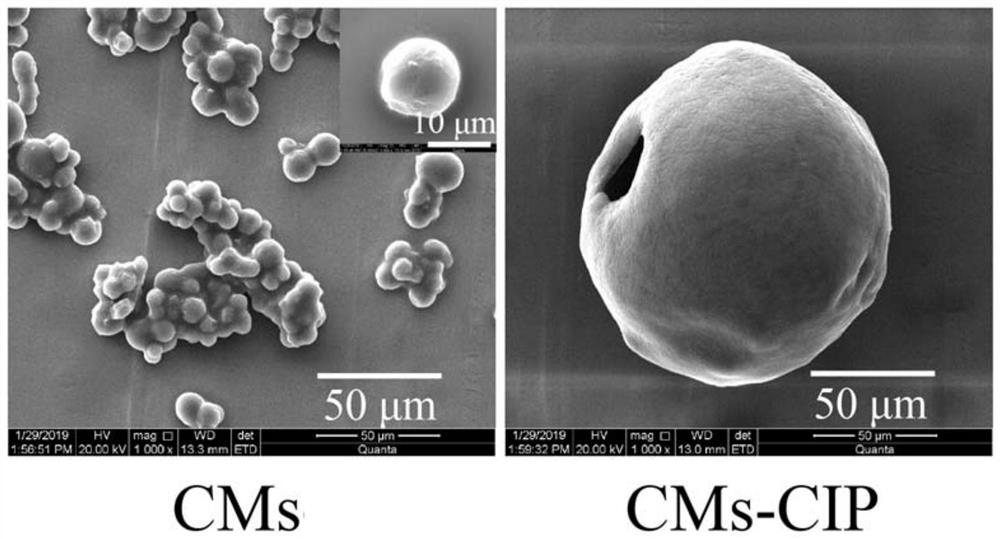
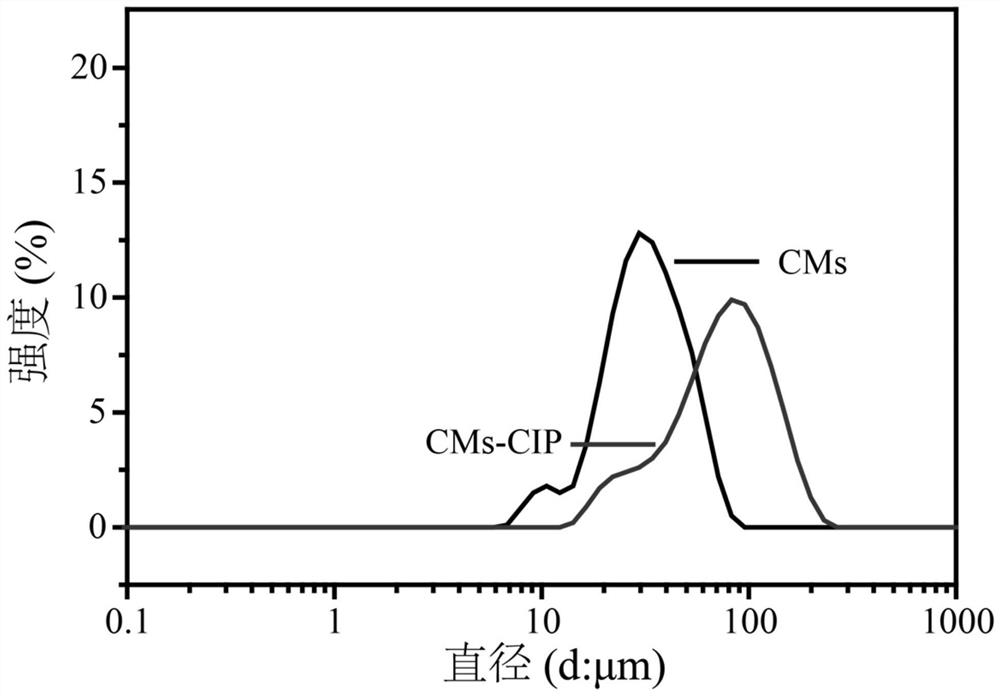
[0075] Embodiment 1: the preparation of chitosan microspheres (CMs)
[0076] (1) take by weighing 1g chitosan, be dissolved in 10mL mass fraction and be in the acetic acid aqueous solution of 3%, prepare chitosan solution;
[0077] (2) Add a certain amount of liquid paraffin and 2g Span-20 into the above-mentioned chitosan solution, and emulsify at 500r / min for 90min under nitrogen protection;
[0078] (3) Under stirring conditions, add 14 mL of formaldehyde with a mass fraction of 3.7% to the above emulsion, and react for 1 hour, then add a certain amount of formaldehyde with a mass fraction of 37%, and react for 1 hour;
[0079] (4) After the reaction is over, pass through ammonia gas to solidify for 25 minutes, then stir in a water bath at 55°C for 30 minutes;
[0080] (5) After the reaction is over, use sherwood oil, acetone and absolute ethanol to ultrasonically wash several times in sequence, and finally the product in absolute ethanol is centrifuged;
[0081] (6) Soak...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com