PLGA cytoskeleton for articular cartilage repair and preparation method and application of PLGA cytoskeleton for articular cartilage repair
A technology of cell scaffolds and chondrocytes, applied in the field of medicine, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory treatment results, poor bionic effects, and long treatment cycles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Embodiment 1: Preparation of PLGA porous scaffold
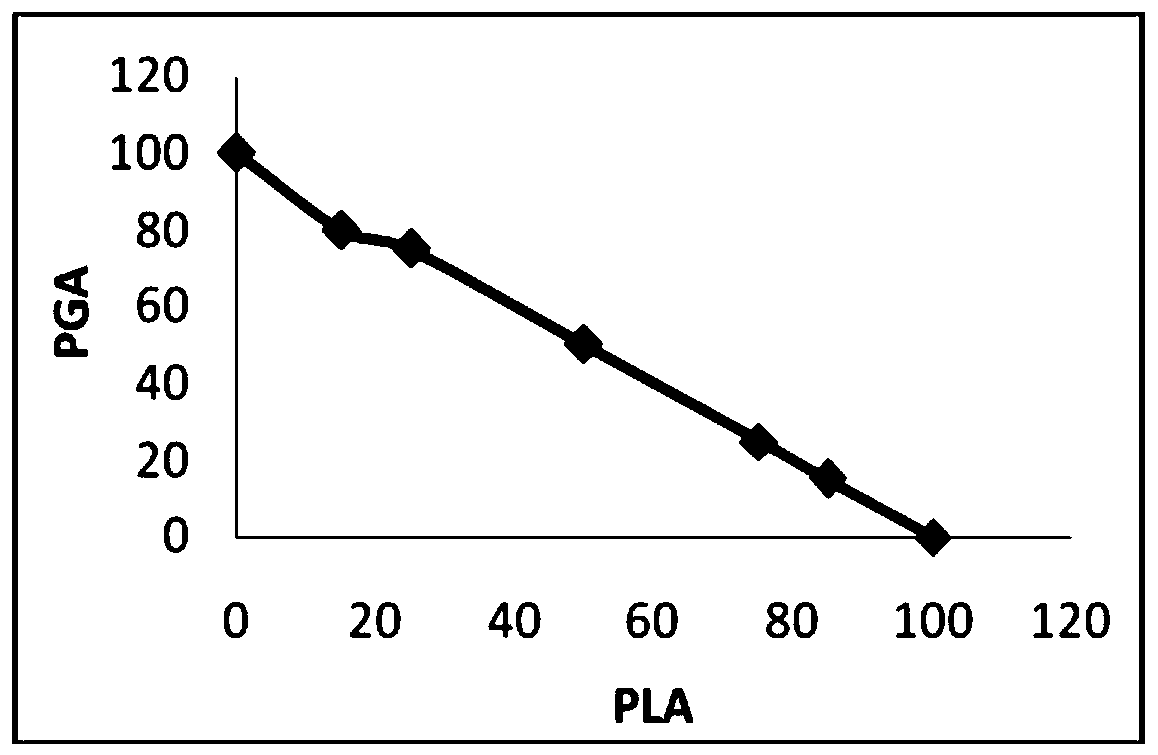
[0078] 1. Preparation of PLGA porous scaffold. The scaffold part of the articular cartilage repair material uses polylactic acid-glycolic acid (PLGA) as the matrix material, which is composed of organic polymer polylactic acid (PLA) and polyglycolic acid (PGA), according to a certain gradient ratio (polylactic acid (PLA): Polyglycolic acid (PGA) = 100:0, 85:15, 75:25, 50:50, 25:75, 15:85, 0:100) polymerization product ( figure 1 ).
[0079] Polylactic acid (PLA), polyglycolic acid (PGA), polylactic acid-glycolic acid (PLGA) monomer chemical structure formula is as follows:
[0080] Polylactic acid [poly(lactic acid), PLA]:
[0081] Polyglycolic acid [poly(glycolic acid), PGA]:
[0082] Polylactic-co-glycolic acid [poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), PLGA]:
[0083] Prepare the PLGA porous scaffold by freeze-drying technique, the steps are as follows:
[0084] a) PLA / The PGA polymerization product—polylactic ac...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Example 2: Primary culture of adult cells
[0111] 1. Chondrocytes. Adult chondrocytes are derived from articular hyaline cartilage in nonweight-bearing areas.
[0112] a) Cartilage sampling preparation. Items to be prepared include trypsin, type II collagenase, DMEM high-glucose medium, PBS buffer, pipettes, culture dishes or flasks of different capacities, centrifuge tubes, filters, gauze, surgical equipment such as tweezers, scissors, etc. for disinfection after supplies.
[0113] b) Cartilage sampling. After anesthesia, disinfect with povidone iodine and deiodine with 75% alcohol, take about 50-100 mg of articular hyaline cartilage from non-weight-bearing parts, and put it into a petri dish filled with PBS buffer.
[0114] c) Repeated pipetting and washing with cold PBS buffer containing antibiotics 3 times. After the third wash, let stand for 5 minutes, discard the upper liquid and floating tissue, and move the cartilage tissue into a clean sterile vessel.
...
Embodiment 3
[0134] Example 3: Preparation of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and its release of growth-promoting factors
[0135] 1. Using a 20ml sterile syringe and a vacuum blood collection tube containing ACD-A anticoagulant, draw about 18ml of blood at room temperature (22°C), and put the blood into four 5ml centrifuge tubes, 4ml in each tube. Platelet-rich plasma preparation should be completed within 4 to 6 hours.
[0136] 2. Preparation of platelet-rich plasma. Platelet-rich plasma with effective concentration was prepared by secondary centrifugation, and the activity levels of cytokines PDGF and TGF-β1 in platelet plasma prepared by this method increased significantly (P<0.01).
[0137] a) Place 4ml of each tube symmetrically in a centrifuge, centrifuge for the first time at 200-400g×10min, take 3mm of plasma above and below the buffy coat after centrifugation, and put it in another centrifuge tube,
[0138] b) Perform a second centrifugation at 200-400 g×10 min, remove the supernata...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com