A kind of method of promoting spore production of pathogenic bacteria of sorrel blight
A technology for pathogenic bacteria and blight, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of few conidia, restrict the application of blight pathogenic bacteria, difficult to complete pathogenicity determination and drug screening test, etc., and achieve the promotion of vegetative growth and reproductive growth. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
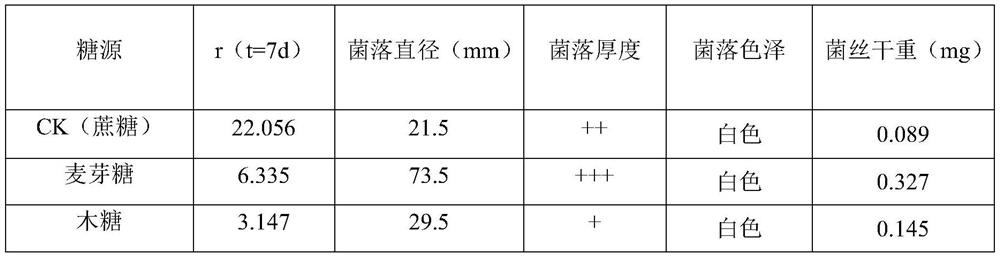
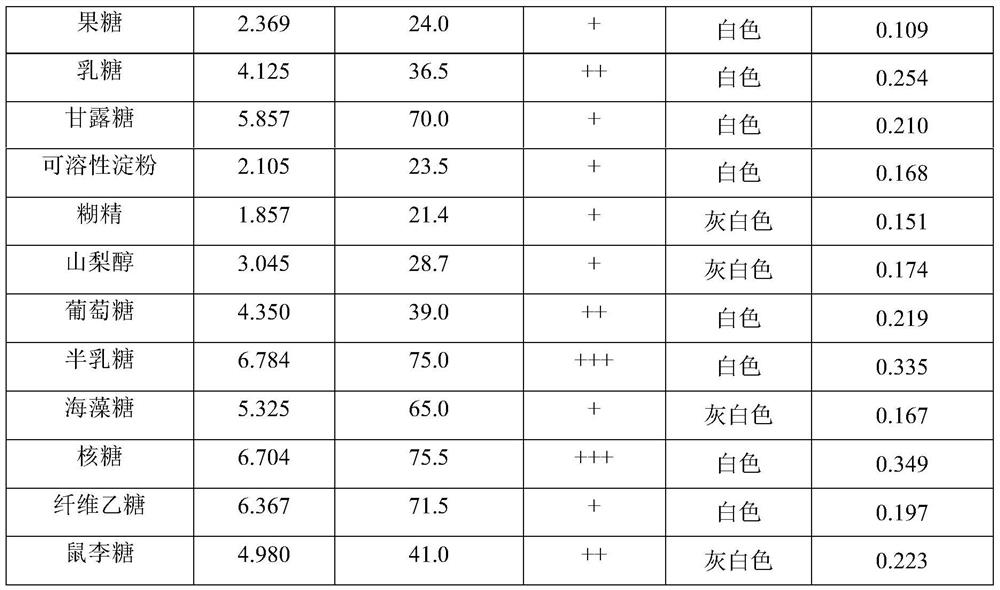
[0032] Embodiment 1: the influence of the culture medium of different carbon source, nitrogen source on the growth of sweet potato blight pathogenic bacteria
[0033] In this example, on the basis of Chapei's medium, the effects of different carbon and nitrogen sources on the pathogen of sweet potato blight were studied by changing the carbon and nitrogen sources.
[0034] The components of Cha's medium are: 1 g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.5 g of potassium chloride, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O) 0.5g, ferrous sulfate is 0.01g, potassium nitrate 3g, sucrose 30g, agar is 20g.
[0035] Maltose, xylose, fructose, lactose, mannose, soluble starch, dextrin, sorbitol, glucose, galactose, trehalose, ribose, cellulose, and rhamnose were used to replace sucrose in Chapei's medium, keeping The nitrogen source in each culture medium was potassium nitrate, and 14 kinds of culture media with different carbon sources were prepared.
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2: the influence of different mediums on the growth of sweet potato blight pathogenic bacteria
[0056] (1) The preparation of Cha's medium with maltose as the sugar source and peptone as the nitrogen source and the cultivation of the pathogenic bacteria of the blight
[0057] Step 1: Take by weighing dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1g, potassium chloride 0.5g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO 4 ·7H 2 (0) 0.5g, ferrous sulfate is 0.01g, peptone 3g, maltose 30g, agar are 20g;
[0058] Step 2: Mix the weighed medicines together, add deionized water to make the volume to 1000mL, and adjust to pH=7;
[0059] Step 3: Place the prepared medium in an autoclave, autoclave at 121°C for 30 minutes, and then take it out for use;
[0060] Step 4: Pour the sterilized culture medium into the plate in a sterile environment for standby;
[0061] Step 5: In a sterile environment, use sterilized tweezers to pick up the sweet potato blight pathogenic bacteria cake with...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Embodiment 3: the impact of culture conditions on the spore production of sweet potato blight pathogenic bacteria
[0094] According to the experimental results of Example 2, it is found that dark culture can not induce sporulation of the pathogenic bacterium of the blight, although the growth rate of the pathogen can be improved through the optimization of the medium, it cannot effectively promote the sporulation. Therefore, the present invention further improves the sporulation of the blight The culture conditions of the pathogenic bacteria were optimized in order to obtain a method that can promote the spore production of the pathogenic bacteria of Blight blight.
[0095] In this example, several different culture media were taken as examples to study the mycelium growth and spore production under different culture conditions.
[0096] A: The culture medium with optimized carbon source and nitrogen source, the medium components are: dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com