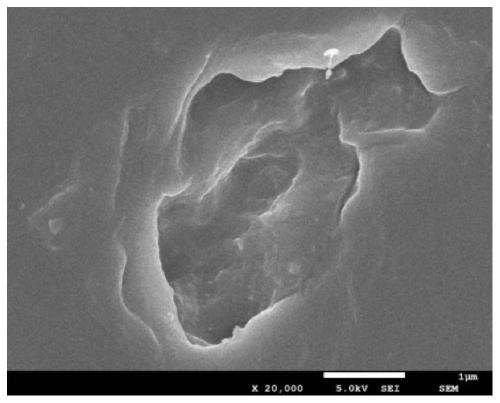
Method for polyethylene biodegradation through pichia guilliermondii
A technology of biodegradation and polyethylene, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve environmental pollution and other problems, and achieve the effect of low cost and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0011] Specific embodiment one: this embodiment utilizes the method for biodegrading polyethylene by Pichia mongoliae, and proceeds according to the following steps:
[0012] 1. Activation of Pichia mongoliana strain: Scrape and inoculate Pichia mongoliana strain stored on YPD slant medium at 4°C to YPD solid medium, and culture at 30°C for 24-48 hours to obtain activation the strain;
[0013] 2. Biodegradation of polyethylene by Pichia mongolica: Scrape the activated strain with an inoculation needle, inoculate it into 80mL YPD liquid medium, and cultivate it at 30°C and 150rpm for 24-48 hours, then centrifuge at 9000rpm to collect the bacteria , washed the collected thalli with sterile normal saline for 3 times to prepare the bacterium suspension, and added chlorinated polyethylene sheets (200 mg) and Pichia mongoliana suspension (10 mL) through ultraviolet irradiation for 2 hours to In a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask with 90mL carbon-free medium (LCFBM), the final bacterial conce...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0017] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: Pichia pastoris Meyerozymaguilliermondii ZJC-1 in step 1 is preserved in the General Microorganism Center (CGMCC) of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, and the preservation address is No. 3, Courtyard No. 1, Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The preservation date is December 17, 2018, and the preservation number is CGMCC No: 16956. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0018] Embodiment 3: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 in that: in step 1, culture at 30° C. for 36 hours. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com