Iron-base sintered and vulcanized material, preparing method thereof, iron-base side plate and oil distribution disc
A technology of iron-based sintering and sintering materials, which is applied in the direction of metal material coating process, coating, solid-state diffusion coating, etc., and can solve problems such as occlusion, adhesive wear on the surface of friction pairs, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
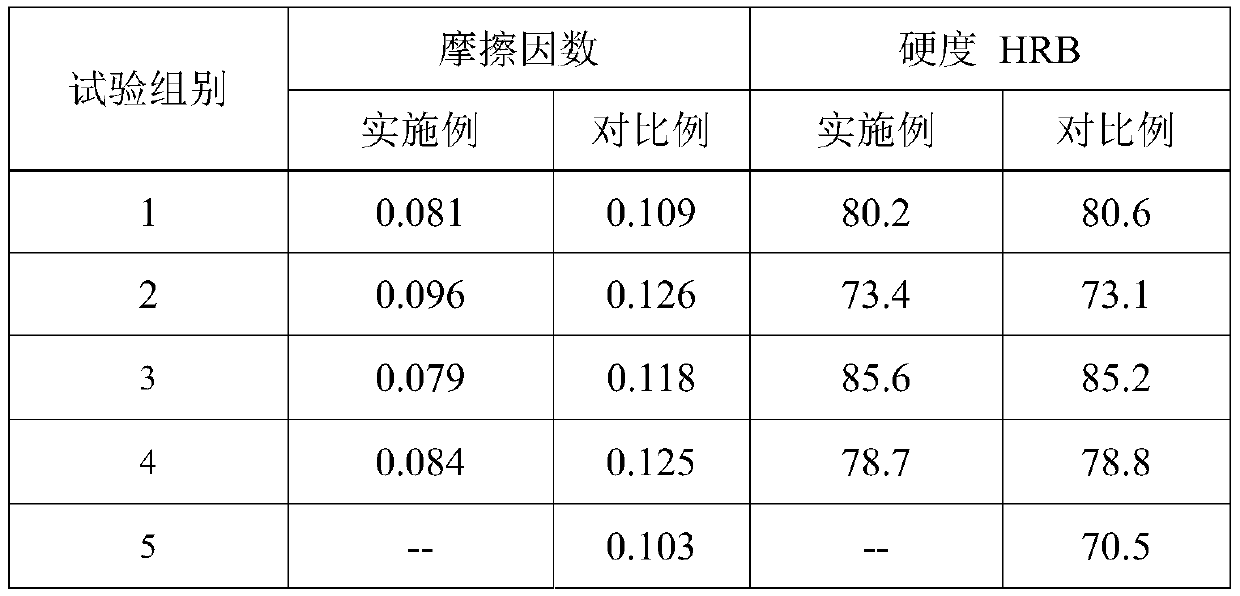
Embodiment 1
[0027] Weighing: Weigh 100 parts of reduced iron powder, 10 parts of copper powder, 0.7 parts of graphite, 0.6 parts of zinc stearate, and 0.05 parts of spindle oil according to the weight ratio;
[0028] Mixing: Use double cone mixer to mix evenly;
[0029] Pressing: Pressing density is 6.6g / cm 3 The wafer sample;
[0030] Sintering: Sintering at 1100°C for 30 minutes; sintered material is prepared;
[0031] Coating: by sieving, evenly spread the sulfur powder on the surface of the sintered material to obtain the coating material; the amount of sulfur accounts for about 20% of the porosity;
[0032] Vulcanization: Place the coating material at a temperature of 118°C for 100 minutes in an argon atmosphere to allow sulfur to enter the pores of the sintered material to obtain the sintered vulcanized material;
[0033] Sample preparation: The vulcanized material is made into test specimens.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Weighing: Weigh 100 parts of reduced iron powder, 15 parts of copper powder, 0.6 parts of graphite, 0.6 parts of zinc stearate, and 0.05 parts of spindle oil by weight;
[0036] Mixing: Use double cone mixer to mix evenly;
[0037] Pressing: Pressing a disc sample with a density of 6.4g / cm3;
[0038] Sintering: Sintering at 1110°C for 30 minutes; sintered material is prepared;
[0039] Coating: through sieving, the sulfur liquid is sprayed on the surface of the sintered material to obtain the coating material; the amount of sulfur accounts for about 80% of the porosity;
[0040] Vulcanization: Place the coating material at a temperature of 130°C for 40 minutes in an air atmosphere to allow sulfur to enter the pores of the sintered material to obtain a sintered vulcanized material;
[0041] Sample preparation: The vulcanized material is made into test specimens.
[0042] The metallographic structure of the vulcanized material prepared in Example 2 after being corroded by a 2% nitric...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Weighing: Weigh 100 parts of reduced iron powder, 8 parts of copper powder, 0.7 parts of graphite, 0.5 parts of zinc stearate, and 0.07 parts of spindle oil according to the weight ratio;
[0045] Mixing: Use double cone mixer to mix evenly;
[0046] Pressing: Pressing a disc sample with a density of 6.8g / cm3;
[0047] Sintering: Sintering at 1100°C for 30 minutes; sintered material is prepared;
[0048] Coating: by sieving, evenly spread the sulfur powder on the surface of the sintered material to obtain the coating material; the amount of sulfur accounts for about 40% of the porosity;
[0049] Vulcanization: Place the coating material at a temperature of 160°C for 20 minutes in a nitrogen atmosphere to allow sulfur to enter the pores of the sintered material to obtain a sintered vulcanized material;
[0050] Sample preparation: The vulcanized material is made into test specimens.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com