Method for recycling rare-earth elements from neodymium iron boron waste with high silicon content and low rare earth content
A recovery method and technology of rare earth elements, which is applied in the field of rare earth waste resource recovery, can solve problems such as the pellets getting bigger and bigger, the pre-roasting process cannot be carried out smoothly, and NdFeB waste cannot be recycled, so as to achieve the effect of improving product quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
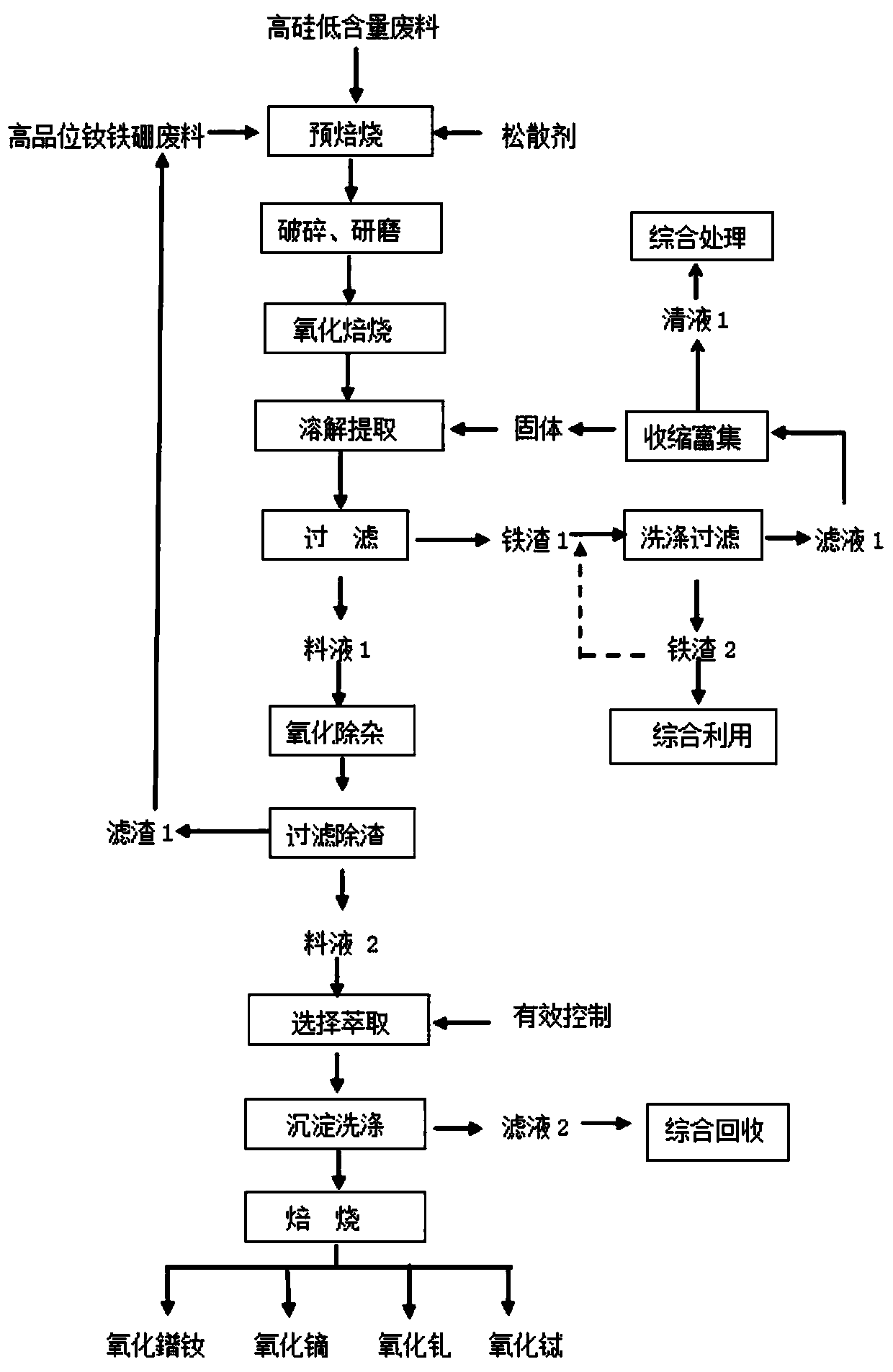
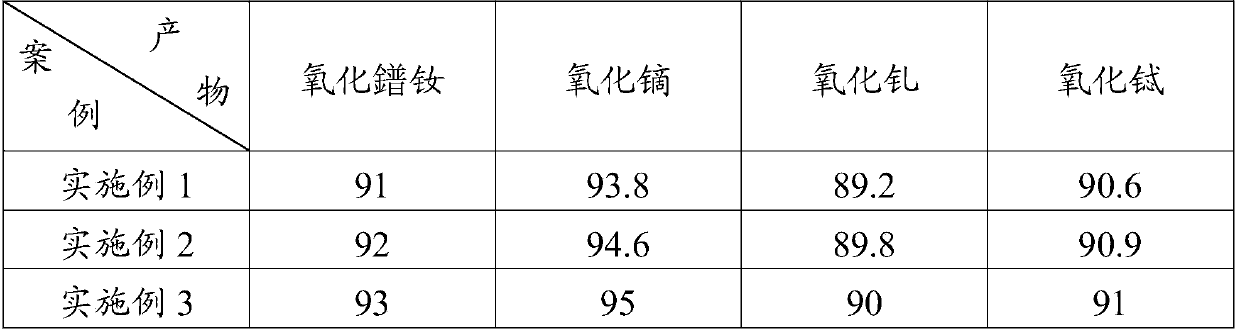
[0052] Mix high-silicon and low-content NdFeB waste (chamfering mud), high-content NdFeB waste (oil sludge) and loose agent iron slag (mass ratio 1:1:1), and pre-roast at 600 ° C for 2 hours. Obtain a coarse material; crush and grind the coarse material to a fine material with a particle size of 200 mesh; oxidize and roast the fine material at 500°C for 2 hours to obtain an oxidized material; use an extraction device to mix the oxidized material and water to adjust Slurry, heating while stirring, when it reaches 60°C, add extractant nitric acid (mass ratio of oxidizing material, water and extractant is 1:0.05:0.5), fully stir for 1h, control pH value to 2.0, carry out dissolution extraction, keep The pH value was kept constant at 2.0, and kept for 2 hours to obtain the extracted slurry; the extracted slurry was filtered with a high-pressure filter press at 60°C to obtain feed liquid 1 and iron slag 1; iron slag 1 and water (mass Ratio 1:0.2) washing and filtering at 50°C to ob...