Process for processing waste circuit boards to prepare copper alloy powder by mechanical physical method
A technology of waste circuit boards and copper alloys, which is applied in the field of electronic waste resource recycling, can solve the problems of large environmental pollution, high energy consumption, and long metallurgical recycling process, and achieve the goal of short process, low energy consumption, and realization of recycling Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
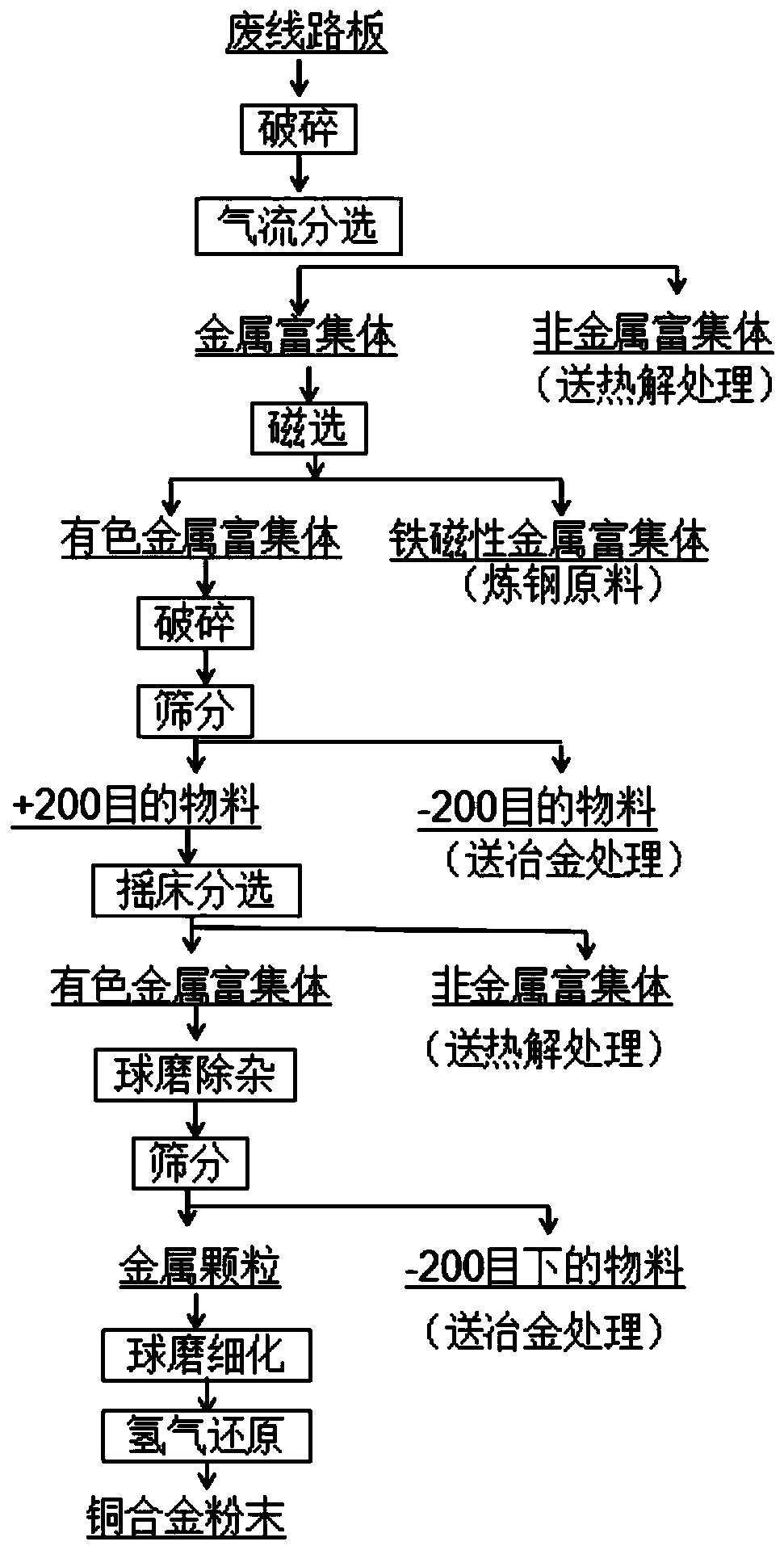
[0031] This embodiment provides a process for preparing copper alloy powder from waste circuit boards by mechanical physical method, including the following steps:
[0032] (1) 100 kg of waste circuit boards were crushed to less than 5 mm, and metals and nonmetals were initially separated by airflow separation to obtain iron-containing metal-enriched bodies, in which the iron content was 16.9 wt.%.
[0033] (2) performing magnetic separation on the ferrous metal-enriched body obtained in step (1) to obtain non-ferrous metal-enriched body and ferromagnetic metal-enriched body respectively;
[0034] (3) Using a hammer crusher to further crush the non-ferrous metal-enriched body obtained in step (2) to less than 0.5 mm, and sieve with a sieve to obtain coarse particle materials larger than 200 mesh;
[0035] (4) Sorting the coarse-grained material larger than 200 meshes obtained in step (3) with a hydraulic shaker to remove most of the non-metals and increase the metal content in...
Embodiment 2
[0040] This embodiment provides a process for preparing copper alloy powder from waste circuit boards by mechanical physical method, including the following steps:
[0041] (1) 100 kg of waste circuit boards were crushed to less than 5 mm, and metals and nonmetals were initially separated by airflow separation to obtain iron-containing metal-enriched bodies, in which the iron content was 16.9 wt.%.
[0042] (2) performing magnetic separation on the ferrous metal-enriched body obtained in step (1) to obtain non-ferrous metal-enriched body and ferromagnetic metal-enriched body respectively;
[0043] (3) Using a hammer crusher to further crush the non-ferrous metal-enriched body obtained in step (2) to less than 0.5 mm, and sieve with a sieve to obtain coarse particle materials larger than 200 mesh;
[0044] (4) Sorting the coarse-grained material larger than 200 meshes obtained in step (3) with a hydraulic shaker to remove most of the non-metals and increase the metal content in...
Embodiment 3
[0049] This embodiment provides a process for preparing copper alloy powder from waste circuit boards by mechanical physical method, including the following steps:
[0050] (1) 100 kg of waste circuit boards were crushed to less than 5 mm, and metals and nonmetals were initially separated by airflow separation to obtain iron-containing metal-enriched bodies, in which the iron content was 16.9 wt.%.
[0051] (2) performing magnetic separation on the ferrous metal-enriched body obtained in step (1) to obtain non-ferrous metal-enriched body and ferromagnetic metal-enriched body respectively;
[0052] (3) Using a hammer crusher to further crush the non-ferrous metal-enriched body obtained in step (2) to less than 0.5 mm, and sieve with a sieve to obtain coarse particle materials larger than 200 mesh;
[0053] (4) Sorting the coarse-grained material larger than 200 meshes obtained in step (3) with a hydraulic shaker to remove most of the non-metals and increase the metal content in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com