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Mix high-silicon and low-content NdFeB waste (wire saw mud), high-content NdFeB waste (slag) and loose agent calcium oxide (mass ratio 1:1:6), and pre-roast at 800 ° C for 3 hours. Obtain a coarse material; crush and grind the coarse material to a fine material with a particle size of 200 mesh; oxidize and roast the fine material at 800°C for 3 hours to obtain an oxidized material; use an extraction device to mix the oxidized material and water to adjust Slurry, heat while stirring, when it reaches 70°C, start to add extractant sulfuric acid (the mass ratio of oxidizing material, water and extractant is 1:0.05:0.5), stir well for 1.5h, control the pH value to 2.0, and dissolve Extraction, keeping the pH value at 3.0, keeping the temperature for 3 hours to obtain the extraction slurry; filtering the extraction slurry with a high-pressure filter press at 80°C to obtain feed liquid 1 and iron slag 1; iron slag 1 and Water (mass ratio 1:1) is washed and filtered at 60°C to ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Mix high-silicon and low-content NdFeB waste (sweeping ash), high-content NdFeB waste (ultrafine powder) and loose agent calcium hydroxide (mass ratio 1:1:10), and pre-roast at 1200 ° C 5h to obtain a coarse material; crush and grind the coarse material to a fine material with a particle size of 300 mesh; oxidize and roast the fine material at 1000°C for 5 hours to obtain an oxidized material; use an extraction device to separate the oxidized material and water Mix and paste, heat while stirring, when it reaches 95°C, start to add extractant hydrochloric acid (the mass ratio of oxidizing material, water and extractant is 1:0.05:0.5), stir well for 2 hours, control the pH value to 5.0, and dissolve Extraction, keeping the pH value at 5.0, keeping the temperature for 5 hours to obtain the extraction slurry; filtering the extraction slurry with a high-pressure filter press at 90°C to obtain feed liquid 1 and iron slag 1; iron slag 1 and Water (mass ratio 1:2) is washed and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com